INZIRQO- hydrochlorothiazide powder, for suspension
INZIRQO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
INZIRQO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Novitium Pharma LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INZIRQO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INZIRQO.
INZIRQO (hydrochlorothiazide), for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 1959
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
INZIRQO™ (hydrochlorothiazide) is a thiazide diuretic indicated for: (1)
- The treatment of hypertension in adult and pediatric patients alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarction (1.1).
- The treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis and renal disease including the nephrotic syndrome in adult and pediatric patients. (1.2).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For the treatment of hypertension in adults: The recommended initial dose in adults is 25 mg orally daily given as a single dose. As needed, increase the dose to 50 mg orally daily, given as a single or two divided doses(2.1).
- For the treatment of edema in adults: The recommended adult dosage is 25 mg to 100 mg orally daily as a single or divided dose. Consider intermittent therapy to reduce the risk of electrolyte imbalances, i.e., administration on alternate days or on 3 to 5 days each week (2.2).
- For the treatment of hypertension and edema in pediatric patients: The recommended pediatric dosage is 1 mg/kg to 2 mg/kg orally per day in single or two divided doses. Do not exceed 37.5 mg per day in patients less than 2 years of age or 100 mg per day in children 2 to less than 13 years of age. Patients less than 6 months of age may require doses up to 3 mg/kg orally per day in two divided doses (2.1, 2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For oral suspension: 10 mg/mL (3) (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Anuria (4)
- Hypersensitivity to hydrochlorothiazide or any ingredient in INZIRQO (4)
- Hypersensitivity to sulfonamide-derived drugs (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Monitor kidney function periodically (5.1)
- Monitor and correct serum electrolytes prior to use and monitor periodically (5.2).
- Monitor blood sugar, lipid levels, uric acid and calcium levels periodically. (5.3)
- Exacerbation or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus (5.4)
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma and acute myopia (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions include hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hyperlipidemia and hypotension. See Adverse Reactions (6) (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-204-1431 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- NSAID: May lead to increased risk of renal impairment and loss of diuretic and antihypertensive effect (7.1).
- Cholestyramine and colestipol: Reduced absorption of thiazides (7.1)
- Lithium: Increased lithium concentrations and lithium toxicity (7.2)
- Antidiabetic drugs: Dosage adjustment of antidiabetic may be required (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
1.2 Edema
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Hypertension
2.2 Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Edema
2.3 Preparation of Oral Suspension
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Impaired Renal Function
5.2 Electrolyte Abnormalities
5.3 Metabolic Disturbances
5.4 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5.5 Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma and Acute Myopia
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect INZIRQO
7.2 Potential for INZIRQO to Affect Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
INZIRQO is indicated for the treatment of hypertension in adult and pediatric patients, to lower blood pressure.
Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes., including the class to which this drug principally belongs.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
INZIRQO can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
-
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Hypertension
The recommended initial dose in adults is 25 mg orally daily given as a single dose. As needed, increase the dose to 50 mg orally daily, given as a single or two divided doses.
Pediatric Patients:
The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 1 to 2 mg/kg per day in one or two divided doses not to exceed 37.5 mg in patients less than 2 years of age and 100 mg in patients 2 to less than 13 years of age. In pediatric patients less than 6 months of age, doses up to 3 mg/kg per day in two divided doses may be required.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for the Treatment of Edema
The recommended adult dosage is 25 mg to 100 mg orally daily as a single or divided dose. Consider intermittent therapy to reduce the risk of electrolyte imbalances, i.e., administration on alternate days or on 3 to 5 days each week.
Pediatric Patients:
The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 1 to 2 mg/kg per day in one or two divided doses not to exceed 37.5 mg in patients less than 2 years of age and 100 mg in patients 2 to less than 13 years of age. In pediatric patients less than 6 months of age, doses up to 3 mg/kg per day in two divided doses may be required.
2.3 Preparation of Oral Suspension
INZIRQO is supplied as a powder for oral suspension and must be reconstituted prior to dispensing.
- Gently shake the bottle to loosen the powder, add 66 mL of water and shake vigorously for minimum of 30 seconds. When reconstituted as directed, the solution will result in a 10 mg/mL concentration of hydrochlorothiazide.
- Store the reconstituted solution at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
- Write the date of expiration of the reconstituted oral suspension (calculated as 30 days after reconstitution) on the bottle label.
