AYVAKIT- avapritinib tablet, film coated
Ayvakit by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ayvakit by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Blueprint Medicines Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AYVAKIT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AYVAKIT.
AYVAKIT (avapritinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AYVAKIT is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Intracranial Hemorrhage: Withhold AYVAKIT for Grade 1 or 2 reactions until resolution and then resume at a reduced dose. Permanently discontinue for recurrent Grade 1 or 2 reactions or first occurrence of Grade 3 or 4 reactions. (2.3, 5.1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Effects: CNS adverse reactions include cognitive impairment, dizziness, sleep disorders, mood disorders, speech disorders, and hallucinations. Depending on the severity, continue AYVAKIT at same dose, withhold and then resume at same or reduced dose upon improvement, or permanently discontinue. (2.3, 5.2)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 20%) are edema, nausea, fatigue/asthenia, cognitive impairment, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hair color changes, increased lacrimation, abdominal pain, constipation, rash and dizziness. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Blueprint Medicines Corporation at 1-888-258-7768 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid coadministration of AYVAKIT with strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If coadministration of AYVAKIT with a moderate inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce dose of AYVAKIT. (2.4, 7.1)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid coadministration of AYVAKIT with strong and moderate CYP3A inducers. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 PDGFRA Exon 18 Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection for GIST Harboring PDGFRA Exon 18 Mutations
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.4. Concomitant Use of Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Intracranial Hemorrhage
5.2 Central Nervous System Effects
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on AYVAKIT
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 PDGFRA Exon 18 Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
AYVAKIT is indicated for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic GIST harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection for GIST Harboring PDGFRA Exon 18 Mutations
Select patients for treatment with AYVAKIT based on the presence of a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of exon 18 mutations is not currently available.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of AYVAKIT is 300 mg orally once daily on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before and 2 hours after a meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Do not make up for a missed dose within 8 hours of the next scheduled dose.
Do not take an additional dose if vomiting occurs after AYVAKIT, but continue with the next scheduled dose.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions and dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1. Recommended Dose Reductions for AYVAKIT for Adverse Reactions Dose Reduction Recommended Dosage *Permanently discontinue AYVAKIT in patients who are unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg once daily. First 200 mg once daily Second 100 mg once daily Table 2. Recommended Dosage Modifications for AYVAKIT for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity* Dosage Modification - * Severity as defined by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0
Intracranial Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Grade 1 or Grade 2 First Occurrence: Withhold AYVAKIT until resolution. Resume at reduced dose.
Subsequent Occurrence: Permanently discontinue.Grade 3 or Grade 4 Permanently discontinue AYVAKIT. Central Nervous System Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Grade 1 Continue AYVAKIT at same dose or withhold until improvement to baseline or resolution. Resume at same dose or reduced dose. Grade 2 or Grade 3 Withhold AYVAKIT until improvement to baseline, Grade 1, or resolution. Resume at same dose or reduced dose. Grade 4 Permanently discontinue AYVAKIT. Other [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 3 or Grade 4 Withhold AYVAKIT until improvement to less than or equal to Grade 2. Resume at same dose or reduced dose, as clinically appropriate. 2.4. Concomitant Use of Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of AYVAKIT with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If concomitant use with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the starting dose of AYVAKIT from 300 mg orally once daily to 100 mg orally once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 100 mg, round, white film-coated, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "100" on the other side.
- 200 mg, capsule shaped, white film-coated, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "200" on the other side.
- 300 mg, capsule shaped, white film-coated, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "300" on the other side.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (e.g., subdural hematoma, intracranial hemorrhage, and cerebral hemorrhage) occurred in 1% of the 267 patients with GIST and overall in 3% of the 335 patients who received AYVAKIT. Events of intracranial hemorrhage occurred in a range from 1.7 months to 19.3 months after initiating AYVAKIT. Overall, 0.9% of patients receiving AYVAKIT required permanent discontinuation for an intracranial hemorrhage; 1.2% required dosage interruption followed by dose reduction.
