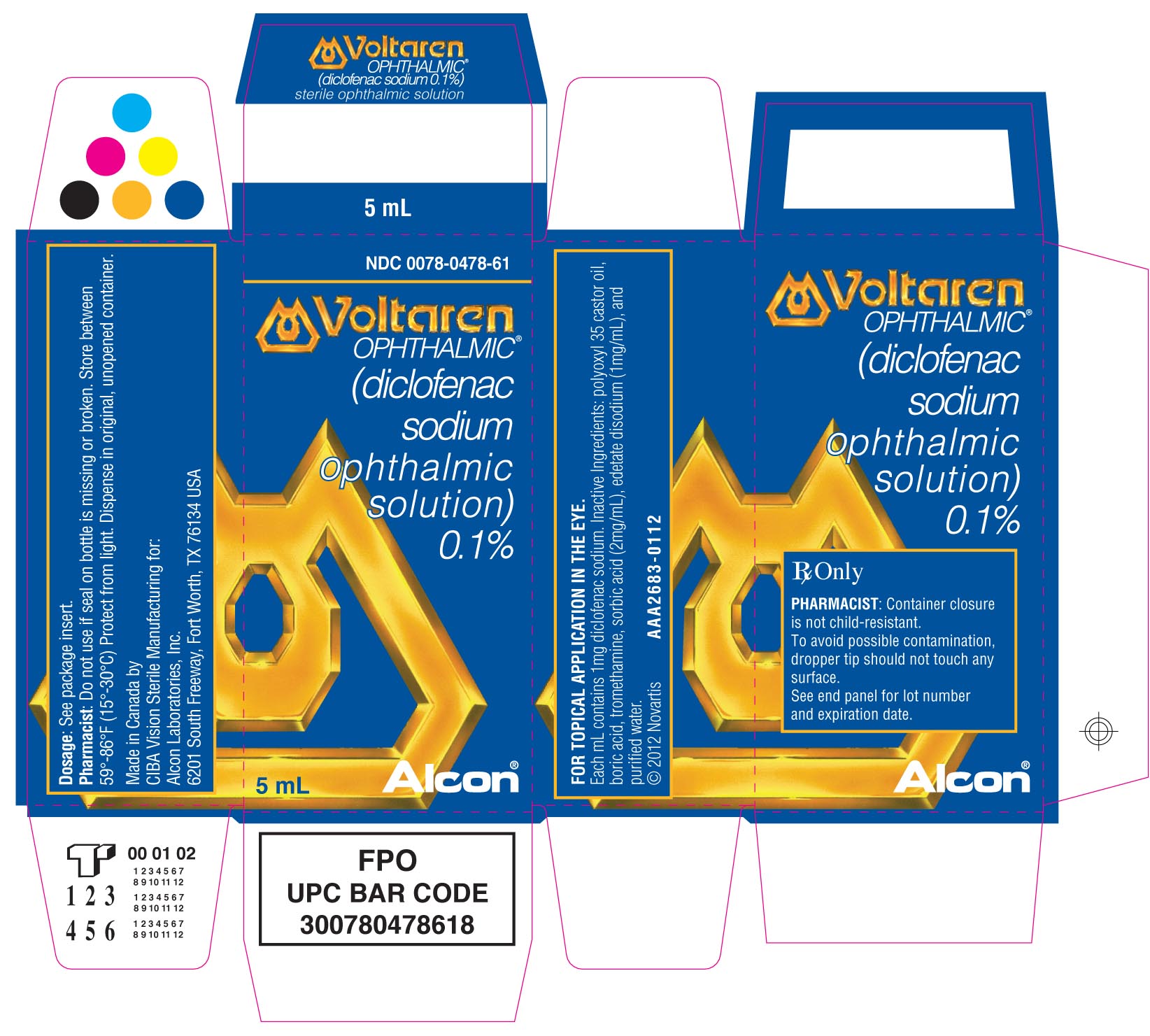
VOLTAREN- diclofenac sodium solution
VOLTAREN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
VOLTAREN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, CIBA Vision Canada, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION SECTION
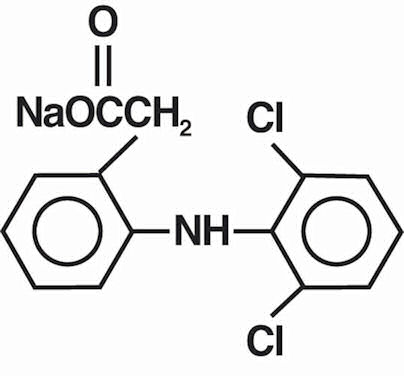
Voltaren Ophthalmic (diclofenac sodium ophthalmic solution) 0.1% solution is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory product for ophthalmic use. Diclofenac sodium is designated chemically as 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt, with an empirical formula of C14H10Cl2NO2Na. The structural formula of diclofenac sodium is:
Voltaren Ophthalmic is available as a sterile solution which contains diclofenac sodium 0.1% (1 mg/mL).
