INJECTAFER- ferric carboxymaltose injection injection, solution
Injectafer by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Injectafer by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by American Regent, Inc., Vifor (International) AG. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Injectafer safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Injectafer.
INJECTAFER® (ferric carboxymaltose injection) for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2013RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Symptomatic Hypophosphatemia. (5.2) 02/2020
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Injectafer is an iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients:
- who have intolerance to oral iron or have had unsatisfactory response to oral iron, or
- who have non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For patients weighing 50 kg (110 lb) or more: Give Injectafer in two doses separated by at least 7 days. Give each dose as 750 mg for a total cumulative dose of 1500 mg of iron per course.
For patients weighing less than 50 kg (110 lb): Give Injectafer in two doses separated by at least 7 days and give each dose as 15 mg/kg body weight.
Injectafer treatment may be repeated if iron deficiency anemia reoccurs. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 750 mg iron/15 mL single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to Injectafer or any of its inactive components. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Observe for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Injectafer administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of each administration. (5.1)
-
Symptomatic Hypophosphatemia: Monitor serum phosphate levels in patients at risk for low serum phosphate who require a repeat course of treatment. (5.2)
- Hypertension: Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of hypertension following each Injectafer administration. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) are nausea, hypertension, flushing, hypophosphatemia, and dizziness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact American Regent at 1-800-734-9236 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Monitor breastfed infants for gastrointestinal toxicity. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Preparation and Administration
2.3 Repeat Treatment Monitoring Safety Assessment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Symptomatic Hypophosphatemia
5.3 Hypertension
5.4 Laboratory Test Alterations
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Trial 1: Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients Who Are Intolerant to Oral Iron or Have Had Unsatisfactory Response to Oral Iron
14.2 Trial 2: Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Recommended dosage for patients weighing 50 kg (110 lb) or more: Give Injectafer in two doses separated by at least 7 days. Give each dose as 750 mg for a total cumulative dose not to exceed 1500 mg of iron per course.
Recommended dosage for patients weighing less than 50 kg (110 lb): Give Injectafer in two doses separated by at least 7 days. Give each dose as 15 mg/kg body weight for a total cumulative dose not to exceed 1500 mg of iron per course.
Each mL of Injectafer contains 50 mg of elemental iron.
2.2 Preparation and Administration
Administer Injectafer intravenously, either as an undiluted slow intravenous push or by infusion. When administered via infusion, dilute up to 750 mg of iron in no more than 250 mL of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, such that the concentration of the infusion is not less than 2 mg of iron per mL and administer over at least 15 minutes.
When added to an infusion bag containing 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, at concentrations ranging from 2 mg to 4 mg of iron per mL, Injectafer solution is physically and chemically stable for 72 hours when stored at room temperature. To maintain stability, do not dilute to concentrations less than 2 mg iron/mL.
Inspect parenteral drug products visually for the absence of particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The product contains no preservatives. Each vial of Injectafer is intended for single-dose only.
When administering as a slow intravenous push, give at the rate of approximately 100 mg (2 mL) per minute. Avoid extravasation of Injectafer since brown discoloration of the extravasation site may be long lasting. Monitor for extravasation. If extravasation occurs, discontinue the Injectafer administration at that site.
Discard unused portion.
2.3 Repeat Treatment Monitoring Safety Assessment
Injectafer treatment may be repeated if iron deficiency anemia reoccurs. Monitor serum phosphate levels in patients at risk for low serum phosphate who require a repeat course of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Injectafer is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Injectafer or any of its components [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving Injectafer. Patients may present with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Injectafer administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of the infusion. Only administer Injectafer when personnel and therapies are immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. In clinical trials, serious anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions were reported in 0.1% (2/1775) of subjects receiving Injectafer. Other serious or severe adverse reactions potentially associated with hypersensitivity which included, but not limited to, pruritus, rash, urticaria, wheezing, or hypotension were reported in 1.5% (26/1775) of these subjects.
5.2 Symptomatic Hypophosphatemia
Symptomatic hypophosphatemia requiring clinical intervention has been reported in patients at risk of low serum phosphate in the postmarketing setting. These cases have occurred mostly after repeated exposure to Injectafer in patients with no reported history of renal impairment. Possible risk factors for hypophosphatemia include a history of gastrointestinal disorders associated with malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins or phosphate, concurrent or prior use of medications that affect proximal renal tubular function, hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency and malnutrition. In most cases, hypophosphatemia resolved within three months.
