PREPOPIK- sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid powder, metered
PREPOPIK by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PREPOPIK by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc., Ferring Production Inc., Ferring Pharmaceuticals (China) Co., Ltd., Jungbunzlauer Ladenburg GmbH, Cambrex Profarmaco Milano S.R.L., Tomita Phamaceutical Co., Ltd., F.M. Howell & Company. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PREPOPIK ® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PREPOPIK ®.
PREPOPIK ® (sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Prepopik is a combination of sodium picosulfate, a stimulant laxative, and magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid which form magnesium citrate, an osmotic laxative, indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults and pediatric patients ages 9 years and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Preparation and Administration
- Each packet of Prepopik must be dissolved with water prior to ingestion and administered according to the dosing regimen. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting and dehydration. (2.2, 5.8)
- Two doses (one packet per dose) of Prepopik are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. The preferred method is the "Split-Dose" method. The alternative is the "Day Before" method. (2.1)
- Additional fluids must be consumed after every dose of Prepopik in both dosing regimens. (2.1, 5.1)
- Do not take oral medications within 1 hour of start of each dose. (2.1, 7.2)
- If taking tetracycline or fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, or penicillamine, take these medications at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of Prepopik. (2.1, 7.3)
- For complete information on preparation before colonoscopy and administration of the dosage regimen, see full prescribing information. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
Split-Dose Dosage Regimen (Preferred Method) (2.2)
- First dose: administer during evening before the colonoscopy
- Second dose: administer the next day, during the morning prior to the colonoscopy.
Day-Before Dosage Regimen (Alternative Method), if Split-Dosing is inappropriate (2.3)
- First dose: administer during afternoon or early evening before the colonoscopy.
- Second dose: administer 6 hours later during evening before colonoscopy.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For oral solution: Each of 2 packets contains 16.1 g of powder for orange flavor or 16.2 g of powder for cranberry flavor : 10 mg sodium picosulfate, 3.5 g magnesium oxide, and 12 g anhydrous citric acid (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities: Encourage adequate hydration, assess concurrent medications, and consider laboratory assessments prior to and after use. (5.1, 5.2, 7.1)
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk. (5.2)
- Seizures: Use caution in patients with a history of seizures and patients at increased risk of seizure, including medications that lower the seizure threshold. (5.3, 7.1)
- Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment or taking concomitant medications that affect renal function: Use caution, ensure adequate hydration and consider testing. (4, 5.4, 7.1)
- Mucosal ulcerations: Consider potential for mucosal ulcerations when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspected inflammatory bowel disease. (5.5)
- Suspected GI obstruction or perforation: Rule out diagnosis before administration. (4, 5.6)
- Patients at risk for aspiration: Observe during administration. (5.7)
- Risk of vomiting and other GI complications with ingestion of undissolved powder: Dissolve each packet in 5 ounces of cold water and administered at separate times according to the dosing regimen. (2.3, 2.4, 5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Adults (>1%): nausea, headache and vomiting. (6.1)
- Pediatrics 9 to 16 years (>5%): nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ferring at 1-888-FERRING (1-888-337-7464) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs that increase risks due to fluid and electrolyte changes. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Preparation and Administration Instructions
2.2 Reconstitution of Prepopik Powder
2.3 Split-Dose Dosing Regimen (Preferred Method)
2.4 Day-Before Dosing Regimen (Alternative Method)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
5.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
5.3 Seizures
5.4 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
5.5 Colonic Mucosal Ulceration, Ischemic Colitis and Ulcerative Colitis
5.6 Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
5.7 Aspiration
5.8 Risk of Vomiting and Other Gastrointestinal Complications with Ingestion of Undissolved Powder
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Risks of Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
7.2 Potential for Reduced Drug Absorption
7.3 Antibiotics
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before administration of Prepopik [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Two doses (one packet per dose) of Prepopik are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy either as a Split-Dose (preferred) or Day-Before dosing regimen.
- The preferred method is the "Split-Dose" method and consists of two separate doses: the first dose during the evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose the next day, the morning of the day of the colonoscopy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- The alternative method is the "Day Before" method and consists of two separate doses: the first dose during the afternoon or early evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose 6 hours later during the evening before the colonoscopy [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Each packet of Prepopik must be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water prior to ingestion and administered according to the dosing regimen. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration and electrolyte disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Additional fluids must be consumed after every dose of Prepopik in both dosing regimens [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Consume only clear fluids (no solid food) from the start of Prepopik treatment until after the colonoscopy.
- Do not eat solid food or dairy and do not drink anything colored red or purple.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take other laxatives while taking Prepopik
- Do not take oral medications within one hour before or after starting Prepopik.
- If taking tetracycline or fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, or penicillamine, take these medications at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of Prepopik [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Stop consumption of all fluids at least 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
2.2 Reconstitution of Prepopik Powder
- Reconstitute the Prepopik powder immediately before each administration. Do not prepare the solution in advance.
- Fill the supplied dosing cup with cold water up to the lower (5-ounce) line on the cup and pour in the contents of one packet of Prepopik powder.
- Stir for 2 to 3 minutes. The reconstituted Prepopik solution may become slightly warm as the powder dissolves.
2.3 Split-Dose Dosing Regimen (Preferred Method)
The Split-Dose regimen is the preferred dosing method. The recommended dosage in adults and pediatric patients 9 years of age and older is shown below. Instruct patients to take two separate doses (one packet per dose) in conjunction with fluids.
Dose 1 – On the day before colonoscopy:
- Instruct patients to consume only clear liquids (no solid food or dairy) on the day before the colonoscopy up until 2 hours before the time of the colonoscopy.
- Take the first dose of Prepopik during the evening before the colonoscopy (e.g., 5:00 to 9:00 PM).
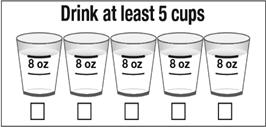
- Follow Prepopik by drinking at least five 8-ounce cups of clear liquids (40 ounces total), using the upper line on the cup, within 5 hours and before bed.
