Clopidogrel by H.J. Harkins Company Inc / H. J. Harkins Company Inc. CLOPIDOGREL tablet
Clopidogrel by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clopidogrel by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by H.J. Harkins Company Inc, H. J. Harkins Company Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
BOXED WARNING
WARNING:DIMINISHED ANTIPLATELET EFFECT IN PATIENTS WITH TWO LOSS-OF-FUNCTION ALLELES OF THE CYP2C19 GENE
The effectiveness of Clopidogrel results from its antiplatelet activity, which is dependent on its conversion to an active metabolite by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, principally CYP2C19 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Clopidogrel at recommended doses forms less of the active metabolite and so has a reduced effect on platelet activity in patients who are homozygous for nonfunctional alleles of the CYP2C19 gene, (termed “CYP2C19 poor metabolizers”). Tests are available to identify patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. Consider use of another platelet P2Y12 inhibitor in patients identified as CYP2C19 poor metabolizers.
-
Indictaions and Usage
1.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Clopidogrel is indicated to reduce the rate of myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke in patients with non-ST-segment elevation ACS [unstable angina (UA)/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)], including patients who are to be managed medically and those who are to be managed with coronary revascularization. Clopidogrel should be administered in conjunction with aspirin.
Clopidogrel is indicated to reduce the rate of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who are to be managed medically. Clopidogrel should be administered in conjunction with aspirin.1.2 Recent MI, Recent Stroke, or Established Peripheral Arterial Disease
In patients with established peripheral arterial disease or with a history of recent myocardial infarction (MI) or recent stroke clopidogrel is indicated to reduce the rate of MI and stroke.
-
Dosage and Administration
2.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome
In patients who need an antiplatelet effect within hours, initiate clopidogrel with a single 300-mg oral loading dose and then continue at 75 mg once daily. Initiating clopidogrel without a loading dose will delay establishment of an antiplatelet effect by several days [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
2.2 Recent MI, Recent Stroke, or Established Peripheral Arterial Disease
75 mg once daily orally without a loading dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
- Dosage forms and Strengths
-
Contraindictaions
4.1 Active Bleeding
Clopidogrel tablets are contraindicated in patients with active pathological bleeding such as peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage.
4.2 Hypersensitivity
Clopidogrel tablets are contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis) to clopidogrel or any component of the product [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Diminished Antiplatelet Activity in Patients with Impaired CYP2C19 Function
Clopidogrel is a prodrug. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by clopidogrel is achieved through an active metabolite. The metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite can be impaired by genetic variations in CYP2C19 [seeBOXED WARNING].
The metabolism of clopidogrel can also be impaired by drugs that inhibit CYP2C19, such as omeprazole or esomeprazole. Avoid concomitant use of clopidogrel with omeprazole or esomeprazole because both significantly reduce the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.2 General Risk of Bleeding
Thienopyridines, including clopidogrel, increase the risk of bleeding.
Thienopyridines inhibit platelet aggregation for the lifetime of the platelet (7-10 days). Because the half-life of clopidogrel’s active metabolite is short, it may be possible to restore hemostasis by administering exogenous platelets; however, platelet transfusions within 4 hours of the loading dose or 2 hours of the maintenance dose may be less effective.
5.3 Discontinuation of clopidogrel tablets
Discontinuation of clopidogrel increases the risk of cardiovascular events. If clopidogrel must be temporarily discontinued (e.g., to treat bleeding or for surgery with a major risk of bleeding), restart it as soon as possible.When possible, interrupt therapy with clopidogrel for five days prior to such surgery. Resume clopidogrel as soon as hemostasis is achieved.
5.4 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
TTP, sometimes fatal, has been reported following use of clopidogrel, sometimes after a short exposure (<2 weeks). TTP is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment including plasmapheresis (plasma exchange). It is characterized by thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (schistocytes [fragmented RBCs] seen on peripheral smear), neurological findings, renal dysfunction, and fever [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.5 Cross-Reactivity among Thienopyridines
Hypersensitivity including rash, angioedema or hematologic reaction have been reported in patients receiving clopidogrel, including patients with a history of hypersensitivity or hematologic reaction to other thienopyridines [see Contraindications (4.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
Adverse Reactions
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling:
Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions and durations of follow up, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clopidogrel has been evaluated for safety in more than 54,000 patients, including over 21,000 patients treated for one year or more. The clinically important adverse reactions observed in trials comparing clopidogrel plus aspirin to placebo plus aspirin and trials comparing clopidogrel alone to aspirin alone are discussed below.
