HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS, CORD BLOOD- human cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cell liquid
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells, Cord Blood by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells, Cord Blood by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Clinimmune Labs, University of Colorado Blood Bank. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HPC, Cord Blood safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HPC, Cord Blood.
HPC, Cord Blood
Injectable Suspension for Intravenous Use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012WARNING: FATAL INFUSION REACTIONS, GRAFT VERSUS HOST DISEASE, ENGRAFTMENT SYNDROME, AND GRAFT FAILURE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Fatal infusion reactions: Monitor patients during infusion and discontinue for severe reactions. Use is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), Dextran 40 or human serum albumin. (4, 5.1, 5.2)
- Graft-vs-host disease (GVHD): GVHD may be fatal. Administration of immunosuppressive therapy may decrease the risk of GVHD. (5.3)
- Engraftment syndrome: Engraftment syndrome may be fatal. Treat engraftment syndrome promptly with corticosteroids. (5.4)
- Graft failure: Graft failure may be fatal. Monitor patients for laboratory evidence of hematopoietic recovery. (5.5)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
HPC (hematopoietic progenitor cells), Cord Blood is an allogeneic cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cell therapy indicated for use in unrelated donor hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation procedures in conjunction with an appropriate preparative regimen for hematopoietic and immunologic reconstitution in patients with disorders affecting the hematopoietic system that are inherited, acquired, or result from myeloablative treatment. (1)
The risk benefit assessment for an individual patient depends on the patient characteristics, including disease, stage, risk factors, and specific manifestations of the disease, on characteristics of the graft, and on other available treatments or types of hematopoietic progenitor cells. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Unit selection and administration of HPC, Cord Blood should be done under the direction of a physician experienced in hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation.
- The recommended minimum dose is 2.5 x 107 nucleated cells/kg at cryopreservation. (2.1)
- Do not administer HPC, Cord Blood through the same tubing with other products except for normal saline. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each unit contains a minimum of 5 x 108 total nucleated cells with at least 1.25 x 106 viable CD34+ cells at the time of cryopreservation. The exact pre-cryopreservation nucleated cell content of each unit is provided on the container label and accompanying records. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known sensitivity to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), Dextran 40 or plasma proteins. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Mortality, from all causes, at 100 days post-transplant was 25%. (6.1)
The most common infusion-related adverse reactions (≥5%) are hypertension, vomiting, nausea, bradycardia, and fever. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ClinImmune Labs, University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank (UCCBB) at 303-724-1306 and FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. Use only if clearly needed. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2012
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: FATAL INFUSION REACTIONS, GRAFT VERSUS HOST DISEASE, ENGRAFTMENT SYNDROME AND GRAFT FAILURE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing
2.2 Preparation for Infusion
2.3 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis
5.2 Infusion Reactions
5.3 Graft-versus-Host Disease
5.4 Engraftment Syndrome
5.5 Graft Failure
5.6 Malignancies of Donor Origin
5.7 Transmission of Serious Infections
5.8 Transmission of Rare Genetic Diseases
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Disease
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Overdosage Experience
10.2 Management of Overdose
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: FATAL INFUSION REACTIONS, GRAFT VERSUS HOST DISEASE, ENGRAFTMENT SYNDROME AND GRAFT FAILURE
Fatal infusion reactions: HPC, Cord Blood administration can result in serious, including fatal, infusion reactions. Monitor patients and discontinue HPC, Cord Blood infusion for severe reactions. Use is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), Dextran 40 or human serum albumin. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]
Graft-vs-host disease (GVHD): GVHD is expected after administration of HPC, Cord Blood, and may be fatal. Administration of immunosuppressive therapy may decrease the risk of GVHD. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Engraftment syndrome: Engraftment syndrome may progress to multiorgan failure and death. Treat engraftment syndrome promptly with corticosteroids. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Graft failure: Graft failure may be fatal. Monitor patients for laboratory evidence of hematopoietic recovery. Prior to choosing a specific unit of HPC, Cord Blood, consider testing for HLA antibodies to identify patients who are alloimmunized. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
HPC (hematopoietic progenitor cells), Cord Blood is an allogeneic cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cell therapy indicated for use in unrelated donor hematopoietic progenitor stem cell transplantation procedures in conjunction with an appropriate preparative regimen for hematopoietic and immunologic reconstitution in patients with disorders affecting the hematopoietic system that are inherited, acquired, or result from myeloablative treatment.
