MACRILEN- macimorelin acetate granule, for solution
Macrilen by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Macrilen by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Novo Nordisk. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MACRILEN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MACRILEN.
MACRILEN (macimorelin) for oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dose is 0.5 mg/kg as a single oral dose, after fasting for at least 8 hours (2.1).
- See Full Prescribing Information for important preparation and administration instructions (2.3).
- Discontinue therapy with strong CYP3A4 inducers, growth hormones and drugs that affect GH release for an adequate length of time before administering MACRILEN (2.2).
- Adequately replace other hormone deficiencies before administering MACRILEN (2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For oral solution: 60 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation: QT prolongation can lead to development of torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Avoid the concomitant use of MACRILEN with drugs that are known to prolong QT interval (5.1, 7.1).
- Potential for False Positive Test Results with Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Discontinue and washout strong CYP3A4 inducers before testing (5.2, 7.2).
- Potential for False Negative Test Results in Recent Onset Hypothalamic Disease: Consider repeat testing if indicated (5.3).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions were dysgeusia, dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea, hunger, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, feeling hot, hyperhidrosis, nasopharyngitis, and sinus bradycardia (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novo Nordisk Inc. at 1-800-727-6500, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2021
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
2.2 Important Recommendations Before MACRILEN Use
2.3 Directions for Preparation and Administration
2.4 Interpretation of MACRILEN Test Results
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 QT Prolongation
5.2 Potential for False Positive Test Results with Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
5.3 Potential for False Negative Test Results in Recent Onset Hypothalamic Disease
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
7.2 Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 Inducers
7.3 Drugs Affecting Growth Hormone Release
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
The recommended dose is a single oral dose of 0.5 mg/kg of macimorelin. The dose is administered as a reconstituted solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] in patients fasted for at least 8 hours.
2.2 Important Recommendations Before MACRILEN Use
- Discontinue strong CYP3A4 inducers prior to MACRILEN use [see Warning and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Discontinue growth hormone (GH) therapy at least one week before administering MACRILEN [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
- Avoid the use of MACRILEN with drugs known to affect pituitary GH secretion [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
- For patients with deficiencies in sex hormones, thyroid hormone and/or glucocorticoid, adequately replace each of the missing hormones before administering MACRILEN.
- Ensure that the patient has fasted for at least 8 hours before MACRILEN use.
2.3 Directions for Preparation and Administration
Prepare and administer by a healthcare professional exactly as follows.
Prepare the MACRILEN solution:
- a. Weigh the patient in kilograms (i.e., kg).
- b. Determine the number of MACRILEN pouches needed to prepare the dose:
- i. For a patient weighing up to 120 kg, use 1 pouch.
- ii. For a patient weighing more than 120 kg, use 2 pouches.
- c. Use a glass or transparent plastic container with graduation in milliliters (i.e., mL) to dissolve the entire contents of the pouch(es) in the appropriate volume of water.
- i. For 1 pouch dissolve in 120 mL of water (corresponds to 60 mg/120 mL).
- ii. For 2 pouches dissolve in 240 mL of water (corresponds to 120 mg/240 mL).
- d. Stir the MACRILEN solution gently for about 2 to 3 minutes (a small amount of un-dissolved particles will remain). The solution will have a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL.
- e. Use the MACRILEN solution within 30 minutes after preparation.
- f. Discard any unused MACRILEN solution.
Determine the volume of MACRILEN solution needed for the test:
- g.
Determine the recommended dose to be administered by multiplying the patient weight in kilogram by 0.5 mg/kg.
For example, a 70 kg patient will need a 35 mg dose.
- h.
Determine the volume of prepared MACRILEN solution to be administered by dividing the recommended dose by 0.5 mg/mL.
For example, a patient requiring a dose of 35 mg will need 70 mL of reconstituted MACRILEN solution.
- i. Use a syringe (without a needle) with graduations in mL to measure the exact volume of MACRILEN solution to be administered and transfer the required volume of MACRILEN solution into a drinking glass.
Administer the MACRILEN solution and perform the test:
- j. Have the patient being tested drink the entire volume of MACRILEN solution in the drinking glass (i.e., the dose) within 30 seconds.
