SODIUM IODIDE I 131 DIAGNOSTIC- sodium iodide i 131 capsule
Sodium Iodide I 131 Diagnostic by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sodium Iodide I 131 Diagnostic by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Jubilant DraxImage Inc., Jubilant HollisterStier General Partnership. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES DIAGNOSTIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES DIAGNOSTIC.
SODIUM IODIDE I 131 capsules, diagnostic, for oral use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1971RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Indications and Use. (1) 6/2016
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for the assessment of thyroid function and for thyroid imaging. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Use careful handling with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to patients and healthcare workers. (2.1, 5.2)
- Follow suitable radioactivity calibration prior to administration. (2.1)
- In an adult patient, recommended doses are (2.2):
- Thyroid Function: 0.185 to 1.1 megabecquerels (MBq) [5 to 30 microcuries (microCi)]
- Thyroid Imaging: 1.85 to 3.70 MBq (50 to 100 microCi)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 3.70 MBq (100 microCi) at the time of calibration (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Fetal Toxicity – I 131 can cause severe and irreversible hypothyroidism in the neonate. Verify absence of pregnancy before administering the product. (4, 5.1, 8.1, 8.3)
- Radiation Risk – I 131 contributes to patients’s long-term cumulative radiation exposure, which is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Ensure safe handling to minimize radiation exposure. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions reported with diagnostic doses of sodium iodide I 131 include nausea, vomiting, itching, rash and hives. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Jubilant DraxImage Inc. at 1-888-633-5343 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
2.3 Radiation Dosimetry
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
5.2 Radiation Exposure
5.3 Risk of Radioactive Uptake Measurement and Imaging Misinterpretation
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Characteristics
11.2 Physical Characteristics
11.3 External Radiation
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is a radioactive drug and should be handled with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to the patient and healthcare worker [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Use waterproof gloves during the entire handling and administration procedure.
- Maintain adequate shielding during the life of the product.
- Open the capsule-containing vial in a well ventilated hood to avoid exposure to trace levels of volatile I-131 which may be present.
- Measure patient dose by a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
Administer Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic orally prior to scanning. The recommended dose of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic for an adult patient is the following:
- Thyroid Function: 0.185 to 1.1 megabecquerels (MBq) [5 to 30 microcuries (microCi)]. Administer 24 hours before uptake measurement.
- Thyroid Imaging (Scintigraphy): 1.85 to 3.70 MBq (50 to 100 microCi). Administer 16 -24 hours before imaging.
Consult the color-coded decay calendar that is updated in January of every year to determine which colored capsule(s) correspond to the prescribed dose: https://www.draximage.com/products/us/draximage-i-131-diagnostic-capsules/ or calculate the correct dose from the date and time of calibration provided on the container label.
Prior to Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic Administration
- Obtain a pregnacy test in females of reproductive potential prior to administration to verify the absence of pregnancy [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Advise patients to maintain a low-iodine diet two weeks prior to radioiodine administration and continue for several days during the uptake or imaging process [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Advise patients to fast at least 2 hours before and 2 hours after administration to ensure absorption.
- Advise patients to hydrate before and after administration of radioiodine and void frequently to ensure rapid excretion.
2.3 Radiation Dosimetry
The biokinetic and radiation dose distributions associated with thyroid uptake of iodide I 131 depend on dietary intake of stable iodine. A range of uptake percentages in an average adult (73.7 kg) are shown in Table 1. For a thyroid blocked from iodide uptake in the production of hormones, the effective half-life of iodide I 131 is approximately 1.4 hours; for "low" to "high" uptake, the effective half-life of I 131 ranges from approximately 80 to 90 hours.
