LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE tablet, film coated
LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dispensing Solutions, Inc., PSS World Medical, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
USE IN PREGNANCY
When used in pregnancy during the second and third trimesters, drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and even death to the developing fetus. When pregnancy is detected, losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets should be discontinued as soon as possible (see WARNINGS, Fetal/Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality).
-
DESCRIPTION
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets 50 mg/ 12.5 mg and losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets 100 mg/ 25 mg combine an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist and a diuretic, hydrochlorothiazide.
Losartan potassium, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt. Its molecular formula is C22H22ClKN6O, and its structural formula is:
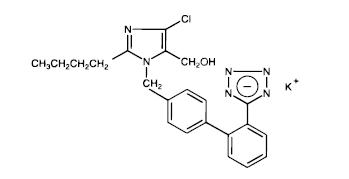
Losartan potassium, USP is off-white to creamish-yellow powder with a molecular weight of 461.01. It is soluble in water.
Oxidation of the 5-hydroxymethyl group on the imidazole ring results in the active metabolite of losartan.
Hydrochlorothiazide is 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its molecular formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2 and its structural formula is:
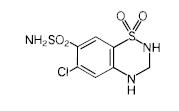
Hydrochlorothiazide, USP is a white or practically white, practically odorless crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 297.74. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n-butylamine, and in dimethylformamide, sparingly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ether, in chloroform, and in dilute mineral acids.
Each losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet intended for oral administration contains losartan potassium, 50 mg or 100 mg and hydrochlorothiazide, 12.5 mg or 25 mg. In addition, each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silica anhydrous, hydroxypropyl cellulose (low substituted), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, maize starch, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, talc and titanium dioxide.
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet 50 mg/ 12.5 mg contains 4.24 mg (0.108 mEq) of potassium and losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet 100 mg/ 25 mg contains 8.48 mg (0.216 mEq) of potassium.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide has been evaluated for safety in 858 patients treated for essential hypertension and 3889 patients treated for hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. In clinical trials with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide, no adverse experiences peculiar to this combination have been observed. Adverse experiences have been limited to those that were reported previously with losartan potassium and/or hydrochlorothiazide. The overall incidence of adverse experiences reported with the combination was comparable to placebo.
In general, treatment with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide was well tolerated. For the most part, adverse experiences have been mild and transient in nature and have not required discontinuation of therapy. In controlled clinical trials, discontinuation of therapy due to clinical adverse experiences was required in only 2.8% and 2.3% of patients treated with the combination and placebo, respectively.
In these double-blind controlled clinical trials, the following adverse experiences reported with losartan-hydrochlorothiazide occurred in ≥1 percent of patients, and more often on drug than placebo, regardless of drug relationship:
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide
(n=858)
Placebo
(n=173)
Body as a Whole
Abdominal pain
Edema/swelling
1.2
1.3
0.6
1.2
Cardiovascular
Palpitation
1.4
0.0
Musculoskeletal
Back pain
2.1
0.6
Nervous/Psychiatric
Dizziness
5.7
2.9
Respiratory
Cough
Sinusitis
Upper respiratory
infection
2.6
1.2
6.1
2.3
0.6
4.6
Skin
Rash
1.4
0.0
The following adverse events were also reported at a rate of 1 % or greater, but were as, or more, common in the placebo group in studies of essential hypertension: asthenia/fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, headache, bronchitis, pharyngitis.
Adverse events occurred at about the same rates in men and women. Adverse events were somewhat more frequent in the elderly compared to non-elderly patients and somewhat more frequent in Blacks compared to non-Blacks for both the losartan and hydrochlorothiazide and the control groups.
A patient with known hypersensitivity to aspirin and penicillin, when treated with losartan potassium, was withdrawn from study due to swelling of the lips and eyelids and facial rash, reported as angioedema, which returned to normal 5 days after therapy was discontinued.
Superficial peeling of palms and hemolysis were reported in one subject treated with losartan potassium.
Losartan Potassium:
Other adverse experiences that have been reported with losartan, without regard to causality, are listed below:
Body as a Whole: Chest pain, facial edema, fever, orthostatic effects, syncope;
Cardiovascular: Angina pectoris, arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, CVA, hypotension, myocardial infarction, second degree AV block;
Digestive: Anorexia, constipation, dental pain, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, gastritis, vomiting;
General disorders and administration site conditions: malaise
Hematologic: Anemia;
Metabolic: Gout;
Musculoskeletal: Arm pain, arthralgia, arthritis, fibromyalgia, hip pain, joint swelling, knee pain, leg pain, muscle cramps, muscle weakness, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, shoulder pain, stiffness;
Nervous System/Psychiatric: Anxiety, anxiety disorder, ataxia, confusion, depression, dream abnormality, hypesthesia, insomnia, libido decreased, memory impairment, migraine, nervousness, panic disorder, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, sleep disorder, somnolence, tremor, vertigo;
Respiratory: Dyspnea, epistaxis, nasal congestion, pharyngeal discomfort, respiratory congestion, rhinitis, sinus disorder;
Skin: Alopecia, dermatitis, dry skin, ecchymosis, erythema, flushing, photosensitivity, pruritus, sweating, urticaria;
Special Senses: Blurred vision, burning/stinging in the eye, conjunctivitis, decrease in visual acuity, taste perversion, tinnitus;
Urogenital: Impotence, nocturia, urinary frequency, urinary tract infection.