- If severe bloating, distention, or abdominal pain occurs, following the first dose, delay the second dose until the symptoms resolve.
Dose 2 – Next morning on the day of colonoscopy (start approximately 5 hours prior to colonoscopy):
- Continue to consume only clear liquids (no solid food or dairy).
- Take the second dose of Prepopik.
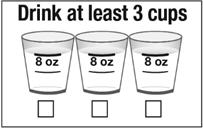
- Following the Prepopik dose, drink at least three 8-ounce cups of clear liquids (24 ounces), using the upper line on the cup, at least 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
2.4 Day-Before Dosing Regimen (Alternative Method)
The Day-Before regimen is the alternative dosing method for patients for whom the Split-Dosing is inappropriate. The recommended dosage in adults and pediatric patients 9 years of age and older is shown below. Instruct patients to take two separate doses (one packet per dose) in conjunction with fluids
Dose 1 – On the day before colonoscopy:
- Instruct patients to consume only clear liquids (no solid food or dairy) on the day before the colonoscopy up until 2 hours before the time of the colonoscopy.
- Take the first dose of Prepopik in the afternoon or early evening before the colonoscopy (e.g., 4:00 to 6:00 PM).
- Following the Prepopik dose, drink at least five 8-ounce cups of clear liquids (40 ounces total), using the upper line on the cup, within 5 hours and before the next dose.
- If severe bloating, distention, or abdominal pain occurs, following the first dose, delay the second dose until the symptoms resolve.
Dose 2 – Approximately 6 hours later in the evening the night before the colonoscopy (e.g., 10:00 PM to 12:00 AM):
- Take the second dose of Prepopik.
- Following the Prepopik dose, drink at least three 8-ounce cups (24 ounces), using the upper line on the cup, of clear liquids within 5 hours and before bed.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Prepopik is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute) which may result in accumulation of magnesium [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Gastrointestinal obstruction or ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Bowel perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Toxic colitis or toxic megacolon
- Gastric retention
- Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in Prepopik [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
Advise patients to hydrate adequately before, during, and after the use of Prepopik. Use caution in patients with congestive heart failure when replacing fluids. If a patient develops significant vomiting or signs of dehydration including signs of orthostatic hypotension after taking Prepopik, consider performing post-colonoscopy lab tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) and treat accordingly. Approximately 20% of adult patients in both arms (Prepopik, 2L of PEG + E plus two × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets) of clinical trials of Prepopik had orthostatic changes (changes in blood pressure and/or heart rate) on the day of colonoscopy. In adult clinical trials orthostatic changes were documented up to seven days post colonoscopy. In a single study of patients 9 to 16 years of age, approximately 20% of patients in Prepopik arms had orthostatic changes (changes in blood pressure and/or heart rate) compared with approximately 7% of those who received the comparator (PEG) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. These changes occurred up to five days post colonoscopy.
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances can lead to serious adverse reactions including cardiac arrhythmias or seizures and renal impairment. Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before treatment with Prepopik . In addition, use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients who have conditions or who are using medications that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or that may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmia, and renal impairment . Fluid and electrolyte disturbances can lead to serious adverse reactions including cardiac arrhythmias or seizures and renal impairment. Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before treatment with Prepopik [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. In addition, use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients who have conditions or who are using medications that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or that may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmia, and renal impairment [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
There have been rare reports of serious arrhythmias associated with the use of ionic osmotic laxative products for bowel preparation. Use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients at increased risk of arrhythmias (e.g., patients with a history of prolonged QT, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or cardiomyopathy). Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Seizures
There have been reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures with the use of bowel preparation products in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities.
Use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients with a history of seizures and in patients at risk of seizure, such as patients taking medications that lower the seizure threshold (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, or patients with known or suspected hyponatremia [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.4 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
Prepopik is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min), accumulation of magnesium in plasma may occur [see Contraindications (4)]. As with other magnesium containing bowel preparations, use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function (such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. These patients may be at increased risk for renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Prepopik. Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients.
5.5 Colonic Mucosal Ulceration, Ischemic Colitis and Ulcerative Colitis
Osmotic laxatives may produce colonic mucosal aphthous ulcerations and there have been reports of more serious cases of ischemic colitis requiring hospitalization. Concurrent use of additional stimulant laxatives with Prepopik may increase this risk. The potential for mucosal ulcerations should be considered when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspected inflammatory bowel disease [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.6 Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
If gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation is suspected, perform appropriate diagnostic studies to rule out these conditions before administering Prepopik [see Contraindications (4)]. Use with caution in patients with severe active ulcerative colitis.
5.7 Aspiration
Patients with impaired gag reflex are at risk for regurgitation or aspiration during the administration of Prepopik. Observe these patients during the administration of Prepopik. Use with caution in these patients.
5.8 Risk of Vomiting and Other Gastrointestinal Complications with Ingestion of Undissolved Powder
Each packet must be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and administered at separate times according to the dosing regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)]. Ingestion of additional water is important to patient tolerance. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or otherwise important adverse reactions for bowel preparations are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Use in Patients with Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Colonic Mucosal Ulceration, Ischemic Colitis and Ulcerative Colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Aspiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Risk of Vomiting and Other Gastrointestinal Complications with Ingestion of Undissolved Powder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In randomized, multicenter, controlled clinical trials, nausea, headache, and vomiting were the most common adverse reactions (>1%) following Prepopik administration. The patients were not blinded to the study drug. Since abdominal bloating, distension, pain/cramping, and watery diarrhea are known to occur in response to colon cleansing preparations, these effects were documented as adverse events in the clinical trials only if they required medical intervention (such as a change in study drug or led to study discontinuation, therapeutic or diagnostic procedures, met the criteria for a serious adverse event), or showed clinically significant worsening during the study that was not in the frame of the usual clinical course, as determined by the investigator.