Monitor serum phosphate levels in patients at risk for low serum phosphate who require a repeat course of treatment. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Hypertension
In clinical studies, hypertension was reported in 3.8% (67/1,775) of subjects in clinical trials 1 and 2. Transient elevations in systolic blood pressure, sometimes occurring with facial flushing, dizziness, or nausea were observed in 6% (106/1,775) of subjects in these two clinical trials. These elevations generally occurred immediately after dosing and resolved within 30 minutes. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypertension following each Injectafer administration [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Laboratory Test Alterations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In two randomized clinical studies [Studies 1 and 2, see Clinical Studies (14)], a total of 1,775 patients were exposed to Injectafer 15 mg/kg body weight up to a maximum single dose of 750 mg of iron on two occasions separated by at least 7 days up to a cumulative dose of 1500 mg of iron.
Adverse reactions reported by ≥1% of treated patients are shown in the following table.
Table 1. Adverse reactions reported in ≥1% of Study Patients in Clinical Trials 1 and 2
- * Includes oral iron and all formulations of IV iron other than Injectafer
Term
Injectafer
(N=1775)
%Pooled Comparators*
(N=1783)
%Oral
iron
(N=253)
%Nausea
7.2
1.8
1.2
Hypertension
3.8
1.9
0.4
Flushing/Hot Flush
3.6
0.2
0.0
Blood Phosphorus Decrease
2.1
0.1
0.0
Dizziness
2.0
1.2
0.0
Vomiting
1.7
0.5
0.4
Injection Site Discoloration
1.4
0.3
0.0
Headache
1.2
0.9
0.0
Alanine Aminotransferase Increase
1.1
0.2
0.0
Dysgeusia
1.1
2.1
0.0
Hypotension
1.0
1.9
0.0
Constipation
0.5
0.9
3.2
Other adverse reactions reported by ≥0.5% of treated patients include abdominal pain, diarrhea, gamma glutamyl transferase increased, injection site pain/irritation, rash, paraesthesia, sneezing. Transient decreases in laboratory blood phosphorus levels (< 2 mg/dL) have been observed in 27% (440/1638) of patients in clinical trials.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Injectafer. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been reported from the post-marketing spontaneous reports with Injectafer: urticaria, dyspnea, pruritus, tachycardia, erythema, pyrexia, chest discomfort, chills, angioedema, back pain, arthralgia, and syncope. One case of hypophosphatemic osteomalacia was reported in a subject who received 500 mg of Injectafer every 2 weeks for a total of 16 weeks. Partial recovery followed discontinuation of Injectafer.
- Cardiac disorders: Tachycardia
- General disorders and administration site conditions: Chest discomfort, chills, pyrexia
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hypophosphatemia
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Arthralgia, back pain, hypophosphatemic osteomalacia (rarely reported event)
- Nervous system disorders: Syncope
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnea
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Angioedema, erythema, pruritus, urticaria
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published studies on the use of ferric carboxymaltose in pregnant women have not reported an association with ferric carboxymaltose and adverse developmental outcomes. However, these studies cannot establish or exclude the absence of any drug-related risk during pregnancy because the studies were not designed to assess for the risk of major birth defects (see Data). There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, administration of ferric carboxymaltose to rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including fetal malformations and increased implantation loss at maternally toxic doses of approximately 12% to 23% of the human weekly dose of 750 mg (based on body surface area).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. Adverse outcomes in pregnancy occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically-recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Untreated iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal outcomes such as post-partum anemia. Adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with iron deficiency anemia include increased risk for preterm delivery and low birth weight.Data
Human DataPublished data from randomized controlled studies, prospective observational studies and retrospective studies on the use of ferric carboxymaltose in pregnant women have not reported an association with ferric carboxymaltose and adverse developmental outcomes. However, these studies cannot establish or exclude the absence of any drug-related risk during pregnancy because of methodological limitations, including that the studies were not primarily designed to capture safety data nor designed to assess the risk of major birth defects. Maternal adverse events reported in these studies are similar to those reported during clinical trials in adult males and non-pregnant females [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Animal Data
Administration of ferric carboxymaltose to rats as an one-hour intravenous infusion up to 30 mg/kg/day iron on gestation days 6 to 17 did not result in adverse embryonic or fetal findings. This daily dose in rats is approximately 40% of the human weekly dose of 750 mg based on body surface area. In rabbits, ferric carboxymaltose was administered as a one-hour infusion on gestation days 6 to 19 at iron doses of 4.5, 9, 13.5, and 18 mg/kg/day. Malformations were seen starting at the daily dose of 9 mg/kg (23% of the human weekly dose of 750 mg). Spontaneous abortions occurred starting at the daily iron dose of 4.5 mg/kg (12% of the human weekly dose based on body surface area). Pre-implantation loss was at the highest dose. Adverse embryonic or fetal effects were observed in the presence of maternal toxicity.
