Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection
EXTENCILLINE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
EXTENCILLINE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Provepharm Inc., Haupt Pharma Latina Srl. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
EXTENCILLINE- benzathine benzylpenicillin
EXTENCILLINE- benzathine benzylpenicillin injection, powder, for suspension
Provepharm Inc.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
----------
Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection
HEALTH CARE PROVIDER LETTER
July 16, 2024
Laboratoires DELBERT
49 Rue Rouelle
75015 Paris
France
Phone : +33(0)1 46 99 68 20
https://laboratoires-delbert.fr/en/
IMPORTANT PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
|
Subject: Temporary Importation of Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection, 1,200,000 units and 2,400,000 units with Foreign, non-U.S. Labeling to Address Supply Shortage |
Dear Healthcare Provider,
To address the ongoing shortages of Bicillin® L-A (penicillin G benzathine injectable suspension) in the United States, Laboratoires Delbert in conjunction with Provepharm Inc. (Provepharm) through its distributors ("Distributors") coordinating with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to temporarily import Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection, 1,200,000 units and 2,400,000 units into the U.S. market. Delbert’s Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection, 1,200,000 units and 2,400,000 units marketed in France and manufactured in Italy for Delbert, is not FDA-approved. Benzathine benzylpenicillin is another name for Penicillin G benzathine.
At this time, no other entity except Provepharm or its Distributors McKesson Corporation, Cencora Global Procurement Ltd., Cardinal Health, Morris & Dickson, Anda Inc., Henry Schein, OptumRx and Direct Success Inc. are authorized by the FDA to import or distribute Extencilline powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection in the U.S.
Effective immediately, Provepharm will distribute the following presentations of Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection, 1,200,000 units and 2,400,000 units to address the critical shortage:
|
Product Description |
Strength |
Packaging |
NDC number |
Lot/ Batch # |
Expiration Date (Labeled) |
|
Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection 1,200,000 units |
1,200,000 units |
20 mL vials of powder for suspension |
81284-521-01 |
72L00127 |
31 OCT 2025 |
|
Extencilline, (benzathine benzylpenicillin) Powder and diluent for reconstitution for injection, 2,400,000 units |
2,400,000 units |
20 mL vials of powder for suspension |
81284-522-01 |
72L00122 |
31 OCT 2025 |
The barcode on the imported product label may not register accurately on the U.S. scanning systems. Institutions should manually input the imported product information into their systems and confirm that the barcode, if scanned, provides correct information. Alternative procedures should be followed to assure that the correct drug product is being used and administered to individual patients.
In addition, the packaging of the imported product does not include serialization information. Delbert’s Extencilline does not meet the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) requirements for the Interoperable Exchange of Information for Tracing of Human, Finished Prescription Drugs.
There are key differences between the U.S. marketed Bicillin® L-A and Extencilline
- Extencilline labeling does not have a boxed warning. Please refer to the Bicillin L-A boxed warning.
- Extencilline carton labeling doesn’t have the warning “Fatal if given by other routes”
- Extencilline contains soy phospholipids and may cause hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria, anaphylactic shock) in patients with a history of allergy to soybeans.
- Extencilline is supplied as powder for reconstitution compared to prefilled disposable syringes for Bicillin L-A. Follow instructions for the preparation of an intramuscular injection of Extencilline in the Preparation section below.
- The volume of Extencilline 1,200,000 units after reconstitution is around 5 mL compared to 2 mL for Bicillin L-A 1,200,000 units. The volume of Extencilline 2,400,000 units after reconstitution is around 7 mL compared to 4 mL for Bicillin L-A 2,400,000 units.
- Extencilline labeling does not include detailed instructions for deep intramuscular administration. Please refer to the Bicillin L-A prescribing information.
- Extencilline does not require any special storage condition. Following reconstitution, benzylpenicillin benzathine should be used immediately.
- Extencilline will be available only by prescription in the U.S. However, the imported product does not have the statement “Rx only” on the labeling
When using Extencilline from Delbert the following advice has to be taken into account:
Method of administration:
For further Information please refer to the full prescribing information enclosed.
Prescription and Labeling:
Extencilline will be available only by prescription in the U.S. However, the imported product does not have the statement “Rx only” on the labeling.
To place an order, please contact one of the authorized Distributors listed below:
- McKesson Corporation,
- Cencora Global Procurement Ltd., (fka Amerisource Bergen)
- Cardinal Health,
- Morris & Dickson
- Anda Inc.
- Henry Schein
- OptumRx
- Direct Success Inc.
Reporting Adverse Events:
Healthcare providers should report adverse events associated with the use of Delbert’s Extencilline to Provepharm at:
Phone: 1-833-727-6556
email: safety-us@provepharm.com
Adverse reactions or quality problems experienced with the use of this product may be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program either online, by regular mail or by fax.
- Complete and submit the report Online: www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm
- Regular Mail or Fax: Download form https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/medwatch/index.cfm or call 1-800-332-1088 to request a reporting form, then complete and return to the address on the pre-addressed form, or submit by fax to 1-800-FDA-0178 (1-800-332-0178).
You may also contact our medical information department at medicalaffairs@provepharm.com if you have any questions about the information contained in this letter or the safe and effective use of Extencilline.
