LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN- calcium folinate tablet
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HEALTH CARE PROVIDER LETTER

URGENT: Important Prescribing Information Letter
Subject:
Temporary Importation of Lederle Leucovorin® (Calcium Folinate tablets, USP) from Canada to Address U.S. Shortfall
December 2025
Dear Health Care Provider,
Due to the limited supply of Leucovorin Calcium tablets, USP in the United States (U.S.) market, Pfizer is coordinating at the request of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to temporarily import unapproved Lederle Leucovorin® (Calcium Folinate tablets, USP) 5 mg tablets marketed in Canada.
This product is manufactured by Pfizer’s Contract Manufacturer, Farmasierra, located in Madrid, Spain. The FDA has not approved Pfizer’s Lederle Leucovorin (Calcium Folinate tablets USP), 5 mg tablets in the U.S.; however, the FDA is permitting the temporary importation and distribution of this product. Leucovorin Calcium tablets, USP, is referred to as Calcium Folinate tablets, USP, outside of the U.S.
Effective immediately, and during this temporary period, Pfizer will distribute the following presentation(s) of unapproved Lederle Leucovorin® (Calcium Folinate, USP):
Product
Strength
Packaging
NDC
Batch
Expiration Date
Canada Marketing Authorization
Lederle Leucovorin®, Calcium Folinate, USP
5 mg Tablet
1x 24 Bottle
0069-5886-24
X773
04-30-2026
Drug Identification Number (DIN) 02170493
Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) 066063817221
Lederle Leucovorin®, Calcium Folinate, USP
5 mg Tablet
1x 24 Bottle
0069-5886-24
X830
10-31-2026
DIN 02170493
GTIN 066063817221
Lederle Leucovorin®, Calcium Folinate, USP
5 mg Tablet
1x 24 Bottle
0069-5886-24
Z361
03-31-2027
DIN 02170493
GTIN 066063817221
Lederle Leucovorin®, Calcium Folinate, USP
5 mg Tablet
1x 100 Bottle
0069-5886-99
X831
10-31-2026
DIN 02170493
GTIN 066063817207
Lederle Leucovorin®, Calcium Folinate, USP
5 mg Tablet
1x 100 Bottle
0069-5886-99
Z362
03-31-2027
DIN 02170493
GTIN 066063817207
It is important to note that there are differences between the FDA-approved Leucovorin Calcium, USP products and the Calcium Folinate tablets, USP, marketed in Canada by Pfizer, Inc. Please see the product side-by-side label comparison table, where FDA-approved Leucovorin Calcium Tablets, USP 5 mg, manufactured by Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc., is used as a reference.
It is important to note the following differences:
- Lederle Leucovorin® (Calcium Folinate tablets, USP) 5 mg tablets is indicated for diminishing the toxicity and counteracting the effect of impaired methotrexate elimination. Treatment of megaloblastic anemias due to folate deficiency, as in sprue, nutritional deficiency, megaloblastic anemias of pregnancy and infancy. FDA-approved Leucovorin Calcium, USP, product is contraindicated for pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias caused by vitamin B12 deficiency.
- The container label will display the text used and approved for marketing Lederle Leucovorin® (Calcium Folinate tablets, USP) in Canada containing English and French text.
- Health Canada has not authorized an indication for pediatric use for the imported product. FDA-approved Leucovorin Calcium, USP, includes a specific warning in the Drug Interactions section regarding folic acid which in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible children. The Canadian Product Monograph does not mention this specific age group (10-12).
- The Canadian Product Monograph includes a Post Marketing section addressing Adverse Drug Reactions, including that cases of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), some fatal, have been reported in patients receiving calcium folinate in combination with other agents known to be associated with these disorders. A contributory role of leucovorin in these occurrences of SJS/TEN cannot be excluded. Fatalities have occurred as a result of gastrointestinal toxicity (predominantly mucositis and diarrhea) and myelosuppression. In patients with diarrhea, rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur.
- The barcode of the imported product label may not register accurately on the U.S. scanning systems. Institutions should manually input the important product information into their systems and confirm that the barcode, if scanned, provides correct information. Alternative procedures should be followed to assure that the correct drug product is being used and administered to individual patients.
- The packaging of the imported product does not include serialization information. Pfizer’s Calcium Folinate, USP, marketed in Canada, does not meet the Drug Supply Chain Security (DSCSA) standards for Interoperable Exchange of Information for Tracing of Human, Finished Prescription Drugs. FDA has created an exemption for the product due to the limited supply.
- Leucovorin Calcium tablet, USP is available only by prescription in the U.S. However, the imported product does not have the statement “Rx only” on the labeling.
Please refer to the package insert for the FDA approved Leucovorin Calcium, USP, full Prescribing Information.
