SODIUM IODIDE I 123 capsule, gelatin coated
SODIUM IODIDE I 123 by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
SODIUM IODIDE I 123 by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Curium US LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Sodium Iodide I 123 (Na123I) for diagnostic use is supplied in capsules for oral administration. The capsules are available in strengths of 3.7 and 7.4 megabecquerels (MBq) (100 and 200 μCi) I-123 at time of calibration.
The radionuclidic composition at calibration is not less than 97.0 percent I-123, not more than 2.9 percent I-125 and not more than 0.1 percent Te-121. The radionuclidic composition at expiration time is not less than 87.2 percent I-123, not more than 12.4 percent I-125 and not more than 0.4 percent Te-121. The ratio of the concentration of I-123 and I-125 changes with time. Graph 1 shows the minimum concentration of I-123 as a function of time and Graph 2 shows the maximum concentration of I-125 as a function of time.
Graph 1. Radionuclidic Concentration of I-123
PERCENT OF TOTAL RADIOACTIVITY:
IODINE-123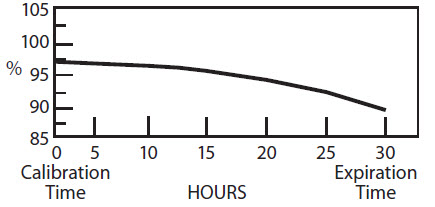
Graph 2. Radionuclidic Concentration of I-125
PERCENT OF TOTAL RADIOACTIVITY:
IODINE-125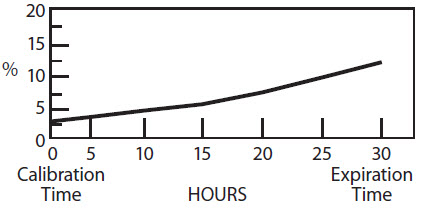
Physical Characteristics
Iodine-123 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 13.2 hours1. The photon that is useful for detection and imaging studies is listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Principal Radiation Emission Data Radiation Mean %
DisintegrationEnergy
(keV)Gamma-2 83.4 159
- 1 Kocher, David C., Radioactive Decay Data Tables. DOE/TIC-11026, 122 (1981).
External Radiation
The specific gamma ray constant for I-123 is 1.6 R/hr-mCi at 1 cm. The first half-value thickness of lead (Pb) for I-123 is 0.005 cm. A range of values for the relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that results from the interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. For example, the use of 1.63 cm of lead will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of about 1,000.
Table 2. Radiation Attenuation by Lead Shielding Shield
Thickness (Pb), cmCoefficient of
Attenuation0.005
0.10
0.88
1.63
2.480.5
10-1
10-2
10-3
10-4Note that these estimates of attenuation do not take into consideration the presence of radionuclidic contaminants.
To correct for physical decay of I-123, the fractions that remain at selected intervals after the time of calibration are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Iodine I-123 Decay Chart: Half-Life 13.2 Hours
HoursFraction
Remaining
HoursFraction Remaining *Time of Calibration
0*
3
6
9
12
151.000
0.854
0.730
0.623
0.533
0.45518
21
24
27
300.389
0.332
0.284
0.242
0.207 -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Sodium iodide I-123 is readily absorbed from the upper gastrointestinal tract. Following absorption, the iodide is distributed primarily within the extracellular fluid of the body. It is trapped and organically bound by the thyroid and concentrated by the stomach, choroid plexus and salivary glands. It is excreted by the kidneys.
The fraction of the administered dose which is accumulated in the thyroid gland may be a measure of thyroid function in the absence of unusually high or low iodine intake or administration of certain drugs which influence iodine accumulation by the thyroid gland. Accordingly, the patient should be questioned carefully regarding previous medications and/or procedures involving radiographic media. Normal subjects can accumulate approximately 10 to 50% of the administered iodine dose in the thyroid gland, however, the normal and abnormal ranges are established by individual physician's criteria. The mapping (imaging) of sodium iodide I-123 distribution in the thyroid gland may provide useful information concerning thyroid anatomy and definition of normal and/or abnormal functioning of tissue within the gland.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
The contents of the capsule are radioactive. Adequate shielding of the preparation must be maintained at all times.
