BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE solution/ drops
Brimonidine Tartrate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Brimonidine Tartrate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Apotex Corp., Apotex Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution.
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution, 0.15% for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions (5.3) 9/2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is an alpha adrenergic agonist indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One drop in the affected eye(s) three times daily, approximately 8 hours apart. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing 0.1% (1 mg/mL) or 0.15% (1.5 mg/mL) brimonidine tartrate. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Potentiation of vascular insufficiency. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions occurring in approximately 5% to 20% of patients receiving brimonidine ophthalmic solution (0.1% to 0.2%) included allergic conjunctivitis, burning sensation, conjunctival folliculosis, conjunctival hyperemia, eye pruritus, hypertension, ocular allergic reaction, oral dryness, and visual disturbance. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antihypertensives/cardiac glycosides may lower blood pressure. (7.1)
- Use with CNS depressants may result in an additive or potentiating effect. (7.2)
- Tricyclic antidepressants may potentially blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. (7.3)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors may result in increased hypotension. (7.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Use with caution in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Neonates and Infants (Pediatric Patients Younger than 2 Years Old)
4.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency
5.2 Severe Cardiovascular Disease
5.3 Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products After Use
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihypertensives/Cardiac Glycosides
7.2 CNS Depressants
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
7.4 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage is one drop of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution in the affected eye(s) three times daily, approximately 8 hours apart. Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure. If more than one topical ophthalmic product is to be used, the different products should be instilled at least 5 minutes apart.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Neonates and Infants (Pediatric Patients Younger than 2 Years Old)
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in neonates and infants (pediatric patients younger than 2 years old) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] .
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution may potentiate syndromes associated with vascular insufficiency. Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution should be used with caution in patients with depression, cerebral or coronary insufficiency, Raynaud's phenomenon, orthostatic hypotension, or thromboangiitis obliterans.
5.2 Severe Cardiovascular Disease
Although brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution had minimal effect on the blood pressure of patients in clinical studies, caution should be exercised in treating patients with severe cardiovascular disease.
5.3 Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products After Use
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface. Do not touch the tip of the dispensing container to the eye or surrounding structures. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Potentiation of Vascular Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Severe Cardiovascular Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Contamination of Topical Ophthalmic Products after Use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Neonates and Infants (Pediatric Patients Younger than 2 Years Old) [see Contraindications (4.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions occurring in approximately 10% to 20% of the subjects receiving brimonidine ophthalmic solution (0.1% to 0.2%) included: allergic conjunctivitis, conjunctival hyperemia, and eye pruritus. Adverse reactions occurring in approximately 5% to 9% included: burning sensation, conjunctival folliculosis, hypertension, ocular allergic reaction, oral dryness, and visual disturbance.
Adverse reactions occurring in approximately 1% to 4% of the subjects receiving brimonidine ophthalmic solution (0.1% to 0.2%) included: abnormal taste, allergic reaction, asthenia, blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blurred vision, bronchitis, cataract, conjunctival edema, conjunctival hemorrhage, conjunctivitis, cough, dizziness, dyspepsia, dyspnea, epiphora, eye discharge, eye dryness, eye irritation, eye pain, eyelid edema, eyelid erythema, fatigue, flu syndrome, follicular conjunctivitis, foreign body sensation, gastrointestinal disorder, headache, hypercholesterolemia, hypotension, infection (primarily colds and respiratory infections), insomnia, keratitis, lid disorder, pharyngitis, photophobia, rash, rhinitis, sinus infection, sinusitis, somnolence, stinging, superficial punctate keratopathy, tearing, visual field defect, vitreous detachment, vitreous disorder, vitreous floaters, and worsened visual acuity.
The following reactions were reported in less than 1% of subjects: corneal erosion, hordeolum, nasal dryness, and taste perversion.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following reactions have been identified during postapproval use of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Bradycardia, depression, hypersensitivity, iritis, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, miosis, nausea, skin reactions (including erythema, eyelid pruritus, rash, and vasodilation), syncope, and tachycardia.
- Apnea, coma, hypotension, hypothermia, hypotonia, lethargy, pallor, respiratory depression, and somnolence have been reported in infants receiving brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solutions.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihypertensives/Cardiac Glycosides
Because brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution may reduce blood pressure, caution in using drugs such as antihypertensives and/or cardiac glycosides with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is advised.
7.2 CNS Depressants
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, the possibility of an additive or potentiating effect with CNS depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, sedatives, or anesthetics) should be considered.
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. It is not known whether the concurrent use of these agents with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution in humans can lead to resulting interference with the IOP lowering effect. Caution is advised in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
7.4 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors may theoretically interfere with the metabolism of brimonidine and potentially result in an increased systemic side-effect such as hypotension. Caution is advised in patients taking MAO inhibitors which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution in pregnant women. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
In animal studies, brimonidine crossed the placenta and entered into the fetal circulation to a limited extent (see Data). Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Data
Human Data
Limited available data from postmarketing safety reports and published literature with topical use of brimonidine ophthalmic solution in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of pregnancy-related adverse outcomes including miscarriage, stillbirth, congenital anomaly, and events experienced by offspring while breastfeeding.
