FLECTOR- diclofenac epolamine patch
Flector by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Flector by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FLECTOR® PATCH 1.3% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FLECTOR PATCH.
FLECTOR PATCH® (diclofenac epolamine patch) 1.3%
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988WARNING: CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL RISK
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Cardiovascular Risk
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk. (5.1)
- Flector Patch is contraindicated in the peri-operative setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4)
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs, including diclofenac, cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events. (5.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
None
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Flector Patch contains diclofenac epolamine, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and is indicated for the topical treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, and contusions. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Patch: 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine. Each individual patch is embossed. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events: Serious and potentially fatal cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke can occur with NSAID treatment. Use the lowest effective dose of Flector Patch in patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. (5.1)
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Effects: NSAIDs can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation. Prescribe Flector Patch with caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. (5.2)
- Hepatic Effects: Elevation of one or more liver tests may occur during therapy with Flector Patch. Discontinue Flector Patch immediately if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen. (5.3)
- Hypertension can occur with NSAID treatment. Monitor blood pressure closely with Flector Patch treatment. (5.4)
- Congestive Heart Failure and Edema: Use Flector Patch with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure. (5.5)
- Renal effects: Long-term administration of NSAIDs can result in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Use Flector Patch with caution in patients at greatest risk of this reaction, including the elderly, those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, and those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors. (5.6)
- Anaphylactic reactions may occur in patients with the aspirin triad and in patients with or without known sensitivity to NSAIDs or prior exposure to Flector Patch. Anaphylaxis type reactions have been reported with NSAID products, including diclofenac products such as Flector Patch. (5.7)
- Skin Reactions: NSAIDs can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. (5.8)
- Pregnancy: Avoid the use of Flector Patch at or beyond 30 weeks gestation. (5.9)
- Preexisting Asthma: Do not administer to patients with aspirin sensitive asthma and use with caution in patients with preexisting asthma. (5.13)
- New or used Flector Patch contains sufficient diclofenac to result in serious harm following accidental exposure by a child or pet. (5.14)
- Eyes: Avoid contact of Flector Patch with eyes and mucosa. (5.15)
- Oral NSAIDs: Avoid concurrent use with oral NSAIDs. (5.16)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse events with Flector Patch are application site reactions. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact King Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-546-4905 or DSP@kingpharm.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Concomitant administration of Flector Patch and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects including increased GI bleeding. (7.1)
- Concomitant use of anticoagulants and diclofenac have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2011
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL RISK
1 INDICATION AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Instructions
2.2 Special Precautions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
5.2 Gastrointestinal Effects – Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
5.3 Hepatic Effects
5.4 Hypertension
5.5 Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
5.6 Renal Effects
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
5.8 Skin Reactions
5.9 Pregnancy
5.10 Corticosteroid Monitoring
5.11 Inflammation
5.12 Hematological Effects
5.13 Preexisting Asthma
5.14 Accidental Exposure in Children
5.15 Eye Exposure
5.16 Oral Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
5.17 Monitoring
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aspirin
7.2 Anticoagulants
7.3 ACE-inhibitors
7.4 Diuretics
7.5 Lithium
7.6 Methotrexate
7.7 Cyclosporine
7.8 Oral Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ankle sprains
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Information on Medication Guide
17.2 Cardiovascular Effects
17.3 Gastrointestinal Effects
17.4 Adverse Skin Reactions
17.5 Hepatotoxicity
17.6 Weight gain and edema
17.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
17.8 Preexisting Asthma
17.9 Eye Exposure
17.10 Effects during pregnancy
17.11 General Information on Use
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL RISK
Cardiovascular Risk
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk [See Warnings and Precautions and (5.1)].
- Flector Patch is contraindicated in the peri-operative setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [See Contraindications (4)].
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 1 INDICATION AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Instructions
The recommended dose of Flector Patch is one (1) patch to the most painful area twice a day.