Bleeding
CURE
In CURE, clopidogrel use with aspirin was associated with an increase in major bleeding (primarily gastrointestinal and at puncture sites) compared to placebo with aspirin (see Table 1). The incidence of intracranial hemorrhage (0.1%) and fatal bleeding (0.2%) were the same in both groups. Other bleeding events that were reported more frequently in the clopidogrel group were epistaxis, hematuria, and bruise.
The overall incidence of bleeding is described in Table 1.
Table 1: CURE Incidence of Bleeding Complications (% patients)
Event
clopidogrel
(+ aspirin)
Placebo
(+ aspirin)
(n=6259)
(n=6303)
Major bleeding†
3.7
2.7
Life-threatening bleeding
2.2
1.8
Fatal
0.2
0.2
5 g/dL hemoglobin drop
0.9
0.9
Requiring surgical intervention
0.7
0.7
Hemorrhagic strokes
0.1
0.1
Requiring inotropes
0.5
0.5
Requiring transfusion (≥4 units)
1.2
1.0
Other major bleeding
1.6
1.0
Significantly disabling
0.4
0.3
Intraocular bleeding with
significant loss of vision
0.05
0.03
Requiring 2–3 units of
blood
1.3
0.9
Minor bleeding¶
5.1
2.4
† Life-threatening and other major bleeding.
¶ Led to interruption of study medication.
COMMIT
In COMMIT, similar rates of major bleeding were observed in the clopidogrel and placebo groups, both of which also received aspirin (see Table 2).Table 2: Incidence of Bleeding Events in COMMIT (% patients)
Type of bleeding
Clopidogrel (+ aspirin) (n=22961)
Placebo
(+ aspirin) (n=22891)
p-value
Major* noncerebral or cerebral bleeding
0.6
0.5
0.59
Major noncerebral
0.4
0.3
0.48
Fatal
0.2
0.2
0.90
Hemorrhagic stroke
0.2
0.2
0.91
Fatal
0.2
0.2
0.81
Other noncerebral bleeding (non-major)
3.6
3.1
0.005
Any noncerebral bleeding
3.9
3.4
0.004
* Major bleeds were cerebral bleeds or non-cerebral bleeds thought to have caused death or that required transfusion.
CAPRIE (Clopidogrel vs. Aspirin)
In CAPRIE, gastrointestinal hemorrhage occurred at a rate of 2.0% in those taking clopidogrel vs. 2.7% in those taking aspirin; bleeding requiring hospitalization occurred in 0.7% and 1.1%, respectively. The incidence of intracranial hemorrhage was 0.4% for clopidogrel compared to 0.5% for aspirin.Other bleeding events that were reported more frequently in the clopidogrel group were epistaxis and hematoma.
Other Adverse Events
In CURE and CHARISMA, which compared clopidogrel plus aspirin to aspirin alone, there was no difference in the rate of adverse events (other than bleeding) between clopidogrel and placebo.
