Cladribine by Apotex Corp. CLADRIBINE tablet
Cladribine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Cladribine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Apotex Corp.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLADRIBINE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLADRIBINE TABLETS.
CLADRIBINE tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1993WARNING: MALIGNANCIES and RISK OF TERATOGENICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
-
Malignancies
Cladribine tablets may increase the risk of malignancy. Cladribine tablets are contraindicated in patients with current malignancy; evaluate the benefits and risks on an individual basis for patients with prior or increased risk of malignancy. (5.1)
- Risk of Teratogenicity
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated for use in pregnant women and in women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception because of the risk of fetal harm. (5.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration (2.1) 5/2024
Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.7) 5/2024
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cladribine tablets are purine antimetabolite indicated for the treatment of relapsing form of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include relapsing-remitting disease in adults. Because of its safety profile, use of cladribine tablets are generally recommended for patients who have had an inadequate response to, or are unable to tolerate, an alternate drug indicated for the treatment of MS. (1, 5)
Limitations of Use
Cladribine tablets are not recommended for use in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) because of its safety profile. (1, 5)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Assessments are required prior to starting each cladribine treatment course. (2.1)
- Cumulative dosage of 3.5 mg/kg administered orally and divided into 2 treatment courses (1.75 mg/kg per treatment course). Each treatment course is divided into 2 treatment cycles. (2.2)
- Cladribine tablets are a cytotoxic drug. (2.4)
- Separate administration from any other oral drug by at least 3 hours. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 10 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Patients with current malignancy. (4)
- Pregnant women, and women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets dosing and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. (4, 8.3)
- HIV infection. (4)
- Active chronic infections (e.g., hepatitis or tuberculosis). (4)
- History of hypersensitivity to cladribine. (4, 5.8)
- Women intending to breastfeed on a cladribine treatment day and for 10 days after the last dose. (4, 8.2)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Lymphopenia: Monitor lymphocyte counts before, during and after treatment. (5.3)
- Infections: Serious, including life-threatening and fatal infections, have occurred. Screen patients for active and latent infections; delay treatment until infection is fully resolved or controlled. Vaccination of patients seronegative to varicella zoster virus (VZV) is recommended prior to treatment. Vaccination of patients seropositive to VZV with zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted, is recommended prior to or during treatment. Administer anti-herpes prophylaxis in patients with lymphocyte counts less than 200 cells per microliter. Monitor for infections. (5.4)
- Hematologic toxicity: Monitor complete blood count before, during and after treatment. (5.5)
- Graft-versus-host-disease with blood transfusion: Irradiation of cellular blood components is recommended. (5.6)
- Liver injury: Clinically significant liver injury has occurred. Obtain tests prior to treatment. Discontinue if clinically significant injury is suspected. (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 20%) are upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and lymphopenia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Immunosuppressive drugs: Consider overlapping effects on immune system, when used sequentially. Concomitant use not recommended. (7.1)
- Hematotoxic drugs: Monitor patients for additive effects on the hematological profile. (7.3)
- Antiviral and antiretroviral drugs: Avoid concomitant use. (7.4)
- BCRP or ENT/CNT inhibitors: May alter bioavailability of cladribine. Avoid concomitant use. (7.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2024
-
Malignancies
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: MALIGNANCIES AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Assessments Prior to Starting Each Cladribine Treatment Course
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Missed Dose
2.4 Administration
2.5 Laboratory Testing and Monitoring to Assess Safety
2.6 Recommended Concomitant Medication
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Malignancies
5.2 Risk of Teratogenicity
5.3 Lymphopenia
5.4 Infections
5.5 Hematologic Toxicity
5.6 Risk of Graft-Versus-Host Disease With Blood Transfusion
5.7 Liver Injury
5.8 Hypersensitivity
5.9 Cardiac Failure
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
8.7 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Hydroxypropyl Betadex-Related Complex Formation
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: MALIGNANCIES AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY
-
Malignancies
Treatment with cladribine tablets may increase the risk of malignancy. Cladribine tablets are contraindicated in patients with current malignancy. In patients with prior malignancy or with increased risk of malignancy, evaluate the benefits and risks of the use of cladribine tablets on an individual patient basis. Follow standard cancer screening guidelines in patients treated with cladribine tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
Risk of Teratogenicity
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated for use in pregnant women and in women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception because of the potential for fetal harm. Malformations and embryolethality occurred in animals. Exclude pregnancy before the start of treatment with cladribine tablets in females of reproductive potential. Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets dosing and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. Stop cladribine tablets if the patient becomes pregnant [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
Malignancies
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cladribine tablets are indicated for the treatment of relapsing form of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include relapsing-remitting disease in adults. Because of its safety profile, use of cladribine tablets is generally recommended for patients who have had an inadequate response to, or are unable to tolerate, an alternate drug indicated for the treatment of MS [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Limitations of Use
Cladribine tablets are not recommended for use in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) because of its safety profile [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Assessments Prior to Starting Each Cladribine Treatment Course
Cancer Screening
Follow standard cancer screening guidelines because of the risk of malignancies [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Pregnancy
Exclude pregnancy prior to treatment with cladribine tablets in females of reproductive potential [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Obtain a CBC with differential including lymphocyte count [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Lymphocytes must be:
- within normal limits before initiating the first treatment course
- at least 800 cells per microliter before initiating the second treatment course
If necessary, delay the second treatment course for up to 6 months to allow for recovery of lymphocytes to at least 800 cells per microliter. If this recovery takes more than 6 months, the patient should not receive further treatment with cladribine tablets.
Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Exclude HIV infection.
- Perform tuberculosis screening.
- Screen for hepatitis B and C.
- Evaluate for acute infection. Consider a delay in cladribine treatment until any acute infection is fully controlled.
- Vaccination of patients who are seronegative for VZV is recommended prior to initiation of cladribine tablets.
- Vaccination of patients who are seropositive to VZV is recommended with zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted. Patients may be administered zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted at any time prior to or during the year 1 or year 2 course of cladribine treatment. These patients may also be administered the vaccine if their lymphocyte counts are ≤ 500 cells per microliter.
- Administer all immunizations (except as noted for VZV) according to immunization guidelines prior to starting cladribine tablets. Administer live-attenuated or live vaccines at least 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting cladribine tablets.
- Obtain a baseline (within 3 months) magnetic resonance imaging prior to the first treatment course because of the risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
Liver Injury
Obtain serum aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin levels prior to each treatment cycle and course [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended cumulative dosage of cladribine tablets is 3.5 mg per kg body weight administered orally and divided into 2 yearly treatment courses (1.75 mg per kg per treatment course) (see Table 1). Each treatment course is divided into 2 treatment cycles:
Administration of First Treatment Course
- First Course/First Cycle: start any time.
- First Course/Second Cycle: administer 23 to 27 days after the last dose of First Course/First Cycle.
Administration of Second Treatment Course
- Second Course/First Cycle: administer at least 43 weeks after the last dose of First Course/Second Cycle.
- Second Course/Second Cycle: administer 23 to 27 days after the last dose of Second Course/First Cycle.
Table 1 Dose of Cladribine tablets per Cycle by Patient Weight in Each Treatment Course
Weight Range Dose in mg (Number of 10 mg Tablets) per Cycle kg First Cycle Second Cycle 40* to less than 50 40 mg (4 tablets) 40 mg (4 tablets) 50 to less than 60 50 mg (5 tablets) 50 mg (5 tablets) 60 to less than 70 60 mg (6 tablets) 60 mg (6 tablets) 70 to less than 80 70 mg (7 tablets) 70 mg (7 tablets) 80 to less than 90 80 mg (8 tablets) 70 mg (7 tablets) 90 to less than 100 90 mg (9 tablets) 80 mg (8 tablets) 100 to less than 110 100 mg (10 tablets) 90 mg (9 tablets) 110 and above 100 mg (10 tablets) 100 mg (10 tablets) *The use of cladribine tablets in patients weighing less than 40 kg has not been investigated. Administer the cycle dosage as 1 or 2 tablets once daily over 4 or 5 consecutive days [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.1)]. Do not administer more than 2 tablets daily.
