These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial).EGRIFTA® (tesamorelin for injection), for subcutaneous useInitial U.S. Approval: 2010
Egrifta by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Egrifta by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Theratechnologies Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
EGRIFTA- tesamorelin
Theratechnologies Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial).
EGRIFTA® (tesamorelin for injection), for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2010 RECENT MAJOR CHANGESDosage and Administration (2) 11/2018 INDICATIONS AND USAGEEGRIFTA is a growth hormone releasing factor (GHRF) analog indicated for the reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy. (1) Limitations of use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost commonly reported adverse reactions (>5%): Arthralgia, injection site erythema, injection site pruritus, pain in extremity, peripheral edema, and myalgia. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact THERA patient supportTM toll free at 1-833-23THERA (1-833-238-4372) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 11/2018 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EGRIFTA is indicated for the reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected adult patients with lipodystrophy.
Limitations of Use:
- Long-term cardiovascular safety of EGRIFTA has not been established. Consider risk/benefit of continuation of treatment in patients who have not had a reduction in visceral adipose tissue.
- EGRIFTA is not indicated for weight loss management as it has a weight neutral effect.
- There are no data to support improved compliance with anti-retroviral therapies in HIV-positive patients taking EGRIFTA
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage and Administration
- Two formulations and strengths are available for EGRIFTA. This Dosage and Administration information only applies to EGRIFTA 2 mg/vial formulation.
- The dose of EGRIFTA is 1.4 mg, 0.35 mL of the reconstituted solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)], injected subcutaneously once daily.
- Inject EGRIFTA into the abdomen. Rotate injection sites to different areas of the abdomen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Do not inject into scar tissue, bruises or the navel.
2.2 Reconstitution Procedure
- Instruct patients to read the Instructions for Use enclosed in the EGRIFTA box.
- Use only the diluent provided, Sterile Water for Injection, USP, to reconstitute EGRIFTA.
- Reconstitute the vial of EGRIFTA lyophilized powder with 0.5 mL of diluent (2 mg per 0.5 mL). Mix by rolling the vial gently in your hands for 30 seconds. Do not shake.
- Inspect the reconstituted vial visually for particulate matter and discoloration. Use only if the solution is clear, colorless and without particulate matter.
- Administer 0.35 mL of EGRIFTA immediately following reconstitution and throw away any unused EGRIFTA solution and diluent. If not used immediately, discard the reconstituted EGRIFTA solution. Do not freeze or refrigerate the reconstituted EGRIFTA solution.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
EGRIFTA for injection is supplied in a single-dose 2 mg vial as a white to off-white lyophilized powder and a diluent of 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
EGRIFTA is contraindicated in patients with:
- Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis due to hypophysectomy, hypopituitarism, pituitary tumor/surgery, head irradiation or head trauma.
- Active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive and its treatment complete prior to instituting therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Known hypersensitivity to tesamorelin or the excipients in EGRIFTA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Pregnant women because modifying visceral adipose tissue offers no benefit in a pregnant woman and could result in fetal harm [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Risk of Neoplasms
New Malignancy
Carefully consider the decision to start treatment with EGRIFTA based on the increased background risk of malignancies in HIV-positive patients.
Active Malignancy
EGRIFTA induces the release of endogenous growth hormone (GH), a known growth factor. Do not treat patients with active malignancy with EGRIFTA [see Contraindications (4)].
History of Malignancy
For patients with a history of non-malignant neoplasms, initiate EGRIFTA therapy after careful evaluation of the potential benefit of treatment. For patients with a history of treated and stable malignancies, initiate EGRIFTA therapy only after careful evaluation of the potential benefit of treatment relative to the risk of re-activation of the underlying malignancy. Discontinue EGRIFTA if there is any evidence of recurrent malignancy.
5.2 Elevated IGF-1 Levels
EGRIFTA stimulates GH production and increases serum IGF-1, a growth factor. The effects of prolonged elevations in IGF-1 levels are unknown. Monitor IGF-1 levels during EGRIFTA therapy. Consider discontinuing EGRIFTA in patients with persistent elevations of IGF-1 levels (e.g., >3 SDS), particularly if the efficacy response is not robust.
Among patients who received EGRIFTA for 26 weeks, 47% had IGF-1 levels greater than 2 standard deviation scores (SDS), and 36% had SDS >3, with this effect seen as early as 13 weeks of treatment. Among those patients who remained on EGRIFTA for a total of 52 weeks, at the end of treatment 34% had IGF-1 SDS >2 and 23% had IGF-1 SDS >3.
5.3 Fluid Retention
Fluid retention may occur during EGRIFTA therapy and is thought to be related to the induction of GH secretion. This manifests as increased tissue turgor and musculoskeletal discomfort resulting in adverse reactions (e.g. edema, arthralgia, carpal tunnel syndrome) which are either transient or resolve with discontinuation of treatment.
5.4 Glucose Intolerance or Diabetes Mellitus
EGRIFTA treatment can result in glucose intolerance. During clinical trials, the percentages of patients with elevated HbA1c (≥ 6.5%) from baseline to Week 26 were 5% and 1% in the EGRIFTA and placebo groups, respectively. An increased risk of developing diabetes with EGRIFTA (HbA1c level ≥ 6.5%) relative to placebo was observed [intent-to-treat hazard odds ratio of 3.3 (CI 1.4, 9.6)].
Evaluate glucose status prior to initiating EGRIFTA. Monitor all patients treated with EGRIFTA periodically to diagnose those who develop impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes. If patients treated with EGRIFTA develop glucose intolerance or diabetes, consider discontinuing EGRIFTA in patients who do not show a clear efficacy response.
EGRIFTA increases IGF-1, monitor patients with diabetes who are receiving treatment with EGRIFTA at regular intervals for potential development or worsening of retinopathy.
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 4% of patients treated with EGRIFTA in clinical trials. Reactions included pruritus, erythema, flushing, urticaria, and rash. In cases of suspected hypersensitivity reactions, advise patients to seek prompt medical attention and immediately discontinue treatment with EGRIFTA.
5.6 Injection Site Reactions
EGRIFTA may cause injection site reactions, including injection site erythema, pruritus, pain, irritation, and bruising. The incidence of injection site reactions was 25% in EGRIFTA-treated patients and 14% in placebo-treated patients during the first 26 weeks of treatment in clinical trials. Rotate injection sites to different areas of the abdomen to decrease injection site reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.7 Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness
Increased mortality in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery or multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure has been reported after treatment with pharmacologic amounts of growth hormone. EGRIFTA is a Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) and since EGRIFTA stimulates growth hormone production, consider discontinuing EGRIFTA in critically ill patients.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increased risk of neoplasms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Elevated IGF-1 levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Fluid retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Glucose intolerance or diabetes mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Injection site reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of the EGRIFTA 2 mg/vial formulation has been established based on clinical trials conducted with the EGRIFTA 1 mg/vial formulation. Adverse reactions for the 1.4 mg dose (2 mg/vial formulation) of EGRIFTA are expected to be similar to those observed with the 2 mg dose (1 mg/vial formulation) of EGRIFTA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Seven hundred and forty HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy and excess abdominal fat were treated with EGRIFTA in clinical trials; of these, 543 received EGRIFTA during the initial 26-week placebo-controlled phase.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions were hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash, urticaria), edema-related reactions (e.g., arthralgia, extremity pain, peripheral edema, carpal tunnel syndrome), hyperglycemia, and injection site reactions (injection site erythema, pruritus, pain, urticaria, irritation, swelling, hemorrhage).
