TREPROSTINIL injection DILUENT- water solution injection
DILUENT by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DILUENT by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Sandoz Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TREPROSTINIL INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TREPROSTINIL INJECTION.
TREPROSTINIL Injection, for subcutaneous or intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: May 2002INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Treprostinil injection is a prostacyclin vasodilator indicated for:
- Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, WHO Group 1) to diminish symptoms associated with exercise. Studies establishing effectiveness included patients with NYHA Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (58%), PAH associated with congenital systemic-to-pulmonary shunts (23%), or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (19%) (1.1)
- Patients who require transition from epoprostenol, to reduce the rate of clinical deterioration. The risks and benefits of each drug should be carefully considered prior to transition. (1.2)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PAH WHO Group 1 in patients with NYHA Class II-IV symptoms:
- Initial dose for patients new to prostacyclin infusion therapy: 1.25 ng/kg/min; increase based on clinical response (increments of 1.25 ng/kg/min per week for the first 4 weeks of treatment, later 2.5 ng/kg/min per week). Avoid abrupt cessation. (2.2, 2.4)
- Mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency: Decrease initial dose to 0.625 ng/kg/min. Severe hepatic insufficiency: No studies performed. (2.5)
Transition from Epoprostenol:
Increase the treprostinil injection dose gradually as the epoprostenol dose is decreased, based on constant observation of response. (2.7)
Administration:
Continuous subcutaneous infusion is the preferred mode. Use intravenous (IV) infusion if subcutaneous infusion is not tolerated. (2.1, 2.6)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Treprostinil injection is supplied in 20 mL vials containing 20, 50, 100, or 200 mg of treprostinil (1 mg/mL, 2.5 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL or 10 mg/mL). (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Chronic intravenous infusions delivered using an external infusion pump with an indwelling central venous catheter are associated with the risk of blood stream infections (BSIs) and sepsis, which may be fatal. (5.1)
- Do not abruptly lower the dose or withdraw dosing. (5.2)
- Treprostinil injection may cause symptomatic hypotension. (5.4)
- Treprostinil injection inhibits platelet aggregation and increases the risk of bleeding. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >3%) reported in clinical studies with treprostinil injection: subcutaneous infusion site pain and reaction, headache, diarrhea, nausea, jaw pain, vasodilatation, edema, and hypotension. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sandoz Inc. at 1-800-525-8747 or contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Treprostinil injection dosage adjustment may be necessary if inhibitors or inducers of CYP2C8 are added or withdrawn. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
1.2 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients Requiring Transition from Epoprostenol
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General
2.2 Initial Dose for Patients New to Prostacyclin Infusion Therapy
2.4 Dosage Adjustments
2.5 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
2.6 Administration
2.7 Patients Requiring Transition from Epoprostenol
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection
5.2 Worsening PAH upon Abrupt Withdrawal or Sudden Large Dose Reduction
5.3 Patients with Hepatic or Renal Insufficiency
5.4 Risk of Symptomatic Hypotension
5.5 Risk of Bleeding
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of CYP2C8 Inhibitors and Inducers on Treprostinil
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
8.7 Patients with Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trials in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
14.2 Flolan-To-Treprostinil Injection Transition Study
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Interruption of Therapy
Overdose
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Treprostinil injection is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, WHO Group 1) to diminish symptoms associated with exercise. Studies establishing effectiveness included patients with NYHA Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (58%), PAH associated with congenital systemic-to-pulmonary shunts (23%), or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (19%) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General
Treprostinil injection can be administered with or without further dilution with Sterile Diluent for treprostinil or similar approved high-pH glycine diluent (e.g. Sterile Diluent for Flolan or Sterile Diluent for Epoprostenol ), Sterile Water for Injection, or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection prior to administration. See Table 1 below for storage and administration time limits for the different diluents.
Diluted treprostinil injection has been shown to be stable at ambient temperature when stored for up to 14 days using high-pH glycine diluent at concentrations as low as 0.004 mg/mL (4,000 ng/mL).
Table 1. Selection of Diluent Diluent
Storage Limits
Administration Limits
None
See Section 16
16 weeks at 40°C
Sterile Diluent for Treprostinil Injection, Flolan, or Epoprostenol
14 days at room temperature
48 hours at 40°C
Sterile Water for Injection
0.9% Sodium Chloride for Injection4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours refrigerated
48 hours at 40°C
2.2 Initial Dose for Patients New to Prostacyclin Infusion Therapy
Treprostinil injection is indicated for subcutaneous (SC) or intravenous (IV) use only as a continuous infusion. Treprostinil injection is preferably infused subcutaneously, but can be administered by a central intravenous line if the subcutaneous route is not tolerated, because of severe site pain or reaction. The infusion rate is initiated at 1.25 ng/kg/min. If this initial dose cannot be tolerated because of systemic effects, reduce the infusion rate to 0.625 ng/kg/min.