Prepopik was compared for colon cleansing effectiveness with a preparation containing two liters (2L) of polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution (PEG + E) and two 5-mg bisacodyl tablets, all administered the day before the procedure. Table 1 displays the most common adverse reactions in Study 1 and Study 2 for the Prepopik Split-Dose and Day-Before dosing regimens, respectively, each as compared to the comparator preparation.
Table 1: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Reactions observed in at Least (>1%) of Patients using the Split-Dose Regimen and Day-Before Regimen * Adverse Reaction Study 1: Split-Dose Regimen Study 2: Day-Before Regimen PREPOPIK
(N=305)
n (% = n/N)2L PEG+E†with 2 × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets
(N=298)
n (% = n/N)PREPOPIK
(N=296)
n (% = n/N)2L PEG+E†with 2 × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets
(N=302)
n (% = n/N)- * abdominal bloating, distension, pain/cramping, and watery diarrhea not requiring an intervention were not collected
- † 2L PEG + E = two liters polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution.
Nausea 8 (2.6) 11 (3.7) 9 (3.0) 13 (4.3) Headache 5 (1.6) 5 (1.7) 8 (2.7) 5 (1.7) Vomiting 3 (1.0) 10 (3.4) 4 (1.4) 6 (2.0) Electrolyte Abnormalities
In general, Prepopik was associated with numerically higher rates of abnormal electrolyte shifts on the day of colonoscopy compared to the preparation containing 2L of PEG + E plus two × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets (Table 2). These shifts were transient in nature and numerically similar between treatment arms at the Day 30 visit.
Table 2: Shifts from Normal Baseline to Outside the Normal Range at Day 7 and Day 30 Laboratory Parameter (direction of change) Visit Study 1: Split-Dose Regimen Study 2: Day-Before Regimen PREPOPIK 2L PEG+E with 2× 5 mg bisacodyl tablets PREPOPIK 2L PEG+E with 2× 5 mg bisacodyl tablets n/N (%) n/N (%) Potassium (low) Day of Colonoscopy 19/260 (7.3) 11/268 ( 4.1 ) 13/274 (4.7) 13/271 (4.8) 24-48 hours 3/302 (1.0) 2/294 (0.7) 3/287 (1.0) 5/292 (1.7) Day 7 11/285 (3.9) 8/279 (2.9) 6/276 (2.2) 14/278 (5.0) Day 30 11/284 (3.9) 8/278 (2.9) 7/275 (2.5) 8/284 (2.8) Sodium (low) Day of Colonoscopy 11/298 (3.7) 3/295 (1.0) 3/286 (1.0) 3/295 (1.0) 24-48 hours 1/303 (0.3) 1/295 (0.3) 1/288 (0.3) 1/293 (0.3) Day 7 2/300 (0.7) 1/292 (0.3) 1/285 (0.4) 1/291 (0.3) Day 30 2/299( 0.7) 3/291 (1.0) 1/284( 0.4) 1/296 (0.3) Chloride (low) Day of Colonoscopy 11/301 (3.7) 1/298 (0.3) 3/287 (1.0) 0/297 (0.0) 24-48 hours 1/303 (0.3) 0/295 (0.0) 2/288 (0.7) 0/293 (0.0) Day 7 1/303 (0.3) 3/295 (1.0) 0/285 (0.0) 0/293 (0.0) Day 30 2/302 (0.7) 3/294 (1.0) 0/285 (0.0) 0/298 (0.0) Magnesium (high) Day of Colonoscopy 34/294 (11.6) 0/294 (0.0) 25/288 (8.7) 1/289 (0.3) 24-48 hours 0/303 (0.0) 0/295 (0.0) 0/288 (0.0) 0/293 (0.0) Day 7 0/297 (0.0) 1/291 (0.3) 1/286 (0.3) 1/285 (0.4) Day 30 1/296 (0.3) 2/290 (0.7) 0/286 (0.0) 0/290 (0.0) Calcium (low) Day of Colonoscopy 2/292 (0.7) 1/286 (0.3) 0/276 (0.0) 2/282 (0.7) 24-48 hours 0/303 (0.0) 0/295 (0.0) 0/288 (0.0) 0/293 (0.0) Day 7 0/293 (0.0) 1/283 (0.4) 0/274 (0.0) 0/278 (0.0) Day 30 0/292 (0.0) 1/282 (0.4) 0/274 (0.0) 1/283 (0.4) Creatinine (high) Day of Colonoscopy 5/260 (1.9) 13/268 (4.9) 12/266 (4.5) 16/270 (5.9) 24-48 hours 1/303 (0.3) 0/295 (0.0) 0/288 (0.0) 0/293 (0.0) Day 7 10/264 (0.4) 13/267 (4.8) 10/264 (3.8) 10/265 (3.8) Day 30 11/264 (4.2) 14/265(5.3) 18/264 (6.8) 10/272 (3.7) eGFR (low) Day of Colonoscopy 22/221 (10.0) 17/214 (7.9) 26/199 (13.1) 25/224 (11.2) 24-48 hours 76/303 (25.1) 72/295 (24.4) 82/288 (28.5) 62/293 (21.2) Day 7 22/223 (10.0) 17/213 (8.0) 11/198 (5.6) 28/219 (12.8) Day 30 24/223(10.8) 21/211 (10.0) 21/199 (10.6) 24/224 (10.7) Pediatrics
In the pediatric patients aged 9 to 16 years who received Prepopik, the most common adverse reactions (> 5%) were nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain [see Clinical Trials (14)]. Electrolytes abnormalities were observed in pediatric patients similar to those seen in adults. Three patients had abnormally low glucose levels (40 to 47 mg/dL). Two patients received Prepopik and one received the comparator (PEG). The abnormal values occurred at the colonoscopy visit for one patient (Prepopik) and at the 5-day follow up visit for the other two patients (Prepopik and PEG). All three patients were asymptomatic.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of other oral formulations of sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid similar to Prepopik. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity: rash, urticaria, purpura, and anaphylaxis [see Contraindications (4)]
Gastrointestinal: abdominal pain, diarrhea, fecal incontinence, aphthoid ileal ulcers, ischemic colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Neurologic: generalized tonic-clonic seizures with and without hyponatremia in epileptic patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Risks of Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
Use caution when prescribing Prepopik for patients with conditions and/or who are taking other drugs that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of renal impairment, seizures, arrhythmias, or QT prolongation in the setting of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
7.2 Potential for Reduced Drug Absorption
Prepopik can reduce the absorption of other co-administered drugs [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]:
- Administer oral medications at least one hour before of the start of administration of Prepopik.