Animal Data
Embryofetal studies were conducted in pregnant rabbits administered brimonidine tartrate by daily oral gavage on gestation days 6 to 18, to target the period of organogenesis. Brimonidine caused miscarriage at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 70-or 50-times the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD] based on AUC, respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%). The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for developmental toxicity in rabbits was 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 9-and 6-fold the RHOD based on AUC, respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%). No treatment-related malformations were observed in rabbits. Signs of maternal sedation and fatigue were observed at all dose levels; the lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) for maternal toxicity was 5 mg/kg/day, based on the dose response for these signs.
Embryofetal studies were conducted in pregnant rats administered brimonidine tartrate by daily oral gavage on gestation days 6 to 15, to target the period of organogenesis. The NOAEL for developmental toxicity was 2.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 1,100-and 750-fold the RHOD based on AUC, respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%). No treatment-related malformations were observed in rats. The LOAEL for maternal toxicity was 2.5 mg/kg/day, based on signs of sedation and fatigue. The maternal NOAEL was 1 mg/kg/day (250-and 180-fold the RHOD based on AUC, respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%).
After pregnant rats received a single oral dose of 14C-brimonidine tartrate, brimonidine and metabolites crossed the placenta and were detectable in fetal blood and organs.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether brimonidine tartrate is excreted in human milk. In animal studies, brimonidine tartrate has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier and is excreted into breast milk after oral administration to lactating rats (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including central nervous system depression and apnea, from brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution in nursing infants, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is not recommended for use during lactation.
Data
Animal Data
After a single oral dose of 14C-labeled brimonidine tartrate to lactating rats, brimonidine and metabolites were detected in milk. After male and female rats received a single oral dose of 14C-brimonidine tartrate, brimonidine crossed the blood-brain barrier. Radiolabel was detected in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and spinal cord.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in pediatric patients younger than 2 years old [see Contraindications (4.1)]. During postmarketing surveillance, apnea, bradycardia, coma, hypotension, hypothermia, hypotonia, lethargy, pallor, respiratory depression, and somnolence have been reported in infants receiving brimonidine.
In a well-controlled clinical study conducted in pediatric glaucoma patients aged 2 to 7 years old, the most commonly observed adverse reactions with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% dosed three times daily were somnolence (50% to 83% in pediatric patients aged 2 to 6 years old) and decreased alertness. In pediatric patients aged 7 years and older (greater than 20 kg), somnolence appears to occur less frequently (25%). Approximately 16% of pediatric patients on brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% discontinued from the study due to somnolence.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Limited information exists on accidental ingestion of brimonidine in adults; the only adverse reaction reported to date has been hypotension. Symptoms of brimonidine overdose have been reported in neonates, infants, and children receiving brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution as part of medical treatment of congenital glaucoma or by accidental oral ingestion [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Treatment of an oral overdose includes supportive and symptomatic therapy; a patent airway should be maintained.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution, 0.15%, sterile, is a relatively selective alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist for topical ophthalmic use.
The structural formula of brimonidine tartrate is:
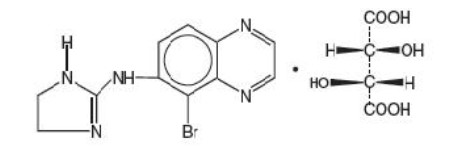
5-bromo-6-(2-imidazolin-2-ylamino) quinoxaline D-tartrate; MW= 442.22
In solution, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution has a clear, greenish-yellow color. It has an osmolality of 250 to 350 mOsmol/kg and a pH of 6.6 to 7.4 (0.15%).
Brimonidine tartrate appears as white to slightly yellowish powder and is soluble in both water (0.6 mg/mL) and in the product vehicle (1.4 mg/mL) at pH 7.7.
