DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE tablet, film coated
Doxycycline Hyclate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Doxycycline Hyclate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Lannett Company, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Rx Only
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
-
DESCRIPTION
Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP are available as a 20 mg formulation of doxycycline for oral administration.
The structural formula of doxycycline hyclate is:
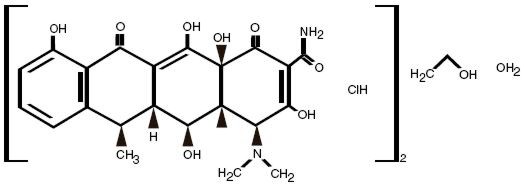
with an empirical formula of (C22H24N2O8HCl)2C2H6OH2O and a molecular weight of 1025.89. The chemical designation for doxycycline is 4-(dimethylamino)-1, 4, 4a, 5, 5a, 6, 11, 12a–octahydro-3, 5, 10, 12, 12a–octahydro-3, 5, 10, 12, 12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1, 11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide monohydrochloride, compound with ethyl alcohol (2:1), monohydrate.
Doxycycline hyclate is a yellow to light-yellow crystalline powder which is soluble in water.
Inactive ingredients in the formulation are: anhydrous lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, and talc.
Each tablet contains 23 mg of doxycycline hyclate equivalent to 20 mg of doxycycline.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
After oral administration, doxycycline hyclate is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Doxycycline is eliminated with a half-life of approximately 18 hours by renal and fecal excretion of unchanged drug.
Mechanism of Action
Doxycycline has been shown to inhibit collagenase activity in vitro1. Additional studies have shown that doxycycline reduces the elevated collagenase activity in the gingival crevicular fluid of patients with adult periodontitis2,3. The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: www.fda.gov/STIC.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of doxycycline following oral administration of doxycycline hyclate tablets were investigated in 4 volunteer studies involving 107 adults. Additionally, doxycycline pharmacokinetics have been characterized in numerous scientific publications4. Pharmacokinetic parameters for doxycycline tablets following single oral doses and at steady-state in healthy subjects are presented as follows:
Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets N Cmax*
(ng/mL)Tmax†
(hr)Cl/F*
(L/hr)t1/2
(hr)- * Mean ± SD
- † Mean and range
- ‡ Steady-State data were obtained from normal volunteers administered a bioequivalent formulation.
Single dose 20 mg
(tablet)20 362±101 1.4
(1.0-2.5)3.85±1.3 18.1±4.85 Steady-State
20 mg BID‡30 790±285 2
(0.98-12.0)3.76±1.06 Not
DeterminedAbsorption: Doxycycline is well absorbed after oral administration. In a single-dose study, concomitant administration of doxycycline hyclate tablets with a 1000 calorie, high-fat, high-protein meal which included dairy products, in healthy volunteers, resulted in a decrease in the rate and extent of absorption and delay in the time to maximum concentrations.
Distribution: Doxycycline is greater than 90% bound to plasma proteins. Its apparent volume of distribution is variously reported as between 52.6 and 134 L4,6.
Metabolism: Major metabolites of doxycycline have not been identified. However, enzyme inducers such as barbiturates, carbamazepine, and phenytoin decrease the half-life of doxycycline.
Excretion: Doxycycline is excreted in the urine and feces as unchanged drug. It is variously reported that between 29% and 55.4% of an administered dose can be accounted for in the urine by 72 hours5,6. Half-life averaged 18 hours in subjects receiving a single 20 mg doxycycline dose.
Special Populations
Geriatric: Doxycycline pharmacokinetics have not been evaluated in geriatric patients.
Pediatric patients (See WARNINGS section).
Gender: Doxycycline pharmacokinetics were compared in 9 men and 11 women under fed and fasted conditions. While female subjects had a higher rate (Cmax) and extent of absorption (AUC), these differences are thought to be due to differences in body weight/lean body mass. Differences in other pharmacokinetic parameters were not significant.
Race: Differences in doxycycline pharmacokinetics among racial groups have not been evaluated.
Renal Insufficiency: Studies have shown no significant difference in serum half-life of doxycycline in patients with normal and severely impaired renal function. Hemodialysis does not alter the half-life of doxycycline.
Hepatic Insufficiency: Doxycycline pharmacokinetics have not been evaluated in patients with hepatic insufficiency.