- k. Observe the patient being tested per routine for the duration of the test.
- l. Draw venous blood samples for GH determination at 30 minutes, 45 minutes, 60 minutes and 90 minutes after administration of MACRILEN.
- m. Prepare serum samples and send to a laboratory for growth hormone determinations.
- n.
- o.
- p.
- q.
- r.
- s.
- t.
- u.
- v.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 QT Prolongation
MACRILEN causes an increase of about 11 msec in the corrected QT (QTc) interval [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. QT prolongation can lead to development of torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia with the risk increasing as the degree of prolongation increases. The concomitant use of MACRILEN with drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval should be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.2 Potential for False Positive Test Results with Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers with MACRILEN can decrease macimorelin plasma levels significantly and thereby lead to a false positive result [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Strong CYP3A4 inducers should be discontinued and enough time should be given to allow washout of CYP3A4 inducers prior to test administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.3 Potential for False Negative Test Results in Recent Onset Hypothalamic Disease
Adult growth hormone (GH) deficiency caused by a hypothalamic lesion may not be detected early in the disease process. Macimorelin acts downstream from the hypothalamus and macimorelin stimulated release of stored GH reserves from the anterior pituitary could produce a false negative result early when the lesion involves the hypothalamus. Repeat testing may be warranted in this situation.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in Table 1 are derived from an open-label, randomized, cross-over study that compared the diagnostic performance of MACRILEN to the insulin tolerance test (ITT) for the diagnosis of adult growth hormone deficiency [see Clinical Studies (14)]. A total of 154 subjects with a high to low pre-test probability of having adult growth hormone deficiency received a single oral dose of 0.5 mg/kg MACRILEN. Out of 154 subjects, 58% were male, 42% female, and 86% of white origin. Median values were for age 41 years (range: 18 – 66 years) and body mass index was 27.5 kg/m2 (range: 16 – 40 kg/m2). Common adverse reactions presented in Table 1 were adverse reactions that were not present at baseline and occurred during MACRILEN dosing in at least two individuals.
Table 1: Common Adverse Reactions Reported in at Least Two Individuals Dosed with MACRILEN in an Open-Label Study Number of Subjects
(n = 154)Proportion of Subjects
(%)Dysgeusia
7
4.5
Dizziness
6
3.9
Headache
6
3.9
Fatigue
6
3.9
Nausea
5
3.2
Hunger
5
3.2
Diarrhea
3
1.9
Upper respiratory tract infection
3
1.9
Feeling hot
2
1.3
Hyperhidrosis
2
1.3
Nasopharyngitis
2
1.3
Sinus bradycardia
2
1.3
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
Co-administration of MACRILEN with drugs that prolong the QT interval (such as antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, thioridazine, ziprasidone), antibiotics (e.g., moxifloxacin), Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications or any other medications known to prolong the QT interval) may lead to development of torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Avoid concomitant use of MACRILEN with drugs that prolong the QT interval. Sufficient washout time of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval prior to administration of MACRILEN is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 Inducers
Co-administration of a strong CYP3A4 inducer with MACRILEN (e.g., carbamazepine, enzalutamide, mitotane, phenytoin, rifampin, St. John's wort, bosentan, efavirenz, etravirine, modafinil, armodafinil, rufinamide) may reduce the plasma macimorelin concentrations and may lead to false positive test results. Discontinue strong CYP3A4 inducers prior to MACRILEN use. Sufficient washout time of strong CYP3A4 inducers prior to administration of MACRILEN is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.3 Drugs Affecting Growth Hormone Release
The following drugs may impact the accuracy of the MACRILEN diagnostic test. Avoid concomitant use of MACRILEN with the following [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]:
- Drugs that directly affect the pituitary secretion of growth hormone (such as somatostatin, insulin, glucocorticoids, and cyclooxygenase inhibitors such as aspirin or indomethacin).
- Drugs that may transiently elevate growth hormone concentrations (such as clonidine, levodopa, and insulin).
- Drugs that may blunt the growth hormone response to MACRILEN (such as muscarinic antagonists: atropine, anti-thyroid medication: propylthiouracil, and growth hormone products). Discontinue growth hormone products at least one week before administering the MACRILEN diagnostic test.
