GOMEKLI- mirdametinib capsule GOMEKLI- mirdametinib tablet, for suspension
Mirdametinib by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Mirdametinib by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GOMEKLI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GOMEKLI.
GOMEKLITM (mirdametinib) capsules, for oral use
GOMEKLITM (mirdametinib) tablets for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GOMEKLI is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of GOMEKLI is 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily, with or without food, for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle. Continue treatment with GOMEKLI until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
Ocular Toxicity: Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment and for new or worsening visual changes or blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity. (5.1)
-
Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Assess ejection fraction by echocardiogram prior to initiating GOMEKLI, every 3 months during the first year, then as clinically indicated thereafter. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity. (5.2)
-
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions: Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions including rash. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity. (5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adults:
- The most common adverse reactions (>25%) were rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, and fatigue. (6.1)
- The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormality (>2%) was increased creatine phosphokinase. (6.1)
Pediatric patients:
- The most common adverse reactions (>25%) were rash, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, paronychia, left ventricular dysfunction, and nausea. (6.1)
- The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (>2%) were decreased neutrophil count and increased creatine phosphokinase. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact SpringWorks Therapeutics Inc. at 1-888-400-7989 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2025
-
Ocular Toxicity: Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment and for new or worsening visual changes or blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity. (5.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating GOMEKLI
2.2 GOMEKLI Dosage Form Overview
2.3 Recommended Dosage
2.4 GOMEKLI Preparation and Administration Instructions
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ocular Toxicity
5.2 Left Ventricular Dysfunction
5.3 Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Associated Plexiform Neurofibromas
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GOMEKLI is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating GOMEKLI
Prior to administration of GOMEKLI:
- conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- assess ejection fraction (EF) by echocardiogram [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 GOMEKLI Dosage Form Overview
GOMEKLI is available in 2 dosage forms: capsules or tablets for oral suspension.
-
GOMEKLI capsules: must be swallowed whole, do not open, break or chew capsules.
- GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension: can be swallowed whole or can be dispersed in drinking water and administered orally as a liquid [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of GOMEKLI is 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily (approximately every 12 hours) with or without food for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle. The maximum dose is 4 mg twice daily. Continue treatment with GOMEKLI until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The recommended dose of GOMEKLI is based on body surface area (BSA) as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage for GOMEKLI Body Surface Area (m2) * Recommended Dosage for Capsules or Tablets for Oral Suspension 0.40 to 0.69 1 mg twice daily 0.70 to 1.04 2 mg twice daily 1.05 to 1.49 3 mg twice daily ≥1.50 4 mg twice daily *The recommended dosage for patients with a BSA less than 0.40 m2 has not been established.
Missed dose: If the patient misses a dose of GOMEKLI, do not take an additional dose. Take the next scheduled dose at the prescribed time.
Vomiting: If vomiting occurs after GOMEKLI administration, do not take an additional dose. Take the next scheduled dose at the prescribed time.
2.4 GOMEKLI Preparation and Administration Instructions
GOMEKLI Capsules
- Swallow GOMEKLI capsules whole with or without food. If more than one capsule is required for a dose, swallow one capsule at a time.
- Do not open, break or chew capsules. Do not administer to patients who are unable to swallow a whole capsule [see GOMEKLI Tablets for Oral Suspension].
GOMEKLI Tablets for Oral Suspension
- GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension can be swallowed whole with or without food. If more than one tablet is required for a dose, swallow one tablet at a time.
- For patients who are not able to swallow whole tablets, prepare GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension dispersed in drinking water and administer orally as a liquid [see Instructions for Use].
Preparation and Administration
- Add the prescribed number of tablets to a dosing cup containing approximately 5 mL to 10 mL of drinking water.
- Gently swirl the water and tablets until the tablets are fully dispersed and an oral suspension is obtained. It takes approximately two to four minutes to fully disperse the tablets. Once the tablets are dispersed, the oral suspension will appear white and cloudy.
- Administer the oral suspension immediately after preparation from a dosing cup or oral syringe.
- After administration of the prepared suspension, add approximately 5 mL to 10 mL of drinking water to the dosing cup and gently swirl to resuspend any remaining particles. Administer the suspension to ensure the full dose is taken.
- Discard the oral suspension if not administered within 30 minutes after preparation.
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Dose Reductions for GOMEKLI for Adverse Reactions Body Surface Area (m2) Reduced Dose* Morning Evening 0.40 to 0.69 1 mg once daily 0.70 to 1.04 2 mg 1 mg 1.05 to 1.49 2 mg 2 mg ≥1.50 3 mg 3 mg *Permanently discontinue GOMEKLI in patients unable to tolerate GOMEKLI after one dose reduction.
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 3.
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Modifications and Management of Adverse Reactions for GOMEKLI Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modification Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Grade ≤ 2 - Continue GOMEKLI at current dose level.
- Consider ophthalmologic examinations every 2 to 4 weeks until resolution to ≤Grade 1 or baseline.
Grade ≥ 3 - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1 or baseline.
- If recovery occurs ≤14 days, resume GOMEKLI at the next lower dose.
- If recovery occurs in >14 days, consider permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI.
Symptomatic Retinal Pigment Epithelium Detachment (RPED) - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1 or baseline.
- Resume GOMEKLI at the same dose.
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) - Permanently discontinue GOMEKLI.
Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Asymptomatic, absolute decrease in LVEF of 10% or greater from baseline and is less than the lower limit of normal - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1.
- Resume GOMEKLI at reduced dose.
Any absolute decrease in LVEF 20% or greater from baseline - Permanently discontinue GOMEKLI.
Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modification Dermatologic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] Intolerable Grade 2 or Grade 3 - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1.
- Resume GOMEKLI at reduced dose.
Grade 3 or 4 Dermatitis Acneiform or Non-Acneiform Rash - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1.
- Resume GOMEKLI at reduced dose.
Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Intolerable Grade 2 or Grade 3 - Withhold GOMEKLI until ≤Grade 1.
- Resume GOMEKLI at reduced dose.
Grade 4 - Consider permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI.
*Per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0 (NCI CTCAE v. 5.0).
- conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ocular Toxicity
GOMEKLI can cause ocular toxicity including retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED), and blurred vision.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ocular toxicity occurred in 25% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 20% were Grade 1 reactions, 3.8% were Grade 2 reactions, and 0.8% were Grade 3 reactions.
Adult Patients
In the adult pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ocular toxicity occurred in 28% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 21% were Grade 1 reactions, 5% were Grade 2 reactions and 1.3% were Grade 3 reactions. Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) occurred in 2.7% of adult patients, including one Grade 3 reaction which required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI. RPED occurred in one adult patient (1.3%). Blurred vision occurred in 9% of adult patients treated with GOMEKLI.
Pediatric Patients
In the pediatric pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ocular toxicity occurred in 19% of patients: 17% were Grade 1 and 1.7% were Grade 2.
Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment, and to evaluate any new or worsening visual changes such as blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.2 Left Ventricular Dysfunction
GOMEKLI can cause left ventricular dysfunction. Treatment with GOMEKLI has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF <55% prior to initiation of treatment.
In the ReNeu study, in adult and pediatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 20%, and decreased LVEF of ≥20% occurred in 0.9% of patients treated with GOMEKLI. All patients with decreased LVEF were identified during routine echocardiography. Decreased LVEF resolved in 75% of these patients.
Adult Patients
In adult patients in the ReNeu study [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 16% of adult patients treated with GOMEKLI. Of the adult patients with decreased LVEF, five patients (9%) required dose interruption, one patient (1.7%) required a dose reduction and one patient required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in adult patients was 70 days.
Pediatric Patients
In pediatric patients in the ReNeu study [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 25%, and decreased LVEF of ≥20% occurred in 1.8% of patients treated with GOMEKLI. Of the pediatric patients with decreased LVEF, one patient (1.8%) required dose interruption of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in pediatric patients was 132 days.
Before initiating GOMEKLI, assess ejection fraction (EF) by echocardiogram. Monitor EF every 3 months during the first year and then as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on the severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.3 Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
GOMEKLI can cause dermatologic adverse reactions including rash.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], rash occurred in 84% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 31% were Grade 2, and 6% were Grade 3. The most frequent rashes (≥2%) included dermatitis acneiform (65%), rash (11%), eczema (8%), maculo-papular rash (4.5%) and pustular rash (3.8%).
Adult Patients
In the pooled adult safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], rash occurred in 92% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 37% were Grade 2 and 8% were Grade 3 reactions. Rash requiring permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI occurred in 11% of adult patients.
Pediatric Patients
In the pooled pediatric safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], rash occurred in 72% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 22% were Grade 2 and 3.4% were Grade 3 reactions.
Rash resulting in permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI occurred in 3.4% of pediatric patients.
Dermatitis acneiform occurred with a higher frequency in patients aged 12 to 17 years (77%) than those aged 2 to 11 years (16%), while non-acneiform rashes occurred with a higher frequency in patients aged 2 to 11 years (53%) than those aged 12 to 17 years (15%).
Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from clinical trials, animal studies and its mechanism of action, GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In ReNeu, a pregnancy reported 31 days after the last dose of GOMEKLI resulted in a first trimester spontaneous abortion.
In embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of mirdametinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryo-fetal mortality, structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at doses approximately equivalent to the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on body surface area (BSA).
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of GOMEKLI. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Dermatologic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to GOMEKLI in 133 patients (75 adults and 58 pediatric patients) in the ReNeu study [see Clinical Studies (14)] (n=114) and Study NF-106 (n=19) [NCT-02096471].
Patients received GOMEKLI 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Among 133 patients who received GOMEKLI, 62% were exposed for one year or longer, 38% were exposed for 2 years or longer, and 12% were exposed for 3 years or longer.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Plexiform Neurofibromas
The safety of GOMEKLI was evaluated in the ReNeu study [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Eligible patients were 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who had symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN). Patients were excluded for abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), uncontrolled hypertension, alanine transaminase (ALT) value of >2 × upper limit of normal (ULN), any current or history of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) or retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED), intraocular pressure >21 mmHg (or upper limit of normal adjusted by age), and history of glaucoma. Patients received GOMEKLI 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Adult Patients
The median age of adult patients (age ≥18) who received GOMEKLI was 35 years (range: 18-69); 64% were female; 85% were White, 9% were Black or African American, 3.4% were Asian, 3.4% were other races or race not reported; and 1.7% were Hispanic or Latino. For adult patients treated with GOMEKLI, the median duration of treatment was 22 months (range: 0.4 to 46 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of adult patients who received GOMEKLI. Serious adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients were COVID-19 (3.4%), nephrolithiasis (3.4%), and in 1 patient each: acute kidney injury, abdominal pain, ischemic colitis, urinary tract infection, retinal vein occlusion, scoliosis, squamous cell carcinoma of skin, cerebrovascular accident and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. One fatal adverse reaction occurred in an adult patient (1.7%) who received GOMEKLI, due to COVID-19.
Permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 22% of adult patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI in ≥1% of adult patients were rash, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, alopecia, dry skin, left ventricular dysfunction, cough, wheezing, COVID-19, peripheral swelling, RVO, dizziness, and vomiting.
Dosage interruptions of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 31% of adult patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥5% of patients included left ventricular dysfunction and COVID-19.
Dose reductions of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 17% of adult patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥5% of patients included rash.
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) were rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, and fatigue. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormality (>2%) was increased creatine phosphokinase.