The risk benefit assessment for an individual patient depends on the patient characteristics, including disease, stage, risk factors, and specific manifestations of the disease, on characteristics of the graft, and on other available treatments or types of hematopoietic progenitor cells.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use only.
Do not irradiate.
2.1 Dosing
The recommended minimum dose is 2.5 x 107 nucleated cells/kg at cryopreservation. Multiple units may be required in order to achieve the appropriate dose.
Matching for at least 4 of 6 HLA-A antigens, HLA-B antigens, and HLA-DRB1 alleles is recommended. The HLA typing and nucleated cell content for each individual unit of HPC, Cord Blood are documented on the container label and/or in accompanying records.
2.2 Preparation for Infusion
HPC, Cord Blood should be prepared by a trained healthcare professional.
- Do not irradiate HPC, Cord Blood.
- See the appended detailed instructions for preparation of HPC, Cord Blood for infusion.
- Once prepared for infusion, HPC, Cord Blood may be stored at 1 to 8°C for up to 4 hours.
- The recommended limit on DMSO administration is 1 gram per kg body weight per day. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
2.3 Administration
HPC, Cord Blood should be administered under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional experienced in hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation.
- Confirm the identity of the patient for the specified unit of HPC, Cord Blood prior to administration.
- Confirm that emergency medications are available for use in the immediate area.
- Ensure the patient is hydrated adequately.
- Premedicate the patient 30 to 60 minutes before the administration of HPC, Cord Blood. Premedications can include any or all of the following: antipyretic, histamine blocker, and corticosteroids.
- Inspect the product for any abnormalities such as unusual particulates and for breaches of container integrity prior to administration. Prior to infusion, discuss all such product irregularities with the laboratory issuing the product for infusion.
- Administer HPC, Cord Blood by intravenous infusion. Do not administer in the same tubing concurrently with products other than 0.9% Sodium Chloride, Injection (USP). HPC, Cord Blood may be filtered through a 170 to 260 micron filter designed to remove clots. Do NOT use a filter designed to remove leukocytes.
- For adults, begin infusion of HPC, Cord Blood at 100 milliliters per hour and increase the rate as tolerated. For children, begin infusion of HPC, Cord Blood at 1 milliliter per kg per hour and increase as tolerated. The infusion rate should be reduced if the fluid load is not tolerated. The infusion should be discontinued in the event of an allergic reaction or if the patient develops a moderate to severe infusion reaction. [See Warnings and Precautions (5) and Adverse Reactions (6)]
- Monitor the patient for adverse reactions during, and for at least six hours after, administration. Because HPC, Cord Blood contains lysed red cells that may cause renal failure, careful monitoring of urine output is also recommended.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each unit of HPC, Cord Blood contains a minimum of 5.0 x 108 total nucleated cells with a minimum of 1.25 x 106 viable CD34+ cells, suspended in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 1% Dextran 40, at the time of cryopreservation.
The exact pre-cryopreservation nucleated cell content is provided on the container label and in accompanying records.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis
Allergic reactions may occur with infusion of HPC, Cord Blood. Reactions include bronchospasm, wheezing, angioedema, pruritus and hives [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, also have been reported. These reactions may be due to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), Dextran 40, or a plasma component of HPC, Cord Blood.
5.2 Infusion Reactions
Infusion reactions are expected to occur and include nausea, vomiting, fever, rigors or chills, flushing, dyspnea, hypoxemia, chest tightness, hypertension, tachycardia, bradycardia, dysgeusia, hematuria, and mild headache. Premedication with antipyretic, histamine antagonists, and corticosteroids may reduce the incidence and intensity of infusion reactions.
