STANDARDIZED MEADOW FESCUE POLLEN- festuca elatior solution TIMOTHY-ORCHARD STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- phleum pratense and dactylis glomerata solution 7 STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- poa pratensis, festuca elatior, dactylis glomerata, lolium perenne, agrositis alba, anthoxanthum odoratum, and phleum pratense solution K-O-R-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba and phleum pratense solution K-O-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata and phleum pratense solution T-O-S STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- phleum pratense, dactylis glomerata and anthoxanthum odoratum solution STANDARDIZED KENTUCKY (JUNE) BLUEGRASS POLLEN- poa pratensis solution STANDARDIZED BERMUDA GRASS POLLEN- cynodon dactylon solution K-O-R-T AND SWEET VERNAL STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX- poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba, phleum pratense, and anthoxanthum odoratum solution STANDARDIZED ORCHARD GRASS POLLEN- dactylis glomerata solution STANDARDIZED REDTOP POLLEN- agrostis alba solution STANDARDIZED SWEET VERNAL GRASS POLLEN- anthoxanthum odoratum solution STANDARDIZED TIMOTHY POLLEN- phleum pratense solution STANDARDIZED PERENNIAL RYEGRASS POLLEN- lolium perenne solution
9 Southern Grass Pollen Mix by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
9 Southern Grass Pollen Mix by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Greer Laboratories, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts.
Standardized Bermuda Grass Pollen (Cynodon dactylon)
Standardized Kentucky Blue (June) Grass Pollen (Poa pratensis)
Standardized Meadow Fescue Grass Pollen (Festuca elatior)
Standardized Orchard Grass Pollen (Dactylis glomerata)
Standardized Perennial Rye Grass Pollen (Lolium perenne)
Standardized Redtop Grass Pollen (Agrostis alba)
Standardized Sweet Vernal Grass Pollen (Anthoxanthum odoratum)
Standardized Timothy Grass Pollen (Phleum pratense)
Solutions for percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous administration.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts can cause severe life-threatening systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. (5.1)
- Do not administer Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts to patients with severe, unstable or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following treatment. Emergency measures and personnel trained in their use must be available immediately in the event of a life-threatening reaction. (5.1)
- Patients with extreme sensitivity to these products, on an accelerated immunotherapy build-up, switching to another lot, receiving high doses of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts, and patients exposed to similar allergens may be at increased risk of a severe allergic reaction. (5.1)
- Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts may not be suitable for patients with certain underlying medical conditions that may reduce their ability to survive a systemic allergic reaction, and for patients receiving medications such as beta-blockers that may make them unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators. (5.1, 5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are indicated for:
Skin test diagnosis of patients with a clinical history of allergy to one or more of the following grass pollens: Bermuda, Kentucky Blue (June), Meadow Fescue, Orchard, Perennial Rye, Redtop, Sweet Vernal, Timothy. (1)
Immunotherapy for the reduction of grass pollen-induced allergic symptoms confirmed by positive skin test or by in vitro testing for pollen-specific IgE antibodies for Bermuda grass pollen, Kentucky Blue (June) grass pollen, Meadow Fescue grass pollen, Orchard grass pollen, Perennial Rye grass pollen, Redtop grass pollen, Sweet Vernal grass pollen, or Timothy grass pollen. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous use only.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for intradermal testing or subcutaneous immunotherapy. For percutaneous testing, the extracts are diluted with sterile diluents in patients expected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction. Dosages vary by mode of administration and by individual response. See full prescribing information for instructions on preparation, administration, and adjustments of dose. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Standardized Bermuda Grass Pollen Allergenic Extract solution is available only at 10,000 Bioequivalent Allergy Units (BAU)/milliliter. (3)
Other Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extract solutions are available as stock concentrates at 10,000 and 100,000 BAU/milliliter. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Severe, unstable or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- History of any severe systemic allergic reaction or any severe local reaction to subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Severe allergic reactions have occurred following the administration of other allergenic extracts and may occur in individuals following the administration of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts in the following situations:
- Extreme sensitivity to Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts, receipt of high doses of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts, or concomitant exposure to similar environmental allergens. (5.1)
- Receiving an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule (e.g., “rush” immunotherapy) or changing from one allergenic lot to another. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in over 26 to 82% of all patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy, are local adverse reactions at the injection site (e.g., erythema, itching, swelling, tenderness, pain). (6)
Systemic adverse reactions, occurring in ≤ 7% of patients, include generalized skin erythema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, rhinitis, wheezing, laryngeal edema, and hypotension. These can be fatal. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GREER Laboratories, Inc. at 1-855-274-1322 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antihistamines and other medications that suppress histamine, including topical corticosteroids, topical anesthetics and tricyclic antidepressants can interfere with skin test results. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