Adverse Events and Product Quality ComplaintsTo report adverse reactions or quality issues, contact Pfizer at 1-800-438-1985.
Adverse reactions or quality problems experienced with the use of this product may be reported to the FDA's MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program either online, by regular mail, or by fax:
- Complete and submit the report Online: www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm
- Regular mail or Fax: download form www.fda.gov/MedWatch/getforms.htm or call 1-800-332-1088 to request a reporting form, then complete and return to the address on the pre-addressed form, or submit by fax to 1-800-FDA-0178 (1-800-332-0178)
- When reporting, please indicate product is Lederle Leucovorin from Pfizer Canada and provide the lot number
Contact InformationPlease contact Pfizer Customer Service at 1-800-533-4535 or dropships@pfizer.com (Mon.–Fri. 8am–5:30pm ET) or your Pfizer representative for any questions you may have regarding this notification.
Sincerely,Caleb Hart
US PAVE Business Unit Lead
Side-by-Side Product Comparison of FDA-approved Leucovorin Calcium, USP, and Imported Product, Lederle Leucovorin Calcium Folinate, USP, Canada
US FDA APPROVED PRODUCT
IMPORTED PRODUCT
Product name
Dosage form and strength
5 mg tablet
5 mg tablet
Container label



Description/Pharmaceutical information
DESCRIPTION
Leucovorin calcium tablets, USP contain either 5 mg or 25 mg leucovorin as the calcium salt of N-[4-[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl)methyl] amino]benzoyl]-L-glutamic acid. This is equivalent to 5.4 mg or 27.01 mg of anhydrous leucovorin calcium, respectively. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The 25 mg tablet also contains D&C yellow no. 10 aluminum lake and FD&C blue no. 1 aluminum lake. Leucovorin is a water soluble form of reduced folate in the folate group; it is useful as an antidote to drugs which act as folic acid antagonists. These tablets are intended for oral administration only.
The structural formula is as follows: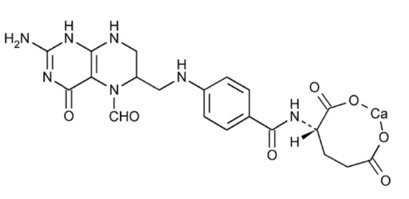
C20 H21 CaN7 O7 M.W. 511.5
SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Drug Substance
Proper name: Leucovorin Calcium (folic acid derivative) is also known as calcium folinate, citrovorum factor, or the calcium salt of 5-formyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolic acid.
Chemical name: L-Glutamic acid, N-[4[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1-4, 5, 6, 7, 8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl) methyl] amino] benzoyl]-, calcium salt (l:l).
Molecular formula and molecular mass: C20H21CaN7O7, 511.51
Structural formula: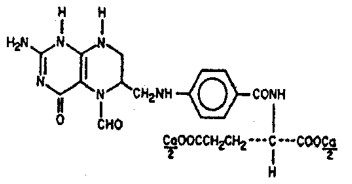
Physicochemical properties: Leucovorin Calcium occurs as a yellowish white or yellow, odourless powder. It is sparingly soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. It decomposes above 250°C. There is 0.004 mEq of calcium per mg of leucovorin in each tablet.
MICROBIOLOGY
No microbiological information is required for this drug product.Clinical pharmacology
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Leucovorin is a racemic mixture of the diastereoisomers of the 5-formyl derivative of tetrahydrofolic acid. The biologically active compound of the mixture is the (-)-L-isomer, known as Citrovorum factor, or (-)-folinic acid. Leucovorin does not require reduction by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase in order to participate in reactions utilizing folates as a source of “one-carbon” moieties. Following oral administration, leucovorin is rapidly absorbed and enters the general body pool of reduced folates. The increase in plasma and serum folate activity (determined microbiologically with Lactobacillus casei) seen after oral administration of leucovorin is predominantly due to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
Twenty normal men were given a single, oral 15 mg dose (7.5 mg/m2) of leucovorin calcium and serum folate concentrations were assayed with L. casei. Mean values observed (± one standard error) were:- a) Time to peak serum folate concentration: 1.72 ± 0.08 hours,
- b) Peak serum folate concentration achieved: 268 ± 18 ng/mL,
- c) Serum folate half-disappearance time: 3.5 hours.
Oral tablets yielded areas under the serum folate concentration-time curves (AUCs) that were 12% greater than equal amounts of leucovorin given intramuscularly and equal to the same amounts given intravenously.
Oral absorption of leucovorin is saturable at doses above 25 mg. The apparent bioavailability of leucovorin was 97% for 25 mg, 75% for 50 mg and 37% for 100 mg.Clinical Studies/Pharmacodynamics
Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical Trials
The clinical trial data on which the original indication was authorized is not available.
