ITOVEBI- inavolisib tablet, film coated
Itovebi by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Itovebi by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Genentech, Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ITOVEBI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ITOVEBI.
ITOVEBI® (inavolisib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Hyperglycemia (5.1) 09/2025 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ITOVEBI is a kinase inhibitor indicated in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant for the treatment of adults with endocrine-resistant, PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer, as detected by an FDA-approved test, following recurrence on or after completing adjuvant endocrine therapy. (1, 14.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer with ITOVEBI based on the presence of one or more PIK3CA mutations in plasma specimen. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: 9 mg orally once daily with or without food. (2.3)
- See Full Prescribing Information for dosage modifications of ITOVEBI due to adverse reactions. (2.4)
- Reduce the starting dose in patients with moderate renal impairment. (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 3 mg and 9 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hyperglycemia: ITOVEBI can cause severe or fatal hyperglycemia including ketoacidosis. Before initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, test fasting plasma glucose (FPG), HbA1c, and optimize blood glucose. Initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as clinically indicated. Interrupt, reduce dose, or discontinue ITOVEBI if severe hyperglycemia occurs. (2.4, 5.1)
- Stomatitis: ITOVEBI can cause severe stomatitis. Consider treating with a corticosteroid-containing mouthwash if stomatitis occurs. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of stomatitis. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue ITOVEBI based on severity. (2.4, 5.2)
- Diarrhea: ITOVEBI can cause diarrhea, which may be severe, and result in dehydration and acute kidney injury. Advise patients to start anti-diarrheal treatment, increase oral fluids, and notify their healthcare provider if severe diarrhea occurs. Interrupt, reduce dose, or discontinue ITOVEBI if severe diarrhea occurs. (2.4, 5.3)
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: ITOVEBI can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective non-hormonal contraception. (5.4, 8.1, 8.3)
Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for pregnancy and contraception information.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, increased fasting glucose, decreased platelets, decreased lymphocytes, stomatitis, diarrhea, decreased calcium, fatigue, decreased potassium, increased creatinine, increased ALT, nausea, decreased sodium, decreased magnesium, rash, decreased appetite, COVID-19 infection, and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Recommended Evaluation Before Initiating ITOVEBI
2.3 Recommended Dosage
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Dosage Modification for Moderate Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hyperglycemia
5.2 Stomatitis
5.3 Diarrhea
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ITOVEBI, in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant, is indicated for the treatment of adults with endocrine-resistant, PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer, as detected by an FDA-approved test, following recurrence on or after completing adjuvant endocrine therapy [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer with ITOVEBI based on the presence of one or more PIK3CA mutations in plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of PIK3CA mutations in breast cancer is available at: http://www.fda.gov/companiondiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Evaluation Before Initiating ITOVEBI
Evaluate fasting plasma glucose (FPG)/blood glucose (FBG) and hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) and optimize blood glucose prior to starting ITOVEBI and at regular intervals during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ITOVEBI is 9 mg taken orally once daily, with or without food, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Advise patients to take ITOVEBI at approximately the same time each day.
Swallow ITOVEBI tablet(s) whole. Do not chew, crush, or split prior to swallowing.
If a patient misses a dose, instruct the patient to take the missed dose as soon as possible within 9 hours. After more than 9 hours, instruct the patient to skip the dose and take the next dose at the scheduled time.
If a patient vomits a dose, instruct patients not to take an additional dose on that day and resume the usual dosing schedule the next day.
Administer ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant. The recommended dosage of palbociclib is 125 mg taken orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment to comprise a cycle of 28 days. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for palbociclib and fulvestrant for dosing information.
For premenopausal and perimenopausal women, administer a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist in accordance with local clinical practice.
For men, consider administering an LHRH agonist in accordance with local clinical practice.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reduction levels of ITOVEBI for adverse reactions are listed in Table 1. Permanently discontinue ITOVEBI if patients are unable to tolerate the second dose reduction.
Table 1: Dose Reduction for Adverse Reactions Dose Level Dose and Schedule Recommended starting dose 9 mg daily First dose reduction 6 mg daily Second dose reduction 3 mg daily The recommended dosage modifications of ITOVEBI for adverse reactions are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modification - * Before initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, test FPG or FBG, and HbA1C levels, and optimize plasma/blood glucose levels in all patients. After initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, monitor FPG or FBG levels based on the recommended schedule, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- † Based on CTCAE version 5.0.
Hyperglycemia*
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]Fasting glucose levels
(FPG or FBG)
> ULN to 160 mg/dL
(> ULN – 8.9 mmol/L)- No adjustment of ITOVEBI required.
- Consider dietary modifications and ensure adequate hydration.
- Initiate or intensify oral anti-hyperglycemic medications for patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia.
Fasting glucose levels
> 160 to 250 mg/dL
(> 8.9 – 13.9 mmol/L)- Withhold ITOVEBI until FPG or FBG ≤ 160 mg/dL (≤ 8.9 mmol/L).
- Initiate or intensify anti-hyperglycemic medications.
- Resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level.
