PROGESTERONE VAGINAL INSERT- progesterone insert
Progesterone vaginal insert by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Progesterone vaginal insert by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by XIROMED, LLC, XIROMED PHARMA ESPANA, S.L., Laboratorios León Farma, S.A.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PROGESTERONE VAGINAL INSERT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PROGESTERONE VAGINAL INSERT.
PROGESTERONE vaginal insert
Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Progesterone vaginal insert is a progesterone indicated to support embryo implantation and early pregnancy by supplementation of corpus luteal function as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) treatment program for infertile women. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dose of progesterone vaginal insert is 100 mg administered vaginally two or three times daily starting the day after oocyte retrieval and continuing for up to 10 weeks total duration. Efficacy in women 35 years of age and older has not been clearly established. The appropriate dose of progesterone vaginal insert in this age group has not been determined. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
100 mg vaginal insert (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
Previous allergic reactions to progesterone or any of the ingredients of progesterone vaginal insert (4)
-
Known missed abortion or ectopic pregnancy (4)
-
Liver disease (4)
-
Known or suspected breast cancer (4)
-
Active arterial or venous thromboembolism or severe thrombophlebitis, or a history of these events (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
Life-threatening arterial or venous thromboembolic disorders may occur during hormone treatment, including treatment with progesterone vaginal insert. Discontinue progesterone vaginal insert if any of these are suspected. (5.1)
-
Observe patients with a history of depression closely. Consider discontinuation if symptoms worsen. (5.2)
-
Progesterone vaginal insert is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products) as this may alter progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal insert. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported (greater than 2%) were post-oocyte retrieval pain, abdominal pain, nausea, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Xiromed, LLC at 1-844-XIROMED (1-844-947-6633) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2025
-
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular or Cerebrovascular Disorders
5.2 Depression
5.3 Use of Other Vaginal Products
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Expected Adverse Reaction Profile Seen with Progesterone
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Luteal Supplementation During Assisted Reproductive Treatment Study
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Vaginal Bleeding
17.2 Common Adverse Reactions with Progesterone
17.3 Coadministration of Vaginal Products
17.4 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
The dose of progesterone vaginal insert is 100 mg administered vaginally two or three times daily starting the day after oocyte retrieval and continuing for up to 10 weeks total duration. Efficacy in women 35 years of age and older has not been clearly established. The appropriate dose of progesterone vaginal insert in this age group has not been determined.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Progesterone vaginal insert should not be used in individuals with any of the following conditions:
-
Previous allergic reactions to progesterone or any of the ingredients of progesterone vaginal insert [see Description (11)]
-
Known missed abortion or ectopic pregnancy
-
Liver disease
-
Known or suspected breast cancer
-
Active arterial or venous thromboembolism or severe thrombophlebitis, or a history of these events
-
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular or Cerebrovascular Disorders
The physician should be alert to earliest signs of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorders, arterial or venous thromboembolism (venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism), thrombophlebitis, or retinal thrombosis. Progesterone vaginal insert should be discontinued if any of these are suspected.
5.2 Depression
Patients with a history of depression need to be closely observed. Consider discontinuation if symptoms worsen.
5.3 Use of Other Vaginal Products
Progesterone vaginal insert is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products) as this may alter progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal insert [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data reflect exposure to progesterone vaginal insert in 808 infertile women (74.9% White, 10.3% Hispanic, 5.4% Black, 5% Asian, and 4.6% Other) in a single Assisted Reproductive Technology 10 week clinical study conducted in the U.S. Progesterone vaginal insert was studied at doses of 100 mg twice daily and 100 mg three times daily. The adverse reactions that occurred at a rate greater than or equal to 2% in either progesterone vaginal insert group are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Number and Frequency of Reported Adverse Reactions in Women Treated with Progesterone Vaginal Insert in an Assisted Reproductive Technology Study
Body System Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg twice daily
(N=404)
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg three times daily (N=404)
Preferred Term Gastrointestinal Disorders Abdominal pain 50 (12%) 50 (12%) Nausea 32 (8%) 29 (7%) Abdominal distension 18 (4%) 17 (4%) Constipation 9 (2%) 14 (3%) Vomiting 13 (3%) 9 (2%) General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 7 (2%) 12 (3%) Infections and Infestations Urinary tract infection 9 (2%) 4 (1%) Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications Post-oocyte retrieval pain 115 (28%) 102 (25%) Nervous System Disorders Headache 15 (4%) 13 (3%) Reproductive System and Breast Disorders Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome 30 (7%) 27 (7%) Uterine spasm 15 (4%) 11 (3%) Vaginal bleeding 13 (3%) 14 (3%) Other less common reported adverse reactions included vaginal irritation, itching, burning, discomfort, urticaria, and peripheral edema.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted for progesterone vaginal insert. Drugs known to induce the hepatic cytochrome-P450-3A4 system (such as rifampin, carbamazepine) may increase the elimination of progesterone.
