DECTOMAX- doramectin injection, solution
Dectomax by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Dectomax by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Zoetis Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Dectomax injectable solution is a ready-to-use, colorless to pale yellow, sterile solution containing 1% w/v doramectin (10 mg/mL). In cattle, Dectomax is formulated to deliver the recommended dosage (200 mcg/kg of body weight) when given by subcutaneous (SC) or intramuscular (IM) injection at the rate of 1 mL/110 lb of body weight. In swine, Dectomax is formulated to deliver the recommended dosage (300 mcg/kg of body weight) when given by IM injection at the rate of 1 mL/75 lb of body weight.
-
PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
Dectomax injectable solution is a highly active, broad-spectrum parasiticide for parenteral administration to cattle and swine. It contains doramectin, a novel fermentation-derived macrocyclic lactone. Doramectin is isolated from fermentations of selected strains derived from the soil organism Streptomyces avermitilis.
A primary mode of action of macrocyclic lactones is to modulate chloride ion channel activity in the nervous system of nematodes and arthropods. Macrocyclic lactones bind to receptors that increase membrane permeability to chloride ions. This inhibits the electrical activity of nerve cells in nematodes and muscle cells in arthropods and causes paralysis and death of the parasites. In mammals, the neuronal receptors to which macrocyclic lactones bind are localized within the central nervous system (CNS), a site reached by only negligible concentrations of doramectin.
One dose of Dectomax injectable solution effectively treats and controls a wide range of roundworm and arthropod parasites that impair the health and productivity of cattle and swine.
Studies have demonstrated the safety margin of Dectomax injection in cattle and swine. In USA trials, no toxic signs were seen in cattle given up to 25 times the recommended dose, or in swine given up to 10 times the recommended dose. Studies also demonstrated safety in neonatal calves and piglets treated with up to 3 times the recommended dose. In males (bulls and boars) and females (cows and sows during folliculogenesis, implantation, organogenesis, and through gestation), a dose 3 times the recommended dose had no effect on breeding performance.
-
PRODUCT INDICATIONS
Cattle
Dectomax injectable solution is indicated for the treatment and control of the following harmful species of gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, eyeworms, grubs (see PRECAUTIONS), sucking lice (see PRECAUTIONS), and mange mites. Consult your veterinarian for assistance in the diagnosis, treatment, and control of parasitism.
- * adults
Gastrointestinal Roundworms
(adults and fourth stage larvae)
Ostertagia ostertagi (including inhibited larvae)
O. lyrata
Haemonchus placei
Trichostrongylus axei
T. colubriformis
T. longispicularis*
Cooperia oncophora
C. pectinata*
C. punctata
C. surnabada (syn. mcmasteri)
Bunostomum phlebotomum*
Strongyloides papillosus*
Oesophagostomum radiatum Trichuris spp.*Lungworms (adults and fourth stage larvae)
Dictyocaulus viviparus
Eyeworms (adults)
Thelazia spp.
Grubs (parasitic stages)
Hypoderma bovis
H. lineatum
Sucking Lice
Haematopinus eurysternus
Linognathus vituli
Solenopotes capillatus
Mange Mites
Psoroptes bovis
Sarcoptes scabiei1 Adults
Dectomax injectable solution has been proved to effectively control infections and to protect cattle from reinfection with Cooperia oncophora and Haemonchus placei for 14 days, Ostertagia ostertagi for 21 days, and C. punctata, Oesophagostomum radiatum, and Dictyocaulus viviparus for 28 days after treatment.
Swine
Dectomax injectable solution is indicated for the treatment and control of the following species of gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, kidney worms, sucking lice (see PRECAUTIONS), and mange mites. Consult your veterinarian for assistance in the diagnosis, treatment, and control of parasitism.
- * adults
Gastrointestinal Roundworms
(adults and fourth stage larvae)
Ascaris suum
Oesophagostomum dentatum
Oesophagostomum quadrispinulatum*
Strongyloides ransomi*
Hyostrongylus rubidus*Lungworms (adults)
Metastrongylus spp.
Kidney Worms (adults)
Stephanurus dentatus
Mange Mites (adults and immature stages)
Sarcoptes scabiei var. suis
Sucking Lice (adults and immature stages)
Haematopinus suis -
DOSAGE
Cattle
Administer Dectomax injectable solution at the recommended dosage of 200 mcg doramectin per kg (91 mcg/lb) of body weight. Each mL contains 10 mg of doramectin, sufficient to treat 110 lb (50 kg) of body weight.
Body Weight (lb) Dose (mL) 110 1 220 2 330 3 440 4 550 5 660 6 770 7 880 8 990 9 1,100 10 Swine
Administer Dectomax injectable solution at the recommended dosage of 300 mcg doramectin per kg (136 mcg/lb) of body weight. Each mL contains 10 mg of doramectin, sufficient to treat 75 lb (34 kg) of body weight.
Body Weight (lb) Dose (mL) 15 0.2 30 0.4 45 0.6 60 0.8 75 1.0 150 2.0 225 3.0 300 4.0 375 5.0 450 6.0 Do not underdose. Ensure each animal receives a complete dose based on a current body weight. Underdosing may result in ineffective treatment, and encourage the development of parasite resistance.