Drug Interactions: (See PRECAUTIONS section)
Clinical Study
In a randomized, multi-centered, double-blind, 9-month Phase 3 study involving 190 adult patients with periodontal disease [at least two probing sites per quadrant of between 5 and 9 mm pocket depth (PD) and attachment level (ALv)], the effects of oral administration of 20 mg twice a day of doxycycline hyclate (using a bioequivalent capsule formulation) plus scaling and root planing (SRP) were compared to placebo control plus SRP. Both treatment groups were administered a course of scaling and root planing in 2 quadrants at Baseline. Measurements of ALv, PD and bleeding-on-probing (BOP) were obtained at Baseline, 3, 6, and 9 months from each site about each tooth in the two quadrants that received SRP using the UNC-15 manual probe. Each tooth site was categorized into one of three strata based on Baseline PD: 0-3 mm (no disease), 4-6 mm (mild/moderate disease), ≥ 7 mm (severe disease). For each stratum and treatment group, the following were calculated at month 3, 6, and 9: mean change in ALv from baseline, mean change in PD from baseline, mean percentage of tooth sites per patient exhibiting attachment loss of ≥ 2 mm from baseline, and percentage of tooth sites with bleeding on probing. The results are summarized in the following table.
Clinical Results at Nine Months of Doxycycline Hyclate Capsules, 20 mg, as an Adjunct to SRP(Bioequivalent to Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, 20 mg) Parameter Baseline Pocket Depth 0-3 mm 4-6 mm ≥ 7 mm - * Alv=Clinical Attachment Level
- † p<0.050 vs. the placebo control group.
- ‡ SD=Standard Deviation
- § PD=Pocket Depth
- ¶ p<0.010 vs. the placebo control group.
- # BOP=Bleeding on Probing
Number of Patients
(Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets 20mg BID)90 90 79 Number of Patients
(Placebo)93 93 78 Mean Gain (SD) in ALv* Doxycycline Hyclate 20 mg BID 0.25 (0.29) mm 1.03 (0.47) mm† 1.55 (1.16)mm† Placebo 0.20 (0.29) mm 0.86 (0.48) mm 1.17 (1.15) mm Mean Decrease (SD‡) in PD§ Doxycycline Hyclate 20 mg BID 0.16 (0.19) mm¶ 0.95 (0.47) mm¶ 1.68 (1.07)mm¶ Placebo 0.05 (0.19) mm 0.69 (0.48) mm 1.20 (1.06) mm % of Sites (SD‡) with loss of ALv* ≥ 2 mm Doxycycline Hyclate 20 mg BID 1.9 (4.2)% 1.3 (4.5)% 0.3 (9.4)%† Placebo 2.2 (4.1)% 2.4 (4.4)% 3.6 (9.4)% % of Sites (SD‡) with BOP# Doxycycline Hyclate 20 mg BID 39 (19)%¶ 64 (18)%† 75 (29)% Placebo 46 (19)% 70 (18)% 80 (29)% -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Doxycycline hyclate tablets are indicated for use as an adjunct to scaling and root planing to promote attachment level gain and to reduce pocket depth in patients with adult periodontitis.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
THE USE OF DRUGS OF THE TETRACYCLINE CLASS DURING TOOTH DEVELOPMENT (LAST HALF OF PREGNANCY, INFANCY AND CHILDHOOD TO THE AGE OF 8 YEARS) MAY CAUSE PERMANENT DISCOLORATION OF THE TEETH (YELLOW-GRAY-BROWN). This adverse reaction is more common during long-term use of the drugs but has been observed following repeated short-term courses. Enamel hypoplasia has also been reported. TETRACYCLINE DRUGS, THEREFORE, SHOULD NOT BE USED IN THIS AGE GROUP AND IN PREGNANT OR NURSING MOTHERS UNLESS THE POTENTIAL BENEFITS MAY BE ACCEPTABLE DESPITE THE POTENTIAL RISKS.
All tetracyclines form a stable calcium complex in any bone forming tissue. A decrease in fibula growth rate has been observed in premature infants given oral tetracyclines in doses of 25 mg/kg every 6 hours. This reaction was shown to be reversible when the drug was discontinued.
Doxycycline can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Results of animal studies indicate that tetracyclines cross the placenta, are found in fetal tissues, and can have toxic effects on the developing fetus (often related to retardation of skeletal development). Evidence of embryotoxicity has also been noted in animals treated early in pregnancy. If any tetracyclines are used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
The catabolic action of the tetracyclines may cause and increase in BUN. Previous studies have not observed an increase in BUN with the use of doxycycline in patients with impaired renal function.
Photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed in some individuals taking tetracyclines. Patients apt to be exposed to direct sunlight or ultraviolet light should be advised that this reaction can occur with tetracycline drugs, and treatment should be discontinued at the first evidence of skin erythema.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Prescribing Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
While no overgrowth by opportunistic microorganisms such as yeast were noted during clinical studies, as with other antimicrobials, doxycycline hyclate tablets therapy may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms including fungi.
The use of tetracyclines may increase the incidence of vaginal candidiasis.