The effect of concomitant vaginal products on the exposure of progesterone from progesterone vaginal insert has not been assessed. Progesterone vaginal insert is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products) as this may alter progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal insert [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Progesterone vaginal insert has been used to support embryo implantation and maintain clinical pregnancy in one clinical study. The live birth outcomes of these pregnancies were as follows:
-
Among the 404 subjects treated with progesterone vaginal insert twice daily, 143 subjects had live births consisting of 85 singletons, 56 twins, and 2 triplets. In this treatment group, 13 subjects had a spontaneous abortion, 1 subject had an ectopic pregnancy, and 7 subjects reported fetal birth defects (3.4% based on 203 livebirths).
-
Among the 404 subjects treated with progesterone vaginal insert three times daily, 155 subjects had livebirths consisting of 91 singletons, 60 twins, and 4 triplets. In this treatment group, 22 subjects had a spontaneous abortion, 4 subjects had an ectopic pregnancy, and 7 subjects reported fetal birth defects (3.1% based on 223 livebirths).
Birth defects reported in the progesterone vaginal insert twice daily group included: one fetus with a cleft palate and intrauterine growth retardation, one fetus with spina bifida, three fetuses with congenital heart defects, one fetus with an umbilical hernia, and one fetus with an intestinal anomaly.
Birth defects reported in the progesterone vaginal insert three times daily group included: one fetus with an esophageal fistula, one fetus with hypospadias and an underdeveloped right ear, one fetus with Down Syndrome and an atrial septal defect, one fetus with congenital heart anomalies, one fetus with DiGeorge's syndrome, one fetus with a hand deformity, and one fetus with cleft palate.
For additional information on the pharmacology of progesterone vaginal insert and pregnancy outcome information [see Clinical Pharmacology (12) and Clinical Studies Sections (14)].
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Detectable amounts of progesterone have been identified in the milk of nursing mothers. The effect of this on the nursing infant has not been determined.
-
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Progesterone vaginal insert contains micronized progesterone.
Progesterone vaginal insert is supplied with polyethylene vaginal applicators.
The active ingredient, progesterone, is present in 100 mg amount along with other excipients. The chemical name for progesterone is pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione. It has a molecular formula of C21H30O2 and a molecular weight of 314.5. Progesterone exists in two polymorphic forms. The form used in progesterone vaginal insert, the alpha-form, has a melting point of 127 to 131°C.