Adverse reactons that occurred more frequently with EGRIFTA relative to placebo and had an incidence ≥1% during the first 26 weeks across all studies are presented in Table 1.
|
* Injection site reaction includes: Injection site erythema, Injection site pruritus, Injection site rash, Injection site urticaria, Injection site pain, Injection site swelling, Injection site irritation, Injection site hemorrhage. |
||
| Preferred Term | Placebo (N=263) | EGRIFTA (N=543) |
| Injection site reaction* Arthralgia Pain in extremity Myalgia Edema peripheral Paresthesia Hypoesthesia Rash Dyspepsia Musculoskeletal pain Pain Pruritus Vomiting Musculoskeletal stiffness Blood creatine phosphokinase increased Carpal tunnel syndrome Joint swelling Muscle strain Night sweats Palpitations | 6 11 5 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 17 13 6 6 6 5 4 4 2 2 2 2 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
In the EGRIFTA clinical trials, mean baseline HbA1c was 5.3% among patients in both the EGRIFTA and placebo groups. Patients receiving EGRIFTA had an increased risk of developing diabetes (HbA1c level ≥ 6.5%) compared with placebo (5% vs. 1%), with a hazard ratio of 3.3 (CI 1.4, 9.6).
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins and peptides, there is a potential for development of anti- EGRIFTA antibodies. The observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay is highly dependent on several factors, including assay sensitivity and specificity, methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medication and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to EGRIFTA with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
In the clinical trials with the EGRIFTA 1 mg/vial formulation, anti-tesamorelin IgG antibodies were detected in 50% of patients treated with EGRIFTA for 26 weeks and 47% of patients who received EGRIFTA for 52 weeks. In the subset of patients with hypersensitivity reactions, anti-tesamorelin IgG antibodies were detected in 85%. Cross-reactivity to endogenous Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) was observed in approximately 60% of patients who developed anti-tesamorelin antibodies. Patients with and without anti-tesamorelin IgG antibodies had similar mean reductions in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and IGF-1 response. In a group of patients who had antibodies to tesamorelin after 26 weeks of treatment (56%) and were re-assessed 6 months later, after stopping EGRIFTA treatment, 18% were still antibody positive.
Neutralizing antibodies to tesamorelin and hGHRH were detected in vitro at Week 52 in 10% and 5% of EGRIFTA-treated patients, respectively. Changes in VAT and IGF-1 levels in patients with or without in vitro neutralizing antibodies were comparable.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs
Co-administration of EGRIFTA with simvastatin, a CYP3A substrate, showed that EGRIFTA had no significant impact on the pharmacokinetics profiles of simvastatin in healthy subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
EGRIFTA stimulates GH production. Published data indicate that GH may modulate cytochrome P450 (CYP450) mediated antipyrine clearance. These data suggest that GH may alter the clearance of compounds known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes (e.g., corticosteroids, sex steroids, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine). Monitor patients for potential interactions when administering EGRIFTA in combination with other drugs known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes.
7.2 Glucocorticoids
GH inhibits 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD-1), a microsomal enzyme required for conversion of cortisone to its active metabolite, cortisol, in hepatic and adipose tissue. EGRIFTA stimulates GH production, therefore, patients receiving glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in maintenance or stress doses following initiation of EGRIFTA. Patients treated with cortisone acetate and prednisone may be affected more than others because conversion of these drugs to their biologically active metabolites is dependent on the activity of 11βHSD-1.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
EGRIFTA is contraindicated in pregnant women because modifying visceral adipose tissue offers no benefit in pregnant women and could result in fetal harm [see Clinical Considerations and Contraindications (4)]. Administration of tesamorelin acetate to rats during organogenesis resulted in hydrocephaly in offspring at a dose of approximately two and four times the clinical dose, based on measured drug exposure (AUC). If EGRIFTA is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, discontinue EGRIFTA.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
During pregnancy, visceral adipose tissue increases due to normal metabolic and hormonal changes. Modifying pregnancy-associated physiologic changes in visceral adipose tissue with EGRIFTA offers no known benefit and could result in fetal harm.
Data
Animal Data
Tesamorelin acetate administration to rats during organogenesis and lactation resulted in hydrocephaly in offspring at a dose of approximately two and four times the clinical dose, respectively, based on measured drug exposure (AUC). Actual animal dose was 1.2 mg/kg. During organogenesis, lower doses approximately 0.1 to 1 times the clinical dose caused delayed skull ossification in rats. Actual animal doses were 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg. No adverse developmental effects occurred in rabbits using doses up to approximately 500 times the clinical dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers in the United States not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV-1 infection. There are no data on the presence of tesamorelin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of both the potential for (1) HIV-1 infection transmission (in HIV-negative infants), (2) developing viral resistance (in HIV-positive patients), and (3) any possible adverse effects of EGRIFTA, mothers should not breastfeed if they receive EGRIFTA.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EGRIFTA in pediatric patients have not been established.
In pediatric patients with open epiphyses, treatment with EGRIFTA may result in linear growth acceleration and excessive growth. EGRIFTA is not indicated for use in pediatric patients with open or closed epiphyses.
11 DESCRIPTION
EGRIFTA contains tesamorelin (as the acetate salt), a human growth hormone-releasing factor (GRF) analog. The peptide precursor of tesamorelin acetate is produced synthetically and is comprised of the 44 amino acid sequence of human GRF. Tesamorelin acetate is made by attaching a hexenoyl moiety, a C6 chain with a double bond at position 3, to the tyrosine residue at the N-terminal part of the molecule. The molecular formula of tesamorelin acetate is C221H366N72O67S x C2H4O2 (x ≈ 7) and its molecular weight (free base) is 5135.9 Daltons. The structural formula of tesamorelin acetate is:

EGRIFTA is a sterile, white to off-white, preservative-free lyophilized powder for subcutaneous injection. After reconstitution with the supplied diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP), a solution of EGRIFTA is clear and colorless. Each single-dose vial of EGRIFTA contains 2 mg of tesamorelin and the following inactive ingredients: 20 mg mannitol, USP, 10 mg sucrose, NF, 0.78 mg histidine, USP and 0.05 mg polysorbate 20, NF.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
In vitro, tesamorelin binds and stimulates human GRF receptors with similar potency as the endogenous GRF [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Growth Hormone-Releasing Factor (GHRF), also known as Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH), is a hypothalamic peptide that acts on the pituitary somatotroph cells to stimulate the synthesis and pulsatile release of endogenous growth hormone (GH), which is both anabolic and lipolytic. GH exerts its effects by interacting with specific receptors on a variety of target cells, including chondrocytes, osteoblasts, myocytes, hepatocytes, and adipocytes, resulting in a host of pharmacodynamic effects. Some, but not all these effects, are primarily mediated by IGF-1 produced in the liver and in peripheral tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Tesamorelin stimulates growth hormone secretion, and subsequently increases IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels. No clinically significant changes in the levels of other pituitary hormones, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and prolactin, were observed in patients receiving EGRIFTA in clinical trials.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of EGRIFTA after subcutaneous administration of a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation) was determined to be less than 4% in healthy adult subjects.
Single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of EGRIFTA have been characterized in healthy subjects and HIV-infected patients without lipodystrophy using a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation). Tesamorelin mean extent of absorption (AUC) was 34% higher in HIV-infected patients than healthy subjects. Tesamorelin peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was similar in HIV-infected patients and healthy subjects. The median peak plasma tesamorelin concentration (Tmax) was 0.15 h in both populations.
