PICATO- ingenol mebutate gel
Picato by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Picato by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by LEO Pharma Inc., LEO Laboratories Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PICATO gel safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PICATO gel.
PICATO® (ingenol mebutate) gel, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Picato gel is an inducer of cell death indicated for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For application of up to one contiguous skin area of approximately 25 cm2 (5 cm × 5 cm) using one unit dose tube. (2)
- Actinic keratosis on the face or scalp: Apply Picato gel, 0.015% to the affected area once daily for 3 consecutive days. (2)
- Actinic keratosis on the trunk or extremities: Apply Picato gel, 0.05% to the affected area once daily for 2 consecutive days. (2)
- Avoid transfer of Picato gel to periocular area. (2)
- Avoid application near and around the mouth and lips. (2)
- For topical use only; not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Gel, 0.015% or 0.05% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to ingenol mebutate or any component of the formulation. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions. Eye disorders, including severe eye pain, chemical conjunctivitis, corneal burn, eyelid edema, eyelid ptosis, periorbital edema can occur after exposure. Avoid accidental transfer of the drug into the eyes and to the periocular area. If accidental exposure occurs, flush eyes with water and seek medical care. (5.1)
Local Skin Reactions. Local skin reactions can occur including severe reactions (e.g., vesiculation/pustulation, erosion/ulceration). Administration of Picato gel is not recommended until skin is healed from any previous drug or surgical treatment. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥2 %) are local skin reactions, application site pain, application site pruritus, application site irritation, application site infection, periorbital edema, nasopharyngitis and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact LEO Pharma Inc. at 1-877-494-4536 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.3 Local Skin Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis of the Face and Scalp
14.2 Actinic Keratosis of the Trunk and Extremities
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For the treatment of actinic keratosis on the face or scalp Picato gel, 0.015% should be applied to the affected area once daily for 3 consecutive days.
For the treatment of actinic keratosis on the trunk or extremities Picato gel, 0.05% should be applied to the affected area once daily for 2 consecutive days.
Picato gel may be applied to the affected area, up to one contiguous skin area of approximately 25 cm2 (e.g., 5 cm × 5 cm) using one unit dose tube. After spreading evenly over the treatment area, the gel should be allowed to dry for 15 minutes. Patients should wash their hands immediately after applying Picato gel and take care not to transfer the applied drug to other areas, including the eye. Patients should avoid washing and touching the treated area for a period of 6 hours after application of Picato gel. Following this time, patients may wash the area with a mild soap.
Avoid transfer of Picato gel to periocular area [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Avoid application near and around the mouth and lips.
For topical use only; not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Picato gel is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to ingenol mebutate or any component of the formulation. Anaphylaxis, as well as allergic reactions leading to hospitalization have been reported in postmarketing use with Picato gel [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Eye disorders, including severe eye pain, chemical conjunctivitis, corneal burn, eyelid edema, eyelid ptosis, periorbital edema can occur after exposure [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
To avoid transfer of the drug into the eyes and to the periocular area during and after application, patients should wash hands well after applying Picato gel. If accidental exposure occurs, the area should be flushed with water and the patient should seek medical care as soon as possible.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and allergic contact dermatitis, have been reported postmarketing [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. If anaphylactic or other clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Picato gel immediately and institute appropriate medical therapy.
5.3 Local Skin Reactions
Severe skin reactions in the treated area, including erythema, crusting, swelling, vesiculation/pustulation, and erosion/ulceration, can occur after topical application of Picato gel [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Administration of Picato gel is not recommended until the skin is healed from any previous drug or surgical treatment.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Ophthalmic Adverse Reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to Picato® gel in 499 subjects with actinic keratosis, including 274 subjects exposed to Picato gel field treatment (skin area of 25 cm2 in the face or scalp regions) at a concentration of 0.015% once daily for 3 consecutive days, and 225 subjects exposed to Picato gel field treatment (skin area of 25 cm2 in the trunk or extremities regions) at a concentration of 0.05% once daily for 2 consecutive days.