This letter is not intended as a complete description of the benefits and risks related to the use of Extencilline. Please refer to the enclosed full prescribing information.
For additional information, please contact Provepharm Inc. at 610-601-8600 or at medicalaffairs@provepharm.com.
Finally, please ensure that your staff and others in your institution who may be involved in the administration of Extencilline receive a copy of this letter and review the information.
Sincerely,
Thierry HOFFMANN
Qualified Person
Side-by-Side Product Comparison of Bicillin L-A and Extencilline
|
US Product |
Imported Product |
||
|
Product Name |
Bicillin L-A |
Extencilline |
|
|
Dosage Form |
injectable suspension |
for injection |
|
|
Label |
|
| |
|
Composition |
Bicillin L-A contains penicillin G benzathine in aqueous suspension with sodium citrate buffer and, as w/v, approximately 0.65% sodium citrate, 0.59% povidone, 0.54% carboxymethylcellulose sodium, 0.53% lecithin, 0.12% methylparaben, and 0.013% propylparaben. Bicillin L-A contains approximately 0.11 mEq of sodium per 600,000 units of penicillin G (approximately 2.59 mg of sodium per 600,000 units of penicillin G). Bicillin L-A suspension in the disposable-syringe formulation is viscous and opaque. It is available in a 1 mL, 2 mL, and 4 mL sizes containing the equivalent of 600,000 (actual volume of 1.17 mL contains 620,100), 1,200,000 (actual volume of 2.34 mL contains 1,240,200), and 2,400,000 (actual volume of 4.67 mL contains 2,475,100) units respectively of penicillin G as the benzathine salt. |
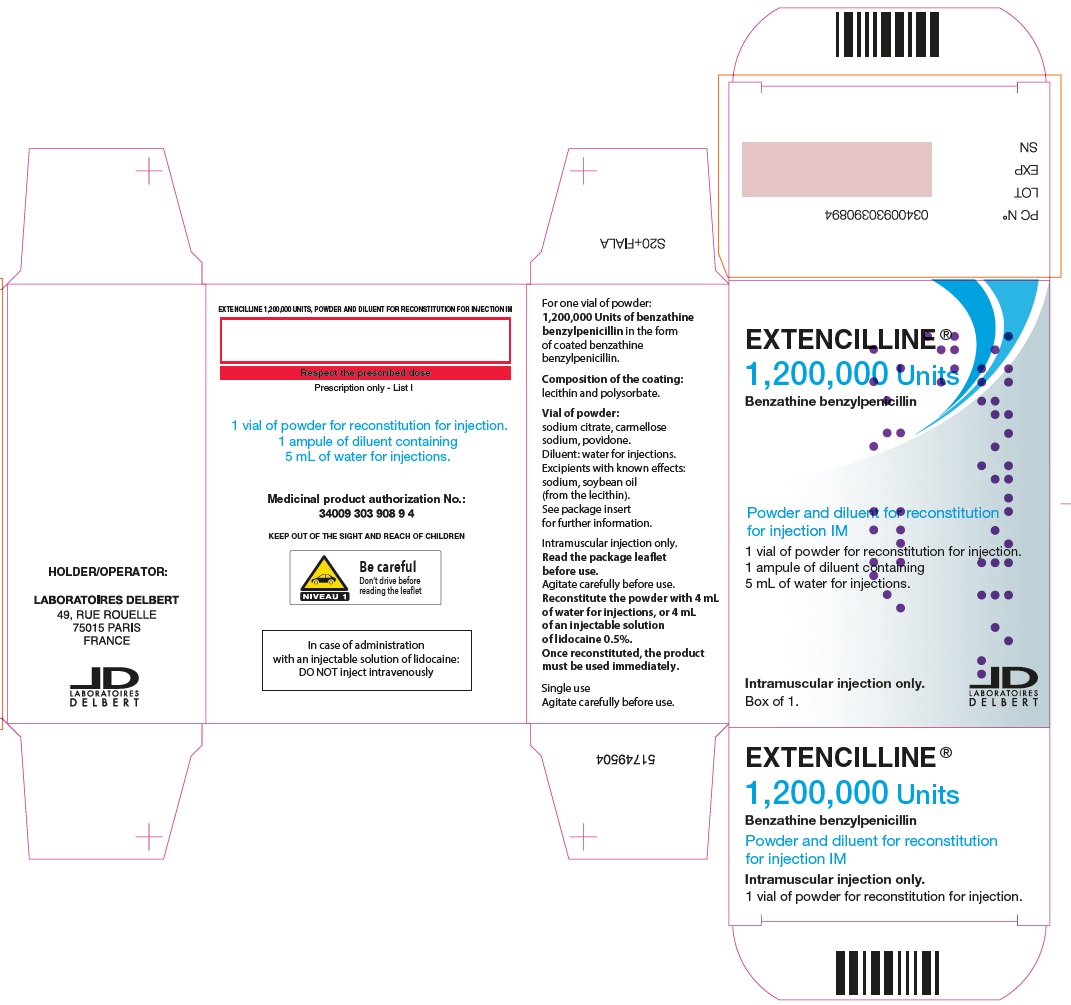
Vial: The active substance is Benzathine benzylpenicillin 1,200,000 units or 2,400,000 units In the form of coated benzathine benzylpenicillin Composition of the coating: lecithin and polysorbate. For one vial of powder The other excipient ingredients are: Carmellose sodium, anhydrous sodium citrate, povidone. This medicine contains sodium, soybean oil (from the lecithin). Diluent for reconstitution : 5 mL Water for injection |
|
|
Indications |
The following infections will usually respond to adequate dosage of intramuscular penicillin G benzathine: Mild-to-moderate infections of the upper-respiratory tract due to susceptible streptococci. Venereal infections—Syphilis, yaws, bejel, and pinta. Medical Conditions in which Penicillin G Benzathine Therapy is indicated as Prophylaxis: Rheumatic fever and/or chorea—Prophylaxis with penicillin G benzathine has proven effective in preventing recurrence of these conditions. It has also been used as follow-up prophylactic therapy for rheumatic heart disease and acute glomerulonephritis. |
Benzylpenicillin benzathine is indicated in adults, adolescents, children and neonates for the treatment and prophylaxis of the following infections For the treatment of: - erysipelas - syphilis: early syphilis (primary and secondary) - latent syphilis (except for neurosyphilis and presence of pathological CSF findings) - yaws - pinta For the prophylaxis of: - rheumatic fever (chorea, rheumatic carditis) - poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis - erysipelas |
|
|
Contraindications |
A history of a previous hypersensitivity reaction to any of the penicillins is a contraindication. |
Hypersensitivity to penicillins. - History of a severe immediate hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) to another beta-lactam agent (e.g. cephalosporin, carbapenem or monobactam). - When lidocaine solution is used as a diluent for reconstitution , contraindications to lidocaine must be excluded before intramuscular injection of benzylpenicillin benzathine. This medicine contains soy phospholipids and may cause hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria, anaphylactic shock). |
|
|
Precautions |
PRECAUTIONS: Prescribing Bicillin L-A in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of a development of drug-resistant bacteria. |
Benzylpenicillin benzathine should not be used in tissues with reduced perfusion. Before initiating therapy with benzylpenicillin benzathine, a careful investigation should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins or other beta-lactam agents. Caution should be exercised in patients with the following conditions: - allergic diathesis or bronchial asthma (there is an increased risk of a hypersensitivity reaction): - renal insufficiency - impaired hepatic function |
|
|
Interactions |
- Tetracycline, a bacteriostatic antibiotic, may antagonize the bactericidal effect of penicillin, and concurrent use of these drugs should be avoided. Concurrent administration of penicillin and probenecid increases and prolongs serum penicillin levels by decreasing the apparent volume of distribution and slowing the rate of excretion by competitively inhibiting renal tubular secretion of penicillin. |