- Administer tetracycline and fluoroquinolone antibiotics [see Drug Interactions (7.3)], iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, and penicillamine at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of Prepopik.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with Prepopik use in pregnant women to determine a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In an animal reproduction study, no adverse developmental effects were observed in pregnant rats when sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid were administered orally at doses 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area during organogenesis.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
A reproduction study with sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid has been performed in pregnant rats following oral administration of up to 2000 mg/kg twice daily (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus due to sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid. A reproduction study in rabbits was not adequate, as treatment-related mortalities were observed at all doses. A pre and postnatal development study with sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in rats showed no evidence of any adverse effect on pre and postnatal development at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg twice daily (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area).
Published reproduction studies with sodium picosulfate in pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not show evidence of harm to the fetus at doses up to 100 mg/kg (approximately 49 and 98 times, respectively, the recommended human dose of 10 mg sodium picosulfate based on body surface area).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of magnesium oxide or anhydrous citric acid in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Published data on lactating women indicate that the active metabolite of sodium picosulfate, bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane (BHPM) remained below the limit of detection (1 ng/mL) in breast milk after both single and multiple doses of 10 mg/day. There are no data on the effects of sodium picosulfate on the breastfed infant or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Prepopik and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Prepopik or the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Prepopik have been established for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in pediatric patients 9 years of age and older. Use of Prepopik in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials of Prepopik in adults and a single, dose-ranging, controlled trial in 78 pediatric patients 9 to 16 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety profile of Prepopik in this pediatric population was similar to that seen in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor for possible hypoglycemia in pediatric patients, as Prepopik has no caloric substrate.
The safety and effectiveness of Prepopik in pediatric patients less than 9 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1201 patients in clinical trials who received Prepopik, 215 (18%) patients were 65 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric patients and younger patients. However, elderly patients are more likely to have decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and may be more susceptible to adverse reactions resulting from fluid and electrolyte abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Prepopik is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min), as accumulation of magnesium in plasma may occur [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function may be at increased risk for renal injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4). Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Prepopik [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of more than the recommended dose of Prepopik may lead to severe electrolyte disturbances, as well as dehydration and hypovolemia, with signs and symptoms of these disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Monitor for fluid and electrolyte disturbances and treat symptomatically.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Prepopik (sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution is available in 2 flavors, orange and cranberry flavor, and is provided in two packets. The contents of each is to be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and consumed.
Each packet for both flavors contains 10 mg sodium picosulfate, 3.5 g magnesium oxide and 12 g anhydrous citric acid. The product also contains the following inactive ingredients: potassium hydrogen carbonate, saccharine sodium and orange or cranberry flavors. The orange flavor contains acacia gum, lactose, ascorbic acid and butylated hydroxyanisole, and the cranberry flavor contains maltodextrin, glyceryl triacetate (triacetin) and sodium octenyl succinated starch. The following is a description of the three active ingredients:
Sodium picosulfate is a stimulant laxative.
Sodium Picosulfate
- Chemical name: 4,4´-(2-pyridylmethylene) diphenyl bis(hydrogen sulfate) disodium salt, monohydrate
- Chemical formula: C18H13NNa2O8S2.H2O
- Molecular weight: 499.4
- Structural formula:
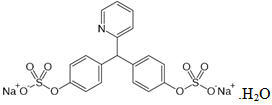
- Sodium picosulfate
Magnesium citrate, which is formed in solution by the combination of magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid, is an osmotic laxative.
Magnesium Oxide
- Chemical name: Magnesium oxide
- Chemical formula: Mg O
- Molecular weight: 40.3
- Structural formula: Mg O
Anhydrous Citric Acid
- Chemical name: 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
- Chemical formula: C6H8O7
- Molecular weight: 192.1
- Structural formula:
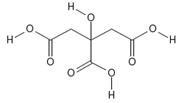
Anhydrous citric acid
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sodium picosulfate is hydrolyzed by colonic bacteria to form an active metabolite: bis-(p-hydroxy-phenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane, BHPM, which acts directly on the colonic mucosa to stimulate colonic peristalsis.
Magnesium oxide and citric acid react to create magnesium citrate in solution, which is an osmotic agent that causes water to be retained within the gastrointestinal tract.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The stimulant laxative activity of sodium picosulfate together with the osmotic laxative activity of magnesium citrate produces a purgative effect which, when ingested with additional fluids, produces watery diarrhea.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After administration of the first packet of Prepopik in 16 healthy subjects, mean maximum concentration (Cmax) for picosulfate of 2.3 ± 1.4 ng/mL was reached at 2 hours. After administration of 2 packets of Prepopik separated by 6 hours, picosulfate reached the mean Cmax of 3.2 ± 2.6 ng/mL at approximately 7 hours (Tmax). In the same study, baseline uncorrected magnesium reached a Cmax of approximately 1.9 mEq/L, which occurred at 10 hours post first packet administration (Tmax). This represents an approximately 20% increase from the baseline.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) for picosulfate was 4199 liters in healthy adults.
