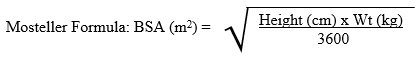NEVIRAPINE tablet, extended release
Nevirapine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Nevirapine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEVIRAPINE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEVIRAPINE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS.
NEVIRAPINE extended-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Fatal and non-fatal hepatotoxicity have been reported in patients taking nevirapine extended-release tablets. Discontinue immediately if clinical hepatitis or transaminase elevations combined with rash or other systemic symptoms occur. Do not restart nevirapine extended-release tablets after recovery. (5.1)
- Fatal and non-fatal skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions, have been reported. Discontinue immediately if severe skin reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, or any rash with systemic symptoms occur. Check transaminase levels immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment. Do not restart nevirapine extended-release tablets after recovery. (5.2)
- Monitoring during the first 18 weeks of therapy is essential. Extra vigilance is warranted during the first 6 weeks of therapy, which is the period of greatest risk of these events. (5.1, 5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Nevirapine extended-release tablets are an NNRTI indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in adults and pediatric patients 6 to less than 18 years of age. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- Based on serious and life-threatening hepatotoxicity observed in controlled and uncontrolled trials, nevirapine extended-release tablets are not recommended to be initiated, unless the benefit outweighs the risk, in:
- adult females with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3
- adult males with CD4+ cell counts greater than 400 cells/mm3 (1, 5.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The 14-day lead in period with immediate-release nevirapine (200 mg once daily) must be strictly followed; it has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency of rash. (2.5, 5.2)
- The nevirapine extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and must not be chewed, crushed, or divided. (2.1)
- Adult patients must initiate therapy with one 200 mg tablet of immediate-release nevirapine once daily for the first 14 days, followed by one 400 mg tablet of nevirapine extended-release once daily. (2.2)
- Adult patients already on a regimen of immediate-release nevirapine twice daily can be switched to nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily without the 14-day lead-in period of immediate-release nevirapine. (2.2)
- Pediatric patients (ages 6 to less than 18 years) must initiate therapy with immediate-release nevirapine (as 150 mg/m2 of nevirapine oral suspension or as nevirapine tablet) at a dose not to exceed 200 mg per day administered once daily for the first 14 days, followed by nevirapine extended-release tablets once daily as shown in the following table. (2.3)
Recommended Dosing for Pediatric Patients 6 to Less Than 18 Years of Age by BSA After the Lead-in Period
BSA Range (m2)
Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets Dose (mg)
0.58 - 0.83
200 mg once daily (2 x 100 mg)
0.84 - 1.16
300 mg once daily (3 x 100 mg)
Greater than or equal to 1.17
400 mg once daily (1 x 400 mg)
- Pediatric patients already on a regimen of twice daily nevirapine oral suspension or immediate-release nevirapine tablets can be switched to nevirapine extended-release tablets once daily without the 14-day lead-in period of nevirapine oral suspension or immediate-release nevirapine tablets. (2.3)
- If any patient experiences rash during the 14-day lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine do not initiate nevirapine extended-release tablets until the rash has resolved. Do not continue the immediate-release nevirapine lead-in dosing regimen beyond 28 days. (2.5)
- If dosing is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart 14-day lead-in dosing. (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 100 mg and 400 mg tablets (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adult patients: The most common adverse reaction is rash. During the lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine, the incidence of Grade 2 or higher drug-related rash in adults is 3%. After the lead-in period the incidence of Grade 2 or higher drug-related rash in subjects taking nevirapine extended-release tablets is 3%. The incidence of Grade 2 or higher drug-related clinical hepatitis after the lead-in phase was 2%. (6.1)
- Pediatric patients: The incidence of Grade 2 or higher drug-related rash was 1%. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mylan at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Women infected with HIV-1 should be instructed not to breastfeed due to the potential for HIV-1 transmission. (8.2)
- No dose adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment with a creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 20 mL per min. Patients on dialysis receive an additional dose of immediate-release nevirapine (200 mg) following each dialysis treatment. (2.5, 8.6)
- Monitor patients with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis carefully for evidence of drug-induced toxicity. Do not administer nevirapine extended-release tablets to patients with Child-Pugh B or C. (5.1, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Considerations
2.2 Adult Patients
2.3 Pediatric Patients
2.4 Monitoring of Patients
2.5 Dosage Adjustment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity and Hepatic Impairment
5.2 Skin Reactions
5.3 Resistance
5.4 Drug Interactions
5.5 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
5.6 Fat Redistribution
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Patients
14.2 Pediatric Patients
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS
HEPATOTOXICITY: Severe, life-threatening, and in some cases fatal hepatotoxicity, particularly in the first 18 weeks, has been reported in patients treated with nevirapine. In some cases, patients presented with non-specific prodromal signs or symptoms of hepatitis and progressed to hepatic failure. These events are often associated with rash. Female gender and higher CD4+ cell counts at initiation of therapy place patients at increased risk; women with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3, including pregnant women receiving nevirapine in combination with other antiretrovirals for the treatment of HIV-1 infection, are at the greatest risk. However, hepatotoxicity associated with nevirapine use can occur in both genders, all CD4+ cell counts and at any time during treatment. Hepatic failure has also been reported in patients without HIV taking nevirapine for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). Use of nevirapine for occupational and non-occupational PEP is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with signs or symptoms of hepatitis, or with increased transaminases combined with rash or other systemic symptoms, must discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
SKIN REACTIONS: Severe, life-threatening skin reactions, including fatal cases, have occurred in patients treated with nevirapine. These have included cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions characterized by rash, constitutional findings, and organ dysfunction. Patients developing signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions must discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately. Transaminase levels should be checked immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment. The 14-day lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg daily dosing has been observed to decrease the incidence of rash and must be followed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
MONITORING FOR HEPATOTOXICITY AND SKIN REACTIONS: Patients must be monitored intensively during the first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine to detect potentially life-threatening hepatotoxicity or skin reactions. Extra vigilance is warranted during the first 6 weeks of therapy, which is the period of greatest risk of these events. Do not restart nevirapine following clinical hepatitis, or transaminase elevations combined with rash or other systemic symptoms, or following severe skin rash or hypersensitivity reactions. In some cases, hepatic injury has progressed despite discontinuation of treatment.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Nevirapine extended-release tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in adults and pediatric patients 6 to less than 18 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2)].
Limitations of Use:
Based on serious and life-threatening hepatotoxicity observed in controlled and uncontrolled trials, nevirapine extended-release tablets are not recommended to be initiated, unless the benefit outweighs the risk, in:
- adult females with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3 or
- adult males with CD4+ cell counts greater than 400 cells/mm3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Considerations
- Nevirapine extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and must not be chewed, crushed, or divided.
- Children should be assessed for their ability to swallow tablets before prescribing nevirapine extended-release tablets.
- Nevirapine extended-release tablets can be taken with or without food.
- No recommendations can be made regarding substitution of four nevirapine extended-release 100 mg tablets for one nevirapine extended-release 400 mg tablet.
2.2 Adult Patients
Patients Not Currently Taking Immediate-Release Nevirapine
Patients must initiate therapy with one 200 mg tablet of immediate-release nevirapine daily for the first 14 days in combination with other antiretroviral agents. The 14-day lead-in period with nevirapine 200 mg daily dosing must be strictly followed (the lead-in period has been observed to decrease the incidence of rash), followed by one 400 mg tablet of nevirapine extended-release once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. If rash persists beyond the 14-day lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine, do not begin dosing with nevirapine extended-release tablets. The lead-in dosing with 200 mg once daily immediate-release nevirapine should not be continued beyond 28 days, at which point an alternative regimen should be sought.
Switching Patients from Immediate-Release Nevirapine to Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets
Patients already on a regimen of immediate-release nevirapine twice daily in combination with other antiretroviral agents can be switched to nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily without the 14-day lead-in period. Patients already on a regimen of immediate-release nevirapine twice daily who switch to nevirapine extended-release tablet therapy should continue with their ongoing clinical and laboratory monitoring.
