Phytonadione by Amneal Pharmaceuticals NY LLC / Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited Oral Solid Dosage Unit PHYTONADIONE tablet
Phytonadione by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Phytonadione by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amneal Pharmaceuticals NY LLC, Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited Oral Solid Dosage Unit. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Phytonadione is a vitamin which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, and nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.
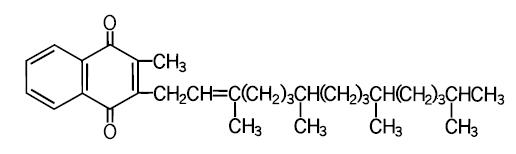
Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1, 4-naphthoquinone. Its empirical formula is C31H46O2 and its structural formula is:
Phytonadione tablets, USP containing 5 mg of phytonadione, USP, is light yellow to yellow colored, round tablets.
Inactive Ingredients
Phytonadione tablets USP, 5 mg contains: acacia, anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate, colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch and talc.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Phytonadione possess the same type and degree of activity as does naturally-occurring vitamin K, which is necessary for the production via the liver of active prothrombin (factor II), proconvertin (factor VII), plasma thromboplastin component (factor IX), and Stuart factor (factor X). The prothrombin test is sensitive to the levels of three of these four factors - II, VII, and X. Vitamin K is an essential cofactor for a microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the post-translational carboxylation of multiple, specific, peptide-bound glutamic acid residues in inactive hepatic precursors of factors II, VII, IX, and X. The resulting gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues convert the precursors into active coagulation factors that are subsequently secreted by liver cells into the blood.
Oral phytonadione is adequately absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract only if bile salts are present. After absorption, phytonadione is initially concentrated in the liver, but the concentration declines rapidly. Very little vitamin K accumulates in tissues. Little is known about the metabolic fate of vitamin K. Almost no free unmetabolized vitamin K appears in bile or urine.
In normal animals and humans, phytonadione is virtually devoid of pharmacodynamic activity. However, in animals and humans deficient in vitamin K, the pharmacological action of vitamin K is related to its normal physiological function; that is, to promote the hepatic biosynthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors.
Phytonadione tablets generally exert their effect within 6 to 10 hours.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Phytonadione tablets are indicated in the following coagulation disorders which are due to faulty formation of factors II, VII, IX and X when caused by vitamin K deficiency or interference with vitamin K activity.
Phytonadione tablets are indicated in:
— anticoagulant-induced prothrombin deficiency caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives;
— hypoprothrombinemia secondary to antibacterial therapy;
— hypoprothrombinemia secondary to administration of salicylates;
— hypoprothrombinemia secondary to obstructive jaundice or biliary fistulas but only if bile salts are administered concurrently, since otherwise the oral vitamin K will not be absorbed.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
An immediate coagulant effect should not be expected after administration of phytonadione.
Phytonadione will not counteract the anticoagulant action of heparin.
When vitamin K1 is used to correct excessive anticoagulant-induced hypoprothrombinemia, anticoagulant therapy still being indicated, the patient is again faced with the clotting hazards existing prior to starting the anticoagulant therapy. Phytonadione is not a clotting agent, but overzealous therapy with vitamin K1 may restore conditions which originally permitted thromboembolic phenomena. Dosage should be kept as low as possible, and prothrombin time should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
Repeated large doses of vitamin K are not warranted in liver disease if the response to initial use of the vitamin is unsatisfactory. Failure to respond to vitamin K may indicate a congenital coagulation defect or that the condition being treated is unresponsive to vitamin K.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Vitamin K1 is fairly rapidly degraded by light; therefore, always protect phytonadione from light. Store phytonadione in closed original carton until contents have been used (see also HOW SUPPLIED, Storage).
Drug Interactions
Temporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants may result, especially when larger doses of phytonadione are used. If relatively large doses have been employed, it may be necessary when reinstituting anticoagulant therapy to use somewhat larger doses of the prothrombin-depressing anticoagulant, or to use one which acts on a different principle, such as heparin sodium.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies of carcinogenicity or impairment of fertility have not been performed with phytonadione. Phytonadione at concentrations up to 2,000 mcg/plate with or without metabolic activation, was negative in the Ames microbial mutagen test.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with phytonadione. It is also not known whether phytonadione can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Phytonadione should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established with phytonadione. Hemolysis, jaundice, and hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, particularly in premature infants, have been reported with vitamin K.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when phytonadione is administered to a nursing woman.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of phytonadione did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions and deaths have been reported following parenteral administration. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration.
Transient “flushing sensations” and “peculiar” sensations of taste have been observed with parenteral phytonadione, as well as rare instances of dizziness, rapid and weak pulse, profuse sweating, brief hypotension, dyspnea, and cyanosis.
Hyperbilirubinemia has been observed in the newborn following administration of parenteral phytonadione. This has occurred rarely and primarily with doses above those recommended.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Phytonadione Tablets
Summary of Dosage Guidelines
(See circular text for details)Adults
Initial Dosage
Anticoagulant-Induced
Prothrombin Deficiency
(caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives)2.5 mg to 10 mg or up to
25 mg (rarely 50 mg)
Hypoprothrombinemia due
to other causes
(Antibiotics; Salicylates or other drugs;
Factors limiting absorption or synthesis)2.5 mg to 25 mg or more
(rarely up to 50 mg)
Anticoagulant-Induced Prothrombin Deficiency in Adults
To correct excessively prolonged prothrombin times caused by oral anticoagulant therapy - 2.5 to 10 mg or up to 25 mg initially is recommended. In rare instances 50 mg may be required. Frequency and amount of subsequent doses should be determined by prothrombin time response or clinical condition (see WARNINGS). If, in 12 to 48 hours after oral administration, the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should be repeated.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes in Adults
If possible, discontinuation or reduction of the dosage of drugs interfering with coagulation mechanisms (such as salicylates, antibiotics) is suggested as an alternative to administering concurrent phytonadione tablets. The severity of the coagulation disorder should determine whether the immediate administration of phytonadione tablets is required in addition to discontinuation or reduction of interfering drugs.
A dosage of 2.5 to 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) is recommended, the amount and route of administration depending upon the severity of the condition and response obtained.
The oral route should be avoided when the clinical disorder would prevent proper absorption. Bile salts must be given with the tablets when the endogenous supply of bile to the gastrointestinal tract is deficient.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Phytonadione tablets USP, 5 mg are supplied as light yellow to yellow colored, round, scored tablets, debossed with “AA” and “05” on either side of scoring and plain on the other side.
They are available as follows:Bottle of 30 Tablets: NDC: 69238-1051-3
Bottle of 100 Tablets: NDC: 69238-1051-1Storage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Always protect phytonadione tablets, USP from light. Store in tightly closed original container and carton until contents have been used (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Oral Solid Dosage Unit
Ahmedabad 382213, INDIADistributed by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807Rev. 10-2017-00
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PHYTONADIONE
phytonadione tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69238-1051 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PHYTONADIONE (UNII: A034SE7857) (PHYTONADIONE - UNII:A034SE7857) PHYTONADIONE 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ACACIELLA ANGUSTISSIMA BARK (UNII: ID3K20OAXF) ANHYDROUS DIBASIC CALCIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: L11K75P92J) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW (Light yellow to yellow) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code AA;05 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69238-1051-3 1 in 1 CARTON 05/15/2018 1 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 69238-1051-1 1 in 1 CARTON 05/15/2018 2 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA209373 05/15/2018 Labeler - Amneal Pharmaceuticals NY LLC (123797875) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited Oral Solid Dosage Unit 650762060 MANUFACTURE(69238-1051) , PACK(69238-1051)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