Pediatric Patients
The median age of pediatric patients (age ≤17 years) who received GOMEKLI was 10 years (range: 2 to 17); 54% were female; 66% were White, 20% were Black or African American, 9% were other races or race not reported, 3.6% were Asian, 1.8% were American Indian or Alaska Native; and 14% were Hispanic or Latino. For pediatric patients treated with GOMEKLI, the median duration of treatment was 22 months (range: 1.6 to 40 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14% of pediatric patients who received GOMEKLI. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% of patients included viral gastrointestinal infections (3.6%) and in 1 patient each: diplopia, musculoskeletal pain, seizure, fall, femoral neck fracture, dehydration and hypertension.
Permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 9% of pediatric patients. Adverse reactions that required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI in ≥1% of patients were urticaria, rash, abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea.
Dosage interruptions of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 30% of pediatric patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥5% of patients included COVID-19.
Dose reductions of GOMEKLI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 13% of pediatric patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage reduction in ≥3% of pediatric patients were rash and decreased neutrophil count.
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) were rash, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, paronychia, left ventricular dysfunction, and nausea. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (>2%) were decreased neutrophil count and increased creatine phosphokinase.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥20%) in Adult and Pediatric Patients with NF1- Associated PN Who Received GOMEKLI in ReNeu Adult N=58 Pediatric N=56 Total N=114 All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4a (%) All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4a (%) All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4a
(%)Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Rashb 90 10 73 3.6 82 7 Gastrointestinal Disorders Diarrheac 59 0 55 5 57 2.6 Nausea 52 0 27 0 40 0 Vomiting 38 0 39 0 39 0 Abdominal Paind 24 3.4 39 3.6 32 3.5 Stomatitise 5 0 20 0 12 0 Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Musculoskeletal Painf 41 5 41 1.8 41 3.5 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 29 1.7 13 0 21 0.9 Pyrexia 7 0 20 0 13 0 Infections and Infestations COVID-19g 22 5 25 0 24 2.6 Paronychia 1.7 0 32 0 17 0 Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 0 0 23 0 11 0 Nervous System Disorders Headacheh 14 1.7 34 1.8 24 1.8 Peripheral Neuropathyi 21 0 3.6 0 12 0 Cardiac Disorders Left Ventricular Dysfunction 16 0 27 1.8 21 0.9 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Coughj 9 0 21 0 15 0 a All reactions were Grade 3 except one fatal case of COVID-19 in an adult.
b Rash includes dermatitis acneiform, eczema, maculo-papular rash, pustular rash, dermatitis, erythematous rash, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, exfoliative rash, skin exfoliation, pruritic rash, papule, papular rash and macular rash.
c Diarrhea includes frequent bowel movements.
d Abdominal pain includes upper abdominal pain, gastrointestinal pain and abdominal discomfort.
e Stomatitis includes mouth ulceration, aphthous ulcer.
f Musculoskeletal pain includes non-cardiac chest pain, back pain, pain in extremity, neck pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, arthralgia, and bone pain.
g Includes one fatal case in an adult.
h Headache includes migraine.
i Peripheral neuropathy includes paresthesia, hypoesthesia, neuralgia, peripheral sensory neuropathy.
j Cough includes upper-airway cough syndrome.
Clinically relevant adverse reactions that occurred in <20% of patients include:
-
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: alopecia, hair color changes
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders: constipation
- Eye Disorders: retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED) and blurred vision
Table 5 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in ReNeu.
Table 5: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥15%) that Worsened from Baseline in Adult and Pediatric Patients with NF1-Associated PN Who Received GOMEKLI in ReNeu Adulta Pediatricb Totalc
Laboratory Abnormalityd,eAll Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4d
(%)All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4d
(%)All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4d
(%)Chemistry Increased Creatine Phosphokinase 55 3.6 59 5 57 4.5 Increased Triglycerides 29 0 45 0 37 0 Decreased Glucose 5 0 36 1.8 21 0.9 Decreased Calciumf 23 0 20 0 21 0 Increased Creatinine 13 0 30 0 21 0 Increased Cholesterol 23 0 16 0 20 0 Increased Alkaline Phosphatase 13 0 29 0 21 0 Decreased Bicarbonate 11 0 21 0 16 0 Increased Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) 9 0 21 0 15 0 Increased Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) 18 0 9 0 13 0 Hematology Decreased Hemoglobin 21 0 29 0 25 0 Decreased Leukocytes 7 0 40 0 23 0 Decreased Neutrophils 7 0 31 11 19 5 Increased Lymphocytes 7 0 27 0 17 0 Decreased Lymphocytes 16 0 1.8 0 9 0 a The denominator used to calculate the rate was 56 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
b The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 55 to 56 based on the number of patients with a
baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
c The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 111 to 112 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
d Graded per NCI-CTCAE version 5.0.
e No Grade 5 laboratory abnormalities were reported in the ReNeu study.
f Calcium corrected for albumin (mmol/L).
- Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from clinical trials, animal studies, and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm or loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant woman. In embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of mirdametinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused embryo-fetal mortality, structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at doses that were approximately equivalent to the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on BSA (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
In ReNeu, a pregnancy reported 31 days after the last dose of GOMEKLI resulted in a first trimester spontaneous abortion.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study, mirdametinib was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 to 17) at doses of 0.3, 0.6, 3 or 5 mg/kg/day. Mirdametinib caused post-implantation loss and decreased fetal body weights at doses ≥3 mg/kg/day (≥5 times the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on BSA). Multiple malformations, including shortening of limbs and absence or shortening of digits, were observed in one fetus and another with hyperflexion variation at the dose of 3 mg/kg/day.
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study, mirdametinib was administered orally to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 7 to 19) at doses of 0.3, 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg/day. Maternal toxicity (decreased body weight and moribund condition) was observed at doses ≥1 mg/kg/day (≥3 times the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on BSA). Two animals had spontaneous abortions at the 1 mg/kg dose on Days 20 and 23. Mirdametinib caused post-implantation loss at doses ≥0.3 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on BSA).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of mirdametinib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on a breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating GOMEKLI.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose.