2.3 Pediatric Patients
Nevirapine extended-release tablets in pediatric patients are dosed based on body surface area (BSA) calculated using the Mosteller formula. All pediatric patients must initiate therapy with immediate-release nevirapine (as 150 mg/m2 of nevirapine oral suspension or as nevirapine tablets), at a dose not to exceed 200 mg per day, administered once daily for the first 14 days. This lead-in period should be used because it has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency of rash. This lead-in period is not required if the patient is already on a regimen of twice daily immediate-release formulation in combination with other antiretroviral agents.
The recommended oral dose of nevirapine extended-release tablets for pediatric patients with a BSA of 1.17 m2 or greater is 400 mg following the lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine. The total daily dose should not exceed 400 mg for any patient.
2.4 Monitoring of Patients
Intensive clinical and laboratory monitoring, including liver enzyme tests, is essential at baseline and during the first 18 weeks of treatment with nevirapine. The optimal frequency of monitoring during this period has not been established. Some experts recommend clinical and laboratory monitoring more often than once per month, and in particular, would include monitoring of liver enzyme tests prior to beginning the 14-day lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine, prior to initiation of nevirapine extended-release tablets, and at two weeks after initiation of nevirapine extended-release tablet therapy. After the initial 18-week period, frequent clinical and laboratory monitoring should continue throughout nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. In some cases, hepatic injury has progressed despite discontinuation of treatment.
Patients already on a regimen of immediate-release nevirapine twice daily who switch to nevirapine extended-release tablets once daily should continue with their ongoing clinical and laboratory monitoring.
2.5 Dosage Adjustment
Patients with Rash
Discontinue nevirapine if a patient experiences severe rash or any rash accompanied by constitutional findings [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Do not initiate therapy with nevirapine extended-release tablets if a patient experiences mild to moderate rash without constitutional symptoms during the 14-day lead-in period of immediate-release nevirapine until the rash has resolved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. The total duration of the once daily lead-in dosing period should not exceed 28 days at which point an alternative regimen should be sought.
Patients with Hepatic Events
If a clinical (symptomatic) hepatic event occurs, permanently discontinue nevirapine. Do not restart nevirapine after recovery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Patients with Dose Interruption
For patients who interrupt nevirapine extended-release tablet dosing for more than 7 days, restart the recommended lead-in dosing with immediate-release nevirapine, using one 200 mg tablet daily for the first 14 days.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients with CrCl greater than or equal to 20 mL per min and not requiring dialysis do not require an adjustment in dosing. The pharmacokinetics of nevirapine have not been evaluated in patients with CrCl less than 20 mL per min. An additional 200 mg dose of immediate-release nevirapine following each dialysis treatment is indicated in patients requiring dialysis. Nevirapine metabolites may accumulate in patients receiving dialysis; however, the clinical significance of this accumulation is not known [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been studied in patients with renal dysfunction.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets, USP are available containing 100 mg or 400 mg of nevirapine, USP.
- The 100 mg tablets are white to off-white, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and N100 on the other side.
- The 400 mg tablets are white to off-white, oval, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and N400 on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Nevirapine extended-release tablets are contraindicated:
- in patients with moderate or severe (Child-Pugh Class B or C, respectively) hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
- for use as part of occupational and non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity and Hepatic Impairment
Severe, life-threatening, and in some cases fatal hepatotoxicity, including fulminant and cholestatic hepatitis, hepatic necrosis and hepatic failure, have been reported in patients treated with nevirapine.
The risk of symptomatic hepatic events regardless of severity is greatest in the first 6 weeks of therapy. The risk continued to be greater in the nevirapine groups in controlled clinical trials through 18 weeks of treatment. However, hepatic events may occur at any time during treatment. In some cases, patients presented with non-specific, prodromal signs or symptoms of fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, liver tenderness or hepatomegaly, with or without initially abnormal serum transaminase levels. Rash was observed in approximately half of the patients with symptomatic hepatic adverse events. Fever and flu-like symptoms accompanied some of these hepatic events. Some events, particularly those with rash and other symptoms, have progressed to hepatic failure with transaminase elevation, with or without hyperbilirubinemia, hepatic encephalopathy, prolonged partial thromboplastin time, or eosinophilia. Rhabdomyolysis has been observed in some patients experiencing skin and/or liver reactions associated with nevirapine use. Hepatitis/hepatic failure may be associated with signs of hypersensitivity which can include severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, or renal dysfunction. Patients with signs or symptoms of hepatitis must be advised to discontinue nevirapine and immediately seek medical evaluation, which should include liver enzyme tests.
The first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine extended-release tablets are a critical period during which intensive clinical and laboratory monitoring of patients is required to detect potentially life-threatening hepatic events. The optimal frequency of monitoring during this period has not been established. Some experts recommend clinical and laboratory monitoring more often than once per month, and in particular, include monitoring of liver enzyme tests at baseline, prior to dose escalation and at two weeks post-dose escalation. After the initial 18-week period, frequent clinical and laboratory monitoring should continue throughout nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment.
Transaminases should be checked immediately if a patient experiences signs or symptoms suggestive of hepatitis and/or hypersensitivity reaction. Transaminases should also be checked immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment. Physicians and patients should be vigilant for the appearance of signs or symptoms of hepatitis, such as fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, bilirubinuria, acholic stools, liver tenderness, or hepatomegaly. The diagnosis of hepatotoxicity should be considered in this setting, even if transaminases are initially normal or alternative diagnoses are possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
If clinical hepatitis or transaminase elevations combined with rash or other systemic symptoms occur, permanently discontinue nevirapine. Do not restart nevirapine after recovery. In some cases, hepatic injury progresses despite discontinuation of treatment.
The patients at greatest risk of hepatic events, including potentially fatal events, are women with high CD4+ cell counts. In a retrospective analysis of pooled clinical trials with immediate-release nevirapine, during the first 6 weeks of treatment women had a 3-fold higher risk than men for symptomatic, often rash-associated, hepatic events (6% versus 2%). Patients with higher CD4+ cell counts at initiation of nevirapine therapy are at higher risk for symptomatic hepatic events. Women with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3 had a 12-fold higher risk of symptomatic hepatic adverse events compared to women with CD4+ cell counts less than 250 cells/mm3 (11% versus 1%). An increased risk was observed in men with CD4+ cell counts greater than 400 cells/mm3 (6% versus 1% for men with CD4+ cell counts less than 400 cells/mm3). However, all patients, regardless of gender, CD4+ cell count, or antiretroviral treatment history, should be monitored for hepatotoxicity since symptomatic hepatic adverse events have been reported at all CD4+ cell counts. Co-infection with hepatitis B or C and/or increased transaminase elevations at the start of therapy with nevirapine are associated with a greater risk of later symptomatic events (6 weeks or more after starting nevirapine) and asymptomatic increases in AST or ALT.
In addition, serious hepatotoxicity (including liver failure requiring transplantation in one instance) has been reported in HIV-1 uninfected individuals receiving multiple doses of immediate-release nevirapine in the setting of post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), an unapproved use. Use of nevirapine extended-release tablets for occupational and non-occupational PEP is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Increased nevirapine trough concentrations have been observed in some patients with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Therefore, carefully monitor patients with either hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis for evidence of drug-induced toxicity. Do not administer nevirapine to patients with moderate or severe (Child-Pugh Class B or C, respectively) hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been evaluated in subjects with hepatic impairment.
5.2 Skin Reactions
Severe and life-threatening skin reactions, including fatal cases, have been reported in patients taking nevirapine. These have occurred most frequently during the first 6 weeks of therapy. These have included cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions characterized by rash, constitutional findings, and organ dysfunction including hepatic failure. Rhabdomyolysis has been observed in some patients experiencing skin and/or liver reactions associated with nevirapine use.
Patients developing signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions (including, but not limited to, severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, and/or hepatitis, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, and renal dysfunction) must permanently discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately. Do not restart nevirapine following severe skin rash, skin rash combined with increased transaminases or other symptoms, or hypersensitivity reaction.
