DURLAZA- acetylsalicylic acid capsule, extended release
DURLAZA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DURLAZA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc., PATHEON PHARMACEUTICALS INC.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DURLAZA™ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DURLAZA.
DURLAZA (aspirin) Extended Release Capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval:2015INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DURLAZA is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated to reduce the risk of death and myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with chronic coronary artery disease, such as patients with a history of MI or unstable angina pectoris or with chronic stable angina and to reduce the risk of death and recurrent stroke in patients who have had an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (1)
Limitation of Use: Use immediate-release aspirin, not DURLAZA in situations where a rapid onset of action is required (such as acute treatment of myocardial infarction or before percutaneous coronary intervention). (1, 4)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose is 162.5 mg per day with a full glass of water at the same time each day (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Capsules, 162.5 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions are Gastrointestinal (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact New Haven Pharmaceuticals at (877) 824-2483 or www.newhavenpharma.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Alcohol: do not take DURLAZA 2 hours before or 1 hour after consuming alcohol (7)
- Dual inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system: Increased risk of renal impairment, hypotension and hyperkalemia (7)
- Anticoagulant and antiplatelets: increased risk of bleeding (7)
- Anticonvulsants: decreased phenytoin concentration and increased serum valproic acid levels (7)
- Methotrexate: increased risk of bone marrow toxicity (7)
- NSAIDs: Increased risk of bleeding. Nonselective NSAIDs may interfere with DURLAZAs antiplatelet effect (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2015
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Bleeding
5.2 Peptic Ulcer Disease
5.3 Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Chronic Coronary Artery Disease
14.2 Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DURLAZA is indicated to:
- Reduce the risk of death and myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with chronic coronary artery disease, such as patients with a history of MI or unstable angina pectoris or with chronic stable angina
- Reduce the risk of death and recurrent stroke in patients who have had an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack
Limitation of Use: Use immediate-release aspirin, not DURLAZA in situations where a rapid onset of action is required (such as acute treatment of myocardial infarction or before percutaneous coronary intervention).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of DURLAZA is one capsule (162.5 mg) once daily. Take the capsules with a full glass of water at the same time each day.
Swallow DURLAZA capsules whole. Do not cut, crush or chew capsules.
Do not take DURLAZA 2 hours before or 1 hour after consuming alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Bleeding
DURLAZA increases the risk of bleeding. Risk factors for bleeding include the use of other drugs that increase the risk of bleeding (e.g., anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and chronic use of NSAIDs) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.2 Peptic Ulcer Disease
DURLAZA may cause gastric ulceration and bleeding. Avoid DURLAZA in patients with active peptic ulcer disease.
5.3 Fetal Toxicity
DURLAZA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Maternal aspirin use during later stages of pregnancy may cause low birth weight, increased incidence for intracranial hemorrhage in premature infants, stillbirths and neonatal death. Because NSAIDs may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus, avoid DURLAZA in the third trimester of pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The following is a list of adverse reactions that have been reported in the literature for products containing low dose aspirin [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Central Nervous System: Agitation, cerebral edema, coma, confusion, dizziness, headache, lethargy, seizures.
Fluid and Electrolyte: Hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis.
Gastrointestinal: Dyspepsia, hepatic enzyme elevation, hepatitis, Reye's Syndrome.
Renal: Interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis, proteinuria, renal insufficiency and failure.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Alcohol: Do not take DURLAZA 2 hours before or 1 hour after consuming alcohol. Alcohol can interfere with the controlled release properties of DURLAZA.
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors: In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or who have compromised renal function, coadministration of NSAIDs, including DURLAZA, with RAS inhibitors may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving RAS inhibitors and DURLAZA.
NSAIDs, including DURLAZA may attenuate the antihypertensive effects of RAS inhibitors.
Anticoagulant and antiplatelets: Increased risk of bleeding
Anticonvulsants: Salicylate can displace protein-bound phenytoin and valproic acid, leading to a decrease in the total concentration of phenytoin and an increase in serum valproic acid levels.
Methotrexate: Salicylate can inhibit renal clearance of methotrexate, leading to bone marrow toxicity, especially in the elderly or renal impaired.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): The concurrent use of DURLAZA with other NSAIDs increases the risk of bleeding and may result in renal impairment.