Following single dose of subcutaneous administration of 1.4 mg of EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial formulation) in healthy subjects, the mean [coefficient of variation (CV)] AUC0-inf was 889.1 (57%) pg.h/mL. The mean (CV) Cmax value was 2956.1 (47%) pg/mL and the median Tmax was 0.15 h.
The systemic exposure (Cmax and AUCs) of tesamorelin is similar between the 1.4 mg dose of EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial formulation) and the 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation).
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution (±SD) of tesamorelin following a single subcutaneous administration of the 1.4 mg dose of EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial formulation) was 4.8 ± 1.9 L/kg in healthy subjects.
Elimination
Mean elimination half-life (t1/2) of tesamorelin was 8 minutes in healthy subjects after single dose subcutaneous administration of the 1.4 mg of EGRIFTA (2 mg/vial formulation).
Specific Populations
Pharmacokinetics of tesamorelin in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, in pediatric patients, or in elderly patients has not been established.
Drug Interactions
Simvastatin
The effect of multiple dose administration of EGRIFTA on the pharmacokinetics of simvastatin and simvastatin acid was evaluated in healthy subjects. Co-administration with simvastatin (a CYP3A substrate) resulted in 8% decrease in extent of absorption (AUCinf) and 5% increase in rate of absorption (Cmax) of simvastatin. For simvastatin acid there was a 15% decrease in AUCinf and 1% decrease in Cmax [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Ritonavir
The effect of multiple dose administration of EGRIFTA on the pharmacokinetics of ritonavir was evaluated in healthy subjects. Co-administration with ritonavir resulted in 9% decrease in AUCinf and 11% decrease in Cmax of ritonavir [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Life-time carcinogenicity studies in rodents have not been conducted with tesamorelin acetate. No potential mutagenicity of tesamorelin acetate was revealed in a battery of tests including induction of gene mutations in bacteria (the Ames test), gene mutations in mammalian cells grown in vitro (hamster CHOK1 cells), and chromosomal damage in intact animals (bone marrow cells in mice). There was no effect on fertility in male or female rats following administration of tesamorelin acetate at doses up to 0.6 mg/kg (approximately equal to clinical exposure) for 28 days in males or 14 days in females.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and effectiveness of the EGRIFTA 2 mg/vial formulation has been established based on adequate and well controlled studies with the EGRIFTA 1 mg/vial formulation, as well as a demonstration of comparable bioavailability between the 1.4 mg EGRIFTA dose (2 mg/vial formulation) and the 2 mg EGRIFTA dose (1 mg/vial formulation) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies were conducted in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy and excess abdominal fat (abdominal lipohypertrophy). Study 1 and 2 consisted of a 26-week Main Phase and a 26-week Extension Phase, respectively. Main inclusion criteria were age 18 to 65 years, a waist circumference ≥95 cm (37.4 inches) and a waist-to-hip ratio ≥0.94 for men and ≥94 cm (37.0 inches) and ≥0.88 for women, respectively, and fasting blood glucose (FBG) <150 mg/dL (8.33 mmol/L). Main exclusion criteria included BMI ≤ 20 kg/m2, type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus, previous treatment with insulin or with oral hypoglycemic or insulin-sensitizing agents, history of malignancy, and hypopituitarism. Patients were on a stable anti-retroviral regimen for at least 8 weeks prior to randomization. Patients meeting the inclusion/exclusion criteria were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation) or placebo subcutaneously daily for 26 weeks. The primary efficacy assessment for each of these studies was the percent change from baseline to Week 26 in visceral adipose tissue (VAT), as assessed by computed tomography (CT) scan at L4-L5 vertebral level. Secondary endpoints included changes from baseline in patient-reported outcomes related to body image, triglycerides, ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol, IGF-1 levels, and safety parameters. Other endpoints included changes from baseline in waist circumference, abdominal subcutaneous tissue (SAT), trunk fat, and lean body mass. In both studies, EGRIFTA-treated patients completing the 26-week treatment period were re-randomized to blinded therapy with either daily placebo or 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation) for an additional 26-week treatment period (Extension Phase) in order to assess maintenance of VAT reduction and to gather long-term safety data. For inclusion in the Extension Phase studies, subjects must have completed the Main Phase with FBG ≤ 150 mg/dL.
Main Phase (Baseline to Week 26):
Study 1 (NCT 00123253)
This study randomized 412 HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy and excess abdominal fat to receive either a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation) (N=273) or placebo (N=137). At baseline for the two groups combined, mean age was 48 years; 86% were male; 75% were white, 14% were Black/African American, and 8% were Hispanic; mean weight was 90 kg; mean BMI was 29 kg/m2; mean waist circumference was 104 cm; mean hip circumference was 100 cm; mean VAT was 176 cm2; mean CD4 cell count was 606 cells/mm3; 69% had undetectable viral load (<50 copies/mL); and 33.7% randomized to EGRIFTA and 36.6% randomized to placebo had impaired glucose tolerance, while 5.6% randomized to EGRIFTA and 6.7% randomized to placebo had diet-controlled diabetes mellitus. The twenty-six week completion rate in Study 1 was 80%.
Study 2 (NCT 00435136)
This study randomized 404 HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy and excess abdominal fat to receive either a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA(1 mg/vial formulation) (N=270) or placebo (N=126). At baseline for the two groups combined, mean age was 48 years; 84% were male; 77% were white, 12% were Black/African American, and 9% were Hispanic; mean weight was 88 kg; mean BMI was 29 kg/m2; mean waist circumference was 105 cm; mean hip circumference was 100 cm; mean VAT was 189 cm2; mean CD4 cell count was 592 cells/mm3; 83% had undetectable viral load (<50 copies/mL); and 44% randomized to EGRIFTA and 40% randomized to placebo had impaired glucose tolerance, while 9% randomized to EGRIFTA and 10% randomized to placebo had diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. The twenty-six week completion rate in Study 2 was 74%.
Results for the Main Phases of Studies 1 and 2 are presented in Table 2 and 3.
|
Baseline data are expressed as mean (SD); Change refers to least-squares mean (LSM); CI: confidence interval. |
|||||
|
1 Results derived from the statistical model: Ln(VAT Week 26/VAT Baseline) = Ln(VAT Baseline) + treatment group |
|||||
| MAIN PHASE (Baseline-Week 26) | |||||
| Study 1 | Study 2 | ||||
|
2 mg EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial) (N=273) | Placebo (N=137) |
2 mg EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial) (N=270) | Placebo (N=126) |
||
| Baseline (cm2) | 178 (77) | 171 (77) | 186 (87) | 195 (95) | |
| Change (cm2) | -27 | 4 | -21 | -0 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -31 (-39,-24) | -21 (-29,-12) | |||
| Mean change (%)1 | -18 | 2 | -14 | -2 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI)1 | -20 (-24, -15) | -12 (-16, -7) | |||
|
Baseline data are expressed as mean (SD); Change refers to least-squares mean (LSM); CI: confidence interval. |
|||||
| MAIN PHASE (Baseline-Week 26) | |||||
| Study 1 | Study 2 | ||||
| 2 mg EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial) (N=273) | Placebo (N=137) | 2 mg EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial)
(N=270) | Placebo (N=126) |
||
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | Baseline | 161 (59) | 168 (75) | 146 (66) | 149 (59) |
| Change | 107 | -15 | 108 | 3 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | 122 (101, 141) | 105 (85, 126) | |||
| IGFBP-3 (mg/L) | Baseline | 3 (1) | 3 (1) | 3 (1) | 3 (1) |
| Change | 0.4 | -0.2 | 0.8 | -0.0 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | 0.6 (0.5, 0.8) | 0.8 (0.5, 1.0) | |||
| Weight (kg) | Baseline | 90 (14) | 90 (14) | 89 (14) | 87 (16) |
| Change | -0.4 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -0.4 (-1.3, 0.5) | 0.2 (-0.7, 1.3) | |||
| Waist circumference (cm) | Baseline | 104 (10) | 105 (9) | 105 (9) | 105 (9) |
| Change | -3 (5) | -1 (4) | -2 (5) | -1 (5) | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -2 (-2.8, -0.9) | -1 (-2.5, -0.3) | |||
At Week 26, treatment with a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA(1 mg/vial formulation) resulted in a reduction from baseline in mean trunk fat of 1.0 kg in Study 1 and 0.8 kg in Study 2, respectively (compared with an increase of 0.4 kg in Study 1 and of 0.2 kg in Study 2, respectively, in patients receiving placebo). Treatment with EGRIFTA resulted in an increase from baseline in mean lean body mass of 1.3 kg in Study 1 and of 1.2 kg in Study 2, respectively (compared with a decrease of 0.2 kg in Study 1 and of 0.03 kg in Study 2, respectively, in patients receiving placebo).