Inactive Ingredients: polyoxyl 35 castor oil, Boric acid, tromethamine, sorbic acid (2 mg/mL), edetate disodium (1 mg/mL), and purified water.
Diclofenac sodium is a faintly yellow-white to light beige, slightly hygroscopic crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in acetonitrile, and insoluble in chloroform and in 0.1N hydrochloric acid. Its molecular weight is 318.14. Voltaren Ophthalmic 0.1% is an iso osmotic solution with an osmolality of about 300 mOsmol/1000 g, buffered at approximately pH 7.2. Voltaren Ophthalmic solution has a faint characteristic odor of castor oil. -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
Pharmacodynamics
Diclofenac sodium is one of a series of phenylacetic acids that has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in pharmacological studies. It is thought to inhibit the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which is essential in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins.
Animal Studies
Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed in animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure.
Pharmacokinetics
Results from a bioavailability study established that plasma levels of diclofenac following ocular instillation of two drops of Voltaren Ophthalmic to each eye were below the limit of quantification (10 ng/mL) over a 4-hour period. This study suggests that limited, if any, systemic absorption occurs with Voltaren Ophthalmic.
Clinical Trials
Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Effects
In two double-masked, controlled, efficacy studies of postoperative inflammation, a total of 206 cataract patients were treated with Voltaren Ophthalmic and 103 patients were treated with vehicle placebo. Voltaren Ophthalmic was favored over vehicle placebo over a 2-week period for the clinical assessments of inflammation as measured by anterior chamber cells and flare.
In double-masked, controlled studies of corneal refractive surgery (radial keratotomy (RK) and laser photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)) patients were treated with Voltaren Ophthalmic and/or vehicle placebo. The efficacy of Voltaren Ophthalmic given before and shortly after surgery was favored over vehicle placebo during the 6-hour period following surgery for the clinical assessments of pain and photophobia. Patients were permitted to use a hydrogel soft contact lens with Voltaren Ophthalmic for up to three days after PRK. - INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
- CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
-
WARNINGS SECTION
The refractive stability of patients undergoing corneal refractive procedures and treated with Voltaren has not been established. Patients should be monitored for a year following use in this setting. With some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs. -
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
General Precautions
All topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal infiltrates, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, and corneal perforation. These events may be sight-threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients experiencing complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface disease (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period-of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events, which may become sight-threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 24 hours prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days postsurgery may increase patient risk for occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
It is recommended that Voltaren Ophthalmic, like other NSAIDs, be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time. Use of the same bottle for both eyes is not recommended with topical eye drops that are used in association with surgery.
Results from clinical studies indicate that Voltaren Ophthalmic has no significant effect upon ocular pressure. However, elevations in intraocular pressure may occur following cataract surgery.Information for Patients
Except for the use of a bandage hydrogel soft contact lens during the first 3 days following refractive surgery, Voltaren Ophthalmic should not be used by patients currently wearing soft contact lenses due to adverse events that have occurred in other circumstances.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats given Voltaren in oral doses up to 2 mg/kg/day (approximately 500 times the human topical ophthalmic dose) revealed no significant increases in tumor incidence. A 2-year carcinogenicity study conducted in mice employing oral Voltaren up to 2 mg/kg/day did not reveal any oncogenic potential. Voltaren did not show mutagenic potential in various mutagenicity studies including the Ames test. Voltaren administered to male and female rats at 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 1000 times the human topical ophthalmic dose) did not affect fertility.