Following the administration of 2 treatment courses, do not administer additional cladribine treatment during the next 2 years. Treatment during these 2 years may further increase the risk of malignancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The safety and efficacy of reinitiating cladribine tablets more than 2 years after completing 2 treatment courses has not been studied.
2.3 Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, patients should not take double or extra doses.
If a dose is not taken on the scheduled day, then the patient must take the missed dose on the following day and extend the number of days in that treatment cycle. If two consecutive doses are missed, the treatment cycle is extended by 2 days.
2.4 Administration
Cladribine tablets are taken orally, with water, and swallowed whole without chewing. Cladribine tablets can be taken with or without food.
Separate administration of cladribine tablets and any other oral drugs by at least 3 hours during the 4 to 5 day cladribine treatment cycles [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6)].
Cladribine tablets are a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures [see References (15)]. Cladribine tablets are an uncoated tablet and must be swallowed immediately once removed from the blister. If a tablet is left on a surface, or if a broken or fragmented tablet is released from the blister, the area must be thoroughly washed with water.
The patient’s hands must be dry when handling the tablets and washed thoroughly afterwards. Avoid prolonged contact with skin.
2.5 Laboratory Testing and Monitoring to Assess Safety
Cancer Screening
Follow standard cancer screening guidelines in patients treated with cladribine tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Complete Blood Count
Obtain complete blood count (CBC) with differential including lymphocyte count:
- before initiating the first treatment course of cladribine tablets
- before initiating the second treatment course of cladribine tablets
- 2 and 6 months after start of treatment in each treatment course; if the lymphocyte count at month 2 is below 200 cells per microliter, monitor monthly until month 6. See Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4) for instructions based on the patient’s lymphocyte counts and clinical status (e.g., infections). Hold cladribine tablets therapy if the lymphocyte count is below 200 cells per microliter
- periodically thereafter and when clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
2.6 Recommended Concomitant Medication
Herpes Prophylaxis
Administer anti-herpes prophylaxis in patients with lymphocyte counts less than 200 cells per microliter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated:
- in patients with current malignancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- in pregnant women and in women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets dosing and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. May cause fetal harm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- in patients with active chronic infections (e.g., hepatitis or tuberculosis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cladribine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- in women intending to breastfeed on a cladribine treatment day and for 10 days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Malignancies
Treatment with cladribine tablets may increase the risk of malignancy. In controlled and extension clinical studies worldwide, malignancies occurred more frequently in cladribine-treated patients [10 events in 3,754 patient-years (0.27 events per 100 patient-years)], compared to placebo patients [3 events in 2,275 patient-years (0.13 events per 100 patient-years)]. Malignancy cases in cladribine patients included metastatic pancreatic carcinoma, malignant melanoma (2 cases), ovarian cancer, compared to malignancy cases in placebo patients, all of which were curable by surgical resection [basal cell carcinoma, cervical carcinoma in situ (2 cases)]. The incidence of malignancies in United States cladribine clinical study patients was higher than the rest of the world [4 events in 189 patient-years (2.21 events per 100 patient-years) compared to 0 events in United States placebo patients]; however, the United States results were based on a limited amount of patient data.
After the completion of 2 treatment courses, do not administer additional cladribine treatment during the next 2 years [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. In clinical studies, patients who received additional cladribine treatment within 2 years after the first 2 treatment courses had an increased incidence of malignancy [7 events in 790 patient-years (0.91 events per 100 patient-years) calculated from the start of cladribine treatment in Year 3]. The risk of malignancy with reinitiating cladribine tablets more than 2 years after the completion of 2 treatment courses has not been studied.
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated in patients with current malignancy. In patients with prior malignancy or with increased risk of malignancy, evaluate the benefits and risks of the use of cladribine tablets on an individual patient basis. Follow standard cancer screening guidelines in patients treated with cladribine tablets.
5.2 Risk of Teratogenicity
Cladribine tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Malformations and embryolethality occurred in animals [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus during cladribine tablets dosing and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course.
In females of reproductive potential, pregnancy should be excluded before initiation of each treatment course of cladribine tablets and prevented by the use of effective contraception during cladribine tablets dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose of each treatment course. Women who become pregnant during treatment with cladribine tablets should discontinue treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]. Cladribine tablets are contraindicated for use in pregnant women and in women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception.
5.3 Lymphopenia
Cladribine tablets cause a dose-dependent reduction in lymphocyte count. In clinical studies, 87% of cladribine-treated patients experienced lymphopenia. The lowest absolute lymphocyte counts occurred approximately 2 to 3 months after the start of each treatment course and were lower with each additional treatment course. In patients treated with a cumulative dose of cladribine tablets 3.5 mg per kg over 2 courses as monotherapy, 26% and 1% had nadir absolute lymphocyte counts less than 500 and less than 200 cells per microliter, respectively. At the end of the second treatment course, 2% of clinical study patients had lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells per microliter; median time to recovery to at least 800 cells per microliter was approximately 28 weeks.
Additive hematological adverse reactions may be expected if cladribine tablets are administered prior to or concomitantly with other drugs that affect the hematological profile [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. The incidence of lymphopenia less than 500 cells per microliter was higher in patients who had used drugs to treat relapsing forms of MS prior to study entry (32.1%), compared to those with no prior use of these drugs (23.8%).
Obtain complete blood count (CBC) with differential including lymphocyte count prior to, during, and after treatment with cladribine tablets. See Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4) for timing of CBC measurements and additional instructions based on the patient’s lymphocyte counts and clinical status (e.g., infections).
5.4 Infections
Serious, including life-threatening or fatal, bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal infections have been reported in patients receiving cladribine tablets. Cladribine tablets reduces the body's immune defense, and an increased risk of infections has been observed in patients receiving cladribine tablets.
Infections occurred in 49% of cladribine-treated patients compared to 44% of placebo patients in clinical studies; serious or severe infections occurred in 2.4% of cladribine-treated patients and 2% of placebo-treated patients. The most frequent serious infections in cladribine-treated patients included herpes zoster and pyelonephritis (see Herpes Virus Infections). Fungal infections were observed, including cases of coccidioidomycosis.
In the postmarketing setting, serious infections have been reported, including nocardiosis, varicella zoster, histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, and toxoplasmosis. The majority of patients with these infections who had an available absolute lymphocyte count at the time of the event had concurrent lymphopenia, consistent with the mechanism of action of cladribine tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
HIV infection, active tuberculosis, and active hepatitis must be excluded before initiation of each treatment course of cladribine tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
Delay initiation of cladribine tablets in patients with an acute infection until the infection is fully resolved or controlled.
Initiation of cladribine tablets in patients currently receiving immunosuppressive or myelosuppressive therapy is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Concomitant use of cladribine tablets with these therapies could increase the risk of immunosuppression.
Tuberculosis
Three of 1,976 (0.2%) cladribine-treated patients in the clinical program developed tuberculosis. All three cases occurred in regions where tuberculosis is endemic. One case of tuberculosis was fatal, and two cases resolved with treatment.
Perform tuberculosis screening prior to initiation of the first and second treatment course of cladribine tablets. Latent tuberculosis infections may be activated with use of cladribine tablets. In patients with tuberculosis infection, delay initiation of cladribine tablets until the infection has been adequately treated.