A pre- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats at intravenous doses up to 18 mg/kg/day of iron (approximately 23% of the weekly human dose of 750 mg on a body surface area basis). There were no adverse effects on survival of offspring, their behavior, sexual maturation or reproductive parameters.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The available published data on the use of ferric carboxymaltose in lactating women demonstrate that iron is present in breast milk. However, the data do not inform the full potential exposure of iron for the breastfed infant. Among the breastfed infants, there were no adverse events reported that were considered related to ferric carboxymaltose exposure through breastmilk. There is no information on the effects of ferric carboxymaltose on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Injectafer in addition to any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from the drug or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Monitor breastfed infants for gastrointestinal toxicity (constipation, diarrhea).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1775 subjects in clinical studies of Injectafer, 50% were 65 years and over, while 25% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Excessive dosages of Injectafer may lead to accumulation of iron in storage sites potentially leading to hemosiderosis. A patient who received Injectafer 18,000 mg over 6 months developed hemosiderosis with multiple joint disorder, walking disability, and asthenia. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia was reported in a patient who received Injectafer 4000 mg over 4 months. Partial recovery followed discontinuation of Injectafer.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Ferric carboxymaltose, an iron replacement product, is an iron carbohydrate complex with the chemical name of polynuclear iron (III) hydroxide 4(R)-(poly-(1→4)-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-oxy-2(R),3(S),5(R),6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoate. It has a relative molecular weight of approximately 150,000 Da corresponding to the following empirical formula:
[FeOx(OH)y(H2O)z]n [{(C6H10O5)m (C6H12O7)}l]k,
where n ≈ 103, m ≈ 8, l ≈ 11, and k ≈ 4
(l represents the mean branching degree of the ligand).The chemical structure is presented below:
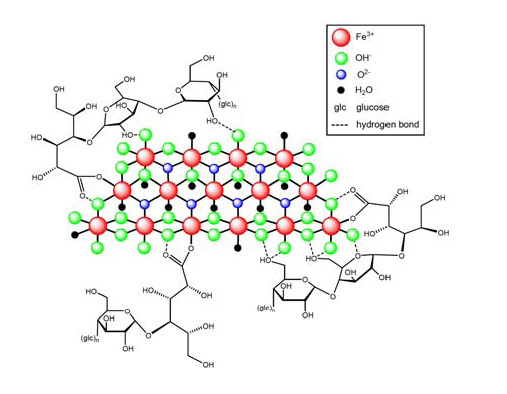
Injectafer (ferric carboxymaltose injection) is a dark brown, sterile, aqueous, isotonic colloidal solution for intravenous injection. Each mL contains 50 mg iron as ferric carboxymaltose in water for injection. Injectafer is available in 15 mL single-dose vials. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may have been added to adjust the pH to 5.0-7.0.
Vial closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ferric carboxymaltose is a colloidal iron (III) hydroxide in complex with carboxymaltose, a carbohydrate polymer that releases iron.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Using positron emission tomography (PET) it was demonstrated that red cell uptake of 59Fe and 52Fe from Injectafer ranged from 61% to 99%. In patients with iron deficiency, red cell uptake of radio-labeled iron ranged from 91% to 99% at 24 days after Injectafer dose. In patients with renal anemia, red cell uptake of radio-labeled iron ranged from 61% to 84% at 24 days after Injectafer dose.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After administration of a single dose of Injectafer of 100 to 1000 mg of iron in iron deficient patients, maximum iron concentration of 37 µg/mL to 333 µg/mL were obtained respectively after 15 minutes to 1.21 hours post dose. The volume of distribution was estimated to be 3 L.
The iron injected or infused was rapidly cleared from the plasma, the terminal half-life ranged from 7 to 12 hours. Renal elimination of iron was negligible.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with ferric carboxymaltose.
Ferric carboxymaltose was not genotoxic in the following genetic toxicology studies: in vitro microbial mutagenesis (Ames) assay, in vitro chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, in vitro mammalian cell mutation assay in mouse lymphoma L5178Y/TK+/- cells, in vivo mouse micronucleus test at single intravenous doses up to 500 mg/kg.
In a combined male and female fertility study, ferric carboxymaltose was administered intravenously over one hour to male and female rats at iron doses of up to 30 mg/kg. Animals were dosed 3 times per week (on Days 0, 3, and 7). There was no effect on mating function, fertility or early embryonic development. The dose of 30 mg/kg in animals is approximately 40% of the human dose of 750 mg based on body surface area.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Trial 1: Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients Who Are Intolerant to Oral Iron or Have Had Unsatisfactory Response to Oral Iron
The safety and efficacy of Injectafer for treatment of iron deficiency anemia were evaluated in two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2). In these two trials, Injectafer was administered at a dose of 15 mg/kg body weight up to a maximum single dose of 750 mg of iron on two occasions separated by at least 7 days up to a cumulative dose of 1500 mg of iron.