Local skin reactions, including erythema, flaking/scaling, crusting, swelling, vesiculation/pustulation, and erosion/ulceration were assessed within the selected treatment area and graded by the investigator on a scale of 0 to 4. A grade of 0 represented no reaction present in the treated area, and a grade of 4 indicated a marked and severe skin reaction that extended beyond the treated area.
Table 1. Investigator Assessment of Maximal Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area during the 57 Days Post Treatment Period (face/scalp trials) Face and Scalp
(n=545)
Picato gel, 0.015% once daily for 3 daysSkin reactions Any Grade* > Baseline Grade 4 Picato gel
(n=274)Vehicle
(n=271)Picato gel
(n=274)Vehicle
(n=271)- * Mild (grade 1), Moderate (grade 2-3) or Severe (grade 4).
Erythema 258 (94%) 69 (25%) 66 (24%) 0 (0%) Flaking/Scaling 233 (85%) 67 (25%) 25 (9%) 0 (0%) Crusting 220 (80%) 46 (17%) 16 (6%) 0 (0%) Swelling 217 (79%) 11 (4%) 14 (5%) 0 (0%) Vesiculation/Pustulation 154 (56%) 1 (0%) 15 (5%) 0 (0%) Erosion/Ulceration 87 (32%) 3 (1%) 1 (0%) 0 (0%) Table 2. Investigator Assessment of Maximal Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area during the 57 Days Post Treatment Period (trunk/extremities trials) Trunk and Extremities
(n=457)
Picato® gel, 0.05% once daily for 2 daysSkin reactions Any Grade* > Baseline Grade 4 Picato gel
(n=225)Vehicle
(n=232)Picato gel
(n=225)Vehicle
(n=232)- * Mild (grade 1), Moderate (grade 2-3) or Severe (grade 4).
Erythema 207 (92%) 43 (19%) 34 (15%) 0 (0%) Flaking/Scaling 203 (90%) 44 (19%) 18 (8%) 0 (0%) Crusting 167 (74%) 23 (10%) 8 (4%) 0 (0%) Swelling 143 (64%) 13 (6%) 7 (3%) 0 (0%) Vesiculation/Pustulation 98 (44%) 2 (1%) 3 (1%) 0 (0%) Erosion/Ulceration 58 (26%) 6 (3%) 2 (1%) 0 (0%) Local skin reactions typically occurred within 1 day of treatment initiation, peaked in intensity up to 1 week following completion of treatment, and resolved within 2 weeks for areas treated on the face and scalp, and within 4 weeks for areas treated on the trunk and extremities.
Adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of subjects treated with Picato gel and at a higher frequency than the vehicle are presented in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3. Adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% of subjects treated with Picato gel and at higher frequency than vehicle (face/scalp trials) Face/Scalp Adverse Reactions Picato gel, 0.015%
(N=274)Vehicle
(N=271)Application Site Pain 42 (15%) 1 (0%) Application Site Pruritus 22 (8%) 3 (1%) Application Site Infection 7 (3%) 0 (0%) Periorbital Edema 7 (3%) 0 (0%) Headache 6 (2%) 3 (1%) Table 4. Adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% of subjects treated with Picato® gel and at higher frequency than vehicle (trunk/extremities trials) Trunk/Extremities Adverse Reactions Picato gel, 0.05%
(N=225)Vehicle
(N=232)Application Site Pruritus 18 (8%) 0 (0%) Application Site Irritation 8 (4%) 1 (0%) Nasopharyngitis 4 (2%) 2 (1%) Application Site Pain 5 (2%) 0 (0%) Less common adverse reactions in subjects treated with Picato gel included: eyelid edema, eye pain, conjunctivitis.