- If FPG or FBG persists > 200 – 250 mg/dL (> 11.1 – 13.9 mmol/L) for 7 days under appropriate anti-hyperglycemic treatment, consider consultation with a healthcare professional experienced in the treatment of hyperglycemia.
Fasting glucose levels
> 250 to 500 mg/dL
(> 13.9 – 27.8 mmol/L)- Withhold ITOVEBI.
- Initiate or intensify anti-hyperglycemic medications.
- Administer appropriate hydration if required.
- If FPG or FBG decreases to ≤ 160 mg/dL (≤ 8.9 mmol/L) within 7 days, resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level.
- If FPG or FBG decreases to ≤ 160 mg/dL (≤ 8.9 mmol/L) in ≥ 8 days, resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
- If FPG or FBG > 250 to 500 mg/dL (> 13.9 – 27.8 mmol/L) recurs within 30 days, withhold ITOVEBI until FPG or FBG decreases to ≤ 160 mg/dL (≤ 8.9 mmol/L). Resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
Fasting glucose levels
> 500 mg/dL
(> 27.8 mmol/L)- Withhold ITOVEBI.
- Initiate or intensify anti-hyperglycemic medications.
- Assess for volume depletion and ketosis and administer appropriate hydration.
- If FPG or FBG decreases to ≤ 160 mg/dL (≤ 8.9 mmol/L), resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
- If FPG or FBG > 500 mg/dL (> 27.8 mmol/L) recurs within 30 days, permanently discontinue ITOVEBI.
Stomatitis
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Grade 1† - No adjustment of ITOVEBI required.
- Initiate or intensify appropriate medical therapy (e.g., corticosteroid-containing mouthwash) as clinically indicated.
Grade 2† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1.
- Initiate or intensify appropriate medical therapy. Resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level.
- For recurrent Grade 2 stomatitis, withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1, then resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
Grade 3† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1.
- Initiate or intensify appropriate medical therapy. Resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
Grade 4† - Permanently discontinue ITOVEBI.
Diarrhea
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]Grade 1† - No adjustment of ITOVEBI required.
- Initiate appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated.
Grade 2† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1, then resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level.
- Initiate or intensify appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated.
- For recurrent Grade 2 diarrhea, withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1, then resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
Grade 3† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1, then resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
- Initiate or intensify appropriate medical therapy and monitor as clinically indicated.
Grade 4† - Permanently discontinue ITOVEBI.
Hematologic Toxicities
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]Grade 1, 2, or 3† - No adjustment of ITOVEBI required.
- Monitor complete blood count and for signs or symptoms of hematologic toxicities as clinically indicated.
Grade 4† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 2.
- Resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level or reduce to one lower dose level as clinically indicated.
Other Adverse Reactions
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]Grade 1† - No adjustment of ITOVEBI required.
Grade 2† - Consider withholding ITOVEBI, if clinically indicated, until recovery to Grade ≤ 1.
- Resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level.
Grade 3 (first event)† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1.
- Resume ITOVEBI at the same dose level or one lower dose level based on clinical evaluation.
Grade 3 (recurrent)† - Withhold ITOVEBI until recovery to Grade ≤ 1.
- Resume ITOVEBI at one lower dose level.
Grade 4† - Permanently discontinue ITOVEBI.
2.5 Dosage Modification for Moderate Renal Impairment
The recommended starting dosage of ITOVEBI for patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min based on CKD-EPI) is 6 mg orally once daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hyperglycemia
Severe or fatal hyperglycemia, including ketoacidosis, can occur in patients treated with ITOVEBI. Ketoacidosis with a fatal outcome has occurred in the postmarketing setting.
Increased fasting glucose occurred in 85% of patients treated with ITOVEBI, including 22% of patients with Grade 2 (FPG > 160 to 250 mg/dL), 12% with Grade 3 (FPG > 250 to 500 mg/dL), and 0.6% with Grade 4 (FPG > 500 mg/dL) events.
In INAVO120, 46% (74/162) of patients who received ITOVEBI were treated with oral anti-hyperglycemic medications and 7% (11/162) were treated with insulin to manage increased fasting glucose. In patients who experienced increased fasting glucose of > 160 mg/dL, 96% (52/54) had an improvement in fasting glucose of at least one grade level with a median time to improvement of 8 days (range: 2 to 43 days).
Among patients with hyperglycemia, the median time to first onset was 7 days (range: 2 to 955 days). Hyperglycemia led to dose interruption in 28%, to dose reduction in 2.5%, and to discontinuation of ITOVEBI in 1.2% of patients.
The safety of ITOVEBI in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus, or Type 2 diabetes mellitus requiring ongoing anti-hyperglycemic treatment have not been studied.
Before initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, test fasting glucose levels (FPG or FBG), HbA1C levels, and optimize fasting glucose.
After initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, or in patients who experience hyperglycemia after initiating treatment with ITOVEBI, monitor or self-monitor fasting glucose levels once every 3 days for the first week (Day 1 to 7), then once every week for the next 3 weeks (Day 8 to 28), then once every 2 weeks for the next 8 weeks, then once every 4 weeks thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Monitor HbA1C every 3 months and as clinically indicated.