2.4 Dosage Adjustments
The goal of chronic dosage adjustments is to establish a dose at which PAH symptoms are improved, while minimizing excessive pharmacologic effects of treprostinil injection (headache, nausea, emesis, restlessness, anxiety and infusion site pain or reaction).
The infusion rate should be increased in increments of 1.25 ng/kg/min per week for the first four weeks of treatment and then 2.5 ng/kg/min per week for the remaining duration of infusion, depending on clinical response. Dosage adjustments may be undertaken more often if tolerated. Avoid abrupt cessation of infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Restarting a treprostinil injection infusion within a few hours after an interruption can be done using the same dose rate. Interruptions for longer periods may require the dose of treprostinil injection to be re-titrated.
2.5 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
In patients with mild or moderate hepatic insufficiency, decrease the initial dose of treprostinil injection to 0.625 ng/kg/min ideal body weight. Treprostinil injection has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology(12.3)].
2.6 Administration
Inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. If either particulate matter or discoloration is noted, do not use.
Preparation
Treprostinil injection is administered by subcutaneous or intravenous infusion at a calculated rate based on a patient’s dose (ng/kg/min), weight (kg) and the treprostinil concentration (mg/mL).
For administration of Undiluted Treprostinil Injection the rate is calculated using the following formula:
- * Conversion factor of 0.00006 = 60 min/hour x 0.000001 mg/ng
Undiluted Infusion Rate (mL/hr)
=
Dose
(ng/kg/min)
×
Weight
(kg)
×
0.00006*
Treprostinil Injection Vial Strength (mg/mL)
For administration of Diluted Treprostinil Injection the rate and concentration is calculated using the following formulas:
Step 1
Diluted Treprostinil Concentration
(mg/mL)=
Dose
(ng/kg/min)×
Weight
(kg)×
0.00006
Infusion Rate
(mL/hour)The volume of treprostinil injection needed to make the required diluted treprostinil concentration for the given reservoir size can then be calculated using the following formula:
Step 2
Volume of Treprostinil Injection
(mL)=
Diluted Treprostinil Injection Concentration
(mg/mL)×
Total Volume of Diluted Treprostinil Injection Solution in Reservoir
(mL)Treprostinil Injection Vial Strength
(mg/mL)The calculated volume of treprostinil injection is then added to the reservoir along with the sufficient volume of diluent to achieve the desired total volume in the reservoir.
Subcutaneous Infusion
Treprostinil injection is administered subcutaneously by continuous infusion, via a subcutaneous catheter, using an infusion pump designed for subcutaneous drug delivery. The infusion pump should: (1) be adjustable to approximately 0.002 mL/hour, (2) have occlusion/no delivery, low battery, programming error and motor malfunction alarms, (3) have delivery accuracy of ±6% or better, (4) be positive pressure driven, and (5) have a reservoir made of polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene or glass. Alternatively, use an infusion pump cleared for use with treprostinil injection. To avoid potential interruptions in drug delivery, the patient must have immediate access to a backup infusion pump and subcutaneous infusion sets.
Intravenous Infusion
External Intravenous Infusion Pump:
Treprostinil injection is administered intravenously by continuous infusion, via a surgically placed indwelling central venous catheter, using an external infusion pump designed for intravenous drug delivery. If clinically necessary, a temporary peripheral intravenous cannula, preferably placed in a large vein, may be used for short term administration of treprostinil injection. Use of a peripheral intravenous infusion for more than a few hours increases the risk of thrombophlebitis. The infusion pump used to administer treprostinil injection should: (1) have occlusion/no delivery, low battery, programming error and motor malfunction alarms, (2) have delivery accuracy of ±6% or better of the hourly dose, (3) be positive pressure driven, and (4) have a reservoir made of polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene or glass. Alternatively, use an infusion pump cleared for use with treprostinil injection. To avoid potential interruptions in drug delivery, the patient must have immediate access to a backup infusion pump and infusion sets.
Infusion sets with an in-line 0.22 or 0.2 micron pore size filter should be used.
2.7 Patients Requiring Transition from Epoprostenol
Transition from epoprostenol to treprostinil injection is accomplished by initiating the infusion of treprostinil injection and increasing it, while simultaneously reducing the dose of intravenous epoprostenol. The transition to treprostinil injection should take place in a hospital with constant observation of response (e.g., walk distance and signs and symptoms of disease progression).
