ILUVIEN- fluocinolone acetonide implant
Iluvien by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Iluvien by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alimera Sciences, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ILUVIEN® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ILUVIEN.
ILUVIEN® (fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant)
0.19 mg
For Intravitreal Injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 1963INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ILUVIEN contains a corticosteroid and is indicated for the treatment of diabetic macular edema (DME) in patients who have been previously treated with a course of corticosteroids and did not have a clinically significant rise in intraocular pressure. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Non-bioerodable intravitreal implant containing 0.19 mg fluocinolone acetonide in a drug delivery system. (3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Intravitreal injections have been associated with endophthalmitis, eye inflammation, increased intraocular pressure, and retinal detachments. Patients should be monitored following the injection. (5.1)
- Use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to bacteria, fungi, or viruses. (5.2)
- The implant may migrate into the anterior chamber if the posterior lens capsule is not intact. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In controlled studies, the most common adverse reactions reported were cataract development and increases in intraocular pressure. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alimera Sciences, Inc. at 1-844-445-8843 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2016
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Ocular or Periocular Infections
4.2 Glaucoma
4.3 Hypersensitivity
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Intravitreal Injection-related Effects
5.2 Steroid-related Effects
5.3 Risk of Implant Migration
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.2 Administration
The intravitreal injection procedure should be carried out under aseptic conditions, which include use of sterile gloves, a sterile drape, a sterile caliper, and a sterile eyelid speculum (or equivalent). Adequate anesthesia and a broad-spectrum microbicide should be given prior to the injection.
The injection procedure for ILUVIEN is as follows:
- The exterior of the tray should not be considered sterile. An assistant (non-sterile) should remove the tray from the carton and examine the tray and lid for damage. If damaged, do not use unit.
If acceptable, the assistant should peel the lid from the tray without touching the interior surface. - Visually check through the viewing window of the preloaded applicator to ensure that there is a drug implant inside.
- Remove the applicator from the tray with sterile gloved hands touching only the sterile interior tray surface and applicator.
Prior to injection, the applicator tip must be kept above the horizontal plane to ensure that the implant is properly positioned within the applicator. - To reduce the amount of air administered with the implant, the administration procedure requires two steps. Before inserting the needle into the eye, remove the protective cap then gently push the applicator button down and slide it to the first stop (at the curved black marks alongside the button track). At the first stop, release the button and it should move to the UP position. If the button does not rise to the UP position, do not proceed with this unit.
- Optimal placement of the implant is inferior to the optic disc and posterior to the equator of the eye. Measure 4 millimeters inferotemporal from the limbus with the aid of calipers for point of entry into the sclera.
- Inspect the tip of the needle to ensure it is not bent.
- Gently displace the conjunctiva so that after withdrawing the needle, the conjunctival and scleral needle entry sites will not align. Care should be taken to avoid contact between the needle and the lid margin or lashes. Insert the needle through the conjunctiva and sclera. To release the implant, while the button is in the UP position, advance the button by sliding it forward to the end of the button track and remove the needle. Note: Ensure that the button reaches the end of the track before removing the needle.
- Remove the lid speculum and perform indirect ophthalmoscopy to verify placement of the implant, adequate central retinal artery perfusion and absence of any other complications.
Following the injection, patients should be monitored for elevation in intraocular pressure and for endophthalmitis. Monitoring may consist of a check for perfusion of the optic nerve head immediately after the injection, tonometry within 30 minutes following the injection, and biomicroscopy between two and seven days following the injection. Patients should be instructed to report without delay any symptoms suggestive of endophthalmitis.
- The exterior of the tray should not be considered sterile. An assistant (non-sterile) should remove the tray from the carton and examine the tray and lid for damage. If damaged, do not use unit.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Ocular or Periocular Infections
ILUVIEN is contraindicated in patients with active or suspected ocular or periocular infections including most viral disease of the cornea and conjunctiva including active epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, mycobacterial infections and fungal diseases.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Intravitreal Injection-related Effects
Intravitreal injections, including those with ILUVIEN, have been associated with endophthalmitis, eye inflammation, increased intraocular pressure, and retinal detachments. Patients should be monitored following the intravitreal injection [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Steroid-related Effects
Use of corticosteroids including ILUVIEN may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma.