2.2 Special Precautions
- Patients should be informed that, if Flector Patch begins to peel-off, the edges of the patch may be taped down. If problems with adhesion persist, patients may overlay the patch with a mesh netting sleeve, where appropriate (e.g. to secure patches applied to ankles, knees, or elbows). The mesh netting sleeve (e.g. Curad® Hold Tite™, Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing) must allow air to pass through and not be occlusive (non-breathable).
- Do not apply Flector Patch to non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology e.g. exudative dermatitis, eczema, infected lesion, burns or wounds.
- Do not wear a Flector Patch when bathing or showering.
- Wash your hands after applying, handling or removing the patch.
- Avoid eye contact.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Flector Patch is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
- Flector Patch is contraindicated in patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.13)].
- Flector Patch is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Flector Patch is contraindicated for use on non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology, including exudative dermatitis, eczema, infection lesions, burns or wounds.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Inform patients about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke [see Contraindications (4)].
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and NSAIDs, such as diclofenac, does increase the risk of serious GI events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Effects – Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
Prescribe NSAIDs, including Flector Patch, with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration. Physicians and patients should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during diclofenac therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. For high risk patients, consider alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs.
5.3 Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations (less than 3 times the upper limit of the normal [ULN] range) or greater elevations of transaminases occurred in about 15% of oral diclofenac-treated patients in clinical trials of indications other than acute pain. Of the markers of hepatic function, ALT (SGPT) is recommended for the monitoring of liver injury.
In clinical trials of an oral diclofenac – misoprostol combination product, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (SGOT) occurred in about 2% of approximately 5,7000 patients at some time during diclofenac treatment (ALT was not measured in all studies).
In an open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated for 2-6 months, patients with oral diclofenac were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of the 3,700 patients and included marked elevations (>8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In this open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (>8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis. Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic.
Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with oral diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations. In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the first 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac. Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
Measure transaminases (ALT and AST) periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with diclofenac, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, monitor transaminases within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reactions can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g. eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), discontinue Flector Patch immediately. To minimize the possibility that hepatic injury will become severe between transaminase measurements, inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms), and the appropriate action patients should take if these signs and symptoms appear.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with Flector Patch, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Exercise caution when prescribing Flector Patch with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., acetaminophen, certain antibiotics, anti-epileptics). Caution patients to avoid taking unprescribed acetaminophen while using Flector Patch.
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including Flector Patch, can lead to new onset or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Use Flector Patch, with caution in patients with hypertension. Monitor blood pressure (BP) closely during the initiation of treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Patients taking ACE inhibitors, thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs.
5.5 Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs, including Flector Patch. Use Flector Patch with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
5.6 Renal Effects
Use caution when initiating treatment with Flector Patch in patients with considerable dehydration.
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of an NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of Flector Patch in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with Flector Patch is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If Flector Patch therapy is initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactic reactions may occur both in patients with the aspirin triad and in patients without known sensitivity to NSAIDs or prior exposure to Flector Patch. Do not prescribe Flector Patch to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Anaphylaxis type reactions have been reported with NSAID products, including diclofenac products, such as Flector Patch [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Seek emergency help in cases where an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.8 Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including Flector Patch, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations, and discontinue use of the drug at the first appearance of skin rash or any other signs of hypersensitivity.
5.9 Pregnancy
Starting at 30 weeks gestation, Flector Patch, and other NSAIDs, should be avoided by pregnant women as premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.10 Corticosteroid Monitoring
Flector Patch cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Slowly taper patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
5.11 Inflammation
The pharmacological activity of Flector Patch in reducing inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
5.12 Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Flector Patch, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Carefully monitor patients receiving Flector Patch who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants.
5.13 Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, do not administer Flector Patch to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and use with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
5.14 Accidental Exposure in Children
Even a used Flector Patch contains a large amount of diclofenac epolamine (as much as 170 mg). The potential therefore exists for a small child or pet to suffer serious adverse effects from chewing or ingesting a new or used Flector Patch. It is important for patients to store and dispose of Flector Patch out of the reach of children and pets.
