MAROPITANT CITRATE tablet
Maropitant Citrate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Maropitant Citrate by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by ZyVet Animal Health Inc, Zydus Animal Health and Investments Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
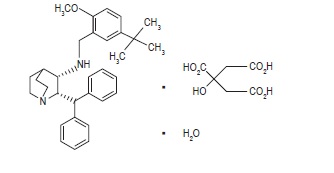
Maropitant is a neurokinin (NK1) receptor antagonist that blocks the pharmacological action of substance P in the central nervous system (CNS). Maropitant is the non-proprietary designation for a substituted quinuclidine. The empirical formula is C32H40N2O C6H8O7 H2O and the molecular weight 678.81. The chemical name is (2S,3S)-2-benzhydryl-N-(5-tert-butyl-2-methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine citrate monohydrate. Each peach-colored, mottled, oval tablet is scored and contains 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet.
The chemical structure of maropitant citrate is:
- INDICATIONS
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 2 -7 months of age: Administer Maropitant Citrate tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 5 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
For Prevention of Acute Vomiting in dogs 7 months of age and older: Administer Maropitant Citrate tablets orally at a minimum dose of 2 mg/kg (0.9 mg/lb) body weight once daily until resolution of acute vomiting.
If vomiting persists despite treatment, the case should be re-evaluated. Maropitant Citrate is most effective in preventing acute vomiting associated with chemotherapy if administered prior to the chemotherapeutic agent.
For prevention of acute vomiting, dispense whole or half tablets in strength(s) that most closely result in a 2 mg/kg dose:
Dog body weight
Number of Tablets
Pounds
Kilograms
16 mg
24 mg
60 mg
8
4
½
15
8
1
25
12
1
50
24
2
65
30
1
130
60
2
Interchangeable use with Maropitant Citrate injectable solution for Prevention of Acute Vomiting:
In dogs that are actively vomiting, to ensure that the full initial dose is administered, Maropitant Citrate injectable solution is recommended at a dose of 1 mg/kg once daily. (See package insert for Maropitant Citrate injectable solution.) Thereafter, for the prevention of acute vomiting, Maropitant Citrate tablets at a dose of 2 mg/kg once daily may be used interchangeably with Maropitant Citrate injectable solution for up to 5 days.
For Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in dogs 4 months and older
For Prevention of Vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs 4 months of age and older: Administer Maropitant Citrate tablets orally at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg (3.6 mg/lb) body weight once daily for up to 2 consecutive days (see WARNINGS and Animal Safety).
Administer Maropitant Citrate tablets a minimum of two hours prior to travel with a small amount of food to mitigate vomiting associated with administration of the dose on an empty stomach; however, refrain from feeding a full meal prior to travel.
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness in Dogs 4 months of age and older:
Dispense whole or half tablets in strengths that most closely result in an 8 mg/kg dose once daily for up to 2 consecutive days:
Dog body weight
Number of Tablets
Pounds
Kilograms
16 mg
24 mg
60 mg
160 mg
2
1
½
3
1.5
½
4
2
1
6
3
1
8
4
2
13
6
2
16
7.5
1
22
10
½
33
15
2
44
20
1
66
30
1 ½
88
40
2
132
60
3
Maropitant Citrate injectable solution should not be used interchangeably with Maropitant Citrate tablets for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness (8mg/kg).
-
WARNINGS
Not for use in humans. Keep out of the reach of children. In case of accidental ingestion, seek medical advice. Topical exposure may elicit localized allergic skin reactions in some individuals. Repeated or prolonged exposure may lead to skin sensitization. Wash hands with soap and water after administering drug. Maropitant Citrate is also an ocular irritant. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
Keep Maropitant Citrate Tablets in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
In puppies younger than 11 weeks of age, histological evidence of bone marrow hypocellularity was observed at higher frequency and greater severity in puppies treated with Maropitant Citrate compared to control puppies. In puppies 16 weeks and older, bone marrow hypocellularity was not observed (see ANIMAL SAFETY).
-
PRECAUTIONS
The safe use of Maropitant Citrate tablets has not been evaluated in dogs used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating bitches.
The safe use of Maropitant Citrate has not been evaluated in dogs with gastrointestinal obstruction, or dogs that have ingested toxins.
Use with caution in dogs with hepatic dysfunction because Maropitant Citrate is metabolized by CYP3A enzymes (see Pharmacokinetics).Use with caution with other medications that are highly protein bound. The concomitant use of Maropitant Citrate with other protein bound drugs has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein bound drugs include NSAIDs, cardiac, anticonvulsant, and behavioral medications.