A total of 108 subjects treated with Picato gel on the face/scalp and 38 subjects treated on the trunk/extremities were followed for 12 months. Results from these studies did not change the safety profile of Picato gel.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Picato (ingenol mebutate) gel, 0.015% and 0.05%: hypersensitivity, allergic contact dermatitis, application site pigmentation changes, application site scarring, herpes zoster, chemical conjunctivitis, and corneal burn, and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on Picato gel use in pregnant women to evaluate a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Systemic concentrations following topical administration of Picato gel were below the limit of quantification of 0.1 ng/ml, and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In animal reproduction studies, ingenol mebutate did not cause malformations in pregnant rats and rabbits when given by the intravenous route of administration during the period of organogenesis (see Data). The available data do not allow the calculation of relevant comparisons between the systemic exposure of ingenol mebutate observed in the animal studies to the systemic exposure that would be expected in humans after topical use of Picato gel.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defects, loss, and other adverse outcomes. The background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2 to 4% and of miscarriage is 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
Intravenous doses of 1.5, 3, and 5 µg/kg/day (9, 18, and 30 μg/m2/day, respectively) ingenol mebutate were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 16) to pregnant female rats. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal development or malformations were noted at doses up to 5 µg/kg/day (30 μg/m2/day).
Intravenous doses of 1, 2, and 4 µg/kg/day (12, 24, and 48 μg/m2/day, respectively) ingenol mebutate were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 18) to pregnant female rabbits. Maternal toxicity (increased breathing rate) was observed at doses ≥ 1 µg/kg/day (12 µg/m2/day). An increase in embryo-fetal mortality was noted at 4 µg/kg/day (48 μg/m2/day). An increased incidence of fetal visceral and skeletal variations was noted in all three ingenol mebutate dose groups.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of ingenol mebutate in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Systemic concentrations following topical administration of Picato® gel were below the limit of quantification of 0.1 ng/mL, and breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the child to Picato gel [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Picato gel and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Picato gel or from the underlying maternal condition.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Picato (ingenol mebutate) gel, 0.015% or 0.05% is a clear colorless gel for topical administration, which contains the active substance ingenol mebutate, an inducer of cell death.
The chemical name of ingenol mebutate is:
2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl-, (1aR,2S,5R,5aS,6S,8aS,9R,10aR)-1a,2,5,5a,6,9,10,10a-octahydro-5,5a-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,7,9-tetramethyl-11-oxo-1H-2,8a-methanocyclopenta [a]cyclopropa[e]cyclodecen-6-yl ester, (2Z) -
or
(1aR,2S,5R,5aS,6S,8aS,9R,10aR)-5,5a-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,7,9-tetramethyl-11-oxo-1a,2,5,5a,6,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H 2,8a-methanocyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]cyclodecen-6-yl (2Z) 2-methylbut-2-enoate.The molecular formula is C25H34O6 and molecular weight is 430.5. Ingenol mebutate is represented by the following structural formula:

Ingenol mebutate is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder.
Picato® gel, 0.015% or 0.05%, contains 150 mcg or 500 mcg of ingenol mebutate, respectively, in each gram of gel consisting of isopropyl alcohol, hydroxyethyl cellulose, citric acid monohydrate, sodium citrate, benzyl alcohol and purified water.
Picato gel is a clear colorless gel and supplied in unit dose laminate tubes, for single use, containing a nominal fill weight of 0.47 g, with a deliverable weight of 0.25 g. The tubes should be discarded after single use.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action by which Picato gel induces cell death in treating AK lesions is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The systemic exposure to Picato gel, 0.05% was assessed in two studies in a total of 16 subjects with AK, following application of approximately 1 g of Picato gel, 0.05% to an area of 100 cm2 of the dorsal forearm once daily for two consecutive days. In these studies, the blood levels of ingenol mebutate and two of its metabolites (acyl isomers of ingenol mebutate) were measured. Blood levels of ingenol mebutate and the two metabolites were below the lower limit of quantification (0.1 ng/mL) in all the blood samples of the subjects evaluated.
Drug Interactions
In vitro studies demonstrated that [3H]-ingenol mebutate undergoes extensive metabolism in human hepatocytes.
In vitro studies to assess the potential of ingenol mebutate to inhibit or induce human cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes demonstrated that ingenol mebutate does not inhibit CYP 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4 or induce CYP 1A2, 2C9, and 3A4. The estimated expected systemic exposure (< 0.1 ng/mL) following topical application of Picato gel, 0.05% to AK subjects in the pharmacokinetic studies described above is negligible compared to the concentrations of ingenol mebutate evaluated in the in vitro studies.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Picato® gel or ingenol mebutate. The effects of ingenol mebutate on fertility have not been evaluated.