10.1 Mechanism of Action
Calcium folinate, the calcium salt of folinic acid (citrovorum factor), is a mixture of the diastereoisomers of the 5-formyl derivative of tetrahydrofolic acid. The biologically active component of the mixture is the (-)-L-isomer. It is a metabolite of folic acid and an essential coenzyme for nucleic acid synthesis used in cytotoxic therapy.
10.2 Pharmacodynamics
Calcium folinate is a reduced form of folic acid, which is readily converted to other reduced folic acid derivatives (e.g., tetrahydrofolate).
Because it does not require reduction by dihydrofolate reductase as does folic acid, calcium folinate is not affected by blockage of this enzyme by folic acid antagonists (dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors). This allows purine and thymidine synthesis, and thus DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, to occur. Calcium folinate may limit methotrexate action on normal cells by competing with methotrexate for the same transport processes into the cell. Calcium folinate rescues bone marrow and gastrointestinal cells from methotrexate but has no apparent effect on pre-existing methotrexate nephrotoxicity.
Calcium folinate is extensively converted to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in the intestine prior to absorption. In this form, it is a major component of the total active human serum folate. Oral absorption is saturable at doses above 25 mg.
Calcium folinate enhances the cytotoxicity of fluoropyrimidines such as 5-fluorouracil (5FU) by their metabolites, methylene tetrahydrofolate and fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate, forming a stable ternary complex with thymidylate synthase and thereby decreasing intracellular levels of that enzyme and the product thymidylate. The cell then dies as a result of thymine starvation.Indications and usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Leucovorin calcium tablets are indicated to diminish the toxicity and counteract the effects of impaired methotrexate elimination and of inadvertent overdosages of folic acid antagonists.Indications & Usage
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN (calcium folinate) is indicated for:- diminishing the toxicity and counteracting the effect of impaired methotrexate elimination.
- treatment of megaloblastic anemias due to folate deficiency, as in sprue, nutritional deficiency, megaloblastic anemias of pregnancy and infancy.
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Leucovorin is improper therapy for pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias secondary to the lack of vitamin B12. A hematologic remission may occur while neurologic manifestations continue to progress.Contraindications
Calcium folinate therapy is contraindicated in patients with:- Known hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. For a complete listing, see DOSAGE FORMS, STRENGTHS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING.
- Pernicious anemia or other megaloblastic anemias where Vitamin B12 is deficient. A hematologic remission may occur while neurologic manifestations continue to progress.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Warnings & Precautions
In the treatment of accidental overdosage of folic acid antagonists, leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting hematologic toxicity decreases.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil. Deaths from severe enterocolitis, diarrhea, and dehydration have been reported in elderly patients receiving weekly leucovorin and fluorouracil.1
Concomitant granulocytopenia and fever were present in some but not all of the patients.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and mortality in a placebo-controlled study.
Serious Warnings and Precautions
- Calcium folinate should only be used with 5-fluorouracil or methotrexate under the direct supervision of a clinician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents.
- Cases of Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), some fatal, have been reported in patients receiving calcium folinate in combination with other agents known to be associated with these disorders.
- Fatalities have occurred as a result of gastrointestinal toxicity (particularly mucusitis and diarrhea) associated with calcium folinate use.
- Fatalities have occurred as a result of myelosuppression associated with calcium folinate use.
- Anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions (including shock) have occurred in patients administered calcium folinate.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Parenteral administration is preferable to oral dosing if there is a possibility that the patient may vomit or not absorb the leucovorin. Leucovorin has no effect on other established toxicities of methotrexate such as the nephrotoxicity resulting from drug and/or metabolite precipitation in the kidney.Warnings And Precautions
General
Since calcium folinate may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil, calcium folinate /fluorouracil combination therapy for advanced colorectal cancer should be administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the use of antimetabolite cancer chemotherapy. Particular care should be taken in the treatment of elderly or debilitated colorectal cancer patients (see 9 DRUG INTERACTIONS and 7.1.4 Geriatrics).
Calcium folinate should only be used with 5-fluorouracil or methotrexate under the direct supervision of a clinician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents.
Treatment-related deaths have been sporadically reported in patients treated with LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil combination therapy regimens. In general, diarrhea or stomatitis/mucositis are the first indications that severe and potentially life-threatening toxicity could develop. Patients who experience these symptoms while receiving any combination therapy regimen incorporating LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil should be carefully followed and further therapy should be withheld until these symptoms resolve.
Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe in patients receiving LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil combination (see 9 DRUG INTERACTIONS, 9.2 Drug Interactions Overview).
