These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRONCHITOL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRONCHITOL.BRONCHITOL® (mannitol) inhalation powder, for oral inhalation useInitial U.S. Approval: 1964
Bronchitol by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Bronchitol by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Chiesi USA, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
BRONCHITOL- mannitol capsule
Chiesi USA, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRONCHITOL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRONCHITOL.
BRONCHITOL® (mannitol) inhalation powder, for oral inhalation use Initial U.S. Approval: 1964 INDICATIONS AND USAGEBRONCHITOL is a sugar alcohol indicated as add-on maintenance therapy to improve pulmonary function in adult patients 18 years of age and older with cystic fibrosis. Use BRONCHITOL only in adults who have passed the BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSInhalation powder: 40 mg mannitol per capsule (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (≥3%) include cough, hemoptysis, oropharyngeal pain, vomiting, bacteria sputum identified, pyrexia, and arthralgia. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Chiesi USA, Inc. at 1-888-661-9260 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 1/2024 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRONCHITOL is indicated as add-on maintenance therapy to improve pulmonary function in adult patients 18 years and older with Cystic Fibrosis. Use BRONCHITOL only for adults who have passed the BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Required Testing and Evaluation Prior to Prescribing BRONCHITOL (BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test)
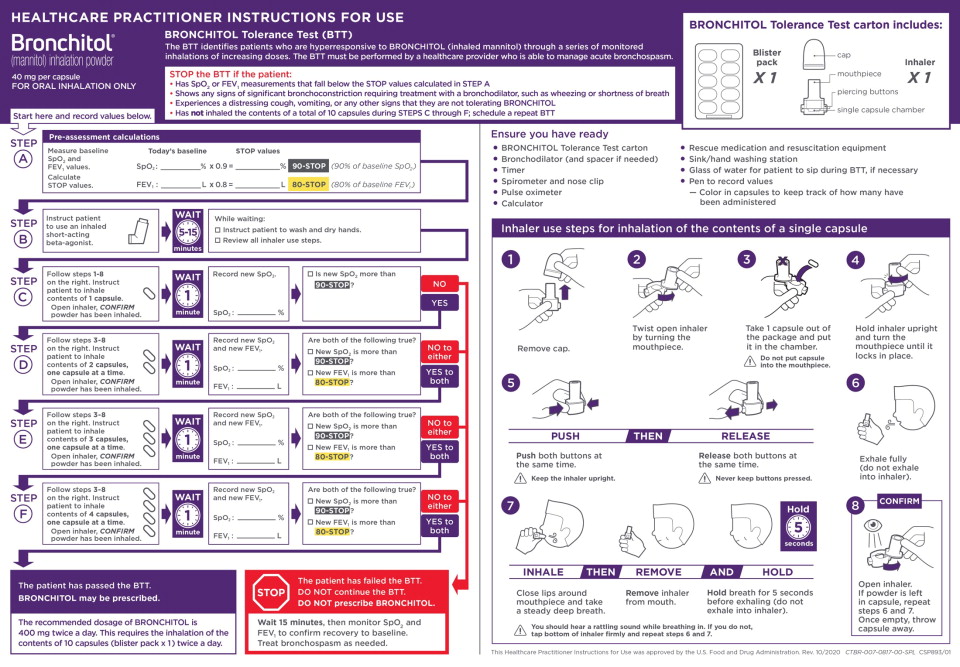
Prior to prescribing BRONCHITOL for treatment of cystic fibrosis, the BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test (BTT) must be administered and performed under the supervision of a healthcare practitioner who is able to manage acute bronchospasm, to identify patients who are suitable candidates for BRONCHITOL maintenance therapy.
- Perform BTT to identify patients who experience bronchospasm, a decrease in FEV1, or a decrease in oxygen saturation with administration of BRONCHITOL. If a patient experiences any of these events during the BTT, the patient has failed the BTT. Do not prescribe BRONCHITOL. If a patient does not experience any of these events during BTT, the patient has passed the BTT and is a candidate for BRONCHITOL therapy.
- Ensure that rescue medication and resuscitation equipment are available for immediate use during the BTT.
- Do not perform the BTT if the patient is considered clinically unstable.
See the BTT Healthcare Practitioner (HCP) Instructions for Use (IFU) for complete instructions and to avoid medication errors associated with BTT dosing and procedures.
Do not use BRONCHITOL add-on maintenance therapy in patients who fail the BTT [see Contraindications (4)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
For patients who have passed the BTT, the recommended dosage of BRONCHITOL is 400 mg twice a day by oral inhalation (the contents of 10 capsules administered individually) via the inhaler [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
A short-acting bronchodilator should be administered by oral inhalation, 5-15 minutes before every dose of BRONCHITOL.
BRONCHITOL should be taken once in the morning and once in the evening, with the later dose taken at least 2-3 hours before bedtime.
2.3 Use and Maintenance of Inhaler
Instruct patients on safe hygiene practices (clean and dry hands thoroughly) and correct inhaler use, including loading of capsules and proper inhalation technique per the Patient Instructions for Use.