In CAPRIE, which compared clopidogrel to aspirin, pruritus was more frequently reported in those taking clopidogrel. No other difference in the rate of adverse events (other than bleeding) was reported.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of clopidogrel. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hemorrhages, including those with fatal outcome, have been reported in patients treated with clopidogrel
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia/pancytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), acquired hemophilia A
Gastrointestinal disorders: Colitis (including ulcerative or lymphocytic colitis), pancreatitis, stomatitis, gastric/duodenal ulcer, diarrhea
General disorders and administration site condition: Fever
Hepato-biliary disorders: Acute liver failure, hepatitis (non-infectious), abnormal liver function test
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactoid reactions, serum sickness
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders: Myalgia, arthralgia, arthritis
Nervous system disorders: Taste disorders, headache
Psychiatric disorders: Confusion, hallucinations
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Bronchospasm, interstitial pneumonitis, eosinophilic pneumonia
Renal and urinary disorders: Increased creatinine levels
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Maculopapular, erythematous or exfoliative rash, urticaria, bullous dermatitis, eczema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), angioedema, drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), erythema multiforme, lichen planus, generalized pruritus
Vascular disorders: Vasculitis, hypotension -
Drug Interactions
7.1 CYP2C19 Inhibitors
Clopidogrel is metabolized to its active metabolite in part by CYP2C19. Concomitant use of drugs that inhibit the activity of this enzyme results in reduced plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and a reduction in platelet inhibition [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Omeprazole or esomeprazole
Avoid concomitant use of clopidogrel with omeprazole or esomeprazole. In clinical studies, omeprazole was shown to reduce significantly the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel when given concomitantly or 12 hours apart. A similar reduction in antiplatelet activity was observed with esomeprazole when given concomitantly with clopidogrel. Dexlansoprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole had less effect on the antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel than did omeprazole or esomeprazole [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].7.2 Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Coadministration of clopidogrel and NSAIDs increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
7.3 Warfarin (CYP2C9 Substrates)
Although the administration of clopidogrel 75 mg per day did not modify the pharmacokinetics of S-warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate) or INR in patients receiving long-term warfarin therapy, coadministration of clopidogrel with warfarin increases the risk of bleeding because of independent effects on hemostasis.
However, at high concentrations in vitro, clopidogrel inhibits CYP2C9.
7.4 SSRIs and SNRIs
Since selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) affect platelet activation, the concomitant administration of SSRIs and SNRIs with clopidogrel may increase the risk of bleeding.
7.5 Repaglinide (CYP2C8 Substrates)
The acyl-β-glucuronide metabolite of clopidogrel is a strong inhibitor of CYP2C8. Clopidogrel can increase the systemic exposure to drugs that are primarily cleared by CYP2C8, thereby needing dose-adjustment and appropriate monitoring.
Clopidogrel increased repaglinide exposures by 3.9-to 5.1-fold [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid concomitant use of repaglinide with clopidogrel. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, initiate repaglinide at 0.5 mg before each meal and do not exceed a total daily dose of 4 mg. Increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required during concomitant use. -
Use in Specfic Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category BReproduction studies performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 500 and 300 mg/kg/day, respectively (65 and 78 times the recommended daily human dose, respectively, on a mg/m2 basis), revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or fetotoxicity due to clopidogrel. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of a human response, clopidogrel should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Studies in rats have shown that clopidogrel and/or its metabolites are excreted in the milk. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from clopidogrel, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric populations have not been established.
A randomized, placebo-controlled trial (CLARINET) did not demonstrate a clinical benefit of clopidogrel in neonates and infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease palliated with a systemic-to-pulmonary arterial shunt. Possible factors contributing to this outcome were the dose of clopidogrel, the concomitant administration of aspirin and the late initiation of therapy following shunt palliation. It cannot be ruled out that a trial with a different design would demonstrate a clinical benefit in this patient population.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in the CAPRIE and CURE controlled clinical studies, approximately 50% of patients treated with clopidogrel were 65 years of age and older, and 15% were 75 years and older. In COMMIT, approximately 58% of the patients treated with clopidogrel were 60 years and older, 26% of whom were 70 years and older.
The observed risk of bleeding events with clopidogrel plus aspirin versus placebo plus aspirin by age category is provided in Table 1 and Table 2 for the CURE and COMMIT trials, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. No dosage adjustment is necessary in elderly patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Experience is limited in patients with severe and moderate renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
-
Overdosage
Platelet inhibition by clopidogrel is irreversible and will last for the life of the platelet. Overdose following clopidogrel administration may result in bleeding complications. A single oral dose of clopidogrel at 1500 or 2000 mg/kg was lethal to mice and to rats and at 3000 mg/kg to baboons. Symptoms of acute toxicity were vomiting, prostration, difficult breathing, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage in animals.
Based on biological plausibility, platelet transfusion may restore clotting ability.
-
Description
Clopidogrel bisulfate, USP is a thienopyridine class inhibitor of P2Y12 ADP platelet receptors. Chemically it is methyl (+)-(S)-α-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H) acetate sulfate (1:1). The empirical formula of clopidogrel bisulfate is C16H16ClNO2SH2SO4 and its molecular weight is 419.9.