The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit the metabolism of Maropitant Citrate has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
Maropitant Citrate causes dose related decreases in appetite and body weight (see ANIMAL SAFETY). To maximize therapeutic potential of Maropitant Citrate, the underlying cause of vomiting should be identified and addressed in dogs receiving Maropitant Citrate.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Prevention of Acute Vomiting (minimum of 2 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during the course of a US field study for the prevention of acute vomiting in dogs treated with maropitant citrate tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally and/or injectable solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily for up to 5 consecutive days:
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
Adverse Reaction
Placebo (n=69)
maropitant citrate (n=206)
# dogs
% occurrence
# dogs
% occurrence
Death during study
4
5.8
10
4.9
Euthanized during study
0
0
2
1
Diarrhea
6
8.7
8
3.9
Hematochezia/bloody stool
5
7.2
4
1.9
Anorexia
2
2.9
3
1.5
Otitis/Otorrhea
0
0
3
1.5
Endotoxic Shock
1
1.4
2
1
Hematuria
0
0
2
1
Excoriation
0
0
2
1
Prevention of Vomiting Due to Motion Sickness (minimum of 8 mg/kg)
The following adverse reactions were reported during US studies for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with maropitant citrate tablets at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally one time. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
1Not associated with motion sickness.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
Adverse Reaction
Placebo (n=195)
maropitant citrate (n=208)
# dogs
% occurrence
# dogs
% occurrence
Hypersalivation
19
9.7
26
12.5
Vomiting1
0
0
11
5.3
Muscle Tremors
1
0.5
2
1
Sedation/Depression
3
1.5
2
1
Retching
3
1.5
1
0.5
Flatulence
0
0
1
0.5
The following adverse reactions were reported during a European field study for the prevention of vomiting due to motion sickness in dogs treated with maropitant citrate at a minimum of 8 mg/kg orally once daily for 2 consecutive days. Dogs may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions.
Frequency of Adverse Reactions by Treatment
Adverse Reaction
Placebo (n=106)
maropitant citrate (n=107)
# dogs
% occurrence
# dogs
% occurrence
Vomiting
4
4
10
9
Drowsiness/Lethargy/Apathy
1
1
8
8
Hypersalivation
2
2
5
5
Anxiety
0
0
2
2
Trembling/Tremors
0
0
2
2
Inappetence
0
0
2
2
Mucus in stool
0
0
1
1
The following Adverse Reactions were reported during the conduct of a US clinical field trial where maropitant citrate tablets were administered once daily for 28 consecutive days to 32 dogs: lethargy, vomiting, inappetence, corneal edema, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Post-Approval Experience (Revised May 2019)
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events reported for dogs are listed in decreasing order of frequency: anorexia, depression/lethargy, hypersalivation, vomiting, diarrhea, trembling, ataxia, allergic reactions, weight loss, convulsion, hyperactivity, and panting.
Cases of ineffectiveness have been reported.
Cases of death (including euthanasia) have been reported.
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact ZyVet Animal Health Inc. at 1-877-779-9838.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics
Mean (±SD) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Maropitant in Beagle Dogs after single dose and repeat oral doses of Maropitant:
1Following once daily doses of maropitant for 14 days.
2Median (Range)
3Ratio=Multiple Dose AUC(0-24)/Single Dose AUC(0-24), Least square means (95% Confidence Interval)
NA= Not Applicable
NC= Not Calculated
PK Parameter
2 mg/kg Single Dose
2 mg/kg repeat Doses 1
8 mg/kg Single Dose
8 mg/kg repeat Doses 1
Tmax2
(hr)
2.0
(1.5 – 3.0)
1.5
(1.0 – 3.0)
1.5
(1.0 – 3.0)
2.5
(1.5 – 7.0)
Cmax
(ng/mL)
154
(111)
304
(165)
588
(416)
1409
(516)
AUC(0-24)
(ng*hr/mL)
1440
(982)
3890
(3030)
6730
(5030)
26600
(9200)
T1/22
(hr)
NC
7.69
(6.21 - 17.8)
NC
25.4
(6.06 - 30.0)
Accumulation Ratio
(Rac)3
NA
2.46
(1.68, 3.61)
NA
4.81
(3.28, 7.05)
Following oral administration, median time to reach Cmax was within 2.5 hr. The absolute bioavailability of maropitant was low (24%) following oral administration of 2 mg/kg maropitant. After an oral dose, prandial status does not significantly affect the extent of oral bioavailability. Greater than dose-proportional drug exposure can be expected with an increase in dose (1-16 mg/kg PO). However as doses increase (20-50 mg/kg PO), the dose proportionality is re-established. Based upon in vitro enzyme kinetics, involvement of a high capacity enzyme (CYP3A12) may contribute to this return to dose linearity. Due to dose dependent pharmacokinetics, the maropitant concentrations reached steady state approximately after 4 and 8 days following 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The observed drug accumulation ratios were 2.46 and 4.81, after oral administration of 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively. The exposure of 10 week old puppies to maropitant was lower than that observed in adult dogs, particularly after repeat doses of 1 or 2 mg/kg. Systemic clearance of maropitant following IV administration was 970, 995, and 533 mL/hr/kg at doses of 1, 2 and 8 mg/kg, respectively.