Trial 1: A Multi-center, Randomized, Active Controlled Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Ferric Carboxymaltose (FCM) in Patients with Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA), (NCT00982007) was a randomized, open-label, controlled clinical study in patients with iron deficiency anemia who had an unsatisfactory response to oral iron (Cohort 1) or who were intolerant to oral iron (Cohort 2) during the 14-day oral iron run-in period. Inclusion criteria prior to randomization included hemoglobin (Hb) <12 g/dL, ferritin ≤100 ng/mL or ferritin ≤300 ng/mL when transferrin saturation (TSAT) ≤30%. Cohort 1 subjects were randomized to Injectafer or oral iron for 14 more days. Cohort 2 subjects were randomized to Injectafer or another IV iron per standard of care [90% of subjects received iron sucrose]. The mean age of study patients was 43 years (range, 18 to 94); 94% were female; 42% were Caucasian, 32% were African American, 24% were Hispanic, and 2% were other races. The primary etiologies of iron deficiency anemia were heavy uterine bleeding (47%) and gastrointestinal disorders (17%).
Table 2 shows the baseline and the change in hemoglobin from baseline to highest value between baseline and Day 35 or time of intervention.
Table 2. Mean Change in Hemoglobin From Baseline to the Highest Value Between Day 35 or Time of Intervention (Modified Intent‑to‑Treat Population)
Hemoglobin (g/dL)
Mean (SD)
Cohort 1
Cohort 2
Injectafer
(N=244)Oral Iron
(N=251)Injectafer
(N=245)IV SCa
(N=237)Baseline
10.6 (1.0)
10.6 (1.0)
9.1 (1.6)
9.0 (1.5)
Highest Value
12.2 (1.1)
11.4 (1.2)
12.0 (1.2)
11.2 (1.3)
Change (from baseline to highest value)
1.6 (1.2)
0.8 (0.8)
2.9 (1.6)
2.2 (1.3)
p-value
0.001
0.001
SD=standard deviation; a: Intravenous iron per standard of care
Increases from baseline in mean ferritin (264.2 ± 224.2 ng/mL in Cohort 1 and 218.2 ± 211.4 ng/mL in Cohort 2), and transferrin saturation (13 ± 16% in Cohort 1 and 20 ± 15% in Cohort 2) were observed at Day 35 in Injectafer-treated patients.
14.2 Trial 2: Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease
Trial 2: REPAIR-IDA, Randomized Evaluation of efficacy and safety of Ferric carboxymaltose in Patients with iron deficiency Anemia and Impaired Renal function, (NCT00981045) was a randomized, open-label, controlled clinical study in patients with non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. Inclusion criteria included hemoglobin (Hb) ≤11.5 g/dL, ferritin ≤ 100 ng/mL or ferritin ≤300 ng/mL when transferrin saturation (TSAT) ≤ 30%. Study patients were randomized to either Injectafer or Venofer. The mean age of study patients was 67 years (range, 19 to 101); 64% were female; 54% were Caucasian, 26% were African American, 18% Hispanics, and 2% were other races.
Table 3 shows the baseline and the change in hemoglobin from baseline to highest value between baseline and Day 56 or time of intervention.
Table 3. Mean Change in Hemoglobin From Baseline to the Highest Value Between Baseline and Day 56 or Time of Intervention (Modified Intent‑to‑Treat Population)
Hemoglobin (g/dL)
Mean (SD)Injectafer
(N=1249)Venofer
(N=1244)Baseline
10.3 (0.8)
10.3 (0.8)
Highest Value
11.4 (1.2)
11.3 (1.1)
Change (from baseline to highest value)
1.1 (1.0)
0.9 (0.92)
Treatment Difference (95% CI)
0.21 (0.13, 0.28)
Increases from baseline in mean ferritin (734.7 ± 337.8 ng/mL), and transferrin saturation (30 ± 17%) were observed prior to Day 56 in Injectafer-treated patients.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
NDC: 0517-0650-01 750 mg iron/15 mL Single-Dose Vial Individually boxed
NDC: 0517-0650-02 750 mg iron/15 mL Single-Dose Vial Packages of 2Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). [See the USP controlled room temperature]. Do not freeze.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Prior History of Reactions to Parenteral Iron Products
Question patients regarding any prior history of reactions to parenteral iron products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to report any signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity that may develop during and following Injectafer administration, such as rash, itching, dizziness, lightheadedness, swelling and breathing problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Injectafer is manufactured under license from Vifor (International) Inc, Switzerland.
