COPIKTRA- duvelisib capsule
Copiktra by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Copiktra by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Verastem, Inc., Packaging Coordinators, Inc., AMRI Rensselaer, Inc., Catalent CTS, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use COPIKTRA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for COPIKTRA.
COPIKTRA (duvelisib), capsules for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: INFECTIONS, DIARRHEA OR COLITIS, CUTANEOUS REACTIONS, and PNEUMONITIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Fatal and/or serious infections occurred in 31% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Withhold COPIKTRA if infection is suspected. (5.1)
- Fatal and/or serious diarrhea or colitis occurred in 18% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for the development of severe diarrhea or colitis. Withhold COPIKTRA. (5.2)
- Fatal and/or serious cutaneous reactions occurred in 5% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Withhold COPIKTRA. (5.3)
- Fatal and/or serious pneumonitis occurred in 5% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and interstitial infiltrates. Withhold COPIKTRA. (5.4)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
COPIKTRA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) after at least two prior therapies. (1.1).
- Relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) after at least two prior systemic therapies.
(1.2).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 25 mg, 15 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are diarrhea or colitis, neutropenia, rash, fatigue, pyrexia, cough, nausea, upper respiratory infection, pneumonia, musculoskeletal pain, and anemia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Verastem, Inc. (Verastem) at 877-7RXVSTM or 1-877-779-8786, or U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A inducers: Avoid co-administration with strong CYP3A inducers. (7.1)
- CYP3A inhibitors: Monitor for COPIKTRA toxicities when co-administered with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Reduce COPIKTRA dose to 15 mg twice daily when co-administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. (7.1)
- CYP3A substrates: Monitor for signs of toxicities when co-administering COPIKTRA with sensitive CYP3A substrates. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: INFECTIONS, DIARRHEA OR COLITIS, CUTANEOUS REACTIONS, and PNEUMONITIS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL)
1.2 Follicular Lymphoma (FL)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing
2.2 Recommended Prophylaxis
2.3 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.4 Dose Modification for Concomitant Use with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infections
5.2 Diarrhea or Colitis
5.3 Cutaneous Reactions
5.4 Pneumonitis
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
5.6 Neutropenia
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on COPIKTRA
7.2 Effects of COPIKTRA on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL EFFICACY
14.1 Efficacy in Relapsed or Refractory CLL/SLL
14.2 Efficacy in Relapsed or Refractory FL
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: INFECTIONS, DIARRHEA OR COLITIS, CUTANEOUS REACTIONS, and PNEUMONITIS
- Fatal and/or serious infections occurred in 31% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Withhold COPIKTRA if infection is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Fatal and/or serious diarrhea or colitis occurred in 18% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for the development of severe diarrhea or colitis. Withhold COPIKTRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Fatal and/or serious cutaneous reactions occurred in 5% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Withhold COPIKTRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Fatal and/or serious pneumonitis occurred in 5% of COPIKTRA-treated patients. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and interstitial infiltrates. Withhold COPIKTRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL)
COPIKTRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory CLL or SLL after at least two prior therapies.
1.2 Follicular Lymphoma (FL)
COPIKTRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory FL after at least two prior systemic therapies.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]; continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing
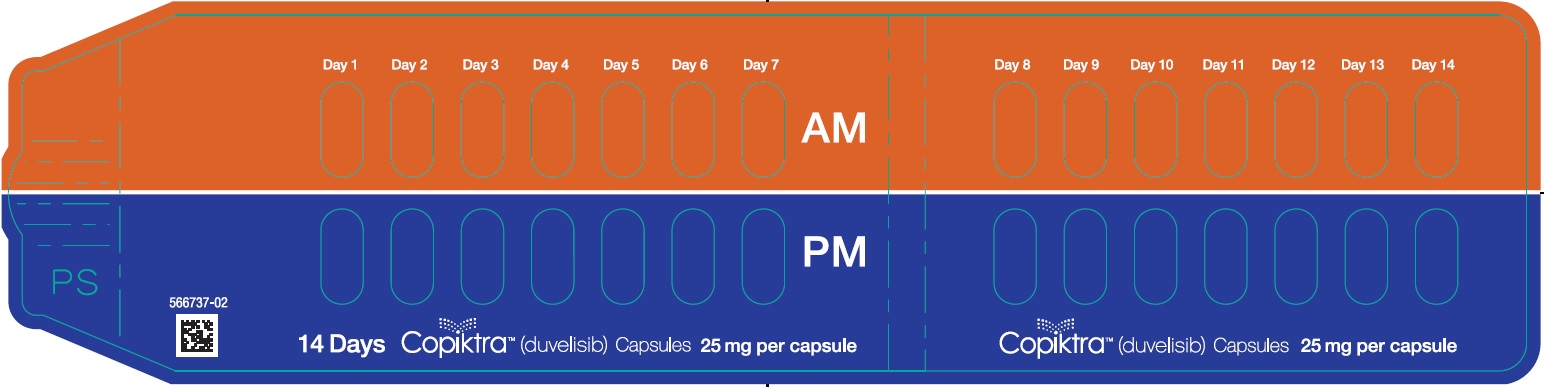
The recommended dose of COPIKTRA is 25 mg administered as oral capsules twice daily (BID) with or without food. A cycle consists of 28 days. The capsules should be swallowed whole. Advise patients not to open, break, or chew the capsules.
Advise patients that if a dose is missed by fewer than 6 hours, to take the missed dose right away and take the next dose as usual. If a dose is missed by more than 6 hours, advise patients to wait and take the next dose at the usual time.
2.2 Recommended Prophylaxis
Provide prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii (PJP) during treatment with COPIKTRA. Following completion of COPIKTRA treatment, continue PJP prophylaxis until the absolute CD4+ T cell count is greater than 200 cells/µL.
Withhold COPIKTRA in patients with suspected PJP of any grade, and discontinue if PJP is confirmed.
Consider prophylactic antivirals during COPIKTRA treatment to prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection including CMV reactivation.
2.3 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Manage toxicities per Table 1 with dose reduction, treatment hold, or discontinuation of COPIKTRA.
Table 1. COPIKTRA Dose Modifications and Toxicity Management Abbreviations: ALT = alanine aminotransferase; ANC = absolute neutrophil count; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; CMV = cytomegalovirus; DRESS = drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic systems; PCR = polymerase chain reaction; PJP = Pneumocystis jirovecii; pneumonia; SJS = Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis; ULN = upper limit of normal Toxicity Adverse Reaction Grade Recommended Management Nonhematologic Adverse Reactions Infections Grade 3 or higher infection - Withhold COPIKTRA until resolved
- Resume at the same or reduced dose (see Table 2)
Clinical CMV infection or viremia (positive PCR or antigen test) - Withhold COPIKTRA until resolved
- Resume at the same or reduced dose (see Table 2)
- If COPIKTRA is resumed, monitor patients for CMV reactivation (by PCR or antigen test) at least monthly
PJP - For suspected PJP, withhold COPIKTRA until evaluated
- For confirmed PJP, discontinue COPIKTRA
Non-infectious Diarrhea or colitis Mild/moderate diarrhea (Grade 1-2, up to 6 stools per day over baseline) and responsive to antidiarrheal agents,
OR
Asymptomatic (Grade 1) colitis- No change in dose
- Initiate supportive therapy with antidiarrheal agents as appropriate
- Monitor at least weekly until resolved
Mild/moderate diarrhea (Grade 1-2, up to 6 stools per day over baseline) and unresponsive to antidiarrheal agents - Withhold COPIKTRA until resolved
- Initiate supportive therapy with enteric acting steroids (e.g., budesonide)
- Monitor at least weekly until resolved
- Resume at a reduced dose (see Table 2)
Abdominal pain, stool with mucus or blood, change in bowel habits, peritoneal signs,
OR
Severe diarrhea (Grade 3, >6 stools per day over baseline)- Withhold COPIKTRA until resolved
- Initiate supportive therapy with enteric acting steroids (e.g., budesonide) or systemic steroids
- Monitor at least weekly until resolved
- Resume at a reduced dose (see Table 2)
- For recurrent Grade 3 diarrhea or recurrent colitis of any grade, discontinue COPIKTRA
Life-threatening - Discontinue COPIKTRA
Cutaneous reactions Grade 1-2 - No change in dose
- Initiate supportive care with emollients, anti-histamines (for pruritus), or topical steroids
- Monitor closely
Grade 3 - Withhold COPIKTRA until resolved
- Initiate supportive care with emollients, anti-histamines (for pruritus), or topical steroids
- Monitor at least weekly until resolved
- Resume at reduced dose (see Table 2)
- If severe cutaneous reaction does not improve, worsens, or recurs, discontinue COPIKTRA
Life-threatening - Discontinue COPIKTRA
SJS, TEN, DRESS (any grade) - Discontinue COPIKTRA
Pneumonitis without suspected infectious cause Moderate (Grade 2) symptomatic pneumonitis - Withhold COPIKTRA
- Treat with systemic steroid therapy
- If pneumonitis recovers to Grade 0 or 1, COPIKTRA may be resumed at reduced dose (see Table 2)
- If non-infectious pneumonitis recurs or patient does not respond to steroid therapy, discontinue COPIKTRA
Severe (Grade 3) or life-threatening pneumonitis - Discontinue COPIKTRA
- Treat with systemic steroid therapy
ALT/AST elevation 3 to 5 × upper limit of normal (ULN) (Grade 2) - Maintain COPIKTRA dose
- Monitor at least weekly until return to < 3 × ULN
> 5 to 20 × ULN (Grade 3) - Withhold COPIKTRA and monitor at least weekly until return to < 3 × ULN
- Resume COPIKTRA at same dose (first occurrence) or at a reduced dose for subsequent occurrence (see Table 2)
> 20 × ULN (Grade 4) - Discontinue COPIKTRA
Hematologic Adverse Reactions Neutropenia Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) 0.5 to 1.0 Gi/L - Maintain COPIKTRA dose
- Monitor ANC at least weekly
ANC less than 0.5 Gi/L - Withhold COPIKTRA.