Urinary recovery of maropitant and its major metabolite was minimal (<1% each). The hepatic metabolism of maropitant involves two cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D15 and CYP3A12. In in vitro enzyme kinetics data suggest that the non-linear kinetics may be partially associated with saturation of the low capacity enzyme (CYP2D15). Plasma protein binding of maropitant was high (99.5%).
Pharmacodynamics
Vomiting is a complex process coordinated centrally by the emetic center which consists of several brainstem nuclei (area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus) that receive and integrate sensory stimuli from central and peripheral sources and chemical stimuli from the circulation and the cerebro-spinal fluid. Maropitant is a neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist which acts by inhibiting the binding of substance P, a neuropeptide of the tachykinin family. Substance P is found in significant concentrations in the nuclei comprising the emetic center and is considered the key neurotransmitter involved in emesis.1 By inhibiting the binding of substance P within the emetic center, maropitant provides broad-spectrum effectiveness against neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) causes of vomiting. In vivo model studies in dogs have shown that maropitant has antiemetic effectiveness against both central and peripheral emetogens including apomorphine, and syrup of ipecac.
1Diemunsch P, Grelot L. Potential of substance P antagonists as antiemetics. [Review] [60 refs]. Drugs. 2000;60:533-46.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Prevention of Acute Vomiting
In laboratory model studies, maropitant citrate tablets dosed at a minimum of 2 mg/kg BW reduced the number of emetic events associated with established neural (central) and humoral (peripheral) stimuli. Following administration of apomorphine (central emetic stimuli), vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with maropitant citrate tablets and 100% (12 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets. Following administration of syrup of ipecac (peripheral emetic stimuli) vomiting was observed in 33% (4 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with maropitant citrate tablets and in 83% (10 of 12) of Beagle dogs treated with placebo tablets.
In a study of 275 canine patients presented to veterinary hospitals with a history of acute vomiting, dogs were initially administered maropitant citrate injectable solution or placebo on Day 0. Following the initial dose, dogs allocated to the maropitant citrate group were treated with either maropitant citrate tablets at a minimum of 2 mg/kg orally or injectable solution at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Dogs allocated to the placebo group were treated using either an injectable placebo solution or placebo tablets once daily at the discretion of the clinician. Of the 199 dogs included in the analysis for effectiveness, 27 of 54 dogs (50%) in the placebo group displayed vomiting at some time during the study and 31 of 145 dogs (21.4%) in the treated group displayed vomiting during the study period.
Percent Of Vomiting For Each Study Day, Based Upon Treatment And Route Of Administration. *2 dogs administered maropitant citrate were not observed on Day 0. Their vomiting status was unknown. 143 was used in the denominator for % vomited.
Days
Treatment
Route
# dogs
$ vomited
% vomited
Day 0
Placebo (54)
SC
54
15
28%
Maropitant Citrate (145)
SC
145(143*)
14
10%
Day 1
Placebo (45)
PO
22
3
14%
SC
23
16
70%
Maropitant Citrate (108)
PO
67
2
3%
SC
41
16
39%
Day 2
Placebo (16)
PO
7
2
29%
SC
9
6
67%
Maropitant Citrate (37)
PO
24
0
0%
SC
13
8
62%
Day 3
Placebo (6)
PO
2
0
0%
SC
4
1
25%
Maropitant Citrate (21)
PO
14
0
0%
SC
7
5
71%
Day 4
Placebo (2)
PO
1
0
0%
SC
1
1
100%
Maropitant Citrate (7)
PO
5
0
0%
SC
2
1
50%
Day 5
Maropitant Citrate (1)
SC
1
0
0%
In US field studies in veterinary patients, maropitant citrate tablets and injectable solution were well tolerated in dogs presenting with various conditions including parvovirus, gastroenteritis, and renal disease. There were no notable differences in mean laboratory values between maropitant citrate -treated and placebo-treated patients.