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 3 months after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings in animals, GOMEKLI may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential. The reversibility of the effects on female fertility in animals is unknown [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GOMEKLI have been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with NF1-PN based on the results of the ReNeu study, a single-arm trial conducted in 58 pediatric patients age ≥2 years [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The ReNeu study demonstrated improvement in overall response rate per REiNS criteria and duration of response.
The safety and effectiveness of GOMEKLI have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years old.
Animal Toxicity Data
In a 3-month repeat-dose toxicology study in rats, oral administration of mirdametinib at doses ≥0.3 mg/kg/day (≥2 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on AUC) resulted in dysplasia in femoral epiphyseal growth plate, metaphyseal hypocellularity of the bone marrow of long bones, and metaphyseal thickening of bone trabeculae of long bones; male rats were more sensitive to these effects.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 133 patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) with symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) who received GOMEKLI 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, 2 (1.5%) were 65 years of age and older and none were 75 years of age and older. Clinical studies of GOMEKLI did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger adult patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild (creatinine clearance: 60-89 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance: 30-59 mL/min) renal impairment. GOMEKLI has not been studied in patients with severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN, or total bilirubin in 1-1.5 x ULN).
The pharmacokinetics of mirdametinib in patients with moderate (bilirubin >1.5 to 3 x ULN and any AST) or severe (bilirubin >3 x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment has not been evaluated [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11
DESCRIPTION
GOMEKLI capsules and tablets for oral suspension contain mirdametinib, a kinase inhibitor. Mirdametinib is chemically known as (R)-N-(2,3-dihydroxypropoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2- fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino) benzamide. The molecular formula is C16H14 F3IN2O4 and the molecular weight is 482.20 g/mol. The structural formula for mirdametinib is:
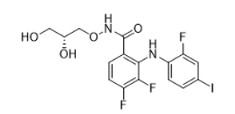
Mirdametinib is a white to tan or pink solid with an aqueous solubility of 0.25 mg/mL and a pH of 7.2 in water at 25°C. The molecule has a pKa of 7.96.
GOMEKLI capsules and tablets for oral suspension are immediate release (IR) dosage forms intended for oral administration.
GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) 1 mg and 2 mg capsules contain 1 mg and 2 mg mirdametinib, respectively, in gelatin capsule and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The gelatin capsule shell contains FD&C blue #1, gelatin, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The capsule is imprinted with white ink that contains butyl alcohol, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, purified water, shellac, strong ammonia solution, and titanium dioxide.
GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) 1 mg tablets for oral suspension contain 1 mg mirdametinib and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, grape flavor, and sucralose. The grape flavor includes corn syrup solids, modified corn starch, and triacetin.
-
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mirdametinib is an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 1 and 2 (MEK1/2). MEK1/2 proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. In vitro, mirdametinib inhibited kinase activity of MEK1 and MEK2 and downstream phosphorylation of ERK.
In a mouse model of NF1, oral dosing of mirdametinib inhibited ERK phosphorylation and reduced neurofibroma tumor volume and proliferation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Mirdametinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are not fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At approximately six times the steady-state exposure associated with the recommended dose of 2 mg/m2, clinically significant QTc interval prolongation was not observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
GOMEKLI pharmacokinetic parameters are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6: Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Characteristics of Mirdametinib General Information
Steady-state [mean (%CV)]Cmax - Adult patients (≥18 years): 188 (52%) ng/mL
- Pediatric patients (2 to17 years): 191 (62%) ng/mL
AUC- Adult patients (≥18 years): 431 (43%) ng·h/mL
- Pediatric patients (2 to 17 years): 459 (46%) ng·h/mL
Time to steady-state Approximately 6 days Accumulation ratio (AUC) [mean] 1.1 to 1.9 Absorption Tmax [median (min, max)] - Tablet: 0.8 (0.4-3) hours post-dose
- Capsule: 1.1 (0-4) hours post-dose
Absolute bioavailability No data are available in humans Food effect [GMR% (90% CI)] (high-fat, high-calorie meal) Cmax 57% (54%, 61%) AUCinf 93% (90%, 96%) Distribution Human plasma protein binding Greater than 99% Apparent volume of distribution [mean (%CV)] 255 L (13%) Elimination Apparent systemic clearance [mean (%CV)] 6.3 L/h (13%) Terminal elimination half-life [mean (%CV)] 28 h (12%) Metabolism
Primary pathwayMetabolism involves glucuronidation and oxidation via UGT (primarily UGT1A6 and UGT2B7) and CES enzymes. Excretion Radioactivity - In urine: 68%
- In feces: 27%
Unchanged mirdametinib - In urine and feces: 9%
- In urine: 0.7%
Abbreviations: AUC: area under the plasma concentration-time curve; AUCinf: AUC from dosing extrapolated to infinity; CI: confidence interval; CES: carboxyl esterase enzyme; Cmax: maximum plasma concentration; CV: coefficient of variation; GMR: geometric least squares mean ratio; UGT: uridine diphosphate (UDP)- glycosyltransferase
Specific Populations
Effects of Age, Sex, and Race
No clinically significant differences in mirdametinib pharmacokinetics were observed based on age (2 to 86 years), sex, and race (11% African American or Black, 12% Asian, 72% White). The effects of moderate or severe hepatic impairment, severe renal impairment, or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on mirdametinib pharmacokinetics are unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
No clinical DDI studies have been conducted. The effect of concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers (that also co-induce UGTs, P-gp, and CES enzymes) on mirdametinib PK is currently unknown.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Mirdametinib does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4.
Mirdametinib does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP3A4.
Transporter Systems: Mirdametinib does not inhibit BCRP, P-gp, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, MATE1, or MATE2K transporters.