- Monitor ANC until > 0.5 Gi/L
- Resume COPIKTRA at same dose (first occurrence) or at a reduced dose for subsequent occurrence (see Table 2)
Thrombocytopenia Platelet count 25 to < 50 Gi/L (Grade 3) with Grade 1 bleeding - No change in dose
- Monitor platelet counts at least weekly
Platelet count 25 to < 50 Gi/L (Grade 3) with Grade 2 bleeding
or
Platelet count < 25 Gi/L (Grade 4)- Withhold COPIKTRA
- Monitor platelet counts until ≥ 25 Gi/L and resolution of bleeding (if applicable)
- Resume COPIKTRA at same dose (first occurrence) or resume at a reduced dose for subsequent occurrence (see Table 2)
Recommended dose modification levels for COPIKTRA are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Dose Modification Levels Dose Level Dose Initial Dose 25 mg twice daily Dose Reduction 15 mg twice daily Subsequent Dose Modification Discontinue COPIKTRA if patient is unable to tolerate 15 mg twice daily. 2.4 Dose Modification for Concomitant Use with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Reduce COPIKTRA dose to 15 mg twice daily when co-administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infections
Serious, including fatal (18/442; 4%), infections occurred in 31% of patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442). The most common serious infections were pneumonia, sepsis, and lower respiratory infections. Median time to onset of any grade infection was 3 months (range: 1 day to 32 months), with 75% of cases occurring within 6 months.
Treat infections prior to initiation of COPIKTRA. Advise patients to report any new or worsening signs and symptoms of infection. For grade 3 or higher infection, withhold COPIKTRA until infection has resolved. Resume COPIKTRA at the same or reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Serious, including fatal, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) occurred in 1% of patients taking COPIKTRA. Provide prophylaxis for PJP during treatment with COPIKTRA. Following completion of COPIKTRA treatment, continue PJP prophylaxis until the absolute CD4+ T cell count is greater than 200 cells/µL. Withhold COPIKTRA in patients with suspected PJP of any grade, and permanently discontinue if PJP is confirmed.
CMV reactivation/infection occurred in 1% of patients taking COPIKTRA. Consider prophylactic antivirals during COPIKTRA treatment to prevent CMV infection including CMV reactivation. For clinical CMV infection or viremia, withhold COPIKTRA until infection or viremia resolves. If COPIKTRA is resumed, administer the same or reduced dose and monitor patients for CMV reactivation by PCR or antigen test at least monthly [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Diarrhea or Colitis
Serious, including fatal (1/442; <1%), diarrhea or colitis occurred in 18% of patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442). The median time to onset of any grade diarrhea or colitis was 4 months (range: 1 day to 33 months), with 75% of cases occurring by 8 months. The median event duration was 0.5 months (range: 1 day to 29 months; 75th percentile: 1 month).
Advise patients to report any new or worsening diarrhea. For non-infectious diarrhea or colitis, follow the guidelines below:
For patients presenting with mild or moderate diarrhea (Grade 1-2) (i.e. up to 6 stools per day over baseline) or asymptomatic (Grade 1) colitis, initiate supportive care with antidiarrheal agents as appropriate, continue COPIKTRA at the current dose, and monitor the patient at least weekly until the event resolves. If the diarrhea is unresponsive to antidiarrheal therapy, withhold COPIKTRA and initiate supportive therapy with enteric acting steroids (e.g. budesonide). Monitor the patient at least weekly. Upon resolution of the diarrhea, consider restarting COPIKTRA at a reduced dose.
For patients presenting with abdominal pain, stool with mucus or blood, change in bowel habits, peritoneal signs, or with severe diarrhea (Grade 3) (i.e. > 6 stools per day over baseline) withhold COPIKTRA and initiate supportive therapy with enteric acting steroids (e.g. budesonide) or systemic steroids. A diagnostic work-up to determine etiology, including colonoscopy, should be performed. Monitor at least weekly. Upon resolution of the diarrhea or colitis, restart COPIKTRA at a reduced dose. For recurrent Grade 3 diarrhea or recurrent colitis of any grade, discontinue COPIKTRA. Discontinue COPIKTRA for life-threatening diarrhea or colitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Cutaneous Reactions
Serious, including fatal (2/442; < 1%), cutaneous reactions occurred in 5% of patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442). Fatal cases included drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Median time to onset of any grade cutaneous reaction was 3 months (range: 1 day to 29 months, 75th percentile: 6 months), with a median event duration of 1 month (range: 1 day to 37 months, 75th percentile: 2 months).
Presenting features for the serious events were primarily described as pruritic, erythematous, or maculo-papular. Less common presenting features include exanthem, desquamation, erythroderma, skin exfoliation, keratinocyte necrosis, and papular rash. Advise patients to report any new or worsening cutaneous reactions. Review all concomitant medications and discontinue any medications potentially contributing to the event. For patients presenting with mild or moderate (Grade 1-2) cutaneous reactions, continue COPIKTRA at the current dose, initiate supportive care with emollients, anti-histamines (for pruritus), or topical steroids, and monitor the patient closely. Withhold COPIKTRA for severe (Grade 3) cutaneous reaction until resolution. Initiate supportive care with steroids (topical or systemic) or anti-histamines (for pruritus). Monitor at least weekly until resolved. Upon resolution of the event, restart COPIKTRA at a reduced dose. Discontinue COPIKTRA if severe cutaneous reaction does not improve, worsens, or recurs. For life-threatening cutaneous reactions, discontinue COPIKTRA. In patients with SJS, TEN, or DRESS of any grade, discontinue COPIKTRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Pneumonitis
Serious, including fatal (1/442; < 1%), pneumonitis without an apparent infectious cause occurred in 5% of patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442). Median time to onset of any grade pneumonitis was 4 months (range: 9 days to 27 months), with 75% of cases occurring within 9 months). The median event duration was 1 month, with 75% of cases resolving by 2 months.
Withhold COPIKTRA in patients who present with new or progressive pulmonary signs and symptoms such as cough, dyspnea, hypoxia, interstitial infiltrates on a radiologic exam, or a decline by more than 5% in oxygen saturation and evaluate for etiology. If the pneumonitis is infectious, patients may be restarted on COPIKTRA at the previous dose once the infection, pulmonary signs and symptoms resolve. For moderate non-infectious pneumonitis (Grade 2), treat with systemic corticosteroids, and resume COPIKTRA at a reduced dose upon resolution. If non-infectious pneumonitis recurs or does not respond to steroid therapy, discontinue COPIKTRA. For severe or life-threatening non-infectious pneumonitis, discontinue COPIKTRA and treat with systemic steroids [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
Grade 3 and 4 ALT and/or AST elevation developed in 8% and 2%, respectively, in patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442). Two percent of patients had both an ALT or AST greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN. Median time to onset of any grade transaminase elevation was 2 months (range: 3 days to 26 months), with a median event duration of 1 month (range: 1 day to 16 months).