Concomitant administration of benzylpenicillin benzathine is not recommended with: - bacteriostatic antibiotics: based on the general principle not to combine bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotics. Caution should be exercised when co-administering the following: - probenecid: the administration of probenecid leads to inhibition of the tubular secretion of benzylpenicillin, resulting in an increase in the serum concentration and prolongation of the elimination half-life. Furthermore, probenecid inhibits the penicillin transport from the cerebrospinal fluid, so that the concomitant administration of probenecid reduces the penetration of benzylpenicillin into brain tissue even further. - methotrexate: when taken at the same time as benzylpenicillin benzathine, the excretion of methotrexate is reduced. This can lead to increased methotrexate toxicity. The combination with methotrexate is not recommended. - anticoagulants: concomitant use with oral anticoagulants may increase the antivitamin K effect and the risk of bleeding. It is recommended that the International Normalized Ratio (INR) is monitored frequently and the posology of the antivitamin K drug adjusted accordingly, both during and after treatment with benzylpenicillin benzathine. |
|
|
Warnings |
NOT FOR INTRAVENOUS USE. DO NOT INJECT INTRAVENOUSLY OR ADMIX WITH OTHER INTRAVENOUS SOLUTIONS. THERE HAVE BEEN REPORTS OF INADVERTENT INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION OF PENICILLIN G BENZATHINE WHICH HAS BEEN ASSOCIATED WITH CARDIORESPIRATORY ARREST AND DEATH. Prior to administration of this drug, carefully read the WARNINGS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections of the labeling. Anaphylaxis SERIOUS AND OCCASIONALLY FATAL HYPERSENSITIVITY (ANAPHYLACTIC) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS ON PENICILLIN THERAPY. THESE REACTIONS ARE MORE LIKELY TO OCCUR IN INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY AND/OR A HISTORY OF SENSITIVITY TO MULTIPLE ALLERGENS. THERE HAVE BEEN REPORTS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY WHO HAVE EXPERIENCED SEVERE REACTIONS WHEN TREATED WITH CEPHALOSPORINS. BEFORE INITIATING THERAPY WITH BICILLIN L-A, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE CONCERNING PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO PENICILLINS, CEPHALOSPORINS, OR OTHER ALLERGENS. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION OCCURS, BICILLIN L-A SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AND APPROPRIATE THERAPY INSTITUTED. SERIOUS ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS REQUIRE IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE. OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS STEROIDS AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, INCLUDING INTUBATION, SHOULD ALSO BE ADMINISTERED AS INDICATED. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported in patients taking penicillin G (the active moiety in Bicillin L-A). When SCAR is suspected, Bicillin L-A should be discontinued immediately and an alternative treatment should be considered. Clostridioides difficile Associated Diarrhea Clostridioides difficile associated-diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Bicillin L-A, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile. C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. Method of Administration Do not inject into or near an artery or nerve. See administration instructions below. Injection into or near a nerve may result in permanent neurological damage. Inadvertent intravascular administration, including inadvertent direct intra-arterial injection or injection immediately adjacent to arteries, of Bicillin L-A and other penicillin preparations has resulted in severe neurovascular damage, including transverse myelitis with permanent paralysis, gangrene requiring amputation of digits and more proximal portions of extremities, and necrosis and sloughing at and surrounding the injection site consistent with the diagnosis of Nicolau syndrome. Such severe effects have been reported following injections into the buttock, thigh, and deltoid areas. Other serious complications of suspected intravascular administration which have been reported include immediate pallor, mottling, or cyanosis of the extremity both distal and proximal to the injection site, followed by bleb formation; severe edema requiring anterior and/or posterior compartment fasciotomy in the lower extremity. The above-described severe effects and complications have most often occurred in infants and small children. Prompt consultation with an appropriate specialist is indicated if any evidence of compromise of the blood supply occurs at, proximal to, or distal to the site of injection.1–9 (See PRECAUTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections.) FOR DEEP INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION ONLY. There have been reports of inadvertent intravenous administration of penicillin G benzathine which has been associated with cardiorespiratory arrest and death. Therefore, do not inject intravenously or admix with other intravenous solutions. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.) Administer by DEEP INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION ONLY in the upper, outer quadrant of the buttock (dorsogluteal) or the ventrogluteal site. Quadriceps femoris fibrosis and atrophy have been reported following repeated intramuscular injections of penicillin preparations into the anterolateral thigh. Because of these adverse effects and the vascularity of this region, administration in the anterolateral thigh is not recommended. |