Use of corticosteroids may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to bacteria, fungi, or viruses.Corticosteroids are not recommended to be used in patients with a history of ocular herpes simplex because of the potential for reactivation of the viral infection.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions associated with ophthalmic steroids including ILUVIEN include cataract formation and subsequent cataract surgery, elevated intraocular pressure, which may be associated with optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects, secondary ocular infection from pathogens including herpes simplex, and perforation of the globe where there is thinning of the cornea or sclera.
ILUVIEN was studied in two multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled, masked trials in which patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) were treated with either ILUVIEN (n=375) or sham (n=185).
Table 1 summarizes safety data available when the last subject completed the last 36 month follow up visit for the two primary ILUVIEN trials. In these trials, subjects were eligible for retreatment no earlier than 12 months after study entry. Over the three year follow up period, approximately 75% of the ILUVIEN treated subjects received only one ILUVIEN implant.
The most common ocular (study eye) and non-ocular adverse reactions are shown in Tables 1 and 2:
Table 1: Ocular Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥1% of Patients and Non-ocular Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥5% of Patients 1 Includes cataract, cataract nuclear, cataract subcapsular, cataract cortical and cataract diabetic in patients who were phakic at baseline. Among these patients, 80% of ILUVIEN subjects vs. 27% of sham-controlled subjects underwent cataract surgery. 2 235 of the 375 ILUVIEN subjects were phakic at baseline; 121 of 185 sham-controlled subjects were phakic at baseline. Adverse Reactions ILUVIEN
(N=375)
n (%)Sham
(N=185)
n (%)Ocular Cataract1 192/2352 (82%) 61/1212 (50%) Myodesopsia 80 (21%) 17 (9%) Eye pain 57 (15%) 25 (14%) Conjunctival haemorrhage 50 (13%) 21 (11%) Posterior capsule opacification 35 (9%) 6 (3%) Eye irritation 30 (8%) 11 (6%) Vitreous detachment 26 (7%) 12 (7%) Conjunctivitis 14 (4%) 5 (3%) Corneal oedema 13 (4%) 3 (2%) Foreign body sensation in eyes 12 (3%) 4 (2%) Eye pruritus 10 (3%) 3 (2%) Ocular hyperaemia 10 (3%) 3 (2%) Optic atrophy 9 (2%) 2 (1%) Ocular discomfort 8 (2%) 1 (1%) Photophobia 7 (2%) 2 (1%) Retinal exudates 7 (2%) 0 (0%) Anterior chamber cell 6 (2%) 1 (1%) Eye discharge 6 (2%) 1 (1%) Non-ocular Anemia 40 (11%) 10 (5%) Headache 33 (9%) 11 (6%) Renal Failure 32 (9%) 10 (5%) Pneumonia 28 (7%) 8 (4%) Increased intraocular Pressure
Table 2: Summary of Elevated IOP Related Adverse Reactions Event ILUVIEN
(N=375)
n (%)Sham
(N=185)
n (%)IOP elevation ≥ 10 mmHg from Baseline 127 (34%) 18 (10%) IOP elevation ≥ 30 mmHg 75 (20%) 8 (4%) Any IOP-lowering medication 144 (38%) 26 (14%) Any surgical intervention for elevated intraocular pressure 18 (5%) 1 (1%) Figure 1: Mean IOP during the study
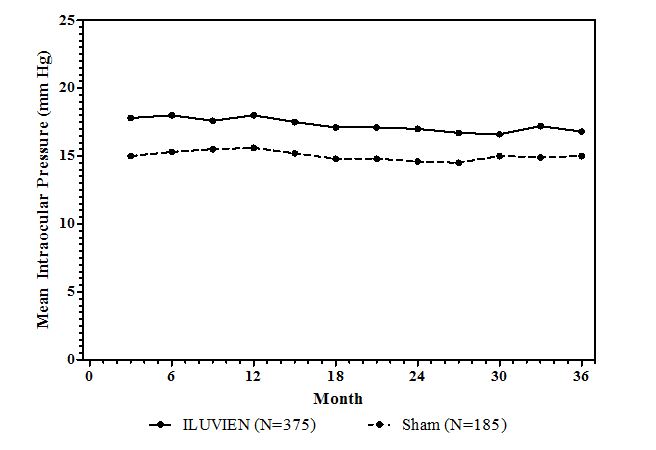
Cataracts and Cataract Surgery
At baseline, 235 of the 375 ILUVIEN subjects were phakic; 121 of 185 sham-controlled subjects were phakic. The incidence of cataract development in patients who had a phakic study eye was higher in the ILUVIEN group (82%) compared with Sham (50%). The median time of cataract being reported as an adverse event was approximately 12 months in the ILUVIEN group and 19 months in the Sham group. Among these patients, 80% of ILUVIEN subjects vs. 27% of sham-controlled subjects underwent cataract surgery, generally within the first 18 months (Median Month 15 for both ILUVIEN group and for Sham) of the studies.6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of ILUVIEN in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to ILUVIEN, or a combination of these factors, include reports of drug administration error and reports of the drug being ineffective.