Manage hyperglycemia with anti-hyperglycemic medications as clinically indicated. During treatment with anti-hyperglycemic medication, continue monitoring fasting glucose levels. Patients with a history of well-controlled Type 2 diabetes mellitus may require intensified anti-hyperglycemic treatment and close monitoring of fasting glucose levels.
Consider consultation with a healthcare professional experienced in the treatment of hyperglycemia, and initiation of fasting glucose monitoring at home for patients who have risk factors for hyperglycemia or who experience hyperglycemia. Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and counsel patients on lifestyle changes.
Based on the severity of the hyperglycemia, ITOVEBI may require dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Stomatitis
Severe stomatitis can occur in patients treated with ITOVEBI.
Stomatitis occurred in 51% of patients treated with ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant, including Grade 3 events in 6% of patients. The median time to first onset was 13 days (range: 1 to 610 days).
Stomatitis led to dose interruption in 10%, to dose reduction in 3.7%, and to discontinuation of ITOVEBI in 0.6% of patients.
In patients who received ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant, 38% used a mouthwash containing corticosteroid for management or prophylaxis of stomatitis.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of stomatitis. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue ITOVEBI based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Diarrhea
Severe diarrhea, including dehydration and acute kidney injury, can occur in patients treated with ITOVEBI.
Diarrhea occurred in 48% of patients treated with ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant, including Grade 3 events in 3.7% of patients. The median time to first onset was 15 days (range: 2 to 602 days).
Diarrhea led to dose interruptions in 7% of patients, and dose reductions in 1.2% of patients. Anti-diarrheal medicines were used in 28% (46/162) of patients who received ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant to manage symptoms.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of diarrhea. Advise patients to increase oral fluids and start anti-diarrheal treatment at the first sign of diarrhea while taking ITOVEBI. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue ITOVEBI based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, ITOVEBI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of inavolisib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality, structural abnormalities, and alterations to growth at maternal exposures approximately equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on area under the curve (AUC).
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 and 8.3)].
ITOVEBI is used in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for pregnancy and contraception information.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Stomatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
INAVO120
The safety of ITOVEBI was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (INAVO120) in 324 patients with PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Patients received either ITOVEBI 9 mg (n=162) or placebo (n=162) with palbociclib and fulvestrant. The median duration of treatment with ITOVEBI was 9 months (range: 0 to 39 months) in the ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 24% of patients who received ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 1% of patients included anemia (1.9%), diarrhea (1.2%), and urinary tract infection (1.2%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.7% of patients who received ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant, including (0.6% each) acute coronary syndrome, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebrovascular accident, COVID-19 infection, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Permanent discontinuation of ITOVEBI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 6% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of ITOVEBI included hyperglycemia (1.2%), and (0.6% each) stomatitis, gastric ulcer, intestinal perforation, anal abscess, increased ALT, decreased weight, bone pain, musculoskeletal pain, transitional cell carcinoma, and acute kidney injury.
Dosage interruptions of ITOVEBI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 69% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 2% of patients included hyperglycemia (28%), neutropenia (23%), COVID-19 infection (16%), stomatitis (10%), diarrhea (7%), thrombocytopenia (4.9%), anemia (4.3%), upper respiratory tract infection (4.3%), decreased white blood cell count (3.7%), pyrexia (3.1%), nausea (2.5%), and fatigue (2.5%).
Dose reductions of ITOVEBI due to adverse reactions occurred in 14% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reduction of ITOVEBI in ≥ 2% of patients were stomatitis (3.7%) and hyperglycemia (2.5%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, increased fasting glucose, decreased platelets, decreased lymphocytes, stomatitis, diarrhea, decreased calcium, fatigue, decreased potassium, increased creatinine, increased ALT, nausea, decreased sodium, decreased magnesium, rash, decreased appetite, COVID-19 infection, and headache.
Adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in INAVO120 are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. Patient-reported symptoms are summarized in Table 5.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥ 10% with ≥ 5% [All Grades] or ≥ 2% [Grade 3-4] Higher Incidence in the ITOVEBI Arm) in INAVO120 Adverse Reaction ITOVEBI + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant
N=162Placebo + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant
N=162All Grades
(%)Grade 3-4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3-4
(%)- * Includes aphthous ulcer, glossitis, glossodynia, lip ulceration, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, and stomatitis.
- † No Grade 4 adverse reactions were observed.
- ‡ Includes other related terms.
- § Includes dry skin, skin fissures, xerosis, and xeroderma.
Gastrointestinal Disorders Stomatitis* 51 6† 27 0 Diarrhea 48 3.7† 16 0 Nausea 28 0.6† 17 0 Vomiting 15 0.6† 5 1.2† General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 38 1.9† 25 1.2† Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Rash‡ 26 0 19 0 Alopecia 19 0 6 0 Dry skin§ 13 0 4.3 0 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 24 0 9 0 Infections and Infestations COVID-19 infection 23 1.9 11 0.6 Urinary tract infection‡ 15 1.2† 9 0 Nervous System Disorders Headache‡ 22 0 14 0 Investigations Decreased weight 17 3.7† 0.6 0 Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in < 10% of patients who received ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant included abdominal pain, dry eye, dysgeusia, and dyspepsia.
