Imiquimod by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. / Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. IMIQUIMOD cream
Imiquimod by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Imiquimod by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use IMIQUIMOD CREAM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IMIQUIMOD CREAM.
IMIQUIMOD cream, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Imiquimod cream, 3.75% is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical, visible, or palpable actinic keratoses (AK) of the face or balding scalp in immunocompetent adults. (1.1)
Imiquimod cream, 3.75% is indicated for the topical treatment of external genital and perianal warts (EGW) in immunocompetent patients 12 years of age or older. (1.2)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For topical use only; not for oral, ophthalmic, intra-anal or intravaginal use. (2.1)
- AK: Apply a thin layer once daily at bedtime to affected area (either entire face or balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period. Apply up to 0.5 grams at each application. (2.2)
- EGW: Apply a thin layer once daily at bedtime until total clearance or up to 8 weeks. Apply up to 0.25 grams at each application. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Cream: 3.75% in pump bottles or unit-dose packets. ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Local Skin Reactions:Intense local inflammatory reactions can occur (e.g., skin weeping, erosion). Dosage interruption may be required. Severe vulvar swelling may occur and lead to urinary retention; interrupt dosing or discontinue for severe vulvar swelling. (2.2, 2.3,5.1)
- Systemic Reactions:Flu-like signs and symptoms have occurred. Consider dosage interruption for systemic reactions. (5.2)
- Ultraviolet Light Exposure Risks:Avoid or minimize exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear protective clothing. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥4%) are local skin reactions (erythema, scabbing/crusting, flaking/scaling/dryness, edema, erosion/ulceration, exudate,), headache, application site pain, application site irritation, application site pruritus, fatigue, influenza-like illness, and nausea. (6.1) (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc., at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDAapproved patient labeling. (6)
(6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2025
- Imiquimod cream, 3.75% is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical, visible, or palpable actinic keratoses (AK) of the face or balding scalp in immunocompetent adults. (1.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
1.2 External Genital Warts
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
2.2 Dosage and Administration for Actinic Keratosis
2.3 Dosage and Administration for External Genital Warts
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
5.2 Systemic Reactions
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure Risks
5.4 Immune Cell Activation in Autoimmune Disease
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
14.2 External Genital Warts
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Imiquimod cream is for topical use only. Imiquimod cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, intra-anal or intravaginal use. Instruct patients on proper application technique.
Wash hands before and after applying imiquimod cream.
Prime the imiquimod cream pump bottle before first use by repeatedly depressing the actuator until the cream is dispensed. It is not necessary to repeat this priming process during treatment.
If a imiquimod cream dose is missed, apply the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
Avoid contact with the eyes, lips, nostrils, or inside the anus and vagina.
Prescribe no more than 2 boxes (56 packets) or two 7.5 g bottle pumps of imiquimod cream for the entire treatment course for AK or EGW.
Discard partially used packets and do not reuse. Discard pump bottles after completion of a full treatment course.2.2 Dosage and Administration for Actinic Keratosis
Use imiquimod cream, 3.75% for the treatment of AK. Apply a thin layer of imiquimod cream once daily before bedtime to the area with AK (either entire face or balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period. Rub in until the cream is no longer visible. Apply up to 0.5 grams (two packets or two full actuations of the pump) of imiquimod cream at each application. Leave imiquimod cream on the skin for approximately 8 hours and then remove with mild soap and water.
For local skin reactions, a dosage interruption of several days may be taken if required based on the patient's discomfort or severity of the local skin reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Do not extend either 2-week treatment cycle due to missed doses or rest periods. Assess response to treatment after resolution of local skin reactions.
A transient increase in lesion counts may be observed during treatment; however, continue dosing as prescribed. Continue treatment for the full treatment course even if all AK appear to be gone.2.3 Dosage and Administration for External Genital Warts
Use imiquimod cream, 3.75% for the treatment of EGW. Apply a thin layer of imiquimod cream once daily before bedtime to EGW until total clearance or for up to 8 weeks. To treat the wart area, use up to 0.25 grams (one packet or one full actuation of the pump) at each application. Leave imiquimod cream on the skin for approximately 8 hours and then remove with mild soap and water.
For local skin reactions, a dosage interruption of several days may be taken if required by the patient's discomfort or severity of the local skin reaction; resume treatment once the reaction subsides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Non-occlusive dressings such as cotton gauze or cotton underwear may be used in the management of skin reactions.
Inform uncircumcised patients treating warts under the foreskin to retract the foreskin and clean the area daily.
Imiquimod cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms, therefore, concurrent use is not recommended. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
Local skin reactions including skin weeping or erosion have been reported with use of imiquimod cream and can occur after a few applications [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Concomitant use of imiquimod cream and any other imiquimod products, in the same treatment area, may increase the risk for and severity of local skin reactions.
Imiquimod cream has the potential to exacerbate inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus host disease.
Severe local inflammatory reactions of the female external genitalia can lead to severe vulvar swelling and to urinary retention.
Avoid sexual (genital, anal, oral) contact while imiquimod cream is on the skin.
To reduce the risk of local skin reactions and manage local skin reactions that occur with imiquimod cream treatment:- Avoid concomitant use of imiquimod cream with any other imiquimod product in the same treatment area.
- Avoid application of imiquimod cream to skin that is not intact (i.e., any area with an abrasion, cut, burn, rash, infection, or other condition that has altered skin integrity).
- An interruption of dosing may be required for local skin reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)]. Interrupt dosing or discontinue imiquimod cream for severe vulvar swelling [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- If severe local skin reactions occur, instruct patients to remove imiquimod cream by washing the treatment area with mild soap and water.
5.2 Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms have been reported with use of imiquimod cream andmay accompany, or even precede, local skin reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Signs and symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, fever, myalgias, arthralgias, malaise and chills. Concomitant use of imiquimod cream and any other imiquimod products may increase the risk for and severity of systemic reactions.
