CARISOPRODOL by Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC / Novast Laboratories, Ltd. / Ingenus Pharmaceuticals NJ, LLC CARISOPRODOL tablet
CARISOPRODOL by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
CARISOPRODOL by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Novast Laboratories, Ltd., Ingenus Pharmaceuticals NJ, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CARISOPRODOL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CARISOPRODOL.
CARISOPRODOL Tablets for Oral use CIV
Initial U.S. Approval: 1959INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dose is 350 mg three times a day and at bedtime. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 350 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 2%) are drowsiness, dizziness, and headache (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ingenus Pharmaceuticals NJ, LLC at 1-877-748-1970 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sedation
5.2 Abuse, Dependence, and Withdrawal
5.3 Seizures
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CNS Depressants
7.2 CYP2C19 Inhibitors and Inducers
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
8.8 Patients with Reduced CYP2C19 Activity
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CARISOPRODOL is indicated for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions in adults.
Limitation of Use
CARISOPRODOL should only be used for short periods (up to two or three weeks) because adequate evidence of effectiveness for more prolonged use has not been established and because acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions are generally of short duration. [seeDosage and Administration (2)].
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sedation
CARISOPRODOL has sedative properties (in the low back pain trials, 13% to 17% of patients who received CARISOPRODOL experienced sedation compared to 6% of patients who received placebo) [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)] and may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery. There have been post-marketing reports of motor vehicle accidents associated with the use of CARISOPRODOL.
Since the sedative effects of CARISOPRODOL and other CNS depressants (e.g., alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants) may be additive, appropriate caution should be exercised with patients who take more than one of these CNS depressants simultaneously.
5.2 Abuse, Dependence, and Withdrawal
Carisoprodol, the active ingredient in CARISOPRODOL, has been subject to abuse, dependence, and withdrawal, misuse and criminal diversion. [seeDrug Abuse and Dependence (9.1, 9.2, 9.3)]. Abuse of CARISOPRODOL poses a risk of overdosage which may lead to death, CNS and respiratory depression, hypotension, seizures and other disorders [seeOverdosage (10)].
Post-marketing experience cases of carisoprodol abuse and dependence have been reported in patients with prolonged use and a history of drug abuse. Although most of these patients took other drugs of abuse, some patients solely abused carisoprodol. Withdrawal symptoms have been reported following abrupt cessation of CARISOPRODOL after prolonged use. Reported withdrawal symptoms included insomnia, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headache, tremors, muscle twitching, ataxia, hallucinations, and psychosis. One of carisoprodol’s metabolites, meprobamate (a controlled substance), may also cause dependence [seeClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
To reduce the risk of CARISOPRODOL abuse assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing. After prescribing, limit the length of treatment to three weeks for the relief of acute musculoskeletal discomfort, keep careful prescription records, monitor for signs of abuse and overdose, and educate patients and their families about abuse and on proper storage and disposal.
5.3 Seizures
There have been post-marketing reports of seizures in patients who received CARISOPRODOL. Most of these cases have occurred in the setting of multiple drug overdoses (including drugs of abuse, illegal drugs, and alcohol) [see Overdosage (10)].
-
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
The data described below are based on 1387 patients pooled from two double blind, randomized, multicenter, placebo controlled, one-week trials in adult patients with acute, mechanical, lower back pain [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In these studies, patients were treated with 250 mg of CARISOPRODOL, 350 mg of CARISOPRODOL, or placebo three times a day and at bedtime for seven days. The mean age was about 41 years old with 54% females and 46% males and 74% Caucasian, 16% Black, 9% Asian, and 2% other.
There were no deaths and there were no serious adverse reactions in these two trials. In these two studies, 2.7%, 2%, and 5.4%, of patients treated with placebo, 250 mg of CARISOPRODOL, and 350 mg of CARISOPRODOL, respectively, discontinued due to adverse events; and 0.5%, 0.5%, and 1.8% of patients treated with placebo, 250 mg of CARISOPRODOL, and 350 mg of CARISOPRODOL, respectively, discontinued due to central nervous system adverse reactions.
Table 1 displays adverse reactions reported with frequencies greater than 2% and more frequently than placebo in patients treated with CARISOPRODOL in the two trials described above.
Table 1. Patients with Adverse Reactions in Controlled Studies Adverse Reaction Placebo
(n=560)
n (%)
CARISOPRODOL 250 mg
(n=548)
n(%)
CARISOPRODOL 350 mg
(n=279)
n (%)
Drowsiness 31 (6) 73 (13) 47 (17) Dizziness 11 (2) 43 (8) 19 (7) Headache 11 (2) 26 (5) 9 (3) 6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following events have been reported during postapproval use of CARISOPRODOL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, postural hypotension, and facial flushing [seeOverdosage (10)].
