KEDRAB- human rabies virus immune globulin injection, solution
KEDRAB by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
KEDRAB by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Kedrion Biopharma Inc., Kamada Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KEDRAB safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KEDRAB.
KEDRAB Rabies Immune Globulin (Human)
Solution for intramuscular injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KEDRAB is a human rabies immunoglobulin (HRIG) indicated for passive, transient post-exposure prophylaxis of rabies infection, when given immediately after contact with a rabid or possibly rabid animal. KEDRAB should be administered concurrently with a full course of rabies vaccine (1).
- Do not administer additional (repeat) doses of KEDRAB once vaccine treatment has been initiated, since this may interfere with the immune response to the rabies vaccine (1).
- Do not administer KEDRAB to persons with a history of a complete pre-exposure or post-exposure rabies vaccination and confirmed adequate rabies antibody titer (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For wound infiltration and intramuscular use (2).
- Post-exposure prophylaxis consists of a single dose of KEDRAB and a full course of rabies vaccine. Administer KEDRAB and the rabies vaccine as soon as possible after exposure (2.1).
- Dosage: 20 IU/kg body weight (2.1).
- Infiltrate as much of the dose as possible into and around the exposure site (if visible); administer the remainder intramuscularly at sites distant from the site of vaccination (2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Single-use vials containing 2 mL or 10 mL ready-to-use ;
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- KEDRAB should not be administered to individuals who have documented previous vaccination against rabies (5.1).
- Shock or anaphylactic reaction may occur following administration of KEDRAB (5.2).
- Individuals with IgA-deficiency and antibodies against IgA may develop hypersensitivity reactions to KEDRAB (5.3).
- Individuals with increased risk of thrombosis and thrombotic complications should be monitored following KEDRAB administration (5.4).
- Individuals receiving KEDRAB, particularly those at increased risk for hemolysis, should be monitored following KEDRAB administration (5.5).
- KEDRAB administration may interfere with development of an immune response to live attenuated viral vaccines (5.6).
- KEDRAB may interfere with serologic tests (5.7).
- KEDRAB may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents such as viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent and theoretically the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent, despite manufacturing steps designed to minimize the risk of viral transmission (5.8, 11).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent adverse events in subjects treated with KEDRAB in clinical trials were injection site pain, headache, muscle pain, and upper respiratory tract infection (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kedrion Biopharma Inc. Customer Service (1-855-353-7466) in the United States. Outside of the United States, the company distributing these products should be contacted. Voluntary reporting of adverse reactions may also be made to the FDA through MedWatch at 1-800-FDA-1088 or on the Internet at www.fda.gov/medwatch. or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Do not administer KEDRAB in the same syringe, or into the same anatomical site, as the rabies vaccine (2, 7).
- Immunization with live vaccines: KEDRAB may interfere with the response to live vaccines, such as measles, mumps, polio or rubella; avoid immunization with live virus vaccines within 3 months after KEDRAB administration, or in the case of measles vaccine, within 4 months after KEDRAB administration (7).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2017
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Previous Rabies Vaccination
5.2 Anaphylactic Shock
5.3 Hypersensitivity
5.4 Thrombosis
5.5 Hemolysis
5.6 Live Attenuated Virus Vaccines
5.7 Interference with Serologic Testing
5.8 Transmissible Infectious Agents
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KEDRAB is a human rabies immunoglobulin (HRIG) indicated for passive, transient post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) of rabies infection, when given immediately after contact with a rabid or possibly rabid animal. KEDRAB should be administered concurrently with a full course of rabies vaccine.
- Do not administer additional (repeat) doses of KEDRAB once vaccine treatment has been initiated, since this may interfere with the immune response to the rabies vaccine.
- Do not administer KEDRAB to patients with a history of a complete pre-exposure or post-exposure vaccination regimen and confirmed adequate rabies antibody titer.1
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For wound infiltration and intramuscular use. Do not administer intravenously.
Local Treatment of Wounds prior to KEDRAB Administration
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Public Health Service Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) have outlined recommendations for passive and active immunization after exposure to an animal suspected of having rabies.1,2,3 Immediate and thorough cleansing of all bite wounds and scratches with soap and water is an important component of post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). A virucidal agent (e.g., povidone-iodine solution) should be used to irrigate the wounds.