Ibuprofen can interfere with the anti-platelet effect of low dose aspirin. Patients who use DURLAZA and take a single dose of ibuprofen 400 mg should dose the ibuprofen at least 2-4 hours or longer after ingestion of DURLAZA. Wait 8 hours after ibuprofen dosing, before giving aspirin, to avoid significant interference.
Nonselective NSAIDs may interfere with the antiplatelet effect of low-dose aspirin.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Avoid use during the third trimester of pregnancy because NSAIDs such as DURLAZA may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Salicylate products have also been associated with alterations in maternal and neonatal hemostasis mechanisms, decreased birth weight, and with perinatal mortality.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Avoid DURLAZA 1 week prior to and during labor and delivery because it can result in excessive blood loss at delivery. Prolonged gestation and prolonged labor due to prostaglandin inhibition have been reported.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from DURLAZA, choose either to discontinue DURLAZA or discontinue nursing.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In a large collaborative overview of aspirin for vascular event prevention, including over 14000 patients over 65 years of age, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Salicylate toxicity may result from acute ingestion (overdose) or chronic intoxication. The early signs of salicylic overdose (salicylism), including tinnitus (ringing in the ears), occur at plasma concentrations approaching 200 mcg/mL. Plasma concentrations of aspirin above 300 mcg/mL are clearly toxic. Severe toxic effects are associated with levels above 400 mcg/mL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A single lethal dose of aspirin in adults is not known with certainty but death may be expected at 30 g. For real or suspected overdose, contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Signs and Symptoms: In acute overdose, severe acid-base and electrolyte disturbances may occur and are complicated by hyperthermia and dehydration. Respiratory alkalosis occurs early while hyperventilation is present, but is quickly followed by metabolic acidosis.
Treatment: Treatment consists primarily of supporting vital functions, increasing salicylate elimination, and correcting the acid-base disturbance. Gastric emptying or lavage is recommended as soon as possible after ingestion, even if the patient has vomited spontaneously. After lavage or emesis, administer activated charcoal, as a slurry, if less than 3 hours have passed since ingestion.
Severity of aspirin intoxication is determined by measuring the blood salicylate level. Monitor acid-base status with serial blood gas and serum pH measurements. Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
In severe cases, hyperthermia and hypovolemia are the major immediate threats to life. Replace fluid intravenously and correct acidosis. Monitor plasma electrolytes and pH to promote alkaline diuresis of salicylate if renal function is normal. Glucose may be required to control hypoglycemia.
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can reduce the body aspirin content. In patients with renal insufficiency or in cases of life-threatening intoxication, dialysis is usually required. Exchange transfusion may be indicated in infants and young children.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
DURLAZA Capsules contain aspirin, which is a platelet aggregation inhibitor, for oral administration. Chemically, aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. It has the following structural formula:
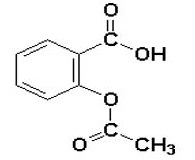
Aspirin is white or almost white crystalline powder or colorless crystals consisting of cubical and squared crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in ethanol. When exposed to moisture, aspirin hydrolyzes into salicylic and acetic acids, and gives off a vinegary odor. It has a molecular weight of 180.16 g/mole and a molecular formula C9H8O4.
Durlaza capsules also include the following inactive ingredients: ethylcellulose, povidone, castor oil, tartaric acid, magnesium stearate, colloidal anhydrous silica, and talc.