The BRONCHITOL inhaler should be discarded and replaced after 7 days of use. If the inhaler does need to be washed, the patient should allow the inhaler to thoroughly air dry before next use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Inhalation powder: 40 mg mannitol per capsule; clear, colorless hard gelatin capsule imprinted with “PXS 40 mg”
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
BRONCHITOL is contraindicated in the following conditions:
-
Hypersensitivity to mannitol or to any of the capsule components
-
Failure to pass the BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test (BTT)
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Bronchospasm
BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test
BRONCHITOL can cause bronchospasm, which can be severe in susceptible individuals. Because of the risk of bronchospasm, prior to prescribing BRONCHITOL, perform the BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test (BTT), to identify patients who are appropriate for maintenance treatment with BRONCHITOL. The BTT must be administered under the supervision of a healthcare practitioner who can treat severe bronchospasm. In clinical trials, 896 adult patients with cystic fibrosis underwent the BTT and 72 patients (8%) failed or did not complete the BTT. Do not prescribe BRONCHITOL if the patient fails the BTT.
Maintenance Therapy
Bronchospasm may occur during inhalation of BRONCHITOL, even in patients who have passed the BTT. An inhaled short-acting bronchodilator must be administered 5-15 minutes before administration of each dose during maintenance therapy. In clinical studies, bronchospasm or bronchial hyperreactivity was reported in 4 of 414 adult patients (1.0%) receiving BRONCHITOL as maintenance therapy and in 2 of 347 adult patients (0.6%) receiving control (50 mg inhaled mannitol), even though these patients had passed the BTT. If bronchospasm occurs following dosing of BRONCHITOL, it should immediately be discontinued and treated with an inhaled short-acting bronchodilator or as medically appropriate.
5.2 Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis may occur with BRONCHITOL use. Hemoptysis was reported in 43 (10.4%) adult patients receiving BRONCHITOL and in 33 (9.5%) adult patients receiving control (50 mg inhaled mannitol) during clinical studies. In patients aged 6 years to 17 years, hemoptysis was reported in 12 of 154 (7.8%) patients who received BRONCHITOL and in 2 of 105 (1.9%) patients who received control. BRONCHITOL has not been studied in patients with a history of episodes of significant hemoptysis (volume greater than 60 mL) in the previous 3 months. BRONCHITOL should be discontinued in the event of hemoptysis. BRONCHITOL is not indicated for use in children and adolescents.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The overall safety profile for BRONCHITOL is based on data from 1,020 CF patients from three 26-week, randomized, double-blind, controlled trials (Trials 1, 2, and 3). While CF patients aged 6 to 17 years were included in two of the three trials, BRONCHITOL is not indicated for use in this age group [see Indications (1), Use in Specific Populations (8)]. The safety data described below are based on 761 adult patients who received at least one dose of study drug in the three trials.
Of the 761 adult patients, 45% of patients were female and 98% were Caucasian; 414 received BRONCHITOL and 347 received control (50 mg inhaled mannitol) for up to 26 weeks. Adult patients treated with BRONCHITOL were ages 18 to 59 years with a mean baseline FEV1 of 62.0% of predicted.
In these three trials, the proportion of adult patients who prematurely discontinued study drug due to adverse reactions was 12.3% for patients treated with BRONCHITOL and 8.6% for patients treated with control. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18.8% of patients treated with BRONCHITOL and 18.4% of patients treated with control. Serious adverse reactions occurring with greater than 1% incidence and more frequently in BRONCHITOL-treated adult patients compared to control-treated patients were CF exacerbations (13.3% vs. 11.2%), hemoptysis (1.4% vs. 1.2%) and lower respiratory tract infection (1.2% vs 0.9%).
The incidence of Adverse Reactions in adults during the 26 week treatment period with BRONCHITOL across the three trials is shown in Table 1.
|
Primary System Organ Class Preferred Term |
BRONCHITOL N = 414 % |
CONTROL N = 347 % |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders |
||
|
Cough |
15.0 |
10.7 |
|
Hemoptysis |
10.4 |
9.5 |
|
Oropharyngeal pain |
7.0 |
4.3 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
||
|
Vomiting |
3.1 |
1.4 |
|
Investigations |
||
|
Bacteria sputum identified |
6.8 |
4.6 |
|
General disorders and administrative site conditions |
||
|
Pyrexia |
4.6 |
2.3 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
||
|
Arthralgia |
3.1 |
2.6 |
In Trials 1, 2, and 3, exacerbations of cystic fibrosis (reported as condition aggravated) occurred in 132 of 414 (32%) adult patients receiving BRONCHITOL and in 114 of 347 (33%) adult patients receiving control (50 mg inhaled mannitol). Exacerbations of cystic fibrosis reported as serious adverse reactions occurred in 55 of 414 adult patients (13%) receiving BRONCHITOL and in 39 of 347 adult patients (11%) receiving control. Within the U.S. adult subgroup (comprising 27% of adults enrolled), exacerbations of cystic fibrosis reported as serious adverse reactions occurred in 23 of 110 (21%) patients receiving BRONCHITOL and in 10 of 93 (11%) patients receiving control. Among the non-U.S. adult subgroup (comprising 73% of adults enrolled), exacerbations of cystic fibrosis reported as serious adverse reactions occurred in 11% of patients in each treatment arm.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug interaction studies have been conducted with mannitol, the active ingredient in BRONCHITOL.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of BRONCHITOL in pregnant women. The available data on BRONCHITOL use in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform any drug-associated risks for major birth defects and miscarriage. Based on animal reproduction studies, no evidence of structural alterations was observed when mannitol was administered to pregnant rats and mice during organogenesis at doses up to approximately 20 and 10 times, respectively, the maximum recommended daily inhalation dose (MRDID) in humans [see Data]. There are risks to the mother associated with cystic fibrosis in pregnancy [see Clinial Considerations]. BRONCHITOL should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the mother and fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the United States general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Cystic fibrosis may increase the risk for preterm delivery.