Mirdametinib is a substrate of BCRP and P-gp transporters.
- Adult patients (≥18 years): 188 (52%) ng/mL
-
13
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Mirdametinib was not carcinogenic in a 6-month study in transgenic rasH2 mice that received oral doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 15 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on AUC).
Mirdametinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. Mirdametinib was not clastogenic in an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay or in an in vivo rat bone marrow chromosomal aberration assay. Mirdametinib was positive in the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
In a dedicated fertility study, male rats were treated with mirdametinib for 28 days before mating with untreated females to Gestational Day 1. Female rats were treated with mirdametinib for 14 days before mating with untreated males to Gestational Day 7. No effects on mating performance or fertility in males or females were observed at doses up to 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the human clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on BSA). In a 3-month repeat-dose toxicology study in rats, mirdametinib caused decreased ovarian organ weight and increased follicular cysts associated with decreases in the number of corpora lutea at doses ≥0.3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 twice daily based on AUC). Findings in male rats included hypoplasia of the spermatogenic epithelium in the testis, decreased content in the epididymis, and inflammation of the prostate at 1 mg/kg (approximately 8-times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 2 mg/m2 based on AUC). The reversibility of effects on ovary and male reproductive organs was not assessed.
-
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Associated Plexiform Neurofibromas
The efficacy of GOMEKLI was evaluated in the ReNeu study (NCT03962543), a multicenter, single-arm study in 114 patients ≥2 years of age with symptomatic, inoperable neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) associated plexiform neurofibromas (PN) causing significant morbidity. An inoperable PN was defined as a PN that cannot be completely surgically removed without risk for substantial morbidity due to: encasement of or close proximity to vital structures, invasiveness, or high vascularity of the PN. Patients received GOMEKLI 2 mg/m2 orally twice daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measure was confirmed overall response rate (ORR), defined as the percentage of patients with complete response (disappearance of the target PN) or partial response (≥20% reduction in PN volume). Responses were assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) using volumetric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analysis per Response Evaluation in Neurofibromatosis and Schwannomatosis (REiNS) criteria modified to be confirmed at a subsequent tumor assessment within 2 to 6 months during the 24-cycle treatment phase. A secondary efficacy outcome measure was duration of response for patients who achieved a confirmed response.
Adults
A total of 58 adult patients received GOMEKLI. The median age was 35 years (range 18 to 69 years); 64% were female, 85% were White, 9% were Black or African American, 3.4% were Asian, 3.4% were other races; and 1.7% were Hispanic or Latino. Approximately half of the patients (53%) had a progressing PN at study entry, 7% had prior treatment with a MEK inhibitor and 69% had prior surgery. Morbidities reported in >25% of patients were pain (90%), disfigurement or major deformity (52%), and motor dysfunction (40%).
Pediatric Patients
A total of 56 pediatric patients received GOMEKLI. The median age was 10 years (range: 2 to 17); 54% were female; 66% were White, 20% were Black or African American, 9% were other races, 3.6% were Asian, 1.8% were American Indian or Alaska Native; and 14% were Hispanic or Latino. Most patients (63%) had a progressing PN at study entry, 11% had prior treatment with a MEK inhibitor and 36% had prior surgery. Morbidities reported in >25% of patients were pain (70%), disfigurement or major deformity (50%), and motor dysfunction (27%).
Efficacy results are provided in Table 7. The median time to onset of response was 7.8 months (range: 4 months to 19 months) for the adult cohort and 7.9 months (range: 4.1 months to 18.8 months) for the pediatric cohort.
Table 7: Efficacy Results by BICR from ReNeu GOMEKLI
Adult (N=58)GOMEKLI
Pediatric (N=56)Confirmed Overall Response Rate a,b,c,n
(%)24 (41%) 29 (52%) 95% CId (29, 55) (38, 65) Duration of Response (DoR) DoR ≥12 monthse 21 (88%) 26 (90%) DoR ≥24 monthse 12 (50%) 14 (48%) Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval.
a Confirmed overall response was defined as two consecutive assessments of PR or CR assessed within 2- 6 months during the Treatment Phase.
b Patients who had no post-baseline MRI assessment or no confirmed overall response were treated as non-responders.
c All partial responses.
d Obtained using the Clopper-Pearson approach.
e Duration of response was assessed based on observed time.