The first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine extended-release tablets are a critical period during which intensive clinical and laboratory monitoring of patients is required to detect potentially life-threatening skin reactions. The optimal frequency of monitoring during this period has not been established. Some experts recommend clinical and laboratory monitoring more often than once per month, and in particular, include monitoring of liver enzyme tests at baseline, prior to dose escalation and at two weeks post-dose escalation. After the initial 18-week period, frequent clinical and laboratory monitoring should continue throughout nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment. In addition, the 14-day lead-in period with nevirapine 200 mg daily dosing has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency of rash [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
If patients present with a suspected nevirapine-associated rash, measure transaminases immediately. Permanently discontinue nevirapine in patients with rash-associated transaminase elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Patients must initiate therapy with immediate-release nevirapine daily for the first 14 days. This lead-in period has been shown to reduce the frequency of rash. Discontinue nevirapine if a patient experiences severe rash or any rash accompanied by constitutional findings. Do not initiate nevirapine extended-release tablets if a patient experiencing a mild to moderate rash without constitutional symptoms during the 14-day immediate-release nevirapine lead-in period of 200 mg/day (150 mg/m2/day in pediatric patients) until the rash has resolved. The total duration of the immediate-release nevirapine lead-in dosing period must not exceed 28 days at which point an alternative regimen should be sought [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Patients must be monitored closely if isolated rash of any severity occurs. Delay in stopping nevirapine treatment after the onset of rash may result in a more serious reaction.
Women appear to be at higher risk than men of developing rash with nevirapine.
In a clinical trial of immediate-release nevirapine, concomitant prednisone use (40 mg per day for the first 14 days of nevirapine administration) was associated with an increase in incidence and severity of rash during the first 6 weeks of nevirapine therapy. Therefore, use of prednisone to prevent nevirapine-associated rash is not recommended.
5.3 Resistance
Nevirapine extended-release tablets must not be used as a single agent to treat HIV-1 or added on as a sole agent to a failing regimen. Resistant virus emerges rapidly when nevirapine is administered as monotherapy. The choice of new antiretroviral agents to be used in combination with nevirapine should take into consideration the potential for cross-resistance. When discontinuing an antiretroviral regimen containing nevirapine extended-release tablets, the long half-life of nevirapine should be taken into account; if antiretrovirals with shorter half-lives than nevirapine are stopped concurrently, low plasma concentrations of nevirapine alone may persist for a week or longer and virus resistance may subsequently develop [see Microbiology (12.4)].
5.4 Drug Interactions
See Table 3 for listings of established and potential drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Concomitant use of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) or St. John’s wort-containing products and nevirapine is not recommended. Co-administration of St. John’s wort with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), including nevirapine, is expected to substantially decrease NNRTI concentrations and may result in sub-optimal levels of nevirapine and lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to nevirapine or to the class of NNRTIs.
Co-administration of nevirapine and efavirenz is not recommended as this combination has been associated with an increase in adverse reactions and no improvement in efficacy.
5.5 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including nevirapine. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution, however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.6 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance” have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Clinical Trial Experience in Adult Patients
The most serious adverse reactions associated with nevirapine are hepatitis, hepatic failure, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions. Hepatitis/hepatic failure may be isolated or associated with signs of hypersensitivity which may include severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, or renal dysfunction [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
The most common clinical toxicity of nevirapine is rash, which can be severe or life-threatening [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Rash occurs most frequently within the first 6 weeks of therapy. Rashes are usually mild to moderate, maculopapular erythematous cutaneous eruptions, with or without pruritus, located on the trunk, face and extremities.
The safety database in nevirapine extended-release tablet clinical trials contains data from 800 subjects treated with nevirapine extended-release tablets and 654 subjects treated with immediate-release nevirapine.
Trial 1100.1486 (VERxVE)
In Trial 1100.1486 (VERxVE) treatment-naïve subjects received a lead-in dose of immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg once daily for 14 days (n = 1068) and then were randomized to receive either immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily (n = 506) or nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily (n = 505). All subjects received tenofovir + emtricitabine as background therapy. Subjects were enrolled with CD4+ counts less than 250 cells/mm3 for women and less than 400 cells/mm3 for men [see Indications and Usage (1)]. Data on potential symptoms of hepatic events were prospectively collected in this trial. The safety data include all subject visits up to the time of the last subject’s completion of the 96-week endpoint in the trial (mean observation period 98 weeks).
After the lead-in period, the incidence of any hepatic event was 9% in the immediate-release nevirapine group and 6% in the nevirapine extended-release tablets group; the incidence of symptomatic hepatic events (anorexia, jaundice, vomiting) was 3% and 2%, respectively. The incidence of GRADE 3 or 4 ALT/AST elevation was 8% in both the immediate-release nevirapine group and nevirapine extended-release tablets group. Overall, there was a comparable incidence of symptomatic hepatic events among men and women enrolled in VERxVE.
Severe or life-threatening rash considered to be related to nevirapine treatment occurred in 1% of subjects during the lead-in phase with immediate-release nevirapine, and in 1% of subjects in either treatment group during the randomization phase. In addition, six cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome were reported in the trial; all but one occurred within the first 30 days of nevirapine treatment.
No Grade 2 or above adverse reactions judged to be related to treatment by the investigator occurred in more than 2% of subjects during the 14-day lead-in with immediate-release nevirapine (200 mg once daily), except for rash which occurred in 4% of subjects.
Adverse reactions of at least moderate intensity (Grades 2 or above) 2% or more of treatment-naïve subjects receiving either immediate-release nevirapine or nevirapine extended-release tablets after randomization in Trial 1100.1486 are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Selected Clinical Adverse Drug Reactions* of at least Moderate Intensity (Grade 2 or Above) Occurring in 2% or More of Adult Subjects - Week 96 Analysis of Trial 1100.1486† - * Excludes laboratory abnormalities reported as ADRs
- † Mean observation period 98 weeks.
- ‡ Rash includes terms rash, rash maculo-papular, erythema nodosum, rash erythematous, rash papular, skin reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
- § Clinical hepatitis includes terms hepatitis, hepatotoxicity, hepatitis acute, liver disorder, hepatitis toxic, hepatic failure, jaundice.
Adverse Drug Reaction
Nevirapine Immediate-Release
N = 506 (%)Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets
N = 505 (%)Rash‡
4
5
Diarrhea
4
4
Headache
4
4
Clinical Hepatitis§
4
2
Abdominal Pain
2
3
Arthralgia
2
2
Pyrexia
2
1
Nausea
2
1
Fatigue
2
2
Laboratory Abnormalities
Liver enzyme test abnormalities (AST, ALT) were observed in subjects receiving nevirapine extended-release tablets. Asymptomatic elevations in GGT occur frequently but are not a contraindication to continue therapy with nevirapine in the absence of elevations in other liver enzyme tests. Laboratory abnormalities that occurred in trial 1100.1486 are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Grade 2 to Grade 4 Laboratory Abnormalities that Represent a Worsening from Baseline Observed in at Least 5% of Subjects in Either Treatment Group - Trial 1100.1486 Laboratory Parameter
(unit)Limit
Nevirapine
Immediate-Release
(%)
(N = 506)Nevirapine
Extended-Release Tablets
(%)
(N = 505)Chemistry
SGPT/ALT (U/L)
Grade 2
2.6-5.0 x ULN
13
10
Grade 3
5.1-10.0 x ULN
3
4
Grade 4
> 10.0 x ULN
4
2
SGOT/AST (U/L)
Grade 2
2.6-5.0 x ULN
9
7
Grade 3
5.1-10.0 x ULN
2
3
Grade 4
> 10.0 x ULN
2
2
Amylase (U/L)
Grade 2
1.6-2.0 x ULN
4
5
Grade 3
2.1-5.0 x ULN
4
2
Grade 4
> 5.0 x ULN
0
< 1
Phosphate (mg/dL)
Grade 2
2.0-2.4 x ULN
38
33
Grade 3
1.0-1.9 x ULN
6
7
Grade 4
< 1.0 x ULN
< 1
0
Hematology
Neutrophils
Grade 2
750-999/mm3
7
4
Grade 3
500-749/mm3
2
2
Grade 4
< 500/mm3
1
1
Lipids
LDL (mg/dL)
Grade 2
160-190 mg/dL
15
15
Grade 3
> 190 mg/dL
5
5
Cholesterol (mg/dL)
Grade 2
240-300 mg/dL
18
19
Grade 3
> 300 mg/dL
4
3
Trial 1100.1526 (TRANxITION)
In Trial 1100.1526 (TRANxITION) subjects on immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily for at least 18 weeks were randomized to either receive nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily (n = 295) or remain on their immediate-release nevirapine treatment (n = 148). Adverse reactions observed for nevirapine extended-release tablet subjects (48 week analysis) were similar to those observed in trial 1100.1486, as displayed in Table 1.