Table 4: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10% with a ≥ 2% [All Grades or Grade 3-4] Higher Incidence in the ITOVEBI Arm) in INAVO120 Laboratory Abnormality ITOVEBI + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant* Placebo + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant† All Grades
(%)Grade 3-4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3-4
(%)ALT = alanine aminotransferase - * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 122 to 160 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
- † The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 131 to 161 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
- ‡ No Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities were observed.
- § Grading according to CTCAE version 4.03.
Hematology Neutrophils (total, absolute) decreased 95 82 97 79 Hemoglobin decreased 88 8‡ 85 2.5‡ Platelets decreased 84 16 71 3.7 Lymphocytes (absolute) decreased 72 9 68 14 Chemistry Glucose (fasting) increased§ 85 12 43 0 Calcium decreased 42 3.1 32 3.7 Potassium decreased 38 6 21 0.6‡ Creatinine increased 38 1.9‡ 30 1.2‡ ALT increased 34 3.1‡ 29 1.2‡ Sodium decreased 28 2.5‡ 19 2.5 Magnesium decreased 27 0.6 21 0 Lipase (fasting) increased 16 1.4‡ 7 0 In INAVO120, patient-reported symptomatic toxicities (i.e., diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, mouth sores, decreased appetite, and rash) were assessed via the Patient-Reported Outcomes – Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (PRO-CTCAE) at baseline, every two weeks through Cycle 3 Day 15, and then Day 1 of every other 28-day cycle until treatment discontinuation.
Completion rates in both arms were > 90% at baseline and > 80% at subsequent time points where > 50% of randomized patients were on treatment.
Table 5: Patient-Reported Symptoms Assessed by PRO-CTCAE in INAVO120 ITOVEBI+P+F = ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm; Placebo+P+F = placebo with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm. - * The symptom attribute scoring is defined by amount/frequency/severity with a score of 0 = 'not at all'/'never'/'none'; 1 = 'a little bit'/'rarely'/'mild'; 2 = 'somewhat'/'occasionally'/'moderate'; 3 = 'quite a bit'/'frequently'/'severe'; 4 = 'very much'/'almost constantly'/'very severe'.
- † The percentage of patients whose symptom score before treatment was 1-4.
- ‡ The percentage of patients whose symptom score increased during treatment, with respect to their score before treatment.
- § The percentage of patients whose symptom score increased to 3 or 4 during treatment, with respect to their score before treatment.
- ¶ The number of patients who provided a score before treatment and at least one on-treatment score.
Symptom (Attribute)* Any Symptom Before Treatment (%)† Any Worsening on Treatment (%)‡ Worsening to Score 3 or 4 (%)§ ITOVEBI + P + F
(N=148)¶Placebo + P + F
(N=152)¶ITOVEBI + P + F
(N=148)¶Placebo + P + F
(N=152)¶ITOVEBI + P + F
(N=148)¶Placebo + P + F
(N=152)¶Diarrhea (frequency), % 23 15 78 49 32 8 Nausea (frequency), % 21 21 59 50 20 11 Vomiting (frequency), % 9 6 35 26 6 3.3 Fatigue (severity), % 72 69 72 58 32 22 Mouth sores (severity), % 11 14 74 52 30 9 Decreased appetite (severity), % 38 28 78 55 26 12 Symptom (Attribute) Baseline Presence Post-baseline Presence ITOVEBI + P + F
(N=148)¶Placebo + P + F
(N=152)¶ITOVEBI + P + F
(N=148)¶Placebo + P + F
(N=152)¶Rash (yes), % 5 5 50 38 Patient-reported overall side-effect impact was assessed using the Modified Bother Item (MBI). Patients provided a response to "I am bothered by side effects of treatment," and at baseline the proportion of patients with MBI responses of "not at all" were 70% in the ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm and 76% in the placebo with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm. At Cycle 2 Day 15, the proportion of patients with MBI responses of "not at all" were 25% in the ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm and 53% in the placebo with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm. Through 31 cycles of treatment, patients in the ITOVEBI with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm reported more side effect bother compared to the placebo with palbociclib and fulvestrant arm.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ITOVEBI. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Ketoacidosis
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
ITOVEBI is used in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for pregnancy information.
Based on animal data and its mechanism of action, ITOVEBI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on the use of ITOVEBI in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of inavolisib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality, structural abnormalities, and alterations to growth at maternal exposures approximately equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC (see Data). Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats received oral doses of inavolisib up to 6 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Administration of doses ≥ 2 mg/kg/day resulted in decreases in fetal body weight and placental weight, post-implantation loss, lower fetal viability, fetal malformations (including kyphosis of vertebral column, fused thoracic arch, microphthalmia) and variations (including dilated renal pelvis, short supernumerary rib, wavy rib). At a dose of 2 mg/kg/day, maternal exposures were 0.9 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
ITOVEBI is used in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for lactation information.
There are no data on the presence of inavolisib or its metabolites in human milk, its effects on milk production or a breastfed child. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise lactating women to not breastfeed during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
ITOVEBI is used in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for contraception and infertility information.
ITOVEBI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with ITOVEBI.