Ingenol mebutate was negative in the Ames test, in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, and in vivo rat micronucleus test, but positive in the Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cell transformation assay.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis of the Face and Scalp
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled, clinical trials, 547 adult subjects with AK on the face or scalp were randomized to treatment with either Picato gel, 0.015% or vehicle gel for 3 consecutive days, followed by an 8 week follow-up period. The trials enrolled subjects with 4 to 8 clinically typical, visible, discrete AK lesions within a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area. Hypertrophic and hyperkeratotic lesions were excluded from treatment. On each scheduled dosing day, the study gel was applied to the entire treatment area. A total of 536 subjects (98%) completed these trials. Study subjects ranged from 34 to 89 years of age (mean 64 years) and 94% had Fitzpatrick skin type I, II, or III. Approximately 85% of subjects were male, and all Picato gel-treated subjects were Caucasian.
Efficacy was assessed at Day 57. Complete clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects with no (zero) clinically visible AK lesions in the treatment area. Partial clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects with 75% or greater reduction in the number of AK lesions at baseline in the selected treatment area. Table 5 presents the efficacy results for each trial.
Table 5. Number and Percent of Subjects Achieving Complete and Partial Clearance at Day 57 in Each Trial Study 1 Study 2 Picato gel, 0.015%
(N=135 )Vehicle
(N=134 )Picato gel, 0.015%
(N=142)Vehicle
(N=136)Complete Clearance Rate 50 (37%) 3 (2%) 67 (47%) 7 (5%) Partial Clearance Rate (≥ 75%) 81 (60%) 9 (7%) 96 (68%) 11 (8%) Table 6 presents the response rates by anatomical location for each trial.
Table 6. Number and Percent of Subjects Achieving Complete Clearance at Day 57 by Anatomical Location and by Trial Study 1 Study 2 Picato gel, 0.015%
(N=135 )Vehicle
(N=134 )Picato gel, 0.015%
(N=142)Vehicle
(N=136)Scalp 4/26 (15%) 0/25 (0%) 9/31 (29%) 1/25 (4%) Face 46/109 (42%) 3/109 (2%) 58/111 (52%) 6/111 (5%) Subjects who achieved complete clearance at Day 57 in Study 1 and Study 2 entered a 12-month follow-up period. Based on 108 Picato gel-treated subjects who achieved complete clearance in Study 1 and Study 2, the recurrence rate at 12 months was 54% where recurrence was defined as the percentage of subjects with any identified AK lesion in the previously treated area who achieved complete clearance at Day 57.
14.2 Actinic Keratosis of the Trunk and Extremities
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical trials, 458 adult subjects with AK on the trunk or extremities were randomized to treatment with either Picato® gel, 0.05% or vehicle gel for 2 consecutive days, followed by an 8 week follow-up period. The trials enrolled subjects with 4 to 8 clinically typical, visible, discrete AK lesions within a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area. Hypertrophic and hyperkeratotic lesions were excluded from treatment. On each scheduled dosing day, the study gel was applied to the entire treatment area. A total of 447 subjects (98%) completed these trials. Study subjects ranged from 34 to 89 years of age (mean 66 years) and 94% had Fitzpatrick skin type I, II, or III. Approximately 62% of subjects were male, and all Picato gel-treated subjects were Caucasian.
Efficacy was assessed at Day 57. Complete clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects with no (zero) clinically visible AK lesions in the treatment area. The partial clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects with 75% or greater reduction in the number of AK lesions at baseline in the selected treatment area. Table 7 presents the efficacy results for each trial.
Table 7. Number and Percent of Subjects Achieving Complete and Partial Clearance at Day 57 in Each Trial Study 3 Study 4 Picato gel, 0.05%
(N=126 )Vehicle
(N=129 )Picato gel, 0.05%
(N=100)Vehicle
(N=103)Complete Clearance Rate 35 (28%) 6 (5%) 42 (42%) 5 (5%) Partial Clearance Rate (≥ 75%) 56 (44%) 9 (7%) 55 (55%) 7 (7%) Table 8 presents the response rates by anatomical location for each trial.