Initiate treprostinil injection at a recommended dose of 10% of the current epoprostenol dose, and then escalate as the epoprostenol dose is decreased (see Table 2 for recommended dose titrations).
Patients are individually titrated to a dose that allows transition from epoprostenol therapy to treprostinil injection while balancing prostacyclin-limiting adverse events. Treat increases in the patient’s symptoms of PAH first with increases in the dose of treprostinil injection. Treat side effects normally associated with prostacyclin and prostacyclin analogs first by decreasing the dose of epoprostenol.
Table 2: Recommended Transition Dose Changes Step Epoprostenol Dose Treprostinil Injection Dose 1
Unchanged
10% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
2
80% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
30% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
3
60% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
50% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
4
40% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
70% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
5
20% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
90% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
6
5% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
110% Starting Epoprostenol Dose
7
0
110% Starting Epoprostenol Dose + additional 5-10% increments as needed
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection
Chronic intravenous infusions of treprostinil injection are delivered using an external infusion pump with an indwelling central venous catheter are associated with the risk of blood stream infections (BSIs) and sepsis, which may be fatal. Therefore, continuous subcutaneous infusion is the preferred mode of administration.
In an open-label study of IV treprostinil (n=47) using an external infusion pump, there were seven catheter-related line infections during approximately 35 patient years, or about 1 BSI event per 5 years of use. A CDC survey of seven sites that used IV treprostinil for the treatment of PAH found approximately 1 BSI (defined as any positive blood culture) event per 3 years of use.
Administration of IV treprostinil injection with a high pH glycine diluent has been associated with a lower incidence of BSIs when compared to neutral diluents (sterile water, 0.9% sodium chloride) when used along with catheter care guidelines.
5.2 Worsening PAH upon Abrupt Withdrawal or Sudden Large Dose Reduction
Avoid abrupt withdrawal or sudden large reductions in dosage of treprostinil injection, which may result in worsening of PAH symptoms.
5.3 Patients with Hepatic or Renal Insufficiency
Titrate treprostinil injection slowly in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency, because such patients will likely be exposed to greater systemic concentrations relative to patients with normal hepatic or renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.5,), Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in labeling: Infections associated with intravenous administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Events with Subcutaneously Administered Treprostinil Injection
Patients receiving treprostinil injection as a subcutaneous infusion reported a wide range of adverse events, many potentially related to the underlying disease (dyspnea, fatigue, chest pain, right ventricular heart failure, and pallor). During clinical trials with subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil injection, infusion site pain and reaction were the most common adverse events among those treated with treprostinil injection. Infusion site reaction was defined as any local adverse event other than pain or bleeding/bruising at the infusion site and included symptoms such as erythema, induration or rash. Infusion site reactions were sometimes severe and could lead to discontinuation of treatment.
Table 3: Percentages of Subjects Reporting Subcutaneous Infusion Site Adverse Events Reaction Pain Placebo Treprostinil Injection Placebo Treprostinil Injection - * based on prescriptions for narcotics, not actual use
- † medications used to treat infusion site pain were not distinguished from those used to treat site reactions
Severe
1
38
2
39
Requiring narcotics*
NA†
NA†
1
32
Leading to discontinuation
0
3
0
7
Other adverse events included diarrhea, jaw pain, edema, vasodilatation and nausea, and these are generally considered to be related to the pharmacologic effects of treprostinil injection, whether administered subcutaneously or intravenously.
Adverse Reactions during Chronic Dosing
Table 4 lists adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 3% more frequent in patients treated with subcutaneous treprostinil injection than with placebo in controlled trials in PAH.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions in Controlled 12-Week Studies of Subcutaneous Treprostinil Injection and at least 3% more frequent than on Placebo Adverse Reaction Treprostinil Injection
(N=236)
Percent of PatientsPlacebo
(N=233)
Percent of PatientsInfusion Site Pain
85
27
Infusion Site Reaction
83
27
Headache
27
23
Diarrhea
25
16
Nausea
22
18
Rash
14
11
Jaw Pain
13
5
Vasodilatation
11
5
Edema
9
3
Reported adverse reactions (at least 3% more frequent on drug than on placebo) are included with the exception of those too general to be informative, and those not plausibly attributable to the use of the drug, because they were associated with the condition being treated or are very common in the treated population.
While hypotension occurred in both groups, the event was experienced twice as frequently in the treprostinil injection group as compared to the placebo group (4% in treprostinil injection treatment group versus 2% in placebo-controlled group). As a potent vasodilator, hypotension is possible with the administration of treprostinil injection.