-
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Preparation for Administration
2.2 Diagnostic Testing
2.3 Immunotherapy
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Systemic Adverse Reactions
5.2 Epinephrine
5.3 Cross-Reactions and Dose Sensitivity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihistamines
7.2 Topical Corticosteroids and Topical Anesthetics
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the Full Prescribing Information are not listed. -
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
- Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts can cause severe life-threatening systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. (5.1)
- Do not administer Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts to patients with severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following treatment.Emergency measures and personnel trained in their use must be available immediately in the event of a life-threatening reaction. (5.1)
- Patients with extreme sensitivity, to Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts, those on an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule, those switching to another allergenic lot, those receiving high doses of the Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts, or those also exposed to similar allergens may be at increased risk of a severe allergic reaction. (5.1)
- Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts may not be suitable for patients with certain underlying medical conditions that may reduce their ability to survive a serious allergic reaction. (5.1)
- Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts may not be suitable for patients who may be unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators, such as those taking beta‑blockers. (5.2)
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GREER Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are indicated for:
- Skin test diagnosis of patients with a clinical history of allergy to one or more of the following grass pollens: Bermuda, Kentucky Blue (June), Meadow Fescue, Orchard, Perennial Rye, Redtop, Sweet Vernal, Timothy.
- Immunotherapy for the reduction of grass pollen-induced allergic symptoms confirmed by positive skin test or by in vitro testing for pollen-specific IgE antibodies for Bermuda grass pollen, Kentucky Blue (June) grass pollen, Meadow Fescue grass pollen, Orchard grass pollen, Perennial Rye grass pollen, Redtop grass pollen, Sweet Vernal grass pollen, or Timothy grass pollen.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous use only.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for intradermal testing or subcutaneous immunotherapy. For percutaneous testing, the extracts are diluted with sterile diluents in patients expected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction. Dosages vary by mode of administration and by individual response.
2.1 Preparation for Administration
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard solution if either of these conditions exist.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for percutaneous and intradermal testing, or for subcutaneous immunotherapy.
Undiluted 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrates are used for percutaneous testing. To prepare 10-fold dilutions for percutaneous testing in patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction, start with a 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 1. The 10-fold dilution series uses 0.5 milliliters of concentrate added to 4.5 milliliters of sterile 50% glycerin diluent. Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
To prepare 10-fold dilutions for intradermal testing and immunotherapy, start with a 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 1. The 10-fold dilution series uses 0.5 milliliters of concentrate added to 4.5 milliliters of sterile diluent (glycerin-free diluents for intradermal testing, glycerin-free or 10% glycerin-saline diluents for immunotherapy). Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
Table 1: 10-fold Dilution Series* Dilution Extract Milliliters of Diluent Dilution Strength (BAU/mL) Dilution Strength (BAU/mL 0 Concentrate 100,000 10,000 1 0.5 mL Concentrate 4.5 10,000 1,000 2 0.5 mL Dilution 1 4.5 1,000 100 3
0.5 mL Dilution 2 4.5 100 10 4 0.5 mL Dilution 3 4.5 10 1 5 0.5 mL Dilution 4 4.5 1 0.1 6 0.5 mL Dilution 5 4.5 0.1 0.01 Undiluted 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrates are used for percutaneous testing. To prepare 5-fold dilutions for percutaneous testing in patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction, start with a 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 2. The 5-fold dilution series uses 1 milliliter of concentrate added to 4 milliliters of sterile 50% glycerin diluent. Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
To prepare 5-fold dilutions for intradermal testing and immunotherapy, start with a 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 2. The 5-fold dilution series uses 1 milliliter of concentrate added to 4 milliliters of sterile diluent (glycerin-free diluents for intradermal testing, glycerin-free or 10% glycerin-saline diluents for immunotherapy). Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
Table 2: 5-fold Dilution Series* Dilution Extract Milliliters of Diluent Dilution Strength (BAU/mL) Dilution Strength (BAU/mL) 0 Concentrate 100,000 10,000 1 1 mL Concentrate 4 20,000 2,000 2 1 mL Dilution 1 4 4,000 400 3 1 mL Dilution 2 4 800 80 4 1 mL Dilution 3 4 160 16 5 1 mL Dilution 4 4 32 3.2 6 1 mL Dilution 5 4 6.4 0.64 2.2 Diagnostic Testing
Diagnostic testing can be performed via percutaneous or intradermal administration of the Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts. A positive skin test reaction should be interpreted in relation to the patient’s history and known exposure to the allergen.