The structural formula is as follows:
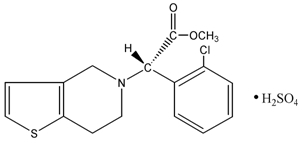
Clopidogrel bisulfate, USP is a white to off-white powder. It is practically insoluble in water at neutral pH but freely soluble at pH 1. It also dissolves freely in methanol, dissolves sparingly in methylene chloride, and is practically insoluble in ethyl ether. It has a specific optical rotation of about +56°.
Clopidogrel tablets USP, 75 mg for oral administration is provided as either pink, round, biconvex, debossed, film-coated tablets containing 97.875 mg of clopidogrel bisulfate which is the molar equivalent of 75 mg of clopidogrel base.
Each tablet contains lactose monohydrate, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, dimethicone and hydrogenated castor oil as inactive ingredients. The pink film coating contains hypromellose 2910, polyethylene glycol 400, titanium dioxide and iron oxide red. -
Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Clopidogrel is an inhibitor of platelet activation and aggregation through the irreversible binding of its active metabolite to the P2Y12 class of ADP receptors on platelets.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Clopidogrel must be metabolized by CYP450 enzymes to produce the active metabolite that inhibits platelet aggregation. The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP-mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible. Consequently, platelets exposed to clopidogrel’s active metabolite are affected for the remainder of their lifespan (about 7 to 10 days). Platelet aggregation induced by agonists other than ADP is also inhibited by blocking the amplification of platelet activation by released ADP.
Dose-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation can be seen 2 hours after single oral doses of clopidogrel. Repeated doses of 75 mg clopidogrel per day inhibit ADP-induced platelet aggregation on the first day, and inhibition reaches steady state between Day 3 and Day 7. At steady state, the average inhibition level observed with a dose of 75 mg clopidogrel per day was between 40% and 60%. Platelet aggregation and bleeding time gradually return to baseline values after treatment is discontinued, generally in about 5 days.
Geriatric Patients
Elderly (≥75 years) and young healthy subjects had similar effects on platelet aggregation.
Renally-Impaired Patients
After repeated doses of 75 mg clopidogrel per day, patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance from 5 to 15 mL/min) and moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance from 30 to 60 mL/min) showed low (25%) inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation.
Hepatically-Impaired Patients
After repeated doses of 75 mg clopidogrel per day for 10 days in patients with severe hepatic impairment, inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was similar to that observed in healthy subjects.
Gender
In a small study comparing men and women, less inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was observed in women.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Clopidogrel is a prodrug and is metabolized to a pharmacologically active metabolite and inactive metabolites.
Absorption
After single and repeated oral doses of 75 mg per day, clopidogrel is rapidly absorbed. Absorption is at least 50%, based on urinary excretion of clopidogrel metabolites.
Effect of Food
Clopidogrel tablets can be administered with or without food. In a study in healthy male subjects when clopidogrel tablets 75 mg per day was given with a standard breakfast, mean inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was reduced by less than 9%. The active metabolite AUC0 to 24 was unchanged in the presence of food, while there was a 57% decrease in active metabolite Cmax. Similar results were observed when a clopidogrel tablets 300 mg loading dose was administered with a high-fat breakfast.
Metabolism
Clopidogrel is extensively metabolized by two main metabolic pathways: one mediated by esterases and leading to hydrolysis into an inactive carboxylic acid derivative (85% of circulating metabolites) and one mediated by multiple cytochrome P450 enzymes. Cytochromes first oxidize clopidogrel to a 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Subsequent metabolism of the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite results in formation of the active metabolite, a thiol derivative of clopidogrel. The active metabolite is formed mostly by CYP2C19 with contributions from several other CYP enzymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2B6 and CYP3A. The active thiol metabolite binds rapidly and irreversibly to platelet receptors, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation for the lifespan of the platelet.
The Cmax of the active metabolite is twice as high following a single 300 mg clopidogrel loading dose as it is after four days of 75 mg maintenance dose. Cmax occurs approximately 30 to 60 minutes after dosing. In the 75 to 300 mg dose range, the pharmacokinetics of the active metabolite deviates from dose proportionality: 4-fold the dose results in 2.0-and 2.7-fold the Cmax and AUC, respectively.Elimination
Following an oral dose of 14C-labeled clopidogrel in humans, approximately 50% of total radioactivity was excreted in urine and approximately 46% in feces over the 5 days post-dosing. After a single, oral dose of 75 mg, clopidogrel has a half-life of approximately 6 hours. The half-life of the active metabolite is about 30 minutes.
