XEGLYZE- abametapir lotion
Xeglyze by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Xeglyze by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dr. Reddys Laboratories, Inc. , Dr. Reddy's Laboratories SA, Groupe Parima Inc., Neopharm Labs Inc, Particle Technology Labs, R.D. Laboratories, Inc., LAURUS LABS LIMITED, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., SGS Life Science Services, KABS Laboratories, SGS India Private Limited, Vimta Labs Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use XEGLYZETM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XEGLYZE.
XEGLYZE (abametapir) lotion, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XEGLYZE is a pediculicide indicated for the topical treatment of head lice infestation in patients 6 months of age and older. XEGLYZE should be used in the context of an overall lice management program:
- Wash (with hot water) or dry-clean all recently worn clothing, hats, used bedding and towels
- Wash personal care items such as combs, brushes and hair clips in hot water
- Use a fine-tooth comb or special nit comb to remove dead lice and nits (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. (2)
- Shake well before use. (2)
- Apply XEGLYZE to dry hair in an amount sufficient (up to the full content of one bottle) to thoroughly coat the hair and scalp. Avoid contact with eyes. (2)
- Massage XEGLYZE into the scalp and throughout the hair; leave on the hair and scalp for 10 minutes and then rinse off with warm water. (2)
- Massage XEGLYZE into the scalp and throughout the hair; leave on the hair and scalp for 10 minutes and then rinse off with warm water. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Lotion: 0.74% [weight by weight]. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Neonatal Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity: Systemic exposure to benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse reactions and death in neonates and low birth-weight infants. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months have not been established. Use is not recommended in pediatric patients under 6 months of age because of the potential for increased systemic absorption. (5.1)
- Risk of Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity from Accidental Ingestion: Administer only under direct supervision of an adult. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence of ≥ 1%) were erythema, rash, skin burning sensation, contact dermatitis, vomiting, eye irritation, pruritus, and hair color changes. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories. Inc., at 1-888-966-8766 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
For 2 weeks after XEGLYZE application, avoid taking drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4, CYP2B6 or CYP1A2. Otherwise, avoid use of XEGLYZE. (7) (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2022
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Neonatal Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity
5.2 Risk of Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity from Accidental Ingestion
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XEGLYZE is indicated for the topical treatment of head lice infestation in patients 6 months of age and older.
XEGLYZE should be used in the context of an overall lice management program:
-
Wash (with hot water) or dry-clean all recently worn clothing, hats, used bedding and towels
-
Wash personal care items such as combs, brushes, and hair clips in hot water
Use a fine-tooth comb or special nit comb to remove dead lice and nits
-
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical use only. XEGLYZE is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. Treatment with XEGLYZE involves a single application.
Shake well before use. Apply XEGLYZE to dry hair in an amount (up to the full content of one bottle) sufficient to thoroughly coat the hair and scalp. Massage XEGLYZE into the scalp and throughout the hair. Avoid contact with eyes. Leave on the hair and scalp for 10 minutes and then rinse off with warm water. Wash hands after application. Hair may be shampooed any time after the treatment.
Discard any unused product. Do not flush contents down sink or toilet.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Neonatal Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity
XEGLYZE contains benzyl alcohol. Systemic exposure to benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” in neonates and low birth weight infants. The “gasping syndrome” is characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, and gasping respirations. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. Premature and low-birth weight infants may be more likely to develop toxicity [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
The safety and effectiveness of XEGLYZE have not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months. Use is not recommended in pediatric patients under 6 months of age because of the potential for increased systemic absorption.
5.2 Risk of Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity from Accidental Ingestion
In order to prevent accidental ingestion in pediatric patients, XEGLYZE should only be administered under direct supervision of an adult.
Ingestion of benzyl alcohol in large quantities may result in gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) and central nervous system (headache, ataxia, convulsions, coma) adverse reactions. Serious adverse reactions may include respiratory depression and death. If accidentally swallowed, advise the patient or the caregiver to call their Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug, and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to a single 10-minute treatment of XEGLYZE in 349 subjects (6 months of age and older) with head lice infestation in randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (Trials 1 and 2). Of these subjects, 21 were 6 months to 4 years of age, 166 subjects were 4 to 12 years of age, 57 subjects were 12 to 18 years of age, and 105 subjects were 18 years of age or older.