5.15 Eye Exposure
Avoid contact of Flector Patch with eyes and mucosa. Advise patients that if eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and consult a physician if irritation persists for more than an hour.
5.16 Oral Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Concomitant use of oral and topical NSAIDs may result in a higher rate of hemorrhage, more frequent abnormal creatinine, urea and hemoglobin. Do not use combination therapy with Flector Patch and an oral NSAID unless the benefit outweighs the risk.
5.17 Monitoring
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Check CBC and a chemistry profile periodically in patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs. Discontinue Flector Patch if abnormal liver tests or renal tests persist or worsen.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In controlled trials during the premarketing development of Flector Patch, approximately 600 patients with minor sprains, strains, and contusions have been treated with Flector Patch for up to two weeks.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
In the controlled trials, 3% of patients in both the Flector Patch and placebo patch groups discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were application site reactions, occurring in 2% of both the Flector Patch and placebo patch groups. Application site reactions leading to dropout included pruritus, dermatitis, and burning.
Common Adverse Events
Localized Reactions
Overall, the most common adverse events associated with Flector Patch treatment were skin reactions at the site of treatment.
Table 1 lists all adverse events, regardless of causality, occurring in ≥ 1% of patients in controlled trials of Flector Patch. A majority of patients treated with Flector Patch had adverse events with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate."
Table 1. Common Adverse Events (by body system and preferred term) in ≥1% of Patients treated with Flector Patch or Placebo Patch* Diclofenac N=572 Placebo N=564 N Percent N Percent - * The table lists adverse events occurring in placebo-treated patients because the placebo-patch was comprised of the same ingredients as Flector Patch except for diclofenac. Adverse events in the placebo group may therefore reflect effects of the non-active ingredients.
- † Includes: application site dryness, irritation, erythema, atrophy, discoloration, hyperhidriosis, and vesicles.
- ‡ Includes: gastritis, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, upper abdominal pain, and dry mouth.
- § Includes: hypoaesthesia, dizziness, and hyperkinesias.
Application Site Conditions 64 11 70 12 Pruritus 31 5 44 8 Dermatitis 9 2 3 <1 Burning 2 <1 8 1 Other† 22 4 15 3 Gastrointestinal Disorders 49 9 33 6 Nausea 17 3 11 2 Dysgeusia 10 2 3 <1 Dyspepsia 7 1 8 1 Other‡ 15 3 11 2 Nervous System Disorders 13 2 18 3 Headache 7 1 10 2 Paresthesia 6 1 8 1 Somnolence 4 1 6 1 Other § 4 1 3 <1 Foreign labeling describes that dermal allergic reactions may occur with Flector Patch treatment. Additionally, the treated area may become irritated or develop itching, erythema, edema, vesicles, or abnormal sensation.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aspirin
When diclofenac is administered with aspirin, the binding of diclofenac to protein is reduced, although the clearance of free diclofenac is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of diclofenac and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
7.2 Anticoagulants
The effects of anticoagulants such as warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
7.3 ACE-inhibitors
NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Consider this interaction in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
7.4 Diuretics
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing observations, have shown that NSAIDs can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, observe the patient closely for signs of renal failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)], as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
7.5 Lithium
NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, observe patients carefully for signs of lithium toxicity.
7.6 Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Use caution when NSAIDs, including diclofenac, are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
7.7 Cyclosporine
Diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal prostaglandins and increase the toxicity of certain drugs. Therefore, concomitant therapy with diclofenac may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. Use caution when diclofenac is administered concomitantly with cyclosporine.