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
- Instruct patients or caregivers to use an oral dosing syringe to correctly measure the prescribed amount of medication. Inform patients that a bottle adapter and oral dosing syringes may be obtained from their pharmacy.
- Advise patients to always shake the bottle well prior to each use.
- INZIRQO may be administered with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Impaired Renal Function
Monitor kidney function periodically. Diuretics can cause hypovolemia which may precipitate acute kidney injury. Patients with chronic kidney disease, heart failure, or volume depletion may be at particular risk of developing acute renal failure on INZIRQO. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in kidney function while on INZIRQO.
5.2 Electrolyte Abnormalities
INZIRQO can cause potentially symptomatic hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, and hypochloremic alkalosis. Hypomagnesemia can result in hypokalemia which appears difficult to treat despite potassium repletion. Hypokalemia is dose dependent. Monitor and correct serum electrolytes prior to use and monitor periodically. Discontinue INZIRQO if hypokalemia is associated with clinical symptoms (e.g., ECG changes, muscular weakness).
5.3 Metabolic Disturbances
INZIRQO may increase blood sugar levels, affect diabetes control, and cause changes in the need for diabetes medication.
INZIRQO may raise serum levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. Monitor blood sugar and lipid levels.
INZIRQO may raise the serum uric acid level due to reduced clearance of uric acid and may cause or exacerbate hyperuricemia and precipitate gout in susceptible patients. Increases in serum uric acid are dose related.
INZIRQO decreases urinary calcium excretion and may cause elevations of serum calcium. Monitor calcium levels in patients with hypercalcemia receiving INZIRQO.
Discontinue thiazides before carrying out tests for parathyroid function.
5.4 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Thiazide diuretics have been reported to cause exacerbation or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
5.5 Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma and Acute Myopia
Hydrochlorothiazide, a sulfonamide, can cause an idiosyncratic reaction resulting in acute angle closure glaucoma and elevated intraocular pressure with or without a noticeable acute myopic shift and/or choroidal effusions. Symptoms include acute onset of decreased visual acuity or ocular pain and typically occur within hours to weeks of drug initiation. Untreated acute angle-closure glaucoma may result in permanent vision loss. Discontinue drug intake. Consider prompt medical or surgical treatments if the intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled. Risk factors for developing acute angle-closure glaucoma may include a history of sulfonamide or penicillin allergy.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions with INZIRQO are described elsewhere:
- Impaired Renal Function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Electrolyte Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Metabolic Disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma and Acute Myopia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported and, within each category, are listed in order of decreasing severity.
Body as a Whole: Weakness.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension including orthostatic hypotension (may be aggravated by alcohol, barbiturates, narcotics or antihypertensive drugs).
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), diarrhea, vomiting, sialadenitis, cramping, constipation, gastric irritation, nausea, anorexia.
Hematologic: Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia.
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactic reactions, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis and cutaneous vasculitis), respiratory distress including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema, photosensitivity, fever, urticaria, rash, purpura.
Metabolic: Electrolyte imbalance, hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hyperuricemia.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle spasm.
Nervous System: Vertigo, paresthesia, dizziness, headache, restlessness.
Renal: Renal failure, renal dysfunction, interstitial nephritis.
Skin and Appendages: Erythema multiforme including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis including toxic epidermal necrolysis, alopecia.
Special Senses: Transient blurred vision, xanthopsia.
Urogenital System: Impotence.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of hydrochlorothiazide.
Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
Hydrochlorothiazide is associated with an increased risk of non-melanoma skin cancer. In a study conducted in the Sentinel System, increased risk was predominantly for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and in white patients taking large cumulative doses. The increased risk for SCC in the overall population was approximately 1 additional case per 16,000 patients per year, and for white patients taking a cumulative dose of ≥ 50,000 mg the risk increase was approximately 1 additional SCC case for every 6,700 patients per year.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect INZIRQO
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents:Administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent, including a selective COX-2 inhibitor can reduce the diuretic, natriuretic, and antihypertensive effects of thiazide diuretics. Therefore, when INZIRQO and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents are used concomitantly, check to determine if the desired effect of the diuretic is obtained.
- Cholestyramine and Colestipol: Absorption of hydrochlorothiazide is impaired in the presence of anionic exchange resins. Stagger the dosage of INZIRQO and the resin such that INZIRQO is administered at least 4 hours before or 4 to 6 hours after the administration of the resin.