Contraception
Infertility
Based on animal studies, ITOVEBI may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of ITOVEBI in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 162 patients who received ITOVEBI in INAVO120, 15% were ≥ 65 years of age, and 3% were ≥ 75 years of age.
Dosage modifications or interruptions of ITOVEBI due to adverse reactions occurred at a higher incidence for patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to younger patients (79% versus 68%, respectively).
Clinical studies of ITOVEBI did not include sufficient numbers of patients ≥ 65 years of age to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Reduce the dosage in patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min based on CKD-EPI) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild renal impairment (eGFR 60 to < 90 mL/min). ITOVEBI has not been evaluated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ITOVEBI contains inavolisib, a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name of inavolisib is (2S)-2-[[2-[(4S)-4-(difluoromethyl)-2-oxo-oxazolidin-3-yl]-5,6-dihydroimidazo[1,2-d][1,4]benzoxazepin-9-yl]amino]propanamide. Inavolisib is a white to off-white, greyish pink, greyish orange, or greyish yellow powder or powder with lumps. Inavolisib demonstrates pH-dependent aqueous solubility; the greatest solubility is at low pH, and solubility decreases with increasing pH. The molecular formula for inavolisib is C18H19F2N5O4 and the molecular weight is 407.37 g/mol. The chemical structure of inavolisib is shown below:
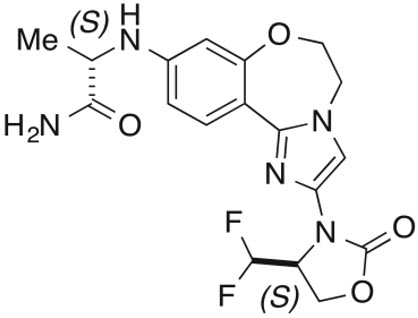
ITOVEBI film-coated tablets are supplied for oral administration with two strengths that contain 3 mg and 9 mg of inavolisib. The tablets also contain lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate. The film-coating contains the following inactive ingredients: polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), titanium dioxide, macrogol/polyethylene glycol, talc, iron oxide red, and iron oxide yellow (in the 9 mg tablet only).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Inavolisib is an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) with inhibitory activity predominantly against PI3Kα. In vitro, inavolisib induced the degradation of mutated PI3K catalytic alpha subunit p110α (encoded by the PIK3CA gene), inhibited phosphorylation of the downstream target AKT, reduced cellular proliferation, and induced apoptosis in PIK3CA-mutated breast cancer cell lines. In vivo, inavolisib reduced tumor growth in PIK3CA-mutated, estrogen receptor-positive, breast cancer xenograft models. The combination of inavolisib with palbociclib and fulvestrant increased tumor growth inhibition compared to each treatment alone or the doublet combinations.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationships
The exposure-response relationship for the efficacy of inavolisib has not been fully characterized. Inavolisib time course of pharmacodynamic response is unknown. Higher systemic exposure of inavolisib was associated with higher incidence of Grade ≥ 2 anemia, Grade ≥ 2 hyperglycemia, and inavolisib dosage modifications due to adverse reactions.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Inavolisib pharmacokinetics are presented as geometric mean (geometric coefficient of variation [geo CV]%) following administration of the approved recommended dosage unless otherwise specified. The inavolisib steady-state AUC is 1,010 h*ng/mL (25%) and Cmax is 69 ng/mL (27%). Steady-state concentrations are predicted to be attained by day 5.
Inavolisib accumulation is approximately 2-fold.
Inavolisib steady-state AUC is proportional with dose from 6 to 12 mg (0.7 to 1.3 times the approved recommended dosage).
Absorption
Inavolisib absolute oral bioavailability is 76%. Inavolisib steady-state median (min, max) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 3 hours (0.5, 4 hours).
Distribution
Inavolisib apparent (oral) volume of distribution is 155 L (26%). Inavolisib plasma protein binding is 37% and is not concentration-dependent in vitro. Inavolisib blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.8.
Elimination
Inavolisib elimination half-life is 15 hours (24%) with a total clearance of 8.8 L/hr (29%).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of inavolisib were observed based on age (27 to 85 years), sex, race (Asian or White), body weight (39 to 159 kg), or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > ULN to ≤ 1.5 × ULN or AST > ULN and total bilirubin ≤ ULN). The effect of moderate to severe hepatic impairment on inavolisib pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Inavolisib AUC was 73% higher in patients with moderate renal impairment compared to patients with normal renal function (eGFR ≥ 90 mL/min).
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of inavolisib were observed in patients with mild renal impairment compared to patients with normal renal function. The effect of severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min) on the pharmacokinetics of inavolisib is unknown.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with inavolisib have not been conducted.
Inavolisib was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. Inavolisib was clastogenic in an in vitro human lymphocyte micronucleus assay. Inavolisib was not genotoxic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus test and did not induce DNA break in a liver comet assay.
Fertility studies with inavolisib have not been conducted. In repeat-dose toxicity studies, inavolisib was administered orally once daily for up to 3 months duration in rats and dogs.