Do not use after the expiration time and date stated on the label.
The prescribed Sodium Iodide I 123 dose should be administered as soon as practical from the time of receipt of product (i.e., as close to calibration time as possible), in order to minimize the fraction of radiation exposure due to the relative increase of radionuclidic contaminants with time.
Sodium iodide I-123, as well as other radioactive drugs, must be handled with care and appropriate safety measures should be used to minimize radiation exposure to clinical personnel. Care should also be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the patient consistent with proper patient management.
Radiopharmaceuticals should be used only by physicians who are qualified by training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or whether sodium iodide I-123 affects fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this drug. It is also not known whether sodium iodide I-123 can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Sodium iodide I-123 should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Ideally, examinations using radiopharmaceuticals, especially those elective in nature, in women of child-bearing capability should be performed during the first few (approximately ten) days following the onset of menses.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended oral dose for the average patient (70 kg) is 3.7 to 14.8 MBq (100 to 400 μCi). The lower part of the dosage range 3.7 MBq (100 μCi) is recommended for uptake studies alone, and the higher part 14.8 MBq (400 μCi) for thyroid imaging. The determination of I-123 concentration in the thyroid gland may be initiated at six hours after administering the dose and should be measured in accordance with standardized procedures.
The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration. The capsules can be utilized up to 30 hours after calibration time and date. Thereafter, discard the capsules in accordance with standard safety procedures. The user should wear waterproof gloves at all times when handling the capsules or container.
Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to several organs of an average patient (70 kg) from oral administration of the maximum dose of 14.8 MBq (400 μCi) of I-123 are shown in Table 4 for thyroid uptakes of 5, 15, and 25%. For comparison at these three values of thyroid uptake, the estimated radiation doses from doses of 3.7 MBq (100 μCi) I-131, also used as thyroid imaging agent, are also included.
Table 4. Absorbed Radiation Dose Estimates as a Function of Maximum Thyroid Uptake for Sodium Iodide I-123* at Time of Calibration and Expiry Compared to Sodium Iodide I-131 Estimated Radiation Absorbed Doses I-123
mGy/14.8 MBq
(rads/400 μCi)
I-131
mGy/3.7 MBq
(rads/100 μCi)Target Organ Maximum Thyroid
Uptake (%)TOC TOE *Concentration at Time of Calibration: 97% I-123, 2.9% I-125, 0.1% Te-121
Concentration at Time of Expiry: 87.2% I-123, 12.4% I-125, 0.4% Te-121
Metabolic model in MIRD Dose Estimate Report 5 followed for I-123 and I-125
Metabolic model in ICRP 30 followed for Te-121
†Bladder voiding interval 4.8 hours.
Bladder† 5 1.7 (0.17) 1.7 (0.17) 2.9 (0.29) 15 1.6 (0.16) 1.6 (0.16) 2.7 (0.27) 25 1.4 (0.14) 1.5 (0.15) 2.4 (0.24) Stomach Wall 5 0.96 (0.096) 0.98 (0.098) 1.7 (0.17) 15 0.89 (0.089) 0.91 (0.091) 1.5 (0.15) 25 0.82 (0.082) 0.85 (0.085) 1.4 (0.14) Small Intestine 5 0.70 (0.070) 0.71 (0.071) 1.2 (0.12) 15 0.65 (0.065) 0.67 (0.067) 1.1 (0.11) 25 0.60 (0.060) 0.62 (0.062) 0.99 (0.099) Liver 5 0.089 (0.0089) 0.13 (0.013) 0.16 (0.016) 15 0.10 (0.010) 0.18 (0.018) 0.28 (0.028) 25 0.11 (0.011) 0.24 (0.024) 0.41 (0.041) Ovaries 5 0.18 (0.018) 0.19 (0.019) 0.18 (0.018) 15 0.17 (0.017) 0.18 (0.018) 0.18 (0.018) 25 0.16 (0.016) 0.18 (0.018) 0.17 (0.017) Skeleton 5 0.11 (0.011) 0.16 (0.016) 0.12 (0.012) 15 0.12 (0.012) 0.18 (0.018) 0.18 (0.018) 25 0.14 (0.014) 0.21 (0.021) 0.24 (0.024) Red Marrow 5 0.12 (0.012) 0.16 (0.016) 0.15 (0.015) 15 0.12 (0.012) 0.18 (0.018) 0.21 (0.021) 25 0.13 (0.013) 0.19 (0.019) 0.27 (0.027) Testes 5 0.076 (0.0076) 0.089 (0.0089) 0.12 (0.012) 15 0.072 (0.0072) 0.087 (0.0087) 0.12 (0.012) 25 0.068 (0.0068) 0.085 (0.0085) 0.12 (0.012) Thyroid 5 25 (2.5) 75 (7.5) 260 (26) 15 77 (7.7) 230 (23) 780 (78) 25 130 (13) 410 (41) 1300 (130) Total Body 5 0.11 (0.011) 0.16 (0.016) 0.24 (0.024) 15 0.14 (0.014) 0.25 (0.025) 0.47 (0.047) 25 0.17 (0.017) 0.35 (0.035) 0.70 (0.070) -
HOW SUPPLIED
Catalog Number 601,602.