7.8 Oral Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Concomitant use of oral and topical NSAIDs may result in a higher rate of hemorrhage, more frequent abnormal creatinine, urea and hemoglobin. Do not use combination therapy with Flector Patch and an oral NSAID unless the benefit outweighs the risk and conduct periodic laboratory evaluations.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C prior to 30 weeks gestation; Category D starting 30 weeks gestation.
Starting at 30 weeks gestation, avoid use of Flector Patch, and other NSAIDS, in pregnant women as premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur, Flector Patch can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman starting at 30 weeks gestation. If this drug is used during this time period in pregnancy, inform the patient of the potential hazard to a fetus. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Prior to 30 weeks gestation, Flector Patch should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnant Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage daily from gestation days 6-15. Maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and increased incidence of skeletal anomalies were noted with 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine, which corresponds to 3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison. Pregnant New Zealand White rabbits were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage daily from gestation days 6-18. No maternal toxicity was noted; however, embryotoxicity was evident at 6 mg/kg/day group which corresponds to 6.5-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Male rats were orally administered diclofenac epolamine (1, 3, 6 mg/kg) for 60 days prior to mating and throughout the mating period, and females were given the same doses 14 days prior to mating and through mating, gestation, and lactation. Embryotoxicity was observed at 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine (3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison), and was manifested as an increase in early resorptions, post-implantation losses, and a decrease in live fetuses. The number of live born and total born were also reduced as was F1 postnatal survival, but the physical and behavioral development of surviving F1 pups in all groups was the same as the deionized water control, nor was reproductive performance adversely affected despite a slight treatment-related reduction in body weight.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effects of Flector Patch on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown. In rat studies, maternal exposure to NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, increased the incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human-milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Flector Patch, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Flector Patch did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Diclofenac, as with any NSAID, is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to Flector Patch may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken when using Flector Patch in the elderly, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdose of Flector Patch. In clinical studies, the maximum single dose administered was one Flector Patch containing 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine. There were no serious adverse events.
Should systemic side effects occur due to incorrect use or accidental overdose of this product, the general measures recommended for intoxication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken.
For additional information about overdose treatment, call a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Flector Patch (10 cm × 14 cm) is comprised of an adhesive material containing 1.3% diclofenac epolamine which is applied to a non-woven polyester felt backing and covered with a polypropylene film release liner. The release liner is removed prior to topical application to the skin.
Diclofenac epolamine is a non-opioid analgesic chemically designated as 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl) amino]benzeneacetic acid, (2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl) ethanol salt, with a molecular formula of C20H24Cl2N2O3 (molecular weight 411.3), an n-octanol/water partition coefficient of 8 at pH 8.5, and the following structure:
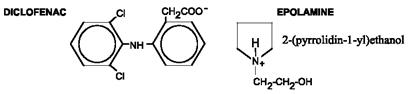
Each adhesive patch contains 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine (13 mg per gram adhesive) in an aqueous base. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: 1,3-butylene glycol, dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, disodium edetate, D-sorbitol, fragrance (Dalin PH), gelatin, kaolin, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, povidone, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, sodium polyacrylate, tartaric acid, titanium dioxide, and purified water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). In pharmacologic studies, diclofenac has shown anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activity. As with other NSAIDs, its mode of action is not known; its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, however, may be involved in its anti-inflammatory activity, as well as contribute to its efficacy in relieving pain associated with inflammation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Flector Patch applied to intact skin provides local analgesia by releasing diclofenac epolamine from the patch into the skin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a single application of the Flector Patch on the upper inner arm, peak plasma concentrations of diclofenac (range 0.7 – 6 ng/mL) were noted between 10 – 20 hours of application. Plasma concentrations of diclofenac in the range of 1.3 – 8.8 ng/mL were noted after five days with twice-a-day Flector Patch application.
Systemic exposure (AUC) and maximum plasma concentrations of diclofenac, after repeated dosing for four days with Flector Patch, were lower (<1%) than after a single oral 50-mg diclofenac sodium tablet.