Clinical Trial Experience in Pediatric Patients
Adverse reactions were assessed in Trial 1100.1518, an open-label, multiple-dose, non-randomized, cross-over trial to evaluate the safety and steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of nevirapine extended-release tablets in HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age. Safety was further examined in an optional extension phase of the trial. Forty subjects who completed the pharmacokinetic part of the trial were treated with nevirapine extended-release tablets once daily in combination with other antiretrovirals for a median duration of 33 weeks. The most frequently reported adverse reactions related to nevirapine extended-release tablets in pediatric subjects were similar to those observed in adults. In pediatric subjects the incidence of Grade 2 or higher drug-related rash was 1%. There were no adverse reactions of Grade 2 or above which were considered to be related to treatment by the investigator that occurred in more than 1% of subjects [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of immediate-release nevirapine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: fever, somnolence, drug withdrawal [see Drug Interactions (7)], redistribution/accumulation of body fat [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Gastrointestinal: vomiting
Liver and Biliary: jaundice, fulminant and cholestatic hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, hepatic failure
Hematology: anemia, eosinophilia, neutropenia
Investigations: decreased serum phosphorus
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, rhabdomyolysis associated with skin and/or liver reactions
Neurologic: paraesthesia
Skin and Appendages: allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, bullous eruptions, ulcerative stomatitis and urticaria have all been reported. In addition, hypersensitivity syndrome and hypersensitivity reactions with rash associated with constitutional findings such as fever, blistering, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, muscle or joint aches, general malaise, fatigue, or significant hepatic abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] plus one or more of the following: hepatitis, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, and/or renal dysfunction have been reported.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Nevirapine is principally metabolized by the liver via the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, 3A and 2B6. Nevirapine is known to be an inducer of these enzymes. As a result, drugs that are metabolized by these enzyme systems may have lower than expected plasma levels when co-administered with nevirapine.
The results of drug interactions studies with immediate-release nevirapine are expected to also apply to nevirapine extended-release tablets. The specific pharmacokinetic changes that occur with co-administration of nevirapine and other drugs are listed in Clinical Pharmacology, Table 4. Clinical comments about possible dosage modifications based on established drug interactions are listed in Table 3. The data in Tables 3 and 4 are based on the results of drug interaction studies conducted in HIV-1 seropositive subjects unless otherwise indicated. In addition to established drug interactions, there may be potential pharmacokinetic interactions between nevirapine and other drug classes that are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system. These potential drug interactions are also listed in Table 3. Although specific drug interaction studies in HIV-1 seropositive subjects have not been conducted for some classes of drugs listed in Table 3, additional clinical monitoring may be warranted when co-administering these drugs.
The in vitro interaction between nevirapine and the antithrombotic agent warfarin is complex. As a result, when giving these drugs concomitantly, plasma warfarin levels may change with the potential for increases in coagulation time. When warfarin is co-administered with nevirapine, anticoagulation levels should be monitored frequently.
Table 3: Established and Potential Drug Interactions: Use with Caution, Alteration in Dose or Regimen May Be Needed Due to Drug Interaction Established Drug Interactions: See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Table 4 for Magnitude of Interaction. - * The interaction between immediate-release nevirapine and the drug was evaluated in a clinical study. The results of drug interaction studies with immediate-release nevirapine are expected to also apply to nevirapine extended-release tablets.
Drug Name
Effect on Concentration of Nevirapine or Concomitant Drug
Clinical Comment
HIV Antiviral Agents: Protease Inhibitors (PIs)
Atazanavir/Ritonavir*
↓ Atazanavir
↑ NevirapineDo not co-administer nevirapine with atazanavir because nevirapine substantially decreases atazanavir exposure and there is a potential risk for nevirapine-associated toxicity due to increased nevirapine exposures.
Fosamprenavir*
↓ Amprenavir
↑ NevirapineCo-administration of nevirapine and fosamprenavir without ritonavir is not recommended.
Fosamprenavir/Ritonavir*
↓ Amprenavir
↑ NevirapineNo dosing adjustments are required when nevirapine is co-administered with 700/100 mg of fosamprenavir/ritonavir twice daily. The combination of nevirapine administered with fosamprenavir/ritonavir once daily has not been studied.
Indinavir*
↓ Indinavir
The appropriate doses of this combination of indinavir and nevirapine with respect to efficacy and safety have not been established.
Lopinavir/Ritonavir*
↓ Lopinavir
Dosing in adult patients: A dose adjustment of lopinavir/ritonavir to 500/125 mg tablets twice daily or 533/133 mg (6.5 mL) oral solution twice daily is recommended when used in combination with nevirapine. Neither lopinavir/ritonavir tablets nor oral solution should be administered once daily in combination with nevirapine.
Dosing in pediatric patients:Please refer to the Kaletra® prescribing information for dosing recommendations based on body surface area and body weight. Neither lopinavir/ritonavir tablets nor oral solution should be administered once daily in combination with nevirapine.
Nelfinavir*
↓ Nelfinavir M8 Metabolite
↓ Nelfinavir CminThe appropriate doses of the combination of nevirapine and nelfinavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established.
Saquinavir/Ritonavir
The interaction between nevirapine and saquinavir/ritonavir has not been evaluated.
The appropriate doses of the combination of nevirapine and saquinavir/ritonavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established.
HIV Antiviral Agents: Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Efavirenz*
↓ Efavirenz
The appropriate doses of these combinations with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established.
Delavirdine
Etravirine
RilpivirinePlasma concentrations may be altered. Nevirapine should not be co-administered with another NNRTI as this combination has not been shown to be beneficial.
Hepatitis C Antiviral Agents
Boceprevir
Plasma concentrations of boceprevir may be decreased due to induction of CYP3A4/5 by nevirapine.
Nevirapine and boceprevir should not be co-administered because decreases in boceprevir plasma concentrations may result in a reduction in efficacy.
Telaprevir
Plasma concentrations of telaprevir may be decreased due to induction of CYP3A4 by nevirapine and plasma concentrations of nevirapine may be increased due to inhibition of CYP3A4 by telaprevir.
Nevirapine and telaprevir should not be co-administered because changes in plasma concentrations of nevirapine, telaprevir, or both may result in a reduction in telaprevir efficacy or an increase in nevirapine-associated adverse events.
Other Agents
Analgesics:
Methadone*
↓ Methadone
Methadone levels were decreased; increased dosages may be required to prevent symptoms of opiate withdrawal. Methadone-maintained patients beginning nevirapine therapy should be monitored for evidence of withdrawal and methadone dose should be adjusted accordingly.Antiarrhythmics:
Amiodarone, disopyramide, lidocainePlasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for this combination have not been established.
Antibiotics:
Clarithromycin*
↓ Clarithromycin
↑ 14-OH clarithromycin
Clarithromycin exposure was significantly decreased by nevirapine; however, 14-OH metabolite concentrations were increased. Because clarithromycin active metabolite has reduced activity against Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex, overall activity against this pathogen may be altered. Alternatives to clarithromycin, such as azithromycin, should be considered.