-
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How supplied
GOMEKLI Capsules are supplied as follows:
Capsule Strength Capsule Description Package Configuration NDC 1 mg Light green body and cap with “MIR 1 mg” printed on the cap in white ink. Bottle of 42 capsules 82448-130-42
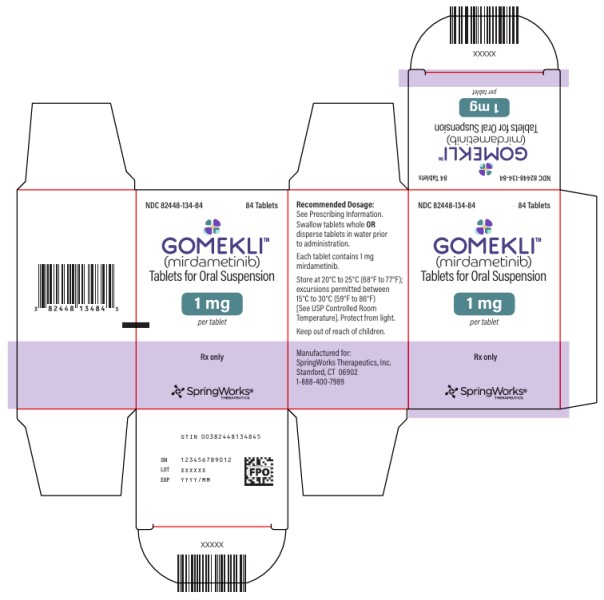
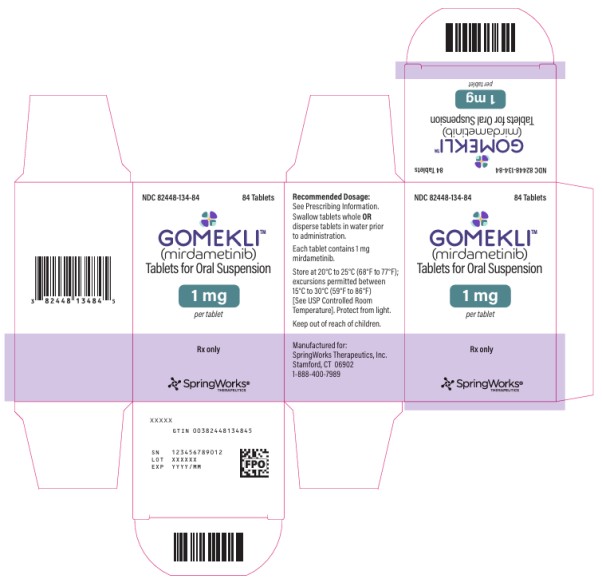
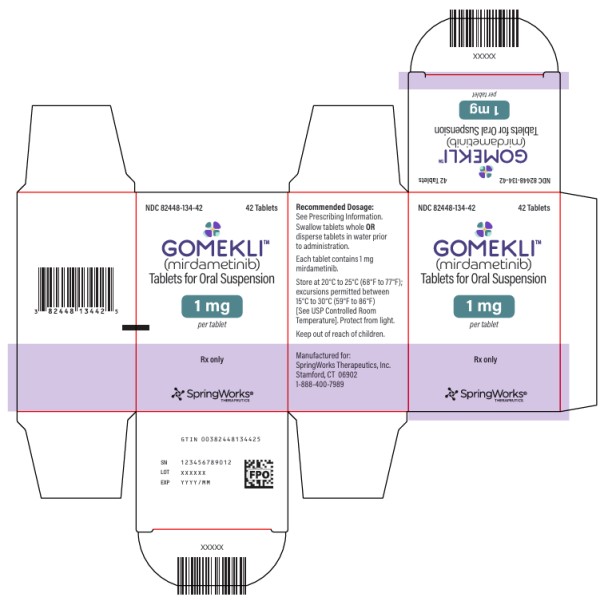
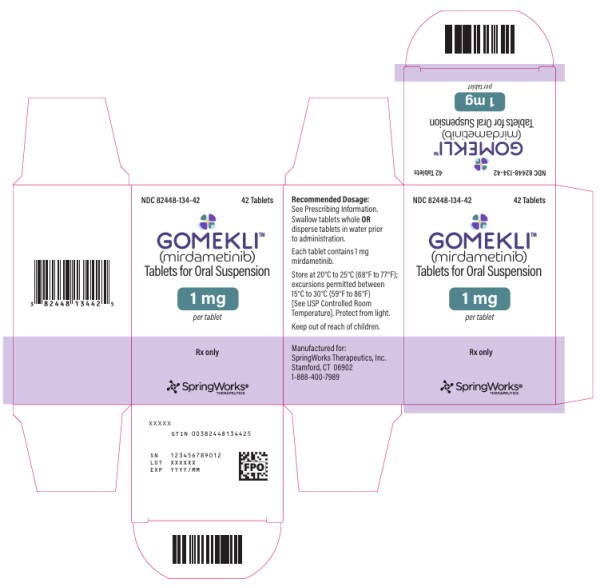
2 mgWhite body and a blue green cap with “MIR 2 mg” printed on the cap in white ink. Bottle of 42 capsules 82448-260-42 Bottle of 84 capsules 82448-260-84 GOMEKLI Tablets for Oral Suspension are supplied as follows:
Tablet Strength Tablet Description Package Configuration NDC
1 mg
White to off-white, oval, grape flavored tablet, debossed with “S” on one side.Bottle of 42 tablets 82448-134-42 Bottle of 84 tablets 82448-134-84 Storage and Handling
Store capsules and tablets for oral suspension at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Protect from light.
-
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Ocular Toxicity
Advise patients and caregivers that GOMEKLI can cause serious ocular effects and to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience any changes in their vision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Advise patients and caregivers that GOMEKLI can cause decreased LVEF and to immediately report any signs or symptoms of left ventricular dysfunction to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Advise patients and caregivers that GOMEKLI can cause severe dermatologic adverse reactions and to contact their healthcare provider if they experience any skin reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Advise patients and caregivers that GOMEKLI can cause alopecia.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 3 months after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females of reproductive potential that GOMEKLI may impair fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Administration
Advise patients to swallow GOMEKLI capsules whole (do not open, break or chew capsules) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Advise patients to either swallow GOMEKLI tablets whole or to disperse GOMEKLI tablets in water and administer orally as a liquid [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Instructions for Use].
Manufactured for:
SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. Stamford, CT 06902
GOMEKLITM is a trademark of SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
©2025 SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
GOMEKLI™ (go-MEK-lee)
(mirdametinib)
capsulesPATIENT INFORMATION GOMEKLI™ (go-MEK-lee)
(mirdametinib)
tablets for oral suspensionWhat is GOMEKLI?
GOMEKLI is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have plexiform neurofibromas that cause symptoms and cannot be completely removed by surgery.
It is not known if GOMEKLI is safe and effective in children under 2 years of age.Before taking GOMEKLI tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have eye problems
- have heart problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. GOMEKLI can harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider should check to see if you are pregnant before you begin treatment with GOMEKLI.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after your last dose.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with GOMEKLI.
Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant:
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 3 months after your last dose.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if your female partner becomes pregnant or thinks she may be pregnant during treatment with GOMEKLI.
- Your healthcare provider should check to see if you are pregnant before you begin treatment with GOMEKLI.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if GOMEKLI passes into your breastmilk.
- Do not breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after your last dose.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
- Do not breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after your last dose.