The capsule shell contains gelatin and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Aspirin [acetylsalicylic acid (ASA)] inhibits prostaglandin synthesis resulting in inhibition of platelet aggregation for their lifespan of about 7-10 days. The acetyl group of aspirin binds with a serine residue of cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1), resulting in irreversible inactivation of the enzyme. Inhibition of COX-1 prevents conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A2 (TXA2), which is a potent agonist of platelet aggregation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The dose-response relationship for DURLAZA and immediate release (IR) aspirin towards COX-1 inhibition was characterized by examining the inhibition of serum TXB2 and urine 11-dehydro-TXB2 at 24 h following a single dose. Doses over the range of 20 mg to 325 mg for DURLAZA and 5 mg to 81 mg for IR aspirin respectively were studied. Half-maximal inhibition of serum TXB2 and urine 11-dehydro-TXB2 occurred with doses of DURLAZA (ID50) about 2-fold the dose of immediate release (IR) aspirin. Based on this relationship, the pharmacodynamic effect of DURLAZA 162.5 mg is similar to that attained with IR aspirin 81 mg. The mean inhibition of serum TXB2 following DURLAZA (82%) is lower when compared to IR aspirin 81 mg (93%) following the first dose. However, upon repeat administration, near maximal inhibition of serum TXB2 is achieved, similar to what is achieved following repeated daily doses of IR aspirin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, DURLAZA exhibits extended release of aspirin from the encapsulated microparticles, thereby prolonging the absorption of aspirin across the GI tract compared to IR aspirin (Figure 1). Once absorbed, aspirin is metabolized, distributed, and excreted in a manner similar to that of aspirin absorbed from IR dosage forms.
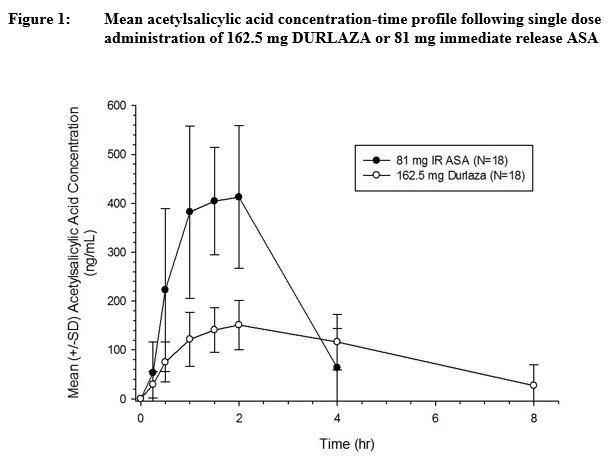
Absorption: Following administration of DURLAZA, the time to reach peak plasma concentration of aspirin is slightly longer compared to following IR aspirin dosage form. Median Tmax for DURLAZA is about 2 h when compared to 1 h following IR aspirin (see Figure 1). The mean Cmax for DURLAZA is approximately 35% of that following IR aspirin 81 mg. The area under the plasma concentration-time curve for aspirin following administration of DURLAZA is approximately 70% of that following IR aspirin. The rate of DURLAZA absorption is dependent on food, alcohol, and gastric pH.
Distribution: The volume of distribution of usual doses of aspirin in normal subjects averages approximately 170 mL/kg of body weight.
Metabolism: Aspirin is rapidly hydrolyzed in the plasma to salicylic acid such that plasma levels of aspirin following DURLAZA administration are essentially undetectable 4-8 hours after dosing. In contrast to immediate release aspirin, measurable levels of salicylic acid at 24 hours following a single dose of DURLAZA were observed. Salicylic acid is primarily conjugated in the liver to form salicyluric acid, a phenolic glucuronide, an acyl glucuronide, and a number of minor metabolites.
Elimination: The mean plasma half-life of aspirin may range from 20 to 60 min. Following therapeutic doses, approximately 10% is found excreted in the urine as salicylic acid, 75% as salicylic acid, and 10% phenolic and 5% acyl glucuronides of salicylic acid.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenesis, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility studies were conducted with DURLAZA. Aspirin is not considered to be genotoxic or carcinogenic. Studies with oral aspirin in pregnant rats demonstrated the occurrence of fetal malformations at oral doses at or above 250 mg/kg [Human equivalent dose (HED) 40 mg/kg].
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Chronic Coronary Artery Disease
This indication is supported by the results of six large, randomized, multi-center, placebo controlled trials of predominantly male post-MI subjects and one randomized placebo-controlled study of men with unstable angina pectoris. Aspirin therapy in MI subjects gave about 20% reduction in the relative risk of the combined endpoint of death or nonfatal reinfarction. In the study of male unstable angina patients, aspirin reduced the event rate from 10% in the placebo patients to 5% in the patients treated with aspirin.