Lymphadenopathy occurred in 2% of subjects with AK treated with imiquimod cream, 3.75% and in no patients in the vehicle arm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. This reaction resolved in all subjects by 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
Consider an interruption of dosing if systemic reactions occur.5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure Risks
Imiquimod cream may cause heightened sunburn susceptibility. Avoid or minimize exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) during use of imiquimod cream. Instruct patients to use sunscreen and wear protective clothing (e.g., a hat). Advise patients not to use imiquimod cream until fully recovered from a sunburn.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Local Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Systemic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Actinic Keratosis
The data described below reflect exposure to imiquimod cream or vehicle in 479 subjects with AK enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (Studies AK1 and AK2) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Subjects applied up to two packets of imiquimod cream, 3.75%, or vehicle once daily, to the skin of the affected area (either entire face or balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no treatment period. Selected adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.Table 1: Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects with AK and at a Greater Frequency than Vehicle in Studies AK1 and AK2
Adverse Reaction Imiquimod Cream, 3.75%
(N=160)Imiquimod Cream, 2.5%
(N=160)Vehicle
(N=159)Headache 10 (6%) 3 (2%) 5 (3%) Application site pruritus 7 (4%) 6 (4%) 1 (<1%) Fatigue 7 (4%) 2 (1%) 0 Nausea 6 (4%) 1 (1%) 2 (1%) Application site irritation 5 (3%) 4 (3%) 0 Application site pain 5 (3%) 2 (1%) 0 Pyrexia 5 (3%) 0 0 Anorexia 4 (3%) 0 0 Dizziness 4 (3%) 1 (<1%) 0 Herpes simplex 4 (3%) 0 1 (<1%) Lymphadenopathy 3 (2%) 4 (3%) 0 Diarrhea 3 (2%) 2 (1%) 0 Arthralgia 2 (1%) 4 (3%) 0 Influenza like illness 1 (<1%) 6 (4%) 0 Oral herpes 0 4 (3%) 0 Cheilitis 0 3 (2%) 0 Local skin reactions were recorded as adverse reactions if they extended beyond the treatment area, or required any medical intervention, or resulted in patient discontinuation from the trial. The incidence and severity of selected local skin reactions are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area in Imiquimod-Treated Subjects with AK as Assessed by the Investigator in Studies AK1 and Ak2
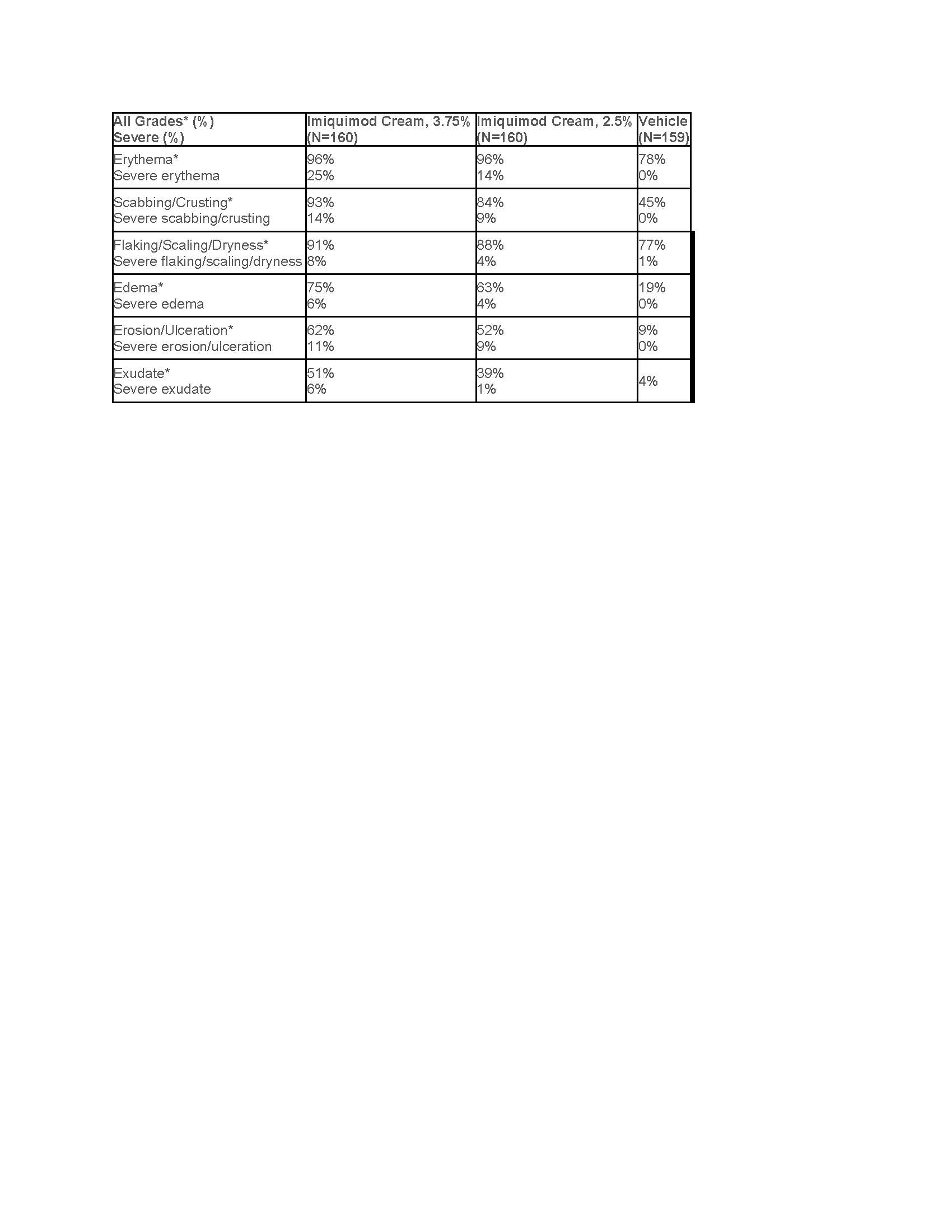
In the AK trials, 11% (17/160) of subjects in the imiquimod cream, 3.75% arm, 7% (11/160) of subjects in the imiquimod cream, 2.5% arm, and 0% in the vehicle arm required rest periods due to adverse local skin reactions.