Therapy with LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN /fluorouracil must not be initiated or continued in patients who have symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity of any severity, until those symptoms have resolved. Patients with diarrhea must be monitored with particular care until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur. Elderly or debilitated patients are at greater risk for severe toxicity receiving this therapy.
Hematologic
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN (calcium folinate) treatment may mask pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias resulting from vitamin B12 deficiency.
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN should not be used for the treatment of macrocytosis caused by direct or indirect DNA synthesis inhibitors (e.g. hydroxycarbamide, cytarabine, mercaptopurine, thioguanine).
Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
The following provides general advice for monitoring patients; however, specific monitoring recommendations may vary with local medical practice.
5-fluorouracil/calcium folinate therapy
Complete blood count (CBC) with differential and platelets: prior to each treatment; weekly during the first two courses; at time of anticipated white blood cell (WBC) nadir in all courses thereafter. Electrolytes and liver function tests: prior to each treatment for the first three courses and prior to every other course thereafter.
Methotrexate/calcium folinate therapy
Serum creatinine levels and serum methotrexate levels: at least once daily.
Urine pH: in cases of methotrexate overdose or delayed excretion, monitor as appropriate, to ensure maintenance of pH ≥7.0.
Neurologic
Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving calcium folinate, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine and anti-epileptic drugs such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and succinimides administration (see 9 DRUG INTERACTIONS).
In epileptic patients treated with phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and succinimides there is a risk to increase the frequency of seizures due to a decrease of plasma concentrations of anti-epileptic drugs. Clinical monitoring, possibly monitoring of the plasma concentrations and, if necessary, dose adaptation of the anti-epileptic drug during calcium folinate administration and after discontinuation is recommended.
Reproductive Health: Female and Male Potential Fertility
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN (calcium folinate) is an intermediate product in the metabolism of folic acid and occurs naturally in the body. No fertility studies have been conducted with calcium folinate in animals.
Skin
Cases of Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), some fatal, have been reported in patients receiving calcium folinate in combination with other agents known to be associated with these disorders. A contributory role of leucovorin in these occurrences of SJS/TEN cannot be excluded (see 3 SERIOUS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS).Drug Interactions
Drug Interactions
Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible children.
Preliminary animal and human studies have shown that small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and, in humans, remain 1 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration. However, high doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil (see WARNINGS).Serious Drug Interactions
Serious Drug Interactions- Treatment-related deaths have been sporadically reported in patients treated with LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil combination therapy regimens. In general, diarrhea or stomatitis/mucositis are the first indications that severe and potentially life-threatening toxicity could develop. Patients who experience these symptoms while receiving any combination therapy regimen incorporating LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil should be carefully followed and further therapy should be withheld until these symptoms resolve (see 9.4 Drug-Drug Interactions).
Drug Interactions Overview
Calcium folinate may diminish the effect of anti-epileptic substances: phenobarbital, primidone, phenytoin and succinimides, and may increase the frequency of seizures (a decrease of plasma levels of enzymatic inductor anticonvulsant drugs may be observed because the hepatic metabolism is increased as folates are one of the cofactors). Seizures and/or syncope have been reported rarely in cancer patients receiving leucovorin, usually in association with fluoropyrimidine administration, and most commonly in those with CNS metastases or other predisposing factors; however, a causal relationship has not been established.
In epileptic patients treated with phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and succinimides there is a risk to increase the frequency of seizures due to a decrease of plasma concentrations of anti-epileptic drugs. Clinical monitoring, possibly monitoring of the plasma concentrations and, if necessary, dose adaptation of the anti-epileptic drug during calcium folinate administration and after discontinuation is recommended.
When calcium folinate is given in conjunction with a folic acid antagonist (eg, cotrimoxazole, pyrimethamine, methotrexate, antibiotic with antifolic effect) the efficacy of the folic acid antagonist may either be reduced or completely neutralised.
Preliminary animal and human studies have shown that small quantities of systemically administered LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN enter the CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and, in humans, remain 1-3 orders of magnitude lower than the usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration. However, high doses of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate.
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil (see 7 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS). When these drugs are administered concurrently in the palliative therapy of advanced colorectal cancer, the dosage of fluorouracil must be reduced. Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN plus fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with fluorouracil alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more commonly and may be more severe in patients receiving the combination (See 7 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS).
Drug-Behavioural Interactions
Interactions with behaviour have not been established.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Table 4 - Established or Potential Drug-Drug Interactionsleucovorin
Source of Evidence
Effect
Clinical comment
Anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, primidone, phenytoin and succinimides)
T
Diminished effect
May increase the frequency of seizures
Folic acid antagonist (eg: cotrimoxazole, pyrimethamine, methotrexate, antibiotic with antifolic effect)
T
Diminished effect
Efficacy may be reduced or completely neutralized
Methotrexate
CT
Diminished effect
small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter the CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and remain 1-3 orders of magnitude lower than the usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration. High doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate
Fluorouracil
CT
Increased toxicity
toxicities were found to be reversible with appropriate modification of 5FU administration
Legend: C = Case Study; CT = Clinical Trial; T = Theoretical
Drug-Food Interactions
Interactions with food have not been established.