Maropitant citrate tablets were used safely in dogs receiving other frequently used veterinary products such as fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions, antimicrobial agents, vaccines, antacids, and antiparasitic agents.
Prevention of Vomiting due to Motion Sickness
In a study of canine veterinary patients taken on a one-hour car journey and treated with either maropitant citrate tablets at a minimum dose of 8 mg/kg BW or placebo tablets 2 hours prior to the journey, 67 of 122 (55%) of dogs vomited during the journey when treated with placebo while 8 of 122 (7%) vomited during the journey after treatment with maropitant citrate tablets. The probability that a dog in this study, prone to motion sickness would NOT vomit during a journey if treated with maropitant citrate tablets was 93%, while the probability was 48% if treated with placebo.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated that maropitant citrate tablets are well tolerated in dogs after oral administration.
Target Animal Safety Study for Acute Vomiting
Fifty six Beagle dogs (28 males and 28 females) approximately 16 weeks of age were administered maropitant citrate tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg. There were 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 2 mg/kg group and 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in all other groups. Maropitant citrate tablets caused decreases in food consumption and body weight that were not dose-dependent and did not persist after cessation of treatment.
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered maropitant citrate tablets orally once daily for 15 days at 0, 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. A dose dependent increase in severity of bone marrow hypoplasia was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia and some tested positive for canine parvovirus.
Beagle dogs approximately 10 weeks of age were administered either placebo tablets for 2 days, maropitant citrate tablets at 8 mg/kg for 2 days, placebo (saline) subcutaneously (SC) for 5 days, maropitant citrate injectable solution at 1 mg/kg SC for 5 days, or maropitant citrate tablets at 2 mg/kg for 5 days (8 dogs in each dose group). Mild pain associated with injection was noted in more dogs and lasted longer in dogs that received maropitant injections compared to saline. Males administered maropitant citrate at 8 mg/kg orally for 2 days had a decrease in food consumption. Body weight and food consumption were variable throughout the 4 week acclimation period. Two dogs that received 8 mg/kg maropitant orally for 2 days were below the reference range for reticulocyte counts. Decreases in reticulocyte counts were also seen in 4 (of 8) placebo treated dogs (SC saline for 5 days). Hypocellular femoral bone marrow described as "minimal" was seen in 1 male that received 1 mg/kg maropitant SC for 5 days; reticulocyte counts were not available for this dog.
Twenty four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) 7 months of age were administered maropitant at doses of 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg orally once daily for 93 consecutive days. Maropitant produced sporadic clinical signs (salivation, emesis), body weight loss, and lower serum albumin levels at 20 mg/kg/day.
Maropitant increased P-R interval, P wave duration, and QRS amplitude in the 20 mg/kg /day dose group.
One female in the 20 mg/kg/day group had increased cellularity of the bone marrow. This female was noted to have lower mean red cell parameters (red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit) and higher platelet counts and reticulocytes.
Target Animal Safety Study for Motion Sickness
Forty Beagle dogs (20 males and 20 females) between 16 – 18 weeks of age were administered maropitant citrate tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8 and 24 mg/kg. There were 16 dogs (8 males and 8 females) in the 0 and 24 mg/kg groups and 8 dogs (4 males and 4 females) in the 8 mg/kg group. At 24 mg/kg, maropitant citrate tablets caused decreases in food consumption, with decreases in body weight, liver and testis weight; and an increase in RBC count indicating hemoconcentration, but the effects on feed consumption, body weight, and RBCs did not persist in the post-treatment recovery period (beyond Day 5).
Beagle dogs approximately 8 weeks of age were administered maropitant citrate tablets orally once daily for 6 days at 0, 8, and 24 mg/kg using a protocol similar to the previous study. One dog in the 24 mg/kg/day group died of unknown causes on study day 2 and a dose dependent increase in occurrence and severity of bone marrow hypoplasia and lymphoid depletion was observed histologically. Interpretation of these study results is complicated by the health status of study animals. Dogs used in the study were weaned early, minimally acclimated to the test facility, and many of the dogs in the study tested positive for coccidia. Additionally, some dogs in the study tested positive for canine parvovirus, however, clinical parvoviral disease was not definitively diagnosed.