Withhold AYVAKIT and then resume at a reduced dose upon resolution, or permanently discontinue AYVAKIT based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Central Nervous System Effects
A broad spectrum of central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions can occur in patients receiving AYVAKIT. These include cognitive impairment, dizziness, sleep disorders, mood disorders, speech disorders, and hallucinations. CNS adverse reactions overall occurred in 58% of 335 patients who received AYVAKIT [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Cognitive impairment occurred in 41% of the 335 patients who received AYVAKIT; 3.6% of these were severe (Grade 3 or 4). Dizziness occurred in 20% of patients; 0.6% of these events were severe. Sleep disorders occurred in 15% of patients; 0.3% of these events were severe. Mood disorders occurred in 13% of patients; 1.5% of these events were severe. Speech disorders occurred in 6% of patients; none of these events were severe. Hallucinations occurred in 2.1% of patients; none of these events were severe. The median time to onset of the first CNS adverse reaction was 6.1 weeks (range 1 day to 1.9 years). Overall, 3.9% of patients required permanent discontinuation of AYVAKIT for a CNS adverse reaction, 17% required a dosage interruption, and 10% required dose reduction.
Depending on the severity, withhold AYVAKIT and then resume at the same dose or at a reduced dose upon improvement, or permanently discontinue AYVAKIT [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, AYVAKIT can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Oral administration of avapritinib during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at exposures approximately 2.7 times the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the 300 mg dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 6 weeks after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Intracranial hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Central nervous system effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to AYVAKIT at 30 mg to 600 mg orally once daily in 335 patients enrolled in one of three clinicals trials conducted in patients with advanced malignancies, including NAVIGATOR [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Among the 335 patients receiving AYVAKIT, 49% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 23% were exposed for greater than 1 year.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Unresectable or Metastatic GIST
The safety of AYVAKIT in patients with unresectable or metastatic GIST was evaluated in NAVIGATOR [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The trial excluded patients with history of cerebrovascular accident or transient ischemic attacks, known risk of intracranial bleeding, and metastases to the brain. Patients received AYVAKIT 300 mg or 400 mg orally once daily (n = 204). Among patients receiving AYVAKIT, 56% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 44% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of patients who received AYVAKIT was 62 years (range: 29 to 90 years), 60% were <65 years, 62% were male, and 69% were White. Patients had received a median of 3 prior kinase inhibitors (range: 0 to 7).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 52% of patients receiving AYVAKIT. Serious adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients who received AYVAKIT were anemia (9%), abdominal pain (3%), pleural effusion (3%), sepsis (3%), gastrointestinal hemorrhage (2%), vomiting (2%), acute kidney injury (2%), pneumonia (1%) and tumor hemorrhage (1%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.4% of patients. Fatal adverse reactions that occurred in more than one patient were sepsis and tumor hemorrhage (1% each).
Permanent discontinuation due to adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients who received AYVAKIT. Adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in more than one patient were fatigue, abdominal pain, vomiting, sepsis, anemia, acute kidney injury, and encephalopathy.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 57% of patients who received AYVAKIT. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in >2% of patients who received AYVAKIT were anemia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hyperbilirubinemia, memory impairment, diarrhea, cognitive disorder, and abdominal pain.
Dose reduction due to an adverse reaction occurred in 49% of patients who received AYVAKIT. Median time to dose reduction was 9 weeks. Adverse reactions requiring dosage reduction in more than 2% of patients who received AYVAKIT were fatigue, anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, memory impairment, nausea and periorbital edema.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were edema, nausea, fatigue/asthenia, cognitive impairment, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hair color changes, increased lacrimation, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, and dizziness. Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions observed in NAVIGATOR.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients Receiving AYVAKIT in NAVIGATOR Adverse Reactions AYVAKIT
N=204All Grades
%Grade ≥ 3
%*Per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03 and 5.0 - * Edema includes face swelling, conjunctival edema, eye edema, eyelid edema, orbital edema, periorbital edema, face edema, mouth edema, pharyngeal edema, peripheral edema, edema, generalized edema, localized edema, peripheral swelling, testicular edema.
- † Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, lower abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, and epigastric discomfort.
- ‡ Cognitive impairment includes memory impairment, cognitive disorder, confusional state, disturbance in attention, amnesia, mental impairment, mental status changes, encephalopathy, dementia, abnormal thinking, mental disorder, and retrograde amnesia.
- § Sleep disorders includes insomnia, somnolence, and sleep disorder.
- ¶ Taste effects include dysgeusia and ageusia.
- # Mood disorders includes agitation, anxiety, depression, depressed mood, dysphoria, irritability, mood altered, nervousness, personality change, and suicidal ideation.
- Þ Rash includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash generalized, and rash papular.
General Edema* 72 2 Fatigue/asthenia 61 9 Pyrexia 14 0.5 Gastrointestinal Nausea 64 2.5 Vomiting 38 2 Diarrhea 37 4.9 Abdominal pain† 31 6 Constipation 23 1.5 Dyspepsia 16 0 Nervous System Cognitive impairment‡ 48 4.9 Dizziness 22 0.5 Headache 17 0.5 Sleep disorders§ 16 0 Taste effects¶ 15 0 Mood disorders# 13 1 Metabolism and nutrition Decreased appetite 38 2.9 Eye Increased lacrimation 33 0 Skin and subcutaneous tissue RashÞ 23 2.1 Hair color changes 21 0.5 Alopecia 13 - Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal Dyspnea 17 2.5 Pleural effusion 12 2 Investigations Weight decreased 13 1 Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients were:
Vascular: hypertension (8%)
Endocrine: thyroid disorders (hyperthyroid, hypothyroid) (3%)
Skin and subcutaneous: palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (1%)
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities observed in NAVIGATOR.
Table 4. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Receiving AYVAKIT in NAVIGATOR Laboratory Abnormality AYVAKIT*
N=204All Grades
(%)Grade ≥ 3
(%)- * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 154 to 201 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Hematology Decreased hemoglobin 81 28 Decreased leukocytes 62 5 Decreased neutrophils 43 6 Decreased platelets 27 0.5 Increased INR 24 0.6 Increased activated partial thromboplastin time 13 0 Chemistry Increased bilirubin 69 9 Increased aspartate aminotransferase 51 1.5 Decreased phosphate 49 13 Decreases potassium 34 6 Decreased albumin 31 2 Decreased magnesium 29 1 Increased creatinine 29 0 Decreased sodium 28 7 Increased alanine aminotransferase 19 0.5 Increased alkaline phosphatase 14 1 -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on AYVAKIT
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Coadministration of AYVAKIT with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor increases avapritinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions of AYVAKIT. Avoid coadministration of AYVAKIT with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If coadministration of AYVAKIT with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of AYVAKIT [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of AYVAKIT with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer decreases avapritinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may decrease efficacy of AYVAKIT. Avoid coadministration of AYVAKIT with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], AYVAKIT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on AYVAKIT use in pregnant women. Oral administration of avapritinib to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at exposure levels approximately 2.7 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a reproductive toxicity study, administration of avapritinib to rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in decreased fetal body weights, post-implantation loss, and increases in visceral (hydrocephaly, septal defect, and stenosis of the pulmonary trunk) and skeletal (sternum) malformations at doses greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.7 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of avapritinib or its metabolites in human milk or the effects of avapritinib on the breastfed child or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 2 weeks following the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating AYVAKIT [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
AYVAKIT can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Based on findings from animal studies, AYVAKIT may impair both male and female fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of AYVAKIT in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 204 patients who received AYVAKIT in NAVIGATOR, 40% were 65 years or older, while 6% were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between these patients and younger adult patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment [creatinine clearance (CLcr) 30 to 89 mL/min estimated by Cockcroft-Gault]. The recommended dose of AYVAKIT has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease (CLcr <15 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild [total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST] or moderate (total bilirubin >1.5 to 3 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. The recommended dose of AYVAKIT has not been established for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Avapritinib is a kinase inhibitor with the chemical name (S)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-(4-(6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4-yl)piperazin-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)ethan-1-amine. The molecular formula is C26H27FN10, and the molecular weight is 498.57 g/mol. Avapritinib has the following chemical structure:
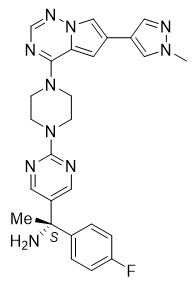
The solubility of avapritinib in 0.1N HCl (pH 1.0) and buffer solutions at pH 2.5, 4.0, and 7.0 (at 25°C) is 3.6 mg/mL, 0.14 mg/mL, 0.07 mg/mL and <0.001 mg/mL respectively, indicating a decrease in solubility with increasing pH.