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Other adverse experiences that have been reported with hydrochlorothiazide, without regard to causality, are listed below:
Body as a Whole: Weakness;
Digestive: Pancreatitis, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), sialadenitis, cramping, gastric irritation;
Hematologic: Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia;
Hypersensitivity: Purpura, photosensitivity, urticaria, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis and cutaneous vasculitis), fever, respiratory distress including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema;
Metabolic: Hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hyperuricemia;
Musculoskeletal: Muscle spasm;
Nervous System/Psychiatric: Restlessness;
Renal: Renal failure, renal dysfunction, interstitial nephritis;
Skin: Erythema multiforme including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis including toxic epidermal necrolysis;
Special Senses: Transient blurred vision, xanthopsia.
Persistent dry cough (with an incidence of a few percent) has been associated with ACE-inhibitor use and in practice can be a cause of discontinuation of ACE-inhibitor therapy. Two prospective, parallel-group, double-blind, randomized, controlled trials were conducted to assess the effects of losartan on the incidence of cough in hypertensive patients who had experienced cough while receiving ACE-inhibitor therapy. Patients who had typical ACE-inhibitor cough when challenged with lisinopril, whose cough disappeared on placebo, were randomized to losartan 50 mg, lisinopril 20 mg, or either placebo (one study, n=97) or 25 mg hydrochlorothiazide (n=135). The double-blind treatment period lasted up to 8 weeks. The incidence of cough is shown below.
Study 1† HCTZ Losartan Lisinopril
Cough 25% 17% 69%
Study 2†† Placebo Losartan Lisinopril
Cough 35% 29% 62%
† Demographics = (89% caucasian, 64% female)
†† Demographics = (90% caucasian, 51% female)
These studies demonstrate that the incidence of cough associated with losartan therapy, in a population that all had cough associated with ACE-inhibitor therapy, is similar to that associated with hydrochlorothiazide or placebo therapy.
Cases of cough, including positive re-challenges, have been reported with the use of losartan in post-marketing experience.
Severe Hypertension:
In a clinical study in patients with severe hypertension (SiDBP ≥110 mmHg), the overall pattern of adverse events reported through six weeks of follow-up was similar in patients treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets as initial therapy and in patients treated with losartan as initial therapy. There were no reported cases of syncope in either treatment group. There were 2 (0.6%) and 0 (0.0%) cases of hypotension reported in the group treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets and the group treated with losartan, respectively. There were 3 (0.8%) and 2 (1.2%) cases of increased serum creatinine (>0.5 mg/dL) in the group treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets and the group treated with losartan, respectively, during the same time period (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Severe Hypertension).
Post-Marketing Experience:
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in post-marketing experience:
Digestive: Hepatitis has been reported rarely in patients treated with losartan.
Hemic: Thrombocytopenia.
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema, including swelling of the larynx and glottis, causing airway obstruction and/or swelling of the face, lips, pharynx, and/or tongue has been reported rarely in patients treated with losartan; some of these patients previously experienced angioedema with other drugs including ACE inhibitors. Vasculitis, including Henoch-Schonlein purpura, has been reported with losartan. Anaphylactic reactions have been reported.
Metabolic and Nutrition: Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia have been reported with losartan.
Musculoskeletal: Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported in patients receiving angiotensin II receptor blockers.
Respiratory: Dry cough (see above) has been reported with losartan.
Skin: Erythroderma has been reported with losartan.
Laboratory Test Findings:
In controlled clinical trials, clinically important changes in standard laboratory parameters were rarely associated with administration of losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
Creatinine, Blood Urea Nitrogen:
Minor increases in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) or serum creatinine were observed in 0.6 and 0.8 percent, respectively, of patients with essential hypertension treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets alone. No patient discontinued taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets due to increased BUN. One patient discontinued taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets due to a minor increase in serum creatinine.
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit:
Small decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit (mean decreases of approximately 0.14 grams percent and 0.72 volume percent, respectively) occurred frequently in patients treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets alone, but were rarely of clinical importance. No patients were discontinued due to anemia.