Monitor hepatic function during treatment with COPIKTRA. For Grade 2 ALT/AST elevation (greater than 3 to 5 × ULN), maintain COPIKTRA dose and monitor at least weekly until return to less than 3 × ULN. For Grade 3 ALT/AST elevation (greater than 5 to 20 × ULN), withhold COPIKTRA and monitor at least weekly until return to less than 3 × ULN. Resume COPIKTRA at the same dose (first occurrence) or at a reduced dose for subsequent occurrence. For grade 4 ALT/AST elevation (greater than 20 × ULN) discontinue COPIKTRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Neutropenia
Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia occurred in 42% of patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID (N = 442), with Grade 4 neutropenia occurring in 24% of all patients. The median time to onset of Grade ≥ 3 neutropenia was 2 months (range: 3 days to 31 months), with 75% of cases occurring within 4 months.
Monitor neutrophil counts at least every 2 weeks for the first 2 months of COPIKTRA therapy, and at least weekly in patients with neutrophil counts < 1.0 Gi/L (Grade 3-4). Withhold COPIKTRA in patients presenting with neutrophil counts < 0.5 Gi/L (Grade 4). Monitor until ANC is > 0.5 Gi/L, resume COPIKTRA at same dose for the first occurrence or a reduced dose for subsequent occurrence [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, COPIKTRA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of duvelisib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including embryo-fetal mortality (resorptions, post-implantation loss, and decreased viable fetuses), alterations to growth (lower fetal weights) and structural abnormalities (malformations) at maternal doses approximately 10 times and 39 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 25 mg BID in rats and rabbits, respectively. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1, 12.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been associated with COPIKTRA in clinical trials and are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Diarrhea or Colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely variable conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Summary of Clinical Trial Experience in B-cell Malignancies
The data described below reflect exposure to COPIKTRA in two single-arm, open-label clinical trials, one open-label extension clinical trial, and one randomized, open-label, actively controlled clinical trial totaling 442 patients with previously treated hematologic malignancies primarily including CLL/SLL (69%) and FL (22%). Patients were treated with COPIKTRA 25 mg BID until unacceptable toxicity or progressive disease. The median duration of exposure was 9 months (range: 0.1 to 53 months), with 36% (160/442) of patients having at least 12 months of exposure.
For the 442 patients, the median age was 67 years (range: 30 to 90 years), 65% were male, 92% were White, and 93% had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 to 1. Patients had a median of 2 prior therapies. The trials required hepatic transaminases at least ≤ 3 times upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 times ULN, and serum creatinine ≤ 1.5 times ULN. Patients were excluded for prior exposure to a PI3K inhibitor within 4 weeks.
Fatal adverse reactions within 30 days of the last dose occurred in 36 patients (8%) treated with COPIKTRA 25 mg BID.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 289 patients (65%). The most frequent serious adverse reactions that occurred were infection (31%), diarrhea or colitis (18%), pneumonia (17%), rash (5%), and pneumonitis (5%).
Adverse reactions resulted in treatment discontinuation in 156 patients (35%), most often due to diarrhea or colitis, infection, and rash. COPIKTRA was dose reduced in 104 patients (24%) due to adverse reactions, most often due to diarrhea or colitis and transaminase elevation. The median time to first dose modification or discontinuation was 4 months (range: 0.1 to 27 months), with 75% of patients having their first dose modification or discontinuation within 7 months.
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 3 summarizes common adverse reactions in patients receiving COPIKTRA 25 mg BID, and Table 4 summarizes the treatment-emergent laboratory abnormalities. The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea or colitis, neutropenia, rash, fatigue, pyrexia, cough, nausea, upper respiratory infection, pneumonia, musculoskeletal pain, and anemia.
Table 3. Common Adverse Reactions (≥ 10% Incidence) in Patients with B-cell Malignancies Receiving COPIKTRA † Grouped term for reactions with multiple preferred terms
a Diarrhea or colitis includes the preferred terms: colitis, enterocolitis, colitis microscopic, colitis ulcerative, diarrhea, diarrhea hemorrhagic
b Transaminase elevation includes the preferred terms: alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, transaminases increased, hypertransaminasemia, hepatocellular injury, hepatotoxicity
c Pneumonia includes the preferred terms: All preferred terms containing "pneumonia" except for "pneumonia aspiration"; bronchopneumonia, bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
d Rash includes the preferred terms: dermatitis (including allergic, exfoliative, perivascular), erythema (including multiforme), rash (including exfoliative, erythematous, follicular, generalized, macular & papular, pruritic, pustular), toxic epidermal necrolysis and toxic skin eruption, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, drug eruption, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Adverse ReactionsCOPIKTRA 25 mg BID
(N = 442)Any Grade
n (%)Grade ≥ 3
n (%)Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Neutropenia †
Anemia †
Thrombocytopenia †
151 (34)
90 (20)
74 (17)
132 (30)
48 (11)
46 (10)Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea or colitis †a
Nausea †
Abdominal pain
Vomiting
Mucositis
Constipation
222 (50)
104 (24)
78 (18)
69 (16)
61 (14)
57 (13)
101 (23)
4 (< 1)
9 (2)
6 (1)
6 (1)
1 (< 1)General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue †
Pyrexia
126 (29)
115 (26)
22 (5)
7 (2)Hepatobiliary disorders
Transaminase elevation †b
67 (15)
34 (8)Infections and infestations
Upper respiratory tract infection †
Pneumonia †c
Lower respiratory tract infection †
94 (21)
91 (21)
46 (10)
2 (< 1)
67 (15)
11 (3)Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Decreased appetite
Edema †
Hypokalemia †
63 (14)
60 (14)
45 (10)
2 (< 1)
6 (1)
17 (4)Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Musculoskeletal pain †
Arthralgia
90 (20)
46 (10)
6 (1)
1 (< 1)Nervous system disorders
Headache †
55 (12)
1 (< 1)Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Cough †
Dyspnea †
111 (25)
52 (12)
2 (< 1)
8 (2)Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash †d
136 (31)
41 (9)Grade 4 adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% of recipients of COPIKTRA included neutropenia (18%), thrombocytopenia (6%), sepsis (3%), hypokalemia and increased lipase (2% each), and pneumonia and pneumonitis (2% each).
Table 4. Most Common New or Worsening Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 20% Any Grade) in Patients with B-cell Malignancies Receiving COPIKTRA a Includes laboratory abnormalities that are new or worsening in grade or with worsening from baseline unknown.
b Percentages are based on number of patients with at least one post-baseline assessment; not all patients were evaluable.
Laboratory ParameteraCOPIKTRA 25 mg BID
(N = 442)Any Grade
n (%)bGrade ≥ 3
n (%)bHematology abnormalities
Neutropenia
Anemia
Thrombocytopenia
Lymphocytosis
Leukopenia
Lymphopenia
276 (63)
198 (45)
170 (39)
132 (30)
129 (29)
90 (21)
184 (42)
66 (15)
65 (15)
92 (21)
34 (8)
39 (9)Chemistry abnormalities
ALT increased
AST increased
Lipase increased
Hypophosphatemia
ALP increased
Serum amylase increased
Hyponatremia
Hyperkalemia
Hypoalbuminemia
Creatinine increased
Hypocalcemia
177 (40)
163 (37)
133 (36)
136 (31)
128 (29)
101 (28)
116 (27)
114 (26)
111 (25)
106 (24)
100 (23)
34 (8)
24 (6)
58 (16)
23 (5)
7 (2)
16 (4)
30 (7)
14 (3)
7 (2)
7 (2)
12 (3)Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities developing in ≥ 2% of patients included neutropenia (24%), thrombocytopenia (7%), lipase increase (4%), lymphocytopenia (3%), and leukopenia (2%).
Summary of Clinical Trial Experience in CLL/SLL
Study 1
The safety data below reflects exposure in a randomized, open-label, actively controlled clinical trial for adult patients with CLL or SLL who received at least one prior therapy. Of 313 patients treated, 158 received COPIKTRA monotherapy and 155 received ofatumumab. The 442-patient safety analysis above includes patients from Study 1.
COPIKTRA was administered at 25 mg BID in 28-day treatment cycles until unacceptable toxicity or progressive disease. The comparator group received 12 doses of ofatumumab with an initial dose of 300 mg intravenous (IV) on Day 1 followed a week later by 7 weekly doses of 2000 mg IV, followed 4 weeks later by 2000 mg IV every 4 weeks for 4 doses.
In the total study population, the median age was 69 years (range: 39 to 90 years), 60% were male, 92% were White, and 91% had an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1. Patients had a median of 2 prior therapies, with 61% of patients having received 2 or more prior therapies. The trial required a hemoglobin ≥ 8 g/dL and platelets ≥ 10,000 µL with or without transfusion support, hepatic transaminases ≤ 3 times upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 times ULN, and serum creatinine ≤ 2 times ULN. The trial excluded patients with prior autologous transplant within 6 months or allogeneic transplant, prior exposure to a PI3K inhibitor or a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, and uncontrolled autoimmune hemolytic anemia or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
During randomized treatment, the median duration of exposure to COPIKTRA was 11.6 months with 72% (114/158) exposed for ≥ 6 months and 49% (77/158) exposed for ≥ 1 year. The median duration of exposure to ofatumumab was 5.3 months, with 77% (120/155) receiving at least 10 of 12 doses.