In male rats, dose-dependent atrophy of the prostate and seminal vesicle and decreased organ weights of the prostate, seminal vesicle, epididymis and testis were observed at doses ≥ 1.5 mg/kg/day (≥ 0.4 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC). In male dogs, focal inspissation of seminiferous tubule contents and multinucleated spermatids in the testis and epithelial degeneration/necrosis in the epididymis were observed following 4 weeks of dosing at ≥ 1.5 mg/kg/day (≥ 2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC) and decreased sperm count was observed following 3 months of dosing at ≥ 1 mg/kg/day (≥ 1.2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC). Findings in dogs were not observed following a recovery period.
In female rats, atrophy in the uterus and vagina, decreased ovarian follicles, and findings suggestive of an interruption/alteration of the estrous cycle were observed following up to 3 months of dosing at doses ≥ 3 mg/kg/day (≥ 1.2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC). Findings in the uterus, vagina, and estrous cycle observed in the 4-week toxicity study were not observed following recovery. Recovery was not assessed in the 3-month study in rats.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Lens degeneration, characterized by lens fiber swelling, separation of lens fibers, and/or accumulation of subcapsular proteinaceous material, was observed in rats at an oral inavolisib dose of 10 mg/kg/day (6.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 9 mg/day based on AUC). In dogs, lens fiber swelling and lens cortex vacuolation were observed at oral inavolisib doses ≥ 0.3 mg/kg/day (≥ 0.5 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC) and ≥ 1 mg/kg/day (≥ 1.2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC), respectively. Lens degeneration was present in rats following a 4-week recovery period but was not present in dogs following a 12-week recovery period.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
INAVO120
INAVO120 (NCT04191499) was a randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of ITOVEBI in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant in adult patients with endocrine-resistant PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative (defined as IHC 0 or 1+, or IHC 2+/ISH-), locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer whose disease progressed during or within 12 months of completing adjuvant endocrine therapy and who have not received prior systemic therapy for locally advanced or metastatic disease. Randomization was stratified by presence of visceral disease (yes or no), endocrine resistance (primary or secondary), and geographic region (North America/Western Europe, Asia, other).
Primary endocrine resistance was defined as relapse while on the first 2 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET) and secondary endocrine resistance was defined as relapse while on adjuvant ET after at least 2 years or relapse within 12 months of completing adjuvant ET.
Patients were required to have HbA1C < 6% and fasting blood glucose < 126 mg/dL. The study excluded patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus or Type 2 diabetes mellitus requiring ongoing anti-hyperglycemic treatment at the start of study treatment.
PIK3CA mutation status was prospectively determined in a central laboratory using the FoundationOne® Liquid CDx assay on plasma-derived circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or in local laboratories using various validated polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or next-generation sequencing (NGS) assays on tumor tissue or plasma. All patients were required to provide both a freshly collected pre-treatment blood sample and a tumor tissue sample for central evaluation and determination of PIK3CA mutation(s) status.
Patients received either ITOVEBI 9 mg (n=161) or placebo (n=164) orally once daily, in combination with palbociclib 125 mg orally once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment to comprise a cycle of 28 days, and fulvestrant 500 mg administered intramuscularly on Cycle 1, Days 1 and 15, and then on Day 1 of every 28-day cycle. Patients received treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In addition, all pre/perimenopausal women and men received an LHRH agonist throughout therapy.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were: median age 54 years (range: 27 to 79 years); 98% female; 38% pre/perimenopausal; 59% White, 38% Asian, 2.5% unknown, 0.6% Black or African American; 6% Hispanic or Latino; and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 (63%) or 1 (36%). Tamoxifen (57%) and aromatase inhibitors (50%) were the most commonly used adjuvant endocrine therapies. Sixty-four percent of patients were considered to have secondary endocrine resistance. Eighty-three percent of patients had received prior chemotherapy (in the neo/adjuvant setting) and 1.2% of patients had been treated with a CDK4/6 inhibitor.
The major efficacy outcome measure was investigator (INV)-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1. Additional efficacy outcome measures included overall survival (OS), INV-assessed objective response rate (ORR), and INV-assessed duration of response (DOR).
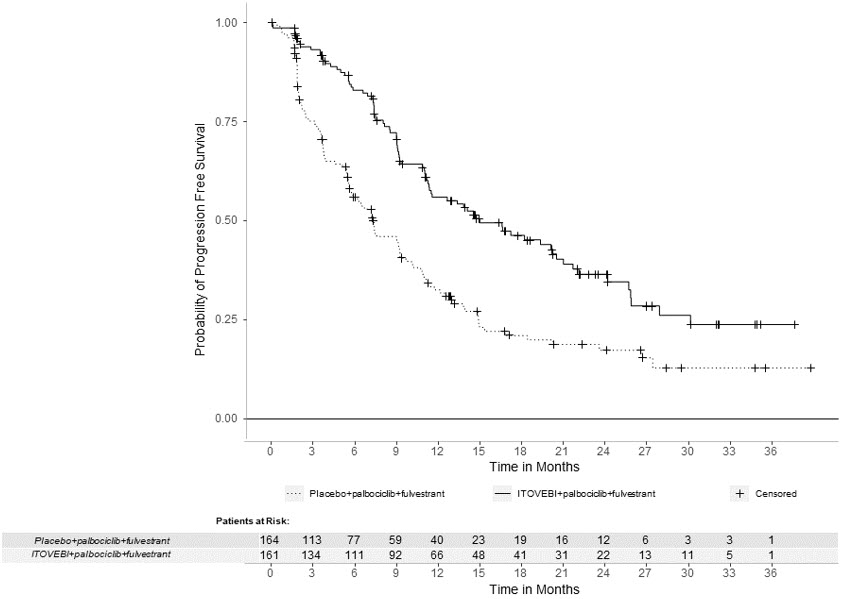
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 6 and Figure 1. INV-assessed PFS results were supported by consistent results from a blinded independent central review (BICR) assessment. At the time of the PFS analysis, OS data were not mature with 30% deaths in the overall population.
