CETRORELIX- cetrorelix acetate kit
Cetrorelix by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Cetrorelix by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Akorn, Abbott Biologicals BV, GP Pharm SA, Reed-Lane, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
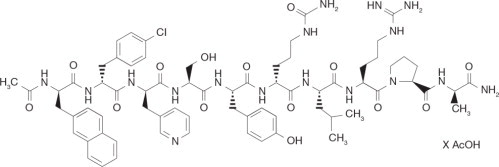
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is a synthetic decapeptide with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonistic activity. Cetrorelix acetate is an analog of native GnRH with substitutions of amino acids at positions 1, 2, 3, 6, and 10. The molecular formula is Acetyl-D-3-(2′-naphtyl)-alanine- D-4-chlorophenylalanine-D-3-(3′-pyridyl)-alanine-L-serine-L-tyrosine-D-citruline-L-leucine-L-arginine-L-proline-D-alanine-amide, and the molecular weight is 1431.06, calculated as the anhydrous free base. The structural formula is as follows:
Cetrorelix acetate
Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg is a sterile lyophilized powder intended for subcutaneous injection after reconstitution with Sterile Water for Injection, USP (pH 5-8), that comes supplied in a 1.0 mL pre-filled syringe. Each vial of cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg contains 0.26-0.27 mg cetrorelix acetate, equivalent to 0.25 mg cetrorelix, and 54.80 mg mannitol.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
GnRH induces the production and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the gonadotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary. Due to a positive estradiol (E2) feedback at midcycle, GnRH liberation is enhanced resulting in an LH-surge. This LH-surge induces the ovulation of the dominant follicle, resumption of oocyte meiosis and subsequently luteinization as indicated by rising progesterone levels.
Cetrorelix acetate for injection competes with natural GnRH for binding to membrane receptors on pituitary cells and thus controls the release of LH and FSH in a dose-dependent manner. The onset of LH suppression is approximately one hour with the 3 mg dose and two hours with the 0.25 mg dose. This suppression is maintained by continuous treatment and there is a more pronounced effect on LH than on FSH. An initial release of endogenous gonadotropins has not been detected with cetrorelix acetate for injection, which is consistent with an antagonist effect.
The effects of cetrorelix acetate for injection on LH and FSH are reversible after discontinuation of treatment. In women, cetrorelix acetate for injection delays the LH-surge, and consequently ovulation, in a dose-dependent fashion. FSH levels are not affected at the doses used during controlled ovarian stimulation. Following a single 3 mg dose of cetrorelix acetate for injection, duration of action of at least 4 days has been established. A dose of cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg every 24 hours has been shown to maintain the effect.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic parameters of single and multiple doses of cetrorelix acetate for injection in adult healthy female subjects are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic parameters of Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection following 3 mg single or 0.25 mg single and multiple (daily for 14 days) subcutaneous (sc) administration. tmax Time to reach observed maximum plasma concentration
t1/2 Elimination half-life
Cmax Maximum plasma concentration; multiple dose Css, max
AUC Area under the curve; single dose AUC0-inf, multiple dose AUCt
CL Total plasma clearance
Vz Volume of distribution
Geometric mean (95% CIln),
* median (min- max)
† arithmetic mean,
‡ Based on iv administration (n=6, separate study 0013)
Single dose 3 mg Single dose 0.25 mg Multiple dose 0.25 mg No. of subjects 12 12 12 tmax* [h] 1.5
(0.5-2)1.0
(0.5-1.5)1.0
(0.5-2)t1/2* [h] 62.8
(38.2-108)5.0
(2.4-48.8)20.6
(4.1-179.3)Cmax [ng/ml] 28.5
(22.5-36.2)4.97
(4.17-5.92)6.42
(5.18-7.96)AUC [ng·h/ml] 536
(451-636)31.4
(23.4-42.0)44.5
(36.7-54.2)CL† [ml/min·kg] 1.28‡ Vz† [l/kg] 1.16‡ Absorption
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is rapidly absorbed following subcutaneous injection, maximal plasma concentrations being achieved approximately one to two hours after administration. The mean absolute bioavailability of cetrorelix acetate for injection following subcutaneous administration to healthy female subjects is 85%.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of cetrorelix acetate for injection following a single intravenous dose of 3 mg is about 1 l/kg. In vitro protein binding to human plasma is 86%.