Other adverse reactions observed in subjects treated with imiquimod cream included: application site bleeding, application site swelling, chills, dermatitis, herpes zoster, insomnia, lethargy, myalgia, pancytopenia, pruritus, squamous cell carcinoma, and
vomiting.External Genital Warts
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials 602 subjects with EGW applied up to one packet of imiquimod cream, 3.75% or vehicle to all warts once daily for up to 8 weeks (Studies EGW1 and EGW2) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were application site reactions and local skin reactions. Selected adverse reactions are listed in Table 3.Table 3: Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects with EGW and at a Greater Frequency than Vehicle in Studies EGW1 and EGW 2
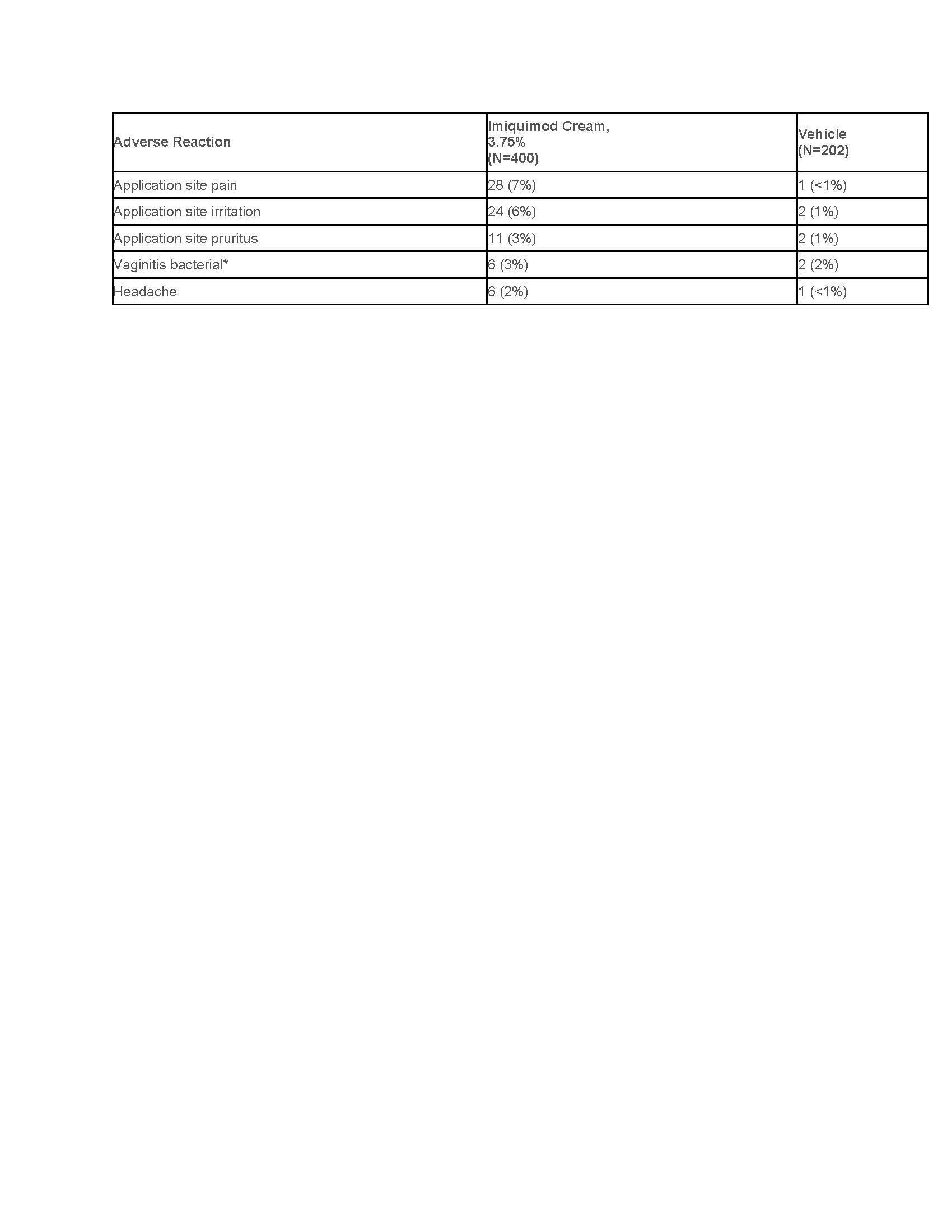
*Percentage based on female population of 6/216 for imiquimod cream, 3.75% and 2/106 for vehicle
Local skin reactions were recorded as adverse reactions if they extended beyond the treatment area, or required any medical intervention, or resulted in patient discontinuation from the trial. The incidence and severity of selected local skin reactions are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Selected Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area in Imiquimod-Treated Subjects with EGW Assessed by the Investigator in Studies EGW1 and EGW2
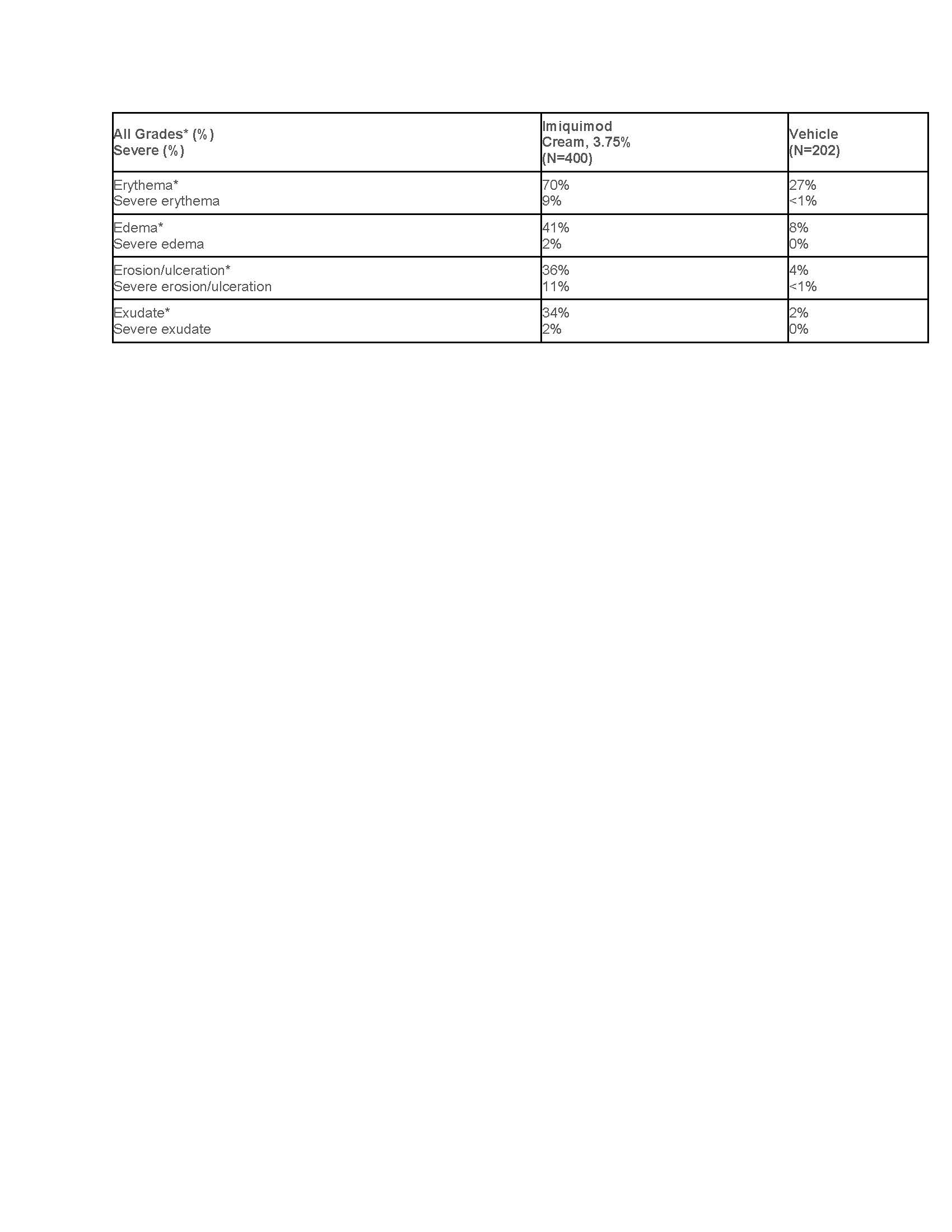
*Mild, moderate, or severe
The frequency and severity of local skin reactions were similar in both sexes, with the following exceptions: a) flaking/scaling occurred in 40% of males and in 26% of females and b) scabbing/crusting occurred in 34% of males and in 18% of females.
In Studies EGW1 and EGW2, 32% (126/400) of subjects who used imiquimod cream, 3.75% and 2% (4/202) of subjects who used vehicle discontinued treatment temporarily (required rest periods) due to adverse local skin reactions, and 1% (3/400) of subjects who used imiquimod cream, 3.75% discontinued treatment permanently due to local skin/application site reactions.