7.2 Potential for INZIRQO to Affect Other Drugs
- Lithium: Increases in serum lithium concentrations and lithium toxicity have been reported during concomitant administration of hydrochlorothiazide. Monitor serum lithium levels during concomitant use and adjust the lithium dose during concomitant administration or discontinuation of hydrochlorothiazide.
- Antidiabetic Drugs (oral agents and insulin): Dosage adjustment of the antidiabetic drug may be required when coadministered with hydrochlorothiazide.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Untreated hypertension during pregnancy can lead to adverse outcomes for the mother and the fetus (see Clinical Considerations). Available data from published observational studies have not demonstrated a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal outcomes with hydrochlorothiazide use during pregnancy. However, there have been rare reports of jaundice, thrombocytopenia, and electrolyte imbalances in infants exposed to thiazide medications during pregnancy.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Hypertension in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, premature delivery, and delivery complications (e.g., need for cesarean section, and post-partum hemorrhage). Hypertension increases the fetal risk for intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine death. Monitor pregnant women with hypertension.
Data
Animal Data
Teratogenic effects: Studies in which hydrochlorothiazide was orally administered to pregnant mice and rats during their respective periods of major organogenesis at doses up to 3000 and 1000 mg hydrochlorothiazide /kg (approximately 146-fold and 97-fold the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area), respectively, provided no evidence of harm to the fetus.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Available data from published literature indicate hydrochlorothiazide is present in human milk (see Data). There are no reports of adverse effects on breastfed infants exposed to hydrochlorothiazide during lactation. Doses of hydrochlorothiazide associated with clinically significant diuresis have been associated with impaired milk production. Consider the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding along with the mother’s clinical need for INZIRQO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from INZIRQO or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
A single study involving one woman and her infant showed a peak concentration of 275 mcg/L at 3 hours following 50 mg dose. No drug was detected (<20 mcg/L) in the infant’s plasma at 2 and 11 hours following the mother’s dose.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Hydrochlorothiazide, USP is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is the 3,4-dihydro derivative of chlorothiazide. It is chemically designated as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2 H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide and has the following structural formula:
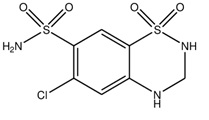
Hydrochlorothiazide, USP is a white, or practically white, crystalline powder which is slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n-butylamine, and in dimethylformamide; sparingly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ether, in chloroform, and in dilute mineral acids. The molecular formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2 and the molecular weight is 297.74.
INZIRQO (hydrochlorothiazide) is supplied in one strength as an off-white to light-brown colored powder for oral suspension. When reconstituted with 66 mL of water, the total volume of the suspension is 80 mL containing 10 mg/mL of hydrochlorothiazide, USP. In addition, INZIRQO contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous citric acid, caramel flavor (artificial flavor, caramel, maltodextrin, molasses, propylene glycol, salt and sucrose), cellulose, peppermint flavor (acacia and natural flavor), potassium sorbate, sucrose, talc and xanthan gum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Thiazides affect the renal tubular mechanisms of electrolyte reabsorption, directly increasing excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Indirectly, the diuretic action of hydrochlorothiazide reduces plasma volume, with consequent increases in plasma renin activity, increases in aldosterone secretion, increases in urinary potassium loss, and decreases in serum potassium.
The mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of thiazides is not fully understood.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Hydrochlorothiazide does not usually affect normal blood pressure. Hydrochlorothiazide affects the distal renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. At maximal therapeutic dosage, all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic efficacy. Hydrochlorothiazide increases excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Natriuresis may be accompanied by some loss of potassium and bicarbonate. After oral use, diuresis begins within 2 hours, peaks in about 4 hours and lasts about 6 to 12 hours.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Over a dose range of 50 to 100 mg, peak plasma hydrochlorothiazide concentrations and exposure (AUC) of INZIRQO increases proportionally with dose in healthy subjects.
Absorption
Following single-dose oral administration of 100 mg INZIRQO to healthy subjects in the fasted state, the AUC and Cmax of hydrochlorothiazide was 5940 ng.h/mL and 972 ng/mL, respectively. The peak plasma hydrochlorothiazide concentrations are achieved at approximately 1.5 hours.
Effect of Food: A food-effect study involving administration of INZIRQO to healthy male and female subjects after a high-fat, high calorie breakfast indicated that the rate of absorption (Cmax) decreased 38%, while the extent of absorption (AUC) remained unchanged, when compared to administration under fasting conditions. The Tmax was delayed by 2 hours.