Metabolism and Elimination
Sodium picosulfate, which is a prodrug, is converted to its active metabolite, BHPM, by colonic bacteria. Plasma concentration of the free BHPM were low, and below the lower limit of quantification (0.1 ng/mL) in 13 out of 16 subjects studied. The fraction of the sodium picosulfate dose excreted unchanged in urine was 0.2%. In urine, the majority of excreted BHPM was in the glucuronide-conjugated form. The terminal half-life of sodium picosulfate was 7.4 hours. The apparent clearance (CL/F) of picosulfate was 629 L/h.
Use in Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Pharmacokinetics of picosulfate was studied in pediatric patients aged from 9 to 16 years old.
For picosulfate, the apparent clearance is from 316 to 409 L/h. The corresponding estimates for apparent volume of distribution are from 2457 to 3935 liters. The derived half-life using these model estimates would be 7 hours. The picosulfate reached the mean Cmax of 3.5 ± 2.1 ng/mL at approximately 6 to 7 hours (Tmax)
The baseline uncorrected mean serum magnesium concentration was 2.02 mEq/L at 10 hours after the first dose of Prepopik and ranged from 1.7 to 2.46 mEq/L in pediatric patients from 9 to 16 years of age.
Drug Interaction Studies
In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, sodium picosulfate did not inhibit the major CYP enzymes (CYP 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 3A4/5) evaluated. Based on an in vitro study using freshly isolated hepatocyte culture, sodium picosulfate is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A4/5.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential or studies to evaluate mutagenic potential have not been performed with Prepopik. Sodium picosulfate was not mutagenic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma assay and the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test.
In an oral fertility study in rats, Prepopik did not cause any significant adverse effect on male or female fertility parameters up to a maximum dose of 2000 mg/kg twice daily (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on the body surface area).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Adults
The colon cleansing efficacy of Prepopik was evaluated for non-inferiority against a comparator in two randomized, investigator-blinded, active-controlled, multicenter US trials in adult patients scheduled to have an elective colonoscopy. In all, 1195 adult patients were included in the primary efficacy analysis: 601 from Study 1, and 594 from Study 2. Patients ranged in age from 18 to 80 years (mean age 56 years); 61% were female and 39% male. Self-identified race was distributed as follows: 90% White, 10% Black, and less than 1% other. Of these, 3% self-identified their ethnicity as Hispanic or Latino.
Patients randomized to Prepopik in the two studies were treated with one of two dosing regimens:
- In Study 1, Prepopik was given by "Split-Dose" (evening before and day of) dosing, where the first packet was taken the evening before the colonoscopy (between 5:00 and 9:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second packet was taken the morning of the colonoscopy (at least 5 hours prior to but no more than 9 hours prior to colonoscopy), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
- In Study 2, Prepopik was given by "Day-Before" (afternoon/evening before only) dosing, where both packets were taken separately on the day before the colonoscopy, with the first packet taken in the afternoon (between 4:00 and 6:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second packet taken in the late evening (approximately 6 hours later, between 10:00 PM and 12:00 AM), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
The comparator was a preparation containing two liters of polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution (PEG + E) and two 5-mg bisacodyl tablets, administered the day before the procedure. All patients in both the Prepopik and comparator groups were limited to a clear liquid diet on the day before the procedure (24 hours before).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing, as assessed by blinded colonoscopists using the Aronchick Scale. The Aronchick scale is a tool used to assess overall colon cleansing. Successful colon cleansing was defined as bowel preparations with >90% of the mucosa seen and mostly liquid stool that were graded excellent (minimal suctioning needed for adequate visualization) or good (significant suctioning needed for adequate visualization) by the colonoscopist.
In both studies, Prepopik was non-inferior to the comparator. In addition, Prepopik provided by Split-Dose dosing met the pre-specified criteria for superiority to the comparator for colon cleansing in Study 1. The comparator in that study was administered entirely on the day prior to colonoscopy. See Tables 3 and 4 below.
Table 3: Proportion of Patients with Successful Colon Cleansing in Study 1 Split-Dose Regimen PREPOPIK
Split-Dose Regimen2L PEG+E* with 2 × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets Difference between treatment groups % (n/N) % (n/N) Difference 95% CI - * 2L PEG + E = two liters polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution.
- † Non-inferior and superior 2L PEG+E with 2 × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets
84 % (256/304) 74% (221/297) 10% (3.4%, 16.2%)† Table 4: Proportion of Patients with Successful Colon Cleansing in Study 2 Day-Before Regimen PREPOPIK
Day-Before Regimen2L PEG+E* with 2 × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets Difference between treatment groups % (n/N) % (n/N) Difference 95% CI - * 2L PEG + E = two liters polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution.
- † Non-inferior
83% (244/294) 80% (239/300) 3 % (-2.9%, 9.6%)† Pediatric Patients 9 Years of Age and Older
Prepopik was evaluated for colon cleansing in a randomized, assessor-blind, multicenter, dose-ranging, active-controlled study in 78 pediatric patients 9 years to 16 years of age. The majority of patients were female (68%), white (91%), and of non-Hispanic or non-Latino ethnicity (95%). The mean age was 12 years of age. All 78 patients were included in the primary efficacy analysis.
Patients aged 9 years to 12 years were randomized into 3 arms (1:1:1):
- Prepopik one-half packet administered as two doses
- Prepopik one-packet administered as two doses
- comparator (oral PEG-based solution per local standard of care).
Patients aged 13 years to 16 years were randomized into 2 arms (1:1):
- Prepopik one-packet administered as two doses
- comparator (oral PEG-based solution per local standard of care)
Patients randomized to Prepopik had two options for dosing, as determined by the investigator. The "Split Dose" regimen was the preferred method and the "Day Before" regimen was the alternative method if the "Split Dose" was not appropriate.