How should I take GOMEKLI? - Take GOMEKLI exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with GOMEKLI if you develop certain side effects.
- Take GOMEKLI twice a day, about 12 hours apart, for 21 days, followed by 7 days off treatment, to complete a 28- day treatment cycle. Your healthcare provider will decide how many treatment cycles are right for you.
- Take GOMEKLI with or without food.
- GOMEKLI comes in 2 different dosage forms, GOMEKLI capsules and GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension. Your healthcare provider will decide the dosage form and dose of GOMEKLI that is right for you.
-
If you take GOMEKLI capsules:
- Swallow each capsule whole with drinking water. If more than 1 capsule is required, swallow 1 capsule at a time.
- Do not open, break, or chew the capsules
- Swallow each capsule whole with drinking water. If more than 1 capsule is required, swallow 1 capsule at a time.
-
If you take GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension, either:
- Swallow each tablet for oral suspension whole with drinking water. If more than 1 tablet is required, swallow 1 tablet at a time.
OR
- Disperse the tablets for oral suspension in drinking water to make a liquid (suspension) before you take or give GOMEKLI.
See the “Instructions for Use” that come with your medicine for instructions on how to prepare and take GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension.
- Swallow each tablet for oral suspension whole with drinking water. If more than 1 tablet is required, swallow 1 tablet at a time.
- If you miss a dose of GOMEKLI, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at your regularly scheduled time.
- If you vomit at any time after taking GOMEKLI, do not take an additional dose. Take your next dose at your regularly scheduled time.
What are the possible side effects of GOMEKLI?
GOMEKLI may cause serious side effects, including:- eye problems. GOMEKLI may cause eye problems that can lead to blindness. Your healthcare provider will check your vision before and during treatment with GOMEKLI. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of eye problems:
- blurred vision
- loss of vision
- other changes to your vision
- heart problems. GOMEKLI may lower the amount of blood pumped by your heart, which is common in children during treatment with GOMEKLI and can also be severe. Your healthcare provider will do tests before you start GOMEKLI treatment, every 3 months during your first year of treatment, and then as needed to make sure your heart is working properly. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of heart problems:
- coughing or wheezing
- tiredness
- shortness of breath
- increased heart rate
- swelling of your ankles and feet
- skin problems. Skin rashes are common with GOMEKLI in both adults and children and can also be severe. GOMEKLI can also cause hair loss (alopecia). Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms of skin problems:
- flat skin rash
- skin redness
- raised bumps on the skin
- itchy rash
- skin bumps that look like acne
- peeling skin
The most common side effects of GOMEKLI in adults include:
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- nausea
- tiredness
- muscle, joint, and bone pain
The most common severe abnormal blood tests in adults include an increased enzyme called creatine phosphokinase (CPK). The most common side effects of GOMEKLI in children include: - diarrhea
- headache
- muscle, joint, and bone pain
- skin redness, swelling, or pain around the fingernails or toenails
- stomach (abdominal) pain
- nausea
- vomiting
The most common severe abnormal blood tests in children include decreased white blood cell (neutrophil) counts and increased CPK.
GOMEKLI may cause fertility problems in females, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have concerns about fertility.
These are not all of the possible side effects of GOMEKLI.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store GOMEKLI?
- Store GOMEKLI at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Protect from light.
General information about the safe and effective use of GOMEKLI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use GOMEKLI for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give GOMEKLI to other people even if they have the
same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about GOMEKLI that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in GOMEKLI?
Active ingredient: mirdametinib
Inactive ingredients:
capsule contains: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. The capsule shell contains: FD&C blue #1, gelatin, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The printing ink contains: butyl alcohol, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, purified water, shellac, strong ammonia solution, and titanium dioxide.
tablet for oral suspension contains: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, grape flavor, and sucralose. The grape flavor includes corn syrup solids, modified corn starch, and triacetin.
Manufactured for SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. Stamford, CT 06902
GOMEKLITM is a trademark of SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
©2025 SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
For more information call 1-888-400-7989 or visit www.GOMEKLI.comThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 02/2025
- have eye problems
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
GOMEKLI™ (go-MEK-lee)
(mirdametinib)
tablets for oral suspensionGOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension can be swallowed whole or prepared and taken as a liquid (oral suspension). This Instructions for Use contains information on how to prepare and take GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension as an oral suspension. Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking GOMEKLI Tablets for Oral Suspension - Read these Instructions for Use before you or your child start taking GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension for the first time and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
- This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your or your child’s medical condition or treatment.
- GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension is for oral use only (taken by mouth).
- Take GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension with or without food.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how many GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension you will need for your or your child’s dose. Always take GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- If you have any questions about how to prepare and take or give a dose of GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension, talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Supplies you will need to take or give GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension
To prepare and take or give GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension, you will need:- the prescribed number of GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension
- a dosing cup provided by your healthcare provider or pharmacist
- if necessary, a 10 mL oral syringe provided by your healthcare provider or pharmacist
- about 10 mL to 20 mL of drinking water
Preparing GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension Step 1: Wash and dry your hands before preparing GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension. Step 2: Add about 5 mL to 10 mL of drinking water to the dosing cup. Note: The amount of water does not need to be exact.
Only use water to prepare the dose.
Step 3: Count the prescribed number of tablets into your hand. 
Step 4: Add the prescribed number of tablets to the water. 
Step 5: Swirl the dosing cup gently to disperse the tablets until no lumps remain.
It will take about 2 to 4 minutes to fully disperse the tablets in the water.
GOMEKLI oral suspension will be white and cloudy and there will be some medicine (residue) visible. Try not to spill any of the prepared oral suspension. If you spill the oral suspension, see “Section C. Cleaning up spilled GOMEKLI oral suspension.“
Important: Take or give GOMEKLI oral suspension right away after preparing the dose. If you cannot take or give it right way, take or give GOMEKLI oral suspension within 30 minutes of preparing the dose.