Fatal adverse reactions within 30 days of the last dose occurred in 12% (19/158) of patients treated with COPIKTRA and in 4% (7/155) of patients treated with ofatumumab.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 73% (115/158) of patients treated with COPIKTRA and most often involved infection (38% of patients; 60/158) and diarrhea or colitis (23% of patients; 36/158).
COPIKTRA was discontinued in 57 patients (36%), most often due to diarrhea or colitis, infection, and rash. COPIKTRA was dose reduced in 46 patients (29%) due to adverse reactions, most often due to diarrhea or colitis and rash.
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 5 summarizes selected adverse reactions in Study 1, and Table 6 summarizes treatment-emergent laboratory abnormalities. The most common adverse reactions with COPIKTRA (reported in ≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea or colitis, neutropenia, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, rash, fatigue, nausea, anemia and cough.
Table 5. Common Nonhematologic Adverse Reactions (≥ 10% Incidence) in Patients with CLL/SLL Receiving COPIKTRA (Study 1) Grades were obtained per CTCAE version 4.03.
† Grouped term for reactions with multiple preferred terms
a Diarrhea or colitis includes the preferred terms: colitis, enterocolitis, colitis microscopic, colitis ulcerative, diarrhea
b Pneumonia includes the preferred terms: All preferred term containing "pneumonia" except for "pneumonia aspiration"; bronchopneumonia, bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
c Rash includes the preferred terms: dermatitis (including allergic, exfoliative, perivascular), erythema (including multiforme), rash (including exfoliative, erythematous, follicular, generalized, macular & papular, pruritic, pustular), toxic skin eruption, drug eruption
d Transaminase elevation includes the preferred terms: alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, transaminases increased, hepatotoxicityAdverse Reactions COPIKTRA
N = 158Ofatumumab
N = 155Any Grade (%) Grade ≥ 3 (%) Any Grade (%) Grade ≥ 3 (%) Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea or colitis †a
Nausea †
Constipation
Abdominal pain
Vomiting
57
23
17
16
15
25
0
<1
3
0
14
11
8
7
7
2
0
0
0
0General disorders and administration site conditions
Pyrexia
Fatigue †
29
25
3
4
10
23
<1
4Hepatobiliary disorders
Transaminase elevation †d
11
6
4
<1Infections and infestations
Upper respiratory tract infection †
Pneumonia †b
Lower respiratory tract infection †
28
27
18
0
22
4
16
8
10
<1
3
1Investigations
Weight decreased
11
0
2
0Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Decreased appetite
Edema †
13
11
0
1
3
5
<1
0Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Musculoskeletal pain †
17
1
12
<1Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Cough †
Dyspnea
23
12
1
3
16
7
0
0Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash †c
27
11
15
<1Table 6. Most Common New or Worsening Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 20% Any Grade) in Patients with CLL/SLL Receiving COPIKTRA (Study 1) Grades were obtained per CTCAE version 4.03. Laboratory Parameter COPIKTRA
N = 158Ofatumumab
N = 155Any Grade (%) Grade ≥ 3 (%) Any Grade (%) Grade ≥ 3 (%) Hematology abnormalities
Neutropenia
Anemia
Thrombocytopenia
Lymphocytosis
67
55
43
30
49
20
16
22
52
36
34
11
37
7
8
6Chemistry abnormalities
ALT increased
Lipase increased
AST increased
Phosphate decreased
Hyperkalemia
Hyponatremia
Amylase increased
Hypoalbuminemia
Creatinine increased
Alkaline phosphatase increased
Hypocalcemia
Hypokalemia
42
37
36
34
31
31
31
31
29
27
25
20
7
12
3
3
4
7
5
2
1
0
1
8
12
15
14
20
24
18
10
15
31
14
17
8
0
3
1
3
1
3
1
1
0
0
1
0Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities that developed in ≥ 2% of COPIKTRA treated patients included neutropenia (32%), thrombocytopenia (6%), lymphopenia (3%), and hypokalemia (2%).
The data above are not an adequate basis for comparison of rates between the study drug and the active control.
Summary of Clinical Trial Experience in FL
The data described below reflect the exposure to COPIKTRA 25 mg BID in 96 patients with relapsed or refractory FL. These patients were included in the 442-patient safety analysis presented above. The median duration of treatment was 24 weeks, with 46% of patients exposed for ≥ 6 months and 19% exposed for ≥ 1 year.
The median age was 64 years (range: 30 to 82 years), and 93% had an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1. Patients had a median of 3 prior systemic therapies.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 58% and most often involved diarrhea or colitis, pneumonia, renal insufficiency, rash, and sepsis. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20% of patients) were diarrhea or colitis, nausea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, neutropenia, cough, anemia, pyrexia, headache, mucositis, abdominal pain, vomiting, transaminase elevation, and thrombocytopenia.
Adverse reactions resulted in COPIKTRA discontinuation in 29% of patients, most often due to diarrhea or colitis and rash. COPIKTRA was dose reduced in 23% due to adverse reactions, most often due to transaminase elevation, diarrhea or colitis, lipase increased, and infection.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on COPIKTRA
CYP3A Inducers
Co-administration with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases duvelisib area under the curve (AUC) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce COPIKTRA efficacy. Avoid co-administration of COPIKTRA with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
CYP3A Inhibitors
Co-administration with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases duvelisib AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of COPIKTRA toxicities. Reduce COPIKTRA dose to 15 mg BID when co-administered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
7.2 Effects of COPIKTRA on Other Drugs
CYP3A Substrates
Co-administration with COPIKTRA increases AUC of a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] which may increase the risk of toxicities of these drugs. Consider reducing the dose of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate and monitor for signs of toxicities of the co-administered sensitive CYP3A substrate.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, COPIKTRA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
There are no available data in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of duvelisib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including embryo-fetal mortality (resorptions, post-implantation loss, and decreased viable fetuses), alterations to growth (lower fetal weights) and structural abnormalities (malformations) at maternal doses 10 times and 39 times the MRHD of 25 mg BID in rats and rabbits, respectively (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, pregnant animals received daily oral doses of duvelisib of 0, 10, 50, 150 and 275 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Administration of duvelisib at doses ≥ 50 mg/kg/day resulted in adverse developmental outcomes including reduced fetal weights and external abnormalities (bent tail and fetal anasarca), and doses ≥ 150 mg/kg/day resulted in maternal toxicity including mortality and no live fetuses (100% resorption) in surviving dams. In another study in pregnant rats receiving oral doses of duvelisib up to 35 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis, no maternal or embryo-fetal effects were observed. The dose of 50 mg/kg/day in rats is approximately 10 times the MRHD of 25 mg BID.
In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, pregnant animals received daily oral doses of duvelisib of 0, 25, 100, and 200 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Administration of duvelisib at doses ≥ 100 mg/kg/day resulted in maternal toxicity (body weight losses or lower mean body weights and increased mortality) and adverse developmental outcomes (increased resorptions and post-implantation loss, abortion, and decreased numbers of viable fetuses). In another study in pregnant rabbits receiving oral doses of duvelisib up to 75 mg/kg/day, no maternal or embryo-fetal effects were observed. The dose of 100 mg/kg/day in rabbits is approximately 39 times the MRHD of 25 mg BID.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of duvelisib and/or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from duvelisib in a breastfed child, advise lactating women not to breastfeed while taking COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
COPIKTRA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Conduct pregnancy testing before initiation of COPIKTRA treatment.
Contraception
Females
Based on animal studies, COPIKTRA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose.
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on testicular findings in animals, male fertility may be impaired by treatment with COPIKTRA [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. There are no data on the effect of COPIKTRA on human fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of COPIKTRA have not been established in pediatric patients. Pediatric studies have not been conducted.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of COPIKTRA included 270 patients (61%) that were 65 years of age and older and 104 (24%) that were 75 years of age and older. No major differences in efficacy or safety were observed between patients less than 65 years of age and patients 65 years of age and older.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
COPIKTRA (duvelisib) is a dual inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases PI3K-δ and PI3K-γ.