Rifabutin*
↑ Rifabutin
Rifabutin and its metabolite concentrations were moderately increased. Due to high intersubject variability, however, some patients may experience large increases in rifabutin exposure and may be at higher risk for rifabutin toxicity. Therefore, caution should be used in concomitant administration.
Rifampin*
↓ Nevirapine
Nevirapine and rifampin should not be administered concomitantly because decreases in nevirapine plasma concentrations may reduce the efficacy of the drug. Physicians needing to treat patients co-infected with tuberculosis and using a nevirapine-containing regimen may use rifabutin instead.
Anticonvulsants:
Carbamazepine, clonazepam, ethosuximidePlasma concentrations of nevirapine and the anticonvulsant may be decreased.
Use with caution and monitor virologic response and levels of anticonvulsants.
Antifungals:
Fluconazole*
↑ Nevirapine
Because of the risk of increased exposure to nevirapine, caution should be used in concomitant administration, and patients should be monitored closely for nevirapine-associated adverse events.
Ketoconazole*
↓ Ketoconazole
Nevirapine and ketoconazole should not be administered concomitantly because decreases in ketoconazole plasma concentrations may reduce the efficacy of the drug.
Itraconazole
↓ Itraconazole
Nevirapine and itraconazole should not be administered concomitantly due to potential decreases in itraconazole plasma concentrations that may reduce efficacy of the drug.
Antithrombotics:
Warfarin
Plasma concentrations may be increased.
Potential effect on anticoagulation. Monitoring of anticoagulation levels is recommended.Calcium Channel Blockers:
Diltiazem, nifedipine, verapamil
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for these combinations have not been established.Cancer Chemotherapy:
Cyclophosphamide
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for this combination have not been established.Ergot Alkaloids:
Ergotamine
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for this combination have not been established.Immunosuppressants:
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for these combinations have not been established.Motility Agents:
Cisapride
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for this combination have not been established.Opiate Agonists:
Fentanyl
Plasma concentrations may be decreased.
Appropriate doses for this combination have not been established.Oral Contraceptives:
Ethinyl estradiol and Norethindrone*
↓ Ethinyl estradiol
↓ Norethindrone
Despite lower ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone exposures when co-administered with nevirapine, literature reports suggest that nevirapine has no effect on pregnancy rates among HIV-infected women on combined oral contraceptives. When co-administered with nevirapine extended-release tablets, no dose adjustment of ethinyl estradiol or norethindrone is needed when used in combination for contraception.When oral contraceptives are used for hormonal regulation during nevirapine extended-release tablet therapy, the therapeutic effect of the hormonal therapy should be monitored.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to nevirapine during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
Available data for nevirapine in pregnant women is from the use of nevirapine immediate-release. Available data from the APR show no difference in the risk of overall major birth defects for nevirapine compared with the background rate for major birth defects of 2.7% in a U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) [see Data]. The rate of miscarriage is not reported in the APR. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15-20%. The background risk of birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. Methodological limitations of the APR include the use of MACDP as the external comparator group. The MACDP population is not disease-specific, evaluates women and infants from a limited geographic area, and does not include outcomes for births that occurred at < 20 weeks gestation.
There is a risk for severe hepatic events in pregnant women exposed to nevirapine extended-release tablets [see Clinical Considerations]. In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes was observed following oral administration of nevirapine during organogenesis in the rat and rabbit, at systemic exposures (AUC) to nevirapine approximately equal (rats) and 50% higher (rabbits) than the exposure in humans at the recommended 400 mg daily dose [see Data].
Clinical Considerations
Maternal Adverse Reactions
Severe hepatic events, including fatalities, have been reported in pregnant women receiving chronic nevirapine therapy as part of combination treatment of HIV-1 infection. Regardless of pregnancy status, women with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3 should not initiate nevirapine unless the benefit outweighs the risk. It is unclear if pregnancy augments the risk observed in non-pregnant women [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Data
Human Data
Based on prospective reports to the APR of over 2600 exposures to nevirapine during pregnancy resulting in live births (including over 1100 exposed in the first trimester), there was no difference between nevirapine and overall birth defects compared with the background birth defect rate of 2.7% in a U.S. reference population of the MACDP. The prevalence of birth defects in live births was 2.8% (95% CI: 1.9%, 4.0%) following first trimester exposure to nevirapine-containing regimens and 3.2% (95% CI: 2.4%, 4.3%) with second/third-trimester exposure to nevirapine-containing regimens.
Animal Data
Nevirapine was administered orally to pregnant rats (at 0, 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg/day), and rabbits (at 0, 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day) through organogenesis (on gestation days 7 through 16 and 6 through 18, respectively). No adverse developmental effects were observed at doses producing systemic exposures (AUC) approximately equivalent to (rats) or approximately 50% higher (rabbits) than human exposure at the recommended daily dose. In rats, decreased fetal body weights were observed at a maternally toxic dose at an exposure approximately 50% higher than the recommended daily dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-1 infected mothers in the United States not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV-1 infection. Published data report that nevirapine immediate-release is present in human milk. There are limited data on the effects of nevirapine on the breastfed infant. There is no information on the effects of nevirapine on milk production. Because of the potential for (1) HIV-1 transmission (in HIV-negative infants), (2) developing viral resistance (in HIV-positive infants), and (3) serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should not breastfeed if they are receiving nevirapine extended-release tablets.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Limited human data are insufficient to determine the risk of infertility in humans. Based on results from animal fertility studies conducted in rats, nevirapine extended-release tablets may reduce fertility in females of reproductive potential. It is not known if these effects on fertility are reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Nevirapine extended-release tablets are indicated for use in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in children 6 years of age or older with a BSA of 1.17 m2 or greater [see Indications and Usage (1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
The use of nevirapine extended-release tablets for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients 6 to less than 18 years of age is based on pharmacokinetic, safety, and antiviral activity data from an open-label trial with nevirapine extended-release tablets. The results of this trial were supported by previous demonstration of efficacy in adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Nevirapine extended-release tablets are not recommended for children less than 6 years of age. Trial 1100.1518 did not provide sufficient pharmacokinetic data for children 3 to less than 6 years of age to support the use of nevirapine extended-release tablets in this age group. Furthermore, nevirapine extended-release tablets are not recommended for children less than 3 years of age because they are not able to swallow tablets.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of nevirapine extended-release tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether elderly subjects respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
In subjects with renal impairment (mild, moderate or severe), there were no significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of nevirapine. Nevirapine is extensively metabolized by the liver and nevirapine metabolites are extensively eliminated by the kidney. Nevirapine metabolites may accumulate in patients receiving dialysis; however, the clinical significance of this accumulation is not known. No adjustment in nevirapine dosing is required in patients with CrCl greater than or equal to 20 mL per min. The pharmacokinetics of nevirapine have not been evaluated in patients with CrCl less than 20 mL per min. In patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis, an additional dose of immediate-release nevirapine (200 mg) following each dialysis treatment is indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been studied in patients with renal dysfunction.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Because increased nevirapine levels and nevirapine accumulation may be observed in patients with serious liver disease, do not administer nevirapine to patients with moderate or severe (Child-Pugh Class B or C, respectively) hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been evaluated in subjects with hepatic impairment.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for nevirapine overdosage. Cases of immediate-release nevirapine overdose at doses ranging from 800 to 1800 mg per day for up to 15 days have been reported. Patients have experienced events including edema, erythema nodosum, fatigue, fever, headache, insomnia, nausea, pulmonary infiltrates, rash, vertigo, vomiting and weight decrease. All events subsided following discontinuation of immediate-release nevirapine.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
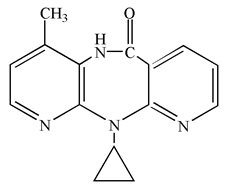
Nevirapine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1). Nevirapine is structurally a member of the dipyridodiazepinone chemical class of compounds.