"Split-Dose" Regimen: (evening before and day of) dosing, where the first dose was taken the evening before the colonoscopy (between 5:00 and 9:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second dose was taken the morning of the colonoscopy (at least 5 hours prior to but no more than 9 hours prior to colonoscopy), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
"Day-Before" Regimen: (afternoon/evening before only) dosing, where both doses were taken separately on the day before the colonoscopy, with the first dose taken in the afternoon (between 4:00 and 6:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second dose taken in the late evening (approximately 6 hours later, between 10:00 PM and 12:00 AM), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
All patients randomized to Prepopik were limited to a clear liquid diet on the day before the procedure. Those who received the comparator were given dietary instructions per the trial site's standard of care.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing as defined as a rating of either "Excellent" (> 90% of mucosa seen, mostly liquid stool, minimal suctioning needed for adequate visualization) or "Good" (> 90% of mucosa seen, mostly liquid stool, significant suctioning needed for adequate visualization) using the Aronchick scale, as assessed by blinded colonoscopists.
The Prepopik regimen of one-half packet administered as two doses did not demonstrate comparable efficacy to the comparator, PEG, in patients 9 to 12 years of age and is not a recommended dosage regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
The Prepopik regimen of one packet administered as two doses demonstrated successful colon cleansing in both the 9 to 12 year age group and the 13 to 16 year age group. The efficacy rates were similar to those observed in the PEG groups, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Proportion of Patients 9 to 16 Years of Age with Successful Colon Cleansing* PREPOPIK One Packet Administered as Two Doses either as Split Dose or Day Before Regimen† PEG Comparator‡ % (n/N) 95% CI % (n/N) 95% CI - * Successful colon cleansing as defined by "Excellent" or "Good" on the Aronchick scale
- † Of the 32 patients, 9 received the Split Dose Regimen and 23 the Day Before Regimen
- ‡ Oral PEG-based preparation was used in the study as per standard of care
Age 9-12 88% (14/16) (62, 98) 81% (13/16) (54, 96) Age 13-16 81% (13/16) (54, 96) 86% (12/14) (57, 98) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Prepopik is supplied in a carton containing 2 packets, each holding 16.1 grams of powder in orange flavor or 16.2 grams of powder in cranberry flavor for oral solution, along with a pre-marked dosing cup. Each packet for both flavors contains 10 mg sodium picosulfate, 3.5 g magnesium oxide and 12 g anhydrous citric acid. The excipients for both flavors include potassium hydrogen carbonate, sodium saccharin, orange or cranberry flavor. The orange flavor contains acacia gum, lactose, ascorbic acid, and butylated hydroxyanisole, and the cranberry flavor contains maltodextrin, glyceryl triacetate (triacetin) and sodium octenyl succinated starch.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Instruct patients:
- Each packet must be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and administered according to the dosing regimen. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8).
- Two doses (one packet per dose) of Prepopik are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy either as a Split-Dose (preferred) or Day-Before dosing regimen.
- Not to take other laxatives while they are taking Prepopik.
- Do not eat solid food or dairy and do not drink anything colored red or purple.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take oral medications within one hour of starting Prepopik.
- If taking tetracycline or fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, or penicillamine, take these medications at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of Prepopik.
- To follow the directions in the Instructions for Use, for either the Split-Dose or the Day-Before regimen, as prescribed.
- To consume additional fluids after each dose of Prepopik.
- To delay the second dose of Prepopik, if severe bloating, distention, or abdominal pain occurs following the first dose until the symptoms resolve.
- To contact their healthcare provider if they develop significant vomiting or signs of dehydration after taking Prepopik or if they experience altered consciousness (e.g. confusion, delirium, loss of consciousness) or seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.4)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: August 2018 MEDICATION GUIDE
PREPOPIK® (prep-ō-pik)
(sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid)
for oral solutionRead and understand this Medication Guide and the Instructions for Use that come with PREPOPIK at least 2 days before your colonoscopy and again before you start taking Prepopik. What is the most important information I should know about Prepopik?
Prepopik and other bowel preparations can cause serious side effects, including: Serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes) in your blood. These changes can cause: - abnormal heartbeats that can cause death.
- seizures. This can happen even if you have never had a seizure.
- kidney problems.
Your chance of having fluid loss and changes in blood salts with Prepopik is higher if you: - have heart problems
- have kidney problems
- take water pills or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms of a loss of too much body fluid (dehydration) while taking Prepopik: - vomiting
- urinating less often than normal
- dizziness
- headache
See "What are the possible side effects of Prepopik?" for more information about side effects. What is Prepopik? Prepopik is a prescription medicine used by adults and children 9 years of age and older, to clean the colon before a colonoscopy. Prepopik cleans your colon by causing you to have diarrhea. Cleaning your colon helps your healthcare provider see the inside of your colon more clearly during your colonoscopy. It is not known if Prepopik is safe and effective in children under 9 years of age. Do not take Prepopik if your healthcare provider has told you that you have: - serious kidney problems.
- a blockage in your intestine (bowel obstruction).
- an opening in the wall of your stomach or intestines (bowel perforation).
- a very dilated intestine (toxic megacolon).
- problems with the emptying of food and fluid from your stomach (gastric retention).
- an allergy to any of the ingredients in Prepopik. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Prepopik.
Before taking Prepopik, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have problems with serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes).
- have a history of seizures or take medicines for seizures.
- are withdrawing from drinking alcohol or from taking benzodiazepines.
- have low blood salt (sodium) level.
- have kidney problems or take medicines for kidney problems.
- have heart problems.
- have stomach or bowel problems including ulcerative colitis.
- have problems with swallowing or gastric reflux.
- are pregnant. It is not known if Prepopik will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Prepopik passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Prepopik while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Prepopik may affect how other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how Prepopik works. Medicines taken by mouth may not be absorbed properly when taken within 1 hour before the start of Prepopik. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take: - medicines for blood pressure or heart problems.
- medicines for kidney problems.
- medicines for seizures.
- water pills (diuretics).
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (pain medicines).
- medicines for depression or mental health problems.
- laxatives. Do not take other laxatives while taking Prepopik.