Section A. Taking or giving GOMEKLI oral suspension by swallowing the oral suspension directly from the dosing cup.
Note: To use an oral syringe to take or give GOMEKLI oral suspension, skip to Section B.Step A1: Take or give the GOMEKLI oral suspension from the dosing cup right away after preparing the dose.
If more than 30 minutes have passed since you prepared the dose, throw away (dispose of) the GOMEKLI oral suspension and start over from Step 1. See “Section D. Disposing of GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension.”
If you are not sure how to throw away the GOMEKLI oral suspension, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Important: After swallowing the oral suspension, there will be some medicine (residue) still inside the dosing cup. The residue may be hard to see. Follow Steps A2 through A4 to make sure that the full dose of GOMEKLI is taken or given.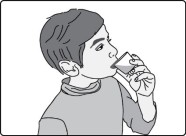
Step A2: Add another 5 mL to 10 mL of drinking water to the same dosing cup. 
Step A3: Swirl the dosing cup gently. 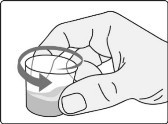
Step A4: Drink or give the water and residue mixture from the dosing cup. 
Step A5: Wash the dosing cup with clean water. Allow the dosing cup to dry completely before storing.
Wash your hands when you are finished.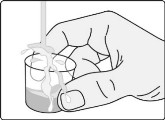
Section B. Taking or giving GOMEKLI oral suspension from an oral syringe. Step B1: Place the tip (open end) of the oral syringe into the prepared medicine and draw up all the GOMEKLI oral suspension from the dosing cup into the oral syringe by pulling back on the plunger.
Important: Take or give the GOMEKLI oral suspension from the oral syringe right away after preparing the dose.
If more than 30 minutes have passed since you prepared the dose, throw away the GOMEKLI oral suspension and start over from Step
1. See “Section D. Disposing of GOMEKLI oral suspension or GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension.”
If you are not sure how to throw away the GOMEKLI oral suspension, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.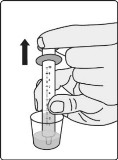
Step B2: Place the tip of the oral syringe inside the mouth pointing toward the inside of either cheek.
If you are giving a dose of GOMEKLI oral suspension to a child, make sure they are sitting upright until all the liquid has been swallowed.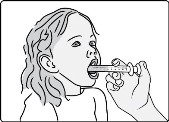
Step B3: Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give the full dose of GOMEKLI. Allow time for all the medicine to be swallowed.
Important: After swallowing the oral suspension, there will be some medicine (residue) still inside the dosing cup and oral syringe. The residue may be hard to see. Follow Steps B4 through B6 to make sure that the full dose of GOMEKLI is given.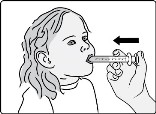
Step B4: Add another 5 to 10 mL of drinking water to the same dosing cup. 
Step B5: Swirl the dosing cup gently. 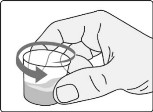
Step B6: Place the tip of the oral syringe into the dosing cup and draw the water and residue mixture into the oral syringe by pulling back on the plunger. Take or give all of the water and residue mixture to the child. Allow time for the water and residue mixture to be swallowed. 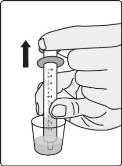
Step B7: Wash the dosing cup and oral syringe with clean water. Pull the plunger out of the oral syringe and wash the oral syringe parts separately.
Allow the parts to dry completely before reassembling and storing.
Wash your hands when you are finished.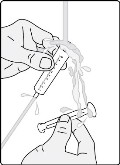
Section C. Cleaning up spilled GOMEKLI oral suspension - If you accidentally spill any GOMEKLI oral suspension, soak up the spilled GOMEKLI oral suspension completely using an absorbent material, such as paper towels, and throw away (dispose of) in the trash.
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
Section D. Disposing of GOMEKLI oral suspension or GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension - If it has been more than 30 minutes since you prepared your dose of GOMEKLI oral suspension or if you have any unused prepared oral suspension, throw away the prepared oral suspension in the trash.
- Throw away unused or expired GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension in the trash.
Section E. Storing GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension
- Store GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Protect from light.
Manufactured for SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. Stamford, CT 06902
GOMEKLITM is a trademark of SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
©2025 SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
For more information call 1-888-400-7989 or visit www.GOMEKLI.comThis Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 02/2025
- Read these Instructions for Use before you or your child start taking GOMEKLI tablets for oral suspension for the first time and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GOMEKLI
mirdametinib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 82448-130 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MIRDAMETINIB (UNII: 86K0J5AK6M) (MIRDAMETINIB - UNII:86K0J5AK6M) MIRDAMETINIB 1 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) BUTYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) DEHYDRATED ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) Product Characteristics Color green (Light Green) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code MIR;1mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 82448-130-42 42 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/11/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219389 02/11/2025 GOMEKLI
mirdametinib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 82448-260 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MIRDAMETINIB (UNII: 86K0J5AK6M) (MIRDAMETINIB - UNII:86K0J5AK6M) MIRDAMETINIB 2 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) BUTYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) DEHYDRATED ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) Product Characteristics Color white, blue Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code MIR;2mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 82448-260-42 42 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/11/2025 2 NDC: 82448-260-84 84 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/11/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219389 02/11/2025 GOMEKLI
mirdametinib tablet, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 82448-134 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MIRDAMETINIB (UNII: 86K0J5AK6M) (MIRDAMETINIB - UNII:86K0J5AK6M) MIRDAMETINIB 1 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) GRAPE (UNII: 6X543N684K) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) Product Characteristics Color white (White to off-white) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 9mm Flavor GRAPE Imprint Code S Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 82448-134-42 42 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/11/2025 2 NDC: 82448-134-84 84 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/11/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219379 02/11/2025 Labeler - SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. (116976800)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.