Other adverse reactions reported in subjects treated with imiquimod cream, 3.75% included: rash, back pain, application site rash, application site cellulitis, application site excoriation, application site bleeding, scrotal pain, scrotal erythema, scrotal ulcer, scrotal edema, sinusitis, nausea, pyrexia, and influenza-like symptoms.6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of imiquimod. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Application Site Disorders:tingling at the application site
Body as a Whole:angioedema
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy, pulmonary edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, palpitations), chest pain, ischemia, myocardial infarction, syncope
Endocrine: thyroiditis
Gastrointestinal System Disorders:abdominal pain
Hematological: decreases in red cell, white cell and platelet counts (including idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura), lymphoma
Hepatic: abnormal liver function
Infections and Infestations:herpes simplex
Musculoskeletal System Disorders:arthralgia
Neuropsychiatric: agitation, cerebrovascular accident, convulsions (including febrile convulsions), depression, insomnia, multiple sclerosis aggravation, paresis, suicide
Respiratory: dyspnea
Urinary System Disorders:proteinuria, urinary retention, dysuria
Skin and Appendages: exfoliative dermatitis, er ythema multiforme, hyperpigmentation, hypertrophic scar, hypopigmentation
Vascular: Henoch-Schönlein purpura syndrome -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports and case series have not established a drugassociated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when imiquimod is used during pregnancy. There are no controlled or large-scale epidemiologic studies and no exposure registries with imiquimod use in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, there were no adverse
developmental effects observed after oral administration of imiquimod in pregnant rats and intravenous administration of imiquimod in pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 28 times and 115 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, and other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.Data
Animal Data
The MRHD was set at two packets per treatment of imiquimod cream, 3.75%, (18.75 mg imiquimod) for the animal multiples of human exposure presented in this label.