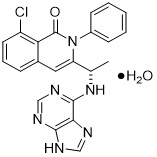
Duvelisib is a white-to-off-white crystalline solid with the empirical formula C22H17ClN6OH2O and a molecular weight of 434.88 g/mol. Hydration can vary with relative humidity. Duvelisib contains a single chiral center as (S) enantiomer. Duvelisib is soluble in ethanol and practically insoluble in water. Duvelisib is described chemically as a hydrate of (S)-3-(1-(9H-purin-6-ylamino)ethyl)-8-chloro-2-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one and has the following chemical structure:
COPIKTRA capsules are for oral administration and are supplied as white to off-white opaque and Swedish orange opaque capsules (25 mg, on anhydrous basis) or pink opaque capsules (15 mg, on anhydrous basis), and contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Capsule shells contain gelatin, titanium dioxide, black ink, and red iron oxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Duvelisib is an inhibitor of PI3K with inhibitory activity predominantly against PI3K-δ and PI3K-γ isoforms expressed in normal and malignant B-cells. Duvelisib induced growth inhibition and reduced viability in cell lines derived from malignant B-cells and in primary CLL tumor cells. Duvelisib inhibits several key cell-signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor signaling and CXCR12-mediated chemotaxis of malignant B-cells. Additionally, duvelisib inhibits CXCL12-induced T cell migration and M-CSF and IL-4 driven M2 polarization of macrophages.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
At the recommended dose of 25 mg BID, reductions in levels of phosphorylated AKT (a downstream marker for PI3K inhibition) were observed in patients treated with COPIKTRA.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of multiple doses of COPIKTRA 25 and 75 mg BID on the QTc interval was evaluated in patients with previously treated hematologic malignancies. Increases of > 20 ms in the QTc interval were not observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Duvelisib exposure increased in a dose-proportional manner over a dose range of 8 mg to 75 mg twice daily (0.3 to 3 times the recommended dosage).
At steady state following 25 mg BID administration of duvelisib in patients, the geometric mean (CV%) maximum concentration (Cmax) was 1.5 (64%) µg/mL and AUC was 7.9 (77%) µgh/mL.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of 25 mg duvelisib after a single oral dose in healthy volunteers was 42%. The median time to peak concentration (Tmax) was observed at 1 to 2 hours in patients.
Effect of Food
COPIKTRA may be administered without regard to food. The administration of a single dose of COPIKTRA with a high-fat meal (fat accounted for approximately 50% of the total caloric content of the meal) decreased Cmax by approximately 37% and decreased the AUC by approximately 6%, relative to fasting conditions.
Distribution
Protein binding of duvelisib is greater than 98% with no concentration dependence. The mean blood-to-plasma ratio was 0.5. The geometric mean (CV%) apparent volume of distribution at steady state (Vss/F) is 28.5 L (62%). Duvelisib is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and BCRP in vitro.
Elimination
The geometric mean (CV%) apparent systemic clearance at steady-state is 4.2 L/hr (56%) in patients with lymphoma or leukemia. The geometric mean (CV%) terminal elimination half-life of duvelisib is 4.7 hours (57%).
Metabolism
Duvelisib is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 CYP3A4.
Excretion
Following a single 25 mg oral dose of radiolabeled duvelisib, 79% of the radioactivity was excreted in feces (11% unchanged) and 14% was excreted in the urine (< 1% unchanged).
Specific Populations
Age (18 to 90 years), sex, race, renal impairment (creatinine clearance 23 to 80 mL/ min), hepatic impairment (Child Pugh Class A, B, and C) and body weight (40 to 154 kg) had no clinically significant effect on the exposure of duvelisib.
Drug Interaction Studies
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Co-administration of strong CYP3A inhibitor ketoconazole (at 200 mg BID for 5 days), a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, with a single oral 10 mg dose of COPIKTRA in healthy adults (n= 16) increased duvelisib Cmax by 1.7-fold and AUC by 4-fold. Based on physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and simulation, the increase in exposure to duvelisib is estimated to be ~2-fold at steady state when concomitantly used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. PBPK modeling and simulation estimated no effect on duvelisib exposures from concomitantly used mild or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Co-administration of 600 mg once daily rifampin, a strong CYP3A inducer, for 7 days with a single oral 25 mg COPIKTRA dose in healthy adults (N = 13) decreased duvelisib Cmax by 66% and AUC by 82%.
The effect of moderate CYP3A4 induction has not been studied [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
CYP3A4 Substrates
Co-administration of multiple doses of COPIKTRA 25 mg BID for 5 days with single oral 2 mg midazolam, a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate, in healthy adults (N = 14), increased in the midazolam AUC by 4.3-fold and Cmax by 2.2-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In Vitro Studies
Duvelisib is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer-resistant protein (BCRP).
Duvelisib does not inhibit OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BCRP, or P-gp.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with duvelisib.
Duvelisib did not cause genetic damage in in vitro or in vivo assays.
Fertility studies with duvelisib were not conducted. Histological findings in male and female rats were observed in the repeat dose toxicity studies and included testis (seminiferous epithelial atrophy, decreased weight, soft testes), and epididymis (small size, oligo/aspermia) in males and ovary (decreased weight) and uterus (atrophy) in females.
-
14 CLINICAL EFFICACY
14.1 Efficacy in Relapsed or Refractory CLL/SLL
Study 1
A randomized, multicenter, open-label trial (Study 1; NCT02004522) compared COPIKTRA versus ofatumumab in 319 adult patients with CLL (N = 312) or SLL (N = 7) after at least one prior therapy. The trial excluded patients with prior autologous transplant within 6 months or allogeneic transplant, prior exposure to a PI3K inhibitor or a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. The trial required hepatic transaminases ≤ 3 times upper limit of normal (ULN), total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 times ULN, and serum creatinine ≤ 2 times ULN.
The study randomized patients with a 1:1 ratio to receive either COPIKTRA 25 mg BID until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity or ofatumumab for 7 cycles. Ofatumumab was administered intravenously at an initial dose of 300 mg, followed one week later by 2000 mg once weekly for 7 doses, and then 2000 mg once every 4 weeks for 4 additional doses.
The approval of COPIKTRA was based on efficacy and safety analysis of patients with at least 2 prior lines of therapy, where the benefit:risk appeared greater in this more heavily pretreated population compared to the overall trial population.
In this subset (95 randomized to COPIKTRA, 101 to ofatumumab), the median patient age was 69 years (range: 40 to 90 years), 59% were male, and 88% had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Forty-six percent received 2 prior lines of therapy, and 54% received 3 or more prior lines. At baseline, 52% of patients had at least one tumor ≥ 5 cm, and 22% of patients had a documented 17p deletion.
During randomized treatment, the median duration of exposure to COPIKTRA was 13 months (range: 0.2 to 37), with 80% of patients receiving at least 6 months and 52% receiving at least 12 months of COPIKTRA. The median duration of exposure to ofatumumab was 5 months (range: < 0.1 to 6).
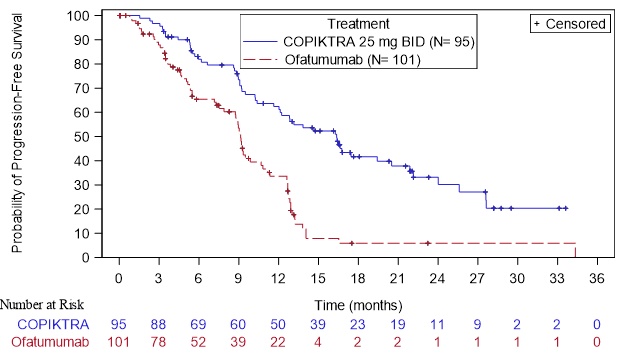
Efficacy was based on progression-free survival (PFS) as assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC). Other efficacy measures included overall response rate. Efficacy of COPIKTRA compared to ofatumumab specifically in patients treated with at least two prior therapies is presented in Table 8 and Figure 1.
Table 8. Efficacy in CLL or SLL After at Least Two Prior Therapies (Study 1) Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; CR = complete response; IRC = Independent Review Committee; PFS = progression-free survival; PR = partial response; SE = standard error
a Kaplan-Meier estimate
b Standard Error of ln(hazard ratio) = 0.2
c IWCLL or revised IWG response criteria, with modification for treatment-related lymphocytosisOutcome per IRC COPIKTRA
N = 95Ofatumumab
N = 101PFS Number of events, n (%) 55 (58) 70 (69) Progressive disease 44 62 Death 11 8 Median PFS (SE), months a 16.4 (2.1) 9.1 (0.5) Hazard Ratio (SE), b
COPIKTRA/ofatumumab0.40 (0.2) Response rate ORR, n (%)c 74 (78) 39 (39) CR 0 (0) 0 (0) PR 74 (78) 39 (39) Difference in ORR, % (SE) 39 (6.4)
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Curve of PFS per IRC In Patients with at Least 2 Prior Therapies (Study 1)
14.2 Efficacy in Relapsed or Refractory FL
Study 2
Efficacy of COPIKTRA in patients with previously treated FL is based on a single-arm, multicenter trial (Study 2; NCT01882803). In this study, COPIKTRA 25 mg BID was administered in patients with FL (N = 83) who were refractory to rituximab and to either chemotherapy or radioimmunotherapy. Refractory disease was defined as less than a partial remission or relapse within 6 months after the last dose. The trial excluded patients with Grade 3b FL, large cell transformation, prior allogeneic transplant, and prior exposure to a PI3K inhibitor or to a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
The median age was 64 years (range: 30 to 82 years), 68% were male, and 37% had bulky disease assessed at baseline (target lesion ≥ 5 cm). Patients had a median of 3 prior lines of therapy (range: 1 to 10), with 94% being refractory to their last therapy and 81% being refractory to 2 or more prior lines of therapy. Most patients (93%) had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1.