Benzylpenicillin benzathine should not be used in tissues with reduced perfusion. Before initiating therapy with benzylpenicillin benzathine, a careful investigation should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins or other beta-lactam agent. Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity and in atopic individuals. If an allergic reaction occurs, benzylpenicillin benzathine must be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Prior to treatment, a hypersensitivity test should be performed if possible. The patient should be made aware of the possible occurrence of allergic symptoms and of the need to report them. Caution should be exercised in patients with the following conditions: - allergic diathesis or bronchial asthma (there is an increased risk of a hypersensitivity reaction): - renal insufficiency - impaired hepatic function Based on a general principle, particularly in some exposed patients, medical observation should if possible be ensured for at last half an hour after the administration of this antibiotic, as severe immediate allergic reactions may occur even after the first administration. Beta-lactams are associated with a risk of encephalopathy (confusion, altered levels of consciousness, epilepsy or movement abnormalities), particularly in cases of overdose or impaired renal function. When treating syphilis, a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may occur as a result of the bactericidal action of penicillin on pathogens. Within 2 to 12 hours after administration headaches, fever, sweating, shivering, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, tachycardia, increased blood pressure followed by hypotension may occur. These symptoms resolve after 10 to 12 hours. Patients should be informed that this is a usual, transient sequela of antibiotic therapy. Appropriate therapy should be instituted to suppress or attenuate a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. With long-term treatment (more than a single dose), periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic and haematopoietic function is recommended. Prolonged use of benzylpenicillin benzathine may occasionally result in an overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms or yeast and patients should be observed carefully for superinfections. Antibiotic-associated colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents including benzylpenicillin benzathine and may range in severity from mild to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea during or subsequent to the administration of any antibiotics. Should antibiotic-associated colitis occur, benzylpenicillin benzathine should be discontinued, a physician be consulted, and an appropriate therapy initiated. Anti-peristaltic drugs are contraindicated in this situation. If neurological involvement cannot be excluded in patients with congenital syphilis, forms of penicillin that reach a higher level in cerebrospinal fluid should be used. In diseases such as severe pneumonia, empyema, sepsis, meningitis or peritonitis, which require higher serum penicillin levels, alternative treatment such as the water soluble alkali salt of benzylpenicillin should be considered. In the event of inadvertent intravascular injection, Hoigné syndrome may occur (symptoms of shock with mortal fear, confusion, hallucinations, possibly cyanosis, tachycardia and motor disorders, although no circulatory collapse), caused by microemboli of the suspension. The symptoms regress within an hour. If progression is severe, parenteral administration of sedatives is indicated. In the event of inadvertent intra-arterial injection, particularly in children, serious complications may occur, such as vascular occlusion, thrombosis and gangrene. Initial signs are pale patches in the skin area of the gluteal region. As a result of high injection pressure, retrograde entry of the injected liquid into the common iliac artery, aorta or spinal arteries may occur. Repeated injections into a limited area of the muscle tissue, which are associated with long term therapy with depot-penicillins (e.g. in the treatment of syphilis) may induce tissue damage and increased local vascularization. Subsequent injections increase the possibility of penetration of injection substance into the blood, either by direct injection into a blood vessel or caused by the injection pressure itself, or by “rubbing” of the depot. During long term therapy it is therefore recommended to administer each injection a large distance from the preceding injection. |
|
|
Dosage and Administration |