Patient Reported Outcomes
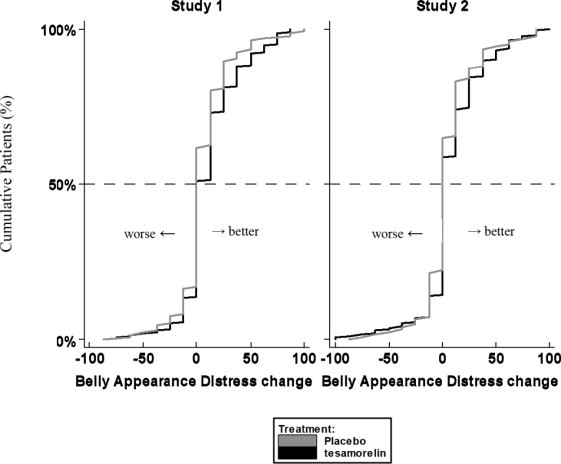
Patients rated the degree of distress associated with their belly appearance on a 9-point rating scale that was then transformed to a score from 0 (extremely upsetting and distressing) to 100 (extremely encouraging). A score of 50 indicated neutral (no feeling either way). A positive change from baseline score indicated improvement, i.e., less distress.
The cumulative distribution of response (change from baseline to 26 weeks) is shown in Figure 1 for both treatment groups. A curve shifted to the right on this scale indicates a greater percentage of patients reporting improvement.
Figure 1. Cumulative Distribution of Response for Belly Appearance Distress
Extension Phase (Weeks 26-52):
In the double-blind Extension Phase, patients on a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg per vial formulation) completing the 26-week Main Phase were re-randomized to receive a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg per vial formulation) or placebo.
Study 1 (NCT 00123253)
This study re-randomized 207 HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy who completed a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA (1 mg/vial formulation) treatment in the Main Phase to receive either EGRIFTA (N=154) or placebo (N=50) for an additional 26-week duration (3:1 randomization ratio). At baseline (Week 26) for the two groups combined, mean age was 48 years; 88% were male; 78% were white, 12% were Black/African American, and 8% were Hispanic; mean weight was 90 kg; mean BMI was 29 kg/m2; mean waist circumference was 102 cm; mean hip circumference was 100 cm; mean VAT was 145 cm2; mean CD4 cell count was 639 cells/mm3; 68% had undetectable viral load (<50 copies/mL); and for those EGRIFTA-treated patients completing the 26-week treatment period that were re-randomized to EGRIFTA (T-T group) or re-randomized to placebo, 37% and 32%, respectively, had impaired glucose tolerance, while 2% re-randomized to EGRIFTA and 6% re-randomized to placebo had diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. The completion rate for patients randomized into the extension phase of Study 1 was 83%.
Study 2 (NCT 00435136)
This study re-randomized 177 HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy who completed EGRIFTA treatment in the Main Phase to receive either a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA(1 mg/vial formulation) (N=92) or placebo (N=85) for an additional 26-week duration (1:1 randomization ratio). At baseline (Week 26) for the two groups combined, mean age was 48 years; 90% were male; 84% were white, 9% were Black/African American, and 7% were Hispanic; mean weight was 89 kg; mean BMI was 28 kg/m2; mean waist circumference was 105 cm; mean hip circumference was 100 cm; mean VAT was 172 cm2; mean CD4 cell count was 579 cells/mm3; 82% had undetectable viral load (<50 copies/mL); and for those EGRIFTA-treated patients completing the 26-week treatment period that were re-randomized to EGRIFTA (T-T group) or re-randomized to placebo, 49% and 51%, respectively, had impaired glucose tolerance, while 4% re-randomized to EGRIFTA and 13% re-randomized to placebo had diet-controlled diabetes mellitus. The completion rate for patients randomized into the extension phase of Study 2 was 81%.
Results for the Extension Phases of Studies 1 and 2 are presented in Table 4 and 5.
|
Week 26 baseline data are expressed as mean (SD). Change refers to least-squares mean (LSM); CI: confidence interval. |
||||
|
1T-T = tesamorelin for Weeks 0-26 and tesamorelin for Weeks 26-52 |
||||
|
2T-P = tesamorelin for Weeks 0-26 and placebo for Weeks 26-52 |
||||
|
3Results derived from the statistical model: Ln(VAT Week 52/Week 26) = Ln(Week 26 VAT) + treatment group |
||||
| EXTENSION PHASE (Week 26-52) | ||||
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
| T-T1
(Week 26-52) (N=154) | T-P2
(Week 26-52) (N=50) | T-T1
(Week 26-52) (N=92) | T-P2
(Week 26-52) (N=85) |
|
| Week 26 (cm2) | 145 (72) | 144 (72) | 166 (89) | 177 (88) |
| Change (cm2) | 3 | 25 | -11 | 24 |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -22 (-34, -10) | -35 (-48, -22) | ||
| Mean change (%)3 | 0 | 22 | -5 | 16 |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI)3 | -17 (-24, -10) | -18 (-24, -11) | ||
Figure 2 shows the percent change in VAT from baseline (Week 0) over time until 52 weeks in completer patients.
Figure 2. Percent Change from Baseline in VAT over Time
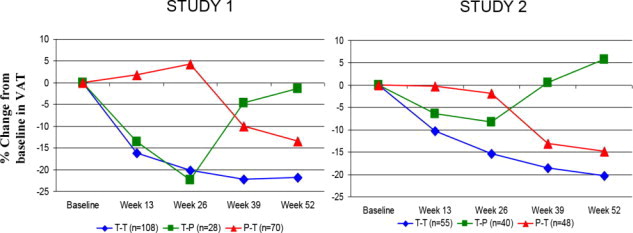
Data in Figure 2 are expressed as mean values. T-T (tesamorelin to tesamorelin) refers to the group of patients who received tesamorelin for Weeks 0-26 and were re-randomized to tesamorelin for Weeks 26-52. T-P (tesamorelin to placebo) refers to the group of patients who received tesamorelin for Weeks 0-26 and were re-randomized to placebo for Weeks 26-52. P-T (placebo to tesamorelin) refers to the group of patients who received placebo for Weeks 0-26 and were switched to tesamorelin (treated open label) for Weeks 26-52.