The median duration of exposure to COPIKTRA was 5 months (range: 0.4 to 24), with 41% of patients receiving at least 6 months and 10% receiving at least 12 months of COPIKTRA.
Efficacy was based on overall response rate and duration of response as assessed by an IRC (Table 9).
Table 9. Efficacy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory FL (Study 2) Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; CR = complete response; IRC = Independent Review Committee; ORR = overall response rate; PR = partial response
a Per IRC according to Revised International Working Group criteria
+ Denotes censored observationEndpoint FL
N = 83ORR, n (%) a 35 (42) 95% CI (31, 54) CR, n (%) 1 (1) PR, n (%) 34 (41) Duration of response Range, months 0.0+ to 41.9+ Patients maintaining response at 6 months, n/N (%) 15/35 (43) Patients maintaining response at 12 months, n/N (%) 6/35 (17) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
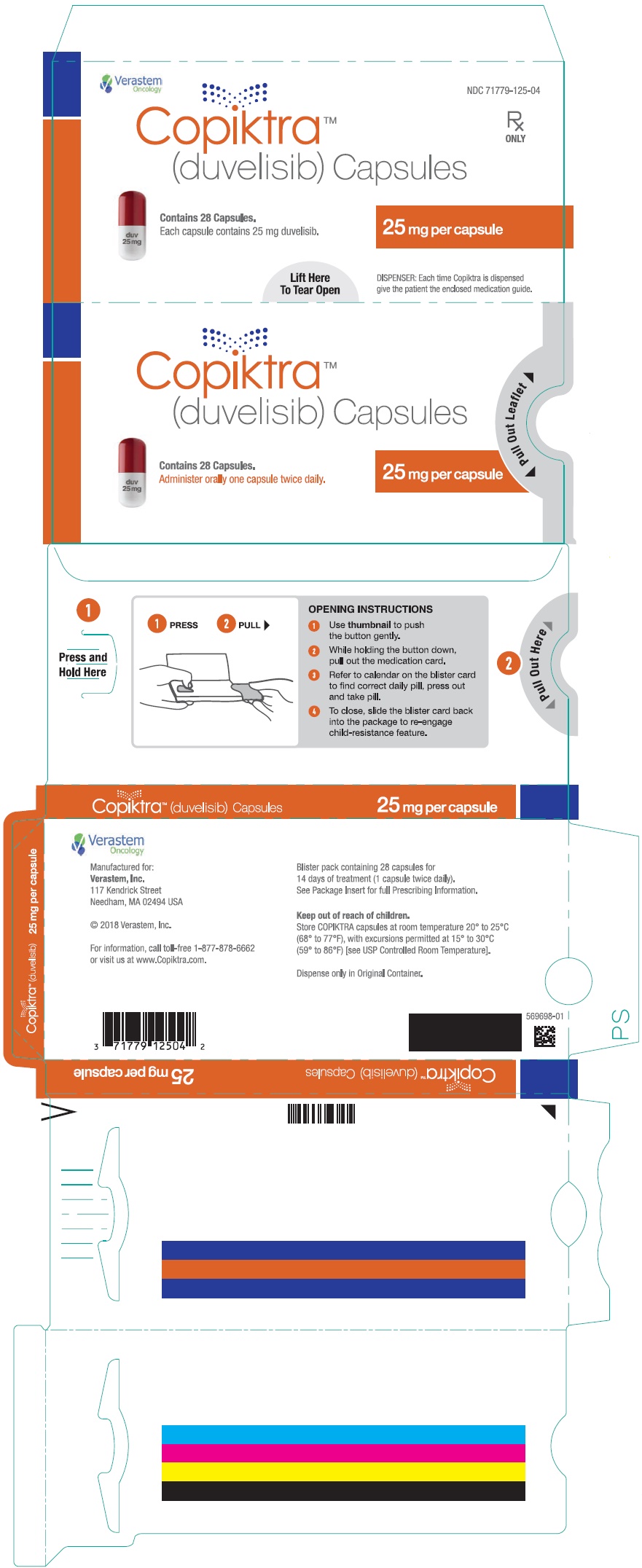
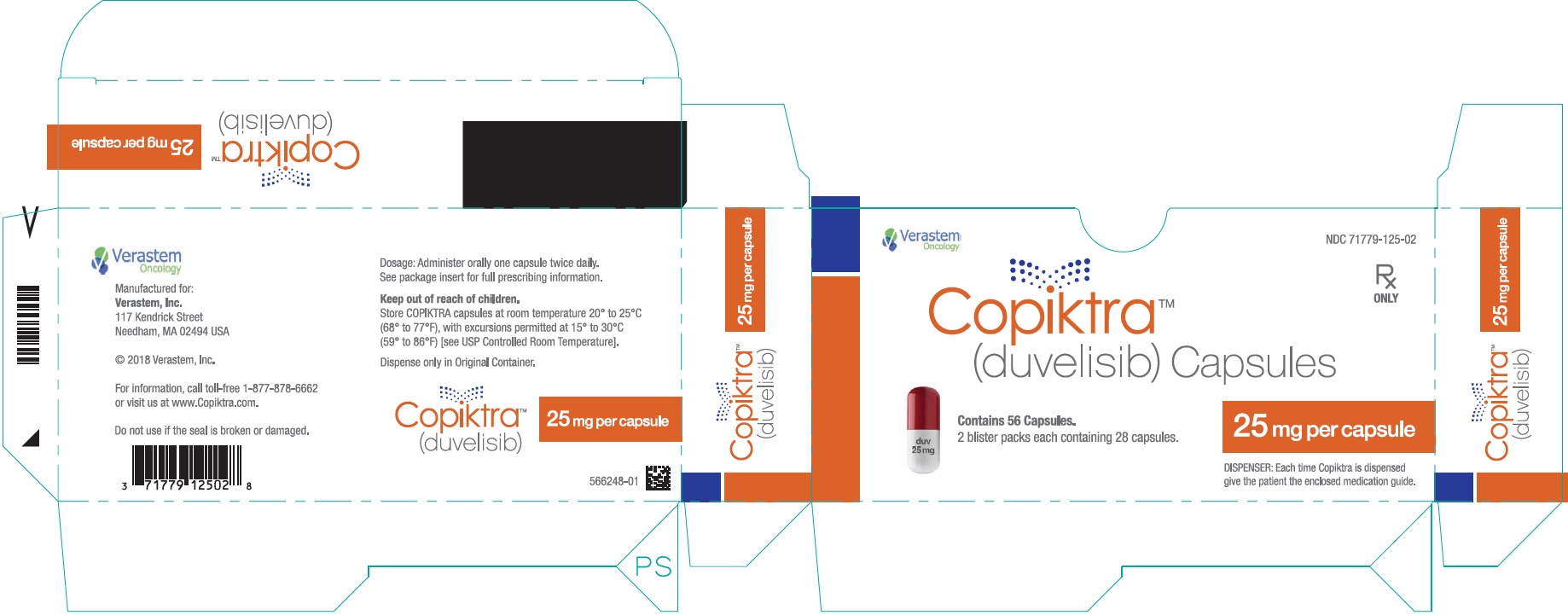
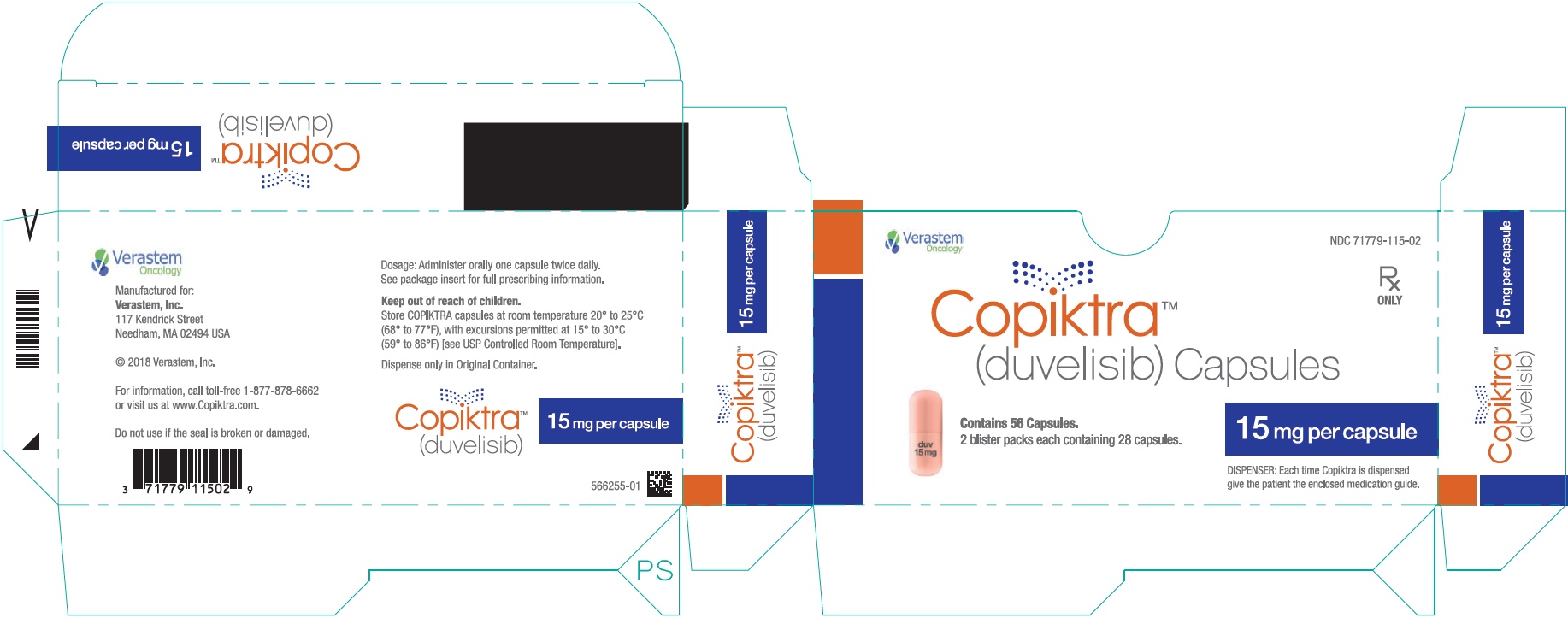
COPIKTRA (duvelisib) capsules are supplied as follows:
Abbreviations: HDPE = high-density polyethylene; NDC = National Drug Code; no. = number Capsule Strength Description Package Configuration NDC No. 25 mg White to off-white and
Swedish orange opaque
capsules marked with "duv
25 mg" in black ink- 14-day (28ct) single blister pack
- 14-day (28ct) carton (1 x 28ct
blister pack per carton) - 28-day (56ct) carton (2 × 28ct
blister packs per carton) - 28-day (56ct) HDPE bottles
- 71779-125-04
- 71779-125-03
- 71779-125-02
- 71779-125-01
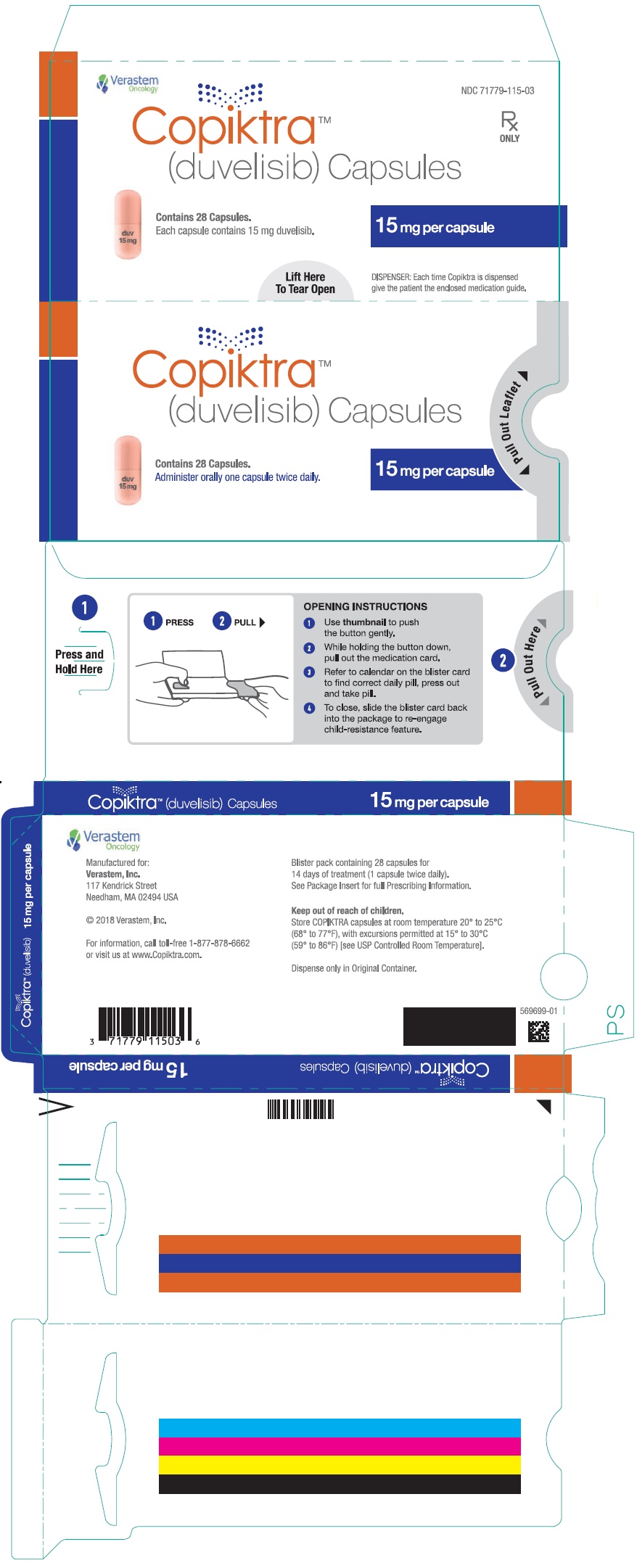
15 mg Pink opaque capsules
marked with “duv 15 mg” in black ink- 14-day (28ct) single blister pack
- 28-day (56ct) carton (2 × 28ct
blister packs per carton) - 56-count HDPE bottles
- 71779-115-03
- 71779-115-02
- 71779-115-01
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F), with excursions permitted at 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Retain in original package until dispensing. Dispense blister packs in original container.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Physicians and healthcare professionals are advised to discuss the following with patients prior to treatment with COPIKTRA:
Infections
Advise patients that COPIKTRA can cause serious infections that may be fatal. Advise patients to immediately report symptoms of infection (e.g. fever, chills) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Diarrhea or Colitis