Streptococcal (Group A) Upper Respiratory Infections (for example, pharyngitis) Adults—a single injection of 1,200,000 units; older pediatric patients—a single injection of 900,000 units; infants and pediatric patients under 60 lbs.—300,000 to 600,000 units. Syphilis Primary, secondary, and latent—2,400,000 units (1 dose). Late (tertiary and neurosyphilis)—2,400,000 units at 7-day intervals for three doses. Congenital—under 2 years of age: 50,000 units/kg/body weight; ages 2 to 12 years: adjust dosage based on adult dosage schedule. Yaws, Bejel, and Pinta—1,200,000 units (1 injection). Prophylaxis—for rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis. Following an acute attack, penicillin G benzathine (parenteral) may be given in doses of 1,200,000 units once a month or 600,000 units every 2 weeks. METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION BICILLIN L-A IS INTENDED FOR INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION ONLY. DO NOT INJECT INTO OR NEAR AN ARTERY OR NERVE, OR INTRAVENOUSLY OR ADMIX WITH OTHER INTRAVENOUS SOLUTIONS. (SEE WARNINGS SECTION.) Administer by DEEP INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION in the upper, outer quadrant of the buttock (dorsogluteal) or the ventrogluteal site. In neonates, infants and small children, the midlateral aspect of the thigh may be preferable. Administration in the anterolateral thigh is not recommended due to the adverse effects observed (see WARNINGS section), and vascularity of this region. When doses are repeated, vary the injection site. Because of the high concentration of suspended material in this product, the needle may be blocked if the injection is not made at a slow, steady rate. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. |
The preparation is strictly for intramuscular injection. 1.General therapy: - Adults and adolescents: 1,200,000 units - Children (> 30 kg body weight): 1,200.000 units. - Children (< 30 kg body weight): 600,000 units Duration of treatment: Single dose Note: In streptococcal diseases, a 10-day minimum course of treatment should be observed to avoid secondary diseases. This is generally ensured with a single injection of 600,000 units, 1,200,000 units or 2,400,000 units. 2. Treatment of syphilis: 2.1. Primary and secondary stage - Adults and adolescents: 2,400,000 units - Children: 50,000 units per kg body weight; however not more than 2,400,000 units. Duration of treatment: Single dose (If clinical symptoms recur or laboratory findings remain strongly positive, treatment should be repeated.) 2.2.Late-stage syphilis (latent seropositive syphilis) - Adults and adolescents: 2,400,000 units - Children: 50,000 units per kg body weight per week; however not more than 2,400,000 units. Duration of treatment: Once weekly for 3 weeks 2.3.Treatment of congenital syphilis (without neurological involvement) - Neonates and infants: 50,000 units per kg body weight Duration of treatment: Single dose 3. Treatment of yaws and pinta: - Adults and adolescents: 1,200,000 units. - Children (> 30 kg body weight): 1,200,000 units - Children (< 30 kg body weight): 600,000 units. Duration of treatment: Single dose 4. Prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis and erysipelas: - Adults and adolescents:1,200,000 units - Children (> 30 kg body weight): 1,200,000 units - Children (< 30 kg body weight): 600,000 units Duration of treatment: a) without cardiac involvement: at least 5 years (or up to 21 years of age) every 3-4 weeks b) transient cardiac involvement: at least 10 years (or up to 21 years of age) every 3-4 weeks c) persistent cardiac involvement: at least 10 years (or up to 40 years of age) every 3-4 weeks; life-long prophylaxis is sometimes necessary. |
|
|
Preparation |
Instructions for the preparation of an intramuscular injection of a dose of 1,200,000 units of benzathine benzylpenicillin: The suspension must be prepared aseptically. 1/ With a graduated syringe for intramuscular injection (needle gauge: 22, 21 or 20), take 4 mL of water for injections from the ampule of diluent contained in the box. The compatibility data are only available with water for injectable preparations and 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution. Warning: the ampule of diluent provided in the box contains 5 mL of water for injections. It is not necessary to use all the contents for the preparation of this suspension. 2/ Into the vial of powder of 1,200,000 units, add the 4 mL of water for injections taken from the ampule of diluent, or the 4 mL of 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution. 3/ Agitate this suspension carefully for at least 20 seconds until a homogenous suspension is obtained, then use the suspension immediately as soon as it is prepared. The suspension obtained in this way corresponds to a dose of 1,200,000 units. This reconstitution must only be done for one single injection. For doses of Extencilline less than 1,200,000 units, withdraw the appropriate volume of the reconstituted product and discard the remainder. For example, withdraw half the volume of the reconstituted 1,200,000 units for a 600,000 units dose of Extencilline. Instructions for the preparation of an intramuscular injection of a dose of 2,400,000 units of benzathine benzylpenicillin: The suspension must be prepared aseptically. 1/ With a graduated syringe for intramuscular injection (needle gauge: 22, 21 or 20), take 5 mL of water for injections from the ampule of diluent contained in the box, or 5 mL of 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution. 2/ Into the vial of powder 2,400,000 units, add the 5 mL of water for injections taken from the ampule of diluent, or 5 mL of 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution. 3/ Agitate this for suspension carefully for at least 20 seconds until a homogenous for suspension is obtained, then use the for suspension immediately as soon as it is prepared. The suspension obtained in this way corresponds to a dose of 2,400,000 units. This reconstitution must only be done for one single injection. For doses of Extencilline less than 2,400,000 units, withdraw the appropriate volume of the reconstituted product and discard the remainder. |