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ILUVIEN in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with fluocinolone acetonide. Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. ILUVIEN should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids are present in human milk and could suppress growth and interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production. The systemic concentration of fluocinolone acetonide following intravitreal treatment with ILUVIEN is low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. It is not known whether intravitreal treatment with ILUVIEN could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Exercise caution when ILUVIEN is administered to a nursing woman.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ILUVIEN is a sterile non-bioerodable intravitreal implant containing 0.19 mg (190 mcg) fluocinolone acetonide in a 36-month sustained-release drug delivery system. ILUVIEN is designed to release fluocinolone acetonide at an initial rate of 0.25 µg/day. ILUVIEN is preloaded into a single-use applicator to facilitate injection of the implant directly into the vitreous. The drug substance is a synthetic corticosteroid, fluocinolone acetonide.
The chemical name for fluocinolone acetonide is (6α,11β, 16α)-6,9-difluoro-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis-(oxy)]-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione. Its chemical structure is:
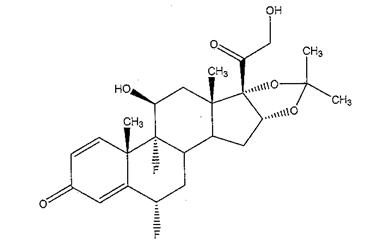
MW 452.50; molecular formula C24H30F206
Fluocinolone acetonide is a white or almost white, microcrystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in methanol, ethanol, chloroform and acetone, and sparingly soluble in ether.
Each ILUVIEN consists of a light brown 3.5mm x 0.37mm implant containing 0.19 mg of the active ingredient fluocinolone acetonide and the following inactive ingredients: polyimide tube, polyvinyl alcohol, silicone adhesive and water for injection.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids inhibit inflammatory responses to a variety of inciting agents including multiple inflammatory cytokines. They inhibit edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, leukocyte migration, capillary proliferation, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation associated with inflammation.
Corticosteroids are thought to act by inhibition of phospholipase A2 via induction of inhibitory proteins collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting release of the common precursor, arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a human pharmacokinetic study of ILUVIEN, fluocinolone acetonide concentrations in plasma were below the lower limit of quantitation of the assay (100 pg/mL) at all post-administration time points from Day 7 through Month 36 following intravitreal administration of a 0.2 mcg/day or 0.5 mcg/day fluocinolone acetonide insert.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been conducted to determine the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of ILUVIEN.
Fluocinolone acetonide was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames test (S. typhimurium and E. coli) and the mouse lymphoma TK assay, or in vivo in the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ILUVIEN was assessed in two three year, randomized (2:1, active: sham), multicenter, double-masked, parallel-groups studies that enrolled patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) that had previously been treated with laser photocoagulation.