-
PREGNANCY SECTION
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C. Reproduction studies performed in mice at oral doses up to 5,000 times (20 mg/kg/day) and in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 2,500 times (10 mg/kg/day) the human topical dose have revealed no evidence of teratogenicity due to Voltaren despite the induction of maternal toxicity and fetal toxicity. In rats, maternally toxic doses were associated with dystocia, prolonged gestation, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival. Voltaren has been shown to cross the placental barrier in mice and rats. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Non-teratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), the use of Voltaren Ophthalmic during late pregnancy should be avoided.
Nursing Women
It is not known whether topical ophthalmic administration of Voltaren Ophthalmic could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
Ocular
Transient burning and stinging were reported in approximately 15% of patients across studies with the use of Voltaren Ophthalmic. In cataract surgery studies, keratitis was reported in up to 28% of patients receiving Voltaren Ophthalmic, although in many of these cases keratitis was initially noted prior to the initiation of treatment. Elevated intraocular pressure following cataract surgery was reported in approximately 15% of patients undergoing cataract surgery.
Lacrimation complaints were reported in approximately 30% of case studies undergoing incisional refractive surgery. The following adverse reactions were reported in approximately 10% or less of patients: abnormal vision, acute elevated IOP, blurred vision, conjunctivitis, corneal deposits, corneal edema, corneal opacity, corneal lesions, discharge, eyelid swelling, eye pain, injection (redness), iritis, irritation, itching, lacrimation disorder, and ocular allergy.Systemic
The following adverse reactions were reported in 3% or less of patients: abdominal pain, asthenia, chills, dizziness, facial edema, fever, headache, insomnia, nausea, pain, rhinitis, viral infection, and vomiting.
Clinical Practice
The following reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of topical diclofenac sodium ophthalmic solution, 0.1% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical diclofenac sodium ophthalmic solution, 0.1%, or a combination of these factors, include corneal erosion, corneal infiltrates, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, corneal ulceration and epithelial breakdown, (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
- OVERDOSAGE SECTION
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
-
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
Voltaren Ophthalmic 0.1% (1 mg/mL) Sterile Solution is supplied in a low density polyethylene (LDPE) white bottle with a LDPE Dropper Tip and Polypropylene grey closure. The 5 mL fill is supplied in a 10 mL size bottle.
Bottles of 5 mL NDC: 0078-0478-61
Store at 15°C to 25°C (59° to 77°F).
Dispense in original, unopened container only.
Alcon®
Made in Canada
Manufactured for:
Alcon Laboratories, Inc.
6201 South Freeway
Fort Worth, TX 76134 USA
© 2012 Novartis
AAA2684-0112 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VOLTAREN
diclofenac sodium solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0078-0478 Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Diclofenac Sodium (UNII: QTG126297Q) (Diclofenac - UNII:144O8QL0L1) Diclofenac Sodium 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Boric Acid (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) Edetate Disodium (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) Polyoxyl 35 Castor Oil (UNII: 6D4M1DAL6O) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Sorbic Acid (UNII: X045WJ989B) Tromethamine (UNII: 023C2WHX2V) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0078-0478-61 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020037 03/28/1991 Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation (002147023) Registrant - Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation (002147023) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations CIBA Vision Canada, Inc. 247191463 MANUFACTURE(0078-0478)
Trademark Results [VOLTAREN]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 VOLTAREN 97900726 not registered Live/Pending |
Novartis AG 2023-04-21 |
 VOLTAREN 97799814 not registered Live/Pending |
Novartis AG 2023-02-17 |
 VOLTAREN 97733998 not registered Live/Pending |
Novartis AG 2022-12-28 |
 VOLTAREN 87617485 5452825 Live/Registered |
Novartis Corporation 2017-09-21 |
 VOLTAREN 79225039 5478104 Live/Registered |
NOVARTIS AG 2017-08-31 |
 VOLTAREN 79072252 3767722 Dead/Cancelled |
Novartis AG 2009-07-10 |
 VOLTAREN 73557006 1394620 Dead/Cancelled |
CIBA-GEIGY CORPORATION 1985-09-05 |
 VOLTAREN 72422688 0960282 Live/Registered |
CIBA-GEIGY LIMITED 1972-04-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.