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness, dizziness, vertigo, ataxia, tremor, agitation, irritability, headache, depressive reactions, syncope, insomnia, and seizures [see Overdosage (10)].
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, and epigastric discomfort.
Hematologic: Leukopenia, pancytopenia.
-
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CNS Depressants
The sedative effects of CARISOPRODOL and other CNS depressants (e.g., alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants) may be additive. Therefore, caution should be exercised with patients who take more than one of these CNS depressants simultaneously. Concomitant use of CARISOPRODOL and meprobamate, a metabolite of CARISOPRODOL, is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 CYP2C19 Inhibitors and Inducers
Carisoprodol is metabolized in the liver by CYP2C19 to form meprobamate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Co-administration of CYP2C19 inhibitors, such as omeprazole or fluvoxamine, with CARISOPRODOL could result in increased exposure of carisoprodol and decreased exposure of meprobamate. Co-administration of CYP2C19 inducers, such as rifampin or St. John’s Wort, with CARISOPRODOL could result in decreased exposure of carisoprodol and increased exposure of meprobamate. Low dose aspirin also showed an induction effect on CYP2C19. The full pharmacological impact of these potential alterations of exposures in terms of either efficacy or safety of CARISOPRODOL is unknown.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Data over many decades of carisoprodol use in pregnancy have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Data on meprobamate, the primary metabolite of carisoprodol, also do not show a consistent association between maternal use of meprobamate and an increased risk of major birth defects (see Data).
In a published animal reproduction study, pregnant mice administered carisoprodol orally at 2.6- and 4.1-times the maximum recommended human dose ([MRHD] of 1400 mg per day [350 mg QID] based on body surface area [BSA] comparison) from gestation through weaning resulted in reduced fetal weights, postnatal weight gain, and postnatal survival (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Retrospective case-control and cohort studies of meprobamate use during the first trimester of pregnancy have not consistently identified an increased risk or pattern of major birth defects. For children exposed to meprobamate in-utero, one study found no adverse effect on mental or motor development or IQ scores.
Animal Data
Embryofetal development studies in animals have not been completed.
In a published pre-and post-natal development animal study, pregnant mice administered carisoprodol orally at 300, 750, or 1200 mg/kg/day (approximately 1-, 2.6-, and 4.1-times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) from 7-days prior to gestation through birth and from lactation through weaning resulted in reduced fetal weights, postnatal weight gain, and postnatal survival at 2.6-and 4.1-times the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from published literature report that carisoprodol and its metabolite, meprobamate, are present in breastmilk. There are no data on the effect of carisoprodol on milk production. There is one report of sedation in an infant who was breastfed by a mother taking carisoprodol (seeClinical Considerations). Because there have been no consistent reports of adverse events in breastfed infants over decades of use, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CARISOPRODOL and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from CARISOPRODOL or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to CARISOPRODOL through breast milk should be monitored for sedation.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of CARISOPRODOL in pediatric patients less than 16 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of CARISOPRODOL in patients over 65 years old have not been established.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The safety and pharmacokinetics of CARISOPRODOL in patients with renal impairment have not been evaluated. Since CARISOPRODOL is excreted by the kidney, caution should be exercised if CARISOPRODOL is administered to patients with impaired renal function. Carisoprodol is dialyzable by hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The safety and pharmacokinetics of CARISOPRODOL in patients with hepatic impairment have not been evaluated. Since CARISOPRODOL is metabolized in the liver, caution should be exercised if CARISOPRODOL is administered to patients with impaired hepatic function.
8.8 Patients with Reduced CYP2C19 Activity
Patients with reduced CYP2C19 activity have higher exposure to carisoprodol. Therefore, caution should be exercised in administration of CARISOPRODOL to these patients. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
CARISOPRODOL contains carisoprodol, a Schedule IV controlled substance. Carisoprodol has been subject to abuse, misuse, and criminal diversion for nontherapeutic use [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.2)].
9.2 Abuse
Abuse of carisoprodol poses a risk of overdosage which may lead to death, CNS and respiratory depression, hypotension, seizures and other disorders [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.2) and Overdosage (10)]. Patients at high risk of CARISOPRODOL abuse may include those with prolonged use of carisoprodol, with a history of drug abuse, or those who use CARISOPRODOL in combination with other abused drugs.