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was the proportion of subjects in whom vision had improved by 15 letters or more from baseline after 24 months of follow-up.
Table 3: Baseline BCVA (Letters) Study 1 Study 2 ILUVIEN
(N=190)Sham
(N=95)ILUVIEN
(N=186)Sham
(N=90)Mean (SD)
Median (Range)53 (13)
57 (19-75)55 (11)
58 (25-69)53 (12)
56 (20-70)55 (11)
58 (21-68)Table 4: Visual Acuity outcomes at Month 24 (All randomized subjects with LOCF) aStudy 1: ILUVIEN, N=190; Sham, N=95
bStudy 2: ILUVIEN, N=186; Sham, N=90Study
Outcomes ILUVIEN Sham Estimated Difference (95% CI)
1aGain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 51 (27%) 14 (15%) 12.1% (2.6%, 21.6%) Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 26 (14%) 5 (5%) 8.4% (1.8%, 15.1%) Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) 3.7 (18.7) 3.2 (13.1) 1.8 (-2.8, 6.3)
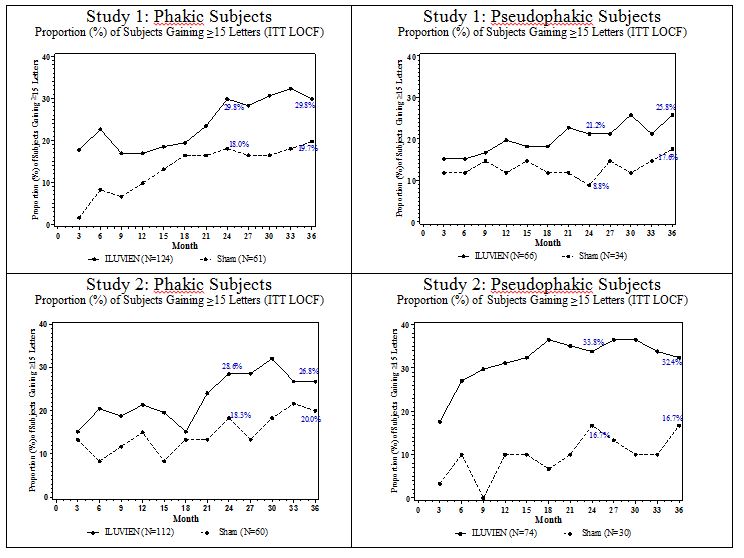
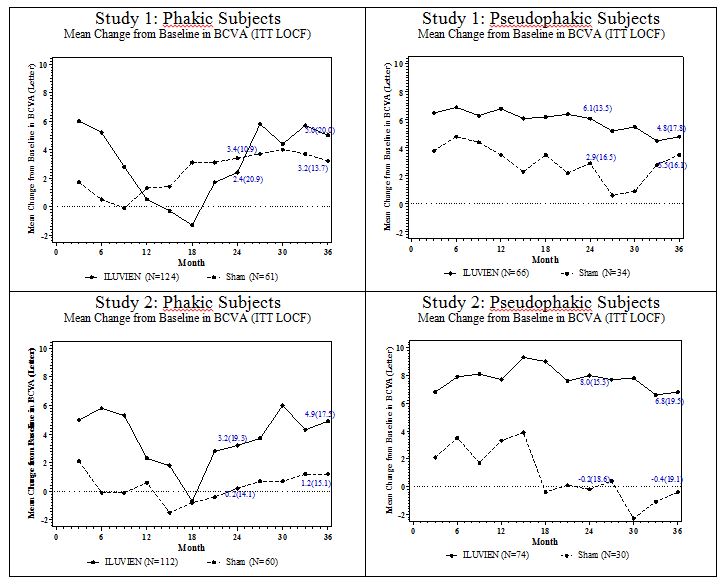
2bGain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 57 (31%) 16 (18%) 13.0% (2.7%, 23.4%) Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 22 (12%) 9 (10%) 1.8% (-5.9%, 9.6%) Mean change from baseline in BCVA (SD) 5.2 (18.0) 0.0 (15.6) 6.1 (1.4, 10.8) Visual acuity outcomes by lens status (Phakic or Pseudophakic) at different visits are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The occurrence of cataracts impacted visual acuity during the study. Patients who were pseudophakic at baseline achieved greater mean BCVA change from baseline at the Month 24 study visit.