Table 1 Absorbed dose per unit activity sodium iodide I 131 administered orally (mGy/MBq) in adult (73.7-kg reference model) Organ Thyroid uptake of I 131 (% administered activity A0) 24 h after oral administration Blocked thyroid
(0% A0)Low uptake
(16% A0)Medium uptake
(26% A0)High uptake
(36% A0)Adrenals 0.044 0.051 0.055 0.059 Bone surfaces 0.030 0.089 0.12 0.16 Brain 0.021 0.093 0.13 0.17 Breast 0.020 0.038 0.048 0.058 Gallbladder wall 0.037 0.043 0.046 0.049 Gastrointestinal tract Stomach wall 0.87 0.77 0.71 0.66 Small intestine wall 0.035 0.033 0.032 0.032 Colon wall 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.14 (Upper large intestine wall) 0.12 0.12 0.12 0.12 (Lower large intestine wall) 0.17 0.17 0.17 0.16 Heart wall 0.062 0.089 0.10 0.12 Kidneys 0.27 0.27 0.27 0.27 Liver 0.050 0.093 0.12 0.14 Lungs 0.053 0.10 0.13 0.15 Muscles 0.026 0.084 0.12 0.15 Oesophagus 0.024 0.10 0.14 0.19 Ovaries 0.038 0.037 0.036 0.035 Pancreas 0.060 0.064 0.066 0.068 Red marrow 0.031 0.072 0.095 0.12 Salivary glands 0.27 0.22 0.19 0.16 Skin 0.019 0.043 0.057 0.071 Spleen 0.064 0.069 0.072 0.075 Testes 0.025 0.024 0.023 0.22 Thymus 0.024 0.10 0.14 0.19 Thyroid 2.2 280 430 580 Urinary bladder wall 0.54 0.45 0.39 0.34 Uterus 0.045 0.042 0.040 0.038 Remaining organs 0.029 0.84 0.11 0.15 Effective dose per administered activity (mSv/MBq) 0.28 14 22 29 -
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
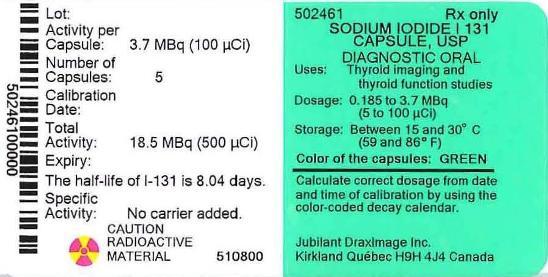
Capsules: Each capsule contains 3.70 MBq (100 microCi) at time of calibration. Half of each capsule is white, while the other half is either pink, yellow, orange, grey or green according to the manufactured lot. The capsule will yield 2.03, 1.11, 0.61, or 0.33 MBq (55, 30, 16.5, or 9 microCi) according to the color-coded decay calendar which assigns a color and capsule activity for each week of the year. https://www.draximage.com/products/us/draximage-i-131-diagnostic-capsules/
Table 2 below displays the (5) weeks activity of the capsule starting from the calibration day.
Table 2 Weekly Activity (MBq and microCi) of Each Capsule Starting from the Calibration Day Week Activity (MBq) Activity (microCi) 1 3.70 100.0 2 2.03 54.9 3 1.11 30.0 4 0.61 16.5 5 0.33 8.9 - 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is contraindicated in pregnancy because sodium iodide I 131 crosses the placenta and can cause severe and irreversible hypothyroidism in the neonate. Multiple reports in the literature describe neonatal hypothryroidism following in utero exposure to sodium iodide I 131. Some of these cases were severe and irreversible. Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to administering Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.2 Radiation Exposure
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure, which is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Follow safe administration instructions to minimize radiation exposure to the patient and healthcare providers [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.3 Risk of Radioactive Uptake Measurement and Imaging Misinterpretation
The recent intake of stable iodine in any form, or the use of thyroid or anti-thyroid drugs will affect the uptake of sodium iodide I 131. Question the patient carefully regarding their exposure to these drugs or procedures involving radiographic contrast media [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis may occur in patients who receive sodium iodide I 131. Although iodine is not considered an allergen, hypersensitivity reactions may occur in relation with excipients or chemical component of the capsule, such as sodium thiosulfate. Obtain and document an allergy history, particularly a sulfite allergy. Emergency resuscitation equipment and personnel should be immediately available [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reaction has been described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use from Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic. Because these reactions are voluntarily reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions associated with the administration of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic are:
- Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea
- General disorders and administration site conditions: local thyroid swelling
- Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: itching, rash, hives, and erythema
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Certain drugs and iodine-containing foods interfere with the accumulation of radioiodide by the thyroid. Review the patients history, current medications, and recent diagnostic tests prior to the administration of Sodium Iodide I-131 Capsules Diagnostic. Advise patients to maintain a low-iodine diet two weeks prior to radioiodine administration and continue for several days during the uptake or imaging process and to discontinue the following products before they undergo the procedure as shown in Table 3:
Table 3 Pharmaceuticals/OTCs/Agents Blocking Radioiodine Uptake Products Recommended duration of withdrawal Thionamide medications
(e.g., propylthiouracil, methimazole carbimazole)3 days Multivitamins containing iodide 10 days Natural or synthetic thyroid hormones
triiodothyronine
thyroxine2 weeks
4 weeks
Iodine containing foods: iodinized salt, dairy products, egg yolks, seafood, turkey, and liver 2 weeks Kelp, agar, carrageenan, Lugol solution 3 weeks Saturated solution of potassium iodide 3 weeks Topical iodine
(e.g., surgical skin preparation)3 weeks Radiographic contrast agents
Water soluble
Lipophilic2 months
6 months
Amiodarone 6 months -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is contraindicated in pregnancy because fetal exposure can lead to neonatal hypothyroidism, which in some cases is severe and irreversible. Data from the published literature describe reports of neonatal thyroid abnormalities after fetal exposure, including agenesis of the thyroid and hypothyroidism (see Clinical Considerations, Data). No animal reproductive studies have been conducted.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
A fetus exposed to sodium iodide I 131 can develop neonatal hypothyroidism. Delay in diagnosis of neonatal hypothyroidism after exposure to sodium iodide I 131 in utero can result in severe sequelae such as decreased mental capacity and delayed skeletal maturation. Monitor thyroid function in any infant born after in utero exposure to sodium iodide I 131.