Table 6: Efficacy Results in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer in INAVO120 Efficacy Endpoint ITOVEBI + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant
N=161Placebo + Palbociclib + Fulvestrant
N=164CI = confidence interval; CR = complete response; DOR = duration of response; PR = partial response - * Per RECIST version 1.1.
- † Based on investigator assessment.
- ‡ Based on confirmed ORR.
Progression-Free Survival*,† Patients with event, n (%) 82 (51) 113 (69) Median, months (95% CI) 15.0 (11.3, 20.5) 7.3 (5.6, 9.3) Hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.43 (0.32, 0.59) p-value < 0.0001 Objective Response Rate*,†,‡ Patients with CR or PR, n (%) 94 (58) 41 (25) 95% CI (50, 66) (19, 32) Duration of Response† Median DOR, months (95% CI) 18.4 (10.4, 22.2) 9.6 (7.4, 16.6) Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Investigator-Assessed Progression-Free Survival in INAVO120
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ITOVEBI is supplied in the following strengths and package configurations:
Package Configuration Tablet Strength NDC Tablet Description Bottle of 28 tablets 3 mg 50242-084-08 Red and round convex-shaped with an "INA 3" debossing on one side Bottle of 28 tablets 9 mg 50242-079-08 Pink and oval-shaped with an "INA 9" debossing on one side -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hyperglycemia
Advise patients that ITOVEBI may cause severe or fatal hyperglycemia, including ketoacidosis, and that monitoring fasting glucose levels before and periodically during therapy is needed. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia (e.g., excessive thirst, urinating more often, blurred vision, confusion, difficulty breathing, or increased appetite with weight loss) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Stomatitis
Advise patients that ITOVEBI may cause stomatitis, which may be severe, and to notify their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of stomatitis (e.g., painful redness, swelling, or sores in the mouth) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Diarrhea
Advise patients that ITOVEBI may cause diarrhea, which may be severe, and to start anti-diarrheal treatment, increase oral fluids, and notify their healthcare provider if diarrhea occurs while taking ITOVEBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Inform pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for pregnancy and contraception information.
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)]. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for lactation information.
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential that ITOVEBI may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information of palbociclib and fulvestrant for infertility information.
Dosing
- Instruct patients to take ITOVEBI at approximately the same time each day [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Instruct patients that if a dose of ITOVEBI is missed, to take the missed dose as soon as possible within 9 hours. After more than 9 hours, skip the dose and take the next dose at the scheduled time [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Instruct patients that if vomiting occurs after taking the ITOVEBI dose, do not take an additional dose on that day. Resume the usual dosing schedule the next day [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 12/2025 PATIENT INFORMATION
ITOVEBI® (eye-TOVE-bee)
(inavolisib)
tablets, for oral useImportant: ITOVEBI is used with palbociclib and fulvestrant. You should also read the Patient Information that comes with palbociclib and fulvestrant. What is ITOVEBI?
ITOVEBI is a prescription medicine used in combination with the medicines palbociclib and fulvestrant to treat adults who have hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer that has an abnormal phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) gene, and has spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes (locally advanced), or to other parts of the body (metastatic), and has come back after hormone (endocrine) therapy.
Your healthcare provider will test your cancer for abnormal PIK3CA genes to make sure that ITOVEBI is right for you.
It is not known if ITOVEBI is safe and effective in children.Before you take ITOVEBI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have a history of diabetes or high blood sugar.
- have kidney problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. ITOVEBI can harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider will check to see if you are pregnant before you start treatment with ITOVEBI.
- You should use effective non-hormonal birth control (contraception) during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after your last dose. Talk to your healthcare provider about what birth control method is right for you during this time.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with ITOVEBI.
- You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after your last dose.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ITOVEBI passes into your breastmilk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with ITOVEBI and for 1 week after your last dose. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with ITOVEBI.
How should I take ITOVEBI? - Take ITOVEBI exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking ITOVEBI unless your healthcare provider tells you.
- Take ITOVEBI 1 time each day, at about the same time each day.
- Take ITOVEBI with or without food.
- Swallow ITOVEBI tablet(s) whole. Do not chew, crush, or split the tablet(s).
- If you miss a dose of ITOVEBI, you may still take your missed dose within 9 hours from the time you usually take it. If it has been more than 9 hours after you usually take your dose, skip the dose for that day. The next day, take the dose at your usual time.