Table 8. Number and Percent of Subjects Achieving Complete Clearance at Day 57 by Anatomical Location and by Trial Study 3 Study 4 Picato gel, 0.05%
(N=126)Vehicle
(N=129)Picato gel, 0.05%
(N=100)Vehicle
(N=103)- * Other includes shoulder, back, leg.
Arm 22/84 (26%) 4/82 (5%) 27/59 (46%) 3/67 (5%) Back of Hand 4/25 (16%) 0/29 (0%) 6/28 (21%) 0/27 (0%) Chest 8/9 (89%) 1/8 (13%) 3/5 (60%) 1/3 (33%) Other* 1/8 (13%) 1/10 (10%) 6/8 (75%) 1/6 (17%) Subjects who achieved complete clearance at Day 57 in Study 4 entered a 12-month follow-up period. Based on 38 Picato gel-treated subjects who achieved complete clearance in Study 4, the recurrence rate at 12 months was 50% where recurrence was defined as the percentage of subjects with any identified AK lesion in the previously treated area who achieved complete clearance at Day 57.
In a separate trial, in an open-label treatment period, subjects were treated for AK lesions on their face or scalp. Those subjects who did not achieve clearance at Day 57 or experienced recurrence after achieving clearance at Day 57 were randomized to receive a second treatment course of Picato gel or its vehicle gel. Some subjects had a treatment benefit with the second treatment course of Picato gel when evaluated 8 weeks after the retreatment.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Picato® gel is a clear colorless gel and is supplied in unit dose laminate tubes containing a nominal fill weight of 0.47 g, with a deliverable weight of 0.25 g. The tubes should be discarded after single use.
Picato gel is available in 2 dosage strengths: 0.015% or 0.05%.
Dosage Strength Number of unit dose tubes per carton NDC# 0.015 % 3 50222-502-47 0.05 % 2 50222-503-47 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that severe eye injury can occur with Picato gel. Advise patients that Picato gel is not for ophthalmic use. Advise patients to avoid application around the eyes. If severe eye pain or other symptoms of accidental exposure occur, advise patients to flush eyes with water and seek medical care [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions can occur with Picato gel. Advise patients of the symptoms of allergic reactions and anaphylaxis, and instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Local Skin Reactions
Inform patients that treatment with Picato gel may lead to local skin reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Important Administration Instructions
Advise patients that Picato gel is for external use only. Advise patients to avoid application near and around the eyes, mouth and lips.
Patients should avoid inadvertent transfer of Picato gel to other areas, or to another person. Instruct patients to:
- allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes after application.
- avoid washing and touching the treated area, or participating in activities that cause excessive sweating, for 6 hours after treatment. Following this time, patients may wash the area with a mild soap and water.
- keep out of the reach of children.
Lactation
Advise breastfeeding women to avoid accidental transfer of Picato gel to the nipple and areola area to prevent direct infant exposure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
PICATO® (Pih-KAY-toe)
(ingenol mebutate)
gelThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 2/2020 Important: For use on the skin only (topical). Do not use Picato gel in, around, or near your eyes, lips, mouth, or vagina. What is Picato gel? - Picato gel, 0.015% is a prescription medicine used on the skin to treat actinic keratosis on the face or scalp.
- Picato gel, 0.05% is a prescription medicine used on the skin to treat actinic keratosis on the body or arms and legs.
It is not known if Picato gel is safe and effective for the treatment of actinic keratosis in children less than 18 years of age.
Who should not use Picato gel?
Do not use Picato gel if you are allergic to ingenol mebutate or any of the ingredients in Picato gel. See the end of this leaflet for a list of the ingredients in Picato gel.What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Picato gel?
Before using Picato gel, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:- are being treated or have been treated for actinic keratosis with other medicines or surgery. You should not use Picato gel until your skin has healed from other treatments.
- have other skin problems or sunburn in the treatment area.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Picato gel can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. If you use Picato gel while breastfeeding, make sure that your treated skin does not come into contact with the infant.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
How should I use Picato gel? - Use Picato gel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Picato gel is for skin use only.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you where to apply Picato gel, and how often, and how long to apply it. Do not apply Picato gel to other areas.
- Do not use more Picato gel than you need to cover the treatment area. Using too much Picato gel, or using it too often, or for too long can increase your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side effects.