The pharmacokinetics of Flector Patch has been tested in healthy volunteers at rest or undergoing moderate exercise (cycling 20 min/h for 12 h at a mean HR of 100.3 bpm). No clinically relevant differences in systemic absorption were observed, with peak plasma concentrations in the range of 2.2 – 8.1 ng/mL while resting, and 2.7 – 7.2 ng/mL during exercise.
Distribution
Diclofenac has a very high affinity (>99%) for human serum albumin.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Metabolism
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4'-hydroxy diclofenac is primarily mediated by CPY2C9. Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CPY2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy and 3'-hydroxy- diclofenac.
Excretion
The plasma elimination half-life of diclofenac after application of Flector Patch is approximately 12 hours. Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of either diclofenac epolamine or Flector Patch.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac epolamine is not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium strains, nor does it induce an increase in metabolic aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes, or the frequency of micronucleated cells in the bone marrow micronucleus test performed in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Male and female Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage (males treated for 60 days prior to conception and during mating period, females treated for 14 days prior to mating through day 19 of gestation). Diclofenac epolamine treatment with 6 mg/kg/day resulted in increased early resorptions and postimplantation losses; however, no effects on the mating and fertility indices were found. The 6 mg/kg/day dose corresponds to 3-times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ankle sprains
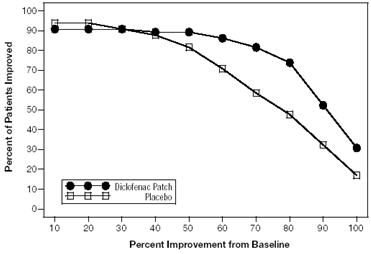
Efficacy of Flector Patch was demonstrated in two of four studies of patients with minor sprains, strains, and contusions. Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with the Flector Patch, or a placebo patch identical to the Flector Patch minus the active ingredient. In the first of these two studies, patients with ankle sprains were treated once daily for a week. In the second study, patients with sprains, strains and contusions were treated twice daily for up to two weeks. Pain was assessed over the period of treatment. Patients treated with the Flector Patch experienced a greater reduction in pain as compared to patients randomized to placebo patch as evidenced by the responder curves presented below.
Figure 1: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at Day 3; 14-Day Study
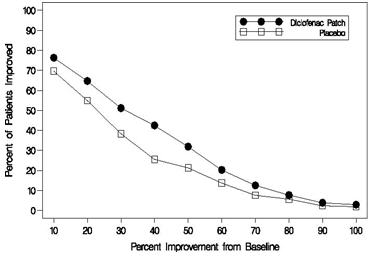
Figure 2: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at End of Study; 14-Day Study
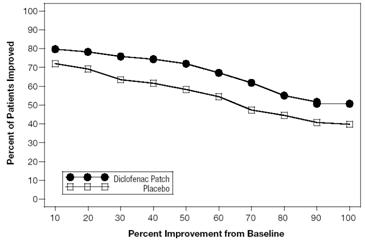
Figure 3: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at Day 3; 7-Day Study
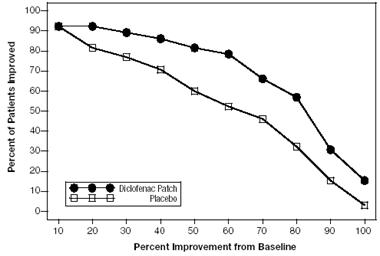
Figure 4: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at End of Study; 7-Day Study
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
The Flector Patch is supplied in resealable envelopes, each containing 5 patches (10 cm × 14 cm), with 6 envelopes per box (NDC: 60793-411-30). Each individual patch is embossed with "FLECTOR PATCH <DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL PATCH> 1.3%".
- Each patch contains 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine in an aqueous base (13 mg of active per gram of adhesive or 1.3%).
- The product is intended for topical use only.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- ENVELOPES SHOULD BE SEALED AT ALL TIMES WHEN NOT IN USE.