Advise patients that COPIKTRA can cause serious diarrhea or colitis (inflammation of the gut) that may be fatal, and to notify their healthcare provider immediately about any new or worsening diarrhea, stool with mucus or blood, or abdominal pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cutaneous Reactions
Advise patients that COPIKTRA can cause a serious skin rash that may be fatal, and to notify their healthcare provider immediately if they develop a new or worsening skin rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pneumonitis
Advise patients that COPIKTRA may cause pneumonitis (inflammation of the lungs) that may be fatal, and to report any new or worsening respiratory symptoms including cough or difficulty breathing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that COPIKTRA may cause significant elevations in liver enzymes, and that monitoring of liver tests is needed. Advise patients to report symptoms of liver dysfunction including jaundice (yellow eyes or yellow skin), abdominal pain, bruising, or bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Neutropenia
Advise patients of the need for periodic monitoring of blood counts. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider immediately if they develop a fever or any sign of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant. Inform female patients of the risk to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 1 month after receiving the last dose of COPIKTRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products, before and during treatment with COPIKTRA [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Instructions for Taking COPIKTRA
Advise patients to take COPIKTRA exactly as prescribed. COPIKTRA may be taken with or without food; the capsules should be swallowed whole [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Advise patients that if a dose is missed by fewer than 6 hours, to take the missed dose right away and take the next dose as usual. If a dose is missed by more than 6 hours, advise patients to wait and take the next dose at the usual time [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Manufactured for:Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA 02494
COPIKTRA is a registered trademark of Verastem, Inc.
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 09/2018
MEDICATION GUIDE
COPIKTRA™ (co-PIK-trah)
(duvelisib)
capsulesWhat is the most important information I should know about COPIKTRA?
COPIKTRA can cause serious side effects, including:
- Infections. Infections are common during COPIKTRA treatment, and can be serious and can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a fever, chills, or other signs of an infection during treatment with COPIKTRA.