AYVAKIT (avapritinib) film-coated tablets for oral use are supplied with three strengths that contain 100 mg, 200 mg or 300 mg of avapritinib. The tablets also contain inactive ingredients: copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet coating consists of polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. The blue printing ink contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, esterified shellac, FD&C blue 1, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Avapritinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets PDGFRA and PDGFRA D842 mutants as well as multiple KIT exon 11, 11/17 and 17 mutants with half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) less than 25 nM. Certain mutations in PDGFRA and KIT can result in the autophosphorylation and constitutive activation of these receptors which can contribute to tumor cell proliferation. Other potential targets for avapritinib include wild type KIT, PDGFRB, and CSFR1.
In in vitro cellular assays, avapritinib inhibited the autophosphorylation of KIT D816V and PDGFRA D842V, mutants associated with resistance to approved kinase inhibitors, with IC50 of 4 nM and 30 nM, respectively. Avapritinib also had anti-tumor activity in mice implanted with an imatinib-resistant patient-derived xenograft model of human GIST with activating KIT exon 11/17 mutations.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationships
Based on the data from NAVIGATOR, exposure-response relationships for any Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction were observed at higher exposures with a faster time to onset for adverse reactions with increasing avapritinib exposure.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of AYVAKIT on the QTc interval was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm study in 27 patients administered dose of 300 mg or 400 mg (1.3 times the approved recommended dose) once daily. No large mean increase in QTc (i.e.> 20 ms) was detected at the mean steady state maximum concentration (Cmax) of 899 ng/mL.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Avapritinib Cmax and AUC increased proportionally over the dose range of 30 mg to 400 mg once daily (0.1 to 1.33 times the recommended dose).
At the recommended dosage of 300 mg once daily, the mean (CV%) steady state Cmax of avapritinib was 813 ng/mL (52%) and the mean steady state area under the concentration-time curve (AUC0-24h) was 15400 h∙ng/mL (48%). Steady state concentration of avapritinib was reached by day 15 following daily dosing and the mean accumulation ratio was 3.1 to 4.6 after repeated dosing.
Absorption
The median time to peak concentration (Tmax) ranged from 2.0 to 4.1 hours following single doses of avapritinib 30 mg to 400 mg (0.1 to 1.33 times the approved recommended dose).
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution of avapritinib is 1200 L (43%). In vitro protein binding of avapritinib is 98.8% and is independent of concentration. The blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.95.
Elimination
The mean plasma elimination half-life of avapritinib was 32 hours to 57 hours following single doses of avapritinib 30 mg to 400 mg (0.1 to 1.33 times the approved recommended dose). The steady state mean apparent oral clearance of avapritinib is 19.5 L/h (48%).