Severe reactions, including respiratory distress, severe bronchospasm, severe bradycardia with heart block or other arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, hypotension, hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, renal compromise, encephalopathy, loss of consciousness, and seizure also may occur. Many of these reactions are related to the amount of DMSO administered. Minimizing the amount of DMSO administered may reduce the risk of such reactions, although idiosyncratic responses may occur even at DMSO doses thought to be tolerated. The actual amount of DMSO depends on the method of preparation of the product for infusion. Limiting the amount of DMSO infused to no more than 1 gm/kg/day is recommended. [See Overdosage (10)]
If infusing more than one unit of HPC, Cord Blood on the same day, do not administer subsequent units until all signs and symptoms of infusion reactions from the prior unit have resolved.
Infusion reactions may begin within minutes of the start of infusion of HPC, Cord Blood, although symptoms may continue to intensify and not peak for several hours after completion of the infusion. Monitor the patient closely during this period. When a reaction occurs, discontinue the infusion and institute supportive care as needed.
5.3 Graft-versus-Host Disease
Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) may occur in patients who have received HPC, Cord Blood. Classic acute GVHD is manifested as fever, rash, elevated bilirubin and liver enzymes, and diarrhea. Patients transplanted with HPC, Cord Blood also should receive immunosuppressive drugs to decrease the risk of GVHD. [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)
5.4 Engraftment Syndrome
Engraftment syndrome is manifested as unexplained fever and rash in the peri-engraftment period. Patients with engraftment syndrome also may have unexplained weight gain, hypoxemia, and pulmonary infiltrates in the absence of fluid overload or cardiac disease. If untreated, engraftment syndrome may progress to multiorgan failure and death. Begin treatment with corticosteroids once engraftment syndrome is recognized in order to ameliorate the symptoms. [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
5.5 Graft Failure
Primary graft failure, which may be fatal, is defined as failure to achieve an absolute neutrophil count greater than 500/uL blood by Day 42 after transplantation. Immunologic rejection is the primary cause of graft failure. Patients should be monitored for laboratory evidence of hematopoietic recovery. Consider testing for HLA antibodies in order to identify patients who are alloimmunized prior to transplantation and to assist with choosing a unit with a suitable HLA type for the individual patient. [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
5.6 Malignancies of Donor Origin
Patients who have undergone HPC, Cord Blood transplantation may develop post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), manifested as a lymphoma-like disease favoring non-nodal sites. PTLD is usually fatal if not treated.
The incidence of PTLD appears to be higher in patients who have received antithymocyte globulin. The etiology is thought to be donor lymphoid cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Serial monitoring of blood for EBV DNA may be warranted in high-risk groups.
Leukemia of donor origin also has been reported in HPC, Cord Blood recipients. The natural history is presumed to be the same as that for de novo leukemia.
5.7 Transmission of Serious Infections
Transmission of infectious disease may occur because HPC, Cord Blood is derived from human blood. Disease may be caused by known or unknown infectious agents. Donors are screened for increased risk of infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), T. pallidum, T. cruzi, West Nile Virus (WNV), transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) agents, and vaccinia. Donors are also screened for clinical evidence of sepsis, and communicable disease risks associated with xenotransplantation. Maternal blood samples are tested for HIV types 1 and 2, HTLV types I and II, HBV, HCV, T. pallidum, WNV, and T. cruzi. These measures do not totally eliminate the risk of transmitting these or other transmissible infectious diseases and disease agents. Report the occurrence of a transmitted infection to ClinImmune Labs, University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank (UCCBB) at 303-724-1306.
Testing is also performed for evidence of donor infection due to cytomegalovirus (CMV); however, this is not a donor selection criterion. The result may be found on the container label and/or in accompanying records.
5.8 Transmission of Rare Genetic Diseases
HPC, Cord Blood may transmit rare genetic diseases involving the hematopoietic system for which donor screening and/or testing has not been performed [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Cord blood donors have been screened by family history to exclude inherited disorders of the blood and marrow. HPC, Cord Blood has been tested to exclude donors with sickle cell anemia, and anemias due to abnormalities in hemoglobins C, D, and E. Because of the age of the donor at the time HPC, Cord Blood collection takes place, the ability to exclude rare genetic diseases is severely limited.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Day-100 mortality from all causes was 25%.