The structural formula is:
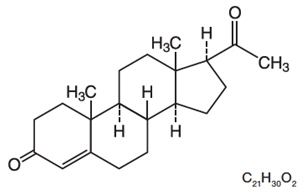
Each progesterone vaginal insert delivers 100 mg of progesterone in a base containing adipic acid, colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone, pregelatinized starch, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Progesterone is a naturally occurring steroid that is secreted by the ovary, placenta, and adrenal gland. In the presence of adequate estrogen, progesterone transforms a proliferative endometrium into a secretory endometrium. Progesterone is necessary to increase endometrial receptivity for implantation of an embryo. Once an embryo is implanted, progesterone acts to maintain a pregnancy.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Progesterone serum concentrations increased following the administration of the progesterone vaginal insert in 12 healthy pre-menopausal females. On single dosing, the mean Cmax was 17.0 ng/mL in the progesterone vaginal insert twice daily group and 19.8 ng/mL in the progesterone vaginal insert three times daily group. On multiple dosing, steady-state concentrations were attained within approximately 1 day after initiation of treatment with progesterone vaginal insert. Both progesterone vaginal insert regimens provided average serum concentrations of progesterone exceeding 10 ng/mL on Day 5. The pharmacokinetic results are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Mean (±Standard Deviation) Serum Progesterone Pharmacokinetic Parameters
Pharmacokinetic
Parameter (unit)
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg twice daily (N=6)
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg three times daily (N=6)
Single Dosing Cmax (ng/mL) 17.0 ± 6.5 19.8 ± 7.2 Tmax (hr) 24.0 ± 0.0 17.3 ± 7.4 AUC0-24 (ng∙hr/mL) 217 ± 113 284 ± 143 Day 5 of Multiple Dosing Cmax (ng/mL) 18.5 ± 5.5 24.1 ± 5.6 Tmax (hr) 18.0 ± 9.4 18.0 ± 9.4 Cmin (ng/mL) 8.9 ± 4.5 10.9 ± 6.7 Cavg (ng/ml) 14.0 ± 4.8 15.9 ± 4.3 AUC0-24 (ng∙hr/mL) 327 ± 127 436 ± 106 Cmax Maximum progesterone serum concentration.
Tmax Time to maximum progesterone serum concentration.
Cavg Average progesterone serum concentration.
AUC0-24 Area under the drug concentration versus time curve from 0 to 24 hours post dose.
Cmin Minimum progesterone serum concentration.
Distribution
Progesterone is approximately 96% to 99% bound to serum proteins, primarily to serum albumin and corticosteroid binding globulin.
Metabolism
Progesterone is metabolized primarily by the liver, largely to pregnanediols and pregnanolones. Pregnanediols and pregnanolones are conjugated in the liver to glucuronide and sulfate metabolites. Progesterone metabolites that are excreted in the bile may be deconjugated and may be further metabolized in the gut via reduction, dehydroxylation, and epimerization.
Excretion
Progesterone undergoes renal and biliary elimination. Following injection of labeled progesterone, 50 to 60% of the excretion of metabolites occurs via the kidney; approximately 10% occurs via the bile and feces. Overall recovery of the labeled material accounts for 70% of an administered dose. Only a small portion of unchanged progesterone is excreted in the bile.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Nonclinical toxicity studies to determine the potential of progesterone vaginal insert to cause carcinogenicity or mutagenicity have not been performed. The effect of progesterone vaginal insert on fertility has not been evaluated in animals.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Luteal Supplementation During Assisted Reproductive Treatment Study
A randomized, open-label, active-controlled study evaluated the efficacy of 10 weeks of treatment with two different daily dosing regimens of progesterone vaginal insert (100 mg twice daily and 100 mg three times daily) for support of implantation and early pregnancy in infertile women participating in an Assisted Reproductive Technology treatment program.
Efficacy was assessed on the endpoint of ongoing pregnancies, defined as the presence of at least one fetal heartbeat seen on ultrasound at 6 weeks post-embryo transfer. The study randomized to progesterone vaginal insert 808 infertile women (74.9% White; 10.3% Hispanic, 5.4% Black, 5% Asian, and 4.6% Other) between 19 and 42 years of age (mean age 33) who had a body mass index <34 kg/m2 at screening.
The ongoing pregnancy rates for subjects treated with both dosing regimens of progesterone vaginal insert were non-inferior (lower bounds of the 95% confidence interval of the difference between progesterone vaginal insert and the active comparator excluded a difference greater than 10%) to the ongoing pregnancy rate for subjects treated with the active comparator. The results of this study are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Ongoing Pregnancy Rates* in Patients Receiving Progesterone Vaginal Insert for Luteal Supplementation and Early Pregnancy While in an Assisted Reproductive Technology Treatment Program
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg twice
daily
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg three times
daily
Number of subjects 404 404 Ongoing pregnancy: n (%) 156 (39%) 171 (42%) 95% Confidence Interval of pregnancy rate [33.8, 43.6] [37.5, 47.3] Pregnancy rate percentage difference between progesterone vaginal insert and comparator -3.6% 0.1% 95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator [-10.3, 3.2] [-6.7, 6.9] * Ongoing pregnancy defined as the presence of at least one fetal heartbeat seen on ultrasound at 6 weeks post-embryo transfer.