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Oral doses of 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period of organogenesis to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal toxicity, fetal effects noted at 20 mg/kg/day (163 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) included increased resorptions, decreased fetal body weights, delays in skeletal ossication, bent limb bones, and two fetuses in one litter (2 of 1567 fetuses) demonstrated exencephaly, protruding tongues, and low-set ears. No treatmentrelated effects on embryofetal toxicity or malformation were noted at 5 mg/kg/day
(28 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period of organogenesis to pregnant female rabbits. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or malformation were noted at 2 mg/kg/day (2.1 times the
MRHD based on BSA comparison), the highest dose evaluated in this study, or 1 mg/kg/day (115 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).A combined fertility and peri- and postnatal development study was conducted in rats. Oral doses of 1, 1.5, 3, and 6 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered to male rats from 70 days prior to mating through the mating period and to female rats from 14 days prior to mating through parturition and lactation. No effects on growth, fertility, reproduction, or postnatal development were noted at doses up to 6 mg/kg/day (25 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison), the highest dose evaluated in this study. In the absence of maternal toxicity, bent limb bones were noted in the F1 fetuses at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (25 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). This fetal effect was also noted in the oral rat embryofetal development study conducted with imiquimod. No treatment-related malformations were noted at 3 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of topically administered imiquimod in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Systemic concentration following topical administration of imiquimod cream is low; therefore, transfer of imiquimod into breastmilk is likely to be low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for imiquimod cream and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from imiquimod cream or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Avoid application of imiquimod cream to areas with increased risk for potential ingestion by or ocular exposure to the breastfeeding child.8.4 Pediatric Use
Actinic Keratosis
The safety and effectiveness of imiquimod cream for the treatment of AK in pediatric patients have not been established.
External Genital Warts
The safety and effectiveness of imiquimod cream for the treatment of EGW in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older have been established. Use of imiquimod cream for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well controlled trials in adults and pediatric subjects [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].The safety and effectiveness of imiquimod cream for the treatment of EGW in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
Molluscum Contagiosum
The safety and effectiveness of imiquimod cream for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in pediatric patients have not been established. Safety and effectiveness of imiquimod cream, 5% was not demonstrated in two randomized, vehicle-controlled, double-blind trials involving 702 pediatric subjects with MC (470 exposed to imiquimod cream; median age 5 years, range 2 to12 years).
Adverse reactions reported in pediatric subjects with MC (and not previously reported) included otitis media (5% imiquimod cream vs. 3% vehicle) and conjunctivitis (3% imiquimod cream vs. 2% vehicle).
In a pharmacokinetics trial in subjects aged 2 to 12 years with extensive MC involving a least 10% of total body surface area; among the 20 subjects with evaluable laboratory assessments, the median white blood cell (WBC) count decreased by 1.4 x 10 9/L and the median absolute neutrophil count decreased by 1.42 x 10 9/L.8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 320 subjects treated with imiquimod cream in the AK clinical trials, 150 subjects (47%) were 65 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of imiquimod cream have been observed between subjects 65 years of age and older and younger adult subjects.
Of the 400 subjects treated with imiquimod cream in the EGW clinical studies, 5 subjects (1%) were 65 years or older. Clinical studies of imiquimod cream for EGW did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects. -
10 OVERDOSAGE
Topical overdosing of imiquimod cream could result in an increased incidence of severe local skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
Hypotension was reported in a clinical trial following multiple oral imiquimod doses of >200 mg (equivalent to ingestion of the imiquimod content of more than 21 packets or pump actuations of imiquimod cream, 3.75% or more than 32 pump actuations of
imiquimod cream, 2.5%). The hypotension resolved following oral or intravenous fluid administration. Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations. -
11 DESCRIPTION
Imiquimod Cream, 3.75% is for topical administration. Each gram contains 37.5 mg of imiquimod in an off-white oil-in-water vanishing cream base consisting of benzyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, glycerin, isostearic acid, methylparaben, polysorbate 60, propylparaben, purified water, sorbitan monostearate, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, and xanthan gum.
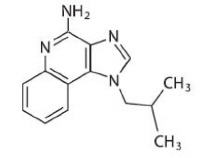
Chemically, imiquimod is 1-(2-methylpropyl)-1 H-imidazol[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine. Imiquimod has a molecular formula of
C 14H 16N 4 and a molecular weight of 240.3. Its structural formula is:
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of imiquimod cream in treating AK and EGW lesions is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of imiquimod cream are unknown.
Imiquimod is a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist that activates immune cells. Topical application to skin is associated with increases in markers for cytokines and immune cells.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following dosing with two packets of imiquimod cream, 3.75% once daily (18.75 mg imiquimod/day) for up to 3 weeks, systemic absorption of imiquimod was observed in all subjects when imiquimod cream was applied to the face and/or scalp in 17 subjects with at least 10 AK lesions. The mean peak serum imiquimod concentration at the end of the trial was approximately 0.323 ng/mL. The median time to maximal concentrations (Tmax) occurred at 9 hours after dosing. Based on the plasma half-life of imiquimod observed at the end of the trial, 29.3±17 hours, steadystate concentrations can be anticipated to occur by Day 7 with once-daily dosing.
Systemic absorption of imiquimod (up to 9.4 mg [one packet]) across the affected skin of 18 subjects with EGW was observed with once daily dosing for 3 weeks in all subjects. The subjects had either a minimum of 8 warts (range 8 to 93) or a surface area involvement of greater than 100 mm 2(range 15 to 620 mm 2) at trial entry. The mean peak serum imiquimod concentration at Day 21 was 0.488 +/- 0.368 ng/mL. The median time to maximal concentrations (Tmax) occurred 12 hours after dosing. Based on the plasma half-life of imiquimod observed at the end of the trial, 24.1+/-12.4 hours, steady-state concentrations can be anticipated to occur by Day 7 with once daily dosing. Because of the small number of subjects present (13 males, 5 females) it was not possible to select out or do an analysis of absorption based on sex/site of application. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) rat carcinogenicity study, imiquimod was administered to Wistar rats on a 2 times per week (up to 6 mg/kg/day) or daily (3 mg/kg/day) dosing schedule for 24 months. No treatment-related tumors were noted in the oral rat carcinogenicity study up to the highest doses tested in this study of 6 mg/kg administered 2 times per week in female rats (7.1 times the MRHD based on weekly AUC comparison), 4 mg/kg administered 2 times per week in male rats (6.1 times the MRHD based on weekly AUC comparison) or 3 mg/kg administered 7 times per week to male and female rats (12 times the MRHD based on weekly AUC comparison).