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological effects. Drug addiction, which develops after repeated drug abuse, is characterized by a strong desire to take a drug despite harmful consequences, difficulty in controlling its use, giving a higher priority to drug use than to obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes physical withdrawal. Drug abuse and drug addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance (for example, abuse or addiction may not be accompanied by tolerance or physical dependence) [seeDrug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
9.3 Dependence
Tolerance is when a patient’s reaction to a specific dosage and concentration is progressively reduced in the absence of disease progression, requiring an increase in the dosage to maintain the same. Physical dependence is characterized by withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Both tolerance and physical dependence have been reported with the prolonged use
of CARISOPRODOL. Reported withdrawal symptoms with CARISOPRODOL include insomnia, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headache, tremors, muscle twitching, anxiety, ataxia, hallucinations, and psychosis. Instruct patients taking large doses of CARISOPRODOL or those taking the drug for a prolonged time to not abruptly stop CARISOPRODOL [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.2)]. -
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentation
Overdosage of CARISOPRODOL commonly produces CNS depression. Death, coma, respiratory depression, hypotension, seizures, delirium, hallucinations, dystonic reactions, nystagmus, blurred vision, mydriasis, euphoria, muscular incoordination, rigidity, and/or headache have been reported with CARISOPRODOL overdosage. Serotonin syndrome has been reported with carisoprodol intoxication. Many of the carisoprodol overdoses have occurred in the setting of multiple drug overdoses (including drugs of abuse, illegal drugs, and alcohol). The effects of an overdose of carisoprodol and other CNS depressants (e.g., alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants) can be additive even when one of the drugs has been taken in the recommended dosage. Fatal accidental and non-accidental overdoses of CARISOPRODOL have been reported alone or in combination with CNS depressants.
Treatment of Overdosage
Basic life support measures should be instituted as dictated by the clinical presentation of the CARISOPRODOL overdose. Vomiting should not be induced because of the risk of CNS and respiratory depression, and subsequent aspiration. Circulatory support should be administered with volume infusion and vasopressor agents if needed. Seizures should be treated with intravenous benzodiazepines and the reoccurrence of seizures may be treated with phenobarbital. In cases of severe CNS depression, airway protective reflexes may be compromised and tracheal intubation should be considered for airway protection and respiratory support.
For decontamination in cases of severe toxicity, activated charcoal should be considered in a hospital setting in patients with large overdoses who present early and are not demonstrating CNS depression and can protect their airway.
For more information on the management of an overdose of CARISOPRODOL, contact a Poison Control Center.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
CARISOPRODOL Tablets are available as 350 mg round, white to off white, tablets.
Carisoprodol is a white, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in acetone; and its solubility is practically independent of pH.
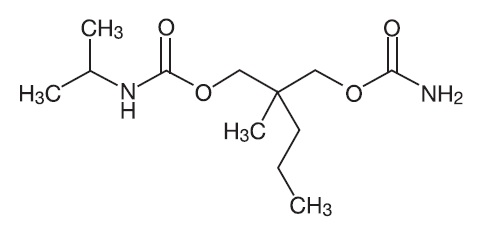
Carisoprodol is present as a racemic mixture. Chemically, carisoprodol is (±)-2-Methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol carbamate isopropylcarbamate and the molecular formula is C12H24N204 , with a molecular weight of 260.33. The structural formula is:
Other ingredients in the CARISOPRODOL drug product include Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Lactose Anhydrous, Microcrystalline cellulose, Magnesium stearate, Pregelatinized starch, Sodium lauryl sulfate and Sodium starch glycolate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of carisoprodol in relieving discomfort associated with acute painful musculoskeletal conditions has not been clearly identified.
In animal studies, muscle relaxation induced by carisoprodol is associated with altered interneuronal activity in the spinal cord and in the descending reticular formation of the brain.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Carisoprodol is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant that does not directly relax skeletal muscles.
A metabolite of carisoprodol, meprobamate, has anxiolytic and sedative properties. The degree to which these properties of meprobamate contribute to the safety and efficacy of CARISOPRODOL is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of carisoprodol and its metabolite meprobamate were studied in a crossover study of 24 healthy subjects (12 male and 12 female) who received single doses of 250 mg and 350 mg CARISOPRODOL (see Table 2). The exposure of carisoprodol and meprobamate was dose proportional between the 250 mg and 350 mg doses. The Cmax of meprobamate was 2.5 ± 0.5 µg/mL (mean ± SD) after administration of a single 350 mg dose of CARISOPRODOL, which is approximately 30% of the Cmax of meprobamate (approximately 8 µg/mL) after administration of a single 400 mg dose of meprobamate.