|
Week 26 baseline data are expressed as mean (SD); Change refers to least-squares mean (LSM); CI: confidence interval. |
|||||
|
1T-T = tesamorelin for Week 0-26 and tesamorelin for Week 26-52 |
|||||
|
2T-P = tesamorelin for Week 0-26 and placebo for Week 26-52 |
|||||
| EXTENSION PHASE (Weeks 26-52) | |||||
| Study 1 | Study 2 | ||||
|
T-T1 (Week 26-52) (N=154) | T-P2
(Week 26-52) (N=50) | T-T1
(Week 26-52) (N=92) | T-P2
(Week 26-52) (N=85) |
||
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | Week 26 | 291 (124) | 281 (105) | 280 (134) | 269 (110) |
| Change | -59 | -137 | -25 | -135 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | 78 (50, 106) | 110 (87, 134) | |||
| IGFBP-3 (mg/L) | Week 26 | 3 (1) | 3 (1) | 3 (1) | 3 (1) |
| Change | -0.2 | -0.5 | -0.3 | -0.9 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | 0.3 (-0.0, 0.6) | 0.6 (0.3, 0.9) | |||
| Weight (kg) | Week 26 | 89 (14) | 92 (17) | 89 (13) | 90 (14) |
| Change | 0.2 | 0.6 | -0.5 | 0.1 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -0.4 (-2, 1) | -0.6 (-2, 1) | |||
| Waist circumference (cm) | Week 26 | 101 (10) | 102 (12) | 101 (9) | 103 (11) |
| Change | -0.2 | 2.4 | -1.1 | 0.2 | |
| Mean treatment difference (95% CI) | -2.6 (-4, -1) | -1.3 (-2, 0) | |||
Patients treated with a 2 mg dose of EGRIFTA(1 mg/formulation) for 52 weeks (T-T group) showed no change between Weeks 26 and 52 in mean trunk fat (increase of 0.1 kg in Study 1 and decrease of 0.5 kg in Study 2, respectively, compared with an increase of 1.4 kg in patients in the T-P group in Study 1 and an increase of 1.09 kg in Study 2, respectively) nor was there a change from Week 26 baseline in mean lean body mass (decrease of 0.1 kg in Study 1 and increase of 0.1 kg in Study 2, respectively, compared with a decrease of 1.8 kg in patients in the T-P group in Study 1 and a decrease of 1.7 kg in Study 2, respectively).
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
EGRIFTA for injection is supplied as a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a 2 mg single-dose vial with a diluent of 10 mL vial of Sterile Water for Injection, USP.
EGRIFTA (NDC: 62064-041-30) is available in a package comprised of two boxes, containing 30 (thirty) 2 mg single-dose vials of EGRIFTA in the medication box and 30 single-dose 10 mL bottles of Sterile Water for Injection, USP diluent with a 30-day supply of disposable syringes and needles in the injection box.
Protect EGRIFTA from light and keep in the original box until time of use. Store EGRIFTA 2 mg/vial up to 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store the Sterile Water for Injection, USP, syringes and needles at controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Increased Risk of Malignancy
Inform patients about the increased background risk of malignancies in HIV-positive patients and for patients with a history of neoplasms, inform them about the risk of malignancy reoccurrence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Elevated IGF-1 Levels
Inform patients that treatment with EGRIFTA increases IGF-1 levels and that they will need periodic monitoring of their IGF-1 levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Fluid Retention
Inform patients that treatment with EGRIFTA may cause fluid retention, resulting in adverse reactions including edema, arthralgia, and carpal tunnel syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Glucose Intolerance or Diabetes Mellitus
Inform patients that treatment with EGRIFTA may result in glucose intolerance or diabetes mellitus. Advise patients that they will need to be monitored to see if impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus develops, and that if they have pre-existing diabetes mellitus, they may need adjustments to their anti-diabetic medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash, urticaria) may occur during treatment with EGRIFTA. Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention and to immediately discontinue treatment with EGRIFTA if a reaction occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Injection Site Reactions
Inform patients that injection site reactions may occur with EGRIFTA, including injection site erythema, pruritus, pain, irritation, and bruising. Advise patients to rotate the site of injection to reduce the risk of injection site reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Pregnancy
Advise women to discontinue EGRIFTA if pregnancy occurs, as the drug offers no known benefit to pregnant women and could result in fetal harm [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Because of both the potential for HIV-1 infection transmission and serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers receiving EGRIFTA should be instructed not to breastfeed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration
Counsel patients that they should never share an EGRIFTA syringe with another person, even if the needle is changed. Sharing of syringes or needles between patients may pose a risk of transmission of infection.
|
PATIENT INFORMATION EGRIFTA® (eh-GRIF-tuh) (tesamorelin for injection) for subcutaneous use 2 mg vial |
|||||
|
Read the Patient Information that comes with EGRIFTA before you start to take EGRIFTA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. |
|||||
|
What is EGRIFTA?
The long term safety of EGRIFTA on the heart and blood vessels (cardiovascular) is not known. EGRIFTA is not for weight loss management. It is not known whether taking EGRIFTA helps improve how well you take antiretroviral medicines. It is not known if EGRIFTA is safe and effective in children. EGRIFTA is not recommended to be used in children with open or closed bone growth plates (epiphyses). |
|||||
|
Who should not use EGRIFTA? Do not take EGRIFTA if you:
|
|||||
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using EGRIFTA? Before using EGRIFTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
|||||
|
How should I use EGRIFTA?
|
|||||
|
What are the possible side effects of EGRIFTA? EGRIFTA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
○ a rash over your body ○ shortness of breath or trouble breathing |
○ hives ○ fast heartbeat |
○ swelling of your face or throat ○ feeling of faintness or fainting |
|||
|
|||||
|
○ redness ○ irritation ○ swelling |
○ itching ○ bleeding |
○ pain ○ rash |
|||
|
|||||
|
The most common side effects of EGRIFTA include: |
|||||
|
○ joint pain |
○ pain in legs and arms |
|
○ muscle pain |
||
|
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800- FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to THERA patient supportTM toll-free at 1-833-23THERA (1-833-238-4372). |
|||||
|
How should I store EGRIFTA 2 mg vial?
Keep EGRIFTA and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|||||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of EGRIFTA Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use EGRIFTA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give EGRIFTA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about EGRIFTA that is written for healthcare professionals. |
|||||
|
What are the ingredients in EGRIFTA? Active ingredient: tesamorelin Inactive ingredients: mannitol, sucrose, histidine, polysorbate 20 Distributed by: Theratechnologies Inc., Montréal, Québec, Canada H3A 1T8 For more information about EGRIFTA, go to www.EGRIFTA.com or contact toll-free at 1-833-23THERA (1-833-238-4372). |
|||||
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 11/2018
Instructions for Use
EGRIFTA® (eh-GRIF-tuh)
(tesamorelin for injection)
for subcutaneous use
2mg/vial
This Instructions for Use (IFU) contains step-by-step information on how to use the 2 mg vial of EGRIFTA. Each 2 mg vial of EGRIFTA must be mixed with 0.5 mL of the Sterile Water for Injection provided in the Injection Box given to you by the pharmacy. You only need one EGRIFTA 2 mg vial from the Medication Box to complete your dose. The recommended dose is 1.4 mg (0.35 mL).
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow this IFU before using EGRIFTA. Your healthcare provider should show you how to mix and inject EGRIFTA before you inject it for the first time. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Keep this IFU in case you need to look at it again later.