In a dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream (up to 5 mg/kg/application imiquimod or 0.3% imiquimod cream) was applied to the backs of mice 3 times per week for 24 months. A statistically significant increase in the incidence of liver adenomas and carcinomas was noted in high dose male mice compared to control male mice (21 times the MRHD based on weekly AUC comparison). An increased number of skin papillomas was observed in vehicle cream control group animals at the treated site only.
Imiquimod revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of five in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma L5178Y assay, Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay, human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay and SHE cell transformation assay) and three in vivogenotoxicity tests (rat and hamster bone marrow cytogenetics assay and a mouse dominant lethal test).
Daily oral administration of imiquimod to rats, throughout mating, gestation, parturition and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility or reproduction, at doses up to 25 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison. -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
In two double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical trials, 479 subjects with AK were treated with imiquimod cream, 3.75%, imiquimod cream, 2.5%, or vehicle (Studies AK1 and AK2). Trials enrolled subjects 18 years of age or older with 5 to 20 typical visible or palpable AK lesions of the face or scalp. Imiquimod cream or vehicle was applied to either the entire face (excluding ears) or balding scalp once daily for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period. Subjects then continued in the trial for an 8-week follow-up period during which they returned for clinical observations and safety monitoring. Trial subjects ranged from 36 to 90 years of age and 54% had Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. All imiquimod cream-treated subjects were White.
On a scheduled dosing day, up to two packets of the trial cream were applied to the entire treatment area prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Efficacy was assessed by AK lesion counts at the 8-week post-treatment visit. All AKs in the treatment area were counted, including baseline lesions as well as lesions which appeared during therapy.
Complete clearance required absence of any lesions including those that appeared during therapy in the treatment area. Complete and partial clearance rates are shown in Tables 5 and 6 below. Partial clearance rate was defined as the percentage of subjects in whom the number of baseline AKs was reduced by 75% or more. The partial clearance rate was measured relative to the numbers of AK lesions at baseline.Table 5: Rate of Subjects with Complete Clearance of AK at 8 Weeks Post-Treatment Imiquimod Cream, 3.75% Imiquimod Cream, 2.5% Vehicle Cream Study AK1 26% (21/81) 23% (19/81) 3% (2/80) Study AK2 46% (36/79) 38% (30/79) 10% (8/79) Table 6: Rate of Subjects with Partial Clearance (≥75%) of AK at 8 Weeks Post-Treatment Imiquimod Cream, 3.75% Imiquimod Cream, 2.5% Vehicle Cream Study AK1 46% (37/81) 42% (34/81) 19% (15/80) Study AK2 73% (58/79) 54% (43/79) 27% (21/79) During treatment, 86% (138/160) of imiquimod Cream, 3.75% subjects and 84% (135/160) of imiquimod cream, 2.5% subjects experienced a transient increase in lesions evaluated as AK relative to the number present at baseline within the treatment area.
14.2 External Genital Warts
In two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials, 601 subjects with EGW were treated with imiquimod cream, 3.75% or a matching vehicle (Studies EGW1 and EGW2). Trials enrolled subjects aged from 15 to 81 years. The baseline 2 2 wart area ranged from 6 to 5,579 mm 2 (median 60 mm 2) and the baseline wart count ranged from 2 to 48 warts. Most subjects had two or more treated anatomic areas at baseline. Anatomic areas included: inguinal, perineal, and perianal areas (both sexes); the glans penis, penis shaft, scrotum, and foreskin (in males); and the vulva (in females). Up to one packet of trial cream was applied once daily. The trial cream was applied to all warts prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Subjects continued applying the trial cream for up to 8 weeks, stopping if they achieved complete clearance of all (baseline and new) warts in all anatomic areas. Subjects who achieved complete clearance of all warts at any time up to the Week 16 visit entered a 12-week follow-up period to assess recurrence.
Complete clearance was defined as clearance of all war ts (baseline and new) in all anatomic areas within 16 weeks from baseline. The complete clearance rates are shown in Table 7. The proportions of subjects who achieved complete clearance at or before a given week (cumulative proportion) for the combined studies are shown in Figure 1. Complete clearance rates by sex for the combined studies are shown in Table 8.
Table 7: Percent of Subjects with Complete Clearance of EGW Within 16 Weeks from Baseline
Imiquimod Cream, 3.75% Vehicle Cream Study EGW1 53/195 (27%) 10/97 (10%) Study EGW2 60/204 (29%) 9/105 (9%) Figure 1: Cumulative Proportion of Subjects Achieving Complete Clearance of EGW by a Given Week (Studies EGW1 and EGW2)
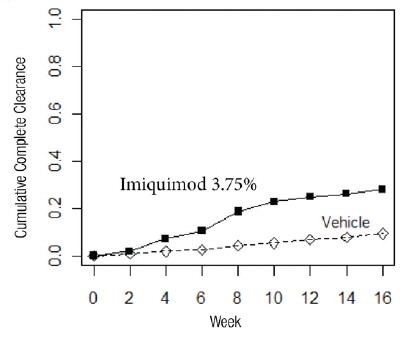
Table 8: Percent of Subjects with Complete Clearance of EGW within 16 Weeks from Baseline by Sex (Studies EGW1 and EGW2)
Imiquimod Cream, 3.75% Vehicle Cream Females 79/216 (37%) 15/106 (14%) Males 34/183 (19%) 4/96 (4%) Of the 113 imiquimod cream, 3.75%-treated subjects who achieved complete clearance in the two trials, 17 (15%) subjects had a recurrence within 12 weeks.