Cetrorelix acetate for injection concentrations in follicular fluid and plasma were similar on the day of oocyte pick-up in patients undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation. Following subcutaneous administration of cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg and 3 mg, plasma concentrations of cetrorelix were below or in the range of the lower limit of quantitation on the day of oocyte pick-up and embryo transfer.
Metabolism
After subcutaneous administration of 10 mg cetrorelix acetate for injection to females and males, cetrorelix acetate for injection and small amounts of (1-9), (1-7), (1-6), and (1-4) peptides were found in bile samples over 24 hours.
In in vitro studies, cetrorelix acetate for injection was stable against phase I- and phase II-metabolism. Cetrorelix acetate for injection was transformed by peptidases, and the (1-4) peptide was the predominant metabolite.
Excretion
Following subcutaneous administration of 10 mg cetrorelix to males and females, only unchanged cetrorelix was detected in urine. In 24 hours, cetrorelix and small amounts of the (1-9), (1-7), (1-6), and (1-4) peptides were found in bile samples. 2-4% of the dose was eliminated in the urine as unchanged cetrorelix, while 5-10% was eliminated as cetrorelix and the four metabolites in bile. Therefore, only 7-14% of the total dose was recovered as unchanged cetrorelix and metabolites in urine and bile up to 24 hours. The remaining portion of the dose may not have been recovered since bile and urine were not collected for a longer period of time.
Special Populations
Pharmacokinetic investigations have not been performed either in subjects with impaired renal or liver function, or in the elderly, or in children (see PRECAUTIONS).
Pharmacokinetic differences in different races have not been determined.
There is no evidence of differences in pharmacokinetic parameters for cetrorelix acetate for injection between healthy subjects and patients undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation.
Drug-Drug Interactions
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been performed with cetrorelix acetate for injection (see PRECAUTIONS).
Clinical Studies
Seven hundred thirty-two (732) patients were treated with cetrorelix acetate for injection in five (two Phase 2 dose-finding and three Phase 3) clinical trials. The clinical trial population consisted of Caucasians (95.5%) and Black, Asian, Arabian and others (4.5%). Women were between 19 and 40 years of age (mean: 32). The studies excluded subjects with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), subjects with low or no ovarian reserve, and subjects with stage III-IV endometriosis.
Two dose regimens were investigated in these clinical trials, either a single dose per treatment cycle or multiple dosing. In the Phase 2 studies, a single dose of 3 mg was established as the minimal effective dose for the inhibition of premature LH surges with a protection period of at least 4 days. When cetrorelix acetate for injection is administered in a multidose regimen, 0.25 mg was established as the minimal effective dose. The extent and duration of LH-suppression is dose dependent.
In the Phase 3 program, efficacy of the single 3 mg dose regimen of cetrorelix acetate for injection and the multiple 0.25 mg dose regimen of cetrorelix acetate for injection was established separately in two adequate and well controlled clinical studies utilizing active comparators. A third non-comparative clinical study evaluated only the multiple 0.25 mg dose regimen of cetrorelix acetate for injection. The ovarian stimulation treatment with recombinant FSH or human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) was initiated on day 2 or 3 of a normal menstrual cycle. The dose of gonadotropins was administered according to the individual patient's disposition and response.
In the single dose regimen study, cetrorelix acetate for injection 3 mg was administered on the day of controlled ovarian stimulation when adequate estradiol levels (400 pg/mL) were obtained, usually on day 7 (range day 5- 12). If hCG was not given within 4 days of the 3 mg dose of cetrorelix acetate for injection, then 0.25 mg of cetrorelix acetate for injection was administered daily beginning 96 hours after the 3 mg injection until and including the day of hCG administration.