Tetanus prophylaxis and measures to control bacterial infection should be given if medically indicated.
2.1 Dosage
Post-exposure prophylaxis consists of a single dose of KEDRAB and a full course of rabies vaccine. The recommended dose of KEDRAB is 20 IU/kg body weight, given at the time of the first vaccine dose. KEDRAB and the first dose of rabies vaccine should be given as soon as possible after exposure, as delays are potentially lethal. However, should a delay occur, KEDRAB should be administered at any time up to and including seven days after the first dose of vaccine. The rabies vaccine should be given according to the manufacturer's instructions.
No more than the recommended dose of KEDRAB should be given because KEDRAB partially suppresses active antibody production following vaccination. For the same reason, additional doses of KEDRAB should not be given, even if the antibody response to vaccination is delayed.
2.2 Administration
- When the bite site is known and infiltration at the bite site is feasible:
- - Infiltrate as much of the dose as possible into and around any detectable bite wounds. Inject any remaining volume intramuscularly into the upper arm deltoid region or, in small children, into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. Administer the remaining KEDRAB at site(s) distant from the site of the rabies vaccine.
- Avoid administration into the gluteal region, where absorbance is unpredictable (unless the exposure site is in the gluteal region):
- When the bite site is unknown or indeterminate (undetectable) or if infiltration is difficult at the bite site (e.g., lips, fingers, knee), administer the full KEDRAB dose by the intramuscular route at a site distant from the site of rabies vaccination.
- If a large intramuscular volume is required (>2 mL for children or >5 mL for adults), administer the total volume in divided doses at different sites.
- If intramuscular administration is contraindicated (e.g., in patients with uncorrectable bleeding disorders), administer KEDRAB subcutaneously. However, note that there are no clinical efficacy data to support administration of KEDRAB by the subcutaneous route.
- Do not mix with the rabies vaccine or administer in the same syringe with the rabies vaccine.
- Do not administer into the same anatomical site(s) as rabies vaccine.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. If either of these conditions exists, DO NOT use KEDRAB; discard the vial.
Further Information on Rabies Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
Consult local or state public health officials if questions arise about the need for rabies prophylaxis.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
KEDRAB is supplied in single-use vials containing 2 mL or 10 mL of ready-to-use solution with a nominal potency of 150 IU/mL.
The 2-mL vial contains a total of 300 IU and the 10-mL vial contains a total of 1,500 IU. The final product is assayed with human rabies immunoglobulin reference standard that is calibrated against the WHO International Standard.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Previous Rabies Vaccination
- Patients who can document previous complete rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis or complete post-exposure prophylaxis should only receive a booster rabies vaccine without KEDRAB, because KEDRAB may interfere with the anamnestic response to the vaccine (ACIP)1.
5.2 Anaphylactic Shock
- KEDRAB should not be injected into a blood vessel because of the risk of severe allergic or hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic shock. KEDRAB can induce a fall in blood pressure associated with an anaphylactic reaction, even in patients who tolerated previous treatment with human immunoglobulin.
- Discontinue KEDRAB injection immediately if there is an allergic or anaphylactic type reaction. In case of shock, implement standard medical treatment. Epinephrine should be available for treatment of acute anaphylactic symptoms.
5.3 Hypersensitivity
- Patients with a history of prior systemic allergic reactions following administration of human immune globulin preparations should be monitored for hypersensitivity.
- KEDRAB contains a small quantity of IgA. Patients who are deficient in IgA have the potential to develop IgA antibodies and may have anaphylactic reactions following administration of blood components containing IgA. The healthcare provider should assess the risks of this reaction against the benefits of administering KEDRAB.
5.4 Thrombosis
- Patients at increased risk of thrombosis or thrombotic complications should be monitored for at least 24 hours after KEDRAB administration.