-
RECOMMENDED TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR SWINE
To effectively initiate control of mange and sucking lice in swine, it is important to treat all animals in the herd. After initial treatment, use Dectomax regularly as follows:
-
ADMINISTRATION
Dry, sterile equipment and aseptic procedures should be used when withdrawing and administering Dectomax. For multiple treatments either automatic injection equipment or an aspirating needle should be used.
Cattle
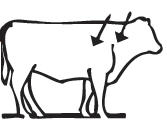
Administer Dectomax injectable solution by SC or IM route. Injections should be made using a 16 gauge needle for adult cattle or an 18 gauge needle for young animals. Needles 1/2–3/4" in length are suggested for SC administration. A 1-1/2" needle is suggested for IM administration. SC injections should be administered under the loose skin in front of or behind the shoulder. IM injections should be administered into the muscular region of the neck. Beef Quality Assurance guidelines recommend SC administration as the preferred route. Swine

Administer Dectomax injectable solution by the IM route. Inject in the neck region using an 18 gauge × 1" needle for young animals; a 16 gauge × 1-1/2" needle for sows and boars. To accurately meter doses administered to piglets, use of a tuberculin syringe and 20 gauge × 1" needle is recommended. - WARNINGS
-
OTHER WARNINGS
Parasite resistance may develop to any dewormer, and has been reported for most classes of dewormers. Treatment with a dewormer used in conjunction with parasite management practices appropriate to the geographic area and the animal(s) to be treated may slow the development of parasite resistance. Fecal examinations or other diagnostic tests and parasite management history should be used to determine if the product is appropriate for the herd prior to the use of any dewormer. Following the use of any dewormer, effectiveness of treatment should be monitored (for example, with the use of a fecal egg count reduction test or another appropriate method). A decrease in a drug's effectiveness over time as calculated by fecal egg count reduction tests may indicate the development of resistance to the dewormer administered. Your parasite management plan should be adjusted accordingly based on regular monitoring.
-
RESIDUE WARNINGS
Cattle: Do not slaughter for human consumption within 35 days of treatment. Not for use in female dairy cattle 20 months of age or older. A withdrawal period has not been established for this product in preruminating calves. Do not use in calves to be processed for veal. Swine: Do not slaughter for human consumption within 24 days of treatment.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Dectomax has been developed specifically for use in cattle and swine only. This product should not be used in other animal species as severe adverse reactions, including fatalities in dogs, may result.
For SC injection in cattle only. For IM injection in swine and cattle. This product is approved for the treatment and control of sucking lice. For treatment of biting lice in cattle, use of Dectomax Pour-On is recommended.
Dectomax is highly effective against all stages of cattle grubs. However, proper timing of treatment is important. For most effective results, cattle should be treated as soon as possible after the end of the heel fly (warble) season.
Destruction of Hypoderma larvae (cattle grubs) at the period when these grubs are in vital areas may cause undesirable host-parasite reactions including the possibility of fatalities. Killing H. lineatum when it is in the tissue surrounding the gullet may cause bloat; killing H. bovis when it is in the vertebral canal may cause staggering or paralysis. These reactions are not specific to treatment with Dectomax, but can occur with any successful treatment of grubs. Cattle should be treated either before or after these stages of grub development. Consult your veterinarian concerning the proper time for treatment.
Cattle treated with Dectomax after the end of the heel fly season may be re-treated with Dectomax during the winter for internal parasites, mange mites, or sucking lice, without danger of grub-related reactions. A planned parasite control program is recommended.
-
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
Studies indicate that when doramectin comes in contact with the soil, it readily and tightly binds to the soil and becomes inactive over time. Free doramectin may adversely affect fish and certain aquatic organisms. Do not permit water runoff from feedlots to enter streams or ponds. Do not contaminate water by direct application or by the improper disposal of drug containers. Dispose of containers in an approved landfill or by incineration.
As with other avermectins, doramectin is excreted in the dung of treated animals and can inhibit the reproduction and growth of pest and beneficial insects that use dung as a source of food and for reproduction. The magnitude and duration of such effects are species and life-cycle specific.
When used according to label directions, the product is not expected to have an adverse impact on populations of dung-dependent insects.
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Multi-Dose Vial Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mL Multi-Dose Vial Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mL Multi-Dose Vial Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DECTOMAX
doramectin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type OTC ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54771-5438 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DORAMECTIN (UNII: KGD7A54H5P) (DORAMECTIN - UNII:KGD7A54H5P) DORAMECTIN 10 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54771-5438-1 100 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE 2 NDC: 54771-5438-2 200 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE 3 NDC: 54771-5438-3 500 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141061 07/30/1996 Labeler - Zoetis Inc. (828851555)
Trademark Results [Dectomax]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DECTOMAX 75219332 2123753 Live/Registered |
ZOETIS SERVICES LLC 1996-12-30 |
 DECTOMAX 74036329 1845017 Live/Registered |
Pfizer Inc. 1990-03-09 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.