The most common infusion-related adverse reactions (≥5%) are hypertension, vomiting, nausea, bradycardia, and fever. (6.1)
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Infusion Reactions
The data described in Table 1 reflect exposure to 442 infusions of HPC, Cord Blood (from multiple cord blood banks) in patients treated using a total nucleated cell dose ≥2.5 x 107/kg on a single-arm trial or expanded access use (The COBLT Study). The population was 60% male, and the median age was 5 years (range 0.05-68 years), and included patients treated for hematologic malignancies, inherited metabolic disorders, primary immunodeficiencies, and bone marrow failure. Preparative regimens and graft-vs-host disease prophylaxis were not standardized. The most common infusion reactions were hypertension, vomiting, nausea, and bradycardia. Hypertension and any grades 3-4 infusion-related reactions occurred more frequently in patients receiving volumes greater than 150 milliliters and in pediatric patients. The rate of serious adverse cardiopulmonary reactions was 0.8%.
Table 1. Incidence of Infusion-Related Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥1% of Infusions (The COBLT Study) Any grade Grade 3-4 Any reaction 65.4% 27.6% Hypertension 48.0% 21.3% Vomiting 14.5% 0.2% Nausea 12.7% 5.7% Sinus bradycardia 10.4% 0 Fever 5.2% 0.2% Sinus tachycardia 4.5% 0.2% Allergy 3.4% 0.2% Hypotension 2.5% 0 Hemogloburia 2.1% 0 Hypoxia 2.0% 2.0% Information on infusion reactions was available from voluntary reports for 47 patients who received HPC, Cord Blood from ClinImmune Labs at a total nucleated cell dose ≥2.5 x 107/kg. The population included 72% males and 28% females, with median age 12 years (range 0.4 - 67.5 years). Preparative regimens and graft-vs-host disease prophylaxis were not standardized. Seventeen patients (36%) had an infusion reaction. Infusion reactions included hypertension, nausea, vomiting, facial flushing, hypoxia, headache, fever and chills, hematuria, and bradycardia.
Other Adverse Reactions
For other adverse reactions, the raw clinical data from the docket were pooled for 1299 patients (120 adult and 1179 pediatric) transplanted with HPC, Cord Blood (from multiple cord blood banks) with total nucleated cell dose ≥2.5 x 107/kg. Sixty-six percent (n=862) underwent transplantation as treatment for hematologic malignancy. The preparative regimens and graft-vs-host disease prophylaxis varied. The median total nucleated cell dose was 6.4 (range, 2.5 - 73.8) x 107/kg. For these patients, Day-100 mortality from all causes was 25%. Primary graft failure occurred in 16%; 42% developed grades 2 - 4 acute graft-vs-host disease; and 19% developed grades 3-4 acute graft-vs-host disease.
Data from published literature and from observational registries, institutional databases, and cord blood bank reviews reported to the docket for HPC, Cord Blood (from multiple cord blood banks) revealed nine cases of donor cell leukemia, one case of transmission of infection, and one report of transplantation from a donor with an inheritable genetic disorder. The data are not sufficient to support reliable estimates of the incidences of these events.
In a study of 364 patients, 15% of the patients developed engraftment syndrome.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with HPC, Cord Blood. It is also not known whether HPC, Cord Blood can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. HPC, Cord Blood should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.4 Pediatric Use
HPC, Cord Blood has been used in pediatric patients with disorders affecting the hematopoietic system that are inherited, acquired, or resulted from myeloablative treatment. [See Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6), and Clinical Studies (14)]
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of HPC, Cord Blood (from multiple cord blood banks) did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. In general, administration of HPC, Cord Blood to patients over age 65 should be cautious, reflecting their greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Overdosage Experience
There has been no experience with overdosage of HPC, Cord Blood in human clinical trials. Single doses of HPC, Cord Blood from ClinImmune Labs up to 6.5 x 108 TNC/kg have been administered. HPC, Cord Blood prepared for infusion may contain dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The maximum tolerated dose of DMSO has not been established, but it is customary not to exceed a DMSO dose of 1 gm/kg/day when given intravenously. Several cases of altered mental status and coma have been reported with higher doses of DMSO.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
HPC, Cord Blood consists of hematopoietic progenitor cells, monocytes, lymphocytes, and granulocytes from human cord blood. Blood recovered from umbilical cord and placenta is volume reduced and partially depleted of red blood cells and plasma.
