ZENALPHA- vatinoxan hydrochloride and medetomidine hydrochloride injection, solution
Zenalpha by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Zenalpha by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dechra Veterinary Products. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- CAUTION:
-
DESCRIPTION:
Zenalpha is a combination of medetomidine and vatinoxan hydrochlorides. Medetomidine is a racemic mixture containing the active enantiomer, dexmedetomidine, an alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist with sedative and analgesic properties. Vatinoxan is a peripherally selective alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist, which partially counteracts the cardiovascular depressive effects of dexmedetomidine at peripheral alpha2-adrenoceptors, while preserving the centrally mediated sedative and analgesic effects of dexmedetomidine.
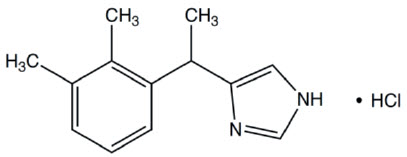
Medetomidine hydrochloride has the chemical name (S,R)-4-[1-(2,3-dimethylphenylethyl)-1H-imidazole hydrochloride. It is a white, crystalline, water soluble substance having a molecular weight of 237 g/mol. The molecular formula is C13H16N2 HCl and the structural formula is:
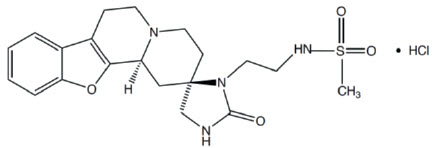
Vatinoxan hydrochloride has the chemical name N-(2-((2R,12bS)-2'-oxo-1,3,4,6,7,12b-hexahydrospiro[benzofuro[2,3-a] quinolizine-2,4'-imidazolidine]-3'-yl) ethyl) methane sulfonamide hydrochloride. It is a white to pale yellow, crystalline substance, sparingly soluble in water and having a molecular weight of 455 g/mol. The molecular formula is C20H26N4O4S HCl and the structural formula is:
Each mL of Zenalpha contains 0.5 mg medetomidine hydrochloride, 10 mg vatinoxan hydrochloride, 32.5 mg mannitol (USP), 4.16 mg citric acid monohydrate (USP), 1.8 mg methylparaben (NF), 0.2 mg propylparaben (NF).
- INDICATION:
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The dose is based on body surface area (BSA). Calculate the dose using 1 mg medetomidine /m2 BSA or use the dosing table below. Note that the mg/kg dosage decreases as body weight increases.
Table 1. IM dose volume based on body weight Dog body weight Dose volume lbs kg mL 4.4 to 7 2 to 3 0.3 7.1 to 9 3.1 to 4 0.4 9.1 to 11 4.1 to 5 0.6 11.1 to 22 5.1 to 10 0.8 22.1 to 29 10.1 to 13 1.0 29.1 to 33 13.1 to 15 1.2 33.1 to 44 15.1 to 20 1.4 44.1 to 55 20.1 to 25 1.6 55.1 to 66 25.1 to 30 1.8 66.1 to 73 30.1 to 33 2.0 73.1 to 81 33.1 to 37 2.2 81.1 to 99 37.1 to 45 2.4 99.1 to 110 45.1 to 50 2.6 110.1 to 121 50.1 to 55 2.8 121.1 to 132 55.1 to 60 3.0 132.1 to 143 60.1 to 65 3.2 143.1 to 154 65.1 to 70 3.4 154.1 to 176 70.1 to 80 3.6 >176 >80 3.8 After administration of Zenalpha, the dog should be allowed to rest quietly until evidence of sedation has occurred (5-15 minutes). The average duration of sedation is 38 minutes. As with all alpha2-adrenoceptor agonists, onset of sedation may be delayed or may be inadequate in some dogs.
Reversal of Zenalpha: Administration of IM atipamezole hydrochloride at the approved dose to reverse IM medetomidine hydrochloride results in reversal of the sedative and cardiovascular effects of Zenalpha. Reversal of sedation occurs within 5-10 minutes after administration of atipamezole hydrochloride.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Do not use Zenalpha in dogs with cardiac disease, respiratory disorders, shock, severe debilitation, that have hypoglycemia or are at risk of developing hypoglycemia, or are stressed due to extreme heat, cold or fatigue.
Zenalpha is contraindicated in dogs with a known sensitivity to medetomidine or vatinoxan.
-
WARNINGS:
Human User Safety Warnings
Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children and pets.
Avoid skin, eye or mucosal contact. Use caution while handling and using filled syringes. Absorption of the active ingredients is possible following exposure via the skin, eye or mucosa. In case of accidental eye exposure, flush eyes with water for 15 minutes, remove contact lenses then continue to flush. In case of accidental skin exposure, wash with soap and water and remove contaminated clothing. If symptoms occur, seek the advice of a physician.