Hepatitis
One clinical study patient died from fulminant hepatitis B infection. Perform screening for hepatitis B and C prior to initiation of the first and second treatment course of cladribine tablets. Latent hepatitis infections may be activated with use of cladribine tablets. Patients who are carriers of hepatitis B or C virus may be at risk of irreversible liver damage caused by virus reactivation. In patients with hepatitis infection, delay initiation of cladribine tablets until the infection has been adequately treated.
Herpes Virus Infections
In controlled clinical studies, 6% of cladribine-treated patients developed a herpes viral infection compared to 2% of placebo patients. The most frequent types of herpes viral infections were herpes zoster infections (2.0% vs. 0.2%) and oral herpes (2.6% vs. 1.2%). Serious herpes zoster infections occurred in 0.2% of cladribine-treated patients.
Vaccination of patients who are seronegative for varicella zoster virus is recommended prior to initiation of cladribine tablets. Administer live-attenuated or live vaccines at least 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting cladribine tablets. Vaccination with zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted is recommended for patients who are seropositive to VZV, either prior to or during cladribine treatment, including when their lymphocyte counts are less than or equal to 500 cells per microliter.
The incidence of herpes zoster was higher during the period of absolute lymphocyte count less than 500 cells per microliter, compared to the time when the patients were not experiencing this degree of lymphopenia. Administer anti-herpes prophylaxis in patients with lymphocyte counts less than 200 cells per microliter.
Patients with lymphocyte counts below 500 cells per microliter should be monitored for signs and symptoms suggestive of infections, including herpes infections. If such signs and symptoms occur, initiate treatment as clinically indicated. Consider interruption or delay of cladribine tablets until resolution of the infection.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is an opportunistic viral infection of the brain caused by the JC virus (JCV) that typically only occurs in patients who are immunocompromised, and that usually leads to death or severe disability. Typical symptoms associated with PML are diverse, progress over days to weeks, and include progressive weakness on one side of the body or clumsiness of limbs, disturbance of vision, and changes in thinking, memory, and orientation leading to confusion and personality changes.
No case of PML has been reported in clinical studies of cladribine in patients with multiple sclerosis. In patients treated with parenteral cladribine for oncologic indications, cases of PML have been reported in the postmarketing setting.
Obtain a baseline (within 3 months) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before initiating the first treatment course of cladribine tablets. At the first sign or symptom suggestive of PML, withhold cladribine tablets and perform an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. MRI findings may be apparent before clinical signs or symptoms.
Vaccinations
Administer all immunizations (except as noted for VZV) according to immunization guidelines prior to starting cladribine tablets. Administer live-attenuated or live vaccines at least 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting cladribine tablets, because of a risk of active vaccine infection (see Herpes Virus Infections). Avoid vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines during and after cladribine treatment while the patient’s white blood cell counts are not within normal limits.
5.5 Hematologic Toxicity
In addition to lymphopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)], decreases in other blood cells and hematological parameters have been reported with cladribine in clinical studies. Mild to moderate decreases in neutrophil counts (cell count between 1,000 cells per microliter and < lower limit of normal (LLN)) were observed in 27% of cladribine-treated patients, compared to 13% of placebo patients whereas severe decreases in neutrophil counts (cell count below 1,000 cells per microliter) were observed in 3.6% of cladribine-treated patients, compared to 2.8% of placebo patients. Decreases in hemoglobin levels, in general mild to moderate (hemoglobin 8 g per dL to < LLN), were observed in 26% of cladribine-treated patients, compared to 19% of placebo patients. Decreases in platelet counts were generally mild (cell count 75,000 cells per microliter to < LLN) and were observed in 11% of cladribine- treated patients, compared to 4% of placebo patients.
In clinical studies at dosages similar to or higher than the approved cladribine dosage, serious cases of thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and pancytopenia (some with documented bone marrow hypoplasia) requiring transfusion and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor treatment have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) for information regarding graft-versus- host disease with blood transfusion].
Obtain complete blood count (CBC) with differential prior to, during, and after treatment with cladribine tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.5)].
5.6 Risk of Graft-Versus-Host Disease With Blood Transfusion
Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease has been observed rarely after transfusion of nonirradiated blood in patients treated with cladribine for non-MS treatment indications.
In patients who require blood transfusion, irradiation of cellular blood components is recommended prior to administration to decrease the risk of transfusion-related graft-versus-host disease. Consultation with a hematologist is advised.
5.7 Liver Injury
Cladribine tablets can cause liver injury. In clinical studies, 0.3% of cladribine-treated patients had liver injury (serious or causing treatment discontinuation) considered related to treatment, compared to 0 placebo patients. Onset ranged from a few weeks to several months after initiation of treatment with cladribine. Signs and symptoms of liver injury, including elevation of serum aminotransferases to greater than 20-fold the upper limit of normal, were observed. These abnormalities resolved upon treatment discontinuation.
Clinically significant and life-threatening liver injury has been reported in patients treated with cladribine tablets in the postmarketing setting. Patients with pre-existing liver disease and patients taking other hepatotoxic drugs may be at increased risk for developing liver injury when taking cladribine tablets. Most reported cases of liver injury associated with cladribine tablets occurred approximately 30 days after initiation (i.e., course 1, cycle 1) of treatment.
Cladribine tablets are not recommended in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 6) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Obtain serum aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin levels prior to each treatment cycle and course [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. If a patient develops clinical signs, including unexplained liver enzyme elevations, or symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction (e.g., unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine), promptly measure serum transaminases and total bilirubin and interrupt or discontinue treatment with cladribine tablets, as appropriate.
5.8 Hypersensitivity
In clinical studies, 11% of cladribine-treated patients had hypersensitivity reactions, compared to 7% of placebo patients. Hypersensitivity reactions that were serious and/or led to discontinuation of cladribine tablets (e.g., dermatitis, pruritis) occurred in 0.5% of cladribine-treated patients, compared to 0.1% of placebo patients. One patient had a serious hypersensitivity reaction with rash, mucous membrane ulceration, throat swelling, vertigo, diplopia, and headache after the first dose of cladribine tablets.
If a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue cladribine therapy. Do not use cladribine tablets in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cladribine [see Contraindications (4)].
5.9 Cardiac Failure
In clinical studies, one cladribine-treated patient experienced life-threatening acute cardiac failure with myocarditis, which improved after approximately one week. Cases of cardiac failure have also been reported with parenteral cladribine used for treatment indications other than multiple sclerosis.
Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of cardiac failure (e.g., shortness of breath, rapid or irregular heartbeat, swelling).
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions and potential risks are discussed, or discussed in greater detail, in other sections of the labeling:
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Risk of Teratogenicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Lymphopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Graft-Versus-Host Disease With Blood Transfusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Liver Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Cardiac Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the clinical trial program of cladribine in MS, 1,976 patients received cladribine for a total of 9,509 patient years. The mean time on study including follow-up was approximately 4.8 years, and approximately 24% of cladribine-treated patients had approximately 8 years of time on study including follow-up. Of these, 923 patients aged 18 to 66 years received cladribine as monotherapy at a cumulative dose of 3.5 mg per kg.
Table 2 shows adverse reactions in Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)] with an incidence of at least 5% for cladribine and higher than placebo. The most common (> 20%) adverse reactions reported in Study 1 are upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and lymphopenia.
Table 2 Adverse Reactions in Study 1 with an Incidence of at Least 5% for Cladribine tablets and Higher than Placebo
Cladribine
(N=440)
%Placebo
(N=435)
%Upper respiratory tract infection 38 32 Headache 25 19 Lymphopenia 24 2 Nausea 10 9 Back pain 8 6 Arthralgia and arthritis 7 5 Insomnia 6 4 Bronchitis 5 3 Hypertension 5 3 Fever 5 3 Depression 5 3 Hypersensitivity
In clinical studies, 11% of cladribine patients had hypersensitivity adverse reactions, compared to 7% of placebo patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Alopecia
Alopecia occurred in 3% of cladribine-treated patients compared to 1% of placebo patients.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome have been reported in patients that had received parenteral cladribine at a higher dosage than that approved for cladribine. These cases occurred several years after treatment.