||
|
Overdosage |
Penicillin in overdosage has the potential to cause neuromuscular hyperirritability or convulsive seizures. |
At extremely high doses, penicillins can induce neuromuscular excitability or epileptiform seizures. If overdose is suspected, clinical monitoring and symptomatic measures are indicated. Beta-lactams pose a risk of encephalopathy (confusion, impaired consciousness, epilepsy, or abnormal movements) and, particularly, in the event of overdose or renal failure. At extremely high doses, penicillins can induce neuromuscular excitability or epileptiform seizures. If overdose is suspected, clinical monitoring and symptomatic measures are indicated. Benzylpenicillin can be hemodialyzed. |
|
|
Adverse Reactions |
As with other penicillins, untoward reactions of the sensitivity phenomena are likely to occur, particularly in individuals who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to penicillins or in those with a history of allergy, asthma, hay fever, or urticaria. As with other treatments for syphilis, the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction has been reported. The following adverse reactions have been reported with Bicillin L-A during post-marketing experience: Skin and Appendages: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). (See WARNINGS) The following have been reported with parenteral penicillin G (the active moiety in Bicillin L-A): General: Hypersensitivity reactions including the following: skin eruptions (maculopapular to exfoliative dermatitis), urticaria, laryngeal edema, fever, eosinophilia; other serum sickness-like reactions (including chills, fever, edema, arthralgia, and prostration); and anaphylaxis including shock and death: severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). (See WARNINGS.) Note: Urticaria, other skin rashes, and serum sickness-like reactions may be controlled with antihistamines and, if necessary, systemic corticosteroids. Whenever such reactions occur, penicillin G should be discontinued unless, in the opinion of the physician, the condition being treated is life-threatening and amenable only to therapy with penicillin G. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should also be administered as indicated. Gastrointestinal: Pseudomembranous colitis. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment. (See WARNINGS section.) Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Neurologic: Neuropathy. Urogenital: Nephropathy. The following adverse events have been temporally associated with parenteral administration of penicillin G benzathine (a component of Bicillin L-A): Body as a Whole: Hypersensitivity reactions including allergic vasculitis, pruritus, fatigue, asthenia, and pain; aggravation of existing disorder; headache, Nicolau syndrome. Cardiovascular: Cardiac arrest; hypotension; tachycardia; palpitations; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary embolism; vasodilation; vasovagal reaction; cerebrovascular accident; syncope. Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting; blood in stool; intestinal necrosis. Hemic and Lymphatic: Lymphadenopathy. Injection Site: Injection site reactions including pain, inflammation, lump, abscess, necrosis, edema, hemorrhage, cellulitis, hypersensitivity, atrophy, ecchymosis, and skin ulcer. Neurovascular reactions including warmth, vasospasm, pallor, mottling, gangrene, numbness of the extremities, cyanosis of the extremities, and neurovascular damage. Metabolic: Elevated BUN, creatinine, and SGOT. Musculoskeletal: Joint disorder; periostitis; exacerbation of arthritis; myoglobinuria; rhabdomyolysis. Nervous System: Nervousness; tremors; dizziness; somnolence; confusion; anxiety; euphoria; transverse myelitis; seizures; coma. A syndrome manifested by a variety of CNS symptoms such as severe agitation with confusion, visual and auditory hallucinations, and a fear of impending death (Hoigne's syndrome), has been reported after administration of penicillin G procaine and, less commonly, after injection of the combination of penicillin G benzathine and penicillin G procaine. Other symptoms associated with this syndrome, such as psychosis, seizures, dizziness, tinnitus, cyanosis, palpitations, tachycardia, and/or abnormal perception in taste, also may occur. Respiratory: Hypoxia; apnea; dyspnea. Skin: Diaphoresis. Special Senses: Blurred vision; blindness. Urogenital: Neurogenic bladder; hematuria; proteinuria; renal failure; impotence; priapism. |
The most frequent and common adverse reactions related to benzylpenicillin benzathine are: candidiasis, diarrhea, nausea, laboratory investigation changes. Description of selected adverse reactions When treating syphilis, a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may occur as a result of bacteriolysis, characterized by fever, chills, general and focal symptoms. In patients with dermatomycosis, para-allergic reactions may occur, as common antigenicity may exist between penicillins and dermatophyte metabolites. In infants, local reactions are possible. It cannot be excluded that, in very rare cases and due to the povidone content, povidone may accumulate in the reticuloendothelial system (RES) or local deposits and foreign body granuloma may occur, which may be confused with tumors. |