In the two multiple dose regimen studies, cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg was started on day 5 or 6 of COS. Both gonadotropins and cetrorelix acetate for injection were continued daily (multiple dose regimen) until the injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Oocyte pick-up (OPU) followed by in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) as well as embryo transfer (ET) were subsequently performed. The results for cetrorelix acetate for injection are summarized below in Table 2.
Table 2: Results of Phase 3 Clinical Studies with Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 3 mg in a single dose (sd) regimen and 0.25 mg in a multiple dose (md) regimen * Progesterone
† Following initiation of cetrorelix acetate for injection therapy
‡ Morning values
§ Median with 5th – 95th percentiles
¶ Mean ± standard deviation
Parameter Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 3 mg (sd, active comparator study) Cetrorelix Acetate for
Injection 0.25 mg (md, active comparator study)Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg (md, non-comparative study) No. of subjects 115 159 303 hCG administered [%] 98.3 96.2 96.0 Oocyte pick-up [%] 98.3 94.3 93.1 LH-surge [%] (LH ≥ 10 U/L and P* ≥ 1 ng/mL) † 0.0 1.9 1.0 Serum E2 [pg/ml] at day hCG‡, § 1125 (470-2952) 1064 (341-2531) 1185 (311-3676) Serum LH [U/L] at day hCG‡, § 1.0
(0.5-2.5)1.5
(0.5-7.6)1.1
(0.5-3.5)No. of follicles ≥ 11 mm at day
hCG¶11.2±5.5 10.8±5.2 10.4±4.5 No. of oocytes: IVF¶ ICSI¶ 9.2±5.2
10.0±4.27.6±4.3
10.1±5.68.5±5.1
9.3±5.9Fertilization rate: IVF¶ ICSI¶ 0.48±0.33
0.66±0.290.62±0.26
0.63±0.290.60±0.26
0.61±0.25No. of embryos transferred¶ 2.6±0.9 2.1±0.6 2.7±1.0 Clinical pregnancy rate [%]
per attempt
per subject with ET22.6
26.320.8
24.119.8
23.3In addition to IVF and ICSI, one pregnancy was obtained after intrauterine insemination. In the five Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials, 184 pregnancies have been reported out of a total of 732 patients (including 21 pregnancies following the replacement of frozen-thawed embryos).
In the 3 mg regimen, 9 patients received an additional dose of 0.25 mg of cetrorelix acetate for injection and two other patients received two additional doses of 0.25 mg cetrorelix acetate for injection. The median number of days of cetrorelix acetate for injection multiple dose treatment was 5 (range 1-15) in both studies.
No drug related allergic reactions were reported from these clinical studies.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is contraindicated under the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity to cetrorelix acetate, extrinsic peptide hormones or mannitol.
- Known hypersensitivity to GnRH or any other GnRH analogs.
- Known or suspected pregnancy, and lactation (see PRECAUTIONS).
- Severe renal impairment
-
WARNINGS
Cetrorelix acetate for injection should be prescribed by physicians who are experienced in fertility treatment. Before starting treatment with cetrorelix acetate for injection, pregnancy must be excluded (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS).
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Cases of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions with the first dose, have been reported during post-marketing surveillance (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). A severe anaphylactic reaction associated with cough, rash, and hypotension, was observed in one patient after seven months of treatment with cetrorelix acetate for injection (10 mg/day) in a study for an indication unrelated to infertility.
Special care should be taken in women with signs and symptoms of active allergic conditions or known history of allergic predisposition. Treatment with cetrorelix acetate for injection is not advised in women with severe allergic conditions.
Information for Patients
Prior to therapy with cetrorelix acetate for injection, patients should be informed of the duration of treatment and monitoring procedures that will be required. The risk of possible adverse reactions should be discussed (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Cetrorelix acetate for injection should not be prescribed if a patient is pregnant.
