VASOPRESSIN injection, solution
VASOPRESSIN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
VASOPRESSIN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Feneral Injectables & Vaccines, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION:
Vasopressin Injection, USP is a sterile solution of synthetic vasopressin of the posterior pituitary gland for intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous use. It is substantially free from the oxytocic principle and is standardized to contain 20 pressor units/mL. The chemical name is Vasopressin, 8-L-arginine and has the following structural formula:
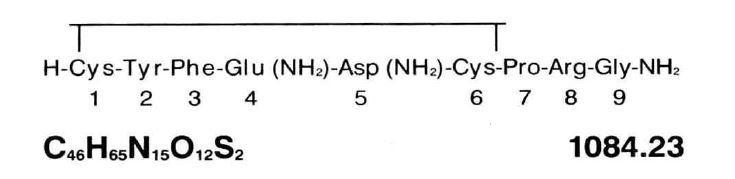
Each mL contains: 20 USP Vasopressin Units, chlorobutanol (anhydrous) 5 mg as preservative; Water for Injection q.s. Glacial acetic acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added for pH adjustment (2.4-4.5).
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
The antidiuretic action of vasopressin is ascribed to increasing reabsorption of water by the renal tubules.
Vasopressin can cause contraction of smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract and of all parts of the vascular bed, especially the capillaries, small arterioles and venules with less effect on the smooth musculature of the large veins. The direct effect on the contractile elements is neither antagonized by adrenergic blocking agents nor prevented by vascular denervation.
Following subcutaneous or intramuscular administration of vasopressin injection, the duration of antidiuretic activity is variable but effects are usually maintained for 2 to 8 hours.
The majority of a dose of vasopressin is metabolized and rapidly destroyed in the liver and kidneys. Vasopressin has a plasma half-life of about 10 to 20 minutes. Approximately 5% of a subcutaneous dose of vasopressin is excreted in urine unchanged after 4 hours.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
- CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS:
This drug should not be used in patients with vascular disease, especially disease of the coronary arteries, except with extreme caution. In such patients, even small doses may precipitate anginal pain, and with larger doses, the possibility of myocardial infarction should be considered.
Vasopressin may produce water intoxication. The early signs of drowsiness, listlessness and headaches should be recognized to prevent terminal coma and convulsions.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Vasopressin should be used cautiously in the presence of epilepsy, migraine, asthma, heart failure or any state in which a rapid addition to extracellular water may produce hazard for an already overburdened system.
Chronic nephritis with nitrogen retention contraindicates the use of vasopressin until reasonable nitrogen blood levels have been attained.
Information for Patients
Side effects such as blanching of skin, abdominal cramps, and nausea may be reduced by taking 1 or 2 glasses of water at the time of vasopressin administration. These side effects are usually not serious and probably will disappear within a few minutes.
Laboratory Tests
Electrocardiograms (ECG) and fluid and electrolyte status determinations are recommended at periodic intervals during therapy.
Drug Interactions
The following drugs may potentiate the antidiuretic effect of vasopressin when used concurrently: carbamazepine; chlorpropamide; clofibrate; urea; fludrocortisone; tricyclic antidepressants.
The following drugs may decrease the antidiuretic effect of vasopressin when used concurrently: demeclocycline; norepinephrine; lithium; heparin; alcohol.
Ganglionic blocking agents may produce a marked increase in sensitivity to the pressor effects of vasopressin.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with vasopressin. It is also not known whether vasopressin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Vasopressin should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Local or systemic allergic reactions may occur in hypersensitive individuals. The following side effects have been reported following the administration of vasopressin:
Body as a Whole
Anaphylaxis (cardiac arrest and/or shock) has been observed shortly after injection of vasopressin.
Cardiovascular
Cardiac arrest, circumoral pallor, arrhythmias, decreased cardiac output, angina, myocardial ischemia, peripheral vasoconstriction, and gangrene.
Gastrointestinal
Abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, passage of gas.
Nervous System
Tremor, vertigo, "pounding" in head.
Respiratory
Bronchial constriction.
Skin and Appendages
Sweating, urticaria, cutaneous gangrene.
Overdosage
Water intoxication may be treated with water restriction and temporary withdrawal of vasopressin until polyuria occurs. Severe water intoxication may require osmotic diuresis with mannitol, hypertonic dextrose, or urea alone or with furosemide.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Vasopressin Injection may be administered IM or subcutaneously.
Ten units (0.5 mL) of Vasopressin Injection will usually elicit full physiologic response in adult patients; 5 units (0.25 mL) will be adequate in many cases. Vasopressin Injection should be given IM at three or four hour intervals as needed. The dosage should be proportionately reduced for pediatric patients. (For an additional discussion of dosage, consult the sections below.)
When determining the dose of Vasopressin Injection for a given case, the following should be kept in mind:
It is particularly desirable to give a dose not much larger than is just sufficient to elicit the desired physiologic response. Excessive doses may cause undesirable side effects-blanching of the skin, abdominal cramps, nausea-which, though not serious, may be alarming to the patient. Spontaneous recovery from such side effects occurs in a few minutes. It has been found that one or two glasses of water given at the time Vasopressin Injection is administered reduces such symptoms.
Abdominal Distention
In the average postoperative adult patient, give 5 units (0.25 mL) initially, increase to 10 units (0.5 mL) at subsequent injections if necessary. It is recommended that Vasopressin Injection be given IM and that injections be repeated at three or four hour intervals as required. Dosage to be reduced proportionately for pediatric patients.
Vasopressin Injection used in this manner will frequently prevent, or relieve, postoperative distention. These recommendations apply also to distention complicating pneumonia or other acute toxemias.
Abdominal Roentgenography
For the average case, two injections of 10 units (0.5 mL) each are suggested. These should be given two hours and one-half hour, respectively, before films are exposed. Many roentgenologists advise giving an enema prior to the first dose of Vasopressin Injection.
Diabetes Insipidus
Vasopressin Injection may be given by injection or administered intranasally on cotton pledgets, by nasal spray, or by dropper. The dose by injection is 5 to 10 units (0.25 to 0.5 mL) repeated two or three times daily as needed. When Vasopressin Injection is administered intranasally by spray or on pledgets, the dosage and interval between treatments must be determined for each patient.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for paticulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Product No. NDC No. 30201 63323-302-01 Vasopressin Injection, USP 20 units, 1 mL in a 2 mL flip-top vial in packages of 25. Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Do not freeze.
Vial stoppers do not contain natural rubber latex.
APP
APP PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC
Schaumburg, IL 60173
45875E
Revised: March 2010
- SAMPLE PACKAGE LABEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VASOPRESSIN
vasopressin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 52584-302(NDC:63323-302) Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VASOPRESSIN (UNII: Y87Y826H08) (VASOPRESSIN - UNII:Y87Y826H08) VASOPRESSIN 20 [USP'U] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CHLOROBUTANOL (UNII: HM4YQM8WRC) 5 mg in 1 mL ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 52584-302-01 1 in 1 BAG 12/17/2013 01/16/2017 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 12/17/2013 Labeler - Feneral Injectables & Vaccines, Inc (108250663)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