- If you vomit after taking a dose of ITOVEBI, do not take an extra dose on that day. Take your regular dose of ITOVEBI at your usual time the next day.
- For women who have not reached menopause or are just starting menopause, your healthcare provider will prescribe a medicine called luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist. For men, your healthcare provider may prescribe a LHRH agonist.
What are the possible side effects of ITOVEBI?
ITOVEBI may cause serious side effects, including:-
High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). High blood sugar is common with ITOVEBI, and may be severe or fatal. Untreated severe hyperglycemia can lead to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis that can happen in people treated with ITOVEBI. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious condition that requires treatment in a hospital and that can lead to death. Your healthcare provider will monitor your blood sugar levels before you start and during treatment with ITOVEBI. Your blood sugar levels may be monitored more often if you have a history of Type 2 diabetes. Your healthcare provider may also ask you to self-monitor and report your blood sugar levels at home. This will be required more frequently in the first 4 weeks of treatment. If you are not sure how to test your blood sugar levels, talk to your healthcare provider. You should stay well-hydrated during treatment with ITOVEBI.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop symptoms of high blood sugar, including:
- difficulty breathing
- nausea and vomiting (lasting more than 2 hours)
- stomach pain
- excessive thirst
- dry mouth
- more frequent urination than usual or a higher amount of urine than normal
- blurred vision
- unusually increased appetite
- weight loss
- fruity-smelling breath
- flushed face and dry skin
- feeling unusually sleepy or tired
- confusion
- Mouth sores (stomatitis). Mouth sores are common with ITOVEBI and may be severe. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any of the following in your mouth:
- pain
- redness
- swelling
- ulcers
- Diarrhea. Diarrhea is common with ITOVEBI and may be severe. Severe diarrhea can lead to the loss of too much body water (dehydration) and kidney injury. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop diarrhea, stomach-area (abdominal) pain, or see mucus or blood in your stool during treatment with ITOVEBI. Your healthcare provider may tell you to drink more fluids or take medicines to treat your diarrhea.
The most common side effects and abnormal blood test results of ITOVEBI when used in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant include:- decreased white blood cell counts, red blood cell counts, and platelet counts
- decreased blood levels of calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium
- increased creatinine blood levels
- tiredness
- increased blood levels of the liver enzyme alanine transaminase (ALT)
- nausea
- rash
- loss of appetite
- COVID-19 infection
- headache
ITOVEBI may affect fertility in males and in females who are able to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all of the possible side effects of ITOVEBI.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store ITOVEBI? - Store ITOVEBI at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store ITOVEBI in the original container and keep the bottle tightly closed to protect from moisture.
General information about the safe and effective use of ITOVEBI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ITOVEBI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ITOVEBI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ITOVEBI that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in ITOVEBI?
Active ingredient: inavolisib
Inactive ingredients: lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate. The tablet film-coating contains iron oxide red, and iron oxide yellow (in the 9 mg tablet only), macrogol/polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, and titanium dioxide.
Distributed by: Genentech, Inc., A Member of the Roche Group, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
ITOVEBI is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
For more information, go to www.ITOVEBI.com or call 1-877-436-3683. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 9 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC: 50242-079-08
Itovebi®
(inavolisib)
Tablets9 mg
Swallow tablets whole.
DO NOT chew, crush,
or split tablets.28 Tablets
Rx only
Genentech11039960
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 3 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC: 50242-084-08
Itovebi®
(inavolisib)
Tablets3 mg
Swallow tablets whole.
DO NOT chew, crush,
or split tablets.28 Tablets
Rx only
Genentech11039843
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ITOVEBI
inavolisib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50242-079 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INAVOLISIB (UNII: L4C1UY2NYH) (INAVOLISIB - UNII:L4C1UY2NYH) INAVOLISIB 9 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A (UNII: H8AV0SQX4D) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape OVAL Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code INA9 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50242-079-08 1 in 1 CARTON 10/14/2024 1 28 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 50242-079-86 1 in 1 CARTON 01/06/2025 2 28 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219249 10/14/2024 ITOVEBI
inavolisib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50242-084 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INAVOLISIB (UNII: L4C1UY2NYH) (INAVOLISIB - UNII:L4C1UY2NYH) INAVOLISIB 3 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A (UNII: H8AV0SQX4D) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) Product Characteristics Color RED Score no score Shape ROUND Size 4mm Flavor Imprint Code INA3 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50242-084-08 1 in 1 CARTON 10/14/2024 1 28 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219249 10/14/2024 Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Registrant - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG 482242971 API MANUFACTURE(50242-079, 50242-084) , ANALYSIS(50242-079, 50242-084) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG 485244961 MANUFACTURE(50242-079, 50242-084) , ANALYSIS(50242-079, 50242-084) , LABEL(50242-079, 50242-084) , PACK(50242-079, 50242-084)
Trademark Results [Itovebi]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ITOVEBI 98720013 not registered Live/Pending |
Genentech, Inc. 2024-08-27 |
 ITOVEBI 98648555 not registered Live/Pending |
Genentech, Inc. 2024-07-15 |
 ITOVEBI 90372806 not registered Live/Pending |
Genentech, Inc. 2020-12-10 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.