- Diarrhea or inflammation of your intestine. Diarrhea or inflammation of your intestine (colitis) is common during COPIKTRA treatment, and can be serious and can lead to death. Your healthcare provider may prescribe an anti-diarrhea medicine for your diarrhea. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any new or worsening diarrhea, stool with mucus or blood, or if you have severe stomach-area (abdominal) pain. Your healthcare provider should prescribe medicine to help your diarrhea and check you at least weekly. If your diarrhea is severe or anti-diarrhea medicines did not work, you may need treatment with a steroid medicine.
-
Skin reactions. Rashes are common with COPIKTRA treatment. COPIKTRA can cause rashes and other skin reactions that can be serious and can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get a new or worsening skin rash, or other skin reactions during treatment with COPIKTRA, including:
- painful sores or ulcers on your skin, lips, or in your mouth
- severe rash with blisters or peeling skin
- rash with itching
- rash with fever
Your healthcare provider may need to prescribe medicines, including a steroid medicine, to help treat your skin rash or other skin reactions.
- Inflammation of the lungs. COPIKTRA can cause inflammation of your lungs which can be serious and can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get new or worsening cough or difficulty breathing. Your healthcare provider may do tests to check your lungs if you have breathing problems during treatment with COPIKTRA. Your healthcare provider may treat you with a steroid medicine if you develop inflammation of the lungs that is not due to an infection.
If you have any of the above serious side effects during treatment with COPIKTRA, your healthcare provider may stop your treatment for a period of time, change your dose of COPIKTRA, or completely stop your treatment with COPIKTRA. See “What are the possible side effects of COPIKTRA?” for more information about side effects.
What is COPIKTRA?
COPIKTRA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies and they did not work or are no longer working.
- Follicular Lymphoma (FL) who have received at least 2 prior therapies and they did not work or are no longer working.
It is not known if COPIKTRA is safe and effective in children less than 18 years of age.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking COPIKTRA?
Before taking COPIKTRA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have intestinal problems
- have lung or breathing problems
- have an infection
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. COPIKTRA can harm your unborn baby.
- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test to see if you are pregnant before you start treatment with COPIKTRA.
- Females who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose of COPIKTRA. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with COPIKTRA.
- Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with COPIKTRA and for at least 1 month after the last dose of COPIKTRA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if COPIKTRA passes into breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose of COPIKTRA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. COPIKTRA and certain other medicines may affect each other.
How should I take COPIKTRA?
- Take COPIKTRA exactly the way your healthcare provider tells you.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of COPIKTRA or tell you to stop taking COPIKTRA. Do not change your dose or stop taking COPIKTRA without talking to your healthcare provider first.
- Swallow COPIKTRA capsules whole.
- Do not open, break, or chew COPIKTRA capsules.
- You may take COPIKTRA with or without food.
- Do not miss a dose of COPIKTRA. If you miss a dose of COPIKTRA by less than 6 hours, take the missed dose right away, and then take the next dose at your usual time. If you miss a dose by more than 6 hours, wait and take the next dose at your usual time.
- If you take too much COPIKTRA, call your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are possible side effects of COPIKTRA?
COPIKTRA may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about COPKTRA?”
- Elevated liver enzymes. COPIKTRA may cause abnormalities in liver blood tests. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests during your treatment with COPIKTRA to check for liver problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any symptoms of liver problems, including yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes (jaundice), pain in the abdominal region, bruising or bleeding more easily than normal.
- Low white blood cell count (neutropenia). Neutropenia is common with COPIKTRA treatment and can sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider should check your blood counts regularly during treatment with COPIKTRA. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a fever or any signs of infection during treatment with COPIKTRA.
Common side effects of COPIKTRA include:
- tiredness
- fever
- cough
- nausea
- upper respiratory infection
- bone and muscle pain
- low red blood cell count
These are not all the possible side effects of COPIKTRA.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store COPIKTRA?
- Store COPIKTRA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep COPIKTRA in its original container until you are ready to take your dose.
Keep COPIKTRA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of COPIKTRA:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use COPIKTRA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give COPIKTRA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about COPIKTRA that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in COPIKTRA?
Active ingredient: duvelisib
Inactive ingredients: Colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose.
Capsule shells contain gelatin, titanium dioxide, black ink, and red iron oxide.Manufactured for: Verastem Inc, Needham, MA 02494
For more information, go to www.COPIKTRA.com or call 1-833-570-2273.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-125-04 - 25 mg Capsule 28 Days Pack Blister Pack Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-125-03 - 25 mg Capsule 14-day 28-count Single Blister Pack
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-125-02 - 25 mg Capsule 28 Days Pack Carton Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-125-01 - 25 mg Capsule 56-count Bottle Label
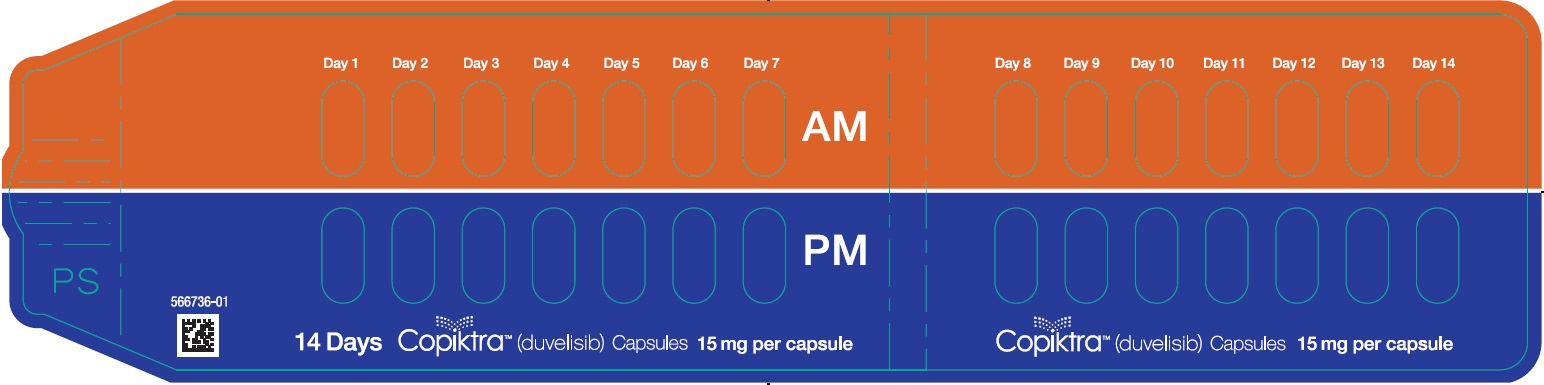
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-115-03 - 15 mg Capsule 28 Days Pack Blister Pack Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-115-03 - 15 mg Capsule 14-day 28-count Single Blister Pack
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-115-02 - 15 mg Capsule 28 Days Pack Carton Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 71779-115-01 - 15 mg Capsule 56-count Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
COPIKTRA
duvelisib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71779-125 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DUVELISIB (UNII: 610V23S0JI) (DUVELISIB - UNII:610V23S0JI) DUVELISIB 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSPOVIDONE (UNII: 2S7830E561) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white opaque) , ORANGE (Swedish orange opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 25mm Flavor Imprint Code duv;25;mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71779-125-02 1 in 1 CARTON 09/25/2018 1 NDC: 71779-125-04 28 in 1 PACKAGE 1 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 71779-125-01 56 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/25/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA211155 09/25/2018 COPIKTRA
duvelisib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71779-115 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DUVELISIB (UNII: 610V23S0JI) (DUVELISIB - UNII:610V23S0JI) DUVELISIB 15 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSPOVIDONE (UNII: 2S7830E561) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Product Characteristics Color PINK (pink opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 15mm Flavor Imprint Code duv;15;mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71779-115-02 2 in 1 CARTON 09/25/2018 1 NDC: 71779-115-03 28 in 1 PACKAGE 1 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 71779-115-01 56 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/25/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA211155 09/25/2018 Labeler - Verastem, Inc. (032472566) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations AMRI Rensselaer, Inc. 124193793 ANALYSIS(71779-125, 71779-115) , API MANUFACTURE(71779-125, 71779-115) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent CTS, LLC 962674474 ANALYSIS(71779-125, 71779-115) , MANUFACTURE(71779-125, 71779-115) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Packaging Coordinators, Inc. 053217022 LABEL(71779-125, 71779-115) , PACK(71779-125, 71779-115)
Trademark Results [Copiktra]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 COPIKTRA 88214907 not registered Live/Pending |
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2018-12-03 |
 COPIKTRA 87041688 5643918 Live/Registered |
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2016-05-18 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.