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967RQ1052-A
-
Patient Information
INJECTAFER (in-jekt-a-fer)
(ferric carboxymaltose injection)
What is INJECTAFER?
INJECTAFER is a prescription iron replacement medicine used to treat iron deficiency anemia in adults who have:-
intolerance to oral iron or who have not responded well to treatment with oral iron, or
-
non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease
It is not known if INJECTAFER is safe and effective for use in children.
Who should not receive INJECTAFER?
Do not receive INJECTAFER if you are allergic to ferric carboxymaltose or any of the ingredients in INJECTAFER. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in INJECTAFER.
Before receiving INJECTAFER, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
-
have had an allergic reaction to iron given into your vein
-
have high blood pressure
-
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if INJECTAFER will harm your unborn baby.
-
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. INJECTAFER passes into your breast milk. It is unknown whether INJECTAFER would pose a risk to your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with INJECTAFER.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How will I receive INJECTAFER?
INJECTAFER is given intravenously (into your vein) by your healthcare provider in 2 doses at least 7 days apart.
What are the possible side effects of INJECTAFER?
INJECTAFER may cause serious side effects, including:-
Allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions. Serious life-threatening allergic reactions have happened in people who receive INJECTAFER. Other serious reactions including itching, hives, wheezing, and low blood pressure also have happened during treatment with INJECTAFER. Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to any iron given by vein.
-
High blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure, sometimes with face flushing, dizziness, or nausea, has happened during treatment with INJECTAFER. Your healthcare provider will check your blood pressure and check for any signs and symptoms of high blood pressure after you receive INJECTAFER.
The most common side effects of INJECTAFER include:
- nausea
- high blood pressure
- flushing
- low levels of phosphorous in your blood
- dizziness
These are not all the possible side effects of INJECTAFER.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about INJECTAFER
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about INJECTAFER that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in INJECTAFER?
Active ingredient: ferric carboxymaltoseInactive ingredients: water for injection. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may have been added to adjust pH to 5.0-7.0.
For more information go to www.injectafer.com or call 1-800-734-9236.
This Patient information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967
Revised: 02/2020
-
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 ML CONTAINER
NDC: 0517-0650-01
Injectafer®
(ferric carboxymaltose injection)
750 mg/15 mL
(50 mg/mL)
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
Single Dose Vial. Discard Unused Portion.
Rx Only
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 ML CARTON (Single Pack)
NDC: 0517-0650-01
Injectafer®
(ferric carboxymaltose injection)
750 mg/15 mL
(50 mg/mL)
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
Single Dose Vial.
Discard Unused Portion.
Rx Only
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 ML CARTON (2-pack)
NDC: 0517-0650-02
Injectafer®
(ferric carboxymaltose injection)
750 mg/15 mL
(50 mg/mL)
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
Two 15-mL Single Dose Vials.
Discard Unused Portion.
Rx Only
AMERICAN
REGENT, INC.
SHIRLEY, NY 11967
- Serialization Label - 1 pack
- Serialization Label - 2 pack
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
INJECTAFER
ferric carboxymaltose injection injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0517-0650 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE (UNII: 6897GXD6OE) (FERRIC CATION - UNII:91O4LML611) FERRIC CATION 50 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0517-0650-01 1 in 1 BOX 08/12/2013 1 15 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0517-0650-02 2 in 1 BOX 10/01/2017 2 15 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA203565 08/12/2013 Labeler - American Regent, Inc. (002033710) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations American Regent, Inc. 116981917 ANALYSIS(0517-0650) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations American Regent, Inc. 606821721 MANUFACTURE(0517-0650) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vifor (International) Inc. 482603065 API MANUFACTURE(0517-0650)
Trademark Results [Injectafer]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 INJECTAFER 87023433 5154434 Live/Registered |
Vifor (International) AG (Vifor (International) Ltd.) (Vifor (International) Inc.) 2016-05-03 |
 INJECTAFER 79073036 3811137 Dead/Cancelled |
Vifor (International) AG (Vifor (International) Ltd.) (Vifor (International) Inc.) 2009-08-28 |
 INJECTAFER 79068076 3728704 Live/Registered |
Vifor (International) AG; (Vifor (International) Ltd.); (Vifor (International) Inc.) 2009-04-07 |
 INJECTAFER 78743098 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Vifor (International) AG (Vifor (International) Ltd.) (Vifor (International) Inc.) 2005-10-29 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