Data
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of mannitol to pregnant rats and mice during the period of organogenesis did not cause fetal structural alterations. The mannitol dose in rats and mice was approximately 20 and 10 times the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose (MRDID) in humans, respectively, (on a mg/m2 basis at maternal doses of 1600 mg/kg/day in both species).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether BRONCHITOL is excreted in human breast milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for BRONCHITOL and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from BRONCHITOL or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
BRONCHITOL is not indicated for use in children and adolescents. The safety and effectivenss of BRONCHITOL have not been established in pediatric patients for cystic fibrosis. Patients aged 6 years to 17 years were included in two 26-week, double-blind clinical trials (Trials 2 and 3). In these trials, 154 patients under 18 years of age received BRONCHITOL and 105 patients received control (50 mg inhaled mannitol). Hemoptysis was reported in 12 of 154 (7.8%) patients who received BRONCHITOL and in 2 of 105 (1.9%) patients who received control.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of BRONCHITOL did not include sufficient numbers of patients with cystic fibrosis who were 65 years of age and older to allow evaluation of safety and efficacy in this population.
8.6 Hepatic and Renal Impairment
Clinical trials of BRONCHITOL did not include patients with hepatic or renal impairment. No specific dose recommendations for these patient populations are available. However, an increase in systemic exposure of mannitol can be expected in patients with renal impairment based on the kidney being its primary route of elimination.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Susceptible persons may experience bronchoconstriction from an overdosage. If excessive coughing and bronchoconstriction occurs, immediately administer an inhaled short-acting bronchodilator and other medical treatments as necessary.
11 DESCRIPTION
BRONCHITOL (mannitol) inhalation powder contains D-Mannitol (referred to throughout as mannitol) as the active ingredient. Mannitol is a hexahydric sugar alcohol, with the following chemical name hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol and chemical structure:
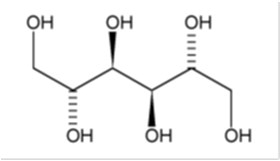
Mannitol is a white or almost white crystalline powder or free-flowing granules with an empirical formula of C6H14O6 and molecular weight of 182.2. Mannitol is freely soluble in water, and very slightly soluble in alcohol. Mannitol shows polymorphism.
BRONCHITOL contains mannitol powder spray dried into particles of respirable size filled into clear, colorless hard gelatin capsules. There are no inactive ingredients in BRONCHITOL.
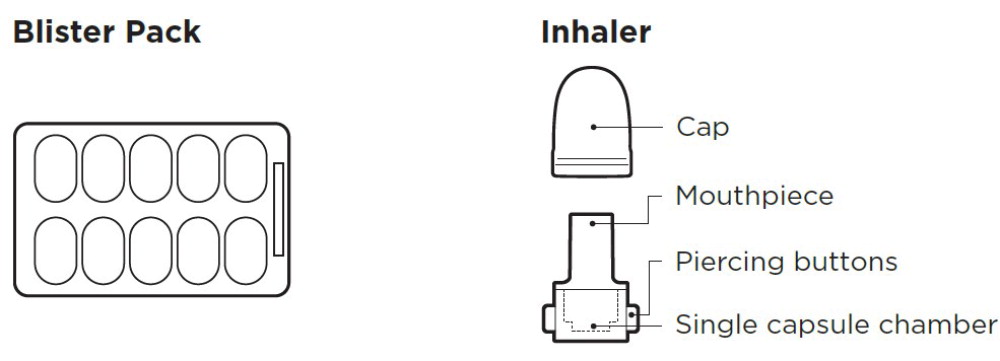
The accompanying white plastic inhaler is comprised of a mouthpiece, blue piercing buttons, capsule chamber, and a removable cap. A blister pack consists of 10 capsules, each containing 40 mg mannitol. After a capsule is placed in the capsule chamber and pierced by firmly pressing and releasing the buttons on the side of the device, the powder within the capsule becomes exposed and ready for dispersion into the airstream generated by the patient upon inhalation through the mouthpiece. Under standardized in vitro test conditions, the inhaler delivers 32.2 mg of mannitol per inhalation when tested at a flow rate of 60 L/min for 2 seconds. The actual amount of drug delivered to the lungs will depend on patient factors, such as inspiratory flow profile.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism of action of BRONCHITOL in improving pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis patients is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral inhalation of 635 mg, the mean mannitol peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 13.71 mcg/mL while the mean extent of systemic exposure (AUC) was 73.15 mcghr/mL. The mean time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) after oral inhalation was 1.5 hour.