Metabolism
Avapritinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 in vitro. Following a single oral dose of approximately 310 mg of radiolabeled avapritinib to healthy subjects, unchanged avapritinib (49%) and its metabolites M690 (hydroxy glucuronide; 35%) and M499 (oxidative deamination; 14%) were the major circulating compounds. Following oral administration of AYVAKIT 300 mg once daily in patients, the steady state AUC of M499 is approximately 80% of the AUC of avapritinib. M499 is not likely to contribute to efficacy at the recommended dose of avapritinib.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of avapritinib were observed based on age (18 to 90 years), sex, race (White, Black, or Asian), body weight (39.5 to 156.3 kg), mild to moderate (CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min estimated by Cockcroft-Gault) renal impairment, or mild (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST) to moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min), end-stage renal disease (CLcr < 15 mL/min), or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 times ULN and any AST) on the pharmacokinetics of avapritinib is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors on Avapritinib: Coadministration of AYVAKIT 300 mg once daily with itraconazole 200 mg once daily (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) is predicted to increase avapritinib AUC by 600% at steady state.
Coadministration of AYVAKIT 300 mg once daily with fluconazole 200 mg once daily (a moderate CYP3A inhibitor) is predicted to increase avapritinib AUC by 210% at steady state [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers on Avapritinib: Coadministration of AYVAKIT 400 mg as a single dose with rifampin 600 mg once daily (a strong CYP3A inducer) decreased avapritinib Cmax by 74% and AUC0-INF by 92%.
Coadministration of AYVAKIT 300 mg once daily with efavirenz 600 mg once daily (a moderate CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease avapritinib Cmax by 55% and AUC by 62% at steady-state [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: In vitro studies indicate that avapritinib is a time-dependent inhibitor as well as an inducer of CYP3A at clinically relevant concentrations.
Avapritinib is an inhibitor of CYP2C9 at clinically relevant concentrations. Avapritinib is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Avapritinib is not an inducer of CYP1A2 or CYP2B6. Avapritinib is a substrate of CYP3A.
M499 is an inhibitor of CYP3A, CYP2C8, or CYP2C9 at clinically relevant concentrations. M499 is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6 at clinically relevant concentrations.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with avapritinib have not been conducted. Avapritinib was not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test). Avapritinib was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration test in human peripheral blood lymphocytes but not clastogenic in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus test.
Avapritinib may impair fertility in humans. Administration of avapritinib to female rats for up to 3 months resulted in cystic degeneration of corpora lutea at doses greater than or equal to 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.3 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose). Administration of avapritinib to male dogs for up to 3 months resulted in hypo-spermatogenesis at doses greater than or equal to 7.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In repeat dose toxicology studies, administration of avapritinib to rats and dogs for up to 3 months resulted in tremors at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.5 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose). Hemorrhage in the brain and spinal cord and choroid plexus edema in the brain occurred in dogs at doses greater than or equal to 7.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 300 mg dose).
An in vitro phototoxicity study in 3T3 mouse fibroblasts and an in vivo phototoxicity study in pigmented rats demonstrated that avapritinib has a slight potential for phototoxicity.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
The efficacy of AYVAKIT was demonstrated in NAVIGATOR (NCT02508532), a multi-center, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Eligible patients were required to have a confirmed diagnosis of GIST and an ECOG performance status (PS) of 0 to 2. Patients received AYVAKIT 300 mg or 400 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The trial initially enrolled patients at a starting dose of 400 mg, which was later reduced to the recommended dose of 300 mg due to toxicity. As there was no apparent difference in overall response rate (ORR) between patients who received 300 mg daily compared to those who received 400 mg daily, these patients were pooled for the efficacy evaluation. The major efficacy outcome measure was ORR based on disease assessment by independent radiological review using modified RECIST v1.1 criteria, in which lymph nodes and bone lesions were not target lesions and progressively growing new tumor nodules within a pre-existing tumor mass was progression. An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DOR).
Patients with GIST Harboring a PDGFRA Exon 18 Mutation
Patients with unresectable or metastatic GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation were identified by local or central assessment using a PCR- or NGS-based assay. The assessment of efficacy was based on a total of 43 patients, including 38 patients with PDGFRA D842V mutations. The median duration of follow up for patients with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations was 10.6 months (range: 0.3 to 24.9 months).