- Curad® Hold Tite™ is a trademark of Medline Industries, Inc., and Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing is a trademark of Derma Sciences, Inc.
Storage
Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15º-30ºC (59º-86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals Inc.
501 Fifth Street
Bristol TN 37620 USA
Telephone: 1-888-840-8884 www.FlectorPatch.comManufactured for: IBSA Institut Biochimique SA, CH-6903 Lugano, Switzerland
Manufactured by: Teikoku Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Sanbonmatsu, Kagawa 769-2695 Japan
FI/165 1086
Ed. VI/2.11
Version February, 2011Repacked by:
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
513 Sandydale Drive
Nipomo, CA 93444 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide
17.1 Information on Medication Guide
Inform patients of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Encourage patients to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed prior to using Flector Patch.
17.2 Cardiovascular Effects
Flector Patch, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, instruct patients to be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and to ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Inform patients of the importance of this follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.3 Gastrointestinal Effects
Flector Patch, like other NSAIDs, may cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, inform patients to be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulceration and bleeding, and to ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Instruct patients of the importance of this follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
17.4 Adverse Skin Reactions
Flector Patch, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious systemic skin reactions may occur without warning, instruct patients to be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and to ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Advise patients to stop Flector Patch immediately if they develop any type of generalized rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
Flector Patch can cause a localized skin reaction at the application site. Advise patients to contact their physicians as soon as possible if they develop any type of localized application site rash.
Instruct patients not to apply Flector Patch to open skin wounds or infections.
17.5 Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop therapy with Flector Patch and seek immediate medical therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
17.6 Weight gain and edema
Patients should promptly report to their physician signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema following treatment with Flector Patch [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
17.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, instruct patients to seek immediate emergency help. Anaphylaxis type reactions have been reported with diclofenac products, including Flector Patch [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
17.8 Preexisting Asthma
Inform patients not to use Flector Patch if they have an aspirin-sensitive asthma. Flector Patch, like other NSAIDs, could cause severe and even fatal bronchospasm in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Instruct patients to discontinue use of Flector Patch and to immediately seek emergency help if they experience wheezing or shortness of breath.
17.9 Eye Exposure
Instruct patients to avoid contact of Flector Patch with the eyes and mucosa. Advise patients that if eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and consult a physician if irritation persists for more than an hour [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
17.10 Effects during pregnancy
Starting at 30 weeks gestation, instruct patients to avoid the use of Flector Patch and other NSAIDS, as premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus may occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
17.11 General Information on Use
- Instruct patients and caregivers to wash their hands after applying, handling or removing the patch.
- Inform patients that, if Flector Patch begins to peel off, the edges of the patch may be taped down. If problems with adhesion persist, patients may overlay the patch with a mesh netting sleeve, where appropriate (e.g. to secure patches applied to ankles, knees, or elbows). The mesh netting sleeve (e.g. Curad® Hold Tite™, Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing) must allow air to pass through and not be occlusive (non-breathable).
- Instruct patients not to wear Flector Patch during bathing or showering. Bathing should take place in between scheduled patch removal and application [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- Instruct patients to store Flector Patch and to discard used patches out of the reach of children and pets. If a child or pet accidentally ingests Flector Patch, instruct patients to seek medical help immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
- Inform patients that Flector Patch should be used only on intact skin.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals Inc
501 Fifth Street
Bristol, TN 37620 USA
Telephone: 1-888-840-8884 www.FlectorPatch.comManufactured for: IBSA Institut Biochimique SA, CH-6903 Lugano, Switzerland
Manufactured by: Teikoku Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Sanbonmatsu, Kagawa 769-2695 Japan
FI/165 1086
Ed. VI/2.11
Version February, 2011Repacked by:
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
513 Sandydale Drive
Nipomo, CA 93444
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This chance increases:
- with longer use of NSAID medicines
- in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a "coronary artery bypass graft" (CABG).
