ATROPINE SULFATE injection
Atropine Sulfate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Atropine Sulfate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP is a sterile solution of atropine sulfate in Water for Injection. Each mL contains Atropine Sulfate 0.4 mg; Sodium Chloride 9 mg; Benzyl Alcohol 9 mg; Water for Injection qs; pH may be adjusted with Sulfuric Acid if necessary. pH 3.0-6.5.
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP may be given intramuscularly, intravenously or subcutaneously. Atropine is a white crystalline alkaloid which may be extracted from belladonna root or may be produced synthetically. It is used as atropine sulfate because this compound has much greater solubility.
Atropine sulfate is an anticholinergic drug. The empirical formula of atropine sulfate is (C17H23NO3)2H2SO4H2O.
The structural formula is: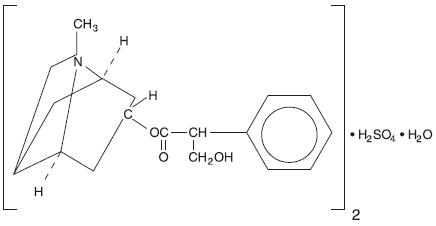
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The most important therapeutic action of atropine is the inhibition of smooth muscle and glands innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves. It also has central nervous system activity, which may be stimulating or depressing depending upon the dose.
Following the administration of usual clinical doses, atropine produces stimulation of the medulla and higher cerebral centers. This effect is manifested by mild central vagal excitation and moderate respiratory stimulation. Atropine sulfate also acts peripherally as a competitive antagonist of the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine. It does not prevent the release of acetylcholine but antagonizes the effect of acetylcholine on the effector cells.
These actions include vasodilation, drying of the mouth, an increase in the pulse rate, inhibition of contractions of the gastrointestinal tract, ureter, and bladder, and reduction of salivary, bronchial, gastric and sweat gland secretions. Following clinical and larger doses, atropine sulfate causes dilation of the pupils and paralysis of accommodation and, in narrow-angle glaucoma, can increase intraocular pressure. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Atropine sulfate is given parenterally as a preanesthetic medication to decrease salivation and bronchial secretions. It is useful in pylorospasm and other spastic conditions of the gastrointestinal tract. For ureteral and biliary colic, atropine sulfate given with morphine may be indicated. Atropine sulfate is indicated for relaxation of the upper gastrointestinal tract and colon during hypotonic radiography.
Atropine is used as an antidote for pilocarpine, physostigmine, isoflurophate, choline esters, certain species of aminata and in poisoning by the organic phosphate cholinesterase inhibitors found in certain insecticides and by chemical warfare “nerve gases”. Large doses relieve the muscarine-like symptoms and some of the central nervous system manifestations. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Conditions at which inhibition of postganglionic cholinergic nerves are undesirable, such as glaucoma and tachycardia. Also contraindicated in asthma, because the parenteral dose which might relieve asthma would have an excessive drying effect upon mucous plugs in the bronchi. Prostatic hypertrophy, while not a contraindication, requires special attention to signs of urinary retention.
-
WARNINGS
Atropine is a highly potent drug and due care is essential to avoid overdosage, especially with intravenous administration. Pediatric populations are more susceptible than adults to the toxic effects of anticholinergic agents.
Atropine I.V. decreased the rate of mexiletine absorption without altering the relative oral bioavailability; this delay in mexiletine absorption was reversed by the combination of atropine and intravenous metoclopramide during pretreatment for anesthesia. Atropine is not removed by dialysis.
This drug is effective in very low dosage and overdose may cause permanent damage or death, especially in children.
This product contains Benzyl Alcohol which has been associated with a fatal gasping syndrome in infants and neonates. -
PRECAUTIONS
General
Doses of 0.5 to 1 mg atropine are mildly stimulating to the CNS. Larger doses may produce mental disturbances; still larger doses are depressing. Death from atropine poisoning, though rare, is usually due to paralysis of the medullary centers.
Information for Patients
Atropine causes dryness of the mouth, and when used with other drugs that can cause dryness of the mouth, the effect is additive. Patients receiving chronic treatment can develop blurred vision, and they should not be involved in activities that require good and clear vision.