The safety of treprostinil injection was also studied in a long-term, open-label extension study in which 860 patients were dosed for a mean duration of 1.6 years, with a maximum exposure of 4.6 years. Twenty-nine (29%) percent achieved a dose of at least 40 ng/kg/min (max: 290 ng/kg/min). The safety profile during this chronic dosing study was similar to that observed in the 12-week placebo controlled study except for the following suspected adverse drug reactions (occurring in at least 3% of patients): anorexia, vomiting, infusion site infection, asthenia, and abdominal pain.
Adverse Events Attributable to the Drug Delivery System
In controlled studies of treprostinil injection administered subcutaneously, there were no reports of infection related to the drug delivery system. There were 187 infusion system complications reported in 28% of patients (23% treprostinil injection, 33% placebo); 173 (93%) were pump related and 14 (7%) related to the infusion set. Eight of these patients (4 treprostinil injection, 4 Placebo) reported non-serious adverse events resulting from infusion system complications. Adverse events resulting from problems with the delivery systems were typically related to either symptoms of excess treprostinil injection (e.g., nausea) or return of PAH symptoms (e.g., dyspnea). These events were generally resolved by correcting the delivery system pump or infusion set problem such as replacing the syringe or battery, reprogramming the pump, or straightening a crimped infusion line. Adverse events resulting from problems with the delivery system did not lead to clinical instability or rapid deterioration. In addition to these adverse events due to the drug delivery system during subcutaneous administration, the following adverse events may be attributable to the IV mode of infusion including arm swelling, paresthesias, hematoma and pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following events have been identified during post-approval use of treprostinil injection. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The following events have been chosen for inclusion because of a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, and potential connection to treprostinil injection. These events are thrombophlebitis associated with peripheral intravenous infusion, thrombocytopenia, bone pain, pruritus, dizziness, arthralgia, myalgia/muscle spasm, and pain in extremity. In addition, generalized rashes, sometimes macular or papular in nature, and cellulitis have been infrequently reported.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of CYP2C8 Inhibitors and Inducers on Treprostinil
Dose adjustment of treprostinil may be necessary when co-administered with CYP2C8 inducers or inhibitors. Human pharmacokinetic studies with an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) indicated that co-administration of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor gemfibrozil increases exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of the CYP2C8 enzyme inducer rifampin decreases exposure to treprostinil. It has not been determined if the changes in exposure of treprostinil with inhibitors or inducers of CYP2C8 observed for the oral administration of treprostinil would be similar for treprostinil administered via the parenteral route [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited case reports of treprostinil use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug- associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. However, there are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension (see Clinical Considerations). In animal studies, no adverse reproductive and developmental effects were seen in rats at about 123 and 48 times the human exposure based on Cmax and AUC, respectively. In rabbits, external fetal and soft tissue malformations and skeletal malformations were observed at about 7 and 5 times the human exposure based on Cmax and AUC, respectively (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and embryo-fetal risk
Pulmonary arterial hypertension is associated with an increased risk of maternal and fetal mortality.
Data
Animal reproduction studies have been conducted with treprostinil via continuous subcutaneous administration and with treprostinil diolamine administered orally. In pregnant rats, continuous subcutaneous infusions of treprostinil during organogenesis and late gestational development, at doses as high as 900 ng treprostinil/kg/min (about 117 times the starting human subcutaneous infusion rate, on a ng/m2 basis and about 16 times the average rate achieved in clinical trials), resulted in no evidence of harm to the fetus. In pregnant rabbits, effects of continuous subcutaneous infusions of treprostinil during organogenesis were limited to an increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations (bilateral full rib or right rudimentary rib on lumbar 1) associated with maternal toxicity (reduction in body weight and food consumption) at a dose of 150 ng treprostinil/kg/min (about 41 times the starting human subcutaneous infusion rate, on a ng/m2 basis, and 5 times the average rate used in clinical trials). In rats, continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil from implantation to the end of lactation, at doses of up to 450 ng treprostinil/kg/min, did not affect the growth and development of offspring. In studies with orally administered treprostinil diolamine, no adverse effect doses for fetal viability/growth, fetal development (teratogenicity), and postnatal development were determined in rats. In pregnant rats, no evidence of harm to the fetus was observed following oral administration of treprostinil diolamine at the highest dose tested (20 mg/kg/day), which represents about 123 and 48 times the human exposure, when based on Cmax and AUC of the average subcutaneous infusion rate achieved in clinical trials, respectively. In pregnant rabbits, external fetal and soft tissue malformations and fetal skeletal malformation occurred. The dose at which no adverse effects were seen (0.5 mg/kg/day) represents about 7 and 5 times the human exposure, when based on Cmax and AUC of the average subcutaneous infusion rate achieved in clinical trials, respectively. No treprostinil treatment-related effects on labor and delivery were seen in animal studies. Animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of treprostinil in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Clinical studies of treprostinil injection did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged ≤16 years to determine whether they respond differently from older patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of treprostinil injection did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency
Treprostinil injection clearance is reduced in patients with hepatic insufficiency. In patients with mild or moderate hepatic insufficiency, decrease the initial dose of treprostinil injection to 0.625 ng/kg/min ideal body weight, and monitor closely. Treprostinil injection has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Patients with Renal Impairment
No dose adjustments are required in patients with renal impairment. Treprostinil is not cleared by dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Signs and symptoms of overdose with treprostinil injection during clinical trials are extensions of its dose-limiting pharmacologic effects and include flushing, headache, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most events were self-limiting and resolved with reduction or withholding of treprostinil injection.