The study population characteristics were median age of 64 years (range: 29 to 90 years), 67% were male, 67% were White, 93% had an ECOG PS of 0-1, 98% had metastatic disease, 53% had largest target lesion >5 cm, and 86% had prior surgical resection. The median number of prior kinase inhibitors was 1 (range: 0 to 5).
Efficacy results in patients with GIST harboring PDGFRA exon 18 mutations including the subgroup of patients with PDGFRA D842V mutations enrolled in NAVIGATOR are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5. Efficacy Results for Patients with GIST Harboring PDGFRA exon 18 mutations in NAVIGATOR Efficacy Parameter PDGFRA exon 18*
N = 43PDGFRA D842V
N = 38Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; NR=not reached; NE=not estimable + Denotes ongoing response - * Exon 18 mutations other than D842V included in this population are: deletion of D842_H845 (n=3); D842Y (n=1); and deletion of D842_H845 with insertion of V (n=1).
- † 11 patients with an ongoing response were followed < 6 months from onset of response.
Overall Response Rate (95% CI) 84% (69%, 93%) 89% (75%, 97%) Complete Response, n (%) 3 (7%) 3 (8%) Partial Response, n (%) 33 (77%) 31 (82%) Duration of Response n=36 n=34 Median in months (range) NR (1.9+, 20.3+) NR (1.9+, 20.3+) Patients with DOR ≥ 6-months, n (%)† 22 (61%) 20 (59%) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
AYVAKIT (avapritinib) tablets are supplied as follows:
- 100 mg, round, white film-coated tablet, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "100" on the other side; available in bottles of 30 tablets (NDC: 72064-110-30).
- 200 mg, capsule shaped, white film-coated tablet, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "200" on the other side; available in bottles of 30 tablets (NDC: 72064-120-30).
- 300 mg, capsule shaped, white film-coated tablet, printed with blue ink "BLU" on one side and "300" on the other side; available in bottles of 30 tablets (NDC: 72064-130-30).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if experiencing neurological signs and symptoms that may be associated with intracranial hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Central Nervous System Effects
Advise patients and caretakers to notify their healthcare provider if they experience new or worsening CNS symptoms. Advise patients not to drive or operate hazardous machinery if they are experiencing CNS adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 6 weeks after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 6 weeks after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 2 weeks following the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential that AYVAKIT may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Administration
Advise patients to take AYVAKIT on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before and at least 2 hours after a meal [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
AYVAKIT™ (aye' vah kit)
(avapritinib)
tablets, for oral useWhat is AYVAKIT?
AYVAKIT is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a certain type of stomach, bowel, or esophagus cancer called gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) that cannot be treated with surgery or that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic), and that is caused by certain abnormal platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) genes. Your healthcare provider will perform a test to make sure that you have this abnormal PDGFRA gene and that AYVAKIT is right for you.
It is not known if AYVAKIT is safe and effective in children.Before taking AYVAKIT, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. AYVAKIT can cause harm to your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with AYVAKIT.
- You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 6 weeks after the final dose of AYVAKIT. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with AYVAKIT.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if AYVAKIT passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with AYVAKIT and for at least 2 weeks after the final dose of AYVAKIT. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
How should I take AYVAKIT? - Take AYVAKIT exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking AYVAKIT unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with AYVAKIT if you develop side effects.
- Take AYVAKIT 1 time each day.
- Take AYVAKIT tablet(s) on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before and at least 2 hours after a meal.
- If you miss a dose of AYVAKIT, take it as soon as you remember unless your next scheduled dose is due within 8 hours. Take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you vomit after taking a dose of AYVAKIT, do not take an extra dose. Take your next dose at your next scheduled time.
What should I avoid while taking AYVAKIT? - Do not drive or operate heavy machinery, if you have confusion or trouble thinking during treatment with AYVAKIT.