Sufficient washout time of drugs affecting growth hormone release prior to administration of MACRILEN is recommended.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk summary
There are no available data with MACRILEN use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with MACRILEN. MACRILEN is indicated as a single dose which limits the risk of adverse developmental outcomes from exposure to MACRILEN.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 – 4% and 15 – 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of macimorelin in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of MACRILEN to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for MACRILEN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from MACRILEN or the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of MACRILEN in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Growth hormone secretion normally decreases with age. Therefore, elderly subjects might require a lower cut-off point for diagnosis of adult growth hormone deficiency. Clinical studies of MACRILEN did not include a sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether elderly patients respond differently from younger subjects.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
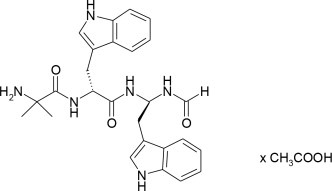
MACRILEN for oral solution is macimorelin acetate, a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist. Macimorelin acetate is described chemically as D-Tryptophanamide, 2-methylalanyl-N-[(1R)-1-(formylamino)-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-acetate.
The molecular formula for macimorelin acetate is C28H34N6O5 with a molecular weight of 534.6 g/mol.
Figure 1: Chemical structure of macimorelin acetate
Each aluminum pouch of MACRILEN contains 60 mg of macimorelin, equivalent to 68 mg of macimorelin acetate, and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, crospovidone, sodium stearyl fumarate, saccharin sodium and colloidal silicon dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Macimorelin stimulates GH release by activating growth hormone secretagogue receptors present in the pituitary and hypothalamus.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
GH stimulation
Maximum GH levels are observed between 30 to 90 minutes after administration of MACRILEN.
Cardiac electrophysiology
The effects of macimorelin on ECG parameters were investigated in a dedicated Thorough QT study that investigated in a 3-way cross-over design with 60 healthy subjects the effects of a supra-therapeutic dose of macimorelin (2 mg/kg) (4 times the recommended dosage) in comparison with placebo and with moxifloxacin. This study showed a mean baseline- and placebo-adjusted change (upper single-sided 95% confidence interval) in QTcF of 9.6 msec (11.4 msec) at 4 h post-dose, which occurred after the mean maximum macimorelin plasma concentration (0.5 h). A similar increase in the QTcF interval was also observed in a single-ascending dose study, which included three dose levels (0.5 mg/kg, and 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg (2 times and 4 times the recommended dosage, respectively). All three dose levels studied showed a similar magnitude of QTcF prolongation in the Thorough QT study, suggesting an absence of dose dependent changes. The mechanism for the observed QTcF prolongation is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The mean plasma macimorelin concentrations are similar between patients with AGHD and healthy subjects for 1.5 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight.
Absorption
The maximum plasma macimorelin concentrations (Cmax) were observed between 0.5 hour and 1.5 hours following oral administration of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight to patients with AGHD under fasting for at least 8 hours. A liquid meal decreased the macimorelin Cmax and AUC by 55% and 49%, respectively.
Elimination
An in vitro human liver microsomes study showed that CYP3A4 is the major enzyme to metabolize macimorelin.
Macimorelin was eliminated with a mean terminal half-life (T1/2) of 4.1 hours following administration of a single oral dose of 0.5 mg macimorelin/kg body weight in healthy subjects.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The diagnostic efficacy of the MACRILEN test was established in a randomized, open-label, single-dose, cross-over study. The objective of the study was to compare the level of agreement between MACRILEN test results and insulin tolerance test (ITT) results in adult patients with different pre-test probability of growth hormone deficiency and healthy control subjects. The four groups of individuals evaluated were:
-
Group A: Adults with a high likelihood of growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
- o Structural hypothalamic or pituitary lesions and low insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and/or
- o Three or more pituitary hormone deficiencies and low IGF-1, or
- o Childhood onset GHD with structural lesions and low IGF-1.
-
Group B: Adults with an intermediate likelihood of GHD
- o Eligible subjects not qualifying for either high or low likelihood.