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
- can happen without warning symptoms
- may cause death
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:- taking medicines called "corticosteroids" and "anticoagulants"
- longer use
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
- different types of arthritis
- menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
- if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
- for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all of your medical conditions.
- about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- if you are pregnant, NSAID medicines should not be used past 30 weeks of pregnancy..
- if you are breastfeeding, talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Serious side effects include: Other side effects include: - heart attack
- stroke
- high blood pressure
- heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention)
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life-threatening allergic reactions
- liver problems including liver failure
- asthma attacks in people who have asthma
- stomach pain
- constipation
- diarrhea
- gas
- heartburn
- nausea
- vomiting
- dizziness
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over–the–counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over–the–counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
NSAID medicines that need a prescription Generic Name Tradename Celecoxib Celebrex Diclofenac Flector, Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) Diflunisal Dolobid Etodolac Lodine, Lodine XL Fenoprofen Nalfon, Nalfon 200 Flurbirofen Ansaid Ibuprofen Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) Indomethacin Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan Ketoprofen Oruvail Ketorolac Toradol Mefenamic Acid Ponstel Meloxicam Mobic Nabumetone Relafen Naproxen Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) Oxaprozin Daypro Piroxicam Feldene Sulindac Clinoril Tolmetin Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals Inc.
501 Fifth Street
Bristol, TN 37620 USA
Telephone: 1-888-840-8884 www.FlectorPatch.comManufactured for: IBSA Institut Biochimique SA, CH-6903 Lugano, Switzerland
Manufactured by: Teikoku Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Sanbonmatsu, Kagawa 769-2695 Japan
FI/165 1086
Ed. VI/2.11
Version February, 2011Repacked by:
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
513 Sandydale Drive
Nipomo, CA 93444
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.3% Carton
NDC: 52959-518-30
FLECTOR® PATCH
(diclofenac epolamine topical patch)
1.3%Rx Only
30 PATCHES (10 CM X 14 CM EACH)
Change patch once every 12 hours.
Fold used patches so that the adhesive side sticks to itself and safely
discard used patches where children and pets cannot get to them.IBSA
King Pharmaceuticals

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FLECTOR
diclofenac epolamine patchProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 52959-518(NDC:60793-411) Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Diclofenac Epolamine (UNII: X5F8EKL9ZG) (Diclofenac - UNII:144O8QL0L1) Diclofenac Epolamine 180 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sorbitol (UNII: 506T60A25R) Butylene Glycol (UNII: 3XUS85K0RA) Dihydroxyaluminum Aminoacetate (UNII: DO250MG0W6) Edetate Disodium (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) Tartaric Acid (UNII: W4888I119H) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Gelatin (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Kaolin (UNII: 24H4NWX5CO) Methylparaben (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) Polysorbate 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) Povidone (UNII: FZ989GH94E) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Propylene Glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium (UNII: K679OBS311) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score Shape RECTANGLE Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 52959-518-05 5 in 1 CARTON 2 NDC: 52959-518-30 30 in 1 CARTON Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021234 01/14/2008 Labeler - H.J. Harkins Company, Inc. (147681894) Registrant - H.J. Harkins Company, Inc. (147681894) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations H.J. Harkins Company, Inc. 147681894 repack, relabel
Trademark Results [Flector]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FLECTOR 90530417 not registered Live/Pending |
Smith, Brian Alan 2021-02-16 |
 FLECTOR 79027520 3280194 Live/Registered |
IBSA INSTITUT BIOCHIMIQUE S.A. 2006-05-29 |
 FLECTOR 75638202 2388657 Dead/Cancelled |
Brian A. Smith 1999-02-15 |
 FLECTOR 73514500 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
FABRICA ELECTROTECNICA JOSA, S.A. 1984-12-20 |
 FLECTOR 72159912 0759991 Dead/Expired |
PARECHOC S.A. 1962-12-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.