If cetrorelix acetate for injection is prescribed to patients for self-administration, information for proper use is given in the Patient Leaflet (see below).
Laboratory Tests
After the exclusion of preexisting conditions, enzyme elevations (ALT, AST, GGT, alkaline phosphatase) were found in 1-2% of patients receiving cetrorelix acetate for injection during controlled ovarian stimulation. The elevations ranged up to three times the upper limit of normal. The clinical significance of these findings was not determined.
During stimulation with human menopausal gonadotropin, cetrorelix acetate for injection had no notable effects on hormone levels aside from inhibition of LH surges.
Drug Interactions
No formal drug interaction studies have been performed with cetrorelix acetate for injection.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed with cetrorelix acetate. Cetrorelix acetate was not genotoxic in vitro (Ames test, HPRT test, chromosome aberration test) or in vivo (chromosome aberration test, mouse micronucleus test). Cetrorelix acetate induced polyploidy in CHL-Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts, but not in V79-Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts, cultured peripheral human lymphocytes or in an in vitro micronucleus test in the CHL-cell line. Treatment with 0.46 mg/kg cetrorelix acetate for 4 weeks resulted in complete infertility in female rats which was reversed 8 weeks after cessation of treatment.
Pregnancy
(see CONTRAINDICATIONS)
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is contraindicated in pregnant women.
When administered to rats for the first seven days of pregnancy, cetrorelix acetate did not affect the development of the implanted conceptus at doses up to 38 μg/kg (approximately 1 time the recommended human therapeutic dose based on body surface area). However, a dose of 139 μg/kg (approximately 4 times the human dose) resulted in a resorption rate and a post implantation loss of 100%. When administered from day 6 to near term to pregnant rats and rabbits, very early resorptions and total implantation losses were seen in rats at doses from 4.6 μg/kg (0.2 times the human dose) and in rabbits at doses from 6.8 μg/kg (0.4 times the human dose). In animals that maintained their pregnancy, there was no increase in the incidence of fetal abnormalities.
The fetal resorption observed in animals is a logical consequence of the alteration in hormonal levels effected by the antigonadotrophic properties of cetrorelix acetate for injection, which could result in fetal loss in humans as well. Therefore, this drug should not be used in pregnant women.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether cetrorelix acetate for injection is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because the effects of cetrorelix acetate for injection on lactation and/or the breast-fed child have not been determined, cetrorelix acetate for injection should not be used by nursing mothers.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The safety of cetrorelix acetate for injection in 949 patients undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation in clinical studies was evaluated. Women were between 19 and 40 years of age (mean: 32). 94.0% of them were Caucasian. Cetrorelix acetate for injection was given in doses ranging from 0.1 mg to 5 mg as either a single or multiple dose.
Table 3 shows systemic adverse events, reported in clinical studies without regard to causality, from the beginning of cetrorelix acetate for injection treatment until confirmation of pregnancy by ultrasound at an incidence ≥ 1% in cetrorelix acetate for injection treated subjects undergoing COS.
Table 3: Adverse Events in ≥1% * Intensity moderate or severe, or WHO Grade II or III, respectively
(WHO preferred term) Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection N=949
% (n)Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome* 3.5 (33) Nausea 1.3 (12) Headache 1.1 (10) Local site reactions (e.g. redness, erythema, bruising, itching, swelling, and pruritus) were reported. Usually, they were of a transient nature, mild intensity and short duration. During post-marketing surveillance, cases of mild to moderate Ovarian Hyperstimulation syndrome and infrequent cases of hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactoid reactions have been reported.
Two stillbirths were reported in Phase 3 studies of cetrorelix acetate for injection.
Congenital Anomalies
Clinical follow-up studies of 316 newborns of women administered cetrorelix acetate for injection were reviewed. One infant of a set of twin neonates was found to have anencephaly at birth and died after four days. The other twin was normal. Developmental findings from ongoing baby follow-up included a child with a ventricular septal defect and another child with bilateral congenital glaucoma.