-
Group C: Adults with a low likelihood of GHD
- o One risk factor for GHD only, such as history of distant traumatic brain injury or one pituitary hormone deficiency only with otherwise normal pituitary function, or
- o Isolated idiopathic childhood onset GHD without additional pituitary deficits.
-
Group D: Healthy adult controls
- o Healthy subjects matching Group A subjects by sex, age ± 5 years, body mass index (BMI ± 2 kg/m2), and estrogen status (females only).
For both the ITT and the MACRILEN test, serum concentrations of growth hormone were measured at 30, 45, 60, and 90 minutes after drug administration. The test was considered positive (i.e., growth hormone deficiency diagnosed) if the maximum serum GH level observed after stimulation was less than the pre-specified cut point value of 2.8 ng/mL for the MACRILEN test or 5.1 ng/mL for the ITT.
The level of negative and positive agreement between the results of the ITT and the MACRILEN test was used to evaluate the performance of the MACRILEN test. In the study, the ITT is used as the benchmark (i.e., a negative ITT indicates absence of disease and a positive ITT indicates presence of disease). Negative agreement is the proportion of subjects with a negative ITT (i.e., those who do not have GHD per the ITT) who also have a negative MACRILEN test. With a high level of negative agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual without GHD per the ITT as having GHD. Positive agreement is the proportion of subjects with a positive ITT (i.e., those who have GHD per the ITT) who also have a positive MACRILEN test. With a high level of positive agreement, the MACRILEN test will not wrongly diagnose an individual with GHD per the ITT as not having GHD. The agreement measures are defined mathematically below (see Table 2).
Table 2: Definition of Agreement between ITT and MACRILEN Insulin Tolerance Test
Total
+
-
MACRILEN
+
a
b
a+b
Positive Agreement (%)=100% x a/(a+c)
-
c
d
c+d
Negative Agreement (%)=100% x d/(b+d)
Total
a+c
b+d
a+b+c+d
Overall Agreement (%)=100% x (a+d)/(a+b+c+d)
Results
One hundred and fifty-seven subjects underwent at least one of the two tests in this study, 59% were male, 41% female, and 86% of white origin. The median age was 41 years (range: 18 – 66 years) and body mass index 27.5 kg/m2 (range: 16 – 40 kg/m2). The study relied on a cross-over design and each participant was to undergo the two diagnostic tests and serve as his or her own control. Data on both tests were available for 140 subjects; 38 (27%) in Group A, 37 (26%) in Group B, 40 (29%) in Group C, and 25 (18%) in Group D. One out of 154 MACRILEN tests (0.6%) performed failed due to a technical error and 27 out of 157 ITTs (17.2%) performed failed because induction of severe hypoglycemia (i.e., the stimulus) could not be achieved.
Two-by-two tables presenting the pre-specified primary analysis results for the ITT and MACRILEN test are shown below for all subjects (Groups A, B, C, and D combined) and for each group separately (see Table 3). The estimates for negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in the overall study population were 94% and 74% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 85% and 63%, respectively. Negative and positive agreement between MACRILEN and the ITT in subjects with intermediate or low risk (Groups B and C) were 93% and 61% with lower 95% confidence interval bounds 80% and 43%, respectively. These results are based on peak GH values (maximum GH concentrations across all measurement timepoints).
Table 3: Diagnostic Outcomes for MACRILEN and the ITT in all Subjects (Groups A, B, C, and D) and in Each Group Separately All Subjects
Insulin Tolerance Test
Total
Agreement Between
+
-
ITT and MACRILEN
MACRILEN
+
55
4
59
Positive
74%
-
19
62
81
Negative
94%
Total
74
66
140
Overall
84%
Group A
High likelihood of AGHDInsulin Tolerance Test
Total
+
-
MACRILEN
+
33
0
33
Positive
89%
-
4
1
5
Negative
100%
Total
37
1
38
Overall
89%
Group B
Intermediate likelihood of AGHDInsulin Tolerance Test
Total
+
-
MACRILEN
+
20
1
21
Positive
67%
-
10
6
16
Negative
86%
Total
30
7
37
Overall
70%
Group C
Low likelihood of AGHDInsulin Tolerance Test
Total
+
-
MACRILEN
+
2
2
4
Positive
33%
-
4
32
36
Negative
94%
Total
6
34
40
Overall
85%
Group D
Healthy controlInsulin Tolerance Test
Total
+
-
MACRILEN
+
0
1
1
Positive
0%
-
1
23
24
Negative
96%
Total
1
24
25
Overall
92%
Repeatability was tested in a subset of 34 subjects who underwent two MACRILEN tests. Agreement between the result of the first test and the second test was observed in 31 cases (91.2%).