Herpes Meningoencephalitis
Fatal herpes meningoencephalitis occurred in one cladribine-treated patient, at a higher dosage and longer duration of therapy than the approved cladribine dosage and in combination with interferon beta-1a treatment.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
SJS and TEN are identified risks of parenteral cladribine for the treatment of oncologic indications.
Seizures
In clinical studies, serious events of seizure occurred in 0.3% of cladribine-treated patients compared to 0 placebo patients. Serious events included generalized tonic-clonic seizures and status epilepticus. It is unknown whether these events were related to the effects of multiple sclerosis alone, to cladribine, or to a combination of both.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of cladribine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections and Infestations: nocardiosis, varicella zoster, histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, and toxoplasmosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hepatobiliary Disorders: liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 3 Drug Interactions with cladribine tablets
7.1 Immunomodulatory, Immunosuppressive, or Myelosuppressive Drugs Clinical Impact Concomitant use of cladribine with immunomodulatory, immunosuppressive, or myelosuppressive drugs may increase the risk of adverse reactions because of the additive effects on the immune system [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Prevention or Management Concomitant use with myelosuppressive or other immunosuppressive drugs is not recommended. Acute short-term therapy with corticosteroids can be administered.
In patients who have previously been treated with immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive drugs, consider potential additive effect, the mode of action, and duration of effect of the other drugs prior to initiation of cladribine.7.2 Interferon-Beta Clinical Impact Concomitant use of cladribine with interferon-beta did not change the exposure of cladribine to a clinically significant effect; however, lymphopenia risk may be increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Prevention or Management Concomitant use is not recommended. 7.3 Hematotoxic Drugs Clinical Impact Concomitant use of cladribine with hematotoxic drugs may increase the risk of adverse reactions because of the additive hematological effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Prevention or Management Monitor hematological parameters. 7.4 Antiviral and Antiretroviral Drugs Clinical Impact Compounds that require intracellular phosphorylation to become active (e.g., lamivudine, zalcitabine, ribavirin, stavudine, and zidovudine) could interfere with the intracellular phosphorylation and activity of cladribine. Prevention or Management Avoid concomitant use. 7.5 Potent ENT, CNT and BCRP Transporter Inhibitors Clinical Impact Cladribine is a substrate of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), equilibrative nucleoside (ENT1), and concentrative nucleoside (CNT3) transport proteins. The bioavailability, intracellular distribution, and renal elimination of cladribine may be altered by potent ENT1, CNT3, and BCRP transporter inhibitors. Prevention or Management Avoid co-administration of potent ENT1, CNT3, or BCRP transporter inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, eltrombopag, curcumin, cyclosporine, dilazep, nifedipine, nimodipine, cilostazol, sulindac, dipyridamole, or reserpine) during the 4 to 5 day cladribine treatment cycles. If this is not possible, consider selection of alternative concomitant drugs with no or minimal ENT1, CNT3, or BCRP transporter inhibiting properties. If this is not possible, dose reduction to the minimum mandatory dose of drugs containing these compounds, separation in the timing of administration, and careful patient monitoring is recommended. 7.6 Potent BCRP and P-gp Transporter Inducers Clinical Impact Possible decrease in cladribine exposure if potent BCRP or P-gp transporter inducers are co-administered. Prevention or Management Consider a possible decrease in cladribine efficacy if potent BCRP (e.g., corticosteroids) or P-gp (e.g., rifampicin, St. John's Wort) transporter inducers are co-administered. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated in pregnant women and in females and males of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception. There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with use of cladribine in pregnant women. Cladribine was embryolethal when administered to pregnant mice and produced malformations in mice and rabbits [see Data]. The observed developmental effects are consistent with the effects of cladribine on DNA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
When cladribine was administered intravenously (0, 0.5, 1.5, or 3 mg/kg/day) to pregnant mice during the period of organogenesis, fetal growth retardation and malformations (including exencephaly and cleft palate) and embryofetal death were observed at the highest dose tested. An increase in skeletal variations was observed at all but the lowest dose tested. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity.
When cladribine was administered intravenously (0, 0.3, 1, and 3 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis, fetal growth retardation and a high incidence of craniofacial and limb malformations were observed at the highest dose tested, in the absence of maternal toxicity. When cladribine was administered intravenously (0, 0.5, 1.5, or 3 mg/kg/day) to mice throughout pregnancy and lactation, skeletal anomalies and embryolethality were observed at all but the lowest dose tested.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Cladribine tablets are contraindicated in breastfeeding women because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5)]. Advise women not to breastfeed during dosing with cladribine and for 10 days after the last dose.
There are no data on the presence of cladribine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
In females of reproductive potential, pregnancy should be excluded before the initiation of each treatment course of cladribine [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Females of reproductive potential should prevent pregnancy by use of effective contraception during cladribine dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. Women who become pregnant during cladribine tablets therapy should discontinue treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Males
As cladribine interferes with DNA synthesis, adverse effects on human gametogenesis could be expected. Therefore, male patients of reproductive potential should take precautions to prevent pregnancy of their partner during cladribine dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients (below 18 years of age) have not been established. Use of cladribine is not recommended in pediatric patients because of the risk of malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with cladribine did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Caution is recommended when cladribine is used in elderly patients, taking into account the potential greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, concomitant diseases, and other drug therapy.
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
The concentration of cladribine is predicted to increase in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 60 to 89 mL per minute). Cladribine tablets are not recommended in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance below 60 mL per minute) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of cladribine is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment. Cladribine tablets are not recommended in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 6) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no experience with overdose of cladribine tablets. Lymphopenia is known to be dose- dependent. Particularly close monitoring of hematological parameters is recommended in patients who have been exposed to an overdose of cladribine tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)].
There is no known specific antidote to an overdose of cladribine tablets. Treatment consists of careful observation and initiation of appropriate supportive measures. Discontinuation of cladribine tablets may need to be considered. Because of the rapid and extensive intracellular and tissue distribution, hemodialysis is unlikely to eliminate cladribine to a significant extent.
-
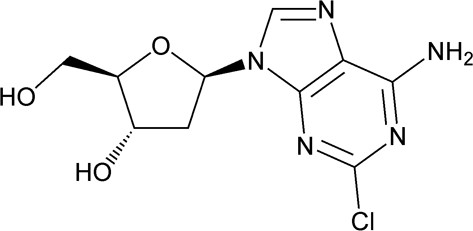
11 DESCRIPTION
Cladribine tablets contains the nucleoside metabolic inhibitor cladribine, which is a white to off-white crystalline powder with the molecular formula C10H12ClN5O3 and molecular weight 285.69 g/mol. It differs in structure from the naturally occurring nucleoside, deoxyadenosine, by the substitution of chlorine for hydrogen in the 2-position of the purine ring.
The chemical name of cladribine is 2-chloro-2′-deoxy-adenosine. The structural formula is shown below:
Cladribine is stable at slightly basic and at neutral pH. The main degradation pathway is hydrolysis and at acidic pH significant decomposition occurs with time. The ionization behavior of the molecule over the pH range 0 to 12 is characterized by a single pKa of approximately 1.21.
Cladribine tablets are provided as 10 mg tablet for oral use. Each 10 mg tablet contains cladribine as an active ingredient and magnesium stearate and sorbitol as inactive ingredients.