Table 1 provides adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of subjects in the XEGLYZE group and at a greater frequency than in the vehicle group.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 1% of the XEGLYZE Group and at a Greater Frequency than in the Vehicle Group (Trials 1 and 2)
Adverse Reactions XEGLYZE
N=349
Subjects (%)Vehicle
N=350
Subjects (%)Erythema 14 (4.0) 6 (2) Rash 11 (3.2) 8 (2.3) Skin burning sensation 9 (2.6) 0 (0.0) Contact dermatitis 6 (1.7) 4 (1.1) Vomiting 6 (1.7) 2 (0.6) Eye irritation 4 (1.2) 2 (0.6) Hair color changes 3 (1) 0 (0.0) During the trials, subjects were monitored for new onset of scalp erythema/edema, scalp pruritus, and eye irritation. The number and percentage of subjects who developed these local adverse reactions after treatment are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Monitored Local Adverse Reactions with New Onset on Day 1 Post-Treatment (Trials 1 and 2)
Adverse Reactions XEGLYZE
Subjects (%)*Vehicle
Subjects (%)*Scalp Erythema/Edema 11 (3.2) 5 (1.4) Scalp Pruritus 2 (1.4) 1 (0.7) Eye Irritation 6 (1.7) 5 (1.4) * For the calculation of the percentages, the denominators are the number of subjects who did not have the monitored local adverse reaction at baseline.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
In vitro studies suggest there is a potential for inhibition of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4, 2B6 and 1A2 enzymes following a single application of XEGLYZE. Use of XEGLYZE with drugs that are substrates of these enzymes may lead to increased systemic concentrations of the interacting drugs. Avoid administration of drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4, CYP2B6, or CYP1A2 within 2 weeks after application of XEGLYZE. If this is not feasible, avoid use of XEGLYZE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on XEGLYZE use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In embryofetal development studies conducted with oral administration of abametapir during organogenesis, no evidence of fetal harm or malformations, independent of maternal toxicity were observed in pregnant rats and rabbits at doses that produced exposures up to 50 times and equivalent to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) in rats and rabbits, respectively. The highest dose evaluated in rabbits was limited due to maternal toxicity associated with the vehicle used in the study (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Systemic embryofetal development studies were performed in rats and rabbits. Oral doses of 10, 25 and 75 mg/kg/day abametapir were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 17) to pregnant rats. In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (lower fetal body weights and delayed ossification) was noted at 75 mg/kg/day. No treatment related effects on malformations were noted at 75 mg/kg/day (50 times the MRHD based on Cmax comparisons).
Oral doses of 4, 16 and 40 mg/kg/day abametapir were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 19) to pregnant rabbits. No treatment related effects on embryofetal toxicity or malformations were noted at 40 mg/kg/day (~1 time the MRHD based on Cmax comparisons). Maternal toxicity related to the vehicle limited the maximum dose in pregnant rabbits.
In a perinatal and postnatal development study in rats, oral doses of 10, 25 and 75 mg/kg/day were administered from the beginning of organogenesis (gestational day 6) through the end of lactation (lactation day 20). In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal lethality, and decreased fetal body weight gain were noted at 75 mg/kg/day. No treatment related effects on postnatal development were noted at 75 mg/kg/day (47 times the MRHD based on Cmax comparisons).
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Risk Summary
No data are available regarding the presence of abametapir in human milk or the effects of abametapir on the breastfed infant or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for XEGLYZE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from XEGLYZE or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of XEGLYZE have been established in pediatric patients 6 months of age and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of XEGLYZE have not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months. XEGLYZE is not recommended in pediatric patients under 6 months of age because of the potential for increased systemic absorption due to a high ratio of skin surface to body mass and the potential for an immature skin barrier.
XEGLYZE contains benzyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse reactions and death in neonates and low birth-weight infants. The “gasping syndrome” (characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, gasping respirations, and high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites found in the blood and urine) has been associated with intravenously administered benzyl alcohol dosages >99 mg/kg/day in neonates and low birthweight infants. Additional symptoms may include gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse.
The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. Premature and low-birthweight infants, as well as patients receiving high dosages, may be more likely to develop toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Because of the risk of accidental ingestion, XEGLYZE should be administered to pediatric patients only under direct adult supervision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of XEGLYZE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger subjects.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
The active pharmacological ingredient in XEGLYZE (abametapir) Lotion is the pediculicide, abametapir, which is a dipyridyl compound. The chemical name of abametapir is 5,5'-dimethyl-2,2'-bipyridinyl.
The structural formula is:
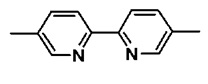
The empirical formula is C12H12N2 and the molecular weight is 184.24.