Important information for use of EGRIFTA
- After mixing EGRIFTA with Sterile Water for Injection, it should look clear and colorless, with no particles in it. Do not use EGRIFTA if it looks cloudy, discolored, or if you see particles in it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
- Do not use EGRIFTA after the expiration date on the EGRIFTA vials.
- Do not use a syringe or needle more than 1 time.
- Do not share your EGRIFTA syringe or needles with other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a serious infection, or get a serious infection from them.
-
If you are missing any supplies from the boxes given to you by the pharmacy or if anything looks damaged call your pharmacist or contact THERA patient supportTM toll-free at 1-833-23THERA (1-833-238-4372) right away.
Preparing for your EGRIFTA injection
Step 1: Find a well-lit, clean, and flat surface, such as a table.
Step 2: Gather your supplies:
- Medication Box that contains 30 EGRIFTA 2 mg vials
- Injection Box that contains the following:
- 30 single-dose 10-mL bottles of Sterile Water for Injection, used for mixing
- 60 sterile 1-mL syringes
- 60 sterile individual 1" 20-gauge needles, used for mixing
- 30 sterile individual ½” 30-gauge needles, used for injection
- Other Supplies Needed
- Alcohol pads
- Sterile gauze
- A “sharps container” or a puncture resistant container for throwing away used needles and syringes after you are done with them.
Material included in Injection Box (a, b, c, d) and Medication Box (e) for the EGRIFTA 2 mg vial:
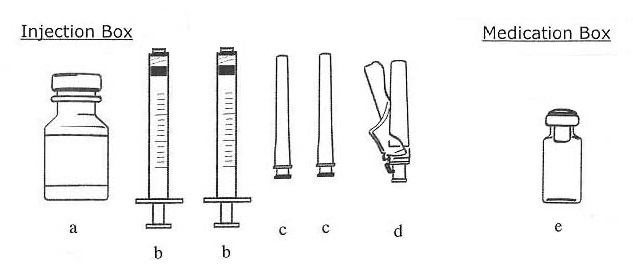
Figure A
Step 3: Take out the following from your Injection Box:
- A Sterile Water for Injection bottle (Figure A, a)
- Two 1-mL syringes (Figure A, b)
- Two 1" 20-gauge needles used for mixing (Figure A, c)
- A ½" 30-gauge needle used for injection (Figure A, d)
Step 4: Take 1 EGRIFTA 2 mg vial (Figure A, e) from the Medication Box.
Step 5: Prepare to use your supplies:
- Wash your hands with soap and water. Dry your hands with a clean towel.
- Take off the plastic caps from the vial of EGRIFTA and Sterile Water bottle.
- Clean the rubber stoppers on top of the vial of EGRIFTA and Sterile Water bottle with an alcohol pad.
How to mix EGRIFTA 2 mg vial
Step 1: Place the 1" 20-gauge needle used for mixing (Figure A, c), with its white protective cap in place, onto the syringe (Figure A, b). Hold the syringe firmly and twist the cap clockwise (to the right) until it closes securely. (See Figure B).
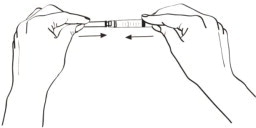
Figure B
Step 2: Remove the protective cap and insert the needle through the rubber stopper of the bottle of Sterile Water (Figure A, a; See Figure C for illustration). Turn the bottle and syringe upside down, pull back the plunger until the liquid reaches the 0.5 mL mark on the syringe, and throw away the bottle containing the unused Sterile Water. (See Figure D)
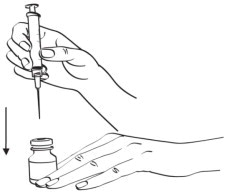
Figure C
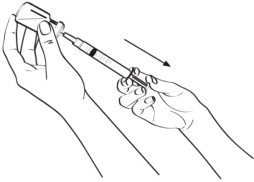
Figure D
Step 3: Take the syringe with needle attached out of the Sterile Water bottle and insert the needle into the EGRIFTA vial. Push the plunger in slowly on a slight angle so water goes down the inside wall of the EGRIFTA vial instead of directly onto the powder to avoid foaming. (See Figure E)
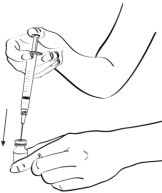
Figure E
Step 4: Take the needle out of the vial and throw away the syringe and needle. (See Figure F and see section How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, bottles and vials?)
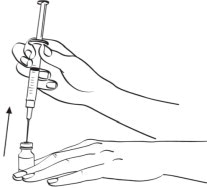
Figure F
Step 5: Roll the vial gently in your hands for 30 seconds, until the Sterile Water and EGRIFTA powder are mixed well. Do not shake the vial. (See Figure G)
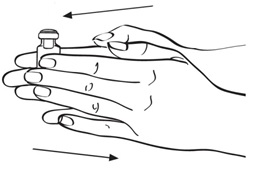
Figure G
Step 6: Place a new unused 1" 20-gauge needle used for mixing (Figure A, c), with its white protective cap in place, onto a a new unused syringe (Figure A, b). Hold the syringe firmly and twist the cap clockwise (to the right) until it closes securely. (See Figure H)

Figure H
Step 7: Remove the protective cap and insert the needle into the EGRIFTA vial (Figure A, a; see Figure I for illustration). Turn the bottle and syringe upside down, and pull down on the syringe until you see just the tip of the needle going through the rubber stopper, then pull back on the plunger until all the liquid inside the vial goes into the syringe. The level of medicine in the syringe should be around the 0.4 mL syringe mark. (See Figure J)
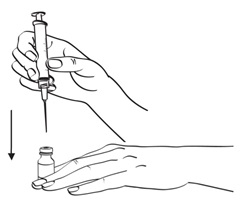
Figure I
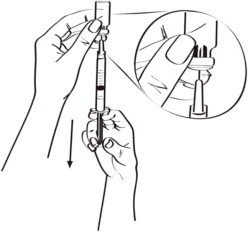
Figure J
Step 8: Take the needle out of the vial. (See Figure K)

Figure K
Step 9: Place the needle cap on its side against a clean flat surface. Without touching the needle, hold the syringe and slide the needle carefully into the protective cap (See Figure L). Push the cap all the way or until it snaps shut (See Figure M). Do not touch the cap until it covers the needle completely.
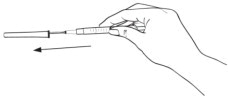
Figure L

Figure M
Step 10: With the cap on the needle, remove the needle by holding the syringe firmly and twisting the cap counterclockwise (to the left). (See Figure N)
Figure N
Step 11: Place a ½" 30-gauge needle used for injection (Figure A, d), with its white protective cap in place, onto the syringe. Hold the syringe firmly and twist the cap clockwise (to the right) until it closes securely. (See Figure O)
Figure O
Where do I inject EGRIFTA?
You should inject EGRIFTA into the skin on your belly (abdomen). (See Figure P)
- Pick an injection site that is around your belly button to the left or right.
- Stay away from any area with scar tissue, bruises, reddening, infection, or irritation.
- Avoid areas with any hard bumps from previous injections.
- Change your injection site around the belly button from one day to the next. This may help prevent bruising or irritation. You may want to keep a note of the date and location of each daily injection to help you remember.