Cladribine tablets also contain hydroxypropyl betadex.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which cladribine exerts its therapeutic effects in patients with multiple sclerosis has not been fully elucidated but is thought to involve cytotoxic effects on B and T lymphocytes through impairment of DNA synthesis, resulting in depletion of lymphocytes.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cladribine tablets causes a dose-dependent reduction in lymphocyte count. The lowest absolute lymphocyte counts occurred approximately 2 to 3 months after the start of each treatment cycle and were lower with each additional treatment cycle. At the end of Year 2, 2% of patients continued to have absolute lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells per microliter. The median time to recovery from lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells per microliter to at least 800 cells per microliter was approximately 28 weeks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Cladribine is a prodrug that becomes active upon phosphorylation to its 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine triphosphate (Cd-ATP) metabolite.
The pharmacokinetic parameters presented below were assessed following oral administration of cladribine 10 mg, unless otherwise specified. The cladribine mean maximum concentration (Cmax) was in the range of 22 to 29 ng/ mL and corresponding mean AUC was in the range of 80 to 101 ng·h/mL.
The Cmax and AUC of cladribine increased proportionally across a dose range from 3 to 20 mg.
No accumulation of cladribine concentration in plasma was observed after repeated dosing.
Absorption
The bioavailability of cladribine was approximately 40%. Following fasted administration of cladribine, the median time to maximum concentration (Tmax) was 0.5 h (range 0.5 to 1.5 hours).
Effect of Food
Following administration of cladribine with a high fat meal, the geometric mean Cmax decreased by 29% and AUC was unchanged. The Tmax was prolonged to 1.5 hours (range 1 to 3 hours). This difference is not expected to be clinically significant.
Distribution
Cladribine mean apparent volume of distribution ranges from 480 to 490 liters. The plasma protein binding of cladribine is 20% and is independent of concentration, in vitro.
Intracellular concentrations of cladribine and/or its metabolites in human lymphocytes were approximately 30 to 40 times extracellular, in vitro.
Cladribine has the potential to penetrate the blood brain barrier. A cerebrospinal fluid/plasma concentration ratio of approximately 0.25 was observed in cancer patients.
Elimination
Cladribine estimated terminal half-life is approximately 1 day. The intracellular half-life of the cladribine phosphorylated metabolites cladribine monophosphate (Cd-AMP) is 15 hours and Cd- ATP is 10 hours. Cladribine estimated median apparent renal clearance is 22.2 liter per hour and non-renal clearance is 23.4 liter per hour.
Metabolism
Cladribine is a prodrug that is phosphorylated to Cd-AMP by deoxycytidine kinase (and also by deoxyguanosine kinase in the mitochondria) in lymphocytes. Cd-AMP is further phosphorylated to cladribine diphosphate (Cd-ADP) and the active moiety Cd-ATP. The dephosphorylation and deactivation of Cd-AMP is catalyzed by cytoplasmic 5’-nucleotidase (5’-Ntase).
The metabolism of cladribine in whole blood has not been fully characterized. However, extensive whole blood and negligible hepatic enzyme metabolism was observed, in vitro.
Excretion
After administration of 10 mg oral cladribine in MS patients, 28.5 [20] (mean [SD]) percent of the dose was excreted unchanged via the renal route. Renal clearance exceeded the glomerular filtration rate, indicating active renal secretion of cladribine.
Specific Populations
No studies have been conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of cladribine in elderly or in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of cladribine based on age (range 18 to 65 years) or gender. The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of cladribine is unknown.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Renal clearance of cladribine was shown to be dependent on creatinine clearance (CLCR). No dedicated studies have been conducted in patients with renal impairment, however patients with mild renal impairment (CLCR of 60 mL to below 90 mL per minute) were included in Study 1. A pooled pharmacokinetic analysis estimated a decrease of 18% in total clearance in a typical subject with a CLCR of 65 mL per minute leading to an increase in cladribine exposure of 25%. Clinical experience in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (i.e., CLCR below 60 mL per minute) is limited [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
No clinically significant differences in cladribine pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with pantoprazole or interferon beta-1a.
No clinically significant differences in ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel pharmacokinetics were observed when a combined oral hormonal contraceptive (containing 150 mcg levonorgestrel and 30 mcg ethinyl estradiol) was used concomitantly with cladribine.
In Vitro Studies
It has been reported that lamivudine can inhibit the phosphorylation of cladribine intracellularly. Potential competition for intracellular phosphorylation exists between cladribine and compounds that require intracellular phosphorylation to become active (e.g., lamivudine, zalcitabine, ribavirin, stavudine, and zidovudine).
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: Cladribine is not a substrate of cytochrome P450 enzymes and does not show significant potential to act as inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4. Cladribine has no clinically meaningful inductive effect on CYP1A2, CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 enzymes.
Transporter Systems: Cladribine is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1) and concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 (CNT3). Inhibition of BCRP in the gastrointestinal tract may increase the oral bioavailability and systemic exposure of cladribine. Intracellular distribution and renal elimination of cladribine may be altered by potent ENT1, CNT3 transporter inhibitors.
12.6 Hydroxypropyl Betadex-Related Complex Formation
Cladribine tablets contain hydroxypropyl betadex that may be available for complex formation with the active ingredients of other drugs. Complex formation between free hydroxypropyl betadex, released from the cladribine tablet formulation, and concomitant ibuprofen, furosemide, and gabapentin was observed. Concomitant use with cladribine tablets may increase the bioavailability of other drugs (especially agents with low solubility), which may increase the risk or severity of adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In mice administered cladribine (0, 0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg) by subcutaneous injection intermittently (7 daily doses followed by 21 days of non-dosing per cycle) for 22 months, an increase in Harderian gland tumors (adenoma) was observed at the highest dose tested.
Mutagenesis
Cladribine was negative for mutagenicity in in vitro (reverse mutation in bacteria, CHO/HGPRT mammalian cell) assays.
Cladribine was positive for clastogenicity in an in vitro mammalian cell assay, in the absence and presence of metabolic activation, and in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
When cladribine (0, 1, 5, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) was administered by subcutaneous injection to male mice prior to and during mating to untreated females, no effects on fertility were observed. However, an increase in non-motile sperm was observed at the highest dose tested. In female mice, administration of cladribine (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 mg/kg/day) by subcutaneous injection prior to and during mating to untreated males and continuing to gestation day 6 caused an increase in embryolethality at the highest dose tested.
In monkeys administered cladribine (0, 0.15, 0.3, or 1.0 mg/kg) by subcutaneous injection intermittently (7 consecutive daily doses followed by 21 days of non-dosing per cycle) for one year, testicular degeneration was observed at the highest dose tested.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of cladribine tablets was demonstrated in a 96-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study in patients with relapsing forms of MS (Study 1; NCT00213135).
Patients were required to have at least 1 relapse in the previous 12 months. The median age was 39 years (range 18 to 65) and the female-to-male ratio was approximately 2:1. The mean duration of MS prior to study enrollment was 8.7 years, and the median baseline neurological disability based on Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score across all treatment groups was 3. Over two thirds of the study patients were treatment-naive for drugs used to treat relapsing forms of MS.
1,326 patients were randomized to receive either placebo (n = 437), or a cumulative oral dosage of cladribine 3.5 mg per kg (n = 433) or 5.25 mg per kg body weight (n = 456) over the 96-week study period in 2 treatment courses. Patients randomized to the 3.5 mg per kg cumulative dose received a first treatment course at Weeks 1 and 5 of the first year and a second treatment course at Weeks 1 and 5 of the second year [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Patients randomized to the 5.25 mg per kg cumulative dose received additional treatment at Weeks 9 and 13 of the first year. Higher cumulative doses did not add any clinically meaningful benefit, but were associated with a higher incidence in grade 3 lymphopenia or higher (44.9% in the 5.25 mg per kg group vs. 25.6% in the 3.5 mg per kg group). Ninety-two percent of patients treated with cladribine 3.5 mg per kg and 87% of patients receiving placebo completed the full 96 weeks of the study.