XEGLYZE is a white to off-white oil in water emulsion, containing 0.74% [weight by weight] of abametapir, intended for topical administration. XEGLYZE contains the following inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol 2.0% , butylated hydroxytoluene, Carbomer Homopolymer Type C, light mineral oil, polysorbate 20, trolamine and water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Abametapir (5,5’-dimethyl 2,2’-bipyridinyl) is a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Metalloproteinases have a role in physiological processes critical to egg development and survival of lice.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of XEGLYZE were evaluated in 3 trials, Trials A, B, and C. Each trial enrolled lice infested subjects who received a single 10-minute application of XEGLYZE. Pharmacokinetic samplings were carried out to 72 hours post-dose in adults and 8 hours post-dose in pediatric subjects in all trials.
Trial A evaluated pharmacokinetics in 6 adult and 12 pediatric subjects 3 to 12 years of age. The mean (%CV) abametapir plasma maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration time curve from 0 to 8 hours post-dose (AUC0-8h) in the adult group were 41 (66%) ng/mL and 121 (50%) ng*h/mL, respectively. The mean (%CV) Cmax and AUC0-8h in the pediatric group were 73 (57%) ng/mL and 264 (62%) ng*h/mL, respectively. The mean (%CV) terminal half-life in adults was 21 (11%) hours.
Trials B and C evaluated pharmacokinetics in 50 pediatric subjects 6 months to 17 years old. The pharmacokinetic results for plasma abametapir are shown in Table 3. Even though the values varied between the 2 trials, abametapir exposure increased as the age of the subject decreased. Abametapir absorption was rapid with a median Tmax of 0.57 to 1.54 hours.
Table 3 Abametapir Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Subjects with Head Lice Infestation
Study Age Group n Cmax (ng/mL)
Mean
(%CV)AUC0-8h
(ng*h/mL)
Mean (%CV)B 6 months to <1 year 1 418 1057 C 5 228 (50%) 688 (43%) B 1 year to <2 years 3 209 (62%) 446 (65%) C 8 147 (49%) 406 (37%) B 2 years to <3 years 6 206 (66%) 633 (57%) C 8 160 (48%) 602 (51%) B 3 years to 17 years 12 121 (60%) 330 (49%) C 7 52 (45%) 194 (39%) Serum concentration of benzyl alcohol, an excipient in the formulation of XEGLYZE, was assessed in Trials B and C. Benzyl alcohol in serum was measurable (limit of quantitation = 0.5 µg/mL) in 7 subjects out of 39 evaluable subjects. The Cmax of benzyl alcohol in these 7 subjects ranged from 0.52 to 3.57 µg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Distribution
Abametapir and its primary human metabolite, abametapir carboxyl, are highly bound to proteins in plasma. Abametapir is 91.3 – 92.3% bound to plasma proteins, and abametapir carboxyl is 96.0% – 97.5% bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
Metabolism
Abametapir is extensively metabolized, primarily by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1A2 to a mono-hydroxylated metabolite (abametapir hydroxyl) and further to a mono-carboxylated metabolite (abametapir carboxyl). Abametapir carboxyl is cleared slowly from the systemic circulation resulting in plasma concentration higher than that of abametapir. Based on data in adults in Trial A above, where sampling was carried out to 72 hours, the ratios of Cmax and AUC0-72h between abametapir carboxyl and abametapir were about 30 and 250, respectively. The elimination half-life of abametapir carboxyl has not been well characterized but is estimated to be approximately (mean ± SD) 71 ± 40 hours or longer in adults.
Excretion
Excretion of abametapir and its human metabolites was not examined in patients.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies suggest that there is a potential for inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4, 2B6, and 1A2 enzymes following application of XEGLYZE due to high and prolonged systemic exposure of the metabolite abametapir carboxyl [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of XEGLYZE or abametapir.
Abametapir was not mutagenic or clastogenic based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames test and human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (rat micronucleus assay).
No effects on fertility have been observed in rats following repeated oral doses of up to 75 mg/kg/dayabametapir (50 times the MRHD based on Cmax comparisons).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two identical multi-center, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (Trials 1 and 2) were conducted in 704 subjects 6 months of age and older with head lice infestation. All subjects received a single application of either XEGLYZE or vehicle control. For the evaluation of efficacy, the youngest subject from each household was considered to be the index subject of the household (N=216). Other enrolled infested household members received the same treatment as the youngest subject and were evaluated for all efficacy and safety parameters. Index subjects ranged from 6 months to 49 years of age (mean 7 years), and approximately 85% of the index subjects were female, and 95% of the index subjects were Caucasian.