What are the possible side effects of AYVAKIT?
AYVAKIT may cause serious side effects, including:- Bleeding in your brain. Stop taking AYVAKIT and tell your healthcare provider if you develop any symptoms such as severe headache, vision problems, severe sleepiness, severe weakness on one side of your body.
- Central nervous system (CNS) effects. CNS side effects are common with AYVAKIT and can be severe. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any new or worsening CNS symptoms including:
- forgetfulness
- confusion
- getting lost
- trouble thinking
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- trouble sleeping
- word finding problems
- seeing objects or hearing things that are not there (hallucinations)
- change in mood or behavior
Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop treatment or decrease your dose which may help your symptoms improve. If symptoms do not improve, your healthcare provider may permanently stop treatment with AYVAKIT.
The most common side effects of AYVAKIT include:- fluid retention or swelling
- nausea
- tiredness
- muscle weakness
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- decreased appetite
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
- increased eye tearing
- constipation
- rash
- dizziness
- hair color changes
These are not all of the possible side effects of AYVAKIT.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store AYVAKIT? - Store AYVAKIT tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
General information about the safe and effective use of AYVAKIT.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not take AYVAKIT for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give AYVAKIT to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about AYVAKIT that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in AYVAKIT?
Active ingredient: avapritinib
Inactive ingredients: copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose.
Film coat: polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Blue printing ink: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, esterified shellac, FD&C blue 1, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
Manufactured for: Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA
© 2020 Blueprint Medicines Corporation. All rights reserved.
For more information, go to www.AYVAKIT.com or call 1-888-258-7768. - are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. AYVAKIT can cause harm to your unborn baby.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AYVAKIT
avapritinib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72064-110 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength avapritinib (UNII: 513P80B4YJ) (avapritinib - UNII:513P80B4YJ) avapritinib 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline cellulose 101 (UNII: 7T9FYH5QMK) Microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Copovidone K25-31 (UNII: D9C330MD8B) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Polyethylene Glycol 4000 (UNII: 4R4HFI6D95) Polyvinyl Alcohol (130000 MW) (UNII: 660SZ0AKDA) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Isopropyl Alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) Ferrosoferric Oxide (UNII: XM0M87F357) Propylene Glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code BLU;100 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72064-110-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212608 01/09/2020 AYVAKIT
avapritinib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72064-120 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength avapritinib (UNII: 513P80B4YJ) (avapritinib - UNII:513P80B4YJ) avapritinib 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline cellulose 101 (UNII: 7T9FYH5QMK) Microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Copovidone K25-31 (UNII: D9C330MD8B) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Polyethylene Glycol 4000 (UNII: 4R4HFI6D95) Polyvinyl Alcohol (130000 MW) (UNII: 660SZ0AKDA) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Isopropyl Alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) Ferrosoferric Oxide (UNII: XM0M87F357) Propylene Glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code BLU;200 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72064-120-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212608 01/09/2020 AYVAKIT
avapritinib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72064-130 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength avapritinib (UNII: 513P80B4YJ) (avapritinib - UNII:513P80B4YJ) avapritinib 300 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline cellulose 101 (UNII: 7T9FYH5QMK) Microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Copovidone K25-31 (UNII: D9C330MD8B) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Polyethylene Glycol 4000 (UNII: 4R4HFI6D95) Polyvinyl Alcohol (130000 MW) (UNII: 660SZ0AKDA) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Isopropyl Alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) Ferrosoferric Oxide (UNII: XM0M87F357) Propylene Glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code BLU;300 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72064-130-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212608 01/09/2020 Labeler - Blueprint Medicines Corporation (021905363)
Trademark Results [Ayvakit]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 AYVAKIT 88589364 not registered Live/Pending |
Blueprint Medicines Corporation 2019-08-22 |
 AYVAKIT 88478478 not registered Live/Pending |
Blueprint Medicines Corporation 2019-06-18 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