The active ingredient is hematopoietic progenitor cells which express the cell surface marker CD34. The potency of cord blood is determined by measuring the numbers of total nucleated cells (TNC) and CD34+ cells, and cell viability. Each unit of HPC, Cord Blood contains a minimum of 5 x 108 total nucleated cells with at least 1.25 x 106 viable CD34+ cells at the time of cryopreservation. The cellular composition of HPC, Cord Blood depends on the composition of cells in the blood recovered from the umbilical cord and placenta of the donor. The actual nucleated cell count, the CD34+ cell count, the ABO group, and the HLA typing are listed on the container label and/or accompanying records sent with each individual unit.
HPC, Cord Blood has the following inactive ingredients: dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and Dextran 40. When prepared for infusion according to instructions, the infusate contains the following inactive ingredients: Dextran 40, human serum albumin, and residual DMSO.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells from HPC, Cord Blood migrate to the bone marrow where they divide and mature. The mature cells are released into the bloodstream, where some circulate and others migrate to tissue sites, partially or fully restoring blood counts and function, including immune function, of blood-borne cells of marrow origin. [See Clinical Studies (14)]
In patients with enzymatic abnormalities due to certain severe types of storage disorders, mature leukocytes resulting from HPC, Cord Blood transplantation may synthesize enzymes that may be able to circulate and improve cellular functions of some native tissues. However, the precise mechanism of action is unknown.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of HPC, Cord Blood, as defined by hematopoietic reconstitution, was demonstrated in one single-arm prospective study and in retrospective reviews of data from an observational database for HPC, Cord Blood and data in the dockets and public information. Sixty-six percent (n=862) of the 1299 patients in the docket and public data underwent transplantation as treatment for hematologic malignancy. Results for patients who received a total nucleated cell dose ≥2.5 x 107/kg are shown in Table 2. Neutrophil recovery is defined as the time from transplantation to an absolute neutrophil count more than 500 per microliter. Platelet recovery is the time to a platelet count more than 20,000 per microliter. Erythrocyte recovery is the time to a reticulocyte count greater than 30,000 per microliter. The total nucleated cell dose and degree of HLA mismatch were inversely associated with the time to neutrophil recovery in the docket data.
Table 2. Hematopoietic Recovery for Patients Transplanted with Total Nucleated Cell (TNC) Dose ≥ 2.5 x 107/kg * HPC, Cord Blood (from multiple cord blood banks)
Data Source The COBLT Study* Docket* and Public Data* ClinImmune Labs
HPC, Cord BloodDesign Single-arm prospective Retrospective Retrospective Number of patients 324 1299 220 Median age (range) 4.6 (0.07 – 52.2) yrs 7.0 (<1 – 65.7) yrs 6.9 (0.1 – 73.1) yrs Gender 59% male
41% female57% male
43% female57% male
43% femaleMedian TNC Dose
(range) (x 107/kg)6.7 (2.6 – 38.8) 6.4 (2.5 – 73.8) 5.8 (2.5 – 65.0) Neutrophil Recovery at Day 42 76%
(95% CI 71% – 81%)77%
(95% CI 75% – 79%)79%
(95% CI 73.5%- 84.4%)Platelet Recovery at Day 100 (20,000/uL) 57%
(95% CI 51% – 63%)
-62%
(95% CI 44.8%-77.5%)Platelet Recovery at Day 100 (50,000/uL) 46%
(95% CI 39% – 51%)45%
(95% CI 42% – 48%)55%
(95% CI 36.0%-72.7%)Erythrocyte Recovery at Day 100 65%
(95% CI 58% – 71%)- - Median time to Neutrophil Recovery 27 days 25 days 25 days Median time to Platelet Recovery (20,000/uL) 90 days - 55 days Median time to Platelet Recovery (50,000/uL) 113 days 122 days 49 days Median time to Erythrocyte Recovery 64 days - - -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
HPC, Cord Blood is supplied as a cryopreserved cell suspension in a sealed bag containing a minimum of 5 x 108 total nucleated cells with a minimum of 1.25 x 106 viable CD34+ cells in a volume of 30-124 milliliters (ISBT 128 Product Code S1393, ISBT 128 Facility Identifier Number W3213). The exact pre-cryopreservation volume and nucleated cell content are provided on the container label and accompanying records.