The primary outcome of Study 1 was the annualized relapse rate (ARR). Additional outcome measures included the proportion of patients with confirmed disability progression, the time to first qualifying relapse, the mean number of MRI T1 Gadolinium-enhancing (Gd+) lesions, and new or enlarging MRI T2 hyperintense lesions. Disability progression was measured in terms of a 3-month sustained change in EDSS score of at least one point, if baseline EDSS score was between 0.5 and 4.5 inclusively, or at least 1.5 points if the baseline EDSS score was 0, or at least 0.5 point if the baseline EDSS score was at least 5, over a period of at least 3 months.
Cladribine 3.5 mg per kg significantly lowered the annualized relapse rate. The results from Study 1 are presented in Table 4.
Table 4 Clinical Outcomes in Study 1 (96 Weeks) - Primary and Secondary Endpoints
Endpoints Cladribine Cumulative Dose 3.5 mg per kg (n = 433) Placebo (n = 437) Clinical Endpoints Annualized relapse rate (ARR) 0.14* 0.33 Relative reduction in ARR 58% Proportion of patients without relapse 81%** 63% Time to 3-month confirmed EDSS progression, HR 0.67** Proportion of patients with 3-month EDSS progression 13% 19% MRI Endpoints Median Number of Active T1 Gd+ Lesions 0* 0.33 Median Number of Active T2 Lesions 0* 0.67 * p < 0.001 compared to placebo
** nominal p < 0.05 compared to placebo
HR: Hazard Ratio
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
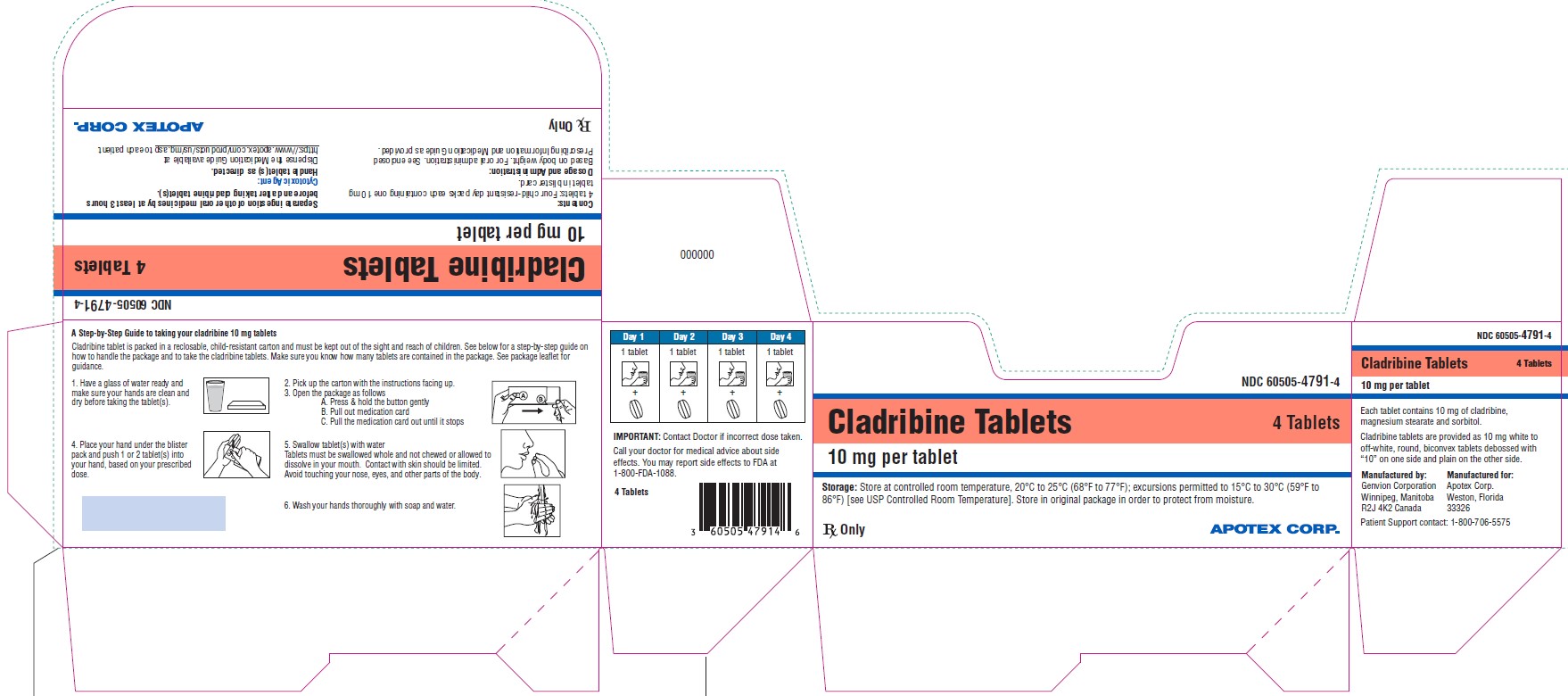
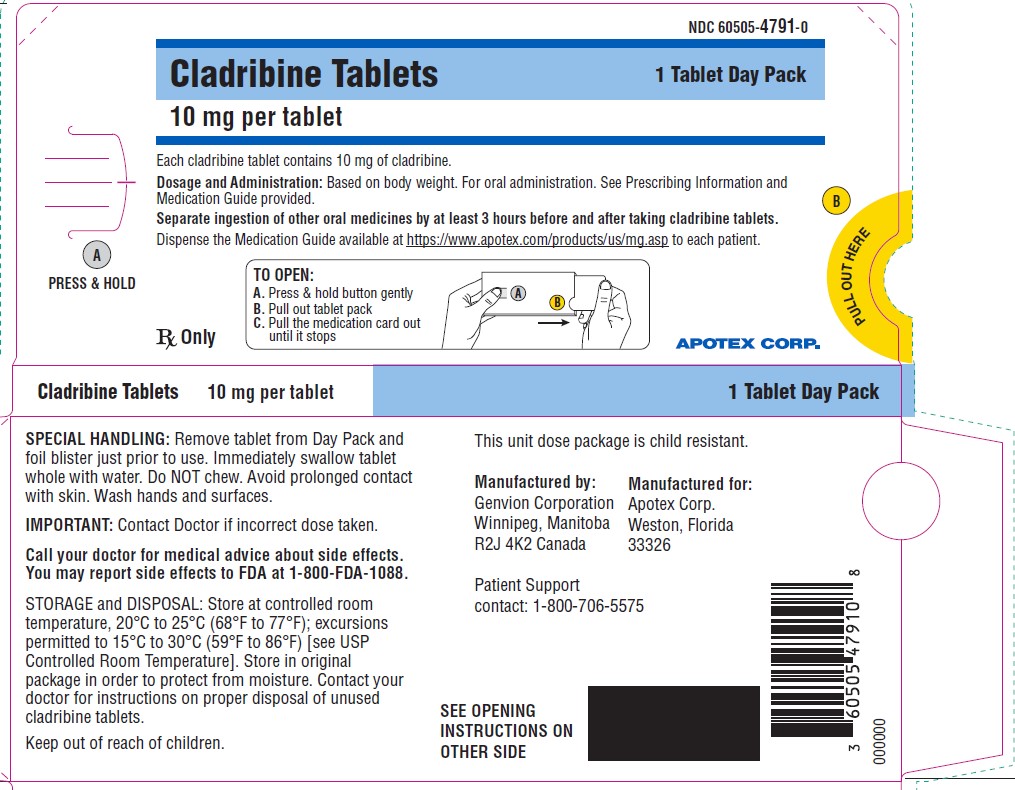
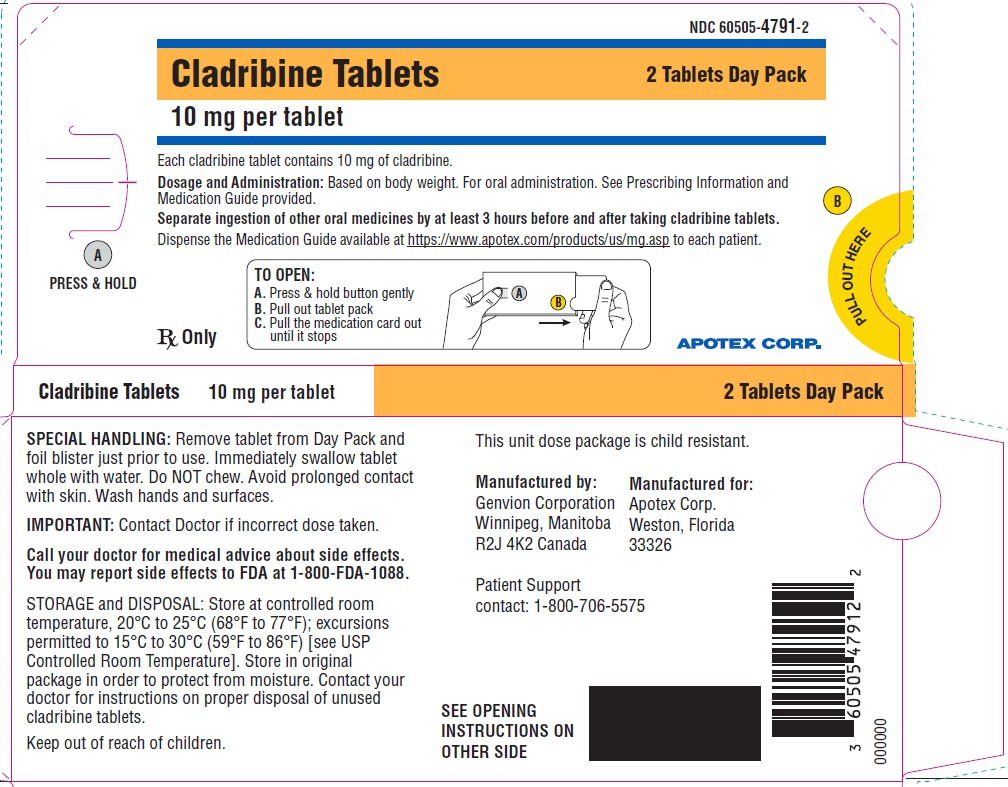
Cladribine tablets, 10 mg, are white to off white, round, biconvex tablets debossed with “10” on one side and plain on the other side. Each tablet is packaged in a child-resistant day pack containing one or two tablets in a blister card.
Dispense one box for each treatment cycle with a Medication Guide [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Presentations
NDC: 60505-4791-4
NDC: 60505-4791-5
NDC: 60505-4791-6
NDC: 60505-4791-7
NDC: 60505-4791-8
NDC: 60505-4791-9
NDC 60505-4791-1Box of 4 tablets: Four day packs each containing one tablet.
Box of 5 tablets: Five day packs each containing one tablet.
Box of 6 tablets: One day pack containing two tablets. Four day packs each containing one tablet.
Box of 7 tablets: Two day packs each containing two tablets. Three day packs each containing one tablet.
Box of 8 tablets: Three day packs each containing two tablets. Two day packs each containing one tablet.
Box of 9 tablets: Four day packs each containing two tablets. One day pack containing one tablet.
Box of 10 tablets: Five day packs each containing two tablets.16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at controlled room temperature, 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in original package in order to protect from moisture.
Cladribine tablets are a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures [see References (15)].1
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Malignancies
Inform patients that cladribine tablets may increase their risk of malignancies. Instruct patients to follow standard cancer screening guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Risk of Teratogenicity
Inform patients that cladribine tablets may cause fetal harm. Discuss with women of childbearing age whether they are pregnant, might be pregnant, or are trying to become pregnant. Before initiating each treatment course, inform patients about the potential risk to the fetus, if female patients or partners of male patients get pregnant during cladribine tablets dosing or within 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Instruct female patients of childbearing potential to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course to avoid pregnancy.
Instruct male patients to take precautions to prevent pregnancy of their partner during cladribine tablets dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course.
Advise patients that female patients or partners of male patients who get pregnant immediately inform their healthcare provider.
Lactation
Inform women that they cannot breastfeed on a cladribine treatment day and for 10 days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Lymphopenia and Other Hematologic Toxicity