Sodium Iodide I 123 is supplied as capsules for oral administration in strengths of 3.7 MBq (100 µCi) (red and white) (NDC: 69945-601-10) and 7.4 MBq (200 µCi) (green and white) (NDC: 69945-602-20) at time of calibration. Each gelatin capsule contains sucrose as a filler. The capsules are packaged in plastic vials containing one capsule of a single strength per vial. The plastic vial is packaged in a lead shield. A package insert is supplied with each lead shield.
Storage and Handling
The contents of the vial are radioactive and adequate shielding and handling precautions must be maintained.
Dispense and preserve capsules in tightly-closed containers that are adequately shielded. Store at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
Storage and disposal of Sodium Iodide I 123 Capsules should be controlled in a manner that is in compliance with the appropriate regulations of the government agency authorized to license the use of this radionuclide.
Curium and the Curium logo are trademarks of a Curium company.
©2018 Curium US LLC. All Rights Reserved.Manufactured by: Curium US LLC
Maryland Heights, MO 63043Made in USA
A601I0
R12/2018
CURIUM™
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - A601C0
Sodium Iodide I 123 Capsules
DIAGNOSTIC
For Oral Administration Only
Store at Controlled Room Temperature
20º to 25°C (68º to 77°F)
READ PACKAGE INSERT FOR DIRECTIONS FOR USE
Rx onlyWARNING: Radioactive drugs must be handled only by qualified personnel in conformity with regulations of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission or state regulatory agencies where applicable. Bottle containing drug should be kept in this container or within a heavier shield.
Manufactured by:
Curium US LLC
Maryland Heights, MO 63043
Made in USA
CURIUM™
CAUTION RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
A601C0
R12/2018
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - A602C0
Sodium Iodide I 123 Capsules
DIAGNOSTIC
For Oral Administration Only
Store at Controlled Room Temperature
20º to 25°C (68º to 77°F)
READ PACKAGE INSERT FOR DIRECTIONS FOR USE
Rx only
WARNING: Radioactive drugs must be handled only by qualified personnel in conformity with regulations of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission or state regulatory agencies where applicable. Bottle containing drug should be kept in this container or within a heavier shield.
Manufactured by:
Curium US LLC
Maryland Heights, MO 63043
Made in USA
CAUTION RADIOACTIVE MATERIALCURIUM™

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SODIUM IODIDE I 123
sodium iodide i 123 capsule, gelatin coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69945-601 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM IODIDE I-123 (UNII: 29UKX3A616) (IODIDE ION I-123 - UNII:98QPV8670C) IODIDE ION I-123 100 uCi Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) Product Characteristics Color RED, WHITE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69945-601-10 1 in 1 CAN 11/04/2015 1 1 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA071909 11/04/2015 SODIUM IODIDE I 123
sodium iodide i 123 capsule, gelatin coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69945-602 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM IODIDE I-123 (UNII: 29UKX3A616) (IODIDE ION I-123 - UNII:98QPV8670C) IODIDE ION I-123 200 uCi Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) Product Characteristics Color GREEN, WHITE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69945-602-20 1 in 1 CAN 04/11/2007 1 1 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA071910 04/11/2007 Labeler - Curium US LLC (079875617)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.