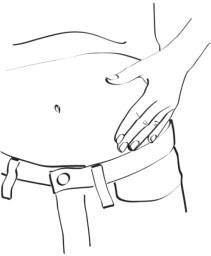
Figure P
How to inject EGRIFTA
- Pick up the syringe and pull the cap straight off the injection needle. Do not twist it. (See Figure Q)
Figure Q
- Tap the syringe gently with your finger to force any air bubbles to rise to the top. Press the plunger to push bubbles out and adjust the volume to the 0.35 mL mark. (See Figure R)
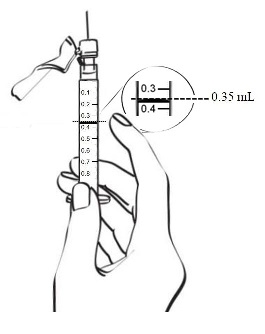
Figure R
- Clean the injection site you have selected with an alcohol pad and let it dry. Hold the syringe in one hand. Use your other hand to hold a cleaned fold of skin for your injection. Hold the skin between your thumb and fingers. (See Figure S)
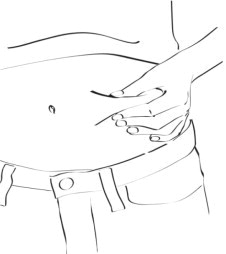
Figure S
- Hold the syringe at a right angle to the skin, like a dart. Push the injection needle into the skin with a quick motion. Most of the needle should go beneath the skin surface. (See Figure T)
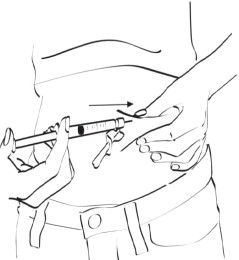
Figure T
- Remove your hand from the pinched area of skin after the needle goes in. Make sure the needle stays in the skin. (See Figure U)

Figure U
- Slowly push the plunger all the way down until all of the medicine in the syringe has been injected under the skin.
- Pull the injection needle out of your skin when the syringe is empty:
- Be careful to pull it out at the same angle you put it in.
- Flip back the pink needle shield until it snaps, covering the injection needle completely. Keep pressing until you hear a click, that means the injection needle is protected. (See Figure V)
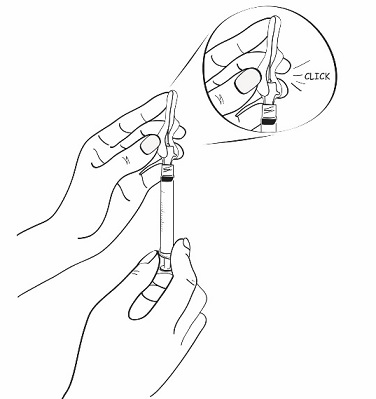
Figure V
- Use a piece of sterile gauze to rub the injection site clean. If there is bleeding, apply pressure to the injection site with gauze for 30 seconds. If bleeding continues, apply a bandage to the site.
How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, bottles and vials?
- Do not recap the needle or remove the needle from the syringe after you inject EGRIFTA.
- Put your used EGRIFTA needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and pens. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal .
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
- If you accidentally prick another person with a used needle, that person should be informed to contact a healthcare provider right away about the accident.
- Keep the sharps container away from children and pets.
|
If you have any questions, call your healthcare provider. You can call THERA patient supportTM toll-free 1-833-23THERA (1-833-238-4372) or visit the EGRIFTA® website at: www.EGRIFTA.com for more information. |
How do I store EGRIFTA 2 mg vial?
- EGRIFTA comes in two boxes given to you by the pharmacy:
- Store the Medication Box of 2 mg EGRIFTA vials at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store the Injection Box of Sterile Water for Injection, syringes and needles at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep EGRIFTA vials in the box and out of the light.
- After mixing, use EGRIFTA right away and throw away any unused EGRIFTA.
- Do not store, freeze or refrigerate EGRIFTA after it has been mixed with the sterile water.
- Throw away the used bottle of Sterile Water for Injection.
- Do not use EGRIFTA after the expiration date printed on the carton and vial labels.
General information about the safe and effective use of EGRIFTA.
Keep EGRIFTA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Thera
technologies
EGRIFTA® is a registered trademark of Theratechnologies Inc.
Distributed by: Theratechnologies Inc., Montréal, Québec, Canada H3A 1T8
Revised: 11/2018
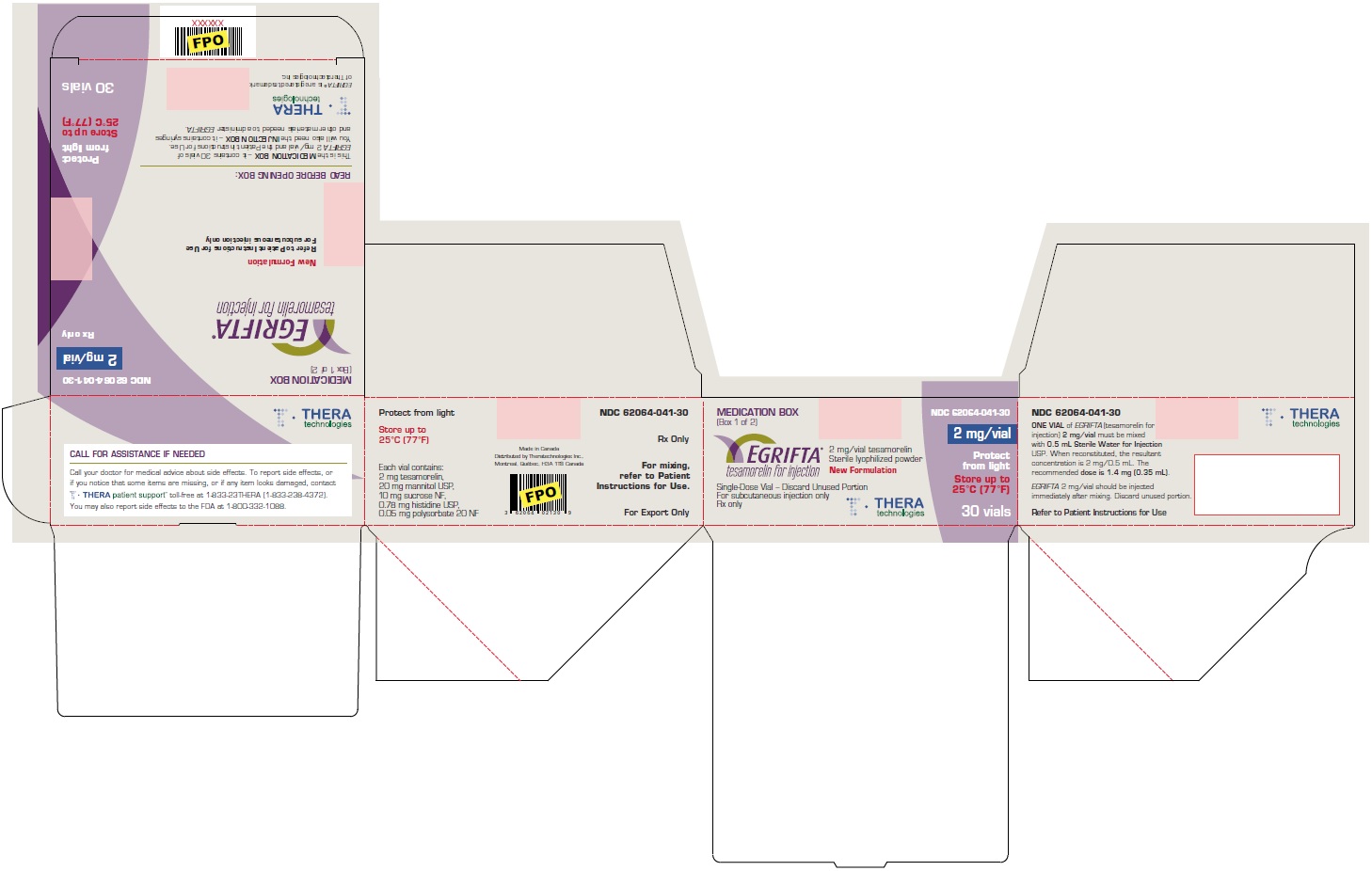
Principal Display Panel - 2 mg Box Label (New Formulation)
MEDICATION BOX
(Box 1 of 2)
NDC: 62064-041-30
2 mg/vial
Rx only
EGRIFTA®
tesamorelin for injection
New Formulation
Refer to Patient Instructions for Use
For subcutaneous injection only
READ BEFORE OPENING BOX:
This is the MEDICATION BOX – it contains 30 vials of
EGRIFTA 2 mg/vial and the patient Instructions for Use.