-
Do not get Picato gel in, around, or near your eyes. Do not touch your eyes while you are applying Picato gel.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water after applying Picato gel. After applying Picato gel, be careful to keep Picato gel on the treated area from coming into contact with your eyes. Irritation may happen if you get Picato gel in your eyes.
- If you accidentally get Picato gel in your eyes, flush them with large amounts of water and get medical care as soon as possible. Also see "What are the possible side effects of Picato gel?"
- Do not get Picato gel in, around, or near your mouth or lips.
- To help prevent accidental transfer of Picato gel to other areas of your body or to another person:
- allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes after you apply Picato gel.
- avoid washing and touching the treated area, or doing activities that cause a lot of sweating, for 6 hours after treatment. After 6 hours, you may wash the area with a mild soap and water.
- Only use a tube of Picato gel 1 time. Throw away any open tube of Picato gel after use even if there is medicine still left in it.
- See the Instructions for Use that comes with your Picato gel for information about the right way to apply it.
What are the possible side effects of Picato gel?
Picato gel may cause serious or severe side effects including:- Eye problems can happen if Picato gel gets in your eyes. Eye problems may include severe eye pain, swelling or drooping of your eyelids, or swelling around your eyes. If you accidentally get Picato gel in your eyes, flush them with large amounts of water and get medical care as soon as possible.
- Serious allergic reactions. Serious allergic reactions have happened with Picato gel, and in some cases have required treatment in a hospital. See "Who should not use Picato gel?". Get medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction:
- swelling of the lips or tongue
- trouble breathing or wheezing
- chest tightness
- dizziness or passing out
-
Local skin reactions.
- Skin reactions in the treatment area are common with Picato® gel. You may get a skin reaction such as mild redness, flaking or scaling, crusting, or swelling. You may also see changes in your skin color (pigmentation changes) and scarring where Picato gel is applied.
-
Severe skin reactions.
- A rare, severe skin reaction (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome) may occur without warning requiring immediate medical attention. Call your healthcare provider if you get skin redness, flaking or scaling, crusting, or swelling that is more severe, or if you get blisters, pus, ulcers or breakdown of your skin.
The most common side effects with Picato gel include: - local skin reactions, see "Local skin reactions" above
- pain, itching, or skin irritation at the treatment area
- infection at the treatment area
- swelling around the eyes
- nose and throat irritation
- headache
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of Picato gel. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to LEO Pharma Inc. at 1-877-494-4536. How should I store Picato gel? - Store Picato gel in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze.
- Picato gel has an expiration date (exp) marked on the end of the tube. Do not use the gel after this date.
- Safely throw away used Picato gel tubes in household trash.
General information about the safe and effective use of Picato gel.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Picato gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Picato gel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Picato gel that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in Picato gel?
Active ingredient: ingenol mebutate
Inactive ingredients: isopropyl alcohol, hydroxyethyl cellulose, citric acid monohydrate, sodium citrate, benzyl alcohol and purified water
Manufactured by: LEO Laboratories Ltd. (LEO Pharma), 285 Cashel Road, Dublin 12, Ireland
Distributed by: LEO Pharma Inc., Seven Giralda Farms, Madison, NJ 07940, USA.
For more information call 1-877-494-4536.
Picato is a registered trademark of LEO Laboratories Ltd.
© 2020, LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved. February 2020 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USEPICATO® (Pih-KAY-toe) (ingenol mebutate) gel, 0.015%
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to apply Picato gel.
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use before you use Picato gel for the first time. Also read the Patient Information leaflet that comes with Picato gel.
Important Information You Need to Know Before Applying Picato gel:
- For topical use only (apply on top of skin)
- Always use Picato gel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- Only use Picato gel, 0.015% to treat actinic keratosis on your face or scalp.
- Apply Picato gel, 0.015% to the skin area to be treated 1 time each day for 3 days in a row. Use a new tube for each day of treatment.
- Avoid touching the treatment area or doing activities that cause a lot of sweating for 6 hours after applying Picato gel. After 6 hours you may wash the treatment area with a mild soap and water.
Do not:
- apply right after taking a shower or less than 2 hours before bedtime.