Drug-Herb Interactions
Interactions with herbal products have not been established.
Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
Interactions with laboratory tests have not been established.Fertility, Pregnancy, & Lactation / Special populations
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with leucovorin. It is also not known whether leucovorin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Leucovorin should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when leucovorin is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use
See Drug Interactions subsection.Special Populations
Pregnant Women
There are no adequate and well-controlled clinical studies conducted in pregnant or breast-feeding women. Animal studies do not indicate reproductive toxicity (see 16 Non-clinical toxicology). There are no indications that folic acid induces harmful effects if administered during pregnancy. During pregnancy, 5-fluorouracil and methotrexate should only be administered on strict indications, where the benefits of the drug to the mother should be weighed against possible hazards to the foetus. Should treatment with methotrexate or other folate antagonists take place despite pregnancy or lactation, there are no limitations as to the use of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN (calcium folinate) to diminish toxicity or counteract the effects.
5-fluorouracil use is generally contraindicated during pregnancy and contraindicated during breast-feeding; this applies also to the combined use of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN (calcium folinate) with 5-fluorouracil.
Please refer also to the health-care professional label for methotrexate, other folate antagonists and 5-fluorouracil-containing medicinal products.
Breast-feeding
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatrics
Pediatrics (< 18 years of age): No data are available to Health Canada; therefore, Health Canada has not authorized an indication for pediatric use.
Geriatrics
Geriatrics: Evidence from clinical studies and experience suggests that use in the geriatric population is associated with differences in safety or effectiveness (WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, General). Deaths from severe enterocolitis, diarrhea and dehydration have been reported in elderly patients receiving leucovorin and fluorouracil. Concomitant granulocytopenia and fever were present in some but not all of the patients.
NON-CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and fertility studies have not been conducted with calcium folinate.
Embryo-fetal reproduction toxicity studies have been performed in rats and rabbits. Rats were dosed up to 1800 mg/m2 which is 9 times the maximum recommended human dose, and rabbits were dosed up to 3300 mg/m2 which is 16 times the maximum recommended human dose. There was no embryo-fetal toxicity noted in rabbits. At the maximum dose in rats, there was a slight increase in early embryonic resorptions and no other adverse effects on embryo-fetal development. No resorptions were noted in dose groups at 5 times the maximum recommended human dose.Adverse reactions
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Allergic sensitization, including anaphylactoid reactions and urticaria, has been reported following the administration of both oral and parenteral leucovorin.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.Adverse Reactions
Adverse Reaction Overview
Allergic sensitization, including anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions (including shock) and urticaria, has been reported following administration of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN.
Table 3 – Adverse Reactions associated with LEDERLE LEUCOVORINSystem Organ Class
Adverse Reaction
Immune system disorders
Frequency undetermined
Allergic reactions, urticarial
Very Rare
Anaphylactoid/ anaphylactoid reactions (including shock)
Nervous System disorders
Rare
Seizures and/or syncope
General disorders and administration site conditions
Frequency undetermined
Fever
Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions
Clinical trials are conducted under very specific conditions. The adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials; therefore, may not reflect the rates observed in practice and should not be compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug. Adverse reaction information from clinical trials may be useful in identifying and approximating rates of adverse drug reactions in real-world use.
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN in Combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)
In combination regimens, the toxicity profile of 5FU is enhanced by LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN. The most common manifestations are mucositis, stomatitis, leukopenia and/or diarrhea, which may be dose-limiting. In clinical trials with this drug combination, these toxicities were found to be reversible with appropriate modification of 5FU administration.
Generally, the safety profile depends on the applied regimen of 5-fluorouracil due to enhancement of the 5- fluorouracil induced toxicities. Additional undesirable effects when used in combination with 5-fluorouracil:
Table 4 – Adverse Reactions associated with LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN in Combination with 5-FUSystem Organ Class
Adverse Reaction
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common
Nausea and Vomiting, diarrhea
Hepatobiliary disorders
Frequency undetermined
Hyperammonemia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Common
Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysaesthesia
General disorders and administration site conditions
Very common
Mucositis, including stomatitis and chelitis
Post-Market Adverse Reactions
Cases of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), some fatal, have been reported in patients receiving calcium folinate in combination with other agents known to be associated with these disorders. A contributory role of leucovorin in these occurrences of SJS/TEN cannot be excluded.