In case of accidental oral intake or self-injection, seek medical advice immediately and show the package insert to the physician. DO NOT DRIVE as sedation, loss of consciousness, and changes in blood pressure may occur.
Persons with cardiovascular disease (for example, hypertension or ischemic heart disease) should take special precautions to avoid any exposure to this product.
Pregnant women should exercise special caution to avoid exposure. Uterine contractions and decreased fetal blood pressure may occur after accidental systemic exposure.
Persons with known hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients should avoid contact with Zenalpha.
Caution should be exercised when handling sedated animals. Handling or any other sudden stimuli, including noise, may cause a defense reaction in an animal that appears to be heavily sedated.
Note to physician: Zenalpha contains medetomidine, an alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, in combination with vatinoxan, a peripherally selective alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist. Symptoms after absorption or accidental self-injection may include dose-dependent sedation, respiratory depression, bradycardia, tachycardia, and hypotension.
Animal Safety Warnings
Zenalpha should not be administered in the presence of pre-existing hypotension, hypoxia or bradycardia. Due to the pronounced cardiovascular effects of alpha2-adrenoceptor agonists, only clinically healthy dogs (American Society of Anesthesiologists [ASA] classes I and II) should be administered Zenalpha. Dogs should be monitored frequently for cardiovascular function and body temperature during sedation.
Zenalpha is not intended for use in cats. The use of Zenalpha in cats has been associated with hypotension.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
Dogs should be monitored frequently during sedation for changes in heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate and body temperature. Tachycardia may occur in some dogs after recovery from sedation.
In the event of hypoxia or apnea, supplemental oxygen should be administered.
Following administration of Zenalpha, a decrease in body temperature may occur and an external heat source may be needed to maintain body temperature. Hypothermia may persist longer than sedation and analgesia.
The analgesic effect of Zenalpha will not last longer than the sedative effects. Additional analgesic(s) should be administered as needed (see Effectiveness).
Nervous, excited or agitated dogs with high levels of endogenous catecholamines may exhibit a reduced pharmacological response to Zenalpha (ineffectiveness). The onset of sedative/analgesic effects could be slowed, or the depth and duration of effects could be diminished or nonexistent. Therefore, allow the dog to rest quietly for 10 to 15 minutes after injection.
With the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist drug class, including Zenalpha, the potential for isolated cases of hypersensitivity, including paradoxical response (excitation) exists.
Repeat dosing with Zenalpha has not been evaluated.
Zenalpha has only been evaluated in fasted dogs; therefore, the effects on fed dogs (for example occurrence of vomiting) has not been characterized.
The concurrent use of anticholinergic medications and Zenalpha has not been evaluated.
Zenalpha may decrease serum glucose in healthy dogs and this effect may persist longer than sedation (see Animal Safety).
The safe use of Zenalpha in dogs with hepatic or renal impairment has not been evaluated.
The safe use of Zenalpha has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 4.5 months old.
The safe use of Zenalpha has not been evaluated in dogs that are pregnant, lactating, or intended for breeding.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
In the field study safety evaluation, 110 dogs received Zenalpha and 113 dogs received dexmedetomidine (control group) for sedation. Dogs ranged in age from 5 months to 14.5 years, weighed 5.1 to 154 lbs, and represented purebreds and breed mixes.
Table 2. Adverse reactions during the field study Adverse Reaction Zenalpha
(N = 110)
n (%)Dexmedetomidine
(N = 113)
n (%)- * Hypothermia that necessitated use of an external heat source
Diarrhea 4 (3.6) 0 (0) Muscle tremor 2 (1.8) 0 (0) Signs of colitis 2 (1.8) 0 (0) Hypothermia* 1 (0.9) 13 (11.5) Vomiting 1 (0.9) 6 (5.3) Involuntary defecation 1 (0.9) 0 (0) Nausea 1 (0.9) 0 (0) Tachycardia, transient 1 (0.9) 0 (0) Prolonged sedation 0 (0) 3 (2.7) Urinary incontinence 0 (0) 2 (1.8) Retching 0 (0) 1 (0.9) Apnea 0 (0) 1 (0.9) Bradycardia 0 (0) 1 (0.9) Hyperthermia 0 (0) 1 (0.9) Field Study Safety
Decreased body temperature occurred within 30 minutes after administration for some dogs in both treatment groups and lasted up to 2 hours in the Zenalpha group and 2-6 hours in the control group. There were 57/110 dogs (51.8%) in the Zenalpha group and 77/113 dogs (68.1%) in the control group that had a body temperature ≤99 °F. The respiratory rates decreased in both groups within 5 minutes post dose compared to baseline. The group mean respiratory rate in the Zenalpha group decreased earlier and recovered faster than the control group. Thirty-nine dogs out of 110 (35.4%) in the Zenalpha group and 33/113 dogs (29.2%) in the control group had respiratory rates < 10 breaths per minute (bpm) during the study. The group mean respiratory rate in the Zenalpha group was lowest at 30 minutes post-treatment (14 bpm) and in the control group was lowest at 90 minutes post-treatment (15.5 bpm). Mucous membrane color and capillary refill time were normal for all dogs at all timepoints during the study.