Liver Function Tests:
Occasional elevations of liver enzymes and/or serum bilirubin have occurred. In patients with essential hypertension treated with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets alone, no patients were discontinued due to these laboratory adverse experiences.
Serum Electrolytes:
See PRECAUTIONS.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 50 mg/ 12.5 mg, are white to off-white, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with "ZD18" on one side and plain on other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC: 68382-142-06 in bottle of 30 tablets
NDC: 68382-142-16 in bottle of 90 tablets
NDC: 68382-142-10 in bottle of 1000 tablets
NDC: 68382-142-40 in bottle of 5000 tablets
Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP 100 mg/ 25 mg, are white to off-white, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with "ZD19" on one side and plain on other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC: 68382-143-06 in bottle of 30 tablets
NDC: 68382-143-16 in bottle of 90 tablets
NDC: 68382-143-10 in bottle of 1000 tablets
NDC: 68382-143-23 in bottle of 4000 tablets
Storage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from light.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
Patient Information Leaflet
Read the Patient Information that comes with losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition and treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?
Do not take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets can harm your unborn baby causing injury and even death. Stop taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets if you become pregnant and call your doctor right away. If you plan to become pregnant, talk to your doctor about other treatment options before taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
What is losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet?
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet contains 2 prescription medicines, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and a diuretic (water pill). It is used to:
- lower high blood pressure (hypertension). Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are not usually the first medicine used to treat high blood pressure.
- lower the chance of stroke in patients with high blood pressure and a heart problem called left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may not help Black patients with this problem.
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets have not been studied in children less than 18 years old.
High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. The losartan ingredient in losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. The hydrochlorothiazide ingredient in losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet works by making your kidneys pass more water and salt.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) is an enlargement of the walls of the left chamber of the heart (the heart’s main pumping chamber). LVH can happen from several things. High blood pressure is the most common cause of LVH.
Who should not take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?
Do not take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets if you:
- are allergic to any ingredients in losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. See a complete list of Ingredients in losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets at the end of this leaflet.
- are allergic to any sulfonamide-containing ("sulfa") medicines. Ask your doctor if you are not sure what sulfonamide-containing ("sulfa") medicines are.
- are not passing urine
What should I tell my doctor before taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?
Tell your doctor about all your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. See "What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?"
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide can pass into your milk and may harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets or breast-feed. You should not do both.
- have been vomiting (throwing up), having diarrhea, sweating a lot, or not drinking enough fluids. These could cause you to have low blood pressure.
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus; SLE)
- have diabetes
- have asthma
- have gout
- have any allergies
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets and certain other medicines may interact with each other. Especially tell your doctor if you are taking:
- potassium supplements
- salt substitutes containing potassium
- water pills ( diuretics)
- lithium (a medicine used to treat a certain kind of depression)
- medicines used to treat pain and arthritis, called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including COX-2 inhibitors.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets??
- Take losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- Your doctor may do blood tests from time to time while you are taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
What are the possible side effects of losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?
Losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may cause the following side effects that may be serious:
- injury or death of unborn babies. See "What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?"
- allergic reaction. Symptoms of an allergic reaction are swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue. Get emergency medical help right away and stop taking losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
- low blood pressure (hypotension). Low blood pressure may cause you to feel faint or dizzy. Lie down if you feel faint or dizzy. Call your doctor right away.
- a new or worsening condition called systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus; SLE)
- if you have kidney problems, you may see a worsening in how well your kidneys work. Call your doctor if you get swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands, or unexplained weight gain.
- If you have liver problems, you may see a worsening in how well your liver works. Call your doctor if you get nausea, pain in the right upper stomach area (abdomen), yellow eyes or skin (which can be itchy).
The most common side effects of losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets in people with high blood pressure are:
- "colds" (upper respiratory infection)
- dizziness
- stuffy nose
- back pain
- fast or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- rash
Tell your doctor if you get any side effect that bothers you or that won’t go away. This is not a complete list of side effects. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How should I store losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets?
- Store losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets at room temperature at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- Keep losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets in a tightly closed container, and keep losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets out of the light.
- Keep losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information that is written for health professionals.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68258-6040(NDC:68382-143) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE (UNII: 0J48LPH2TH) (HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE - UNII:0J48LPH2TH) HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 25 mg LOSARTAN POTASSIUM (UNII: 3ST302B24A) (LOSARTAN - UNII:JMS50MPO89) LOSARTAN POTASSIUM 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE, LOW SUBSTITUTED (UNII: 2165RE0K14) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color white (WHITE TO OFF WHITE) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (CAPSULE) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code ZD19 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68258-6040-3 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 68258-6040-9 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078235 10/04/2010 Labeler - Dispensing Solutions, Inc. (066070785) Registrant - PSS World Medical, Inc. (101822682) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dispensing Solutions, Inc. 066070785 relabel, repack
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