If a skin test with a grass pollen extract mixture elicits a positive reaction, then the single-species grass pollen extracts can be used to determine the degree of sensitivity to each individual grass species and to guide in the selection of extracts and their concentration for immunotherapy, if indicated.
Percutaneous Skin Testing
Determine the patient’s sensitivity to the grass pollen allergens.
Preparation and Dose
For percutaneous testing (prick or puncture), use 10,000 or 100,000 BAU/milliliter stock concentrates. If a lower concentration is desired in patients suspected to be at greater risk for a systemic allergic reaction, 10-fold or 5‑fold dilutions of the concentrate can be tested.
Prick test: Place one drop of extract with appropriate controls on the skin and, with a skin test device, pierce through the drop into the skin with a slight lifting motion. Alternatively, use skin test devices loaded with the extract from the storage trays in a similar manner or in accordance with the device manufacturer’s recommendations.
Puncture test: Place one drop of extract or control on the skin and pierce the skin through the drop with a skin test device perpendicular to the skin. Alternatively, use skin test devices loaded with the extract from the storage trays in a similar manner, or in accordance with the device manufacturer’s recommendations.
Interpreting Results
When using percutaneous skin test devices, follow the directions provided with the test devices. A glycerinated histamine control solution (6 milligrams/milliliter or 1 milligram/milliliter histamine base) may be used as the positive control. A 50% glycerin-saline solution may be used as the negative control.
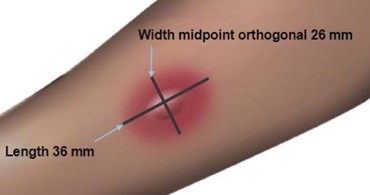
Read and record skin test responses 15 to 20 minutes after exposure. Individual patient reactivity can vary with time, allergen potency, and/or immunotherapy, as well as testing technique. The most reliable method of recording a skin test reaction is to measure the largest diameter of both wheal and erythema. While some correlation exists between the size of the skin test reaction and the degree of sensitivity, other factors should be considered in the diagnosis of allergy to specific allergens (see Figure 1 below).
Figure 1: Measurement of Wheal and Flare
Use a paper or plastic millimeter skin reaction guide as shown below.

Fifteen minutes after application of the skin test, measure the length and midpoint orthogonal width of each flare and wheal from the inner edge of the reaction.

The length of the skin test is defined as the largest diameter and the width of the skin test is defined as the diameter perpendicular to the length at its midpoint. Consider the wheal and flare as separate entities. First, measure the flare and then independently measure the wheal.
Measuring the Flare
Measuring the Wheal
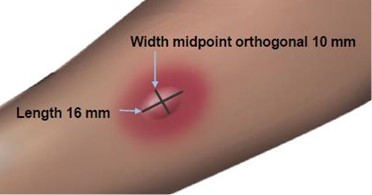
The average diameter measurement in the example above of the flare is (26 mm + 36 mm)/2 = 31 mm and the average diameter of the wheal is (10 mm + 16 mm)/2 = 13 mm.
Responses to positive controls should be at least 3 millimeters larger than responses to the negative controls.
Negative controls should elicit no reaction or only reactions of small diameters (less than 2 millimeters wheal, less than 5 millimeters erythema).
If either the positive or negative control response does not meet the above criteria, results for the allergenic extracts tested at the same time should be considered invalid and be repeated.
Intradermal Skin Testing
Preparation and Dose
For intradermal testing, use 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts stock concentrate solution. Dilute the stock concentrate solution with sterile diluent [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Use normal or buffered saline or normal saline with human serum albumin (HSA) diluent. If the result from the initial test dose is negative, subsequent intradermal tests using increasingly stronger doses may be performed up to the maximum recommended strength of 200 BAU/milliliters dilution of the extract concentrate solution.
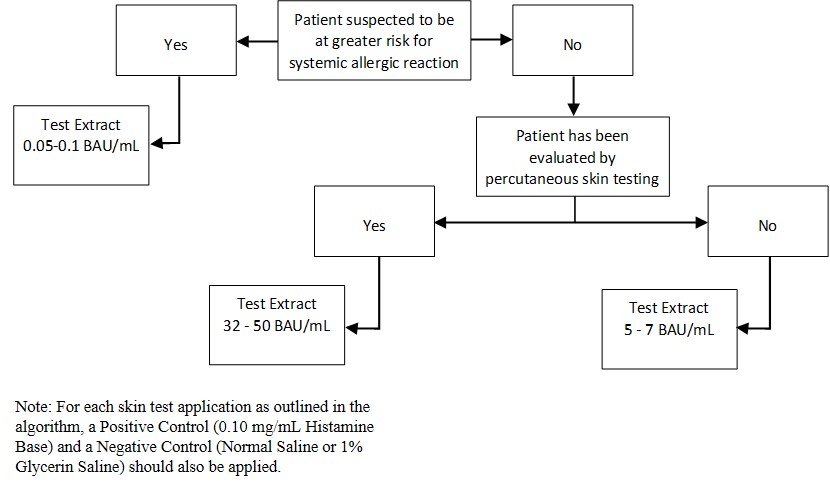
Inject 0.02 milliliters of the extract solution intradermally according to the algorithm shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2: Algorithm for Dilution of Stock Concentration Solution of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts for Intradermal Skin Testing
2.3 Immunotherapy
For subcutaneous administration only.