Doxycycline hyclate tablets should be used with caution in patients with a history or predisposition to oral candidiasis. The safety and effectiveness of doxycycline hyclate tablets has not been established for the treatment of periodontitis in patients with coexistent oral candidiasis.
If superinfection is suspected, appropriate measures should be taken.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Laboratory Tests
In long term therapy, periodic laboratory evaluations of organ systems, including hematopoietic, renal, and hepatic studies should be performed.
Drug Interactions
Because tetracyclines have been shown to depress plasma prothrombin activity, patients who are on anticoagulant therapy may require downward adjustment of their anticoagulant dosage.
Since bacterial antibiotics, such as the tetracycline class of antibiotics, may interfere with the bactericidal action of members of the β-lactam (e.g. penicillin) class of antibiotics, it is not advisable to administer these antibiotics concomitantly.
Absorption of tetracyclines is impaired by antacids containing aluminum, calcium, or magnesium, and iron containing preparations, and by bismuth subsalicylate.
Barbiturates, carbamazepine, and phenytoin decrease the half-life of doxycycline.
The concurrent use of tetracycline and methoxyflurane has been reported to result in fatal renal toxicity. Concurrent use of tetracyclines may render oral contraceptives less effective.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
False elevations of urinary catecholamine levels may occur due to interference with the fluorescence test.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Doxycycline hyclate has not been evaluated for carcinogenic potential in long-term animal studies. Evidence of oncogenic activity was obtained in studies with related compounds, i.e., oxytetracycline (adrenal and pituitary tumors), and minocycline (thyroid tumors).
Doxycycline hyclate demonstrated no potential to cause genetic toxicity in an in vitro point mutation study with mammalian cells (CHO/HGPRT forward mutation assay) or in an in vivo micronucleus assay conducted in CD-1 mice. However, data from an in vitro assay with CHO cells for potential to cause chromosomal aberrations suggest that doxycycline hyclate is a weak clastogen.
Oral administration of doxycycline hyclate to male and female Sprague-Dawley rats adversely affected fertility and reproductive performance, as evidenced by increased time for mating to occur, reduced sperm motility, velocity, and concentration, abnormal sperm morphology, and increased pre-and post-implantation losses. Doxycycline hyclate induced reproductive toxicity at all dosages that were examined in this study, as even the lowest dosage tested (50 mg/kg/day) induced a statistically significant reduction in sperm velocity. Note that 50 mg/kg/day is approximately 10 times the amount of doxycycline hyclate contained in the recommended daily dose of doxycycline hyclate tablets for a 60 kg human when compared on the basis of body surface area estimates (mg/m2). Although doxycycline impairs the fertility of rats when administered at sufficient dosage, the effect of doxycycline hyclate tablets on human fertility is unknown.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy Category D. (See WARNINGS section). Results from animal studies indicate that doxycycline crosses the placenta and is found in fetal tissues.
Nursing Mothers
Tetracyclines are excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from doxycycline, the use of doxycycline hyclate tablets in nursing mothers is contraindicated. (See WARNINGS section).
Pediatric Use
The use of doxycycline hyclate tablets in infancy and childhood is contraindicated (See WARNINGS section).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of a bioequivalent form of doxycycline hyclate capsules: In clinical trials of adult patients with periodontal disease 213 patients received 20 mg BID over a 9 - 12 month period. The most frequent adverse reactions occurring in studies involving treatment with a bioequivalent form of doxycycline hyclate capsules or placebo are listed below:
Incidence (%) of Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of Doxycycline Hyclate Capsules, 20 mg(Bioequivalent to Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, 20 mg) vs. Placebo Adverse Reaction Doxycycline Hyclate
Capsules 20 mg BID
(n=213)Placebo
(n=215)Note: Percentages are based on total number of study participants in each treatment group. Headache 55 (26%) 56 (26%) Common Cold 47 (22%) 46 (21%) Flu Symptoms 24 (11%) 40 (19%) Tooth Ache 14 (7%) 28 (13%) Periodontal Abscess 8 (4%) 21 (10%) Tooth Disorder 13 (6%) 19 (9%) Nausea 17 (8%) 12 (6%) Sinusitis 7 (3%) 18 (8%) Injury 11 (5%) 18 (8%) Dyspepsia 13 (6%) 5 (2%) Sore Throat 11 (5%) 13 (6%) Joint Pain 12 (6%) 8 (4%) Diarrhea 12 (6%) 8 (4%) Sinus Congestion 11 (5%) 11 (5%) Coughing 9 (4%) 11 (5%) Sinus Headache 8 (4%) 8 (4%) Rash 8 (4%) 6 (3%) Back Pain 7 (3%) 8 (4%) Back Ache 4 (2%) 9 (4%) Menstrual Cramp 9 (4%) 5 (2%) Acid Indigestion 8 (4%) 7 (3%) Pain 8 (4%) 5 (2%) Infection 4 (2%) 6 (3%) Gum Pain 1(<1%) 6 (3%) Bronchitis 7 (3%) 5 (2%) Muscle Pain 2 (1%) 6 (3%) Adverse Reactions for Tetracyclines: The following adverse reactions have been observed in patients receiving tetracyclines:
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis, and inflammatory lesions (with vaginal candidiasis) in the anogenital region. Hepatotoxicity has been reported rarely. Rare instances of esophagitis and esophageal ulcerations have been reported in patients receiving the capsule forms of the drugs in the tetracycline class. Most of these patients took medications immediately before going to bed. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Section).