Distribution
Based on intravenous administration, the volume of distribution of mannitol was 34.3 L.
Elimination
Metabolism
Mannitol is metabolized in a CYP-independent manner through the glycolytic pathway via dehydrogenation to fructose. The extent of metabolism of mannitol appears to be small. This is evident from a urinary excretion of about 87% of unchanged drug after an intravenous dose to healthy patients.
Excretion
Following oral inhalation, the elimination half-life of mannitol was 4.7 hours. The mean terminal elimination half-life for mannitol in plasma remained unchanged regardless of the route of administration (oral, inhalation, and intravenous). The urinary excretion rate versus time profile for mannitol was consistent for all routes of administration. The total clearance after intravenous administration was 5.1 L/hr while the renal clearance was 4.4 L/hr. Therefore, the clearance of mannitol was predominately via the kidney. Following inhalation of 635 mg of mannitol in 18 healthy patients, about 55% of the total dose was excreted in the urine as unchanged mannitol. Following oral or intravenous administration of a 500 mg dose, the corresponding values were 54% and 87% of the dose, respectively.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic and Renal Impairment: Formal pharmacokinetic studies using BRONCHITOL have not been conducted in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Since the drug is eliminated primarily via the kidney, an increase in systemic exposure can be expected in renally impaired patients.
Drug Interaction Studies
No formal drug interaction studies have been conducted with BRONCHITOL.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In 2-year carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice mannitol did not show evidence of carcinogenicity at oral dietary concentrations up to 5% (or 7,500 mg/kg on a mg/kg basis). These doses were approximately 55 and 30 times the MRHDID, respectively, on a mg/m2 basis.
Mutagenesis
Mannitol tested negative in the following assays: bacterial gene mutation assay, in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in WI-38 human cells, in vivo chromosomal aberration assay in rat bone marrow, in vivo dominant lethal assay in rats, and in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
The effect of inhaled mannitol on fertility has not been investigated.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of BRONCHITOL for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) was evaluated in 3 randomized, double-blind, controlled trials (Trials 1, 2, and 3).
All three trials were 26-week, randomized, double-blind, controlled studies in patients with CF. Trial 1 (NCT02134353) evaluated patients 18 years of age or older with baseline FEV1 >40% to <90% of predicted. Trial 2 (NCT00446680) evaluated patients 6 years of age or older with baseline FEV1>30% to <90% of predicted. Trial 3 (NCT00630812) evaluated pateints 6 years of age or older with baseline FEV1>40% to <90% of predicted. All three trials excluded CF patients with an episode of hemoptysis (>60 mL) in the 3 months prior to enrollment. The use of inhaled hypertonic saline was not permitted in any of the three trials, but continued use of their other standard of care CF therapies were allowed (e.g., bronchodilators, inhaled antibiotics, and dornase alfa). While CF patients aged 6 to 17 years were included in Trials 2 and 3, BRONCHITOL is not indicated for use in this age group [see Indications (1), Warnings and Precautions (5), Adverse Reactions (6), Use in Specific Populations (8)].
Patients were randomized to receive either BRONCHITOL 400 mg or control (50 mg inhaled mannitol) twice daily. Each dose of BRONCHITOL was preceded by use of an inhaled short-acting bronchodilator (albuterol or equivalent) taken 5 to 15 minutes prior to initiation of BRONCHITOL dosing. The primary efficacy endpoint in all three studies was improvement in lung function as determined by the mean change from baseline in pre-dose FEV1 (mL) over 26 weeks of treatment and was analyzed using the pattern mixture model with multiple imputation.
Trial 1 evaluated 423 adult patients with a mean age of 28 years and a mean FEV1 63.9% predicted (range: 40.3% = minimum, 89.6% = maximum).
Treatment with BRONCHITOL resulted in a statistically significant improvement in FEV1. In Trial 1, the treatment difference between BRONCHITOL and control for the adjusted mean change in FEV1 from baseline over 26 weeks was 51 mL (95% CI 6 to 97 mL) shown in Table 2.
|
Control (N=214) |
BRONCHITOL (N=209) |
|
|
Adjusted mean change from baseline |
12 mL |
63 mL |
|
Adjusted mean difference (95% CI), p-value |
51 mL (6 to 97 mL), p=0.028 |
|
Trials 2 and 3 evaluated 295 and 305 patients, respectively. For the adjusted mean difference in the change from baseline in FEV1 over 26 weeks in the intention-to-treat population in Trials 2 and 3, the treatment difference between BRONCHITOL and Control was 68 mL (95% CI: 24 to 113 mL) and 52 mL (95% CI: -3 to 107 mL), respectively.
Post-hoc descriptive analyses of the adult subgroups from Trials 2 and 3 were performed. The adult subgroup analyses in Trial 2 and 3 evaluated 209 and 157 adult patients, respectively. In Trial 2, there was an adjusted mean difference in the change from baseline in FEV1 over 26 weeks in the intention-to-treat population of adults of 78 mL (95% CI: 21 to 135 mL). In Trial 3, there was an adjusted mean difference in the change from baseline in FEV1 over 26 weeks in the intention-to-treat population of adults of 78 mL (95% CI: 2 to 153 mL).
