AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE solution/ drops
Azelastine Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Azelastine Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, 0.05% is a sterile ophthalmic solution containing azelastine hydrochloride, a relatively selective H 1-receptor antagonist for topical administration to the eyes. Azelastine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 418.37. Azelastine hydrochloride is sparingly soluble in water, methanol and propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in ethanol, octanol and glycerine. Azelastine hydrochloride is a racemic mixture with a melting point of 225°C. The chemical name for azelastine hydrochloride is (±)-1-(2H)-phthalazinone,4-[(4-chlorophenyl) methyl]-2-(hexahydro-1-methyl-1H-azepin-4-yl)-, monohydrochloride and is represented by the following chemical structure:
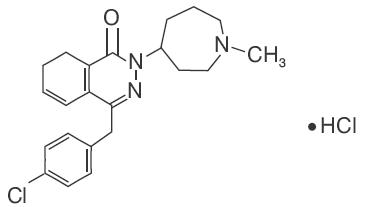
Empirical chemical structure: C 22H 24CIN 3OHCl
Each mL of azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, 0.05% contains: Active: 0.5 mg azelastine hydrochloride, equivalent to 0.457 mg of azelastine base; Preservative: 0.25 mg benzalkonium chloride solution (50%) USP-NF; Inactives: disodium edetate dihydrate, hypromellose, sorbitol solution, sodium hydroxide and water for injection. It has a pH of approximately 5 to 6.5 and an osmolality of approximately 271 to 312 mOsmol/L. -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Azelastine hydrochloride is a relatively selective histamine H 1 antagonist and an inhibitor of the release of histamine and other mediators from cells (e.g., mast cells) involved in the allergic response. Based on in-vitro studies using human cell lines, inhibition of other mediators involved in allergic reactions (e.g., leukotrienes and PAF) has been demonstrated with azelastine hydrochloride. Decreased chemotaxis and activation of eosinophils has also been demonstrated.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Absorption of azelastine following ocular administration was relatively low. A study in symptomatic patients receiving one drop of azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution in each eye two to four times a day (0.06 to 0.12 mg azelastine hydrochloride) demonstrated plasma concentrations of azelastine hydrochloride to generally be between 0.02 and 0.25 ng/mL after 56 days of treatment. Three of nineteen patients had quantifiable amounts of N-desmethylazelastine that ranged from 0.25 to 0.87 ng/mL at Day 56.
Based on intravenous and oral administration, the elimination half-life, steady-state volume of distribution and plasma clearance were 22 hours, 14.5 L/kg and 0.5 L/h/kg, respectively. Approximately 75% of an oral dose of radiolabeled azelastine hydrochloride was excreted in the feces with less than 10% as unchanged azelastine. Azelastine hydrochloride is oxidatively metabolized to the principal metabolite, N-desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. In-vitro studies in human plasma indicate that the plasma protein binding of azelastine and N-desmethylazelastine are approximately 88% and 97%, respectively.Clinical Trials
In a conjunctival antigen challenge study, azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution was more effective than its vehicle in preventing itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. Azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution had a rapid (within 3 minutes) onset of effect and a duration of effect of approximately 8 hours for the prevention of itching.
In environmental studies, adult and pediatric, patients with seasonal allergic conjunctivitis were treated with azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution for two to eight weeks. In these studies, azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution was more effective than its vehicle in relieving itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. - INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
Information for Patients
To prevent contaminating the dropper tip and solution, care should be taken not to touch any surface, the eyelids or surrounding areas with the dropper tip of the bottle. Keep bottle tightly closed when not in use. This product is sterile when packaged.
Patients should be advised not to wear a contact lens if their eye is red. Azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution should not be used to treat contact lens related irritation. The preservative in azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Patients who wear soft contact lenses and whose eyes are not red, should be instructed to wait at least ten minutes after instilling azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution before they insert their contact lenses.Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Azelastine hydrochloride administered orally for 24 months was not carcinogenic in rats and mice at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day and 25 mg/kg/day, respectively. Based on a 30 µL drop size, these doses were approximately 25,000 and 21,000 times higher than the maximum recommended ocular human use level of 0.001 mg/kg/day for a 50 kg adult.
Azelastine hydrochloride showed no genotoxic effects in the Ames test, DNA repair test, mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay, mouse micronucleus test, or chromosomal aberration test in rat bone marrow. Reproduction and fertility studies in rats showed no effects on male or female fertility at oral doses of up to 25,000 times the maximum recommended ocular human use level. At 68.6 mg/kg/day (57,000 times the maximum recommended ocular human use level), the duration of the estrous cycle was prolonged and copulatory activity and the number of pregnancies were decreased. The numbers of corpora lutea and implantations were decreased; however, the implantation ratio was not affected.Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C. Azelastine hydrochloride has been shown to be embryotoxic, fetotoxic, and teratogenic (external and skeletal abnormalities) in mice at an oral dose of 68.6 mg/kg/day (57,000 times the recommended ocular human use level). At an oral dose of 30 mg/kg/day (25,000 times the recommended ocular human use level), delayed ossification (undeveloped metacarpus) and the incidence of 14 th rib were increased in rats. At 68.6 mg/kg/day (57,000 times the maximum recommended ocular human use level) azelastine hydrochloride caused resorption and fetotoxic effects in rats. The relevance to humans of these skeletal findings noted at only high drug exposure levels is unknown.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether azelastine hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when azelastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is administered to a nursing woman.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In controlled multiple-dose studies where patients were treated for up to 56 days, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were transient eye burning/stinging (approximately 30%), headaches (approximately 15%) and bitter taste (approximately 10%). The occurrence of these events was generally mild.
The following events were reported in 1 to 10% of patients: asthma, conjunctivitis, dyspnea, eye pain, fatigue, influenza-like symptoms, pharyngitis, pruritus, rhinitis and temporary blurring. Some of these events were similar to the underlying disease being studied. - DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE
azelastine hydrochloride solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68071-4359(NDC:47335-938) Route of Administration INTRAOCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 0L591QR10I) (AZELASTINE - UNII:ZQI909440X) AZELASTINE HYDROCHLORIDE 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68071-4359-6 6 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 03/26/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078738 05/31/2010 Labeler - NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc. (010632300) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc. 010632300 relabel(68071-4359)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