Drug Interactions
Atropine, by slowing gastric emptying and gastrointestinal mobility, may interfere with the absorption of other medications. The effect of atropine on dryness of the mouth may be increased if it is given with other drugs that have anticholinergic action.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with atropine sulfate. It is also not known whether atropine sulfate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Atropine sulfate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Individual tolerance varies greatly, but these systemic doses are likely to produce the following effects:
0.5 mg - Slight dryness of nose and mouth, bradycardia. 1 mg - Greater dryness of nose and mouth, with thirst; slowing, then acceleration of heart; slight mydriasis. 2 mg - Very dry mouth, tachycardia, with palpitation, mydriasis, slight blurring of near vision. 5 mg - Increase in the above symptoms plus disturbance of speech, difficulty in swallowing, headache, hot, dry skin, restlessness with asthenia. 10 mg and over - Above symptoms to extreme degree, plus ataxia, excitement, disorentation, hallucinations, delirium and coma. 65 mg - May be fatal. A scarlatiniform rash may occur. Atropine may produce fever, particularly in children, through inhibition of heat loss by evaporation. Although large doses of atropine may cause an alarming condition, recovery is usual.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Toxic doses from atropine are not uncommon, especially in children.
Symptoms
The principle manifestations of poisoning with atropine are delirium, tachycardia and fever.
Treatment
In the treatment of atropine poisoning, respiratory assistance and symptomatic support are indicated. Physostigmine salicylate, 1 to 5 mL of a dilution containing 1 mg per 5 mL of saline, should be administered intravenously. Administer the smaller dose in children and administer in not less than 2 minutes. Monitor with ECG. Medication can be repeated every 5 minutes for a total dose of 2 mg in children and every 30 minutes for a total dose of 6 mg in adults.
The fatal dose of atropine in children may be as low as 10 mg. In an adult, recovery after 1,000 mg of atropine sulfate has been reported. Death is usually due to paralysis of the medullary centers. The fatality rate is less than 1%. If the patient survives 24 hours, they will probably recover. -
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The usual dose of atropine sulfate is 0.4 to 0.6 mg. Suggested dosages for pediatric patients are as follows:
7 - 16 lbs. – 0.1 mg 40 - 65 lbs. – 0.3 mg
17 - 24 lbs. – 0.15 mg 65 - 90 lbs. – 0.4 mg
24 - 40 lbs. – 0.2 mg Over 90 lbs. – 0.4 to 0.6 mgTable of Dosage Equivalents Atropine Sulfate Solution (mL required) mg required 1 mg per mL 0.4 mg per mL 1 1 0.80 0.80 0.60 0.60 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.40 1 0.30 0.30 0.75 0.25 0.25 0.63 0.20 0.20 0.50 0.18 0.18 0.45 0.15 0.15 0.38 0.12 0.12 0.30 0.10 0.10 0.25 These doses may be exceeded in certain cases.
For hypotonic radiography of the gastrointestinal tract, the usual adult dose is 1 mg intramuscularly.
Adults suspected of contact with organic phosporous insecticides of the parathion type should be given atropine sulfate 0.8 mg intramuscularly. If an atropine effect is not apparent within 30 minutes or if definite symptoms of the poisoning occur (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pupillary constriction, pulmonary edema, fasciculations of eyelids and tongue, jerky ocular movements and excessive sweating, salivation and bronchial secretion), atropine sulfate 2 mg should be given intramuscularly at hourly intervals until signs of atropinization are observed. Up to 2 or 3 times of this dose (4 to 6 mg) may be required in severe cases.Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP is available in the following:
0.4 mg/mL
20 mL multiple dose vial packaged in 10s (NDC: 0641-6006-10)
Use only if solution is clear and seal intact.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F), excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact West-Ward Pharmaceutical Corp. at 1-877-845-0689, or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
For Product Inquiry call 1-877-845-0689.
Manufactured by:

WEST-WARD
PHARMACEUTICALSEatontown, NJ 07724 USA
Revised June 2011
462-416-01
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP
8 mg/20 mL (0.4 mg/mL)
20 mL Multiple Dose Vial
NDC: 0641-6006-01
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP
8 mg/20 mL (0.4 mg/mL)
10 x 20 mL Multiple Dose Vials
NDC: 0641-6006-10
- SERIALIZATION IMAGE
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ATROPINE SULFATE
atropine sulfate injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0641-6006 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ATROPINE SULFATE (UNII: 03J5ZE7KA5) (ATROPINE - UNII:7C0697DR9I) ATROPINE SULFATE 0.4 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 9 mg in 1 mL BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) 9 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SULFURIC ACID (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0641-6006-10 10 in 1 CARTON 01/01/1971 1 NDC: 0641-6006-01 20 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 01/01/1971 Labeler - West-Ward Pharmaceuticals Corp. (946499746)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