-
get Picato gel in, around, or near your eyes. Do not touch your eyes while you are applying Picato gel.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water after applying it. After applying Picato gel, be careful to keep Picato gel on the treated area from coming into contact with your eyes. Irritation may happen if you get Picato gel in your eyes.
- If you accidentally get Picato gel in your eyes, flush them with large amounts of water and get medical care as soon as possible. Also see the section of Patient Information leaflet section called "What are the possible side effects of Picato gel?".
- get Picato gel in, around, or near your lips and mouth.
Applying Picato gel
Step 1. Open a new tube each time you use Picato gel.
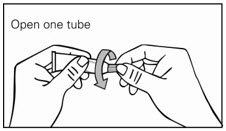
Step 2. Remove cap from tube just before use. (See Figure A.)
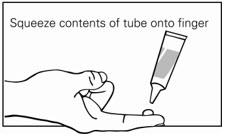
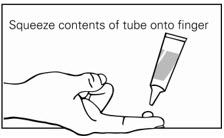
Step 3. Squeeze the gel from the tube onto a fingertip. (See Figure B.) Only use enough gel needed to cover the affected area, as directed by your healthcare provider. One tube contains enough gel to cover a skin area of about 2 inches by 2 inches.
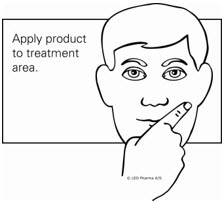
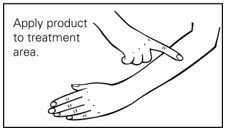
Step 4. Spread the gel evenly over only the skin area to be treated. Do not get in, around or near the eyes, lips, and mouth. Allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes. (See Figure C.)
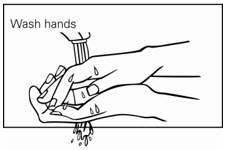
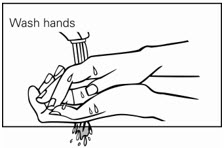
Step 5. Wash your hands right away after applying Picato® gel. (See Figure D.)
Step 6. Safely throw away (dispose of) the tube after use.
Repeat the above steps for each day of treatment.
To help prevent transfer of Picato gel to other areas of your body or to another person, allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes after you apply Picato gel.
Storing Picato gel
- Store Picato gel in a refrigerator at 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Do not freeze.
- Picato gel has an expiration date (exp) marked on the end of the tube. Do not use the gel after this date.
Disposing of Picato gel
- Safely throw away used Picato gel tubes in household trash.
For more information call: 1-877-494-4536.
Manufactured by:
LEO Laboratories Ltd. (LEO Pharma)
285 Cashel Road
Dublin 12, IrelandDistributed by:
LEO Pharma Inc.
Seven Giralda Farms
Madison, NJ 07940, USAPicato is a registered trademark of LEO Laboratories Ltd.
© 2020, LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved. February 2020This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 2/2020 -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USEPICATO® (Pih-KAY-toe) (ingenol mebutate) gel, 0.05%
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to apply Picato gel.
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use before you use Picato gel for the first time. Also read the Patient Information leaflet that comes with Picato gel.
Important Information You Need to Know Before Applying Picato gel:
- For topical use only (apply on top of skin)
- Always use Picato gel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- Only use Picato gel, 0.05% to treat actinic keratosis on your body, arms, hands or legs.
- Apply Picato gel, 0.05% to the skin area to be treated 1 time each day for 2 days in a row. Use a new tube for each day of treatment.
- Avoid touching the treatment area or doing activities that cause a lot of sweating for 6 hours after applying Picato gel. After 6 hours you may wash the treatment area with a mild soap and water.
Do not:
- apply right after taking a shower or less than 2 hours before bedtime.
-
get Picato gel in, around, or near your eyes. Do not touch your eyes while you are applying Picato gel.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water after applying it. After applying Picato gel, be careful to keep Picato gel on the treated area from coming into contact with your eyes. Irritation may happen if you get Picato gel in your eyes.
- If you accidentally get Picato gel in your eyes, flush them with large amounts of water and get medical care as soon as possible. Also see the section of Patient Information leaflet section called "What are the possible side effects of Picato gel?".