|
|
Usage in pregnancy |
Safe use in pregnancy and lactation has not been established; therefore, use in pregnant women, nursing mothers or women who may become pregnant requires that possible benefits be weighed against possible hazards to mother and child. |
Benzylpenicillin benzathine crosses the placenta. 10-30% of maternal plasma concentrations are found in the foetal circulation. High concentrations are also reached in the amniotic fluid. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. Benzylpenicillin benzathine can be used during pregnancy when appropriately indicated and with due consideration of the benefits and risks. Breast-feeding Benzylpenicillin benzathine is excreted in human milk in small amounts. The concentration in maternal milk may reach 2 to 15% of the mother’s serum concentrations. Although no undesirable effects in infants fed on breast milk have been reported to date, consideration must nevertheless be given to the possibility of sensitization or interference with the intestinal flora. Breast-feeding should be stopped in the case of occurrence of diarrhea, candidosis or rash in the child. In infants also being fed on baby food, mothers should express and discard breast milk during benzylpenicillin benzathine treatment. Breast-feeding can be resumed 24 hours after finishing treatment. |
|
|
Storage Conditions |
Store in a refrigerator, 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F). Keep from freezing. |
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions. Following reconstitution, benzylpenicillin benzathine should be used immediately. |
|
|
How Supplied |
2 mL size, containing 1,200,000 units per syringe, (21 gauge, thin-wall 1-1/2-inch needle), with 0.22 mEq of sodium per 1,200,000 units of penicillin G (5.17 mg of sodium per 1,200,000 units of penicillin G), NDC: 60793-701-10. 4 mL size, containing 2,400,000 units per syringe (18 gauge, × 1–1/2-inch needle), with 0.45 mEq of sodium per 2,400,000 units of penicillin G (10.32 mg of sodium per 2,400,000 units of penicillin G), NDC: 60793-702-10. |
1 vial and 1 glass ampule of diluent for reconstitution |
Instruction on how to prepare and administer Extencilline
Instructions for the preparation of an intramuscular injection of a dose of 1,200,000 units of benzathine benzylpenicillin:
The suspension must be prepared aseptically.
1/ With a graduated syringe for intramuscular injection (needle gauge: 22, 21 or 20), take 4 mL of water for injections from the ampule of diluent contained in the box. The compatibility data are only available with water for injectable preparations and 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution. Warning: the ampule of diluent provided in the box contains 5 mL of water for injections. It is not necessary to use all the contents for the preparation of this suspension.
2/ Into the vial of powder of 1,200,000 units, add the 4 mL of water for injections taken from the ampule of diluent, or the 4 mL of 1.0% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution.
3/ Agitate this suspension carefully for at least 20 seconds until a homogenous suspension is obtained, then use the suspension immediately as soon as it is prepared. The suspension obtained in this way corresponds to a dose of 1,200,000 units.
This reconstitution must only be done for one single injection.
For doses of Extencilline less than 1,200,000 units, withdraw the appropriate volume of the reconstituted product and discard the remainder. For example, withdraw half the volume of the reconstituted 1,200,000 units for a 600,000 units dose of Extencilline.
Instructions for the preparation of an intramuscular injection of a dose of 2,400,000 units of benzathine benzylpenicillin:
The suspension must be prepared aseptically.
1/ With a graduated syringe for intramuscular injection (needle gauge: 22, 21 or 20), take 5 mL of water for injections from the ampule of diluent contained in the box, or 5 mL of 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution.
2/ Into the vial of powder 2,400,000 units, add the 5 mL of water for injections taken from the ampule of diluent, or 5 mL of 1% or 0.5% lidocaine injectable solution.
3/ Agitate this for suspension carefully for at least 20 seconds until a homogenous for suspension is obtained, then use the for suspension immediately as soon as it is prepared. The suspension obtained in this way corresponds to a dose of 2,400,000 units.
This reconstitution must only be done for one single injection.
For doses of Extencilline less than 2,400,000 units, withdraw the appropriate volume of the reconstituted product and discard the remainder.
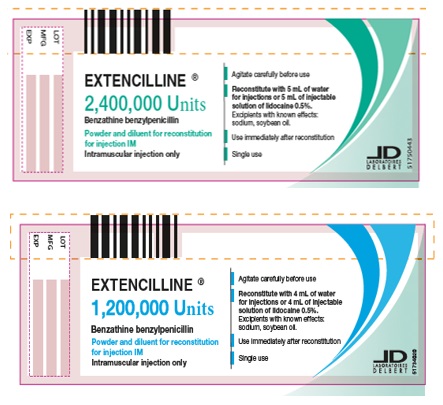
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1,200,000 Units Carton
EXTENCILLINE®
1,200,000 Units
Benzathine benzylpenicillin
Powder and diluent for reconstitution
for injection IM
1 vial of powder for reconsitution for injection.
1 ampule of diluent containing
5 mL of water for injections.
Intramuscular injection only.
Box of 1.