- Patients at increased risk of thrombosis include patients with acquired or hereditary hypercoagulable states, prolonged immobilization, in-dwelling vascular catheters, advanced age, estrogen use, a history of venous or arterial thrombosis, cardiovascular risk factors (including history of atherosclerosis and/or impaired cardiac output), and hyperviscosity syndromes (including cryoglobulinemias, fasting chylomicronemia and/or high triglyceride levels, and monoclonal gammopathies).
- Consider measurement of baseline blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
5.5 Hemolysis
- Hemolysis may occur in patients receiving immune globulin products, particularly those who are determined to be at increased risk. Patients at increased risk include those with non-O blood group types, those with underlying associated inflammatory conditions, and those receiving high cumulative doses of immune globulins over the course of several days.
- Clinical symptoms and signs of hemolysis include fever, chills and dark urine. If any of these occur, perform appropriate laboratory testing and administer medical therapy as indicated.
5.6 Live Attenuated Virus Vaccines
- KEDRAB administration may interfere with the development of an immune response to live attenuated virus vaccines.
- - Avoid immunization with measles vaccine within 4 months after KEDRAB administration.
- - Avoid immunization with other live attenuated virus vaccines within 3 months after KEDRAB administration.
5.7 Interference with Serologic Testing
- A transient rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient's blood may result in misleading positive results of serologic tests after KEDRAB administration.
- Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens, e.g., A, B, and D, may interfere with serologic tests for red cell antibodies such as the antiglobulin test (Coombs' test).
5.8 Transmissible Infectious Agents
- KEDRAB is derived from human plasma; therefore, the potential exists that KEDRAB administration may transmit infectious agents such as viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
- The risk of transmitting an infectious agent has been minimized by
- - Screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses
- - Testing for certain viral infections
- - Inactivating and removing certain viruses during the manufacturing process [see Description (11)].
Despite these measures, KEDRAB administration can still potentially transmit infectious diseases. There is also the possibility that unknown infectious agents may be present in KEDRAB.
Any infection considered to have possibly been transmitted by this product should be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider to Kedrion Biopharma Inc. Customer Service (1-855-353-7466) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates of adverse reactions in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
KEDRAB was evaluated in three single-center, controlled clinical trials. Subjects in the clinical studies of KEDRAB were healthy adults, primarily white and ranged in age from 18 to 72 years. A total of 160 subjects were treated in these three studies, including 91 subjects who received single intramuscular doses of KEDRAB (20 IU/kg) with or without rabies vaccine.
Table 1 summarizes adverse events (assessed by the investigator as related or unrelated to study treatment) occurring in >3% of subjects in the clinical trials of KEDRAB. The most frequent adverse events in the KEDRAB group (>6%) were injection site pain, headache, muscle pain, and upper respiratory tract infection (Table 1).
Table 1: Adverse Events Occurring in >3% of Subjects in All Studies Combined Data are presented as number of subjects (% of subjects)
KEDRAB
N = 91Comparator HRIG
N = 84Saline Placebo + Vaccine
N = 8Injection site pain 30 (33) 26 (31) 2 (25) Headache 14 (15) 11 (13) 3 (38) Muscle pain 8 (9) 6 (7) 0 (0) Upper respiratory tract infection 8 (9) 8 (10) 0 (0) Joint pain 5 (6) 0 (0) 1 (13) Dizziness 5 (6) 3 (4) 0 (0) Fatigue 5 (6) 2 (2) 0 (0) Abdominal pain 4 (4) 1 (1) 0 (0) Blood in urine 4 (4) 2 (2) 0 (0) Nausea 4 (4) 3 (4) 0 (0) Feeling faint 4 (4) 1 (1) 0 (0) Bruising 3 (3) 1 (1) 0 (0) Sunburn 3 (3) 0 (0) 0 (0) White blood cells in urine 3 (3) 4 (5) 0 (0) Less common adverse events were joint pain, dizziness, fatigue, abdominal pain, blood in urine, nausea, feeling faint, bruising, sunburn, and white blood cells in urine.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Do not administer additional (repeat) doses of KEDRAB once vaccination has been initiated, since additional doses of KEDRAB may interfere with the immune response to the vaccine.
- Do not administer KEDRAB into the same anatomical site(s) as rabies vaccine.