The chemical name of nevirapine is 11-Cyclopropyl-5,11-dihydro-4-methyl-6H-dipyrido[3,2-b:2’,3’-e][1, 4]diazepin-6-one. Nevirapine, USP is a white to off-white, odorless to nearly odorless crystalline powder with the molecular weight of 266.30 and the molecular formula C15H14N4O. Nevirapine has the following structural formula:
Nevirapine extended-release tablets, USP are for oral administration. Each tablet contains 100 mg or 400 mg of nevirapine and the inactive ingredients hypromellose, lactose monohydrate and sodium stearyl fumarate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Adults
Absorption and Bioavailability
The single-dose pharmacokinetics of nevirapine extended-release tablets was studied in 17 healthy volunteers. Nevirapine was absorbed with a median tmax of approximately 24 hrs. The mean Cmax and AUC0-∞ of nevirapine were 2060 ng per mL and 161,000 ng*hr/mL, respectively. The bioavailability of 400 mg of nevirapine extended-release tablets, relative to 400 mg of immediate-release nevirapine, was approximately 75%.
The multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of nevirapine extended-release tablets was studied in 24 HIV-1 infected subjects who switched from chronic immediate-release nevirapine to nevirapine extended-release tablets. The mean nevirapine AUC0-24,ss and Cmin,ss after 19 days of nevirapine extended-release tablet dosing under fasted conditions were 82,000 ng*hr/mL and 2920 ng per mL, respectively. When nevirapine extended-release tablets were administered under fed conditions, the mean nevirapine AUC0-24,ss and Cmin,ss were 96,700 ng*hr/mL and 3150 ng per mL, respectively. The bioavailability of 400 mg of nevirapine extended-release tablets, relative to 400 mg of immediate-release nevirapine, under fasted and fed conditions, was 80% and 94%, respectively. The difference in the bioavailability of nevirapine, when nevirapine extended-release tablets are dosed under fasted or fed conditions, is not considered clinically relevant. Nevirapine extended-release tablets can be taken with or without food.
Distribution
Nevirapine is highly lipophilic and is essentially nonionized at physiologic pH. Following intravenous administration to healthy adults, the apparent volume of distribution (Vdss) of nevirapine was 1.21 ± 0.09 L/kg, suggesting that nevirapine is widely distributed in humans. Nevirapine readily crosses the placenta and is also found in breast milk [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)]. Nevirapine is about 60% bound to plasma proteins in the plasma concentration range of 1-10 mcg per mL. Nevirapine concentrations in human cerebrospinal fluid (n = 6) were 45% (± 5%) of the concentrations in plasma; this ratio is approximately equal to the fraction not bound to plasma protein.
Metabolism/Elimination
In vivo studies in humans and in vitro studies with human liver microsomes have shown that nevirapine is extensively biotransformed via cytochrome P450 (oxidative) metabolism to several hydroxylated metabolites. In vitro studies with human liver microsomes suggest that oxidative metabolism of nevirapine is mediated primarily by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isozymes from the CYP3A and CYP2B6 families, although other isozymes may have a secondary role. In a mass balance/excretion trial in eight healthy male volunteers dosed to steady-state with immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg given twice daily followed by a single 50 mg dose of 14C-nevirapine, approximately 91.4 ± 10.5% of the radiolabeled dose was recovered, with urine (81.3 ± 11.1%) representing the primary route of excretion compared to feces (10.1 ± 1.5%). Greater than 80% of the radioactivity in urine was made up of glucuronide conjugates of hydroxylated metabolites. Thus cytochrome P450 metabolism, glucuronide conjugation, and urinary excretion of glucuronidated metabolites represent the primary route of nevirapine biotransformation and elimination in humans. Only a small fraction (less than 5%) of the radioactivity in urine (representing less than 3% of the total dose) was made up of parent compound; therefore, renal excretion plays a minor role in elimination of the parent compound.
Nevirapine is an inducer of hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolic enzymes 3A and 2B6. Nevirapine induces CYP3A and CYP2B6 by approximately 20-25%, as indicated by erythromycin breath test results and urine metabolites. Autoinduction of CYP3A and CYP2B6 mediated metabolism leads to an approximately 1.5- to 2-fold increase in the apparent oral clearance of nevirapine as treatment continues from a single dose to two-to-four weeks of dosing with 200-400 mg per day of immediate-release nevirapine. Autoinduction also results in a corresponding decrease in the terminal phase half-life of nevirapine in plasma, from approximately 45 hours (single dose) to approximately 25-30 hours following multiple dosing with 200-400 mg per day.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
HIV-1 seronegative adults with mild (CrCl 50-79 mL per min; n = 7), moderate (CrCl 30-49 mL per min; n = 6), or severe (CrCl less than 30 mL per min; n = 4) renal impairment received a single 200 mg dose of immediate-release nevirapine in a pharmacokinetic trial. These subjects did not require dialysis. The trial included six additional subjects with renal failure requiring dialysis.
In subjects with renal impairment (mild, moderate or severe), there were no significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of nevirapine. However, subjects requiring dialysis exhibited a 44% reduction in nevirapine AUC over a one-week exposure period. There was also evidence of accumulation of nevirapine hydroxy-metabolites in plasma in subjects requiring dialysis. An additional 200 mg dose of immediate-release nevirapine following each dialysis treatment is indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been studied in patients with renal dysfunction.
Hepatic Impairment
In a steady-state trial comparing 46 subjects with mild (n = 17; expansion of some portal areas; Ishak Score 1-2), moderate (n = 20; expansion of most portal areas with occasional portal-to-portal and portal-to-central bridging; Ishak Score 3-4), or severe (n = 9; marked bridging with occasional cirrhosis without decompensation indicating Child-Pugh A; Ishak Score 5-6) fibrosis as a measure of hepatic impairment, the multiple dose pharmacokinetic disposition of nevirapine and its five oxidative metabolites were not altered. However, approximately 15% of these subjects with hepatic fibrosis had nevirapine trough concentrations above 9,000 mcg per mL (2-fold the usual mean trough). Therefore, patients with hepatic impairment should be monitored carefully for evidence of drug-induced toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The subjects studied were receiving antiretroviral therapy containing immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily for at least 6 weeks prior to pharmacokinetic sampling, with a median duration of therapy of 3.4 years.
In a pharmacokinetic trial where HIV-1 negative cirrhotic subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A; n = 6) or moderate (Child-Pugh B; n = 4) hepatic impairment received a single 200 mg dose of immediate-release nevirapine, a significant increase in the AUC of nevirapine was observed in one subject with Child-Pugh B and ascites suggesting that patients with worsening hepatic function and ascites may be at risk of accumulating nevirapine in the systemic circulation. Because nevirapine induces its own metabolism with multiple dosing, this single-dose trial may not reflect the impact of hepatic impairment on multiple-dose pharmacokinetics.
Do not administer nevirapine to patients with moderate or severe (Child-Pugh Class B or C, respectively) hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]. Nevirapine extended-release tablets have not been evaluated in patients with hepatic impairment.
Gender
In the multinational 2NN trial of immediate-release nevirapine, a population pharmacokinetic substudy of 1077 subjects was performed that included 391 females. Female subjects showed a 13.8% lower clearance of nevirapine than did men. Since neither body weight nor Body Mass Index (BMI) had an influence on the clearance of nevirapine, the effect of gender cannot solely be explained by body size.
The effects of gender on the pharmacokinetics of nevirapine extended-release tablets have been investigated in Trial 1100.1486. Female subjects tend to have higher (approximately 20-30%) trough concentrations in both nevirapine extended-release tablets and immediate-release nevirapine treatment groups.
Race
An evaluation of nevirapine plasma concentrations (pooled data from several clinical trials) from HIV-1-infected subjects (27 Black, 24 Hispanic, 189 Caucasian) revealed no marked difference in nevirapine steady-state trough concentrations (median Cmin,ss = 4.7 mcg per mL Black, 3.8 mcg per mL Hispanic, 4.3 mcg per mL Caucasian) with long-term treatment with immediate-release nevirapine at 400 mg per day. However, the pharmacokinetics of nevirapine have not been evaluated specifically for the effects of ethnicity.