Fatalities have occurred as a result of gastrointestinal toxicity (predominantly mucositis and diarrhea) and myelosuppression. In patients with diarrhea, rapid clinical deterioration leading to death can occur.Overdosage
OVERDOSAGE
Excessive amounts of leucovorin may nullify the chemotherapeutic effect of folic acid antagonists.Overdose
Overdosage
Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin converted in the body by the action of folate reductase to folinic acid (calcium folinate), which is rapidly eliminated in the urine.
Folic acid has low acute and chronic toxicity in humans. There have been no reported sequelae in patients who have received significantly more calcium folinate than the recommended dosage. However, excessive amounts of calcium folinate may nullify the chemotherapeutic effect of folic acid antagonists. No adverse effects have been noted in adults after the ingestion of 400 mg/day for 5 months or 10 mg/day for 5 years.
Should overdosage of the combination of 5-fluorouracil and calcium folinate occur, the overdosage instructions for 5-FU should be followed.
For management of a suspected drug overdose, contact your regional poison control centre.
Dosage and administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Leucovorin calcium tablets are intended for oral administration. Because absorption is saturable, oral administration of doses greater than 25 mg is not recommended.
Impaired Methotrexate Elimination or Inadvertent Overdosage
Leucovorin rescue should begin as soon as possible after an inadvertent overdosage and within 24 hours of methotrexate administration when there is delayed excretion (see WARNINGS). Leucovorin 15 mg (10 mg/m2) should be administered IM, IV, or PO every 6 hours until serum methotrexate level is less than 10 -8 M. In the presence of gastrointestinal toxicity, nausea, or vomiting, leucovorin should be administered parenterally.
Serum creatinine and methotrexate levels should be determined at 24-hour intervals. If the 24-hour serum creatinine has increased 50% over baseline or if the 24-hour methotrexate level is greater than 5 x 10 -6 M or the 48 hour level is greater than 9 x 10 -7 M, the dose of leucovorin should be increased to 150 mg (100 mg/m2) IV every 3 hours until the methotrexate level is less than 10 -8 M. Doses greater than 25 mg should be given parenterally (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Hydration (3 L/d) and urinary alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate should be employed concomitantly. The bicarbonate dose should be adjusted to maintain the urine pH at 7 or greater.
The recommended dose of leucovorin to counteract hematologic toxicity from folic acid antagonists with less affinity for mammalian dihydrofolate reductase than methotrexate (i.e., trimethoprim, pyrimethamine) is substantially less, and 5 to 15 mg of leucovorin per day has been recommended by some investigators.
Patients who experience delayed early methotrexate elimination are likely to develop reversible non-oliguric renal failure. In addition to appropriate leucovorin therapy, these patients require continuing hydration and urinary alkalinization, and close monitoring of fluid and electrolyte status, until the serum methotrexate level has fallen to below 0.05 micromolar and the renal failure has resolved.
Some patients will have abnormalities in methotrexate elimination or renal function following methotrexate administration, which are significant but less severe. These abnormalities may or may not be associated with significant clinical toxicity. If significant clinical toxicity is observed, leucovorin rescue should be extended for an additional 24 hours (total 14 doses over 84 hours) in subsequent courses of therapy. The possibility that the patient is taking other medications which interact with methotrexate (e.g., medications which may interfere with methotrexate elimination or binding to serum albumin) should always be reconsidered when laboratory abnormalities or clinical toxicities are observed.Dosage & Administration
Recommended Dose and Dosage Adjustment
Impaired methotrexate Elimination or Accidental Overdosage:
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN rescue should begin as soon as possible after an inadvertent overdosage and within 24 hours of methotrexate administration when there is delayed excretion (WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS). As the time interval between the administration of antifolate and LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN rescue increases, the effectiveness of LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN in counteracting toxicity decreases.
There are no fixed guidelines regarding the dose of methotrexate that triggers an automatic subsequent calcium folinate administration, since tolerance to this folate antagonist depends on various factors. The dose of methotrexate varies, nevertheless folinate rescue is necessary when methotrexate is given at doses exceeding 500 mg/m2 and has to be considered with doses of 100 mg - 500 mg/m2.
Calcium folinate rescue treatment should commence approximately 24 hours after the beginning of methotrexate infusion. Dosage regimens vary depending upon the dose of methotrexate administered. In general, calcium folinate should be administered at a dose of 15 mg (approximately 10 mg/m2) every 6 hours for 10 doses, either parenterally by intramuscular injection, bolus intravenous injection, intravenous infusion, or orally using calcium folinate tablets.
