BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE lotion, augmented
Betamethasone Dipropionate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Betamethasone Dipropionate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by E. Fougera & Co. a division of Fougera Pharmaceuticals Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE Lotion (Augmented), 0.05% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE Lotion (Augmented), 0.05%.
BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE lotion (Augmented), 0.05% for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1983RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
- Warnings and Precautions Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions (5.2) 05/2019
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% is a corticosteroid indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses in patients 13 years of age and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Apply a few drops to the affected skin areas once or twice daily and massage lightly until the lotion disappears.(2)
- Discontinue therapy when control is achieved. (2)
- Limit therapy to no more than 2 consecutive weeks. (2)
- Use no more than 50 mL per week. (2)
- Do not use with occlusive dressings unless directed by a physician. (2)
- Avoid use on the face, groin, or axillae, or if skin atrophy is present at the treatment site. (2)
- Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Lotion, 0.05% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medicine. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Effects on endocrine system: Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% can cause reversible HPA axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency during and after withdrawal of treatment. Risk factor(s) include the use of high-potency topical corticosteroids, use over a large surface area or to areas under occlusion, prolonged use, altered skin barrier, liver failure, and use in pediatric patients. Modify use should HPA axis suppression develop. (5.1, 8.4)
- Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions: Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% may increase the risk of cataracts and glaucoma. If visual symptoms occur, consider referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (<1%) are: erythema, folliculitis, pruritus, and vesiculation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fougera Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-800-645-9833 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
5.3 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a few drops of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% to the affected skin areas once or twice daily and massage lightly until the lotion disappears.
Therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, reassessment of diagnosis may be necessary. Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% is a super-high-potency topical corticosteroid. Treatment with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% should be limited to 2 consecutive weeks and amounts should not exceed 50 mL per week because of the potential for the drug to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% should not be used with occlusive dressings unless directed by a physician.
Avoid use on the face, groin, or axillae, or if skin atrophy is present at the treatment site.
Avoid contact with eyes. Wash hands after each application.
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% is for topical use only. It is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. This may occur during treatment or after withdrawal of treatment. Factors that predispose to HPA axis suppression include the use of high-potency steroids, large treatment surface areas, prolonged use, use of occlusive dressings, altered skin barrier, liver failure, and young age. Evaluation for HPA axis suppression may be done by using the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test.
In a trial evaluating the effects of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the HPA axis, betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% was applied once daily at 7 mL per day for 21 days to diseased scalp and body skin in subjects with scalp psoriasis, betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% was shown to lower plasma cortisol levels below normal limits in 2 out of 11 subjects. HPA axis suppression in these subjects was transient and returned to normal within a week. In one of these subjects, plasma cortisol levels returned to normal while treatment continued.
If HPA axis suppression is documented, gradually withdraw the drug, reduce the frequency of application, or substitute with a less potent corticosteroid. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of steroid withdrawal may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids.
Cushing's syndrome and hyperglycemia may also occur with topical corticosteroids. These events are rare and generally occur after prolonged exposure to excessively large doses, especially of high-potency topical corticosteroids.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Use of topical corticosteroids, including betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%, may increase the risk of posterior subcapsular cataracts and glaucoma. Cataracts and glaucoma have been reported postmarketing with the use of topical corticosteroid products, including betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Avoid contact of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% with eyes. Advise patients to report any visual symptoms and consider referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation.
5.3 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing. If irritation develops, topical corticosteroids should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In controlled clinical trials, adverse reactions associated with the use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% reported at a frequency of less than 1% included erythema, folliculitis, pruritus, and vesiculation.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Postmarketing reports for local adverse reactions to topical corticosteroids may also include: skin atrophy, striae, telangiectasias, burning, irritation, dryness, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, hypertrichosis, and miliaria.
Hypersensitivity reactions, consisting of predominantly skin signs and symptoms, e.g., contact dermatitis, pruritus, bullous dermatitis, and erythematous rash have been reported.
Ophthalmic adverse reactions of cataracts, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and central serous chorioretinopathy have been reported with the use of topical corticosteroids, including topical betamethasone products.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% use in pregnant women to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Observational studies suggest an increased risk of low birthweight infants with the use of greater than 300 grams of potent or very potent topical corticosteroid during a pregnancy. Advise pregnant women that betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% may increase the risk of having a low birthweight infant and to use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible.
In animal reproduction studies, increased malformations, including umbilical hernias, cephalocele, and cleft palate, were observed after intramuscular administration of betamethasone dipropionate to pregnant rabbits. The available data do not allow the calculation of relevant comparisons between the systemic exposure of betamethasone dipropionate in animal
studies to the systemic exposure that would be expected in humans after topical use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Betamethasone dipropionate has been shown to cause malformations in rabbits when given by the intramuscular route at doses of 0.05 mg/kg. The abnormalities observed included umbilical hernias, cephalocele, and cleft palate.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data regarding the excretion of betamethasone dipropionate in breast milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production after topical application of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% to women who are breastfeeding.