Preparation and Dose
Stock concentrates of GREER Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are available at 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter in 50% glycerin-saline for immunotherapy. Stock concentrates are diluted in normal saline, buffered saline, HSA-saline, or 10% glycerin-saline, depending on the patient’s reactivity to the diluent. See Table 1 and Table 2 for dilution preparation.
Administration of Immunotherapy
Administer immunotherapy by subcutaneous injection in the lateral aspect of the upper arm or thigh. Avoid injection directly into any blood vessel.
The optimal interval between doses of allergenic extract varies among individuals. Injections are usually given 1 to 2 times per week until the maintenance dose is reached, at which time the injection interval is increased to 2, then 3, and finally 4 weeks. Dosages vary by mode of administration, and by clinical response and tolerance. The minimum course of treatment may be three to five years, depending on the clinical response.
Guidelines for Immunotherapy
The initial dose of the extract should be based on the skin test reactivity. In patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction by history and skin test, the initial dose of the extract should be 0.05 to 0.1 milliliter of a 0.1 to 0.64 BAU/milliliter extract dilution. Patients not suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction may be started at a 0.1 milliliter of a 10 to 16 BAU/milliliter extract dilution.
The dose of allergenic extract is increased at each injection by no more than 50% of the previous dose, and the next increment is governed by the response to the last injection.
Select the maximum tolerated maintenance dose based on the patient's clinical response and tolerance. Doses larger than 0.2 milliliter of the stock concentrate are rarely administered because an extract mixed in 50% glycerin diluent can cause discomfort upon injection.
Dosage Modification Guidelines for Immunotherapy
The following conditions may indicate a need to withhold or reduce the dosage of immunotherapy.
- Symptoms of rhinitis and/or asthma
- Infection accompanied by fever
- Exposure to excessive amounts of clinically relevant environmental allergen prior to a scheduled injection
- Large local reactions that persist for longer than 24 hours can be an indication for repeating the previous dose or reducing the dose at the next administration
Any evidence of a systemic adverse reaction is an indication for a significant reduction (at least 75%) in the subsequent dose. Repeated systemic adverse reactions are sufficient reason for the cessation of further attempts to increase the dose.
Local adverse reactions require a decrease in the next dose by at least 50%. Proceed cautiously in subsequent dosing. In situations prompting dose reduction, once the reduced dose is tolerated, a cautious increase in dosage can be attempted.
Changing extract to a different lot or from a different manufacturer: When switching to a different lot of extract, or from another manufacturer’s extract, decrease the starting dose. Because manufacturing processes and sources of raw materials differ among manufacturers, the interchangeability of extracts from different manufacturers cannot be assured. In general, a dose reduction of 50 to 75% of the previous dose should be adequate, but each situation must be evaluated separately, considering the patient’s history of sensitivity, tolerance of previous injections, and other factors. Dose intervals should not exceed one week when rebuilding the dose.
Unscheduled gaps between treatments: Patients can lose tolerance to allergen injections during prolonged periods between doses which increases their risk for an adverse reaction. The duration of tolerance between injections varies from patient to patient.
During the build-up phase, when patients receive injections 1 to 2 times per week, repeat or reduce the extract dosage if there has been a substantial time interval between injections. This depends on: 1) the concentration of allergen immunotherapy extract that is to be administered; 2) a previous history of systemic reactions; and 3) the degree of variation from the prescribed interval of time, with longer intervals since the last injection leading to greater reductions in the dose to be administered.
This suggested approach to dose modification, due to unscheduled gaps between treatments during the build-up phase, is not based on published evidence. The individual physician should use this or a similar protocol for the specific clinical setting.
Similarly, if unscheduled gaps occur during maintenance therapy, it may be necessary to reduce the dosage and bring the patient up to maintenance dosing using an established build-up protocol.