Four pregnancies that resulted in therapeutic abortion in Phase 2 and Phase 3 controlled ovarian stimulation studies had major anomalies (diaphragmatic hernia, trisomy 21, Klinefelter syndrome, polymalformation, and trisomy 18). In three of these four cases, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) was the fertilization method employed; in the fourth case, in vitro fertilization (IVF) was the method employed.
The minor congenital anomalies reported include: supernumerary nipple, bilateral strabismus, imperforate hymen, congenital nevi, hemangiomata, and QT syndrome.
The causal relationship between the reported anomalies and cetrorelix acetate for injection is unknown. Multiple factors, genetic and others (including, but not limited to ICSI, IVF, gonadotropins, and progesterone) make causal attribution difficult to study.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS contact Akorn Operating Company LLC at 1-800-932-5676 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ovarian stimulation therapy with gonadotropins (FSH, hMG) is started on cycle Day 2 or 3. The dose of gonadotropins should be adjusted according to individual response. Cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg may be administered subcutaneously once daily during the early- to mid-follicular phase.
Cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg is administered on either stimulation day 5 (morning or evening) or day 6 (morning) and continued daily until the day of hCG administration.
When assessment by ultrasound shows a sufficient number of follicles of adequate size, hCG is administered to induce ovulation and final maturation of the oocytes. No hCG should be administered if the ovaries show an excessive response to the treatment with gonadotropins to reduce the chance of developing ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Administration
Cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg can be administered by the patient herself after appropriate instructions by her doctor.
Directions for using Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg with the enclosed needles and pre-filled syringe:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water.
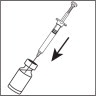
- Flip off the plastic cover of the vial and wipe the aluminum ring and the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
- Twist the injection needle with the yellow mark (20 gauge) on the pre-filled syringe.
- Push the needle through the center of the rubber stopper of the vial and slowly inject the solvent into the vial
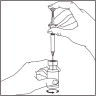
- Leaving the syringe in the vial, gently swirl the vial until the solution is clear and without residues. Avoid forming bubbles.
- Draw the total contents of the vial into the syringe. If necessary, invert the vial and pull back the needle as far as needed to withdraw the entire contents of the vial.
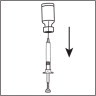
- Replace the needle with the yellow mark by the injection needle with the grey mark (27 gauge).
- Invert the syringe and push the plunger until all air bubbles have been expelled.
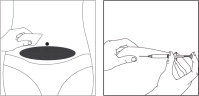
- Choose an injection site in the lower abdominal area, preferably around, but staying at least one inch away from the navel. Choose a different injection site each day to minimize local irritation. Use a second alcohol swab to clean the skin at the injection site and allow alcohol to dry. Gently pinch up the skin surrounding the site of injection.
- Inject the prescribed dose as directed by your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
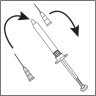
- Use the syringe and needles only once. Dispose of the syringe and needles properly after use. If available, use a medical waste container for disposal.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
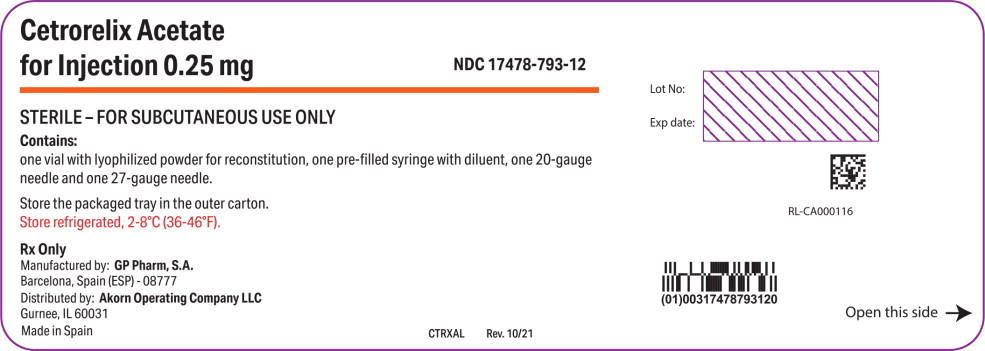
Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg is available in a carton of one packaged tray (NDC: 17478-793-12).