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
BRONCHITOL (mannitol) inhalation powder:
-
40 mg of mannitol per capsule
-
capsules are clear, colorless and imprinted in black with “PXS” on cap and “40 mg” on body
-
supplied in cartons containing 10, 140 or 560 capsules in blister packs co-packaged with 1, 1, and 4 inhalers respectively in a carton
|
Pack Quantities |
Inhalers |
Capsules |
NDC Number |
|
4-week Treatment Pack (4 x 7-day treatment packs) |
4 |
560 |
10122-212-56 |
|
7-day Treatment Pack |
1 |
140 |
10122-212-14 |
|
Bronchitol Tolerance Test |
1 |
10 |
10122-212-04 |
BRONCHITOL should be stored between 68°F-77°F (20°C-25°C) with excursions permitted between 59°F-86°F (15°C-30°C). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not refrigerate. Do not freeze.
The Training Kit (NDC: 10122-216-01), containing empty gelatin capsules, should be stored between 68°F-77°F (20°C-25°C) with excursions permitted from 59°F-86°F (15°C-30°C).
BRONCHITOL should only be used with the provided inhaler, which is a white plastic inhaler comprised of a mouthpiece, blue piercing buttons, capsule chamber, and a removable cap. All remaining unused (opened and unopened) blister packs and the inhalers should be properly discarded. Be sure to read the accompanying BRONCHITOL instructions completely before administration. If you have any questions, contact the supplier at 1-888-661-9260.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Patient Instructions for Use).
BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test
Inform patients that a BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test is required prior to beginning treatment with BRONCHITOL. The BRONCHITOL Tolerance Test must be performed by a healthcare practitioner equipped to monitor oxygen saturation (SpO2), perform spirometry (FEV1), and manage acute bronchospasm.
Inhaled Short-Acting Bronchodilator Use
Instruct patients that an inhaled short-acting bronchodilator such as albuterol must always be administered 5 to 15 minutes prior to every dose of BRONCHITOL.
Bronchospasm
Prior to administration, inform patients that bronchospasm can occur with inhalation of BRONCHITOL. If patient experiences bronchospasm, instruct the patient to discontinue BRONCHITOL and contact their healthcare practitioner right away.
Hemoptysis
Inform patients that hemoptysis can occur with inhalation of BRONCHITOL. If a patient experiences hemoptysis, instruct patients to discontinue BRONCHITOL and contact their healthcare practitioner right away.
Administration
Instruct patients on the proper administration of BRONCHITOL with the inhaler. The recommended dosage is 10 capsules (400 mg) twice a day. This requires inhaling the contents of 10 capsules administered individually once in the morning and once at least 2-3 hours before bed.
Manufactured by:
Pharmaxis Ltd
20 Rodborough Rd
Frenchs Forest NSW 2086
AUSTRALIA
Manufactured for:
Chiesi USA, Inc.
Cary, NC 27518
USA
BRONCHITOL® is a registered trademark of Pharmaxis Ltd
CTBR-001-1120-01-SPL-1
|
Patient Information BRONCHITOL® (BRONK-ih-tol) (mannitol) inhalation powder for oral inhalation use |
|
What is BRONCHITOL?
BRONCHITOL should not be used in children and adolescents. It is not known if BRONCHITOL is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age. |
|
Do not take BRONCHITOL if you:
|
|
Before you use BRONCHITOL, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of the medicines you take and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
How should I use BRONCHITOL? See the step-by-step Patient Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information leaflet.
Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical care right away if your breathing problems get worse while taking BRONCHITOL. |
|
What are the possible side effects of BRONCHITOL? BRONCHITOL may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of BRONCHITOL include:
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of BRONCHITOL. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Chiesi USA, Inc. at 1-888-661-9260. |
|
How should I store BRONCHITOL?