It is possible that topical administration of large amounts of betamethasone dipropionate could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breast milk, use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Advise breastfeeding women not to apply betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% directly to the nipple and areola to avoid direct infant exposure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% in pediatric patients younger than 13 years of age is not recommended due to the potential for HPA axis suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In an open-label HPA axis safety trial in subjects 3 months to 12 years of age with atopic dermatitis, betamethasone dipropionate cream (augmented), 0.05% was applied twice daily for 2 to 3 weeks over a mean body surface area of 58% (range 35% to 95%). In 19 of 60 (32%) evaluable subjects, adrenal suppression was indicated by either a ≤5 mcg/dL pre-stimulation cortisol, or a cosyntropin post-stimulation cortisol ≤18 mcg/dL and/or an increase of <7 mcg/dL from the baseline cortisol. Out of the 19 subjects with HPA axis suppression, 4 subjects were tested 2 weeks after discontinuation of betamethasone dipropionate cream (augmented), 0.05% and 3 of the 4 (75%) had complete recovery of HPA axis function. The proportion of subjects with adrenal suppression in this trial was progressively greater, the younger the age group.
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of systemic toxicity when treated with topical drugs. They are, therefore, also at greater risk of HPA axis suppression and adrenal insufficiency upon the use of topical corticosteroids.
Rare systemic effects such as Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in pediatric patients, especially those with prolonged exposure to large doses of high potency topical corticosteroids.
Local adverse reactions including skin atrophy have also been reported with use of topical corticosteroids in pediatric patients.
Avoid use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% in the treatment of diaper dermatitis.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% included 56 subjects who were 65 years of age and over and 9 subjects who were 75 years of age and over. There was a numerical difference for application site reactions (most frequently reported events were burning and stinging) which occurred in 15% (10/65) of geriatric subjects and 11% (38/342) of subjects less than 65 years of age. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. However, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
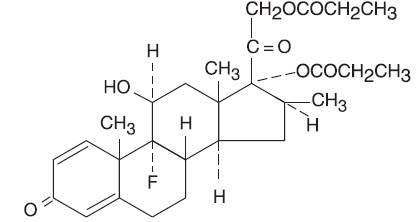
Betamethasone Dipropionate Lotion USP (Augmented), 0.05% contains betamethasone dipropionate USP, a synthetic adrenocorticosteroid, for topical use. Betamethasone, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of corticosteroid activity and a slight degree of mineralocorticoid activity. Betamethasone dipropionate is the 17,21-dipropionate ester of betamethasone.
Chemically, betamethasone dipropionate is 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17,21-dipropionate, with the molecular formula C28H37FO7, a molecular weight of 504.6, and the following structural formula:
It is a white to creamy-white, odorless powder insoluble in water; freely soluble in acetone and in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Each gram of betamethasone dipropionate lotion USP (augmented), 0.05% contains: 0.643 mg betamethasone dipropionate, USP (equivalent to 0.5 mg betamethasone) in a colorless, clear to translucent lotion base of purified water, isopropyl alcohol (30%), phosphoric acid used to adjust the pH, hydroxypropyl cellulose, propylene glycol, and monobasic sodium phosphate (monohydrate).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids play a role in cellular signaling, immune function, inflammation, and protein regulation; however, the precise mechanism of action of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% in corticosteroid responsive dermatoses is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Vasoconstrictor Assay
Trials performed with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% indicate that it is in the super-high range of potency as demonstrated in vasoconstrictor trials in healthy subjects when compared with other topical corticosteroids. However, similar blanching scores do not necessarily imply therapeutic equivalence.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
No pharmacokinetic trials have been conducted with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed through normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids enter pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees, are metabolized primarily in the liver, and excreted by the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of betamethasone dipropionate. Betamethasone was negative in the bacterial mutagenicity assay (Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli), and in the mammalian cell mutagenicity assay (CHO/HGPRT). It was positive in the in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay, and equivocal in the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Studies in rabbits, mice, and rats using intramuscular doses up to 1, 33, and 2 mg/kg, respectively, resulted in dose-related increases in fetal resorptions in rabbits and mice.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% for the treatment of corticosteroid- responsive dermatoses have been evaluated in two randomized vehicle controlled trials, one in scalp psoriasis and one in seborrheic dermatitis. A total of 263 subjects, of whom 131 received betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% were included in these trials. These trials evaluated betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% applied once daily for 21 days.