Each packaged tray contains: one glass vial containing 0.26 – 0.27 mg cetrorelix acetate (corresponding to 0.25 mg cetrorelix), one pre-filled glass syringe with 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (pH 5-8), one 20 gauge needle (yellow) and one 27 gauge needle (grey).
Storage
Store Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg refrigerated, 2-8°C (36-46°F). Store the packaged tray in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Rx only
Manufactured by:
GP Pharm, S.A.
Barcelona, Spain (ESP) – 08777Distributed by:
Akorn Operating Company LLC
Gurnee, IL 60031Made in Spain
CTRX00N Rev. 10/21
-
Patient Leaflet
Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg
Active ingredient: cetrorelix acetate
Summary
Cetrorelix acetate for injection blocks the effects of a natural hormone, called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH controls the secretion of another hormone, called luteinizing hormone (LH), which induces ovulation during the menstrual cycle. During hormone treatment for ovarian stimulation, premature ovulation may lead to eggs that are not suitable for fertilization. Cetrorelix acetate for injection blocks such undesirable premature ovulation.
Uses
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is used to prevent premature ovulation during controlled ovarian stimulation.
General Cautions
Do not use Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection if you
- have kidney disease
- are allergic to cetrorelix acetate, mannitol or exogenous peptide hormones (medicines similar to cetrorelix acetate for injection) or
- are pregnant, or think that you might be pregnant, or if you are breast-feeding.
Consult your doctor before taking cetrorelix acetate for injection if you have had severe allergic reactions.
Proper Use
Ovarian stimulation therapy is started on cycle Day 2 or 3. Cetrorelix acetate for injection 0.25 mg is injected under the skin once daily, as directed by your physician. When an ultrasound examination shows that you are ready, another drug (hCG) is injected to induce ovulation.
How should you use Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection?
You may self-inject cetrorelix acetate for injection after special instruction from your doctor.
To fully benefit from cetrorelix acetate for injection, please read carefully and follow the instructions given below, unless your doctor advises you otherwise.
Cetrorelix acetate for injection is for injection under the skin of the lower abdominal area, preferably around, but staying at least one inch away from the belly button. Choose a different injection site each day to minimize local irritation.
Dissolve cetrorelix acetate for injection powder only with the water contained in the pre-filled syringe.
Do not use a cetrorelix acetate for injection solution if it contains particles or if it is not clear.
Before you inject cetrorelix acetate for injection yourself, please read the following instructions carefully:
Directions for using Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg with the enclosed needles and pre-filled syringe:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- On a clean flat surface, lay out everything you need (one vial of powder, one pre-filled syringe, one injection needle with a yellow mark, and one injection needle with a grey mark)
- Flip off the plastic cover of the vial. Wipe the aluminum ring and the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
- Take the injection needle with the yellow mark and remove the wrapping. Take the pre-filled syringe and remove the cover. Twist the needle on the syringe and remove the cover of the needle.
- Push the needle through the center of the rubber stopper of the vial. Inject the water into the vial by slowly pushing down on the plunger of the syringe.
- Leave the syringe in the vial. While carefully holding the syringe and vial, swirl gently to mix the powder and water together. When it is mixed, it will look clear and have no particles in it. Do not shake or you will create bubbles in your medicine.
- Draw the total contents of the vial into the syringe. If liquid is left in the vial, invert the vial, pull back the needle until the opening of the needle is just inside the stopper. If you look from the side through the gap in the stopper, you can control the movement of the needle and the liquid. It is important to withdraw the entire contents of the vial.