Keep BRONCHITOL and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of BRONCHITOL. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BRONCHITOL for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BRONCHITOL to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This leaflet summarizes the most important information about BRONCHITOL. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about BRONCHITOL that is written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in BRONCHITOL? Active ingredient: mannitol Inactive ingredients: There are no inactive ingredients in BRONCHITOL. Capsules: gelatin and water. The imprinting ink contains shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, purified water, strong ammonia solution, potassium hydroxide and black iron oxide E172. Manufactured by: Pharmaxis Ltd 20 Rodborough Road Frenchs Forest NSW 2086 AUSTRALIA Manufactured for: Chiesi USA, Inc. Cary, NC 27518 USA 1-888-661-9260 BRONCHITOL is registered in the US Patent and Trademark Office. All trademarks referenced herein are the property of their prospective owners. For more information about BRONCHITOL or how to use your inhaler, call 1-888-661-9260. |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration 1/2024
|
PATIENT INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE BRONCHITOL® (mannitol) inhalation powder for oral inhalation use |
|
|
This Patient Instructions for Use contains information on how to take BRONCHITOL. |
|
| Each BRONCHITOL box contains: | |
|
7-Day Treatment Pack
|
4-Week Treatment Pack
|
 |
|
|
Important Information You Need to Know Before Using BRONCHITOL
|
|
|
Preparing to use BRONCHITOL BRONCHITOL is supplied to people in cartons containing 140 or 560 capsules in blister packs. Supplies you will need to use BRONCHITOL:
|
|
| Before using BRONCHITOL:
Use an inhaled bronchodilator 5 to15 minutes before using BRONCHITOL (See Figure A). |
|
 |
|
|
Clean and dry hands well (See Figure B). |
|
 |
|
|
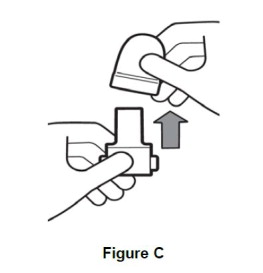
Inhaler use steps for inhalation of the contents of a single capsule: Step 1. Remove cap (See Figure C) |
|
 |
|
|
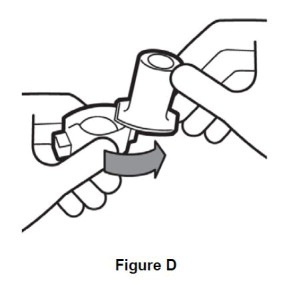
Step 2. Twist open inhaler by turning the mouthpiece to the right. (See Figure D). |
|
 |
|
|
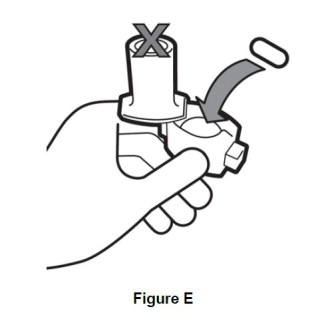
Step 3. Take 1 capsule out of the blister pack and put it in the chamber.(See Figure E). Do not place capsule into the mouthpiece of the inhaler. |
|
 |
|
|
Step 4. Hold inhaler upright and turn the mouthpiece to the left until it locks in place. (See Figure F). |
|
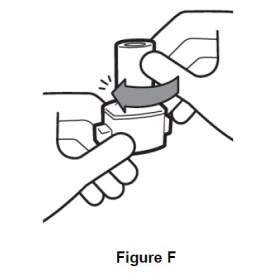 |
|
|
Step 5. Push both piercing buttons at the same time. Release both piercing buttons at the same time (See Figure G). Keep inhaler upright. Never keep piercing buttons pressed. |
|
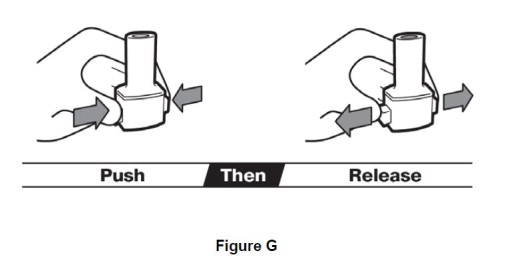 |
|
|
Step 6. Breathe out (exhale) fully (See Figure H). Do not breathe out into inhaler. |
|
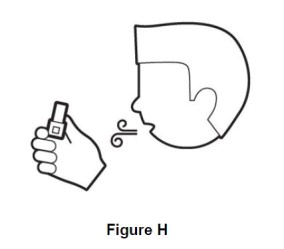 |
|
|
Step 7. Close lips around the mouthpiece and take a steady deep breath in through your mouth. Do not breathe through your nose. Remove inhaler from mouth. Hold breath for 5 seconds before exhaling, do not breathe out (exhale) into inhaler (See Figure I).
You should hear a rattling sound while breathing in. If you do not, tap bottom of inhaler firmly and repeat steps 6 and 7. |
|
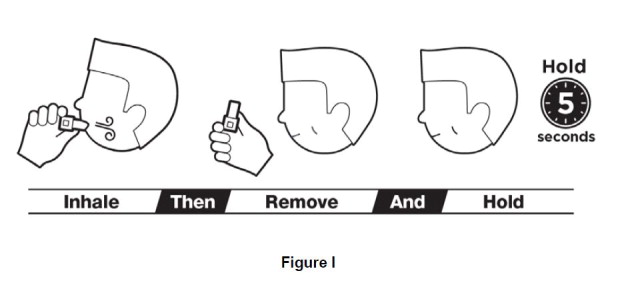 |
|
|
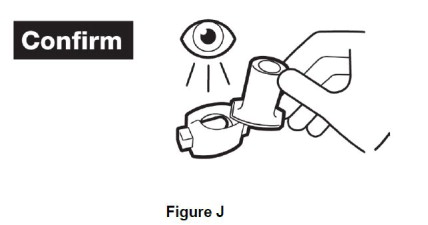
Step 8. Open the inhaler by turning the cap to the right. If powder is left in capsule, repeat steps 6 and 7. After the capsule is empty, throw away. (See Figure J). |
|
 |
|
|
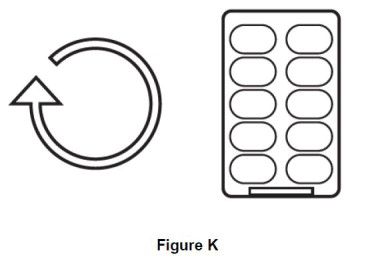
Step 9. Repeat steps 3 to 8 for all 10 capsules in 1 blister pack (See Figure K).