Store HPC, Cord Blood at or below -150°C until ready for thawing and preparation.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients receiving HPC, Cord Blood:
- Report immediately any signs and symptoms of acute infusion reactions, such as fever, chills, fatigue, breathing problems, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, or muscle aches.
- Report immediately any signs or symptoms suggestive of graft-vs-host disease, including rash, diarrhea, or yellowing of the eyes.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARATION FOR INFUSION
1 Equipment, reagents, Materials, and forms
Equipment
Water bath
Plasma Extractor
Centrifuge - refrigerated
Balance
Tubing stripers
Sealer
Hemocytometer chamber
Cell counter
ThermometerReagents
5% Albumin (human), USP
10% Dextran 40 in Sodium Chloride Solution, USPMaterials
Plasma transfer set
150 mL double transfer pack, 150 mL transfer pack, or 300 mL transfer pack
Centrifuge bag
Plastic tubing clip
Sterile disposable syringes: 1, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 mL
18 gauge needle
70% isopropyl alcohol
Sterile waterForms Provided by ClinImmune Labs
Transplant Center Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells, Cord Blood (HPC, Cord Blood) Thaw Worksheet
Form E5.103 - HPC, Cord Blood Release Report
Form E6.251 - Human Cord Blood Unit Receipt Form
Form E8.102 - Adverse Product Event and Infusion Reaction2 ADMINISTRATIVE REQUIREMENTS
-
Immediately following receipt of product - Complete Form E6.251 – HPC Unit Receipt Form and fax it to ClinImmune Labs (303-724-1849). Document:
- Patient's name, medical record number
- Date and time prior to opening the dry shipper
- Weight of the dry shipper
- Match of the HPC, Cord Blood identification number expected with the HPC, Cord Blood number received
- Condition of the HPC, Cord Blood upon arrival (i.e., still frozen)
- Internal temperature of the dry shipper
- Transplant facility information
- Comments and/or explanation for any deviations
- Prior to thawing - Review and complete all transport verification to document receipt of the unit against Form E5-103 – HPC, Cord Blood Release Report. If there are any errors or ambiguity, do not proceed. Report any problems to ClinImmune Labs (303-724-1306) and the transplant physician.
- During thawing - Complete the thaw worksheet.
- Ensure that Form E8.102 (Adverse Product Event and Infusion Reaction) accompanies the product to the transplant unit.
- Return the dry shipper as soon as possible. After transplant, return the metal canister at earliest convenience.
Contact Information for ClinImmune Labs at the University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank (UCCBB):
UCCBB 1999 North Fitzsimmons Parkway, Suite 160 Aurora, CO 80045 Cord Blood Bank Hours: Monday – Friday, 8:00 AM – 5:00 PM (Mountain Time) Cord Blood Bank Phone Number: 303-724-1306 Cord Blood Bank Fax Number: 303-724-1849 Pagers: Cord Blood Bank Coordinator 303-266-0254 Cord Blood Bank Director 303-266-3043 Cord Blood Bank Medical Director 303-266-0763 or 303-540-1914 3 VERIFICATION OF PRODUCT IDENTITY
HPC, Cord Blood is shipped frozen in an overwrap in the metal canister. HPC, Cord Blood must be kept at or below -150° C, either inside the container used for shipping (Dry-Shipper) or in vapor phase of a Liquid Nitrogen (LN2) storage device at the Transplant Center (recommended).
- Check the HPC, Cord Blood identification number (ID) on the label to confirm its identity with the ID of the expected product as soon as it is received (Figure 1).