Monitoring of the serum methotrexate (MTX) concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of therapy. If serum creatinine increases after methotrexate therapy or if methotrexate plasma concentrations are above certain threshold (see Table 1), the dose of calcium folinate should be increased according to the plasma methotrexate concentrations as soon as the risk is recognized. In the presence of gastrointestinal toxicity, nausea, or vomiting, calcium folinate should be administered parenterally. In the case of intravenous administration, no more than 160 mg of calcium folinate should be injected per minute due to the calcium content of the solution. Further, oral administration of doses greater than 25 mg is not recommended since the digestive absorption of calcium folinate is saturable; these doses should be administered parenterally.
In addition to calcium folinate administration, measures to ensure the prompt excretion of methotrexate are an integral part of the calcium folinate rescue treatment. These measures include:- a) Maintenance of urine output above 2,500 mL/24 hr in adults by increased oral or intravenous fluids 12 hours before and for 36 hours after the end of methotrexate infusion.
- b) Alkalinisation of urine so that the urinary pH is greater than 7.0 before methotrexate infusion.
- Foods, drinks and drugs that may increase urinary acidity should be avoided during the therapy.
- c) Plasma methotrexate concentration and serum creatinine should be measured at least 24, 48, and 72 hours after the initiation of the methotrexate infusion. These measurements must be continued until the plasma methotrexate level is less than 5 x 10-8 molar. (0.05 μm).
Delayed methotrexate excretion may be seen in some patients. This may be caused by a third space accumulation (as seen in ascites or pleural effusion for example), renal insufficiency or inadequate hydration (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS). Under such circumstances, higher doses of calcium folinate and/or prolonged administration may be indicated. Some dosage and administration guidelines are given in Table 1.
Table 1: Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Calcium Folinate RescueClinical situation
Laboratory findings
Calcium folinate dosage and duration
Normal methotrexate Elimination
Serum methotrexate level ≤ 10 μM at 24 hours after administration, ≤ 1 μM at 48 hours, and < 0.1 μM at 72 hours.
15 mg PO, IM, or IV every 6 hours for 60 hours (10 doses starting at 24 hours after start of methotrexate infusion).
Delayed late methotrexate elimination
Serum methotrexate level remaining > 0.1 μM at 72 hours, and > 0.1 μM at 96 hours after administration.
Continue 15 mg PO, IM, or IV every 6 hours, until methotrexate level is less than 0.1 μM.
Delayed early methotrexate elimination and/or evidence of acute renal failure
Serum methotrexate level of > 10 μM at 24 hours, or > 1 μM at 48 hours after administration OR a 100% or greater increase in serum creatinine level at 24 hours after methotrexate administration.
150 mg IV every 3 hours, until methotrexate level is less than 1 μM; then 15 mg
IV every 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 0.1 μM.
Hydration (3 L/d) and urinary alkalinization with NaHCO3 should be employed concomitantly. The bicarbonate dose should be adjusted to maintain the urine pH at 7.0 or greater.
Megaloblastic Anemia Due to Folic Acid Deficiency:
Doses up to 15 mg daily have been suggested.
Health Canada has not authorized an indication for pediatric use.
Administration
Tablets are administered orally.How supplied/Composition & form/Storage and handling/References
HOW SUPPLIED
Leucovorin calcium tablets USP, 5 mg are available as white, round, biconvex tablets, debossed with "stylized b" on one side and 484 on the other side, packaged in bottles of 30 (NDC: 0555-0484-01) and 100 (NDC: 0555-0484-02) tablets. Leucovorin calcium tablets USP, 25 mg are available as pale green, round, biconvex tablets, debossed with "stylized b" on one side and 485 on the other side, packaged in bottles of 25 (NDC: 0555-0485-27) tablets.REFERENCES
- 1. Grem JL, Shoemaker DD, Petrelli NJ, Douglas HO. Severe and fatal toxic effects observed in treatment with high- and low-dose leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil for colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rep 1987;71:1122.
- 2. Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW et al. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J Med 1986;314:1600-1606.
Composition & Form
Dosage Forms Composition And Packaging
Table 2 – Dosage Forms, Strengths, Composition and PackagingRoute of Administration
Dosage Form / Strength/Composition
Non-medicinal Ingredients
Oral
Tablet 5 mg
Each tablet contains 5 mg of folinic acid as calcium folinate
Lactose, Magnesium Stearate, Microcrystalline
Cellulose, Sodium Starch Glycolate and Starch
Pregelatinized 1500
Availability:
Bottles of 24 tablets
Bottles of 100 tablets
Storage & Handling
Special Handling Instructions
There are no special handling instructions for this drug product.
Storage And Stability
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN Tablets 5 mg:
Tablets should be stored at 15-30°C. Protect from light.Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics after intravenous, intramuscular and oral administration of a 25 mg dose of calcium folinate were studied in male volunteers.