Inform patients that cladribine tablets decreases lymphocyte counts and may also decrease counts of other blood cells. A blood test should be obtained before starting a treatment course, 2 and 6 months after start of treatment in each treatment course, periodically thereafter, and when clinically needed. Advise patients to keep all appointments for lymphocyte monitoring during and after cladribine treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)].
Infections
Inform patients that infections, some of which were serious, have been reported in patients receiving cladribine tablets. Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider promptly if fever or other signs of infection such as aching, painful muscles, headache, generally feeling unwell or loss of appetite occur while on therapy or after a course of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Advise patients that PML has happened with parenteral cladribine used in oncologic indications. Inform the patient that PML is characterized by a progression of deficits and usually leads to death or severe disability over weeks or months. Instruct the patient of the importance of contacting their doctor if they develop any symptoms suggestive of PML. Inform the patient that typical symptoms associated with PML are diverse, progress over days to weeks, and include progressive weakness on one side of the body or clumsiness of limbs, disturbance of vision, and changes in thinking, memory, and orientation leading to confusion and personality changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Advise patients that some vaccines containing live virus (live attenuated vaccines) should be avoided during and after treatment with cladribine tablets. Advise patients to complete any live or live-attenuated vaccinations at least 4 to 6 weeks prior to initiation of cladribine tablets. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider prior to receiving any vaccinations.
Liver Injury
Inform patients that liver injury has been reported in patients receiving cladribine tablets. Instruct patients treated with cladribine tablets to report promptly any symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice. A blood test should be obtained prior to each treatment cycle and course with cladribine tablets and as clinically indicated thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Hypersensitivity
Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions, including skin reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Cardiac Failure
Advise patients that cladribine tablets may cause cardiac failure. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of cardiac failure (e.g., shortness of breath, rapid or irregular heartbeat, swelling) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Treatment Handling and Administration
Instruct patients that cladribine tablets are a cytotoxic drug and to use care when handling cladribine tablets, limit direct skin contact with the tablets, and wash exposed areas thoroughly. Advise patients to keep the tablets in the original package until just prior to each scheduled dose and consult their pharmacist on the proper disposal of unused tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)].
Dispense with Medication Guide available at https://www.apotex.com/products/us/mg.asp
Rx Only
APOTEX INC.
CLADRIBINE TABLETS
10 mg
Manufactured by:
Genvion Corporation
Winnipeg, Manitoba
R2J 4K2 CanadaManufactured for:
Apotex Corp.
Weston, Florida
USA 33326Rev: 4
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Cladribine (klad′ ri been) Tablets,
for oral use
Medication Guide available at https://www.apotex.com/products/us/mg.asp
What is the most important information I should know about cladribine tablets?
Cladribine tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
- Risk of cancer (malignancies). Treatment with cladribine tablets may increase your risk of developing cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about your risk of developing cancer if you receive cladribine tablets. You should follow your healthcare provider's instructions about screening for cancer.
-
Cladribine tablets may cause birth defects if used during pregnancy. Women must not be pregnant when they start treatment with cladribine tablets or become pregnant during cladribine tablets dosing and within 6 months after the last dose of each yearly treatment course. Stop your treatment with cladribine tablets and call your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant during treatment with cladribine tablets.