Subjects participating in the study were stratified at randomization by age and ovarian reserve (as measured by serum FSH levels). The ongoing pregnancy rates for these subgroups are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Ongoing Pregnancy Rates in Age- and Ovarian Reserve-Defined Subgroups Receiving Progesterone Vaginal Insert for Luteal Supplementation and Early Pregnancy While in an Assisted Reproductive Technology Treatment Program
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg twice
daily
Progesterone vaginal insert
100 mg three times
daily
Subjects age < 35 years (N)
Ongoing pregnancy: n (%)
Pregnancy rate percentage difference between progesterone vaginal insert and comparator
95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator
247
111 (45%)
0.5%
[-8.3, 9.3]
247
117 (47%)
2.9%
[-5.9, 11.7]
Subjects 35 to 42 years of age (N)
Ongoing pregnancy: n (%)
Pregnancy rate percentage difference between progesterone vaginal insert and comparator
95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator
157
45 (28%)
-10.1%
[-20.3, 0.3]
157
54 (34%)
-4.4%
[-14.9, 6.3]
Subjects with FSH < 10 IU/L (N)
Ongoing pregnancy: n (%)
Pregnancy rate percentage difference between progesterone vaginal insert and comparator
95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator
350
140 (40%)
-2.0%
[-9.3, 5.3]
347
150 (43%)
1.2%
[-6.1, 8.5]
Subjects with FSH between 10 and 15 IU/L (N)
Ongoing pregnancy: n (%)
Pregnancy rate percentage difference between progesterone vaginal insert and comparator
95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator
46
16 (35%)
-12.2%
[-31.0, 7.7]
51
20 (39%)
-7.7%
[-26.6, 11.6]
In subjects under the age of 35 or with serum FSH levels less than 10 IU/L, results from both dosing regimens were non-inferior to the results from the comparator with respect to ongoing pregnancy rates. In women age 35 and older and in women with serum FSH levels between 10 and 15 IU/L, the results with respect to ongoing pregnancy rates for both dosing regimens of progesterone vaginal insert did not reach the criteria for non-inferiority.
Subjects who became pregnant received study medication for a total of 10 weeks. Patients over 34 kg/m2 were not studied. The efficacy of progesterone vaginal insert in this patient group is unknown.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each progesterone vaginal insert is a yellowish-white oblong-shaped insert debossed with "201" on one side and "XI" on the other side. Each progesterone vaginal insert, 100 mg, is packed individually in a sealed foil pouch. These pouches are available in cartons packed:
-
21 vaginal inserts with 21 disposable vaginal applicators (NDC: 70700-201-70)
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (17.4).
17.1 Vaginal Bleeding
Inform patients of the importance of reporting irregular vaginal bleeding to their doctor as soon as possible.
17.2 Common Adverse Reactions with Progesterone
Inform patients of the possible side effects of progesterone therapy such as headaches, breast tenderness, bloating, mood swings, irritability, and drowsiness.
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
IMPORTANT: For Vaginal Use Only.
Read the patient information that comes with progesterone vaginal insert before you start to use it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. Your doctor may do a physical exam before prescribing progesterone vaginal insert.
What is progesterone vaginal insert?
Progesterone vaginal insert is a vaginal insert that contains the hormone progesterone. Progesterone vaginal insert is for women who need extra progesterone while undergoing treatment in an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program.
Progesterone is one of the hormones essential for helping you to become and to stay pregnant. If you are undergoing ART treatment, your doctor may prescribe progesterone vaginal insert to provide the progesterone your body needs.
Who should not use progesterone vaginal insert?
Do not use progesterone vaginal insert if you:
-
Are allergic to anything in progesterone vaginal insert. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients.
-
Have unusual vaginal bleeding that has not been evaluated by a doctor.
-
Currently have or have had liver problems.
-
Have or have had blood clots in the legs, lungs, eyes, or elsewhere in your body.
Progesterone vaginal insert may not be right for you. Before starting progesterone vaginal insert, tell your doctor about all your health problems.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vaginal products, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Some medicines may affect progesterone vaginal insert.