- Wearing protective cryogloves, transfer the HPC, Cord Blood from the Dry-Shipper to the vapor phase of a LN2 storage tank.
- Carefully open the canister while it is in the vapor of the freezer to prevent the bag from cracking and the yellow port covers from popping off (Figure 2).
- Work carefully to avoid damaging the frozen plastic product bag.
- Check the bar-coded label on the product against your records to verify that the bar code and visually-readable printed number absolutely conforms to the information previously provided and the documentation included with the HPC, Cord Blood product (Form E6.251 - Human Cord Blood Unit Receipt Form).
NOTE: If there is any error or ambiguity with regard to the product ID, close the canister and keep the product at LN2 temperature. Immediately advise the staff of ClinImmune Labs, UCCBB and the transplant physician. Do not proceed until the problem is resolved. If your LN2 storage tanks have no space to store the product in its canister, add LN2 to the UCCBB dry-shipper to maintain the product frozen until a completely satisfactory determination is made. 4 METHOD
4.1 Preparation of Water Bath
- A water bath with minimum 2 L capacity is recommended.
- Clean water bath with 70% isopropyl alcohol and fill with appropriate volume of sterile water.
- Maintain the temperature of the water bath between 36-38°C prior to thawing the HPC, Cord Blood.
4.2 Preparation of Wash Media
- Prepare wash media no sooner than one hour prior to the thaw for infusion. Media expires 4 hours after preparation.
- Determine the total volume of media needed. For reconstitution only, use an equal volume of media to the total HPC, Cord Blood cryo volume. For wash and reconstitution, use twice the total HPC, Cord Blood cryo volume.
Example: 50 mL of HPC, Cord Blood cryo volume
For reconstitution only: 50 mL of media are needed.
For reconstitution and wash: 100 mL of media are needed. - Prepare the media by mixing equal amounts of 5% albumin and 10% Dextran 40.
Example: To prepare 50 mL of media, mix 25 mL of 5% albumin and 25 mL of 10% Dextran 40.
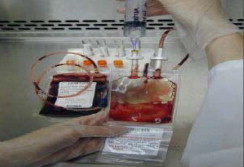
4.3 Thawing HPC, Cord Blood
- Carefully cut and remove the overwrap (Figures 3, 4, and 5).
- Put the HPC, Cord Blood into a sterile centrifuge bag and place HPC, Cord Blood in the water bath. If there are two cryo bags for the same HPC, Cord Blood, thaw both bags in separate sterile centrifuge bags at the same time.
- Thaw the HPC, Cord Blood until all frozen portions dissolve into solution.
- Take the bag(s) out of the water bath, remove the HPC, Cord Blood from the sterile bag(s), and place it into a laminar flow hood.
- To access a bag with a configuration as shown in Figures 6 and 7, remove the yellow port protector and insert a plasma transfer set into the port. For a bag with configuration as shown in Figure 8, open the port by twisting the upper part of the port.
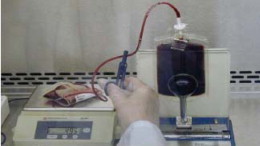
- Measure the volume by syringe or weight as per transplant center procedures.
- Remove a small volume for quality control (QC) testing as per transplant center procedures. If the HPC, Cord Blood has two cryo bags, pool both portions together in the same transfer bag before removing the sample.
- The thawed HPC, Cord Blood is ready for reconstitution or washing (see below).
4.4 Reconstituting and Washing HPC, Cord Blood
For reconstituting HPC, Cord Blood (dilution)
- If using a 150 mL double transfer pack, clamp off one of the bags with a plastic clip and drain the HPC, Cord Blood into the open transfer bag (Figure 9).
For two cryo bags, drain both bags into the double transfer bag or use a 300 mL transfer bag.
- Use a hemostat to clamp the line to the transfer bag containing the HPC, Cord Blood.
- Wash the cryo bag by injecting the wash media (equal to the total volume of the frozen HPC, Cord Blood) into the empty bag and rinsing thoroughly (Figure 10).
- Open the hemostat and slowly drain the wash media into the bag with the HPC, Cord Blood while gently mixing the cells in the bag with a rocking motion. Seal off the empty freezing bag.