Data
Human Data
Literature reports of maternal exposures to sodium iodide I 131 at doses of 330-8300 MBq during 4-26 weeks estimated gestational age. There were various adverse pregnancy outcomes; the most common was hypothyroidism in infants and children.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Advise women to discontinue breastfeeding after administration of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic. Infant exposure to sodium iodide I 131 via breast milk is expected and may lead to hypothyroidism in the infant because sodium iodide I 131 in breast milk may reach concentrations equal to or greater than concentrations in maternal plasma (see Data).Data
Published studies show that sodium iodide I 131 is transferred into breast milk and is taken up by the thyroid of the breastfed infant.8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Sodium Iodide I 131 is contraindicated in pregnancy because it causes fetal hypothyroidism [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential and verify the absence of pregnancy before administering Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].8.4 Pediatric use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established. Published reports suggest that the thyroid gland of pediatric patients is more sensitive to the adverse effects of sodium iodide I 131 (e.g., increased risk of radiation absorption).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical experience has not identified differences in safety or effectiveness in geriatric patients compared to younger patients. However, elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function and radiation exposure is greater in patients with impaired renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Radiation exposure following Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is greater in patients with impaired renal function compared to patients with normal renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
In the event of an overdosage of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic, monitor for thyroid suppression and consider administering a thyroid blocking agent (e.g. potassium iodide (KI) or perchlorate). Promote frequent voiding and encourage patients to maintain hydration to minimize radiation exposure.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Characteristics
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic is a radiodioactive diagnostic agent containing sodium iodide I 131 and supplied for oral administration in a gelatin capsule. Each capsule contains no-carrier-added sodium iodide I 131, disodium edetate dihydrate USP as a stabilizer, sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate USP as a reducing agent, and dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous USP.
Sodium Iodide I 131 is designated chemically as Na131I and has a molecular weight of 153.99.
11.2 Physical Characteristics
Iodine I 131 decays by beta emission and associated gamma emission with a physical half-life of 8.04 days. The principal radiation emissions are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 Principal Radiation Emission Data from Decay of Sodium Iodide I 131 Radiation Mean % per Disintegration Mean Energy (keV) Beta-1 2.13% 69.4 Beta-3 7.20% 96.6 Beta-4 89.4% 191.6 Gamma-7 6.14% 284.3 Gamma-14 81.2% 364.5 Gamma-18 7.12% 637.0 11.3 External Radiation
The specific gamma-ray constant for iodine I 131 is 4.26 x 10-13 Cm2kg-1MBq-1s-1 (2.2 Rcm2/mCihr). The first half-value thickness of lead (Pb) for iodine I 131 is 0.27 cm. A range of values for the relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by iodine I 131 that results from interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 5. For example, the use of 2.59 cm of Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of about 100.
Table 5 Radiation Attenuation of Iodine I 131 by Lead Shielding Shield Thickness (Pb) cm Coefficient of Attenuation 0.27 0.5 0.56 0.25 0.99 10-1 2.59 10-2 4.53 10-3 To correct for physical decay of iodine I 131, the fractions that remain at selected intervals after the time of calibration are shown in Table 6.