In controlled clinical trials using an external infusion pump, seven patients received some level of overdose and in open-label follow-on treatment seven additional patients received an overdose; these occurrences resulted from accidental bolus administration of treprostinil injection, errors in pump programmed rate of administration, and prescription of an incorrect dose. In only two cases did excess delivery of treprostinil injection produce an event of substantial hemodynamic concern (hypotension, near-syncope).
One pediatric patient was accidentally administered 7.5 mg of treprostinil injection via a central venous catheter. Symptoms included flushing, headache, nausea, vomiting, hypotension and seizure-like activity with loss of consciousness lasting several minutes. The patient subsequently recovered.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Treprostinil injection is a sterile solution of treprostinil formulated for subcutaneous or intravenous administration. Treprostinil injection is supplied in 20 mL multi-dose vials in four strengths, containing 20 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, or 200 mg (1 mg/mL, 2.5 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL or 10 mg/mL) of treprostinil. Each mL also contains 5.3 mg sodium chloride (except for the 10 mg/mL strength which contains 4.0 mg sodium chloride), 3 mg metacresol, 6.3 mg sodium citrate, and water for injection. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid may be added to adjust pH between 6.0 and 7.2.
Treprostinil is chemically stable at room temperature and neutral pH.
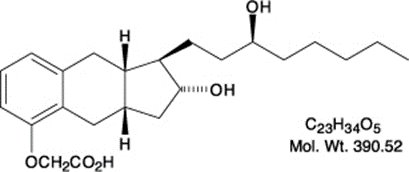
Treprostinil is (1R,2R,3aS,9aS)-[[2,3,3a,4,9,9a-Hexahydro-2-hydroxy-1-[(3S)-3-hydroxyoctyl]-1H-benz[f]inden-5-yl]oxy]acetic acid. Treprostinil has a molecular weight of 390.52 and a molecular formula of C23H34O5.
The structural formula of treprostinil is:
Sterile Diluent for Treprostinil Injection is a high-pH (pH~10.4) glycine diluent supplied in a 50 mL single-dose vial containing 50 mL of Sterile Diluent for Treprostinil Injection. Each vial contains 94 mg glycine, 73.3 mg sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), and water for injection.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The major pharmacologic actions of treprostinil are direct vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds, and inhibition of platelet aggregation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In animals, the vasodilatory effects reduce right and left ventricular afterload and increase cardiac output and stroke volume. Other studies have shown that treprostinil causes a dose-related negative inotropic and lusitropic effect. No major effects on cardiac conduction have been observed.
Treprostinil produces vasodilation and tachycardia. Single doses of treprostinil up to 84 mcg by inhalation produce modest and short-lasting effects on QTc, but this is apt to be an artifact of the rapidly changing heart rate. Treprostinil administered by the subcutaneous or intravenous routes has the potential to generate concentrations many-fold greater than those generated via the inhaled route; the effect on the QTc interval when treprostinil is administered parenterally has not been established.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of continuous subcutaneous treprostinil injection are linear over the dose range of 2.5 to 125 ng/kg/min (corresponding to plasma concentrations of about 260 pg/mL to 18,250 pg/mL) and can be described by a two-compartment model. Dose proportionality at infusion rates greater than 125 ng/kg/min has not been studied.
Subcutaneous and intravenous administration of treprostinil injection demonstrated bioequivalence at steady state at a dose of 10 ng/kg/min.
Absorption
Treprostinil injection is relatively rapidly and completely absorbed after subcutaneous infusion, with an absolute bioavailability approximating 100%. Steady-state concentrations occurred in approximately 10 hours. Concentrations in patients treated with an average dose of 9.3 ng/kg/min were approximately 2,000 ng/L.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of the drug in the central compartment is approximately 14L/70 kg ideal body weight. Treprostinil injection at in vitro concentrations well above what is clinically relevant was 91% bound to human plasma protein.