Tolerance Studies
Twenty four Beagle dogs (14 males and 10 females) between 11 and 25 weeks of age were administered maropitant citrate tablets in 2 phases with 8 dogs per group. In the first phase the dogs were administered 0, 20 or 30 mg/kg orally once daily for 7 days and in the second phase 0, 40, or 50 mg/kg once daily for 7 days.
Maropitant citrate tablets administered at 20 and 30 mg/kg caused occasional vomiting. Maropitant citrate tablets administered at 40 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg caused clinically relevant signs of weight loss, vomiting, soft stools, weakness, lethargy, salivation and hypokalemia. Additionally, leukopenia characterized by a neutropenia and a trend toward decreasing plasma phosphorus values was seen. Decreased heart rate and prolonged corrected QT intervals were seen in all treatment groups in a dose dependent manner.
Twenty-four Beagle dogs (12 males and 12 females) approximately 28 weeks of age were administered maropitant (mesylate salt) orally once daily for 90 days at 0, 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg. End of study body weights in the 20 mg/kg group were 8-15% lower than baseline body weights.
- STORAGE CONDITIONS
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Maropitant Citrate peach colored, mottled tablets are scored with a break line, and contain 16, 24, 60 or 160 mg of maropitant as maropitant citrate per tablet. Each tablet is marked with "31 and U","32 and U", "33 and U","34 and U" for 16, 24, 60 and 160mg respectively.
Each tablet size is available in the following strengths and are supplied in blister packs containing 4 tablets:
16 mg, 24 mg, 60mg and 160 mg contains 1 blister per carton (4 tablets) and
16 mg contains 10 blisters per carton (40 tablets)
24 mg contains 10 blisters per carton (40 tablets)
60 mg contains 10 blisters per carton (40 tablets)
160 mg contains 5 blisters per carton (20 tablets)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
For oral use in dogs only
Antiemetic
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
16 mg
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747

For oral use in dogs only
Antiemetic
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
24 mg
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747

For oral use in dogs only
Antiemetic
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
60 mg
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747

For oral use in dogs only
Antiemetic
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
160 mg
4 Tablets Per Blister Card
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747

16 mg
Antiemetic
For oral use in dogs only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by
or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets per Blister Card, 10 Blisters per Carton (40 Tablets)
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747
24 mg
Antiemetic
For oral use in dogs only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by
or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets per Blister Card, 10 Blisters per Carton (40 Tablets)
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747

60 mg
Antiemetic
For oral use in dogs only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by
or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets per Blister Card, 10 Blisters per Carton (40 Tablets)
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747
160 mg
Antiemetic
For oral use in dogs only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by
or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
4 Tablets per Blister Card, 5 Blisters per Carton (20 Tablets)
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-747
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MAROPITANT CITRATE
maropitant citrate tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 86117-027 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAROPITANT CITRATE (UNII: LXN6S3999X) (MAROPITANT - UNII:4XE2T9H4DH) MAROPITANT 16 mg Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (Peach) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 31;U Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 86117-027-17 1 in 1 CARTON 1 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK 2 NDC: 86117-027-36 10 in 1 CARTON 2 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200747 06/01/2023 MAROPITANT CITRATE
maropitant citrate tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 86117-028 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAROPITANT CITRATE (UNII: LXN6S3999X) (MAROPITANT - UNII:4XE2T9H4DH) MAROPITANT 24 mg Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (Peach) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code 32;U Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 86117-028-17 1 in 1 CARTON 1 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK 2 NDC: 86117-028-36 10 in 1 CARTON 2 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200747 06/01/2023 MAROPITANT CITRATE
maropitant citrate tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 86117-029 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAROPITANT CITRATE (UNII: LXN6S3999X) (MAROPITANT - UNII:4XE2T9H4DH) MAROPITANT 60 mg Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (Peach) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code 33;U Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 86117-029-17 1 in 1 CARTON 1 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK 2 NDC: 86117-029-36 10 in 1 CARTON 2 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200747 06/01/2023 MAROPITANT CITRATE
maropitant citrate tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 86117-030 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAROPITANT CITRATE (UNII: LXN6S3999X) (MAROPITANT - UNII:4XE2T9H4DH) MAROPITANT 160 mg Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (Peach) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code 34;U Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 86117-030-17 1 in 1 CARTON 1 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK 2 NDC: 86117-030-37 5 in 1 CARTON 2 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200747 06/01/2023 Labeler - ZYVET ANIMAL HEALTH INC. (117047560) Registrant - ZYVET ANIMAL HEALTH INC. (117047560)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.