Table 2. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Carisoprodol and Meprobamate (Mean ± SD, n=24) 250 mg
CARISOPRODOL
350 mg
CARISOPRODOL
Carisoprodol Cmax (μg/mL) 1.2 ± 0.5 1.8 ± 1.0 AUCinf (μg*hr/mL) 4.5 ± 3.1 7.0 ± 5.0 Tmax (hr) 1.5 ± 0.8 1.7 ± 0.8 T1/2 (hr) 1.7 ± 0.5 2.0 ± 0.5 Meprobamate Cmax (μg/mL) 1.8 ± 0.3 2.5 ± 0.5 AUCinf (μg*hr/mL) 32 ± 6.2 46 ± 9.0 Tmax (hr) 3.6 ± 1.7 4.5 ± 1.9 T1/2 (hr) 9.7 ± 1.7 9.6 ± 1.5 Absolute bioavailability of carisoprodol has not been determined. The mean time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) of carisoprodol was approximately 1.5 to 2 hours.
Food Effect
Co-administration of a high-fat meal with CARISOPRODOL (350 mg tablet) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of carisoprodol. Therefore, CARISOPRODOL may be administered with or without food.
Elimination
Metabolism:
The major pathway of carisoprodol metabolism is via the liver by cytochrome enzyme CYP2C19 to form meprobamate. This enzyme exhibits genetic polymorphism (see Patients with Reduced CYP2C19 Activity below).
Excretion:
Carisoprodol is eliminated by both renal and non-renal routes with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 2 hours. The half-life of meprobamate is approximately 10 hours.
Specific Populations
Sex
Exposure of carisoprodol is higher in female than in male subjects (approximately 30-50% on a weight adjusted basis). Overall exposure of meprobamate is comparable between female and male subjects.
Patients with Reduced CYP2C19 Activity
CARISOPRODOL should be used with caution in patients with reduced CYP2C19 activity. Published studies indicate that patients who are poor CYP2C19 metabolizers have a 4-fold increase in exposure to carisoprodol, and concomitant 50% reduced exposure to meprobamate compared to normal CYP2C19 metabolizers. The prevalence of poor metabolizers in Caucasians and African Americans is approximately 3-5% and in Asians
is approximately 15-20%. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of carisoprodol.
Mutagenesis
CARISOPRODOL was not formally evaluated for genotoxicity. In published studies, carisoprodol was mutagenic in the in vitro mouse lymphoma cell assay in the absence of metabolizing enzymes, but was not mutagenic in the presence of metabolizing enzymes. Carisoprodol was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay using Chinese hamster ovary cells with or without the presence of metabolizing enzymes. Other types of genotoxic tests resulted in negative findings. Carisoprodol was not mutagenic in the Ames reverse mutation assay using S. typhimurium strains with or without metabolizing enzymes, and was not clastogenic in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay of circulating blood cells.
Impairment of Fertility
CARISOPRODOL was not formally evaluated for effects on fertility. A published reproductive study in which female mice received carisoprodol orally at doses of 300, 750, or 1200 mg/kg/day (approximately 1, 2.6, and 4.1 times the MRHD of 1400 mg per day [350 mg QID] based on body surface area [BSA] comparison) from 1-week prior to mating, to 27-weeks post-mating found no alteration in fertility although an alteration
in reproductive cycles characterized by a greater time spent in estrus was observed at a carisoprodol dose of 1200 mg/kg/day. In a 13-week toxicology study that did not determine fertility, mouse testes weight and sperm motility were reduced at a dose of 1200 mg/kg/day (maternal doses equivalent to 4.2-times the MRHD based on BSA comparison). In both studies, the no effect level was 750 mg/kg/day, corresponding
to approximately 2.6-times the MRHD based on a BSA comparison. The significance of these findings for human fertility is not known. -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of CARISOPRODOL for the relief of acute, idiopathic mechanical low back pain was evaluated in two, 7-day, double blind, randomized, multicenter, placebo controlled, U.S. trials (Studies 1 and 2). Patients had to be 18 to 65 years old and had to have acute back pain (3 days of duration) to be included in the trials. Patients with chronic back pain; at increased risk for vertebral fracture (e.g., history of osteoporosis); with a history of spinal pathology (e.g., herniated nucleus pulposus, spondylolisthesis or spinal stenosis); with inflammatory back pain, or with evidence of a neurologic deficit were excluded from participation.
Concomitant use of analgesics (e.g., acetaminophen, NSAIDs, tramadol, opioid agonists), other muscle relaxants, botulinum toxin, sedatives (e.g., barbiturates, benzodiazepines, promethazine hydrochloride), and anti-epileptic drugs was prohibited.