Drug Interactions
Effect of other drugs on ClopidogrelClopidogrel is metabolized to its active metabolite in part by CYP2C19. Concomitant use of certain inhibitors of this enzyme results in reduced plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and a reduction in platelet inhibition.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
The effect of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) on the systemic exposure to the clopidogrel active metabolite following multiple doses of clopidogrel tablets 75 mg evaluated in dedicated drug interaction studies is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Exposure to Clopidogrel Active Metabolite Following Multiple Doses of Clopidogrel Tablets, 75 mg Alone or with Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
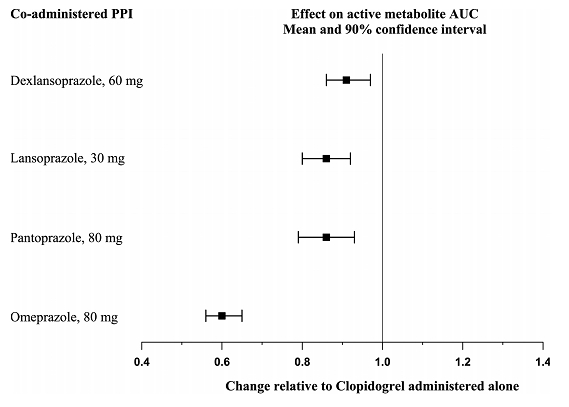
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic parameters measured in these studies showed that the interaction was highest with omeprazole and least with dexlansoprazole.
Effect of Clopidogrel on other drugs
In vitro studies have shown that the glucuronide metabolite of clopidogrel is a strong inhibitor of CYP2C8. Concomitant administration of repaglinide with clopidogrel increased the systemic exposure to repaglinide (AUC0-∞) by 5.1-fold following the loading dose (300 mg) and by 3.9-fold on day 3 of the maintenance dose (75 mg) of clopidogrel [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].12.5 Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C19 is involved in the formation of both the active metabolite and the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Clopidogrel active metabolite pharmacokinetics and antiplatelet effects, as measured by ex vivo platelet aggregation assays, differ according to CYP2C19 genotype. Patients who are homozygous for nonfunctional alleles of the CYP2C19 gene are termed “CYP2C19 poor metabolizers”. Approximately 2% of White and 4% of Black patients are poor metabolizers; the prevalence of poor metabolism is higher in Asian patients (e.g., 14% of Chinese). Tests are available to identify patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers.
A crossover study in 40 healthy subjects, 10 each in the four CYP2C19 metabolizer groups, evaluated pharmacokinetic and antiplatelet responses using 300 mg followed by 75 mg per day and 600 mg followed by 150 mg per day, each for a total of 5 days. Decreased active metabolite exposure and diminished inhibition of platelet aggregation were observed in the poor metabolizers as compared to the other groups.
Table 3: Active Metabolite Pharmacokinetics and Antiplatelet Responses by CYP2C19 Metabolizer Status
Dose
Poor (n=10)
Intermediate* (n=10)
Normal (n=10)
Ultrarapid† (n=10)
Cmax (ng/mL)
300 mg (24 h)
11 (4)
23 (11)
32 (21)
24 (10)
600 mg (24 h)
17 (6)
39 (23)
44 (27))
36 (13)
75 mg (Day 5)
4 (1)
12 (5)
13 (7)
12 (6)
150 mg (Day 5)
7 (2)
18 (7)
19 (5)
16 (9)
IPA (%)††
300 mg (24 h)
24 (26)
37 (21)
39 (28)
40 (21)
600 mg (24 h)
32 (25)
56 (22)
49 (23)
51 (28)
75 mg (Day 5)
37 (23)
60 (18)
58 (19)
56 (13)
150 mg (Day 5)
61 (14)
74 (14)
73 (9)
68 (18)
VASP-PRI (%)†††
300 mg (24 h)
91 (12)
78 (12)
68 (16)
73 (12)
600 mg (24 h)
85 (14)
56 (26)
48 (20)
51 (20)
75 mg (Day 5)
83 (13)
50 (16)
39 (14)
40 (9)
150 mg (Day 5)
61 (18)
29 (11)
24 (10)
20 (10)
Values are mean (SD)
* Intermediate metabolizers have one but not two nonfunctional alleles
† Ultrarapid metabolizers have at least one gain-of-function allele
†† Inhibition of platelet aggregation with 5mcM ADP; larger value indicates greater platelet inhibition
††† Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein – platelet reactivity index; smaller value indicates greater platelet inhibition
-
Non Clinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
There was no evidence of tumorigenicity when clopidogrel was administered for 78 weeks to mice and 104 weeks to rats at dosages up to 77 mg/kg per day, which afforded plasma exposures >25 times that in humans at the recommended daily dose of 75 mg.