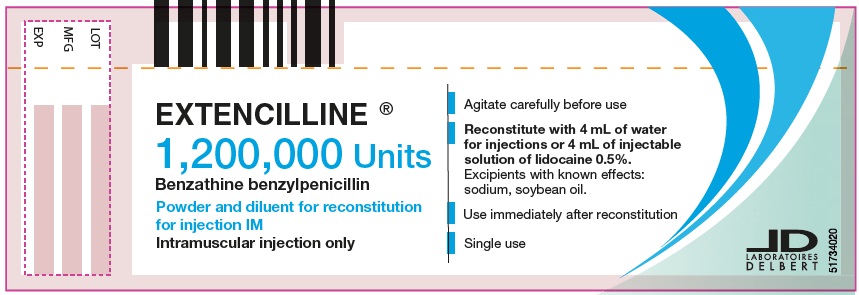
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1,200,000 Units Vial
EXTENCILLINE®
1,200,000 Units
Benzathine benzylpenicillin
Powder and diluent for reconstitution
for injection IM
Intramuscular injection only
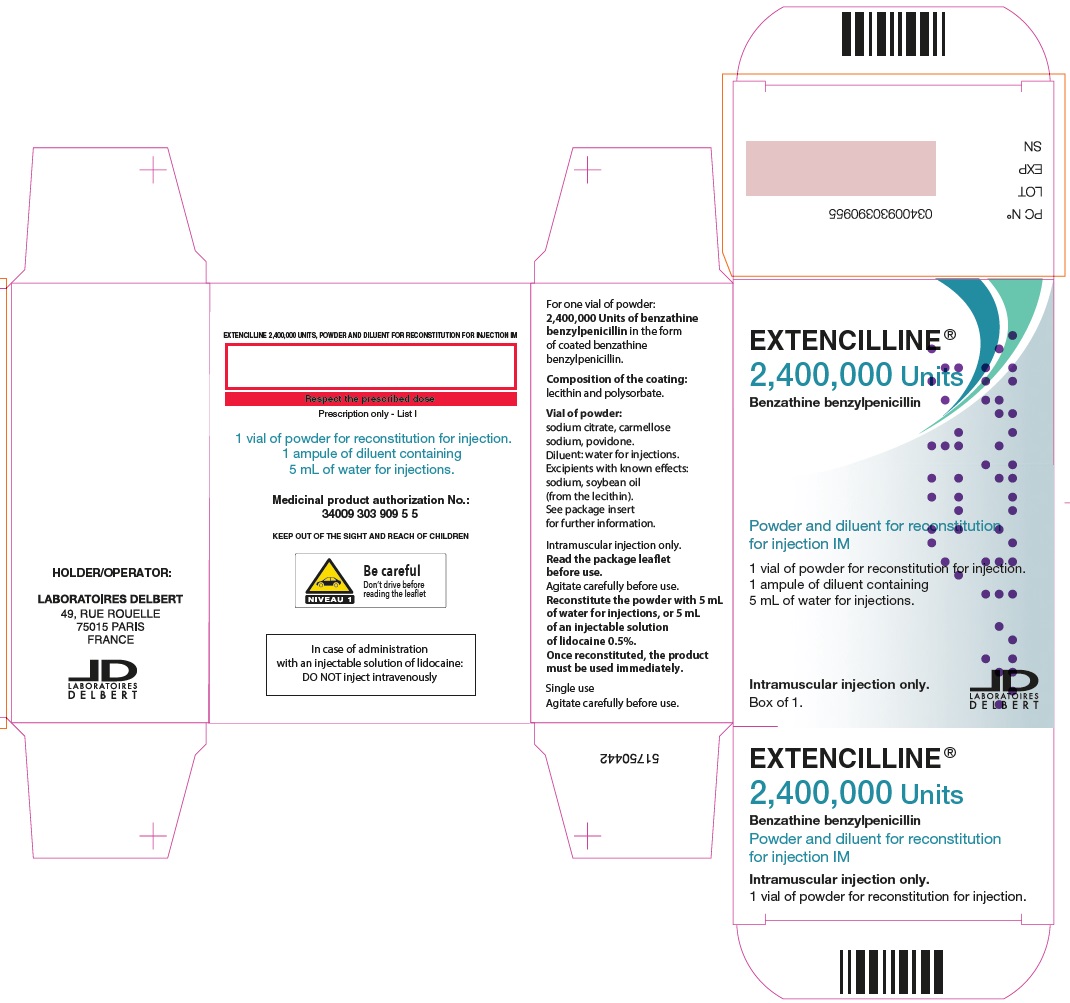
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2,400,000 Units Carton
EXTENCILLINE®
2,400,000 Units
Benzathine benzylpenicillin
Powder and diluent for reconstitution
for injection IM
1 vial of powder for reconsitution for injection.
1 ampule of diluent containing
5 mL of water for injections.
Intramuscular injection only.
Box of 1.
| EXTENCILLINE
benzathine benzylpenicillin kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| EXTENCILLINE
benzathine benzylpenicillin kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| EXTENCILLINE
benzathine benzylpenicillin injection, powder, for suspension |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| EXTENCILLINE
benzathine benzylpenicillin injection, powder, for suspension |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Provepharm Inc. (086861066) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haupt Pharma Latina Srl | 338690598 | manufacture(81284-521, 81284-523, 81284-735, 81284-522, 81284-524) | |
Trademark Results [EXTENCILLINE]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 EXTENCILLINE 79352711 not registered Live/Pending |
CHIWA PHARMA 2022-09-16 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.