Table 6 Physical Decay Chart: Iodine I 131, Half-Life 8.04 days - * Calibration Time
Days Fraction Remaining Days Fraction Remaining Days Fraction Remaining 0* 1.000 11 0.388 22 0.151 1 0.918 12 0.356 23 0.138 2 0.842 13 0.327 24 0.127 3 0.773 14 0.300 25 0.116 4 0.709 15 0.275 26 0.107 5 0.651 16 0.253 27 0.098 6 0.597 17 0.232 28 0.090 7 0.548 18 0.213 29 0.083 8 0.503 19 0.195 30 0.076 9 0.461 20 0.179 10 0.423 21 0.164 -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Iodine is actively transported by the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) protein, in thyroid follicular cells. Iodide is concentrated in follicular cells up to 50 times higher than in the plasma. Iodide is metabolically oxidized by thyroid peroxidase to iodinium (I+) which in turn iodinates tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin (tri or tetra-iodinated tyrosine). The gamma emission of Iodine I 131 is imaged or counted.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic, 90% of the administered radioactivity of sodium iodide I 131 is systemically absorbed in the first 60 minutes.Distribution
Following absorption, sodium iodide I 131 is distributed within the extra-cellular space. It is actively transported by the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) protein and binds to thyroglobulin resulting in accumulation in the thyroid. The thyroid uptake of iodide is usually increased in hyperthyroidism and in goiter, and is decreased in hypothyroidism. Sodium iodide I 131 also accumulates in the stomach, choroid plexus, salivary glands breast, liver, gall bladder, and kidneys.Elimination
Metabolism
In thyroid follicular cells, iodide is oxidized through the action of thyroid peroxidase to iodinium (I+) which in turn iodinates tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin.Excretion
Sodium iodide I 131 is excreted in urine and feces. The normal range of urinary excretion is 37% to 75% of the administered dose, varying with the thyroid and renal function of the patient. Fecal excretion is about 10%. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Each capsule contains 3.70 megabecquerels (100 microCi) at time of calibration. Half of each capsule is white, while the other half is either pink, yellow, orange, grey or green according to the manufactured lot.
- The capsules are packaged in plastic vials containing 5 capsules of the same strength and same color. (NDC: 65174-461-05).
- Consult the color-coded decay calendar that is updated in January of each year to help you establish which colored capsules correspond to your prescribed dose: https://www.draximage.com/products/us/draximage-i-131-diagnostic-capsules/ or calculate the correct dosage from the date and time of calibration provided on the container label.
- The calibration date and expiration date are indicated on the vial container label.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic between 15 °C and 30 °C (59 °F and 86 °F).
Store and dispose of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic in compliance with the appropriate regulations of the government agency authorized to license the use of this radionuclide.
This radiopharmaceutical is approved for use by persons under license by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission or the relevant regulatory authority of an Agreement State.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Administration Instructions
- Advise patients to hydrate before and after administration of Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic and void frequently to ensure rapid excretion [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Advise patients to fast at least 2 hours before and 2 hours after administration to ensure absorption [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Advise patients to maintain a low-iodine diet two weeks prior to radioiodine administration and continue for several days during the uptake or imaging process [See Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Fetal Toxicity
Advise female patients of reproductive potential of the risk of neonatal hypothyroidism with fetal exposure [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].Lactation
Advise women to discontinue breastfeeding after Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules Diagnostic administration [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)]. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Capsule 3.7 MBq (Gray)
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Capsule 3.7 MBq (Yellow)
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Capsule 3.7 MBq (Orange)
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Capsule 3.7 MBq (Pink)
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Capsule 3.7 MBq (Green)
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SODIUM IODIDE I 131 DIAGNOSTIC
sodium iodide i 131 capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 65174-461 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Sodium Iodide I-131 (UNII: 29VCO8ACHH) (IODIDE ION I-131 - UNII:4GC1FOQ22U) IODIDE ION I-131 100 mCi Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Edetate Disodium (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) Sodium Thiosulfate (UNII: HX1032V43M) Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous (UNII: 22ADO53M6F) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (one half is opaque white and other may be opaque pink, yellow, orange, grey or green) Score no score Shape CAPSULE ( # 2) Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65174-461-05 5 in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/01/2006 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021305 05/01/2006 Labeler - Jubilant DraxImage Inc. (243604761) Registrant - Jubilant DraxImage Inc. (243604761) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Jubilant HollisterStier General Partnership 246762764 MANUFACTURE(65174-461)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.