The following medicines should be taken at least 2 hours before starting Prepopik and not less than 6 hours after taking Prepopik: - tetracycline
- fluoroquinolone antibiotics
- iron
- digoxin (Lanoxin)
- chlorpromazine
- penicillamine (Cuprimine, Depen)
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure if you are taking the medicines listed above. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. How should I take Prepopik? See the Instructions for Use for dosing instructions. You must read, understand, and follow these instructions to take Prepopik the right way. - Take Prepopik exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not take Prepopik powder that has not been mixed with water. It may increase your risk of nausea, vomiting, and fluid loss (dehydration).
- Each packet of Prepopik powder must be mixed with 5 ounces of cold water before drinking.
- It is important for you to drink the additional prescribed amount of clear liquids listed in the Instructions for Use to prevent fluid loss (dehydration).
- Two doses of Prepopik are required for a complete colonoscopy preparation. 1 packet of Prepopik for oral solution equals 1 dose.
- There are 2 different methods for taking Prepopik. It is better (preferred) to use the Split-Dose method. If you cannot do the Split-Dose method, you can take Prepopik using the Day-Before method. See the Instructions for Use for more information.
- All people taking Prepopik should follow these general instructions starting 1 day before your colonoscopy:
- only drink clear liquids all day and the next day until 2 hours before your colonoscopy. Stop drinking all fluids at least 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
- after taking Prepopik if you have any bloating or feeling like your stomach is upset, wait to take your second dose until your stomach feels better.
-
While taking Prepopik, do not:
- take any other laxatives.
- take any medicines by mouth (oral) within 1 hour of starting Prepopik.
- eat solid foods, dairy such as milk, or alcohol while taking Prepopik and until after your colonoscopy.
- eat or drink anything colored red or purple.
Contact your healthcare provider right away if after taking Prepopik you have severe vomiting, signs of dehydration, changes in consciousness such as feeling confused, delirious or fainting (loss of consciousness) or seizures after taking Prepopik. Prepopik can cause serious side effects, including: - See "What is the most important information I should know about Prepopik?"
- Changes in certain blood tests. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests after you take Prepopik to check your blood for changes. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of too much fluid loss, including:
- vomiting
- stomach-area (abdomen) cramping
- seizures
- nausea
- urinate less than usual
- heart problems
- bloating
- trouble drinking clear liquids
- dizziness
- trouble swallowing
- Ulcers of the bowel or bowel problems (ischemic colitis). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have severe stomach-area (abdomen) pain or rectal bleeding.
The most common side effects of Prepopik in adults include: - nausea
- headache
- vomiting
The most common side effects of Prepopik in children 9 to 16 years of age include: - nausea
- vomiting
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
These are not all the possible side effects of Prepopik. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. How should I store Prepopik? - Store Prepopik at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Prepopik and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of Prepopik. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Prepopik for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Prepopik to other people, even if they are going to have the same procedure you are. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Prepopik that is written for health professionals. What are the ingredients in Prepopik? Prepopik comes in a carton containing 2 packets, each containing 16.1 grams of powder in orange flavor or 16.2 grams of powder in cranberry flavor, along with a pre-marked dosing cup. Active ingredients: sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid Inactive ingredients: potassium hydrogen carbonate, saccharin sodium, orange flavor which contains acacia gum, lactose, ascorbic acid and butylated hydroxyanisole or the cranberry flavor which contains maltodextrin, glyceryl triacetate (triacetin) and sodium octenyl succinated starch. Manufactured for: Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054, USA
For more information, go to www.ferring.com or call 1-888-337-7464. -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Prepopik® (prep- o-pik)
(sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid)
for oral solutionBefore Taking Prepopik
There are 2 different methods for taking Prepopik. It is better (preferred) to use the Split-Dose method. If you cannot use the Split-Dose method, you can take Prepopik using the Day-Before method. Talk with your healthcare provider before you start if you have any questions.
- Start a clear-liquid diet the day before your colonoscopy. Only drink clear liquids all day the day before your colonoscopy, and the next day until 2 hours before your colonoscopy. Stop drinking all fluids at least 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
- You must drink enough clear liquids to keep your body hydrated for the entire day before your colonoscopy.
Important:
See Table 1 for a list of liquids you can drink for your clear liquid diet.
Important:
See Table 2 for the items you cannot eat or drink before your colonoscopy.
Important:
- Prepopik is a powder that must be added to cold water right before use.
- Do not prepare the solution ahead of time. Take Prepopik right after it is prepared.
- Do not swallow the powder without adding it to cold water first.
Split-Dose Instructions
Dose 1 – In the evening the day before your colonoscopy (sometime between 5:00 PM to 9:00 PM)
-
Fill the dosing cup with cold water up to the lower line (5 ounces).
Note: Do not use any other clear liquid to mix Prepopik.
- Open 1 packet of Prepopik and add all of the powder to the cold water in the dosing cup. To open the Prepopik packet cut along the dotted line at the top of the packet using scissors.
- Stir for 2 to 3 minutes to dissolve the powder. Use a clock or timer The dosing cup may feel slightly warm as the powder dissolves. This is normal.
- Drink all the solution right away.
Note: Prepopik powder should be mixed in cold water immediately before use. Do not prepare the solution ahead of time or store the solution for later use. Do not refrigerate or add ice to the solution.
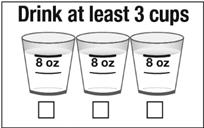
- Follow this Prepopik dose by drinking at least five 8 ounce cups of clear liquid (using the upper line on the dosing cup provided- see figure below) over the next 5 hours.
- After taking Prepopik if you have any bloating or feeling like your stomach is upset, wait to take your second dose until your stomach feels better.
Important: See Table 1 for a list of acceptable clear liquids.
Dose 2 - In the morning of colonoscopy (approximately 5 hours prior to colonoscopy)
Note: Do not eat solid food. Drink only clear liquids. -
Fill the dosing cup with cold water up to the lower line (5 ounces).