- get Picato gel in, around, or near your lips and mouth.
Applying Picato gel
Step 1. Open a new tube each time you use Picato gel.
Step 2. Remove cap from tube just before use. (See Figure A.)
Step 3. Squeeze the gel from the tube onto a fingertip. (See Figure B.) Only use enough gel needed to cover the affected area, as directed by your healthcare provider. One tube contains enough gel to cover a skin area of about 2 inches by 2 inches.
Step 4. Spread the gel evenly over only the skin area to be treated. Do not get in, around or near the eyes, lips, and mouth. Allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes. (See Figure C.)
Step 5. Wash your hands right away after applying Picato® gel. (See Figure D.) If you are treating your hands you should only wash the fingertip which you used for applying the gel.
Step 6. Safely throw away (dispose of) the tube after use.
Repeat the above steps for each day of treatment.
To help prevent transfer of Picato gel to other areas of your body or to another person, allow the treated area to dry for 15 minutes after you apply Picato gel.
Storing Picato gel
- Store Picato gel in a refrigerator at 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Do not freeze.
- Picato gel has an expiration date (exp) marked on the end of the tube. Do not use the gel after this date.
Disposing of Picato gel
- Safely throw away used Picato gel tubes in household trash.
For more information call: 1-877-494-4536.
Manufactured by:
LEO Laboratories Ltd. (LEO Pharma)
285 Cashel Road
Dublin 12, IrelandDistributed by:
LEO Pharma Inc.
Seven Giralda Farms
Madison, NJ 07940, USAPicato is a registered trademark of LEO Laboratories Ltd.
© 2020, LEO Pharma Inc. All rights reserved. February 2020This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 2/2020 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.47 g Tube Carton - 0.015%
NDC: 50222-502-47
Rx onlyPicato®
(ingenol mebutate) gel0.015%
For Topical Use on Face or Scalp Only
Not for Oral, Ophthalmic, or Intravaginal Use3 Unit Dose Tubes
Net Wt. 0.47 g in each tube
Must be refrigerated
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.47 g Tube Carton - 0.05%
NDC: 50222-503-47
Rx onlyPicato®
(ingenol mebutate) gel0.05%
For Topical Use on Trunk or Extremities Only
Not for Oral, Ophthalmic, or Intravaginal Use2 Unit Dose Tubes
Net Wt. 0.47 g in each tube
Must be refrigerated
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PICATO
ingenol mebutate gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50222-502 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ingenol mebutate (UNII: 7686S50JAH) (ingenol mebutate - UNII:7686S50JAH) ingenol mebutate 150 ug in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (2000 MPA.S AT 1%) (UNII: S38J6RZN16) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50222-502-91 3 in 1 CARTON 01/23/2012 1 0.47 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 50222-502-47 3 in 1 CARTON 01/23/2012 2 0.47 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202833 01/23/2012 PICATO
ingenol mebutate gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50222-503 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ingenol mebutate (UNII: 7686S50JAH) (ingenol mebutate - UNII:7686S50JAH) ingenol mebutate 500 ug in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (2000 MPA.S AT 1%) (UNII: S38J6RZN16) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50222-503-47 2 in 1 CARTON 01/23/2012 1 0.47 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 50222-503-92 2 in 1 CARTON 01/23/2012 2 0.47 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202833 01/23/2012 Labeler - LEO Pharma Inc. (832692615) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations LEO Laboratories Ltd. 219532322 manufacture(50222-502, 50222-503) , analysis(50222-502, 50222-503)
Trademark Results [Picato]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PICATO 90109898 not registered Live/Pending |
Qingying Wu 2020-08-12 |
 PICATO 85239691 4222579 Live/Registered |
LEO LABORATORIES LIMITED 2011-02-11 |
 PICATO 81040634 1040634 Dead/Cancelled |
General Mills, Inc. 0000-00-00 |
 PICATO 79037305 3360077 Live/Registered |
LEO Laboratories Limited 2007-02-27 |
 PICATO 72100594 0742000 Dead/Cancelled |
GENERAL MUSIC STRINGS LIMITED 1960-07-11 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.