- Remove a small volume of the reconstituted product for QC testing (such as complete blood count (CBC), CFU, CD34+ counts, viability, and sterility) as per transplant center procedures.
- Allow five minutes for the cells to equilibrate.
- HPC, Cord Blood is ready for infusion or for washing out the cryoprotectant.
- The recommended expiration time is four hours at 1-8°C from the time of thaw.
For removing cryoprotectant (washing)
- Centrifuge the diluted HPC, Cord Blood (with ports up) at 1300 rpm (473 x g) for ten minutes at 1-6°C.
- Remove the supernatant (equal volume of added wash media) using a plasma extractor (Figure 11).
- Slowly add the remaining washing media (that was not used in reconstitution).
- Mix the bag gently.
- Remove a small volume of the reconstituted product for QC testing (such as CBC, CFU, CD34+ counts, viability, and sterility) as per transplant center procedures.
- HPC, Cord Blood is ready for infusion.
- The recommended expiration time is four hours at 1-8°C from the time of thaw.
5. EMERGENCY PRODUCT RECOVERY IN THE EVENT OF A CONTAINER FAILURE
- Emergency product recovery at transport: If the alarm is blinking red upon receipt of the dry shipper, document on Form E6.251 and immediately use an alternative means to monitor and document the dry shipper temperature. If the temperature is higher than -150°C and there are ice crystals observed in the HPC, Cord Blood, immediately store the HPC, Cord Blood in liquid nitrogen vapor phase and notify the transplant physician. Document the temperature on Form E6.251 and notify ClinImmune Labs, University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank immediately at 303-724-1306.
- Emergency product recovery at thaw: If any cracks or port integrity leaks are observed in the cryo bag at thaw, remove the HPC, Cord Blood from the water bath and clamp off the leaking portion of the bag with a hemostat. If the HPC, Cord Blood is still frozen, continue to thaw the product with the leaking site clamped tightly. Once thawed, remove the HPC, Cord Blood from the water bath, recover cells in the sterile thawing bag if there are any, and contact the appropriate transplant center staff immediately for further instruction. Document all findings on Form E8.102 and fax it to the ClinImmune Labs, University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank at 303-724-1849
Distributed by:
ClinImmune Labs
University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank (UCCBB)
1999 North Fitzsimmons Parkway, Suite 160
Aurora, CO 80045
US License #1855Issued: 05/2012
-
Immediately following receipt of product - Complete Form E6.251 – HPC Unit Receipt Form and fax it to ClinImmune Labs (303-724-1849). Document:
-
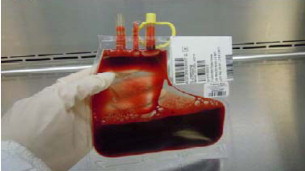
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – Bag Label
HPC, Cord Blood
Approx & VOL.: mL
Additives & Vol.: mL DMSO
DEXTRAN. < mL HESPAN
< mL CPD. EtO may persist
For Intravenous Infusion
Do Not Irradiate
Do Not Use Leukoreduction Filters
Store at <= -150CCaution: Federal Law prohibits
distribution without a prescriptionClinImmune Labs – UCCBB
12635 E. Montview Blvd.
Aurora, CO 80045 -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS, CORD BLOOD
human cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cell liquidProduct Information Product Type LICENSED MINIMALLY MANIPULATED CELLS Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HUMAN CORD BLOOD HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELL (UNII: XU53VK93MC) (HUMAN CORD BLOOD HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELL - UNII:XU53VK93MC) HUMAN CORD BLOOD HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELL 500000000 in 30 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Hetastarch (UNII: 875Y4127EA) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Dextran 40 (UNII: K3R6ZDH4DU) Dimethyl Sulfoxide (UNII: YOW8V9698H) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 ISBT:W3213-S1393 30 mL in 1 BAG Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125391 05/24/2012 Labeler - Clinimmune Labs, University of Colorado Blood Bank (781310011) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Clinimmune Labs, University of Colorado Blood Bank 781310011 MANUFACTURE
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.