Breathe in (inhale) contents of each capsule one after another until all 10 capsules in the blister pack are used. |
|
 |
|
|
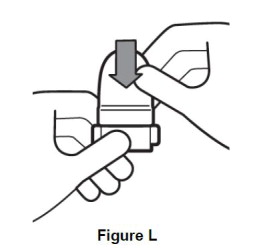
Step 10. After inhaling contents of all 10 capsules, close mouthpiece and place cap on inhaler (See Figure L). |
|
 |
|
|
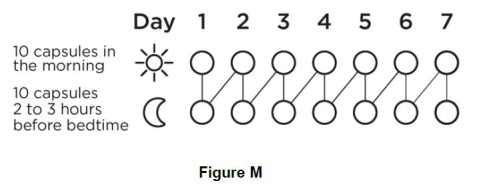
Step 11. Continue using BRONCHITOL for 7 days then throw away (discard) the inhaler (See Figure M). |
|
 |
|
|
How should I store BRONCHITOL?
Cleaning your BRONCHITOL inhaler.
Caring for your BRONCHITOL inhaler.
For more information about BRONCHITOL or how to use your inhaler, call 1-888-661-9260. Manufactured by: Pharmaxis Ltd 20 Rodborough Road Frenchs Forest NSW 2086 AUSTRALIA Manufactured for: Chiesi USA, Inc. Cary, NC 27518 USA 1-888-661-9260 BRONCHITOL is registered in the US Patent and Trademark Office. This Patient Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 1/2024 CTBR-009-0817-00-SPL-1 |
|
Principal Display Panel - 40 mg 4 Week Carton Label
Rx Only
NDC: 10122-212-56
Caution: Federal Law Prohibits Dispensing Without A Prescription
Bronchitol®
(mannitol) inhalation powder
40 mg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Do Not Swallow Bronchitol Capsules
Complete entire package (56 Blister Packs) for 28 days treatment
Contents:
56 Blister Cards: 560 capsules (40 mg each)
4 Bronchitol devices: For use with enclosed capsules only
See package insert for complete dosage information
For more information, call 1-888-661-9260.

Principal Display Panel - 40 mg 7 Day Carton Label
Rx Only
NDC: 10122-212-14
Bronchitol®
(mannitol) inhalation powder
40 mg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Do Not Swallow Bronchitol Capsules
Complete entire package (14 Blister Packs) for 7 days treatment
Contents:
- 14 Blister Packs: 140 capsules (40 mg each)
- 1 Bronchitol inhaler: For use with enclosed capsules only
- Quick reference guide
- Package Insert
See package insert for complete dosage information
For more information, call 1-888-661-9260.

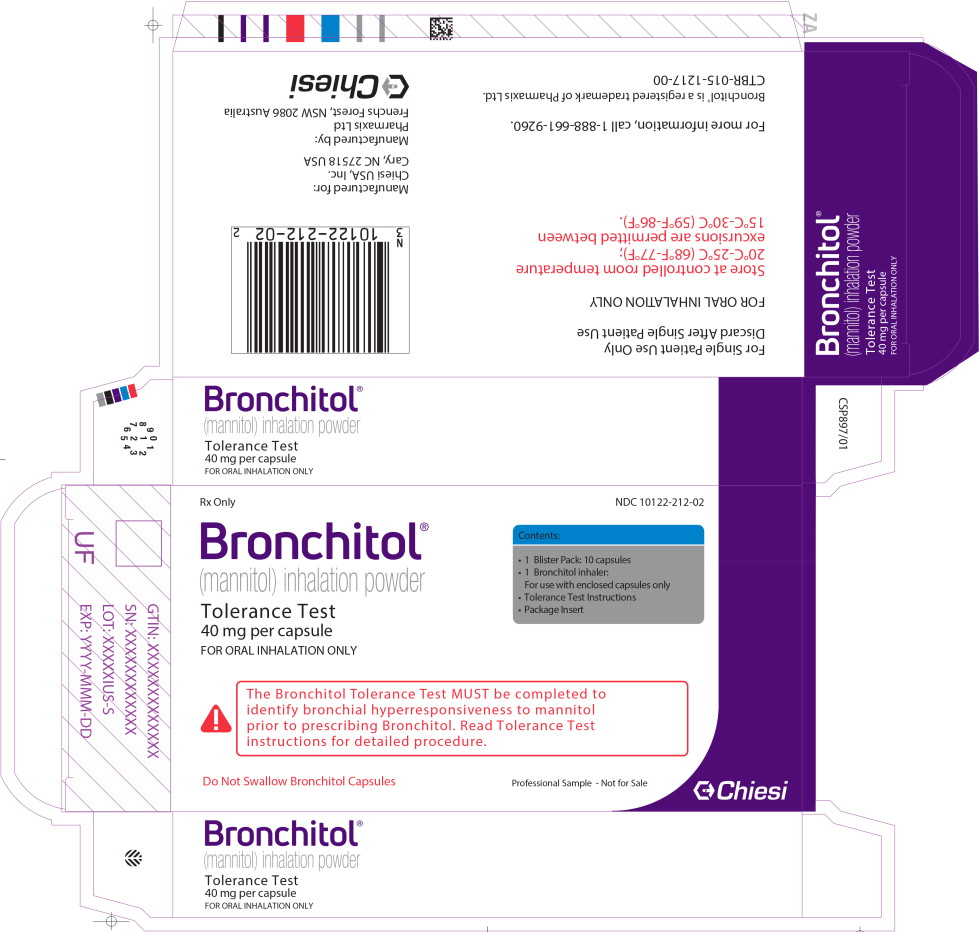
Principal Display Panel - 40 mg Tolerance Test Carton Label
Rx Only
NDC: 10122-212-02
Bronchitol®
(mannitol) inhalation powder
Tolerance Test
40 mg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Contents:
- 1 Blister Pack: 10 capsules
- 1 Bronchitol inhaler:
For use with enclosed capsules only - Tolerance Test Instructions
- Package Insert
The Bronchitol Tolerance Test MUST be completed to
identify bronchial hyperresponsiveness to mannitol
prior to prescribing Bronchitol. Read Tolerance Test
instructions for detailed procedure.