- CONTACT INFORMATION:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Medetomidine is a potent non-narcotic alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist which produces sedation and analgesia. These effects are dose dependent in depth and duration. Medetomidine is a racemic mixture containing the active enantiomer dexmedetomidine. Within the central nervous system, sympathetic neurotransmission is inhibited and the level of consciousness decreases. Respiratory rate and body temperature can also decrease. In the peripheral vasculature, medetomidine stimulates alpha2-adrenoceptors within vascular smooth muscle which induces vasoconstriction and hypertension which consequently decreases the heart rate and cardiac output. Dexmedetomidine also induces a number of other alpha2-adrenoceptor mediated effects, which include piloerection, depression of motor and secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract, diuresis and hyperglycemia.
Vatinoxan is a peripherally selective alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist which lacks activity in the central nervous system. By limiting its effects to peripheral organ systems, vatinoxan will prevent or attenuate the cardiovascular and other effects of dexmedetomidine outside the central nervous system when administered simultaneously with the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist. The central effects of dexmedetomidine remain unaltered, although vatinoxan will reduce the duration of sedation and analgesia induced by dexmedetomidine, predominantly by increasing the clearance of the latter via improving the cardiovascular function.
No pharmacokinetic assessment was performed on Zenalpha [medetomidine (1 mg/m2) + vatinoxan (20 mg/m2)]. However, after IM administration of a pilot formulation of medetomidine (1 mg/m2) + vatinoxan (30 mg/m2), both medetomidine and vatinoxan were rapidly and highly absorbed from the injection site. Maximal plasma concentration was reached at 12.6 ± 4.7 (mean ± standard deviation) minutes and 17.5 ± 7.4 minutes for dexmedetomidine (the active enantiomer of medetomidine) and vatinoxan, respectively. Vatinoxan increased the volume of distribution and the clearance of dexmedetomidine. Thus, the clearance of dexmedetomidine was increased two-fold when given in combination with vatinoxan. The same phenomena were also observed with intravenous administration.
Medetomidine plasma protein binding is high (85-90%). Medetomidine is mainly oxidized in the liver, a smaller amount undergoes methylation in the kidneys, and excretion is mainly via urine. Vatinoxan plasma protein binding is approximately 70%. Low levels are detectable in the central nervous system. Only a small amount (<5%) of vatinoxan dose has been found to be excreted via the urine.
-
EFFECTIVENESS:
A prospective, randomized, masked, multi-center study was conducted at six veterinary clinics to evaluate the effectiveness of Zenalpha to provide sedation and analgesia for non-painful or mildly painful, non-invasive procedures and examinations in client-owned dogs. Effectiveness was evaluated in 208 of the 223 enrolled dogs (109 in the Zenalpha group and 99 in the control group). Dogs ranged in age from 5 months to 14.5 years, weighed 5.1 to 154 lbs (2.3-70 kg) and represented purebreds and breed mixes. Dogs received one IM injection of Zenalpha at 1 mg/m2 medetomidine and 20 mg/m2 vatinoxan, or dexmedetomidine at 0.5 mg/m2 (control group) to produce sedation prior to conduct of the examination or procedure. Procedures included: radiographic examination or diagnostic imaging, ear examination and treatment, eye examination and treatment, anal sac treatment, dermatological examination and procedures, dental examination, dental biopsy, dental minor extraction, fine needle aspiration/superficial biopsy, minor surgery to remove dermal masses, drain seroma or abscess, nail trimming, coat grooming, venous blood draw and intravenous catheter placement. Many dogs underwent more than one procedure while sedated.