-
Group A: Adults with a high likelihood of growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
MACRILEN 60 mg is supplied as white to off-white granules in an aluminum pouch. Each pouch contains 60 mg macimorelin (equivalent to 68 mg macimorelin acetate) that when reconstituted with 120 mL of water provides a 60 mg/120 mL (0.5 mg/mL) macimorelin solution.
MACRILEN is available in boxes containing 1 pouch per box (NDC: 0169-1401-01).
Before administration, MACRILEN for oral solution must be reconstituted by a healthcare professional [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Store pouches under refrigeration at 2-8°C (36-46°F).
The solution must be used within 30 minutes after preparation. Discard unused portion.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Instruct patients to discontinue treatment with GH at least one week before administering MACRILEN. Also, instruct patients to discontinue other medications that may interfere with the diagnostic test results prior to MACRILEN administration [see Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
Instruct patients to fast for at least 8 hours before MACRILEN administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
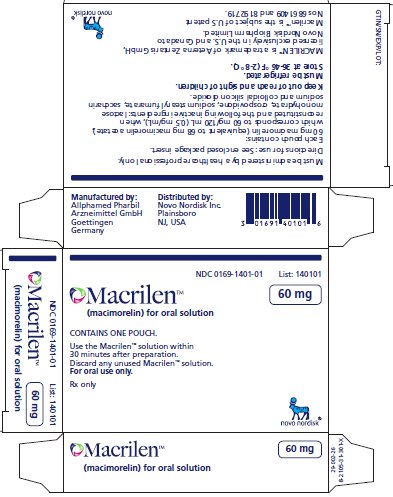
Manufactured by:
Allphamed Pharbil Arzneimittel GmbH, Goettingen, GermanyDistributed by: Novo Nordisk Inc. Plainsboro, NJ, USA
MACRILEN™ is a trademark of Aeterna Zentaris GmbH, licensed exclusively in the U.S. and Canada to Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
MACRILEN is the subject of U.S. Patent Nos. 6,861,409 and 8,192,719.
For information contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
1-800-727-6500
www.novonordisk-us.com
Revised: 7/2021
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC: 0169-1401-01 List: 140101
Macrilen™
(macimorelin) for oral solution
60 mg
CONTAINS ONE POUCH.
Use the Macrilen™ solution within
30 minutes after preparation.
Discard any unused Macrilen™ solution.
For oral use only.
Rx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MACRILEN
macimorelin acetate granule, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-1401 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MACIMORELIN (UNII: 8680B21W73) (MACIMORELIN - UNII:8680B21W73) MACIMORELIN 60 mg in 1 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Lactose Monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Saccharin Sodium (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) CROSPOVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2S7830E561) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-1401-01 1 in 1 CARTON 01/31/2022 02/28/2027 1 60 mg in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA205598 01/31/2022 02/28/2027 Labeler - Novo Nordisk (622920320)
Trademark Results [Macrilen]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 MACRILEN 98886441 not registered Live/Pending |
AETERNA ZENTARIS GmbH 2024-12-05 |
 MACRILEN 87978806 5624293 Live/Registered |
AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH 2017-09-08 |
 MACRILEN 87601284 not registered Live/Pending |
AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH 2017-09-08 |
 MACRILEN 87222769 5813944 Live/Registered |
AEterna Zentaris GmbH 2016-11-01 |
 MACRILEN 86213980 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH 2014-03-07 |
 MACRILEN 86213977 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH 2014-03-07 |
 MACRILEN 86005271 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
AEterna Zentaris GmbH 2013-07-09 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.