Do Not Swallow Bronchitol Capsules
Professional Sample - Not for Sale
Chiesi
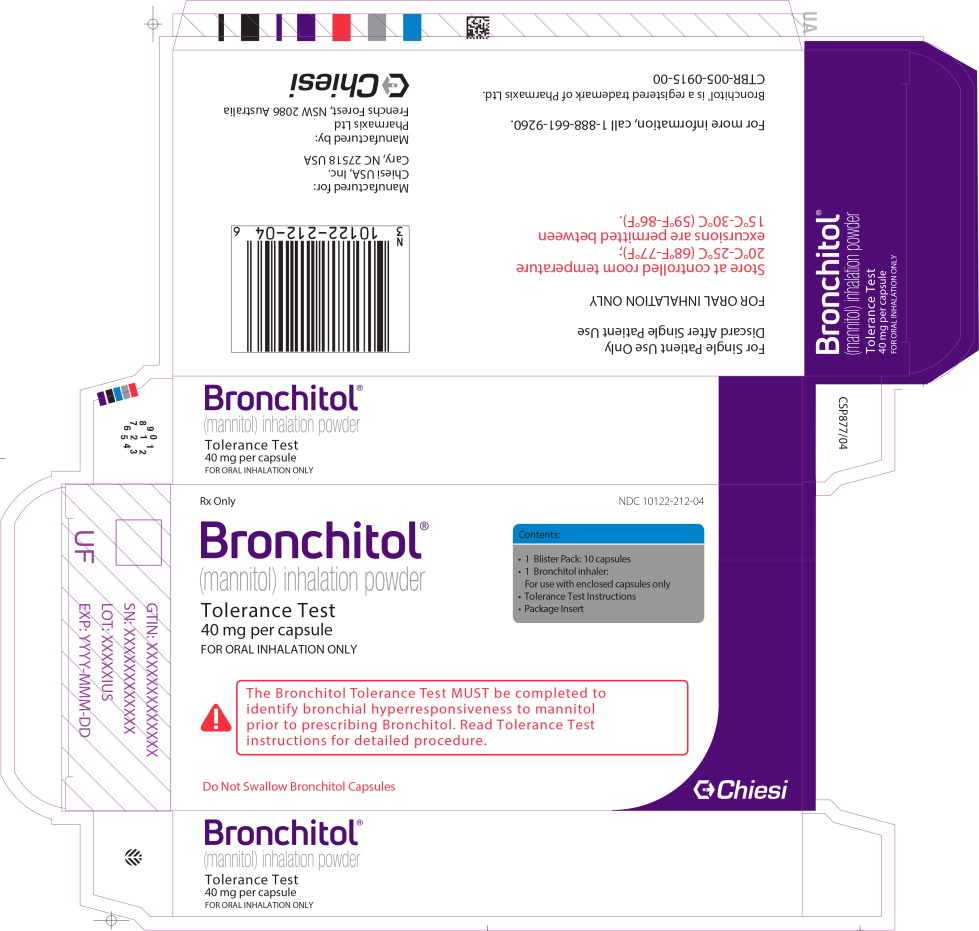
Principal Display Panel - 40 mg Tolerance Test Carton Label
Rx Only
NDC: 10122-212-04
Bronchitol®
(mannitol) inhalation powder
Tolerance Test
40 mg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Contents:
- 1 Blister Pack: 10 capsules
- 1 Bronchitol inhaler:
For use with enclosed capsules only - Tolerance Test Instructions
- Package Insert
The Bronchitol Tolerance Test MUST be completed to
identify bronchial hyperresponsiveness to mannitol
prior to prescribing Bronchitol. Read Tolerance Test
instructions for detailed procedure.
Do Not Swallow Bronchitol Capsules
Chiesi
| BRONCHITOL
mannitol capsule |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Chiesi USA, Inc. (088084228) |
Trademark Results [Bronchitol]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 BRONCHITOL 79012340 3107109 Live/Registered |
Pharmaxis Ltd 2005-06-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.