- KEDRAB contains other antibodies that may interfere with the response to live vaccines such as measles, mumps, polio or rubella. Avoid immunization with live virus vaccines within 3 months after KEDRAB administration, or in the case of measles vaccine, within 4 months after KEDRAB administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
KEDRAB has not been studied in pregnant women. Therefore, the risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in pregnant women who are exposed to KEDRAB is unknown. Animal developmental or reproduction toxicity studies have not been conducted with KEDRAB. It is not known whether KEDRAB can cause harm to the fetus when administered to a pregnant woman or whether KEDRAB can affect reproductive capacity. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background of major birth defects occurs in 2-4% of the general population and miscarriage occurs in 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of KEDRAB in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for KEDRAB and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from KEDRAB or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KEDRAB in the pediatric population have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of KEDRAB did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Clinical experience with HRIG products has not identified differences in effectiveness between elderly and younger patients (ACIP)1.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
KEDRAB is a sterile, non-pyrogenic aqueous solution of anti-rabies immunoglobulin (≥95% protein as IgG). The product is stabilized with 0.3 M glycine and has a pH of 5.5 ± 0.5. It does not contain preservatives and the vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex. KEDRAB is a clear to opalescent liquid.
KEDRAB is prepared from human plasma from donors hyper-immunized with rabies vaccine. Individual plasma units are tested using FDA-licensed serologic assays for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and for antibodies to hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1/2), as well as by FDA-licensed Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for hepatitis B virus (HBV), HCV and HIV-1. Each plasma unit must be non-reactive (negative) in all tests. Plasma is also tested by in-process NAT procedures for HAV and parvovirus B19. Each plasma unit must be non-reactive to HAV, while the limit in the manufacturing pool is set not to exceed 104 IU per mL for parvovirus B19.
To reduce the risk of viral transmission further, the manufacturing process for KEDRAB includes three steps specifically designed to remove or inactivate viruses. The first of these is solvent/detergent (S/D) treatment with a mixture of tri-(n-butyl) phosphate (TnBP) and Octynoxol 9, which inactivates enveloped viral agents such as HIV, HBV and HCV. The second and third are heat-treatment (pasteurization) steps, which can inactivate both enveloped and non–enveloped viruses, and a nanofiltration (NF) step which removes viruses on the basis of size. The effectiveness of the S/D treatment, pasteurization and nanofiltration procedures for reducing viral content has been assessed using a series of viruses with a range of physico-chemical characteristics. The results of the viral challenge studies are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Log10 Virus Reduction during Manufacture of KEDRAB Abbreviations: BVDV: bovine viral diarrhea virus; EMCV: encephalomyocarditis virus; HIV-1: human immunodeficiency virus 1; HRIG: human rabies immune globulin; PPV: Porcine parvovirus; PRV: Pseudorabies virus; S/D: solvent/detergent; WNV: West Nile Virus
Process Step Enveloped Viruses Non-enveloped Viruses HIV-1 BVDV PRV WNV EMCV PPV S/D treatment >4.99 >5.70 >4.38 >5.46 Not tested Not tested Heat treatment >6.21 >5.67 Not tested >6.33 3.30 Not tested Nanofiltration Not tested Not tested >6.58 Not tested >7.66 3.41 Global Log10 Reduction Factor >11.20 >11.37 >10.96 >11.79 >10.96 3.41 -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Rabies is a zoonotic disease caused by RNA viruses in the family Rhabdoviridae, genus Lyssavirus. Virus is typically present in the saliva of rabid mammals and is transmitted primarily through a bite. KEDRAB is infiltrated into the inoculation site (i.e., at the beginning of anti-rabies PEP) to previously unvaccinated persons, to provide immediate passive rabies virus neutralizing antibody protection until the patient's immune system responds to vaccination by actively producing antibodies.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
A protective threshold for rabies virus neutralizing activity (RVNA) has never been established. However, the WHO has generally accepted a RVNA of at least 0.5 IU/mL measured 14 days after initiation of PEP as protective. By comparison, the ACIP recommends complete neutralization of rabies virus at a 1:5 serum dilution by a rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT) from 1 to 2 weeks after prophylaxis; this corresponds to RVNA ~0.1-0.2 IU/mL. In support of these recommendations, there has been almost no documented clinical disease when the current rabies PEP regimen is administered appropriately (ACIP) 1.