After intravenous administration, serum total reduced folates (as measured by Lactobacillus casei assay) reached a mean peak of 1259 ng/mL (range 897-1625). The mean time to peak was 10 minutes. This initial rise in total reduced folates was primarily due to the parent compound 5-formyl-THF (measured by Streptococcus faecalis assay), which rose to 1206 ng/mL at 10 minutes. A sharp drop in parent compound followed and coincided with the appearance of the metabolite (also active), 5-methyl-THF, which became the predominant circulating form of the drug. The mean peak of 5-methyl-THF was 258 ng/mL and occurred at 1.3 hours. The terminal half-life for total reduced folates was 6.2 hours.
After intramuscular injection, the mean peak of serum total reduced folates was 436 ng/mL (range 240-725) and occurred at 52 minutes. Similar to IV administration, the initial sharp rise was due to the parent compound. The mean peak of 5-formyl-THF was 360 ng/mL and occurred at 28 minutes. The level of the metabolite 5-methyl-THF increased subsequently over time until at 1.5 hours it represented 50% of the circulating total folates. The mean peak of 5-methyl-THF was 226 ng/mL at 2.8 hours. The terminal half-life of total reduced folates was 6.2 hours. There was no difference of statistical significance between IM and IV administration in the AUC for total reduced folates, 5-formyl-THF or 5-methyl-THF.
After oral administration of calcium folinate reconstituted with the aromatic elixir, the mean peak concentration of serum total reduced folates was 393 ng/mL (range 160-550). The mean time to peak was 2.3 hours and the terminal half-life was 5.7 hours. The major component was the metabolite 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to which calcium folinate is partially converted in the intestinal mucosa. The mean peak of 5-methyl-THF was 367 ng/mL at 2.4 hours. The peak level of the parent compound was 51 ng/mL at 1.2 hours. The AUC of total reduced folates after oral administration of the 25 mg dose was 92% of the AUC after intravenous administration.
Following oral administration, calcium folinate is rapidly absorbed and enters the general body pool of reduced folates. Folate is concentrated in the liver and cerebrospinal fluid although distribution occurs to all body tissues. Folates are mainly excreted in the urine, with small amounts in the faeces. Parenteral administration of calcium folinate gives higher peak plasma levels than oral administration, but the total plasma folate pool of folinic acid plus its metabolite (N5methyl—H4-folate) remains unchanged. Oral absorption of calcium folinate is saturable at doses above 25 mg.36 The apparent bioavailability of calcium folinate was 97% for 25 mg, 75% for 50 mg and 37% for 100 mg.
Calcium folinate is the calcium salt of 5-formyl tetrahydrofolic acid. It is an active metabolite of folinic acid and an essential coenzyme of nucleic acid synthesis in cytotoxic chemotherapy. Calcium folinate is frequently used to diminish the toxicity and counteract the action of folate antagonists, such as methotrexate. Calcium folinate and folate antagonists share the same membrane transport carrier and compete for transport into cells, stimulating folate antagonist efflux. It also protects cells from the effect of folate antagonists by repletion of the reduced folate pool. Calcium folinate serves as a pre-reduced source of H4 folate: it can therefore bypass folate antagonist blockage and provide a source for the various coenzyme forms of folic acid. Calcium folinate is also frequently used in the biochemical modulation of fluoropyridine (5-FU) to enhance its cytotoxic activity. 5-FU inhibits thymidylate synthase (TS), a key enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis, and calcium folinate enhances TS inhibition by increasing the intracellular folate pool, thus stabilizing the 5-FU-TS complex and increasing 5-FU activity. A folic acid deficiency is produced during therapy with the folic acid antagonists, aminopterin and amethopterin (methotrexate), used as antineoplastic agents and with the chemotherapeutic agent, pyrimethamine. These agents competitively inhibit the conversion of folic acid to folinic acid. Their affinity for folate reductase is so much greater than that of folic acid that not even large doses of folic acid will correct the drug-induced deficiency. In the event of a severe toxic reaction, the already reduced form, folinic acid, can be given, since it can be used directly to form new coenzyme. - PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 24 count bottle label
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 count bottle label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LEDERLE LEUCOVORIN
calcium folinate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0069-5886 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEUCOVORIN CALCIUM (UNII: RPR1R4C0P4) (LEUCOVORIN - UNII:Q573I9DVLP) LEUCOVORIN 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A (UNII: H8AV0SQX4D) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (yellowish-white) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (convex) Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0069-5886-24 24 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/18/2025 03/31/2027 2 NDC: 0069-5886-99 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/18/2025 03/31/2027 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date Unapproved drug for use in drug shortage 12/18/2025 03/31/2027 Labeler - Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc (134489525)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