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% was shown to be effective in relieving the signs and symptoms of corticosteroid responsive dermatoses.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Betamethasone Dipropionate Lotion USP (Augmented), 0.05% is supplied as follows:
NDC: 0168-0267-30, 30 mL bottle
NDC: 0168-0267-60, 60 mL bottle
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Inform patients of the following:
- Discontinue therapy when control is achieved, unless directed otherwise by the physician.
- Use no more than 50 mL per week of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% and for no longer than 2 consecutive weeks.
- Avoid contact with the eyes.
- Advise patients to report any visual symptoms to their healthcare providers.
- Avoid use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the face, underarms, or groin areas unless directed by the physician.
- Do not occlude the treatment area with bandage or other covering, unless directed by the physician.
- Note that local reactions and skin atrophy are more likely to occur with occlusive use, prolonged use or use of higher potency corticosteroids.
- Advise a woman to use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while pregnant or breastfeeding. Advise breastfeeding women not to apply betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% directly to the nipple and areola to avoid direct infant exposure.
-
Patient Package Insert
Patient Information
Betamethasone Dipropionate Lotion USP (Augmented), 0.05%
(BAY-ta-METH-a-sone)
Important information:Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% is for use on skin only. Do not use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% in your eyes, mouth, or vagina.
What is betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%?
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% is prescription corticosteroid medicine used on the skin (topical) for the relief of redness, swelling, heat, pain (inflammation) and itching, caused by certain skin problems in people 13 years of age and older.
- Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% should not be used in children under 13 years of age.
Do not use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% if you are allergic to betamethasone dipropionate or any of the ingredients in betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
Before using betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had irritation or other skin reaction to a steroid medicine in the past.
- have thinning of the skin (atrophy) at the treatment site.
- have diabetes.
- have adrenal gland problems.
- have liver problems.
- have cataracts or glaucoma.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% will harm your unborn baby. If you use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% during pregnancy, use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the smallest area of the skin and for the shortest time needed.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% passes into your breast milk. Breastfeeding women should use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest time needed while breastfeeding. Do not apply betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% directly to the nipple and areola to avoid contact with your baby.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take other corticosteroid medicines by mouth, or injection or use other products on your skin or scalp that contain corticosteroids.
Do not use other products containing a steroid medicine with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% without talking to your healthcare provider first.
How should I use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%?
- Use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Apply a few drops of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% to the affected skin area 1 or 2 times each day and massage lightly until the lotion disappears. Do not use more than 50 mL of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% in 1 week.
- Do not use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% for longer than 2 weeks in a row unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Tell your healthcare provider if the treated skin area does not get better after 2 weeks of treatment with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
- Do not bandage, cover, or wrap the treated skin area unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% should not be used to treat diaper rash or redness.
- Avoid using betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% on the face, groin, or underarms (armpits) or if thinning of the skin (atrophy) is present at the treatment site.
- Wash your hands after applying betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% unless you are using the medicine to treat your hands.
What are the possible side effects of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%?
Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% may cause serious side effects, including:
- Betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% can pass through your skin. Too much betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% passing through your skin can cause your adrenal glands to stop working properly. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check for adrenal gland problems.
- Cushing’s syndrome, a condition that happens when your body is exposed to too much of the hormone cortisol.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
- Effects on growth and weight in children.
- Vision problems. Topical corticosteroids including betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% may increase your chance of developing cataract(s) and glaucoma. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop blurred vision or other vision problems during treatment with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
- Skin problems. Skin problems including, allergic reactions (contact dermatitis) may happen during treatment with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%. Stop using betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% and tell your healthcare provider if you develop any skin reactions or have problems with healing during treatment with betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
The most common side effects of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% include: redness of the skin, inflamed hair follicles, itching and blistering.
These are not all of the possible side effects of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%?
- Store betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Keep betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05% that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in betamethasone dipropionate lotion (augmented), 0.05%?
Active ingredient: augmented betamethasone dipropionate, USP
Inactive ingredients: purified water; isopropyl alcohol (30%); phosphoric acid used to adjust the pH; hydroxypropyl cellulose; propylene glycol; and monobasic sodium phosphate (monohydrate).
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mL Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mL Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE
betamethasone dipropionate lotion, augmentedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0168-0267 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE (UNII: 826Y60901U) (BETAMETHASONE - UNII:9842X06Q6M) BETAMETHASONE 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (1600000 WAMW) (UNII: RFW2ET671P) phosphoric acid (UNII: E4GA8884NN) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 3980JIH2SW) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0168-0267-30 30 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2007 2 NDC: 0168-0267-60 60 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2007 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA077111 05/21/2007 Labeler - E. Fougera & Co. a division of Fougera Pharmaceuticals Inc. (043838424)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.