It is also supported by a randomized, multi-center, double-blind trial designed to assess the effect of aspirin in reducing the risk of MI in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris. Aspirin reduced the relative risk of the primary combined endpoint of nonfatal MI, fatal MI, and sudden death by 34%. The secondary endpoint for vascular events (the first occurrence of MI, stroke, or vascular death) was also significantly reduced.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
DURLAZA Capsules, 162.5 mg, are supplied as follows:
Size 2 white to off-white opaque capsules imprinted with the name Durlaza
Bottles of 30 capsules NDC: 58487-001-01
Bottles of 90 capsules NDC: 58487-001-02
Special Precautions for Storage: Store at 25 °C (77 °F); excursions permitted to 15 - 30°C (59 -86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients prior to initiating treatment with DURLAZA and periodically during the course of ongoing treatment:
Bleeding
- Inform patients that they may bruise or bleed more easily or that it may take longer to stop bleeding and to report to their physician any prolonged, unusual or excessive bleeding. Inform patients to notify their physician about blood in their stool or urine and the signs and symptoms of occult bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of GI side effects and seek medical advice when experiencing any of these signs and symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Hypersensitivity
- Advise the patient to discontinue DURLAZA and seek immediate medical attention if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur [see Contraindications (4)].
Alcohol Consumption
- Inform patients they should not take DURLAZA 2 hours before or 1 hour after consuming alcohol. Counsel patients who drink three or more alcoholic drinks every day about the risk of bleeding involved in chronic, heavy alcohol use while taking DURLAZA [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Administration Instructions
- Advise patients to swallow DURLAZA capsules whole and not to chew or crush them.
- Remind patients not to discontinue DURLAZA without first notifying and discussing with their physician. Advise patients not to use extra medicine to make up a missed dose.
- Advise patients not to take ibuprofen around the same time as DURLAZA [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Pregnancy and Lactation
- Advise patients that ASA containing products such as DURLAZA cause harm to fetuses especially during the third trimester of pregnancy. Inform patients to notify their physician if they are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, breastfeed or are considering breastfeeding prior or during receiving treatment with DURLAZA [See Use in Special Populations (8.2, 8.3)].
Manufactured for New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
North Haven, CT 06473
DURLAZA Capsules manufactured in USA
Distributed by Cardinal Health 105, Inc. -
PACKAGE LABEL
NDC: 58487-001-02
DURLAZA™
(ASPIRIN)
Extended Release Capsules
162.5 mg
Rx Only
90 Capsules
DOSAGE: See package insert for full Prescribing Information.
Take DURLAZA once daily.
Swallow capsules whole.
Do not cut, crush or chew.
Each capsule contains 162.5 mg of aspirin.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep out of reach of children.
www.durlaza.com
Manufactured for:
New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
North Haven, CT 06473
Made in USA
©2015 New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
19959
LOT:
EXP:

-
PACKAGE LABEL
NDC: 58487-001-01
DURLAZA™
(ASPIRIN)
Extended Release Capsules
162.5 mg
Rx Only
30 Capsules
DOSAGE: See package insert for full Prescribing Information.
Take DURLAZA once daily.
Swallow capsules whole.
Do not cut, crush or chew.
Each capsule contains 162.5 mg of aspirin.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep out of reach of children.
Manufactured for:
New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
North Haven, CT 06473
Made in USA
www.durlaza.com
©2015 New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
19958
LOT:
EXP:
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DURLAZA
acetylsalicylic acid capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58487-001 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Aspirin (UNII: R16CO5Y76E) (Aspirin - UNII:R16CO5Y76E) Aspirin 162.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Ethylcelluloses (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) Povidones (UNII: FZ989GH94E) Castor Oil (UNII: D5340Y2I9G) Tartaric Acid (UNII: W4888I119H) Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Gelatin (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape OVAL (OBLONG) Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code DURLAZA Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58487-001-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 58487-001-02 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA200671 09/25/2015 Labeler - New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (078715268) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations PATHEON PHARMACEUTICALS INC. 005286822 MANUFACTURE(58487-001)
Trademark Results [DURLAZA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DURLAZA 86041501 4851723 Live/Registered |
New Haven Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2013-08-19 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.