Metabolism and Excretion
Treprostinil is substantially metabolized by the liver, primarily by CYP2C8. In a study conducted in healthy volunteers using [14C] treprostinil, 79% and 13% of the subcutaneous dose was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively, over 10 days. Only 4% was excreted as unchanged treprostinil in the urine. Five metabolites were detected in the urine, ranging from 10% to 16% and representing 64% of the dose administered. Four of the metabolites are products of oxidation of the 3-hydroxyloctyl side chain and one is a glucuroconjugated derivative (treprostinil glucuronide). The identified metabolites do not appear to have activity.
The elimination of treprostinil (following subcutaneous administration) is biphasic, with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 4 hours using a two compartment model. Systemic clearance is approximately 30 L/hour for a 70 kg person.
Based on in vitro studies treprostinil does not inhibit or induce major CYP enzymes.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Insufficiency
In patients with portopulmonary hypertension and mild (n=4) or moderate (n=5) hepatic insufficiency, treprostinil injection at a subcutaneous dose of 10 ng/kg/min for 150 minutes had a Cmax that was 2-fold and 4-fold, respectively, and an AUC0-∞ that was 3-fold and 5-fold, respectively, values observed in healthy subjects. Clearance in patients with hepatic insufficiency was reduced by up to 80% compared to healthy adults.
Renal Impairment
In patients with severe renal impairment requiring dialysis (n=8), administration of a single 1 mg dose of orally administered treprostinil pre- and post-dialysis resulted in an AUC0-inf that was not significantly altered compared to healthy subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of CYP2C8 Inhibitors and Inducers on Treprostinil
Co-administration of an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) with gemfibrozil (600 mg twice a day), a CYP2C8 enzyme inhibitor, doubles the AUC and Cmax of treprostinil in healthy adults. Co-administration of an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) with rifampin (600 mg/day), a CYP2C8 enzyme inducer, decreases AUC of treprostinil by 22%.
Effect of Treprostinil on Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
In vitro studies of human hepatic microsomes showed that treprostinil does not inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A. Additionally, treprostinil does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A isoenzymes.
Effect of Other Drugs on Treprostinil
Human pharmacokinetic studies with an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) indicated that co-administration of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor gemfibrozil increases exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of the CYP2C8 enzyme inducer rifampin decreases exposure to treprostinil.
Drug interaction studies have been carried out with treprostinil (oral or subcutaneous) co-administered with acetaminophen (4 g/day), esomeprazole (40 mg/day), bosentan (250 mg/day), sildenafil (60 mg/day), warfarin (25 mg/day), and fluconazole (200 mg/day), respectively, in healthy volunteers. These studies did not show a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of treprostinil. Treprostinil does not affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of warfarin. The pharmacokinetics of R- and S- warfarin and the INR in healthy subjects given a single 25 mg dose of warfarin were unaffected by continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil at an infusion rate of 10 ng/kg/min.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A two-year rat carcinogenicity study was performed with treprostinil inhalation at target doses of 5.26, 10.6, and 34.1 mcg/kg/day. There was no evidence for carcinogenic potential associated with treprostinil inhalation in rats at systemic exposure levels up to about 34 and 1 times the human exposure, when based on Cmax and AUC of the average subcutaneous infusion rate achieved in clinical trials, respectively. In vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology studies did not demonstrate any mutagenic or clastogenic effects of treprostinil. Treprostinil sodium did not affect fertility or mating performance of male or female rats given continuous subcutaneous (sc) infusions at rates of up to 450 ng treprostinil/kg/min [about 59 times the recommended starting human sc infusion rate (1.25 ng/kg/min) and 8 times the average rate (9.3 ng/kg/min) achieved in clinical trials, on a ng/m2 basis]. In this study, males were dosed from 10 weeks prior to mating and through the 2-week mating period. Females were dosed from 2 weeks prior to mating until gestational day 6.
Treprostinil diolamine did not demonstrate any carcinogenic effects in mouse or rat carcinogenicity studies. Oral administration of treprostinil diolamine to Tg.rasH2 mice at 0, 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg/day in males and 0, 3, 7.5 and 15 mg/kg/day in females daily for 26 weeks did not significantly increase the incidence of tumors. The exposures, when based on AUC, obtained at the highest dose levels used in males and females are about 7- and 15-fold, respectively, the human exposure of the average subcutaneous infusion rate achieved in clinical trials. Oral administration of treprostinil diolamine to Sprague Dawley rats at 0, 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg/day daily for 104 weeks did not significantly increase the incidence of tumors. The exposures obtained at the highest dose levels used in males and females are about 18- and 26-fold, respectively, the human exposure of the average subcutaneous infusion rate achieved in clinical trials.