KEDRAB has the potential to attenuate the patient's immune response to rabies vaccine. This was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized study where 16 healthy subjects were administered either KEDRAB (20 IU/kg IM) or saline placebo followed by three doses of a rabies vaccine (Table 3). Lower RVNA levels were seen in the KEDRAB + vaccine group compared to the placebo + vaccine group at all time-points beginning on Day 14, confirming that KEDRAB interferes with the host immune response to rabies vaccine.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
A randomized, single-dose, two-period, two-treatment, two-sequence, double-blind, crossover study assessed the pharmacokinetics of KEDRAB. Twenty-six healthy volunteer subjects were randomized to receive a single IM injection of 20 IU/kg HRIG on two separate occasions (KEDRAB or Comparator HRIG). Subjects received the second treatment (A or B) following the 42-day test period and a 21-day washout period. Single dose IM injection of KEDRAB resulted in maximum plasma RVNA levels of 0.25 IU/mL. The median Tmax was 7 days (range: 3 – 14 days). The elimination half-life was approximately 17.9 days. A statistical analysis of the pharmacokinetic parameters showed that KEDRAB was not bioequivalent to the Comparator HRIG (Table 3).
Table 3: Statistical Analysis of Rabies Virus Neutralizing Antibody Pharmacokinetic Parameters - Crossover Study of KEDRAB Abbreviations: AUC: area under the concentration-time curve; Cmax: maximum concentration; inf: infinity; IU: international units; mL: milliliter; PK: Pharmacokinetic; RVNA: rabies virus neutralizing antibody
Parameter Units Geometric LS Mean Values Test/Reference
(%)90% Confidence
Interval
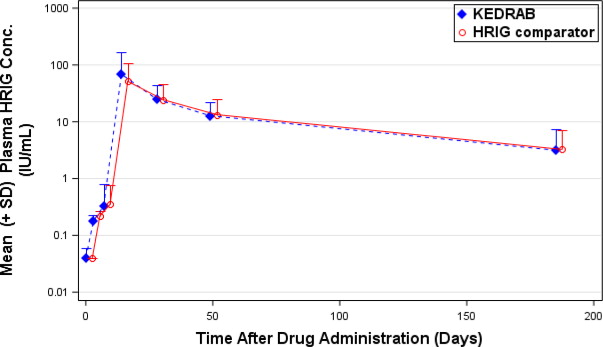
(%)KEDRAB Comparator HRIG Cmax IU/mL 0.24 0.30 81.71 75.34-88.62 AUC0-last Day*IU/mL 5.08 6.17 82.35 77.39-87.63 AUC0-inf Day*IU/mL 6.64 7.86 84.44 78.63-90.68 A plot of plasma rabies virus neutralizing antibody titer concentration versus time (Figure 1) demonstrated that, in both treatment groups, plasma rabies virus neutralizing antibody concentrations declined in a biphasic manner after the absorption phase was complete.
Figure 1: Plasma HRIG Concentrations [Mean (±SD)] at Scheduled PK Sampling Days (Semi-log Scale), Phase 2/3 Study, Pharmacokinetic Analysis
Additionally, a prospective, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority, study evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety and effectiveness of simulated post-exposure prophylaxis with KEDRAB with co-administration of active rabies vaccine in 118 healthy subjects. Subjects were randomized into two treatment groups (59 per treatment group) to receive intramuscular KEDRAB or comparator HRIG at a dose of 20 IU/kg on Day 0, and rabies vaccine on Days 0, 3, 7, 14 and 28. The peak plasma RVNA was 71.9 IU/mL and 53.9 IU/mL for KEDRAB and comparator HRIG respectively. For both treatment groups, the median Tmax was 14 days (range: 14 – 49 days). The half-lives were 48.6 hours and 52.7 hours for KEDRAB and comparator HRIG respectively.