No trials were conducted directly comparing the 3.75% and 5% concentrations of imiquimod cream in the treatment of external genital warts.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Imiquimod cream is white to slightly yellow in color. Imiquimod cream USP, 3.75%, is supplied as white plastic 30 mL pump bottle, equipped with a white cap. The 7.5 g pump delivers no fewer than 28 full actuations.
- 3.75% cream, NDC: 51672-4174-9
Imiquimod cream USP, 3.75%, is also supplied in unit-dose foil packets which contain 0.25 g of cream:
- 3.75% cream, box of 28 packets, NDC: 51672-4174-6
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Important Administration Instructions
Inform all patients of the following [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]:
Imiquimod cream is for topical use only and avoid contact with the eyes, lips, nostrils, or inside the anus and vagina. Instruct patients to rinse their mouth or eyes with water right away if contact with these areas occur.
Wash their hands before and after applying imiquimod cream.
If a imiquimod cream dose is missed, apply the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
Discard and do not reuse partially used packets.
Discard pump bottles after completion of a full treatment course.
Inform patients with EGW of the following [see Dosage and Administration 2.3 and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
Uncircumcised patients treating warts under the foreskin should retract the foreskin and clean the area daily.
Imiquimod cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms; therefore, concurrent use is not recommended.
Avoid sexual (genital, anal, oral) contact while imiquimod cream is on the skin.
Do not bandage or otherwise occlude the treatment area.
Lactation
Advise breastfeeding women to avoid application of imiquimod cream to areas with increased risk for potential ingestion by or ocular exposure to the breastfeeding child [see Use in Specic Populations (8.2)].
Local Skin Reactions
Inform patients of the following [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
Local skin reactions may occur during treatment with imiquimod cream, ranging from mild to severe in intensity and extending beyond the application site onto the surrounding skin, and may require an interruption of dosing.
For female patients being treated for EGW, apply imiquimod cream at the opening of the vagina, avoiding intravaginal application because local skin reactions may cause difficulty in passing urine.
If severe local skin reactions occur, remove imiquimod cream by washing the treatment area with mild soap and water.
Contact their healthcare provider promptly if they experience any sign or symptom at the application site that restricts or prohibits their daily activity or makes continued application of imiquimod cream difficult.
Because of local skin reactions, during treatment and until healed, the treatment area is likely to appear noticeably different from normal skin.
Local Hypopigmentation and Hyperpigmentation
Inform patients that localized hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation have been reported following use of imiquimod cream and these skin color changes may be permanent in some patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Systemic Reactions
Inform patients that they may experience flu-like systemic signs and symptoms during treatment with imiquimod cream and these symptoms may require an interruption of dosing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Ultraviolet Light Exposure Risks
Instruct patients to avoid or minimize exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using imiquimod cream. Instruct patients to use protective clothing and to not use imiquimod cream if sunburned [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Patient Information
Imiquimod (im i' kwi mod) Cream
Important: For use on the skin only (topical). Do not use imiquimod cream in or near your lips, mouth, eyes or inside your anus, vagina, or nose.
What is imiquimod cream?
- Imiquimod cream, 3.75% is a prescription medicine for skin use only (topical) to treat actinic keratosis on the face or balding scalp in adults with a normal immune system.
- Imiquimod cream, 3.75% is a prescription medicine for use on the skin only (topical) to treat external genital and perianal warts in people 12 years and older.
It is not known if imiquimod cream is safe and effective in the treatment of:
- human papilloma virus (HPV) disease of the urethra, the inside of the vagina (intravaginal), cervix, rectum, or inside of the anus (intra-anal)
- actinic keratosis, when treated with more than one 2-cycle treatment course in the same affected area
- people with extreme sensitivity to sunlight (xeroderma pigmentosum)
- a type of skin cancer called superficial basal cell carcinoma
- people who have a weakened immune system
It is not known if imiquimod cream is safe and effective for the treatment of actinic keratosis in children less than 18 years of age.
It is not known if imiquimod cream is safe and effective in children less than 12 years of age for external genital and perianal warts.
Before using imiquimod cream, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have problems with your immune system, including autoimmune disease or long-lasting (chronic) graft versus host disease
- are being treated or have been treated with other medicines or surgery. You should not use imiquimod cream until your skin has healed from other treatments.
- have other skin problems or sunburn.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if imiquimod cream can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if imiquimod cream passes into your breast milk. If you breastfeed during treatment with imiquimod cream, avoid contact of your treated skin with your baby’s mouth or eyes. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use imiquimod cream.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.How should I use imiquimod cream?
- Use imiquimod cream exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your healthcare provider should show you how to apply imiquimod cream.
- Apply imiquimod cream 1 time a day just before your bedtime. Do not use more imiquimod cream than you need to cover the affected area. Using too much imiquimod cream, or using it too often, or for too long can increase your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side effects.
- Your healthcare provider may prescribe imiquimod cream in a packet or pump.
Imiquimod cream packet:
o Open a packet of imiquimod cream just before use.
o After applying imiquimod cream, the opened packet should be thrown away even if all the imiquimod cream was not used.
Imiquimod cream pump:
o Remove the cap.
o Before using the pump for the first time only, prime the pump by pressing the top of the pump all the way down repeatedly until the cream appears. The cream obtained from priming should be dispensed into a tissue and then thrown away (discarded). The pump is now primed and is ready to use. You will not have to repeat this priming process during your treatment.
o When dispensing the cream, slightly tilt the pump as shown.-
- Firmly press the top of the pump all the way down to dispense the cream onto your hand or fingertip.