In Study 1, patients were randomized to one of three treatment groups (i.e., CARISOPRODOL 250 mg, CARISOPRODOL 350 mg, or placebo) and in Study 2 patients were randomized to two treatment groups (i.e., CARISOPRODOL 250 mg or placebo). In both studies, patients received study medication three times a day and at bedtime for seven days.
The primary endpoints were the relief from starting backache and the global impression of change, as reported by patients, on Study Day 3. Both endpoints were scored on a 5-point rating scale from 0 (worst outcome) to 4 (best outcome) in both studies. The primary statistical comparison was between the CARISOPRODOL 250 mg and placebo groups in both studies. The proportion of patients who used concomitant acetaminophen, NSAIDs, tramadol, opioid agonists, other muscle relaxants, and benzodiazepines was similar in the treatment groups.
The results for the primary efficacy evaluations in the acute, low back pain studies are presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Results of the Primary Efficacy Endpoints* in Studies 1 and 2 - * The primary efficacy endpoints (Relief from Starting Backache and Global Impression of Change) were assessed by the patients on Study Day 3. These endpoints were scored on a 5-point rating scale from O (worst outcome) to 4 (best outcome).
- † Mean is the least squared mean and SE is the standard error of the mean. The ANOVA model was used for the primary statistical comparison between the CARISOPRODOL 250 mg and placebo groups.
Study Parameter Placebo CARISOPRODOL 250 mg CARISOPRODOL 350 mg 1 Number of Patients n=269 n=264 n=273 Relief from Starting Backache, Mean (SE)† 1.4 (0.1) 1.8 (0.1) 1.8 (0.1) Difference between CARISOPRODOL and Placebo, Mean (SE)† (95% CI) 0.4
(0.2, 0.5)
0.4
(0.2, 0.6)
Global Impression of Change, Mean (SE)† 1.9 (0.1) 2.2 (0.1) 2.2 (0.1) Difference between CARISOPRODOL and Placebo, Mean (SE)† (95% CI) 0.2
(0.1, 0.4)
0.3
(0.1, 0.4)
2 Number of Patients n=278 n=269 Relief from Starting Backache, Mean (SE)† 1.1 (0.1) 1.8 (0.1) Difference between CARISOPRODOL and Placebo, Mean (SE)† (95% CI) 0.7
(0.5, 0.9)
Global Impression of Change, Mean (SE)† 1.7 (0.1) 2.2 (0.1) Difference between CARISOPRODOL and Placebo, Mean (SE)† (95% CI) 0.5
(0.4, 0.7)
Patients treated with CARISOPRODOL experienced improvement in function as measured by the Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) score on Days 3 and 7.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
350 mg Tablets: White to off white, Round convex tablets, debossed with ‘CL: above ‘022’ on one side available in:
Bottles of 100 NDC: 50742-656-01.
Bottles of 500 NDC: 50742-656-05.
Bottles of 1000 NDC: 50742-656-10.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients should be advised to contact their physician if they experience any adverse reactions to CARISOPRODOL.
Sedation
Advise patients that CARISOPRODOL may cause drowsiness and/or dizziness, and has been associated with motor vehicle accidents. Patients should be advised to avoid taking CARISOPRODOL before engaging in potentially hazardous activities such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Avoidance of Alcohol and Other CNS Depressants
Advise patients to avoid alcoholic beverages while taking CARISOPRODOL and to check with their doctor before taking other CNS depressants such as benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants, sedating antihistamines, or other sedatives [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].
CARISOPRODOL Should Only Be Used for Short-Term Treatment
Advise patients that treatment with CARISOPRODOL should be limited to acute use (up to two or three weeks) for the relief of acute, musculoskeletal discomfort. In the post-marketing experience with CARISOPRODOL, cases of dependence, withdrawal, and abuse have been reported with prolonged use. If the musculoskeletal symptoms still persist, patients should contact their healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Lactation
Advise nursing mothers using CARISOPRODOL to monitor neonates for signs of sedation [seeUse in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured for:
Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Orlando, FL 32839-6408Rx Only
554100
Revised: 05/2019
ingenus
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CARISOPRODOL
carisoprodol tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50742-656 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CARISOPRODOL (UNII: 21925K482H) (CARISOPRODOL - UNII:21925K482H) CARISOPRODOL 350 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (UNII: RFW2ET671P) ANHYDROUS LACTOSE (UNII: 3SY5LH9PMK) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code CL;022 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50742-656-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2019 2 NDC: 50742-656-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040823 05/21/2019 Labeler - Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC (833250017) Registrant - Novast Laboratories, Ltd. (527695995) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ingenus Pharmaceuticals NJ, LLC 964680206 manufacture(50742-656) , pack(50742-656) , analysis(50742-656) , label(50742-656)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