Clopidogrel was not genotoxic in four in vitro tests (Ames test, DNA-repair test in rat hepatocytes, gene mutation assay in Chinese hamster fibroblasts, and metaphase chromosome analysis of human lymphocytes) and in one in vivo test (micronucleus test by oral route in mice).
Clopidogrel was found to have no effect on fertility of male and female rats at oral doses up to 400 mg/kg per day (52 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis).
-
Patient Medication Information
Clopidogrel Tablets USP
(kloe pid' oh grel)Read this Medication Guide before you start taking clopidogrel tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?
1. Clopidogrel tablets may not work as well in people who:
have certain genetic factors that affect how the body breaks down clopidogrel. Your doctor may do genetic tests to make sure clopidogrel tablets are right for you.
take certain medicines, especially omeprazole (Prilosec®) or esomeprazole (Nexium®)Your doctor may change the medicine you take for stomach acid problems while you take clopidogrel tablets.2. Clopidogrel tablets can cause bleeding which can be serious and can sometimes lead to death. Clopidogrel is a blood thinner medicine that lowers the chance of blood clots forming in your body. While you take clopidogrel tablets:
you may bruise and bleed more easily
you are more likely to have nose bleeds
it will take longer for any bleeding to stopCall your doctor right away if you have any of these signs or symptoms of bleeding:
unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time
blood in your urine (pink, red or brown urine)
red or black stools (looks like tar)
bruises that happen without a known cause or get larger
cough up blood or blood clots
vomit blood or your vomit looks like coffee groundsDo not stop taking clopidogrel tablets without talking to the doctor who prescribes it for you. People who stop taking clopidogrel tablets too soon, have a higher risk of having a heart attack, or dying. If you must stop clopidogrel tablets because of bleeding, your risk of a heart attack may be higher.
What are clopidogrel tablets?
Clopidogrel tablets are prescription medicine used to treat people who have any of the
following:
chest pain due to heart problems
poor circulation in their legs (peripheral arterial disease)
a heart attack
a strokeClopidogrel tablets are used alone or with aspirin to lower your chance of having another serious problem with your heart or blood vessels such as heart attack, stroke, or blood clot that can lead to death.
Platelets are blood cells that help your blood clot normally. Clopidogrel tablets help to prevent platelets from sticking together and forming a clot that can block an artery.
It is not known if clopidogrel tablets are safe and effective in children.
Who should not take clopidogrel tablets?
Do not take clopidogrel tablets if you:
currently have a condition that causes bleeding, such as a stomach ulcer
are allergic to clopidogrel or other ingredients in clopidogrel tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in clopidogrel tablets.What should I tell my doctor before taking clopidogrel tablets?
Before you take clopidogrel tablets, tell your doctor if you:
have a history of bowel (gastrointestinal) or stomach ulcers
have a history of bleeding problems
plan to have surgery or a dental procedure. See “How should I take clopidogrel tablets?”
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if clopidogrel will harm your unborn baby
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if clopidogrel passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take clopidogrel tablets or breastfeed. You should not do both without talking to your doctor.
have had an allergy or reaction to any medicine used to treat your disease.Tell all of your doctors and your dentist that you are taking clopidogrel tablets. They should talk to the doctor who prescribed clopidogrel tablets for you before you have any surgery or invasive procedure.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription, non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Clopidogrel tablets may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how clopidogrel works. See “What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?”