- For women who are able to become pregnant:
- Your healthcare provider should order a pregnancy test for you before you begin your first and second yearly treatment course of cladribine tablets to make sure that you are not pregnant. Your healthcare provider will decide when to do the test.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) on the days on which you take cladribine tablets and for at least 6 months after the last dose of each yearly treatment course.
Ask your healthcare provider which contraception method is right for you.
- For men with female partners who are able to become pregnant:
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during the days on which you take cladribine tablets and for at least 6 months after the last dose of each yearly treatment course.
- For women who are able to become pregnant:
What are cladribine tablets?
Cladribine tablets are prescription medicine used to treat relapsing form of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include relapsing-remitting disease in adults. Because of its risks, cladribine tablets are generally used in people who have tried another MS medicine that they could not tolerate or that has not worked well enough.
Cladribine tablets are not recommended for use in people with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS).
It is not known if cladribine tablets are safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
Do not take cladribine tablets if you:
- have cancer (malignancy).
- are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are a woman of childbearing age or a man able to father a child and you are not using birth control. See “What is the most important information I should know about cladribine tablets?”
- are human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive.
- have active infections, including tuberculosis (TB), hepatitis B or C.
- are allergic to cladribine.
- are breastfeeding. See “Before you take cladribine tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:”
Before you take cladribine tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- think you have an infection.
- have heart failure.
- have liver or kidney problems.
- have taken, take, or plan to take medicines that affect your immune system or your blood cells, or other treatments for MS. Certain medicines can increase your risk of getting an infection.
- have had a recent vaccination or are scheduled to receive any vaccinations. You should not receive live or live- attenuated vaccines within the 4 to 6 weeks before you start your treatment with cladribine tablets. You should not receive these types of vaccines during your treatment with cladribine tablets and until your healthcare provider tells you that your immune system is no longer weakened.
- have or have had cancer.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if cladribine passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed on the days on which you take cladribine tablets, and for 10 days after the last dose. See “Do not take cladribine tablets if you:”
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I take cladribine tablets?
- Cladribine tablets are given as two yearly treatment courses.
- Each yearly treatment course consists of 2 treatment weeks (also called cycles) that will be about a month apart. Your healthcare provider will tell you when you have to start your treatment weeks and how many tablets per week you need, depending on your weight. Each treatment week is 4 or 5 days.
- Your pharmacist will dispense a carton of cladribine tablets for each treatment week. The prescribed number of tablets per day are provided in child resistant day packs.
- Take cladribine tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Do not change your dose or stop taking cladribine tablets unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Take cladribine tablets with water and swallow whole without chewing. Cladribine tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Swallow cladribine tablets right away after opening the blister pack.
- Your hands must be dry when handling cladribine tablets and washed well with water afterwards.
- Limit contact with your skin. Avoid touching your nose, eyes and other parts of the body. If you get cladribine tablets on your skin or on any surface, wash it right away with water.
- Take cladribine tablets at least 3 hours apart from other medicines taken by mouth during the 4- to 5- day cladribine treatment week.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember on the same day. If the whole day passes before you remember, take your missed dose the next day. Do not take 2 doses at the same time. Instead, you will extend the number of days in that treatment week.
Your healthcare provider will continue to monitor your health during the 2 yearly treatment courses, and for at least another 2 years during which you do not need to take cladribine tablets. It is not known if cladribine tablets are safe and effective in people who restart cladribine treatment more than 2 years after completing 2 yearly treatment courses.
What are the possible side effects of cladribine tablets?
Cladribine tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about cladribine tablets?”
- low blood cell counts. Low blood cell counts have happened and can increase your risk of infections during your treatment with cladribine tablets. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests before you start treatment with cladribine tablets, during your treatment with cladribine tablets, and afterward, as needed.
-
serious infections such as:
- Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi that may be life-threatening or cause death.
-
TB, hepatitis B or C, and shingles (herpes zoster). Fatal cases of TB and hepatitis have happened with cladribine during clinical studies. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any symptoms of the following infection related problems or if any of the symptoms get worse, including:
- fever
- loss of appetite
- aching painful muscles
- burning, tingling, numbness or itchiness of the skin in the affected area
- headache
- skin blotches, blistered rash and severe pain
- feeling of being generally unwell
-
progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML is a rare brain infection that usually leads to death or severe disability. Although PML has not been seen in MS patients taking cladribine tablets, it may happen in people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms of PML get worse over days to weeks. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any new or worsening neurologic signs or symptoms of PML, that have lasted several days, including:
- weakness on 1 side of your body
- changes in your vision
- loss of coordination in your arms and legs
- changes in your thinking or memory
- decreased strength
- confusion
- problems with balance
- changes in your personality
-
liver problems. Cladribine tablets may cause liver damage. Your risk of developing serious liver problems may be higher if you already have liver problems or take other medicines that also affect your liver. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your liver:
-
before you start taking cladribine tablets
-
before each course and cycle of cladribine tablets treatment
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems: - nausea
- loss of appetite
- vomiting
- your skin or the whites or your eyes turn yellow
- stomach pain
- dark urine
- tiredness
-
- allergic reactions (hypersensitivities). Cladribine tablets can cause serious allergic reactions. Stop your treatment with cladribine tablets and go to the closest emergency room for medical help right away if you have any signs or symptoms of allergic reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include: skin rash, swelling or itching of the face, lips, tongue or throat, or trouble breathing.
- heart failure. Cladribine tablets may cause heart failure, which means your heart may not pump as well as it should. Call your healthcare provider or go to the closest emergency room for medical help right away if you have any signs or symptoms such as shortness of breath, a fast or irregular heartbeat, or unusual swelling in your body.
Your healthcare provider may delay or completely stop treatment with cladribine tablets if you have severe side effects.
The most common side effects of cladribine tablets include:
- upper respiratory infection
- headache
- low white blood cell counts
These are not all the possible side effects of cladribine tablets. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store cladribine tablets?
- Cladribine tablets comes in a child resistant package.
- Store cladribine tablets at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C).
- Store cladribine tablets in the original package to protect from moisture.
- Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about how to safely throw away any unused or expired cladribine tablets and packaging.
Keep cladribine tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of cladribine tablets:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use cladribine tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give cladribine tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about cladribine tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in cladribine tablets?
Active ingredient: cladribine
Inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate and sorbitol.
Cladribine tablets also contain hydroxypropyl betadex.
For more information, call toll-free 1-800-706-5575 or go to www.apotex.com
Rx Only
APOTEX INC.
CLADRIBINE TABLETS
10 mg
Manufactured by:
Genvion Corporation
Winnipeg, Manitoba
R2J 4K2 CanadaManufactured for:
Apotex Corp.
Weston, Florida
USA 33326Revised: May 2024
Rev: 4
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Carton - Box of 4 Tablets
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - DAY PACK - 1 Tablet
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - DAY PACK - 2 Tablets
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLADRIBINE
cladribine tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60505-4791 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Cladribine (UNII: 47M74X9YT5) (Cladribine - UNII:47M74X9YT5) Cladribine 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Sorbitol (UNII: 506T60A25R) HYDROXYPROPYL BETADEX (UNII: 1I96OHX6EK) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND (biconvex) Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code 10 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60505-4791-4 4 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 2 NDC: 60505-4791-5 5 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 3 NDC: 60505-4791-6 6 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 4 NDC: 60505-4791-7 7 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 5 NDC: 60505-4791-8 8 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 6 NDC: 60505-4791-9 9 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 7 NDC: 60505-4791-1 10 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/25/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA218425 11/25/2025 Labeler - Apotex Corp. (845263701)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.