Know what medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines to show to the doctor and
pharmacist.
How should I use progesterone vaginal insert?
-
Use progesterone vaginal insert exactly as prescribed. The usual dose of progesterone vaginal insert is one insert placed in your vagina 2 to 3 times a day for up to a total of 10 weeks, unless your healthcare provider advises otherwise.
-
Place a progesterone insert in your vagina with the disposable applicator provided.
Follow the steps below:
1. Unwrap the applicator.
2. Put one insert in the space provided at the end of the applicator. The insert should fit snugly and not fall out.
3. Place applicator with the insert into the vagina while you are standing, sitting, or when lying on your back with your knees bent. Gently place the thin end of the applicator well into the vagina.
4. Push the plunger to release the insert.
5. Remove the applicator and throw it away in the trash.
Other information for using progesterone vaginal insert
-
If you forget a dose of progesterone vaginal insert, take the dose as soon as you remember, but do not use more than your daily dose.
-
Call your doctor if you use too much progesterone vaginal insert.
-
Do not use any other vaginal products when you are using progesterone vaginal insert.
What are the possible side effects of progesterone vaginal insert?
Common side effects seen with ART and progesterone vaginal insert included pelvic pain after surgery, abdominal pain, nausea, and swollen ovaries (ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome).
Other reported side effects included abdominal bloating, headache, urinary infections, uterine cramping, constipation, vomiting, tiredness, and vaginal bleeding.
Vaginal products with progesterone may also cause vaginal irritation, burning, and discharge.
Serious Risks of Progesterone
Progesterone can increase your chance of getting blood clots. Blood clots can be serious and lead to death.
Serious blood clots include those in the:
-
legs (thrombophlebitis)
-
lungs (pulmonary embolus)
-
eyes (blindness)
-
heart (heart attack)
-
brain (stroke)
Call your doctor or get medical help right away if you have:
-
persistent pain in the lower leg (calf)
-
sudden shortness of breath
-
coughing up blood
-
sudden blindness, partial or complete
-
severe chest pain
-
sudden, severe headache, vomiting, dizziness, or fainting
-
weakness in an arm or leg, or trouble speaking
-
yellowing of the skin and/or white of the eyes indicating possible liver problem
Other risks of progesterone use include:
-
headache
-
breast tenderness
-
bloating or fluid retention
-
mood swings and depression
-
irritability
-
drowsiness
Call your doctor immediately if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
These are not all the side effects with progesterone vaginal insert. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I store progesterone vaginal insert?
-
Store progesterone vaginal insert at room temperature, 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
-
Do not use progesterone vaginal insert after the expiration date that is printed on the carton.
-
Keep progesterone vaginal insert and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about progesterone vaginal insert
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use progesterone vaginal insert for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give progesterone vaginal insert to other women, even if they have the same condition as you do. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about progesterone vaginal insert. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about progesterone vaginal insert that was written for healthcare professionals. For more information, call Xiromed, LLC at 844-XIROMED (844-947-6633).
What are the ingredients in progesterone vaginal insert?
Active Ingredient: progesterone
Inactive Ingredients: adipic acid, colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone, pregelatinized starch, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
Manufactured for:
Xiromed, LLC
Florham Park, NJ 07932
Made in Spain
PI-201-02
Revised: 11/2025
-
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PROGESTERONE VAGINAL INSERT
progesterone insertProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70700-201 Route of Administration VAGINAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROGESTERONE (UNII: 4G7DS2Q64Y) (PROGESTERONE - UNII:4G7DS2Q64Y) PROGESTERONE 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) ADIPIC ACID (UNII: 76A0JE0FKJ) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (yellowish-white) Score Shape OVAL (Oblong) Size Flavor Imprint Code 201;XI Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70700-201-70 1 in 1 CARTON 09/23/2025 1 NDC: 70700-201-69 21 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC: 70700-201-68 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA218391 09/23/2025 Labeler - XIROMED, LLC (080228637) Registrant - XIROMED PHARMA ESPANA, S.L. (468835741) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Laboratorios León Farma, S.A. 467782459 analysis(70700-201) , label(70700-201) , manufacture(70700-201) , pack(70700-201)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