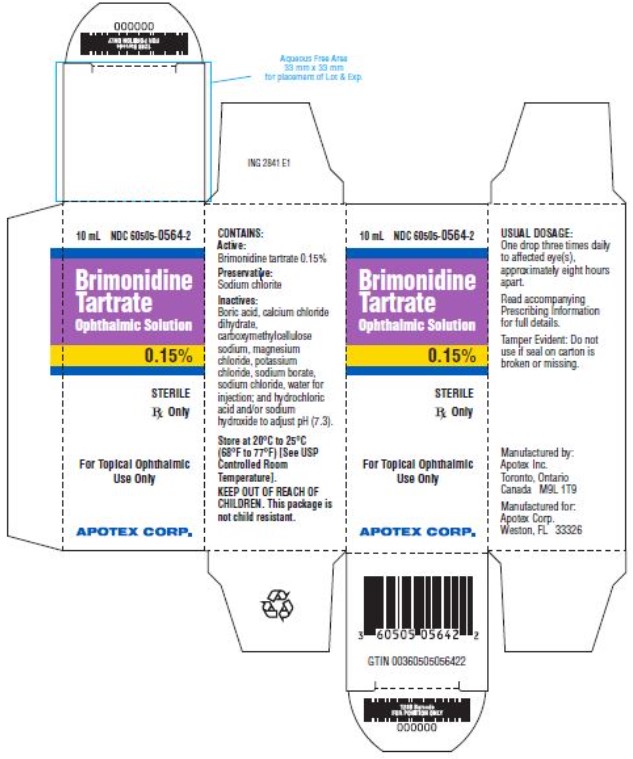
Each mL of Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution contains the active ingredient brimonidine tartrate 0.15% (1.5 mg/mL) with the inactive ingredients boric acid; calcium chloride dihydrate; carboxymethylcellulose sodium; magnesium chloride; potassium chloride; sodium borate; sodium chloride; sodium chlorite (0.08 mg/mL) as a preservative; water for injection; and hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is a relatively selective alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist with a peak ocular hypotensive effect occurring at two hours post-dosing.
Fluorophotometric studies in animals and humans suggest that brimonidine tartrate has a dual mechanism of action by reducing aqueous humor production and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No compound-related carcinogenic effects were observed in either mice or rats following a 21-month and 24-month study, respectively. In these studies, dietary administration of brimonidine tartrate at doses up to 2.5 mg/kg/day in mice and 1 mg/kg/day in rats achieved approximately 93 and 76 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose (RHOD) based on Cmax respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%.
Mutagenesis
Brimonidine tartrate was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a series of in vitro and in vivo studies including the Ames bacterial reversion test, chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells, and three in vivo studies in CD-1 mice: a host-mediated assay, cytogenetic study, and dominant lethal assay.
Impairment of Fertility
A reproduction and fertility study in rats with brimonidine tartrate demonstrated no adverse effect on male or female fertility at oral doses up to 1 mg/kg (approximately 180 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD] based on estimated AUC) respectively for brimonidine tartrate 0.15%.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Elevated IOP presents a major risk factor in glaucomatous field loss. The higher the level of IOP, the greater the likelihood of optic nerve damage and visual field loss. Brimonidine tartrate has the action of lowering intraocular pressure with minimal effect on cardiovascular and pulmonary parameters.
Clinical studies were conducted to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and acceptability of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, 0.15% compared with ALPHAGAN® administered three-times-daily in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Those results indicated that brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution, 0.15% is comparable in IOP lowering effect to ALPHAGAN® (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.2%, and effectively lowers IOP in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension by approximately 2 to 6 mmHg.
A clinical study was conducted to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and acceptability of ALPHAGAN® P (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.1% compared with ALPHAGAN® administered three-times-daily in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Those results indicated that ALPHAGAN® P (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.1% is equivalent in IOP lowering effect to ALPHAGAN® (brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution) 0.2% and effectively lowers IOP in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension by approximately 2 to 6 mmHg.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution is supplied sterile, in white opaque LDPE ophthalmic bottles with white translucent LDPE ophthalmic droppers and purple opaque ophthalmic HDPE plastic caps as follows:
0.15%
5 mL in 5 mL bottle NDC: 60505-0564-1
10 mL in 11 mL bottle NDC: 60505-0564-2
15 mL in 15 mL bottle NDC: 60505-0564-3 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Handling the Container
Instruct patients that ocular solutions, if handled improperly or if the tip of the dispensing container contacts the eye or surrounding structures, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Always replace the cap after using. If solution changes color or becomes cloudy, do not use. Do not use the product after the expiration date marked on the bottle.
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
Use with Other Ophthalmic Drugs
Advise patients that if more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
Potential for Decreased Mental Alertness
As with other similar medications, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution may cause fatigue and/or drowsiness in some patients. Caution patients who engage in hazardous activities of the potential for a decrease in mental alertness.
The trademarks referenced herein are owned by their respective companies.
Manufactured by: Manufactured for:
Apotex Inc. Apotex Corp.
Toronto, Ontario Weston, Florida
Canada M9L 1T9 33326
Revised: October 2025
- Bottle Label
- Carton Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE
brimonidine tartrate solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60505-0564 Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE (UNII: 4S9CL2DY2H) (Brimonidine - UNII:E6GNX3HHTE) BRIMONIDINE TARTRATE 1.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) CALCIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: M4I0D6VV5M) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM BORATE (UNII: 91MBZ8H3QO) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: K679OBS311) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM CHLORITE (UNII: G538EBV4VF) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60505-0564-1 1 in 1 CARTON 01/31/2022 1 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 60505-0564-2 1 in 1 CARTON 03/14/2022 2 10 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 3 NDC: 60505-0564-3 1 in 1 CARTON 01/31/2022 3 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078479 01/31/2022 Labeler - Apotex Corp. (845263701) Registrant - Apotex Inc. (209429182)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.