Changing from non-stabilized to human serum albumin (HSA) stabilized diluents: Allergenic extracts prepared with diluents containing HSA and 0.4% phenol are more stable than those prepared with diluents that do not contain stabilizers. When switching from a non-stabilized to an HSA-stabilized diluent, consider lowering the dose for immunotherapy.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Systemic Adverse Reactions
Serious systemic adverse reactions have occurred following the administration of other allergenic extracts and may occur in individuals following the administration of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts in the following situations:
- Extreme sensitivity to grass pollen allergenic extracts
- Receipt of an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule (e.g., “rush” immunotherapy)
- Receipt of high doses of grass pollen allergenic extracts or concomitant exposure to similar environmental allergens
- Change from one allergenic lot to another allergenic lot
High-risk patients have had fatal reactions. Consider using more dilute preparations in patients suspected to be at greater risk of systemic allergic reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Administer Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts in a healthcare setting under the supervision of a physician prepared to manage a severe systemic or a severe local allergic reaction. Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following administration. 1
5.2 Epinephrine
Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions that may reduce the ability to survive a serious allergic reaction or increase the risk of adverse reactions after epinephrine administration. Examples of these medical conditions include but are not limited to: markedly compromised lung function (either chronic or acute), unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction, significant arrhythmia, and uncontrolled hypertension.
These products may not be suitable for patients who are taking medications that can potentiate or inhibit the effect of epinephrine. These medications include:
Βeta-adrenergic blockers: Patients taking beta-adrenergic blockers may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat serious systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Specifically, beta-adrenergic blockers antagonize the cardiostimulating and bronchodilating effects of epinephrine.
Alpha-adrenergic blockers, ergot alkaloids: Patients taking alpha-adrenergic blockers may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat serious systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Specifically, alpha-adrenergic blockers antagonize the vasoconstricting and hypertensive effects of epinephrine. Similarly, ergot alkaloids may reverse the pressor effects of epinephrine.
Tricyclic antidepressants, levothyroxine sodium, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and certain antihistamines: The adverse effects of epinephrine may be potentiated in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants, levothyroxine sodium, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and the antihistamines chlorpheniramine, and diphenhydramine.
Cardiac glycosides, diuretics: Patients who receive epinephrine while taking cardiac glycosides or diuretics should be observed carefully for the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Cross-Reactions and Dose Sensitivity
Since many grass species tend to cross-react, the total allergen content should be considered in determining the maximum maintenance dose of the mixture.
Determine the initial dilution of allergenic extract, starting dose, and progression of dosage based on the patient’s history and results of skin tests [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. 2 Strongly positive skin tests can be indicators for potential systemic reactions.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 26 to 82% of all patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy are local adverse reactions at the injection site (e.g., erythema, itching, swelling, tenderness, pain). 1 Systemic adverse reactions, occurring in 7% of patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy, 3 include generalized skin erythema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, rhinitis, wheezing, laryngeal edema, and hypotension. These adverse reactions can be fatal. 1
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihistamines
Do not perform skin testing with allergenic extracts within 3 to 10 days of use of first-generation H 1-histamine receptor blockers (e.g., clemastine, diphenhydramine) and second-generation antihistamines (e.g., loratadine, cetirizine). These products suppress histamine skin test reactions and could mask a positive response. 2
7.2 Topical Corticosteroids and Topical Anesthetics
Topical corticosteroids can suppress skin reactivity; therefore, discontinue use at the skin test site for 2 to 3 weeks before skin testing. Avoid use of topical local anesthetics at skin test sites as they can suppress flare responses. 2
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants can have potent antihistamine effects that can affect skin testing. If tricyclic medication has been recently discontinued, allow 7 to 14 days before initiating skin testing. 2
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. There are no human or animal data to establish the presence or absence of Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts-associated risks during pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are present in human milk. Data are not available to assess the effects of these extracts on the breastfed child or on milk production/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from the extracts or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
For use of these products in children younger than 5 years of age, consideration should be given to the patients’ ability to comply and cooperate with allergen immunotherapy and the potential for difficulty in communicating with the child regarding systemic reactions. 1
8.5 Geriatric Use
Data are not available to determine if subjects 65 years of age and older respond differently to allergen immunotherapy than younger subjects.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts include Standardized Bermuda Grass Pollen ( Cynodon dactylon) at 10,000 BAU/milliliter, 50% glycerin volume/volume, and 0.4% phenol (preservative); and the following grasses at both 10,000 BAU/milliliter and 100,000 BAU/milliliter, 50% glycerin volume/volume, and 0.4% phenol: Standardized Kentucky Blue (June) Grass Pollen ( Poa pratensis), Standardized Meadow Fescue Grass Pollen ( Festuca elatior), Standardized Orchard Grass Pollen ( Dactylis glomerata), Standardized Perennial Rye Grass Pollen ( Lolium perenne), Standardized Redtop Grass Pollen ( Agrostis alba), Standardized Sweet Vernal Grass Pollen ( Anthoxanthum odoratum), and Standardized Timothy Grass Pollen ( Phleum pratense). Inactive ingredients include 0.25% sodium chloride for isotonicity and 0.25% sodium bicarbonate as a buffer.
Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts should be clear light yellow to brownish solutions that are free of particulate matter.
Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are labeled in BAU/milliliter. Bioequivalent Allergy Units are assigned based on comparison by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to references from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). CBER references are assigned unitage based on quantitative skin testing. 4,5,6,7 CBER references which can be diluted 1:5,000,000 to intradermally elicit a 50 millimeter sum of erythema diameter response in highly puncture reactive subjects are assigned 100,000 BAU/milliliter; whereas references diluted 1:500,000 which elicit the same 50 millimeter sum of erythema diameter response are assigned 10,000 BAU/milliliter.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The skin test reaction results from interaction of the introduced allergen and allergen-specific IgE antibodies bound to mast cells, leading to mast cell degranulation and release of histamine, tryptase and other mediators, which results in the formation of the wheal and flare.
The precise mechanisms of action of allergen immunotherapy are not known. Immunologic responses to immunotherapy include changes in allergen-specific IgE levels, allergen-specific IgG levels, and regulatory T cell responses. 1
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
-
15 REFERENCES
- Cox L, Nelson H, Lockey R. Allergen immunotherapy: a practice parameter third update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011:S1-S55.
- Bernstein IL, Li JT, Bernstein DI, et al. Allergy diagnostic testing: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;100:S1-148.
- Greenberg MA, Kaufman CR, Gonzalez GE, et al. Late and immediate systemic-allergic reactions to inhalant allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986;77:865-870.
- Turkeltaub PC, Rastogi SC, Baer H, et al. A standardized quantitative skin-test assay of allergen potency and stability: studies on the allergen dose-response curve and effect of wheal, erythema, and patient selection on assay results. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982; 70:343-352.
- ELISA competition assay. Methods of the Allergenic Products Testing Laboratory. Rockville, MD: Laboratory of Immunobiochemistry, Division of Allergenic Products and Parasitology, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration; October 1993. (On file)
- Turkeltaub PC, Rastogi SC. Quantitative intradermal procedure for evaluation of subject sensitivity to standardized allergenic extracts and for assignment of bioequivalent allergy units to reference preparations using the ID50EAL method. Rockville, MD: Laboratory of Immunobiochemistry, Division of Allergenic Products and Parasitology, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration; November 1994. (On file)
- Turkeltaub PC. Assignment of bioequivalent allergy units based on biological standardization methods. Arb Paul Ehrlich Inst Bundesamt Sera Impfstoffe Frankf A M. 1988;(82):19-40.
- Implementation of Efficacy Review, Allergenic Extracts, Federal Register 1985; 50: 3082-3288.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
GREER Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts and mixes are supplied as stock concentrates at 10,000 BAU/milliliter and 100,000 BAU/milliliter in 50% glycerin for use in percutaneous skin testing, intradermal testing, and subcutaneous immunotherapy. Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts are labeled in BAU/milliliter and are provided in 5, 10, and 50 milliliter vials. Note, the total potency of mixes containing standardized grasses may be cumulative.
Standardized Bermuda Grass Pollen Allergenic Extract solution is available only at 10,000 BAU/milliliter.