You will also need the INJECTION BOX – it contains syringes
and other materials needed to administer EGRIFTA.
Protect
from light
Store up to
25°C (77°F)
Theratechnologies
EGRIFTA® is a registered trademark
of Theratechnologies Inc.
30 vials
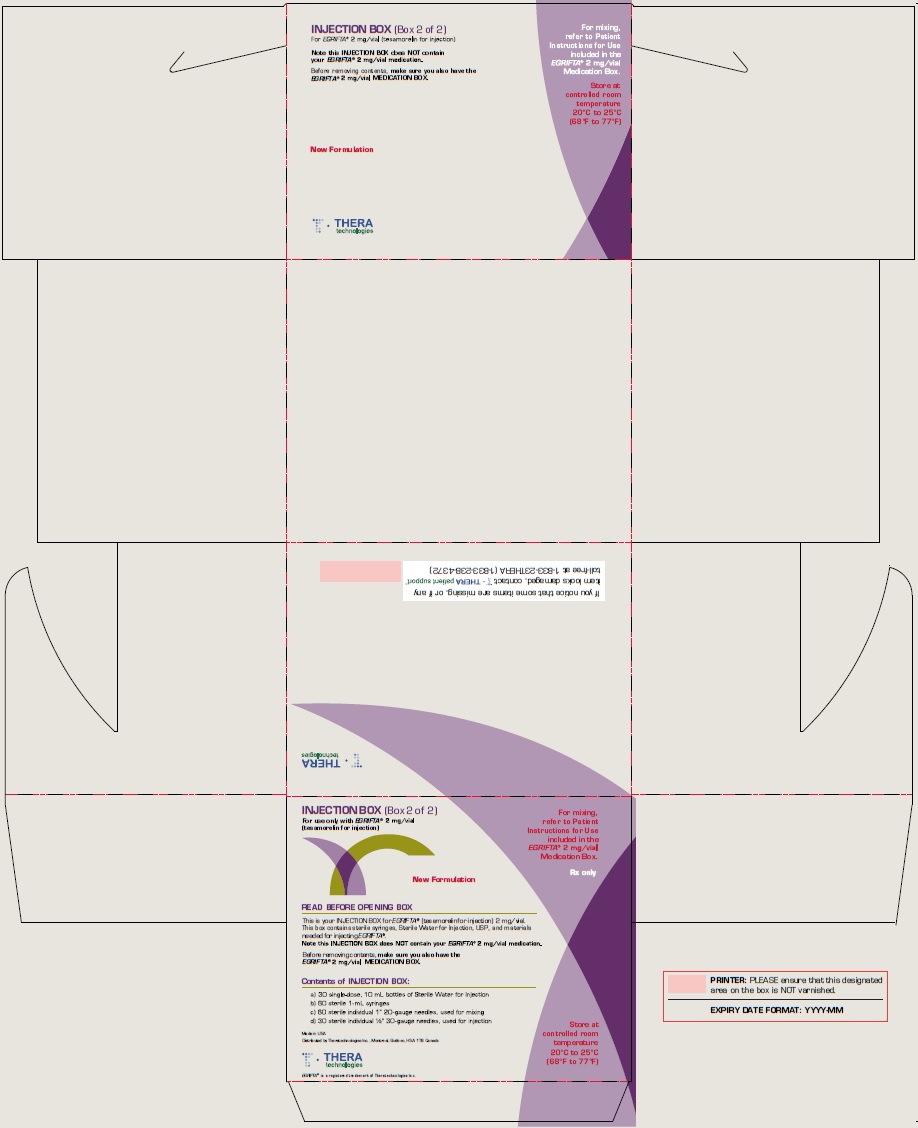
Principal Display Panel - 10 ml Bottles Box Label (New Formulation)
INJECTION BOX (Box 2 of 2)
For use only with EGRIFTA® 2 mg/vial
(tesamorelin for injection)
New Formulation
For mixing,
refer to Patient
Instructions for Use
included in the
EGRIFTA® 2 mg/vial
Medication Box.
Rx only
READ BEFORE OPENING BOX
This is your INJECTION BOX for EGRIFTA® (tesamorelin for injection) 2 mg/vial.
This box contains sterile syringes, Sterile Water for Injection USP, and materials
needed for injecting EGRIFTA®.
Note this INJECTION BOX does NOT contain your EGRIFTA® 2 mg/vial medication.
Before removing contents, make sure you also have the
EGRIFTA® 2 mg/vial MEDICATION BOX.
Contents of INJECTION BOX:
a) 30 single-dose, 10 mL bottles of Sterile Water for Injection
b) 60 sterile 1-mL syringes
c) 60 sterile individual 1" 20-gauge needles, used for mixing
d) 30 sterile individual ½" 30-gauge needles, used for injection
Store at
controlled room
temperature
20°C to 25°C
(68°F to 77°F)
Made in USA
Distributed by Theratechnologies Inc., Montréal, Québec, H3A 1T8, Canada
Theratechnologies
EGRIFTA® is a registered trademark of Theratechnologies Inc.
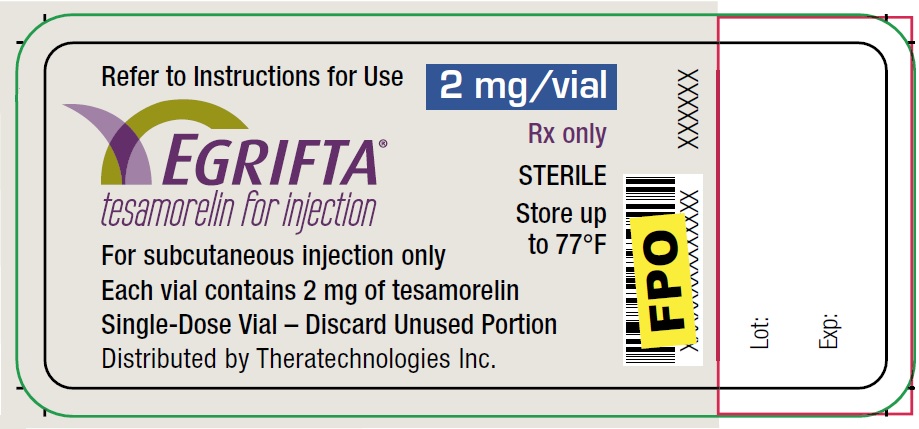
Principal Display Panel - 2 mg Vial Label (New Formulation)
Refer to Instructions for Use
2 mg/vial
EGRIFTA®
tesamorelin for injection
Rx only
STERILE
Store at
up to 77°F
For subcutaneous injection only
Each vial contains 2 mg of tesamorelin
Single-Dose Vial - Discard unused Portion
Distributed by Theratechnologies Inc.
| EGRIFTA
tesamorelin kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Theratechnologies Inc. (252017520) |