Treprostinil diolamine was tested in vivo in a rat micronucleus assay and did not induce an increased incidence of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trials in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
Two 12-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies compared continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil injection to placebo in a total of 470 patients with NYHA Class II (11%), III (81%), or IV (7%) PAH. PAH was idiopathic/heritable in 58% of patients, associated with connective tissue diseases in 19%, and the result of congenital systemic-to-pulmonary shunts in 23%. The mean age was 45 (range 9 to 75 years). About 81% were female and 84% were Caucasian. Pulmonary hypertension had been diagnosed for a mean of 3.8 years. The primary endpoint of the studies was change in 6-minute walking distance, a standard measure of exercise capacity. There were many assessments of symptoms related to heart failure, but local discomfort and pain associated with treprostinil injection may have substantially unblinded those assessments. The 6-minute walking distance and an associated subjective measurement of shortness of breath during the walk (Borg dyspnea score) were administered by a person not participating in other aspects of the study. Treprostinil injection was administered as a subcutaneous infusion, described in Section 2, DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, and the dose averaged 9.3 ng/kg/min at Week 12. Few subjects received doses greater than 40 ng/kg/min. Background therapy, determined by the investigators, could include anticoagulants, oral vasodilators, diuretics, digoxin, and oxygen but not an endothelin receptor antagonist or epoprostenol. The two studies were identical in design and conducted simultaneously, and the results were analyzed both pooled and individually.
Hemodynamic Effects
As shown in Table 5, chronic therapy with treprostinil injection resulted in small hemodynamic changes consistent with pulmonary and systemic vasodilation.
Table 5: Hemodynamics during Chronic Administration of Treprostinil Injection in Patients with PAH in 12-Week Studies Hemodynamic Parameter Baseline Mean change from baseline at Week 12 Treprostinil Injection
(N=204-231)Placebo
(N=215-235)Treprostinil Injection
(N=163-199)Placebo
(N=182-215)- * Denotes statistically significant difference between treprostinil injection and placebo, p<0.05.
CI
(L/min/m2)2.4 ± 0.88
2.2 ± 0.74
+0.12 ± 0.58*
-0.06 ± 0.55
PAPm
(mmHg)62 ± 17.6
60 ± 14.8
-2.3 ± 7.3*
+0.7 ± 8.5
RAPm
(mmHg)10 ± 5.7
10 ± 5.9
-0.5 ± 5.0*
+1.4 ± 4.8
PVRI
(mmHg/L/min/m2)26 ± 13
25 ± 13
-3.5 ± 8.2*
+1.2 ± 7.9
SVRI
(mmHg/L/min/m2)38 ± 15
39 ± 15
-3.5 ± 12*
-0.80 ± 12
SvO2
(%)62 ± 100
60 ± 11
+2.0 ± 10*
-1.4 ± 8.8
SAPm
(mmHg)90 ± 14
91 ± 14
-1.7 ± 12
-1.0 ± 13
HR
(bpm)82 ± 13
82 ± 15
-0.5 ± 11
-0.8 ± 11
CI = cardiac index; PAPm = mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PVRI = pulmonary vascular resistance indexed; RAPm = mean right atrial pressure; SAPm = mean systemic arterial pressure; SVRI = systemic vascular resistance indexed; SvO2 = mixed venous oxygen saturation; HR = heart rate.
Clinical Effects
The effect of treprostinil injection on 6-minute walk, the primary endpoint of the 12-week studies, was small and did not achieve conventional levels of statistical significance. For the combined populations, the median change from baseline on treprostinil injection was 10 meters and the median change from baseline on placebo was 0 meters from a baseline of approximately 345 meters. Although it was not the primary endpoint of the study, the Borg dyspnea score was significantly improved by treprostinil injection during the 6-minute walk, and treprostinil injection also had a significant effect, compared with placebo, on an assessment that combined walking distance with the Borg dyspnea score. Treprostinil injection also consistently improved indices of dyspnea, fatigue and signs and symptoms of pulmonary hypertension, but these indices were difficult to interpret in the context of incomplete blinding to treatment assignment resulting from infusion site symptoms.
14.2 Flolan-To-Treprostinil Injection Transition Study
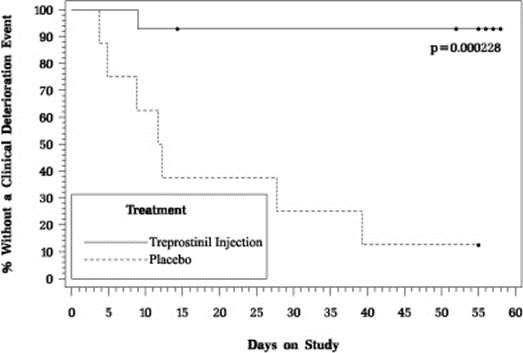
In an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients on stable doses of Flolan were randomly withdrawn from Flolan to placebo or treprostinil injection. Fourteen treprostinil injection and 8 placebo patients completed the study. The primary endpoint of the study was the time to clinical deterioration, defined as either an increase in Flolan dose, hospitalization due to PAH, or death. No patients died during the study.