Cholestyramine and Colestipol Resins: Absorption of hydrochlorothiazide is impaired in the presence of anionic exchange resins. Single doses of either cholestyramine or colestipol resins reduced the bioavailability of hydrochlorothiazide by up to 85% and 43%, respectively.
Distribution
Hydrochlorothiazide binds to albumin (40% to 70%) and distributes into erythrocytes. It crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Elimination
Following oral administration of INZIRQO, plasma hydrochlorothiazide concentrations decline biexponentially, with a terminal elimination half-life of about 10 hours. At least 61% of the oral dose is eliminated unchanged in the urine within 24 hours.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Two year feeding studies in mice and rats conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) uncovered no evidence of a carcinogenic potential of hydrochlorothiazide in female mice (at doses of up to approximately 600 mg/kg/day) or in male and female rats (at doses of up to approximately 100 mg/kg/day). The NTP, however, found equivocal evidence for hepatocarcinogenicity in male mice.
Hydrochlorothiazide was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames mutagenicity assay of Salmonella typhimurium strains TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, TA 1537, and TA 1538 and in the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) test for chromosomal aberrations, or in vivo in assays using mouse germinal cell chromosomes, Chinese hamster bone marrow chromosomes, and the Drosophila sex-linked recessive lethal trait gene. Positive test results were obtained only in the in vitro CHO Sister Chromatid Exchange (clastogenicity)and in the Mouse Lymphoma Cell (mutagenicity) assays, using concentrations of hydrochlorothiazide from 43 to 1300 mcg/mL, and in the Aspergillus nidulans nondisjunction assay at an unspecified concentration.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
INZIRQO (hydrochlorothiazide) is supplied as an off-white to light-brown colored powder for oral suspension in one strength containing 800 mg of hydrochlorothiazide, USP in a HDPE bottle.
When reconstituted as directed, INZIRQO forms an off-white to light brown colored suspension with caramel, peppermint flavor. The total volume of the suspension is 80 mL containing 10 mg of hydrochlorothiazide, USP per mL (70954-522-10).
16.2 Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
Keep this and all medication out of the reach of children.
Store reconstituted solutions of INZIRQO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma and Acute Myopia
Advise patients to discontinue INZIRQO and seek immediate medical attention if they experience symptoms of Acute Myopia or Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
Instruct patients taking hydrochlorothiazide to protect skin from the sun and undergo regular skin cancer screening [see Postmarketing Experience (6.2)].
Recommended Administration
Advise patients to always shake the bottle well before each use and measure the dose using a calibrated oral dosing syringe to ensure that the dose is measured and administered accurately. Inform patients that a bottle adapter and oral dosing syringes may be obtained from their pharmacy.
Advise patients never to use household teaspoons or tablespoons to measure INZIRQO.
Advise patients that the oral suspension should be stored at room temperature (20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F)).
INZIRQO may be taken with or without meals.
Discard any unused suspension 30 days after reconstitution.
Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Distributed by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
Baudette, MN 56623
LB4824-01
INZIRQO is a pending trademark of ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
INZIRQO (hydrochlorothiazide) Powder for Oral Suspension, 10 mg/mL
NDC: 70954-522-10 - 80 mL (when reconstituted)

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
INZIRQO
hydrochlorothiazide powder, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70954-522 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE (UNII: 0J48LPH2TH) (HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE - UNII:0J48LPH2TH) HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 10 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) POTASSIUM SORBATE (UNII: 1VPU26JZZ4) POWDERED CELLULOSE (UNII: SMD1X3XO9M) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) MALTODEXTRIN (UNII: 7CVR7L4A2D) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) CARAMEL (UNII: T9D99G2B1R) MOLASSES (UNII: LSU3YX0KZO) ACACIA (UNII: 5C5403N26O) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Off-white to light brown) Score Shape Size Flavor CARAMEL, PEPPERMINT Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70954-522-10 80 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/30/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219141 01/30/2025 Labeler - ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (145588013) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Novitium Pharma LLC 080301870 ANALYSIS(70954-522) , LABEL(70954-522) , MANUFACTURE(70954-522) , PACK(70954-522)
Trademark Results [INZIRQO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 INZIRQO 97829294 not registered Live/Pending |
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2023-03-08 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.