Clopidogrel may increase blood levels of other medicines such as repaglinide (Prandin®).Taking clopidogrel tablets with certain other medicines may increase your risk of bleeding.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:aspirin, especially if you have had a stroke. Always talk to your doctor about whether you should take aspirin along with clopidogrel tablets to treat your condition.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of NSAID medicines if you are not sure.
warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of SSRI or SNRI medicines if you are not sure.Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take clopidogrel tablets?
Take clopidogrel tablets exactly as your doctor tells you.
Do not change your dose or stop taking clopidogrel tablets without talking to your doctor first. Stopping clopidogrel tablets may increase your risk of heart attack or stroke.
Take clopidogrel tablets with aspirin as instructed by your doctor.
If you miss a dose, take clopidogrel tablets as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses of clopidogrel tablets at the same time unless your doctor tells you to.
If you take too much clopidogrel tablets, call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
Talk with your doctor about stopping your clopidogrel tablets before you have surgery. Your doctor may tell you to stop taking clopidogrel tablets at least 5 days before you have surgery to avoid excessive bleeding during surgery.What are the possible side effects of clopidogrel tablets?
Clopidogrel tablets can cause serious side effects including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about clopidogrel tablets?”
A blood clotting problem called Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP). TTP can happen with clopidogrel tablets, sometimes after a short time (less than 2 weeks). TTP is a blood clotting problem where blood clots form in blood vessels; and can happen anywhere in the body. TTP needs to be treated in a hospital right away, because it may cause death. Get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms and they can not be explained by another medical condition:purplish spots (called purpura) on the skin or in the mouth (mucous membranes) due to bleeding under the skin
your skin or the whites of your eyes are yellow (jaundice)
you feel tired or weak
your skin looks very pale
fever
fast heart rate or feeling short of breath
headache
speech changes
confusion
coma
stroke
seizure
low amount of urine, or urine that is pink or has blood in it
stomach area (abdominal) pain
nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
vision changesTell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. Tell your doctor if you develop an allergic reaction including skin reactions while taking clopidogrel tablets.
These are not all the possible side effects of clopidogrel tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store clopidogrel tablets?
Store clopidogrel tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77° F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30° C (59° to 86° F).
Keep clopidogrel tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about clopidogrel tablets
Medicines are sometimes used for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not take clopidogrel tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give clopidogrel tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about clopidogrel tablets. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about clopidogrel tablets that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, call 1-888-943-3210.
What are the ingredients in clopidogrel tablets?
Active ingredient: clopidogrel bisulfate
Inactive ingredients:
Tablet: lactose monohydrate, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, dimethicone and hydrogenated castor oil as inactive ingredients. The pink film coating contains hypromellose 2910, polyethylene glycol 400, titanium dioxide and iron oxide red.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Macleods Pharma USA, INC,
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
Manufactured by:
Macleods Pharmaceutical Ltd.
Baddi, Himachal Pradesh, India.
Revised: July 2017
Coumadin®is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma Company.
Prilosec® and Nexium® are registered trademarks of AstraZeneca.
Prandin® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk Inc.Jantoven®is a registered trademark of USL Pharma.
PM01622205 -
How Supplied
Clopidogrel Tablets USP, 75 mg are available as pink colored, circular, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "L 11" on one side and plain on other side. Tablets are provided as follows:
NDC: 33342-060-07 Bottle of 30 tablets
NDC: 33342-060-10 Bottle of 90 tabletsNDC: 33342-060-15 Bottle of 500 tablets
NDC: 33342-060-12 Blister pack of 100 tablets (10 x 10 Unit Dose)
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77° F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30° C (59° to 86° F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Package Label,Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLOPIDOGREL
clopidogrel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 76519-1016 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE (UNII: 08I79HTP27) (CLOPIDOGREL - UNII:A74586SNO7) CLOPIDOGREL 75 mg Product Characteristics Color pink Score score with uneven pieces Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code L11 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 76519-1016-2 200 in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/06/2017 2 NDC: 76519-1016-3 30 in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/06/2017 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202928 11/06/2017 Labeler - H.J. Harkins Company Inc (147681894) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations H. J. Harkins Company Inc. 147681894 relabel(76519-1016) , repack(76519-1016) , manufacture(76519-1016)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