Black subjects (n = 80/group) in Trial 1100.1486 showed approximately 30 to 35% higher trough concentrations than Caucasian subjects (250-325 subjects/group) in both immediate-release nevirapine and nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment groups over 96 weeks of treatment at 400 mg per day.
Geriatric Patients
Nevirapine pharmacokinetics in HIV-1-infected adults do not appear to change with age (range 18-68 years); however, nevirapine has not been extensively evaluated in patients beyond the age of 65 years [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of nevirapine extended-release tablets were assessed in HIV-1 infected children 3 to less than 18 years of age. Children enrolled received weight or body surface area dose-adjusted immediate-release nevirapine in combination with other antiretrovirals for a minimum of 18 weeks and then were switched to nevirapine extended-release tablets in combination with other antiretrovirals for 10 days, after which steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters were determined.
Overall, the mean systemic nevirapine exposures in children 6 to less than 18 years of age following administration of nevirapine extended-release tablets and immediate-release nevirapine were similar. Based on intensive PK data (N = 17), the observed geometric mean ratios of nevirapine extended-release tablets to immediate-release nevirapine were approximately 97% for Cmin,ss and 94% for AUCss with 90% confidence intervals within 80%-125%; the ratio for Cmax,ss was lower and consistent with a once daily extended-release dosage form.
Trial 1100.1518 did not provide sufficient pharmacokinetic data for children 3 to less than 6 years of age to support the use of nevirapine extended-release tablets in this age group.
Drug Interactions
[See Drug Interactions (7).]
Nevirapine induces hepatic cytochrome P450 metabolic isoenzymes 3A and 2B6. Co-administration of nevirapine extended-release tablets and drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2B6 may result in decreased plasma concentrations of these drugs and attenuate their therapeutic effects.
While primarily an inducer of cytochrome P450 3A and 2B6 enzymes, nevirapine may also inhibit this system. Among human hepatic cytochrome P450s, nevirapine was capable in vitro of inhibiting the 10-hydroxylation of (R)-warfarin (CYP3A). The estimated Ki for the inhibition of CYP3A was 270 micromolar, a concentration that is unlikely to be achieved in patients as the therapeutic range is less than 25 micromolar. Therefore, nevirapine may have minimal inhibitory effect on other substrates of CYP3A.
Nevirapine does not appear to affect the plasma concentrations of drugs that are substrates of other CYP450 enzyme systems, such as 1A2, 2D6, 2A6, 2E1, 2C9, or 2C19.
Table 4 (see below) contains the results of drug interaction trials performed with immediate-release nevirapine and other drugs likely to be co-administered. The effects of nevirapine on the AUC, Cmax, and Cmin of co-administered drugs are summarized. Results of drug interaction studies with immediate-release nevirapine are expected to also apply to nevirapine extended-release tablets.
Table 4: Drug Interactions: Changes in Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Co-administered Drug in the Presence of Immediate-Release Nevirapine (All Interaction Studies were Conducted in HIV-1 Positive Subjects) § = Cmin below detectable level of the assay.
↑ = Increase, ↓ = Decrease, ↔ = No Effect- * For information regarding clinical recommendations, [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- † Parallel group design; n = 23 for atazanavir/ritonavir + nevirapine, n = 22 for atazanavir/ritonavir without nevirapine. Changes in atazanavir PK are relative to atazanavir/ritonavir 300/100 mg alone.
- ‡ Based on between-trial comparison.
- § Pediatric subjects ranging in age from 6 months to 12 years.
- ¶ Parallel group design; n for nevirapine + lopinavir/ritonavir, n for lopinavir/ritonavir alone.
- # Based on historical controls.
Co-administered Drug
Dose of
Co-administered DrugDose Regimen of Immediate-Release Nevirapine
n
% Change of Co-administered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI)
Antiretrovirals
AUC
Cmax
Cmin
300/100 mg QD day 4-13, then 400/100 mg QD, day 14-23
200 mg BID day 1-23. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry.
23
Atazanavir
300/100 mg
↓ 42
(↓ 52 to ↓ 29)Atazanavir
300/100 mg
↓ 28
(↓ 40 to ↓ 14)Atazanavir
300/100 mg
↓ 72
(↓ 80 to ↓ 60)Atazanavir
400/100 mg
↓ 19
(↓ 35 to ↑ 2)Atazanavir
400/100 mg
↑ 2
(↓ 15 to ↑ 24)Atazanavir
400/100 mg
↓ 59
(↓ 73 to ↓ 40)Darunavir/Ritonavir‡
400/100 mg BID
200 mg BID
8
↑ 24
(↓ 3 to ↑ 57)↑ 40
(↑ 14 to ↑ 73)↑ 2
(↓ 21 to ↑ 32)Didanosine
100-150 mg BID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
18
↔
↔
§
Efavirenz*
600 mg QD
200 mg QD x 14 days; 400 mg QD x 14 days
17
↓ 28
(↓ 34 to ↓ 14)↓ 12
(↓ 23 to ↑ 1)↓ 32
(↓ 35 to ↓ 19)Fosamprenavir
1400 mg BID
200 mg BID. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry.
17
↓ 33
(↓ 45 to ↓ 20)↓ 25
(↓ 37 to ↓ 10)↓ 35
(↓ 50 to ↓ 15)Fosamprenavir/Ritonavir
700/100 mg BID
200 mg BID. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry.
17
↓ 11
(↓ 23 to ↑ 3)↔
↓ 19
(↓ 32 to ↓ 4)Indinavir*
800 mg q8H
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
19
↓ 31
(↓ 39 to ↓ 22)↓ 15
(↓ 24 to ↓ 4)↓ 44
(↓ 53 to ↓ 33)300/75 mg/m2 (lopinavir/ritonavir)§
7 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg QD x 2 weeks; BID x 1 week
12, 15¶
↓ 22
(↓ 44 to ↑ 9)↓ 14
(↓ 36 to ↑ 16)↓ 55
(↓ 75 to ↓ 19)Lopinavir*
400/100 mg BID (lopinavir/ritonavir)
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID
> 1 year22, 19¶
↓ 27
(↓ 47 to ↓ 2)↓ 19
(↓ 38 to ↑ 5)↓ 51
(↓ 72 to ↓ 26)Maraviroc#
300 mg SD
200 mg BID
8
↑ 1
(↓ 35 to ↑ 55)↑ 54
(↓ 6 to ↑ 151)↔
Nelfinavir*
750 mg TID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
23
↔
↔
↓ 32
(↓ 50 to ↑ 5)Nelfinavir-M8 metabolite
↓ 62
(↓ 70 to ↓ 53)↓ 59
(↓ 68 to ↓ 48)↓ 66
(↓ 74 to ↓ 55)Ritonavir
600 mg BID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
18
↔
↔
↔
Stavudine
30-40 mg BID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
22
↔
↔
§
Zalcitabine
0.125-
0.25 mg TID200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
6
↔
↔
§
Zidovudine
100-200 mg TID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
11
↓ 28
(↓ 40 to ↓ 4)↓ 30
(↓ 51 to ↑ 14)§
Other Medications
AUC
Cmax
Cmin
Clarithromycin*
500 mg BID
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
15
↓ 31
(↓ 38 to ↓ 24)↓ 23
(↓ 31 to ↓ 14)↓ 56
(↓ 70 to ↓ 36)Metabolite
14-OH-clarithromycin↑ 42
(↑ 16 to ↑ 73)↑ 47
(↑ 21 to ↑ 80)↔
0.035 mg (as Ortho-Novum® 1/35)
1 mg (as Ortho-Novum® 1/35)200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
10
↓ 20
(↓ 33 to ↓ 3)
↔
§
↓ 19
(↓ 30 to ↓ 7)↓ 16
(↓ 27 to ↓ 3)§
Depomedroxy-
progesterone acetate150 mg every 3 months
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
32
↔
↔
↔
Fluconazole
200 mg QD
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
19
↔
↔
↔
Ketoconazole*
400 mg QD
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
21
↓ 72
(↓ 80 to ↓ 60)↓ 44
(↓ 58 to ↓ 27)§
Methadone*
Individual Subject Dosing
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID ≥ 7 days
9
In a controlled pharmacokinetic trial with 9 subjects receiving chronic methadone to whom steady-state nevirapine therapy was added, the clearance of methadone was increased by 3-fold, resulting in symptoms of withdrawal, requiring dose adjustments in 10 mg segments, in 7 of the 9 subjects. Methadone did not have any effect on nevirapine clearance.