Bioequivalent assessment showed that KEDRAB was not bioequivalent to the comparator HRIG when co-administered with a five-dose rabies vaccine regimen (Table 4). Furthermore, the RVNA on Day 3 was lower in the KEDRAB with rabies vaccine group relative to the Comparator HRIG with vaccine group (0.188±0.051 vs 0.229±0.054, P=0.0005). However, these pharmacokinetic differences are not expected to affect clinical outcomes.
Table 4: Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Rabies Virus Neutralizing Antibody between KEDRAB and a Comparator HRIG Administered with Rabies Vaccine Abbreviations: AUC: area under the concentration-time curve; Cmax: maximum concentration; inf: infinity; IU: international units; mL: milliliter; RVNA: rabies virus neutralizing antibody
Parameter Units Geometric LS Mean Values Test/Reference
(%)90% Confidence
Interval
(%)KEDRAB (Test)
Comparator HRIG
(Reference)
Cmax IU/mL 44.87 36.02 124.59 90.62-171.28 AUC0-last Day*IU/mL 1741.40 1686.03 103.28 79.03-134.98 AUC0-inf Day*IU/mL 2045.87 1916.90 106.73 80.48-141.54 Please see Clinical Studies (14) section for clinical efficacy.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of KEDRAB administered concurrently with rabies vaccine was studied in a single-center, randomized, comparator HRIG-controlled clinical study. Study subjects were healthy adults 18 to 72 years of age who were without significant acute or chronic illness. A total of 118 subjects (59 per treatment group) received intramuscular KEDRAB or comparator HRIG at a dose of 20 IU/kg on Day 0, and rabies vaccine on Days 0, 3, 7, 14 and 28. The mean age of study subjects was 45 years; subjects were, predominantly white (93%), and 64% were women. The efficacy variable was RVNA, as assessed by RFFIT, on Day 14. Efficacy analyses were performed on the As-Treated Population, which comprised the 116 study subjects who received KEDRAB or comparator HRIG and at least 3 of the 5 doses of rabies vaccine before Day 14.
Efficacy, considered when RVNA titer is 0.5 IU/mL or higher on Day 14 (as established by the WHO), was met by 56/57 subjects (98.2%) in the KEDRAB group and 59/59 subjects in the comparator HRIG group (Table 5). The lower limit of the 90% CI was greater than the pre-specified non-inferiority margin of -10%; thus, KEDRAB was non-inferior to comparator HRIG.
Table 5: Subjects with Geometric Mean RVNA ≥0.5 IU/mL on Day 14 (As-Treated Population) a 'Pa' and 'Pb' are the proportion of participants with IgG antibody titer ≥0.5 IU/mL on Day 14 in Groups A and B, respectively. Group A = KEDRAB +Rabies Vaccine, Group B = Control HyperRAB®+Rabies Vaccine.
b based on Farrington-Manning score statistic.
Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; HRIG: human rabies immune globulin; IU: international units; mL: milliliter
KEDRAB with Rabies Vaccine
(N=57)Comparator HRIG with Rabies Vaccine
(N=59)Rabies virus neutralizing antibody titer ≥0.5 IU/mL, n (%) 56 (98.2) 59 (100) Exact 95% CI for proportion (%) (90.6, 100) (93.9, 100) Difference (Pa-Pb)a (%) -1.8 Exact 90% CI for differenceb (%) (-8.1, 3.0) Additional efficacy analyses included pharmacokinetics [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
-
15 REFERENCES
- Human rabies prevention—United States, 2008: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR 2008;57 (No. RR-3).
- Use of a Reduced (4-Dose) Vaccine schedule for postexposure prophylaxis to prevent human rabies: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR 2010;59 (No. RR-2).
- WHO 2013, Expert Consultation on Rabies. Second Report. Geneva: WHO Press. Technical Report Series (No. 982).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- Each carton of KEDRAB contains a single-use vial containing 2 mL or 10 mL of ready-to-use solution with a potency of 150 IU/mL.
- The 2-mL vial contains a total of 300 IU which is sufficient for a child weighing 15 kg (33 lb). (NDC: 76125-150-02). The 10-mL vial contains a total of 1500 IU which is sufficient for an adult weighing 75 kg (165 lb). (NDC: 76125-150-10)
- Store KEDRAB at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Do not freeze.