During the study period, treprostinil injection effectively prevented clinical deterioration in patients transitioning from Flolan therapy compared to placebo (Figure 1). Thirteen of 14 patients in the treprostinil injection arm were able to transition from Flolan successfully, compared to only 1 of 8 patients in the placebo arm (p=0.0002).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Treprostinil injection is supplied in 20-mL multi-dose vials as sterile solutions in water for injection, individually packaged in cartons. Unopened vials of treprostinil injection are stable until the date indicated when stored at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
A single vial of treprostinil injection should be used for no more than 30 days after the initial introduction into the vial.
Treprostinil injection is supplied as:
Treprostinil Injection
Concentration
Carton of 1 NDC
20 mg/20 mL
1 mg/mL
NDC: 0781-3420-80
50 mg/20 mL
2.5 mg/mL
NDC: 0781-3425-80
100 mg/20 mL
5 mg/mL
NDC: 0781-3427-80
200 mg/20 mL
10 mg/mL
NDC: 0781-3430-80
Sterile Diluent for treprostinil injection is supplied separately as:
- NDC: 0781-6021-94 Carton of one 50 mL Single-dose vial
Discard unused portion.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Interruption of Therapy
Advise patients and caregivers to seek medical attention if they experience signs or symptoms of abrupt withdrawal of therapy or suspect a pump malfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Overdose
Inform patients and their caregivers to seek medical attention if they experience signs or symptoms of treprostinil overdose [see Overdosage (10)].
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Sandoz Inc.
Distributed by
Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
Rev. April 2019
46239048
-
20 mg Carton
NDC: 0781-3420-80
Treprostinil
Injection
20 mg/20 mL
(1 mg/mL)
Rx Only
For Subcutaneous or
Intravenous Infusion
Only
Sterile
20 mL
Multi-Dose Vial
SANDOZ – A Novartis Division
-
50 mg Carton
NDC: 0781-3425-80
Treprostinil
Injection
50 mg/20 mL
(2.5 mg/mL)
Rx Only
For Subcutaneous or
Intravenous Infusion
Only
Sterile
20 mL
Multi-Dose Vial
SANDOZ – A Novartis Division
-
100 mg Carton
NDC: 0781-3427-80
Treprostinil
Injection
100 mg/20 mL
(5 mg/mL)
Rx Only
For Subcutaneous or
Intravenous Infusion
Only
Sterile
20 mL
Multi-Dose Vial
SANDOZ – A Novartis Division
-
200 mg Carton
NDC: 0781-3430-80
Treprostinil
Injection
200 mg/20 mL
(10 mg/mL)
Rx Only
For Subcutaneous or
Intravenous Infusion
Only
Sterile
20 mL
Multi-Dose Vial
SANDOZ – A Novartis Division
- Sterile Diluent
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TREPROSTINIL
treprostinil injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0781-3420 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TREPROSTINIL (UNII: RUM6K67ESG) (TREPROSTINIL - UNII:RUM6K67ESG) TREPROSTINIL 20 mg in 20 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0781-3420-80 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2019 1 20 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203649 03/25/2019 TREPROSTINIL
treprostinil injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0781-3425 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TREPROSTINIL (UNII: RUM6K67ESG) (TREPROSTINIL - UNII:RUM6K67ESG) TREPROSTINIL 50 mg in 20 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0781-3425-80 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2019 1 20 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203649 03/25/2019 TREPROSTINIL
treprostinil injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0781-3427 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TREPROSTINIL (UNII: RUM6K67ESG) (TREPROSTINIL - UNII:RUM6K67ESG) TREPROSTINIL 100 mg in 20 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0781-3427-80 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2019 1 20 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203649 03/25/2019 TREPROSTINIL
treprostinil injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0781-3430 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TREPROSTINIL (UNII: RUM6K67ESG) (TREPROSTINIL - UNII:RUM6K67ESG) TREPROSTINIL 200 mg in 20 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0781-3430-80 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2019 1 20 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203649 03/25/2019 DILUENT
water solution injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0781-6021 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) (WATER - UNII:059QF0KO0R) WATER 1 mL in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0781-6021-94 1 in 1 CARTON 03/25/2019 1 50 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203649 03/25/2019 Labeler - Sandoz Inc (005387188)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.