GREER Standardized Grass Pollen Allergenic Extracts and mixes are supplied as follows:
Standardized Bermuda Grass Pollen (Cynodon dactylon) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0200-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0200-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0200-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Bluegrass, Kentucky (June) Grass Pollen (Poa pratensis) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0201-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0201-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0201-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0202-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0202-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0202-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Meadow Fescue Grass Pollen (Festcua elatoir) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0203-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0203-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0203-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0204-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0204-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0204-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Orchard Grass Pollen (Dactylis glomerata) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0205-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0205-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0205-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0206-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0206-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0206-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Perennial Rye Grass Pollen (Lolium perenne) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0209-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0209-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0209-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0210-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0210-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0210-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Redtop Grass Pollen (Agrostis alba) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0207-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0207-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0207-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0208-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0208-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0208-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Sweet Vernal Grass Pollen (Anthoxanthum odoratum) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0211-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0211-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0211-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0212-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0212-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0212-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Timothy Grass Pollen (Phelum pratense) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0213-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0213-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0213-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0214-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0214-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0214-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized Timothy - Orchard Grass Pollen Mix (equal parts mix) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0226-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0215-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0215-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0215-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized K-O-T Grass Pollen Mix (equal parts mix of Kentucky, Orchard, and Timothy pollens) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0216-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0216-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0216-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0217-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0217-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0217-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized K-O-R-T Grass Pollen Mix (equal parts mix of Kentucky, Orchard, Redtop, and Timothy pollens) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0218-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0218-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0218-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0219-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0219-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0219-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized K-O-R-T & Sweet Vernal Pollen Mix (equal parts mix of Kentucky, Orchard, Redtop, Timothy and Sweet Vernal pollens) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0220-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0220-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0220-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0221-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0221-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0221-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized 7 Grass Pollen Mix (equal parts mix of Kentucky, Meadow Fescue, Orchard, Perennial Ryegrass, Redtop, Sweet Vernal and Timothy pollens) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0222-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0222-2 10,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0222-4 10,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0223-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0223-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0223-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials Standardized T-O-S Grass Pollen Mix (equal parts mix of Timothy, Orchard and Sweet Vernal pollens) NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0224-5 10,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0227-5 100,000 BAU/mL, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0227-2 100,000 BAU/mL, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0227-4 100,000 BAU/mL, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 9 Southern Grass Pollen Mix [equal parts mix of 10,000 BAU/mL Bermuda and 100,000 BAU/mL each Kentucky, Meadow Fescue, Orchard, Perennial Rye, Redtop, Sweet Vernal, Timothy pollens and non-standardized Johnson Grass (Sorghum halpense) pollen extract] NDC Number Strength/Container 22840-0225-5 Concentrate, 5 mL dropper vial for prick (skin) testing 22840-0225-2 Concentrate, 10 mL multiple-dose vials 22840-0225-4 Concentrate, 50 mL multiple-dose vials 16.2 Storage and Handling
Maintain at 2 to 8°C (36 to 46°F) during storage and use.
Dilutions of concentrated extract result in a glycerin content of less than 50%, which can result in reduced stability. Extract dilutions at 1:100 volume/volume of the 10,000 BAU/milliliter or 100,000 BAU/milliliter should be kept no longer than a month, and more dilute solutions no more than a week. The potency of a dilution can be checked by skin test comparison to a fresh dilution of the extract on a known grass-allergic patient.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Instruct patient to remain under observation in the office for 30 minutes or longer after an injection.
Caution patient that reactions can occur more than 30 minutes after skin testing or an injection.
Instruct patient to recognize the following symptoms as adverse reactions and to immediately return to the office or immediately seek other medical attention if any of these symptoms occur following skin testing or an injection:
- Unusual swelling and/or tenderness at the injection site
- Hives or itching of the skin
- Swelling of face and/or mouth
- Sneezing, coughing or wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Dizziness or faintness
Manufacturer:
U.S. License No. 308
Greer Laboratories, Inc.
Lenoir, NC 28645 U.S.A - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
STANDARDIZED MEADOW FESCUE POLLEN
festuca elatior solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0203 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: A0WFQ8P6N1) (FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:A0WFQ8P6N1) FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0203-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0203-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0203-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101838 09/15/1968 TIMOTHY-ORCHARD STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
phleum pratense and dactylis glomerata solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0215 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 50000 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 50000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0215-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0215-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0215-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 7 STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, festuca elatior, dactylis glomerata, lolium perenne, agrositis alba, anthoxanthum odoratum, and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0223 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN (UNII: 4T81LB52R0) (LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN - UNII:4T81LB52R0) LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: A0WFQ8P6N1) (FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:A0WFQ8P6N1) FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 14285.714 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0223-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0223-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0223-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 K-O-R-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0218 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 2500 [BAU] in 1 mL POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 2500 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 2500 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 2500 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0218-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0218-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0218-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 K-O-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0217 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0217-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0217-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0217-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 K-O-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0216 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0216-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0216-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0216-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 T-O-S STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