- Keep vial in carton until use.
- KEDRAB may be stored at room temperatures not exceeding 25 °C (77 °F) for up to one month.
- Use within one month after removal from refrigeration, Do not return to refrigeration.
- Do not use after the expiration date printed on the label.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
The KEDRAB manufacturing process includes three valid and effective viral elimination steps. In addition, the process allows the removal of thrombogenic activity.
Inform patients that KEDRAB is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease (e.g., viruses and, theoretically, the CJD agent). Explain that the risk of KEDRAB transmitting an infectious agent has been reduced by screening the plasma donors, by testing the donated plasma for certain virus infections, and by a process demonstrated to inactivate and/or remove certain viruses during manufacturing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Inform patients of symptoms of a possible viral infection, including headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, weakness, malaise, diarrhea, or, in the case of hepatitis, jaundice.
Distributed by:
Kedrion Biopharma Inc.
Parker Plaza, 400 Kelby St.
Fort Lee, NJ 07024
United StatesManufactured by:
Kamada Ltd.
Beit Kama
MP Negev 8532500
IsraelUS License No. 1826
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 2mL Carton Label
NDC-76125-150-02
KEDRAB
Rabies Immune Globulin (Human)150 IU/mL
For wound infiltration and intramuscular
use. Do not administer intravenously.Store at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Do not freeze.
Single use vial. Discard any unused
contents.Preservative Free, Latex Free, Sterile,
Pyrogen Free.The patient and physician should discuss
the risks and benefits of this product.Rx only
2 mL
KAMADA
KEDRION
BIOPHARMA -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 2mL Vial Label
NDC-76125-150-03
KEDRAB Rabies Immune Globulin (Human) 150 IU/ml
For wound infiltration and intramuscular use. Do not administer intravenously.
See package insert for dosage information. Single use vial.
Store at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Do not freeze. Rx only
Distributed by: Kedrion Biopharma Inc.
Parker Plaza, 400 Kelby St, Fort Lee, NJ 07024 United States
Manufactured by: Kamada Ltd. Beit Kama MP Negev 8532500 Israel
U.S. License No. 18262mL
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 10mL Carton Label
NDC-76125-150-10
KEDRAB
Rabies Immune Globulin (Human)150 IU/mL
For wound infiltration and intramuscular
use. Do not administer intravenously.Store at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Do not freeze.
Single use vial. Discard any unused
contents.Preservative Free, Latex Free, Sterile,
Pyrogen Free.The patient and physician should discuss
the risks and benefits of this product.Rx only
10 mL
KAMADA
KEDRION
BIOPHARMA -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 10mL Vial Label
NDC-76125-150-11
KEDRAB Rabies Immune Globulin (Human) 150 IU/ml
For wound infiltration and intramuscular use. Do not administer intravenously.
See package insert for dosage information. Single use vial.
Store at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Do not freeze. Rx only
Distributed by: Kedrion Biopharma Inc.
Parker Plaza, 400 Kelby St, Fort Lee, NJ 07024 United States
Manufactured by: Kamada Ltd. Beit Kama MP Negev 8532500 Israel
U.S. License No. 182610mL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
KEDRAB
human rabies virus immune globulin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC: 76125-150 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Human Rabies Virus Immune Globulin (UNII: 95F619ATQ2) (Human Rabies Virus Immune Globulin - UNII:95F619ATQ2) Human Rabies Virus Immune Globulin 150 [iU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Glycine (UNII: TE7660XO1C) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 76125-150-02 1 in 1 BOX 1 NDC: 76125-150-03 2 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 76125-150-10 1 in 1 BOX 2 NDC: 76125-150-11 10 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125613 11/08/2017 Labeler - Kedrion Biopharma Inc. (078622209) Registrant - Kamada Ltd. (600251631) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Kamada Ltd. 649062486 MANUFACTURE, LABEL, PACK, ANALYSIS
Trademark Results [KEDRAB]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 KEDRAB 87636954 5623863 Live/Registered |
Kamada Ltd. 2017-10-06 |
 KEDRAB 86173344 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Kamada Ltd. 2014-01-23 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.