- Detach the syringe from the needle and lay down the syringe. Take the injection needle with the grey mark and remove its wrapping. Twist the needle on the syringe and remove the cover of the needle
- Invert the syringe and push the plunger until all air bubbles have been pushed out. Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface
- Choose an injection site in the lower abdominal area, preferably around, but at least one inch away from the belly button. Choose a different injection site each day to minimize local irritation. Take a second alcohol swab and clean the skin at the injection site and allow alcohol to dry. Inject the prescribed dose as directed by your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
- Use the syringe and needles only once. Dispose of the syringe and needles immediately after use (put the covers on the needles to avoid injury). A medical waste container should be used for disposal
SPECIAL ADVICE
Storage
How is Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection to be stored?
Store Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection in a cool dry place protected from excess moisture and heat.
Store Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection 0.25 mg in the refrigerator at 2-8°C (36-46°F). Keep the packaged tray in the outer carton in order to protect it from light.
How long may Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection be stored?
Do not use the Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection powder or the pre-filled syringe after the expiration date, which is printed on the labels and on the carton, and dispose of the vial and the syringe properly.
How long can you keep Cetrorelix Acetate for Injection after preparation of the solution?
The solution should be used immediately after preparation.
Store the medicine out of the reach of children.
If you suspect that you may have taken more than the prescribed dose of this medicine, contact your doctor immediately. This medicine was prescribed for your particular condition. Do not use it for another condition or give the drug to others.
This leaflet provides a summary of the information about cetrorelix acetate for injection. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for uses other than those listed in the Leaflet. If you have any questions or concerns, or want more information about cetrorelix acetate for injection, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
This Leaflet has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
October 2021
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel Text for Container Label:
Cetrorelix Acetate
for Injection 0.25 mg NDC: 17478-793-12
STERILE – FOR SUBCUTANEOUS USE ONLY
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel Text for Carton Label:
Cetrorelix Acetate
for Injection 0.25 mg NDC: 17478-793-12
Sterile – for subcutaneous use only
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS USE ONLY
Rx Only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel Text for Container Label:
Cetrorelix Acetate
for Injection 0.25 mg NDC: 17478-794-12
STERILE – FOR SUBCUTANEOUS USE ONLY
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel Text for Syringe Label:
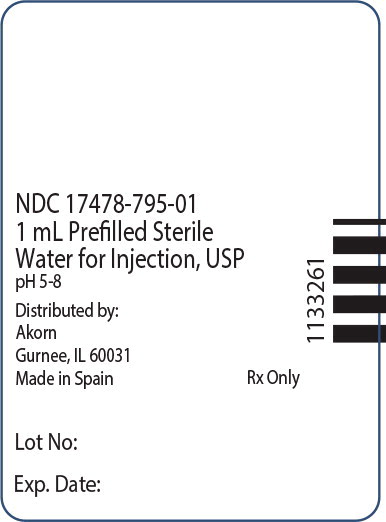
NDC: 17478-795-01
1 mL Prefilled Sterile
Water for Injection, USP
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CETRORELIX
cetrorelix acetate kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17478-793 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17478-793-12 1 in 1 CARTON 10/24/2022 1 1 in 1 TRAY; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE 1 mL Part 2 1 SYRINGE 1 mL Part 1 of 2 CETRORELIX
cetrorelix acetate injection, powder, for solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 17478-794 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Cetrorelix Acetate (UNII: W9Y8L7GP4C) (Cetrorelix - UNII:OON1HFZ4BA) Cetrorelix 0.25 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17478-794-12 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA215737 Part 2 of 2 STERILE WATER
water injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 17478-795 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17478-795-01 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA215737 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA215737 10/24/2022 Labeler - Akorn (117693100) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Abbott Biologicals BV 489049423 PACK(17478-795) , MANUFACTURE(17478-795) , ANALYSIS(17478-795) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations GP Pharm SA 462006581 MANUFACTURE(17478-794) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Reed-Lane, Inc. 001819879 LABEL(17478-793) , PACK(17478-793)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.