phleum pratense, dactylis glomerata and anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0227 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 33333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0227-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0227-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0227-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED KENTUCKY (JUNE) BLUEGRASS POLLEN
poa pratensis solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0202 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0202-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0202-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0202-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED BERMUDA GRASS POLLEN
cynodon dactylon solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0200 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CYNODON DACTYLON POLLEN (UNII: 175F461W10) (CYNODON DACTYLON POLLEN - UNII:175F461W10) CYNODON DACTYLON POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0200-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0200-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0200-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101836 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED MEADOW FESCUE POLLEN
festuca elatior solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0204 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: A0WFQ8P6N1) (FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:A0WFQ8P6N1) FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0204-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0204-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0204-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101838 09/15/1968 K-O-R-T AND SWEET VERNAL STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba, phleum pratense, and anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0220 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 2000 [BAU] in 1 mL POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 2000 [BAU] in 1 mL ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 2000 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 2000 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 2000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0220-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0220-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0220-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 K-O-R-T STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0219 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 25000 [BAU] in 1 mL POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 25000 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 25000 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 25000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0219-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0219-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0219-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED KENTUCKY (JUNE) BLUEGRASS POLLEN
poa pratensis solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0201 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0201-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0201-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0201-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED ORCHARD GRASS POLLEN
dactylis glomerata solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0206 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0206-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0206-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0206-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101839 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED REDTOP POLLEN
agrostis alba solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0207 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0207-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0207-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0207-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101840 09/15/1968 TIMOTHY-ORCHARD STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
phleum pratense and dactylis glomerata solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0226 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 5000 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 5000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0226-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 T-O-S STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
phleum pratense, dactylis glomerata and anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0224 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 3333.333 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0224-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 7 STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, festuca elatior, dactylis glomerata, lolium perenne, agrositis alba, anthoxanthum odoratum, and phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0222 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN (UNII: 4T81LB52R0) (LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN - UNII:4T81LB52R0) LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: A0WFQ8P6N1) (FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:A0WFQ8P6N1) FESTUCA PRATENSIS POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 1428.5714 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0222-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0222-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0222-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED SWEET VERNAL GRASS POLLEN
anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0212 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0212-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0212-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0212-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101842 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED TIMOTHY POLLEN
phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0213 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0213-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0213-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0213-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED TIMOTHY POLLEN
phleum pratense solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0214 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0214-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0214-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0214-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101843 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED REDTOP POLLEN
agrostis alba solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0208 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0208-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0208-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0208-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101840 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED PERENNIAL RYEGRASS POLLEN
lolium perenne solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0209 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN (UNII: 4T81LB52R0) (LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN - UNII:4T81LB52R0) LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0209-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0209-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0209-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101841 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED PERENNIAL RYEGRASS POLLEN
lolium perenne solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0210 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN (UNII: 4T81LB52R0) (LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN - UNII:4T81LB52R0) LOLIUM PERENNE POLLEN 100000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0210-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0210-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0210-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101841 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED SWEET VERNAL GRASS POLLEN
anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0211 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, PERCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0211-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0211-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0211-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101842 09/15/1968 K-O-R-T AND SWEET VERNAL STANDARDIZED GRASS POLLEN MIX
poa pratensis, dactylis glomerata, agrostis alba, phleum pratense, and anthoxanthum odoratum solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0221 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN (UNII: HU8V6E7HOA) (AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN - UNII:HU8V6E7HOA) AGROSTIS GIGANTEA POLLEN 20000 [BAU] in 1 mL POA PRATENSIS POLLEN (UNII: SCB8J7LS3T) (POA PRATENSIS POLLEN - UNII:SCB8J7LS3T) POA PRATENSIS POLLEN 20000 [BAU] in 1 mL ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN (UNII: 2KIK19R45Y) (ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN - UNII:2KIK19R45Y) ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM POLLEN 20000 [BAU] in 1 mL DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 20000 [BAU] in 1 mL PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN (UNII: 65M88RW2EG) (PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN - UNII:65M88RW2EG) PHLEUM PRATENSE POLLEN 20000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0221-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0221-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0221-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101837 09/15/1968 STANDARDIZED ORCHARD GRASS POLLEN
dactylis glomerata solutionProduct Information Product Type STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC: 22840-0205 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN (UNII: 83N78IDA7P) (DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN - UNII:83N78IDA7P) DACTYLIS GLOMERATA POLLEN 10000 [BAU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 22840-0205-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 22840-0205-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 22840-0205-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101839 09/15/1968 Labeler - Greer Laboratories, Inc. (024671414) Registrant - Greer Laboratories, Inc. (024671414) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Greer Laboratories, Inc. 024671414 manufacture(22840-0200, 22840-0201, 22840-0202, 22840-0203, 22840-0204, 22840-0205, 22840-0206, 22840-0207, 22840-0208, 22840-0209, 22840-0210, 22840-0211, 22840-0212, 22840-0213, 22840-0214, 22840-0215, 22840-0216, 22840-0217, 22840-0218, 22840-0219, 22840-0220, 22840-0221, 22840-0222, 22840-0223, 22840-0224, 22840-0226, 22840-0227)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


