Efficacy was assessed as the proportion of index subjects who were treated with a single 10-minute application and were free of live lice at all follow-up visits on Days 1, 7, and 14. Subjects with live lice at any time up to the final evaluation were considered treatment failures. Table 4 presents the proportion of subjects who were free of live lice at all visits Day 1 through Day 14 in Trials 1 and 2.
Table 4: Proportion of Index Subjects Free of Live Lice at All Visits Days 1 Through 14 After Treatment
Trial 1 Trial 2 XEGLYZE (N=53) Vehicle (N=55) XEGLYZE (N=55) Vehicle (N=53) Treatment Success 43 (81.1%) 28 (50.9%) 45 (81.8%) 25 (47.2%) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
XEGLYZE is a white to off-white oil in water emulsion containing 0.74% [weight by weight] abametapir and supplied in a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) safety-coated single-use round amber glass bottle affixed with a polypropylene child resistant cap (NDC # 43598-921-11) featuring a tri-foil inner liner. The container is filled to a nominal 200 g (approximately 7 oz. or 210 mL) of the lotion.
Store upright at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Inform the patient and caregiver of the following instructions:
- Do not ingest XEGLYZE.
- Keep out of reach of children. Use on children should be under the direct supervision of an adult because of the risk of benzyl alcohol toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Avoid contact with eyes.
- Wash hands after application.
- Hair may be shampooed any time after the treatment.
- Treatment with XEGLYZE involves a single application. Do not re-treat.
- Discard any unused portion. Do not flush contents down sink or toilet.
Manufactured by Groupe Parima Inc., for Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, S.A. Elisabethenanlage 11, 4051 Basel, Switzerland
Distributed by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Inc., 107 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540
XeglyzeTM is a registered trademark of Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, S.A.
Issued: 01 / 2022
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
XEGLYZE (zeg’ lyze)
(abametapir)
Lotion
Important: XEGLYZE is for use on scalp hair and scalp only. Do not use XEGLYZE in your mouth, eyes, or vagina.
What is XEGLYZE?
XEGLYZE is a prescription medicine used to get rid of head lice in people 6 months of age and older. After XEGLYZE is rinsed off, a fine-tooth comb may be used to remove dead lice and nits from the hair and scalp. All personal items exposed to the hair or lice should be washed in hot water or dry-cleaned. See “How do I stop the spread of lice?” at the end of the XEGLYZE Instructions for Use.It is not known if XEGLYZE is safe and effective in children under 6 months of age.
Before you use XEGLYZE, tell your healthcare provider if you or your child: - have any skin conditions or sensitivities
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if XEGLYZE can harm your unborn baby
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if XEGLYZE passes into your breast milk.
How should I use XEGLYZE?
See the “Instructions for Use” for detailed information about the right way to apply XEGLYZE.- Use XEGLYZE exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the treatment that is right for you. Do not change your treatment without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Use XEGLYZE on dry hair.
- Completely cover all of your hair and scalp with XEGLYZE.
- Children will need an adult to apply XEGLYZE for them.
- Do not swallow XEGLYZE. If swallowed, call your Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
- Do not get XEGLYZE into your eyes. If XEGLYZE gets in your eye, gently flush with water. Wash your hands after you apply XEGLYZE.
- You may shampoo your hair any time after the treatment.
- When you complete your dose of XEGLYZE, do not use XEGLYZE again. Throw away any unused XEGLYZE. Do not flush XEGLYZE down sink or toilet.
What are the possible side effects of XEGLYZE?
The most common side effects of XEGLYZE include:- Redness of the skin or scalp
- Rash
- Burning sensation of the skin
- Skin irritation
- Vomiting
- Eye irritation
- Itchy scalp
- Changes in your hair color
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of XEGLYZE. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store XEGLYZE?
- Store upright at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Do not refrigerate or freeze XEGLYZE.
- Discard (throw away) any unused product.
General information about the safe and effective use of XEGLYZE
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use XEGLYZE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give XEGLYZE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can also ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about XEGLYZE that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in XEGLYZE?
Active ingredient: abametapir
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol 2.0%, butylated hydroxytoluene, carbomer homopolymer type C, light mineral oil, polysorbate 20, trolamine and water.Manufactured by Groupe Parima, Inc., for Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, S.A. Elisabethenanlage 11,
4051 Basel, Switzerland
XEGLYZE is a registered trademark of Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, S.A.Distributed by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Inc.,
107 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540.This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Issued: 01/2022
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Instructions for Use
XEGLYZE (zeg' lyze)
(abametapir)
Lotion
Important: XEGLYZE is for use on scalp hair and scalp only. Do not use XEGLYZE in your mouth, eyes, or vagina.