Effectiveness of Zenalpha was based on: 1) the ability to complete the planned examination or procedure while the dog was sedated, and 2) demonstration of less severe cardiovascular adverse effects (determined by heart rate) compared to the control group. Respiratory rate, body temperature, analgesia, and adverse reactions were evaluated as secondary variables for the safety assessment (see Adverse Reactions). Dogs were evaluated at 5, 15, 30, 60, and 90 minutes and 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 hours post-treatment. The success rate for ability to complete the procedure was 94.5% (103/109) in the Zenalpha group and 90.9% (90/99) in the control group. The Zenalpha group mean heart rate remained within the normal range (60-140 bpm), while the control group mean heart rate was below normal from 15-180 minutes post-treatment. The mean heart rate in the Zenalpha group was lowest at 15 minutes (64 bpm) and the mean heart rate in the control group was lowest at 90 minutes (45 bpm). There were 9 dogs (8.3%) in the Zenalpha group and 54 dogs (52.4%) in the control group that had heart rates <40 beats per minute (bpm) during sedation. Zenalpha met the criteria for success because it was not inferior to the control product for sedation and completion of the procedure and provided a decrease in the occurrence of bradycardia.
Dogs in the Zenalpha group typically had a shorter time to onset of sedation and shorter duration of sedation compared to the control group. The mean time to onset of sedation was 14 minutes in the Zenalpha group and 18 minutes in the control group. The mean duration of sedation in the Zenalpha group was 38 minutes (maximum of 90 min.) and in the control group was 90 minutes (maximum 5 hrs. 28 min.). The analgesic effects in the Zenalpha and the control groups were similar, and both waned with the loss of sedation.
The results of the field study demonstrated that Zenalpha is safe and effective, and provides sedation and analgesia needed to perform common non-painful or mildly painful veterinary examinations and procedures. Dogs treated with Zenalpha had a shorter time to onset of sedation, shorter duration of sedation (recovered quicker), and less cardiovascular and respiratory depression and adverse reactions compared to dogs in the control group.
-
ANIMAL SAFETY:
In a 4-day laboratory study using final market formulation, 32 healthy Beagle dogs (4 dogs/sex/group) aged 4.5 - 6.5 months were administered saline control, 1/20 medetomidine/vatinoxan, 3/60 medetomidine/vatinoxan, or 5/100 medetomidine/vatinoxan mg/m2 Body Surface Area (BSA) by intravenous injection. These Zenalpha doses correspond to 1, 3, or 5X the recommended intramuscular dose. The administration of Zenalpha resulted in sedation, hypotension, hypothermia, and initially sinus bradycardia followed later by sinus tachycardia as the dogs recovered from sedation. Generally, dogs were provided supplemental heat support starting at 1 or 2 hours post-dose and continuing through 4 hours post-dose. Dogs recovered from sedation within 4 hours for the 1X group and 4-8 hours for the 3 and 5X groups. Physiologic variables returned to baseline within 8 hours post-dose in all dose groups. Bloodwork was evaluated 3-4 hours post-dose. Two dogs in the 5X group had decreased blood glucose on post-dose bloodwork. One dog in the 1X group and one dog in the 3X group had decreased potassium on post-dose bloodwork. Clinical observations included mucoid, soft, or watery feces and observations of salivation, trembling, tremors, vocalization, defecation or vomiting after dosing, injected sclera, struggling after dosing, and skin cool to touch. There were no Zenalpha-related effects on moribundity, body weight, ophthalmological examinations, mucous membrane color, capillary refill time, gross pathology observations, organ weights, or histopathological findings.
- STORAGE INFORMATION:
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Zenalpha is supplied in 10 mL multi-dose glass vials. Each mL contains 0.5 mg medetomidine hydrochloride and 10 mg vatinoxan hydrochloride.
NDC: 17033-090-05
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-551

Manufactured for:
Dechra Veterinary Products
7015 College Boulevard, Suite 525
Overland Park, KS 66211 USAManufactured in Sweden.
US Patent No(s). 10,058,538 and 9,409,919 by Vetcare Oy.
Zenalpha is a registered trademark of Dechra Limited.
Rev. September 20222006825
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mL Vial Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZENALPHA
vatinoxan hydrochloride and medetomidine hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17033-090 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength vatinoxan hydrochloride (UNII: 66932R910R) (vatinoxan - UNII:342EYN0QFD) vatinoxan hydrochloride 10 mg in 1 mL medetomidine hydrochloride (UNII: BH210P244U) (medetomidine - UNII:MR15E85MQM) medetomidine hydrochloride 0.5 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17033-090-05 1 in 1 CARTON 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141551 05/15/2022 Labeler - Dechra Veterinary Products (362142734)
Trademark Results [Zenalpha]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ZENALPHA 79272974 not registered Live/Pending |
Dechra Limited 2019-10-08 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.