Skin: maculopapular and erythematous rashes. Exfoliative dermatitis has been reported but is uncommon. Photosensitivity is discussed above. (See WARNINGS Section).
Renal toxicity: Rise in BUN has been reported and is apparently dose related. (See WARNINGS Section).
Hypersensitivity reactions: urticaria, angioneurotic edema, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid purpura, serum sickness, pericarditis, and exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Blood: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia have been reported.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
THE DOSAGE OF DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE TABLETS DIFFERS FROM THAT OF DOXYCYCLINE USED TO TREAT INFECTIONS. EXCEEDING THE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE MAY RESULT IN AN INCREASED INCIDENCE OF SIDE EFFECTS INCLUDING THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANT MICROORGANISMS.
Doxycycline hyclate tablets 20 mg twice daily as an adjunct following scaling and root planing may be administered for up to 9 months. Doxycycline hyclate tablets should be taken twice daily at 12 hour intervals, usually in the morning and evening. It is recommended that if doxycycline hyclate tablets is taken close to meal times, allow at least one hour prior to or two hours after meals. Safety beyond 12 months and efficacy beyond 9 months have not been established.
Administration of adequate amounts of fluid along with the tablets is recommended to wash down the drug and reduce the risk of esophageal irritation and ulceration. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS section).
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets, USP (equivalent to 20 mg doxycycline) are white, round, film coated tablets, debossed LCI on one side and 1336 on the other side.
The tablets are available in:
bottles of 60 (NDC: 0527-1336-06),
bottles of 100 (NDC: 0527-1336-01), and
bottles of 1000 (NDC: 0527-1336-10).Dispense in a tight light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
REFERENCES
1. Golub L.M., Sorsa T., Lee H-M, Ciancio S., Sorbi D., Ramamurthy N.S., Gruber B., Salo T., Konttinen Y.T.: Doxycycline Inhibits Neutrophil (PMN)-type Matrix Metalloproteinases in Human Adult Periodontitis Gingiva. J. Clin. Periodontol 1995; 22: 100-109.
2. Golub L.M., Ciancio S., Ramamurthy N.S., Leung M., McNamara T.F.: Low-dose Doxycycline Therapy: Effect on Gingival and Crevicular Fluid Collagenase Activity in Humans. J. Periodont Res 1990; 25:321-330.
3. Golub L.M., Lee H.M., Greenwald R.A., Ryan M.E., Salo T., Giannobile W.V.: A Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor Reduces Bone-type Collagen Degradation Fragments and Specific Collegenases in Gingival Crevicular Fluid During Adult Periodontitis. Inflammation Research 1997; 46: 310-319.
4. Saivain S., Houin G.: Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Doxycycline and Minocycline. Clin.Pharmacokinetics 1988; 15; 355-366.
5. Schach von Wittenau M., Twomey T.: The Disposition of Doxycycline by Man and Dog. Chemotherapy 1971; 16: 217-228.
6. Campistron G., Coulais Y., Caillard C., Mosser J., Pontagnier H., Houin G.: Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Doxycycline in Humans. Arzneimittel Forschung 1986; 36: 1705-1707.
Distributed by:
Lannett Company, Inc.
Philadelphia, PA 19154CIB70527C
Rev. 04/18
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 0527-1336-01
Lannett
DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE TABLETS, USP
20 mg
(equivalent to 20 mg doxycycline)Rx Only
100 TABLETS

20 mg 100 count
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE
doxycycline hyclate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0527-1336 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE (UNII: 19XTS3T51U) (DOXYCYCLINE ANHYDROUS - UNII:334895S862) DOXYCYCLINE ANHYDROUS 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS LACTOSE (UNII: 3SY5LH9PMK) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code LCI;1336 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0527-1336-06 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/10/2005 2 NDC: 0527-1336-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/10/2005 3 NDC: 0527-1336-10 1000 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/10/2005 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA065277 11/10/2005 Labeler - Lannett Company, Inc. (002277481) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Lannett Company, Inc. 006422406 LABEL(0527-1336) , MANUFACTURE(0527-1336) , PACK(0527-1336)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.