Figure 2: Proportion of subjects with >=15 Letters Improvement from Baseline BCVA in the Study Eye
Figure 3: Mean BCVA Change from Baseline
The BCVA outcomes for the Pseudophakic and Phakic subgroups from Studies 1 and 2 at Month 24 are presented in Table 5.
Table 5: Visual Acuity outcomes at Month 24 (Subgroup for pooled data with LOCF) aPseudophakic : ILUVIEN, N=140; Sham, N=64
bPhakic: ILUVIEN, N=236; Sham, N=121Lens Status Outcomes ILUVIEN Sham Estimated Difference (95% CI)
aPseudophakicGain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 39 (28%) 8 (13%) 15.4% (4.4%, 26.3%) Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 7 (5%) 7 (11%) -5.9% (-14.4%, 2.5%) Mean change from baseline in BCVA
(SD)7.1 (14.5) 1.5 (17.4) 5.6 (0.7, 10.6)
bPhakicGain of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 69 (29%) 22 (18%) 11.1% (2.1%, 20.1%) Loss of ≥15 letters in BCVA (n (%)) 41 (17%) 7 (6%) 11.6% (5.2%, 18%) Mean change from baseline in BCVA
(SD)2.8 (20.1) 1.8 (12.6) 1 (-2.5 ,4.4) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ILUVIEN® (fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant) 0.19 mg is supplied in a sterile single use preloaded applicator with a 25-gauge needle, packaged in a tray sealed with a lid inside a carton.
NDC: 68611-190-02
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Steroid-related Effects
Advise patients that a cataract may occur after treatment with ILUVIEN. If this occurs, advise patients that their vision will decrease, and they will need an operation to remove the cataract and restore their vision.Advise patients that they may develop increased intraocular pressure with ILUVIEN treatment, and the increased IOP may need to be managed with eye drops, or surgery.
Intravitreal Injection-related Effects
Advise patients that in the days following intravitreal injection of ILUVIEN, patients are at risk for potential complications including in particular, but not limited to, the development of endophthalmitis or elevated intraocular pressure.When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients that if the eye becomes red, sensitive to light, painful, or develops a change in vision, they should seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist.Driving and Using Machines
Inform patients that they may experience temporary visual blurring after receiving an intravitreal injection. Advise patients not to drive or use machines until this has been resolved.
Manufactured for:
Alimera Sciences, Inc.
6120 Windward Parkway
Alpharetta, GA 30005
Patented. See: www.alimerasciences.com
ALIMERA
SCIENCES - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ILUVIEN
fluocinolone acetonide implantProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68611-190 Route of Administration INTRAVITREAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FLUOCINOLONE ACETONIDE (UNII: 0CD5FD6S2M) (FLUOCINOLONE ACETONIDE - UNII:0CD5FD6S2M) FLUOCINOLONE ACETONIDE 0.19 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYVINYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 532B59J990) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68611-190-02 1 in 1 CARTON 10/15/2014 1 1 in 1 TRAY 1 1 in 1 APPLICATOR; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA201923 10/15/2014 Labeler - Alimera Sciences, Inc. (135745292)
Trademark Results [Iluvien]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ILUVIEN 86375920 4805342 Live/Registered |
Alimera Sciences, Inc. 2014-08-25 |
 ILUVIEN 85554862 4393220 Live/Registered |
Alimera Sciences, Inc. 2012-02-28 |
 ILUVIEN 85236699 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Alimera Sciences, Inc. 2011-02-08 |
 ILUVIEN 77561097 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Alimera Sciences, Inc. 2008-09-03 |
 ILUVIEN 77162736 4045625 Live/Registered |
Alimera Sciences, Inc. 2007-04-23 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.