Before you use XEGLYZE, it is important that you read the Patient Information and Instructions for Use. Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use so that you use XEGLYZE the right way. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have questions about the right way to use XEGLYZE.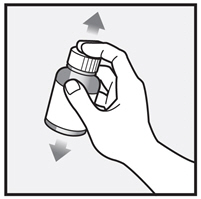
Step 1: Your hair and scalp must be dry before you apply XEGLYZE. Shake XEGLYZE bottle well right before use.
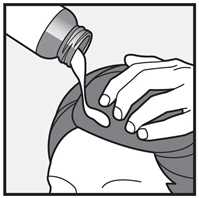
Step 2: Remove the cap and apply XEGLYZE directly to dry hair and scalp.

Step 3: Completely cover your scalp and hair closest to the scalp first, and then apply outwards towards the ends of your hair.
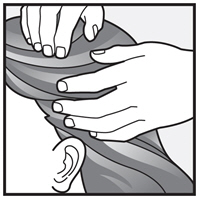
Step 4: Rub XEGLYZE throughout your hair and scalp.
Use enough XEGLYZE to completely cover your entire scalp and all of your hair so that all lice and eggs are exposed to the lotion. You may need to use the full bottle. Be sure that each hair is coated from the scalp to the tip.
Step 5: Leave XEGLYZE on your hair and scalp for 10 minutes after it has been applied. Use a timer or clock. Start timing after you have completely covered your hair and scalp with XEGLYZE.
You or anyone who helps you apply XEGLYZE should wash their hands after application.
Step 6: After 10 minutes, rinse XEGLYZE from your hair and scalp with warm water.
A fine-tooth comb or special nit comb may be used to remove dead lice and nits.
You may shampoo your hair any time after the treatment.How do I stop the spread of lice?
To help prevent the spread of lice from one person to another, here are some steps you can take:
- Avoid direct head-to-head contact with anyone known to have live, crawling lice.
- Do not share combs, brushes, hats, scarves, bandannas, ribbons, barrettes, hair bands, towels, helmets, or other hair-related personal items with anyone else, whether they have lice or not.
- Disinfect combs and brushes used by an infected person by soaking them in hot water (at least 130°F) for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Avoid sleepovers and slumber parties during lice outbreaks. Lice can live in bedding, pillows, and carpets that have recently been used by someone with lice.
- Machine wash and dry clothing, bed linens, and other items used by anyone having lice. Machine wash at high temperatures (130°F) and the high heat drying cycle. Clothing and items that are not washable can be dry-cleaned OR sealed in a plastic bag and stored for 2 weeks.
These Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 01/2022
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
CONTAINER LABEL
NDC: 43598-921-11
Xeglyze (abametapir) Lotion, 0.74%
For topical use on the scalp hair and scalp only.
Rx only
200 g

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
CARTON LABEL
NDC: 43598-921-11
Xeglyze (abametapir) Lotion, 0.74%
For topical use on the scalp hair and scalp only.
Rx only
200 g

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
XEGLYZE
abametapir lotionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 43598-921 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Abametapir (UNII: 6UO390AMFB) (Abametapir - UNII:6UO390AMFB) Abametapir 0.74 g in 100 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Polysorbate 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) CARBOMER HOMOPOLYMER TYPE C (UNII: 4Q93RCW27E) Trolamine (UNII: 9O3K93S3TK) Butylated Hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) Benzyl Alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) Light Mineral Oil (UNII: N6K5787QVP) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 43598-921-11 1 in 1 CARTON 01/29/2021 1 200 g in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA206966 01/29/2021 Labeler - Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc. (802315887) Registrant - DR. REDDY'S LABORATORIES SA (483739079) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Groupe Parima Inc. 252437850 pack(43598-921) , manufacture(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Neopharm Labs Inc 243379372 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Particle Technology Labs 808076947 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations R.D. Laboratories, Inc. 603223066 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations LAURUS LABS LIMITED 915075687 api manufacture(43598-921) , analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 650443430 api manufacture(43598-921) , analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations SGS North America Inc. 808308303 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations KABS Laboratories 253940472 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations SGS India Private Limited 650786127 analysis(43598-921) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vimta Labs Limited 675597260 analysis(43598-921)
Trademark Results [Xeglyze]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 XEGLYZE 90812737 not registered Live/Pending |
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories SA 2021-07-06 |
 XEGLYZE 87514849 not registered Live/Pending |
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, S. A. 2017-07-03 |
 XEGLYZE 86164493 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
DR. REDDY'S LABORATORIES, S.A 2014-01-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.