Note: Do not use any other clear liquid to mix Prepopik.
- Open the second packet of Prepopik and add all the powder to the cold water in the dosing cup.
- Stir for 2 to 3 minutes to dissolve the powder. Use a clock or timer.
- Drink all the solution right away.
Note: Prepopik powder should be mixed in cold water immediately before use. Do not prepare the solution ahead of time or store the solution for later use. Do not refrigerate or add ice to the solution.
- Follow this Prepopik dose by drinking at least three 8 ounce cups of clear liquids (using the upper line on the dosing cup- see figure below). You can continue to drink clear liquids up to 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
Important: See Table 1 for a list of acceptable clear liquids.
Stop drinking clear liquids 2 hours before your colonoscopy, or as advised by your healthcare provider.
Day-Before Instructions Dose 1 – In the afternoon or early evening the day before your colonoscopy (sometime between 4:00 PM to 6:00 PM) -
Fill the dosing cup with cold water up to the lower line (5 ounces).
Note: Do not use any other clear liquid to mix Prepopik.
- Open 1 packet of Prepopik and add all the powder to the cold water in the dosing cup. To open the Prepopik packet cut along the dotted line at the top of the packet using scissors.
- Stir for 2 to 3 minutes to dissolve the powder. Use a clock or timer. The dosing cup may feel slightly warm as the powder dissolves. This is normal.
- Drink all the solution right away.
Note: Prepopik powder should be mixed in cold water immediately before use. Do not prepare the solution ahead of time or store the solution for later use. Do not refrigerate or add ice to the solution.
- Follow this Prepopik dose by drinking at least five 8 ounce cups of clear liquids (using the upper line on the dosing cup- see figure below) over the next 5 hours.
After taking Prepopik if you have any bloating or feeling like your stomach is upset, wait to take your second dose until your stomach feels better.
Important: See Table 1 for a list of acceptable clear liquids.
Dose 2 – In the evening before your colonoscopy (sometime between 10:00 PM to 12:00 AM):
Note: Do not eat solid food. Drink only clear liquids. -
Fill the dosing cup with cold water up to the lower line (5 ounces).
Note: Do not use any other clear liquid to mix Prepopik.
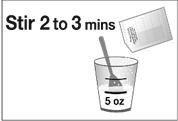
- Open the second packet of Prepopik and add all of the powder to the cold water in the dosing cup.Stir for 2 to 3 minutes to dissolve the powder. Use a clock or timer.
- Drink all of this solution right away.
Note: Prepopik powder should be mixed in cold water immediately before use. Do not prepare the solution ahead of time or store the solution for later use. Do not refrigerate or add ice to the solution.
- Follow this Prepopik dose by drinking at least three 8 ounce cups of clear liquids (using the upper line on the dosing cup- see figure below) over the next 5 hours.
Important: See Table 1 for a list of acceptable clear liquids.
Stop drinking clear liquids 2 hours before your colonoscopy, or as advised by your healthcare provider.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: August 2018
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 Packet Carton - Orange
Rx only
NDC: 55566-9300-2Orange
FlavorPrepopik®
(sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and
anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution
10 mg/3.5 g/12 g per packetATTENTION PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Contains 2 packets
Store at 25°C (77°F)
Excursions permitted at 15-30°C (59-86°F)
[See USP controlled room temperature]FERRING
PHARMACEUTICALS
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 Packet Carton - Cranberry
Rx only
NDC: 55566-9700-1Cranberry
FlavorPrepopik®
(sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and
anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution
10 mg/3.5 g/12 g per packetATTENTION PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Contains 2 packets
Store at 25°C (77°F)
Excursions permitted at 15-30°C (59-86°F)
[See USP controlled room temperature]FERRING
PHARMACEUTICALS
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PREPOPIK
sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid powder, meteredProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55566-9300 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM PICOSULFATE (UNII: LR57574HN8) (DEACETYLBISACODYL - UNII:R09078E41Y) SODIUM PICOSULFATE 10 mg in 16.1 g MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM OXIDE 3.5 g in 16.1 g ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) (ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID - UNII:XF417D3PSL) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID 12 g in 16.1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) ORANGE (UNII: 5EVU04N5QU) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor ORANGE Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55566-9300-2 2 in 1 CARTON 07/16/2012 05/31/2020 1 NDC: 55566-9300-0 16.1 g in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202535 07/16/2012 05/31/2020 PREPOPIK
sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid powder, meteredProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55566-9700 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM PICOSULFATE (UNII: LR57574HN8) (DEACETYLBISACODYL - UNII:R09078E41Y) SODIUM PICOSULFATE 10 mg in 16.2 g MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM OXIDE 3.5 g in 16.2 g ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) (ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID - UNII:XF417D3PSL) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID 12 g in 16.2 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) CRANBERRY (UNII: 0MVO31Q3QS) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor CRANBERRY Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55566-9700-1 2 in 1 CARTON 09/05/2014 05/31/2020 1 NDC: 55566-9700-0 16.2 g in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202535 09/05/2014 05/31/2020 Labeler - Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. (103722955) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ferring Production Inc. 079510999 LABEL(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ferring Pharmaceuticals (China) Co., Ltd. 527903976 MANUFACTURE(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Jungbunzlauer Ladenburg GmbH 322121609 API MANUFACTURE(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , ANALYSIS(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cambrex Profarmaco Milano S.R.L. 438051401 API MANUFACTURE(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , ANALYSIS(55566-9300, 55566-9700) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Tomita Phamaceutical Co., Ltd. 690643499 API MANUFACTURE(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700) , ANALYSIS(55566-9300, 55566-9700) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations F.M. Howell & Company 962888116 PACK(55566-9300, 55566-9700)
Trademark Results [PREPOPIK]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PREPOPIK 97861286 not registered Live/Pending |
Ferring B.V. 2023-03-28 |
 PREPOPIK 85665077 4333945 Live/Registered |
Ferring B.V. 2012-06-29 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.