Applying imiquimod cream:
- Wash the area where imiquimod cream will be applied with mild soap and water.
- Allow the area to dry.
- Wash your hands well.
- Apply a thin layer of imiquimod cream onlyto the affected area(s) to be treated.
- Rub imiquimod cream in all the way until you cannot see the cream on the affected area(s).
- Wash your hands well after applying imiquimod cream.
- After about 8 hours, wash the treated area(s) with mild soap and water. Do not leave imiquimod cream on your skin longer than prescribed. If you forget to apply imiquimod cream, apply the next dose of imiquimod cream at your regularly scheduled time.
When using imiquimod cream for actinic keratosis:
- Do not get imiquimod cream in or near your eyes, in or on your lips, or in your nose.
- If you get imiquimod cream in your mouth or in your eyes, rinse well with water right away.
- Apply imiquimod cream to the skin of the affected area for 2 weeks, then stop using for 2 weeks, then apply again for 2 weeks.
- If you have been prescribed imiquimod cream packets, do not use more than 2 packets for each daily application.
- If you have been prescribed imiquimod cream pump, do not dispense more than 2 pumps for each daily application.
When using imiquimod cream for external genital or perianal warts:
- Do not get imiquimod cream in or on your anus or vagina.
- Treatment should continue until the warts are completely gone or for up to 8 weeks. Imiquimod cream will not cure your genital or perianal warts. New warts may develop during treatment with imiquimod cream.
- Uncircumcised males treating warts under their penis foreskin must pull their foreskin back and clean before treatment and clean daily during treatment.
- Females treating genital warts must be careful when applying imiquimod cream around the vaginal opening.
- If you have been prescribed imiquimod cream packets, do not use more than 1 packet for each daily application.
- If you have been prescribed imiquimod cream pump, do not dispense more than 1 pump for each daily application.
What should I avoid while using imiquimod cream?
- Do not cover the treated area with bandages or other closed dressings.
Cotton gauze dressings can be used. Cotton underwear can be worn after applying imiquimod cream to the genital or perianal area.
- Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight as much as possible during treatment with imiquimod cream. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing if you go outside during daylight.
- Do not have sexual contact including genital, anal, or oral sex when imiquimod cream is on your genital or perianal skin. Imiquimod cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms. This means they may not work as well to prevent pregnancy.
- Avoid using imiquimod cream and any other imiquimod products in the same treatment area. They have the same active ingredients (imiquimod) and may increase your risk for side effects.
What are the possible side effects of imiquimod cream?
Imiquimod cream may cause serious side effects, including:
- Treatment site skin reactions. Skin reactions including drainage (weeping) or breakdown of the outer layer of your skin (erosion) can happen after a few applications of imiquimod cream. Swelling outside of the vagina (vulvar swelling) may happen in females. Females should take special care if applying the cream at the opening of the vagina because skin reactions can cause pain or swelling, and may cause problems passing urine. If you get skin reactions, wash the treated area with mild soap and water.
Stop imiquimod cream right away and call your healthcare provider if you get any skin reactions that affect your daily activities, or that do not go away.
- Flu-like symptoms. Tell your healthcare provider if you get tiredness, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, muscle pain, and joint pain.
Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop or completely stop your treatment with imiquimod cream if you develop treatment site skin reactions or flu-like symptoms.
The most common side effects of imiquimod cream include:- skin reactions including skin redness, scabbing, crusting, flaking, scaling, dryness, swelling
- headache
- itching at the treatment area
- tiredness
- nausea
- skin irritation
- pain at the treatment area
These are not all of the possible side effects of imiquimod cream.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc., at 1-866-923-4914.
How do I store imiquimod cream?
- Store imiquimod cream at room temperature 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Store imiquimod cream pumps upright.
- Do not freeze.
- Safely throw away imiquimod cream that is out of date, unused or partially used.
Keep imiquimod cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about imiquimod cream:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use imiquimod cream for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give imiquimod cream to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about imiquimod cream that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in imiquimod cream?
Active Ingredient:imiquimod
Inactive Ingredients:benzyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, glycerin, isostearic acid, methylparaben, polysorbate 60, propylparaben, purified water, sorbitan monostearate, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, and xanthan gum.
This patient information leaflet has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Distributed by:Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
Cranbury, NJ 08512Revised: November 2025
5201526-1125-04 27 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 28 Packet Carton
NDC: 51672-4174-6
Box of 28 Single Use Packets
Net Wt. per Packet 0.25 g
Net Wt. per Box 7 gImiquimod Cream USP 3.75%
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY
NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC, ORAL, OR INTRAVAGINAL USERx only
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7.5 g Bottle Carton
Net Wt. 7.5 g
NDC: 51672-4174-9
Imiquimod Cream USP 3.75%
Pump
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY
NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC, ORAL OR INTRAVAGINAL USE
Store Upright
Delivers no fewer than 28 full actuationsKeep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
Rx only


-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
IMIQUIMOD
imiquimod creamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51672-4174 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength IMIQUIMOD (UNII: P1QW714R7M) (IMIQUIMOD - UNII:P1QW714R7M) IMIQUIMOD 37.5 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) CETYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 936JST6JCN) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) ISOSTEARIC ACID (UNII: X33R8U0062) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) POLYSORBATE 60 (UNII: CAL22UVI4M) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SORBITAN MONOSTEARATE (UNII: NVZ4I0H58X) STEARYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) PETROLATUM (UNII: 4T6H12BN9U) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Product Characteristics Color white (White to Faintly Yellow) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51672-4174-6 28 in 1 CARTON 01/26/2021 1 NDC: 51672-4174-8 0.25 g in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51672-4174-9 1 in 1 CARTON 10/14/2021 2 7.5 g in 1 BOTTLE, PUMP; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA205971 01/26/2021 Labeler - Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. (146974886) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. 600072078 manufacture(51672-4174)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.