Rifabutin*
150 or 300 mg QD
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
19
↑ 17
(↓ 2 to ↑ 40)↑ 28
(↑ 9 to ↑ 51)↔
Metabolite 25-O-desacetyl-rifabutin
↑ 24
(↓ 16 to ↑ 84)↑ 29
(↓ 2 to ↑ 68)↑ 22
(↓ 14 to ↑ 74)Rifampin*
600 mg QD
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days
14
↑ 11
(↓ 4 to ↑ 28)↔
§
Because of the design of the drug interaction trials (addition of 28 days of nevirapine therapy to existing HIV-1 therapy), the effect of the concomitant drug on plasma nevirapine steady-state concentrations was estimated by comparison to historical controls.
Administration of rifampin had a clinically significant effect on nevirapine pharmacokinetics, decreasing AUC and Cmax by greater than 50%. Administration of fluconazole resulted in an approximate 100% increase in nevirapine exposure, based on a comparison to historic data [see Drug Interactions (7)]. The effect of other drugs listed in Table 4 on nevirapine pharmacokinetics was not significant. No significant interaction was observed when tipranavir was co-administered with low-dose ritonavir and nevirapine.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Nevirapine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) of HIV-1. Nevirapine binds directly to reverse transcriptase (RT) and blocks the RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by causing a disruption of the enzyme’s catalytic site. The activity of nevirapine does not compete with template or nucleoside triphosphates. HIV-2 RT and eukaryotic DNA polymerases (such as human DNA polymerases α, ß, γ, or δ) are not inhibited by nevirapine.
Antiviral Activity
The antiviral activity of nevirapine has been measured in a variety of cell lines including peripheral blood mononuclear cells, monocyte-derived macrophages, and lymphoblastoid cell lines. In an assay using human embryonic kidney 293 cells, the median EC50 value (50% inhibitory concentration) of nevirapine was 90 nM against a panel of 2923 wild-type isolates of HIV-1 that were primarily (93%) clade B clinical isolates from the United States. The 99th percentile EC50 value was 470 nM in this trial. The median EC50 value was 63 nM (range 14-302 nM, n = 29) against clinical isolates of HIV-1 clades A, B, C, D, F, G, and H, and circulating recombinant forms CRF01_AE, CRF02_AG and CRF12_BF. Nevirapine had no antiviral activity in cell culture against group O HIV-1 isolates (n = 3) or HIV-2 isolates (n = 3) replicating in cord blood mononuclear cells. Nevirapine in combination with efavirenz exhibited strong antagonistic anti-HIV-1 activity in cell culture and was additive to antagonistic with the protease inhibitor ritonavir or the fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide. The anti-HIV-1 activity of nevirapine was not antagonistic in combination with the NRTIs abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir and zidovudine, and the protease inhibitors amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir and tipranavir. The anti-HIV-1 activity of nevirapine was antagonized by the anti-HBV drug adefovir and by the anti-HCV drug ribavirin in cell culture.
Resistance
HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility (100- to 250-fold) to nevirapine emerge in cell culture. Genotypic analysis showed mutations in the HIV-1 RT gene encoding Y181C and/or V106A substitutions depending upon the virus strain and cell line employed. Time to emergence of nevirapine resistance in cell culture was not altered when selection included nevirapine in combination with several other NNRTIs.
Phenotypic and genotypic changes in HIV-1 isolates from treatment-naïve subjects receiving either nevirapine (n = 24) or nevirapine and zidovudine (n = 14) were monitored in Phase 1 and 2 trials ranging from 1 to 12 weeks or longer. After 1 week of nevirapine monotherapy, isolates from 3/3 subjects had decreased susceptibility to nevirapine in cell culture. One or more of the RT mutations resulting in amino acid substitutions K103N, V106A, V108I, Y181C, Y188C, and G190A were detected in HIV-1 isolates from some subjects as early as 2 weeks after therapy initiation. By week eight of nevirapine monotherapy, 100% of the subjects tested (n = 24) had HIV-1 isolates with a greater than 100-fold decrease in susceptibility to nevirapine in cell culture compared to baseline, and had one or more of the nevirapine-associated RT resistance substitutions. Nineteen of these subjects (80%) had isolates with Y181C substitutions regardless of dose.
Genotypic analysis of isolates from antiretroviral-naïve subjects experiencing virologic failure (n = 71) receiving nevirapine once daily (n = 25) or twice daily (n = 46) in combination with lamivudine and stavudine (trial 2NN) for 48 weeks showed that isolates from 8/25 and 23/46 subjects, respectively, contained one or more of the following NNRTI resistance-associated substitutions: Y181C, K101E, G190A/S, K103N, V106A/M, V108I, Y188C/L, A98G, F227L, and M230L.
For trial 1100.1486, genotypic analysis was performed for baseline and on-therapy isolates from 23 and 34 subjects who experienced virologic failure in the nevirapine extended-release tablet and immediate-release nevirapine treatment group, respectively. Nevirapine resistance-associated substitutions developed in the on-therapy isolates of 78% (18/23) of the subjects who had virologic failures in the nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment group and 88% (30/34) of the subjects in the immediate-release nevirapine treatment group, respectively. The Y181C nevirapine resistance-associated substitution was found alone or in combination with other nevirapine resistance-associated substitutions (K101E, K103N, V106A, V108I, V179D/E/I, Y188 C/F/H/L/N, G190A, P225H, F227L, M230L) in isolates from 14 subjects failing nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment and 25 subjects failing immediate-release nevirapine treatment. On-therapy isolates from 1 subject in nevirapine extended-release tablet treatment group developed a novel amino acid substitution Y181I and isolates from another subject in the immediate-release nevirapine treatment group developed a novel amino acid substitution Y188N. Phenotypic analysis showed that Y188N and Y181I substitutions conferred 103- and 22-fold reductions in susceptibility to nevirapine, respectively.
Cross-resistance
Rapid emergence of HIV-1 strains which are cross-resistant to NNRTIs has been observed in cell culture. Nevirapine-resistant HIV-1 isolates were cross-resistant to the NNRTIs delavirdine, efavirenz, and etravirine. The Y188N conferred 22- and 7-fold reductions in susceptibility to delavirdine and efavirenz, respectively, but showed no decrease in susceptibility to etravirine. Similarly, the Y181I substitution reduced susceptibility to delavirdine and etravirine 3- and 8-fold, respectively, but did not reduce susceptibility to efavirenz. However, nevirapine-resistant isolates were susceptible to the NRTIs ddI and ZDV. Similarly, ZDV-resistant isolates were susceptible to nevirapine in cell culture.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats were carried out with nevirapine. Mice were dosed with 0, 50, 375 or 750 mg/kg/day for two years. Hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas were increased at all doses in males and at the two high doses in females. In studies in which rats were administered nevirapine at doses of 0, 3.5, 17.5 or 35 mg/kg/day for two years, an increase in hepatocellular adenomas was seen in males at all doses and in females at the high dose. The systemic exposure (based on AUCs) at all doses in the two animal studies was lower than that measured in humans at the 200 mg twice daily dose of immediate-release nevirapine. The mechanism of the carcinogenic potential is unknown.
Mutagenesis
However, in genetic toxicology assays, nevirapine showed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic activity in a battery of in vitro and in vivo studies. These included microbial assays for gene mutation (Ames: Salmonella strains and E. coli), mammalian cell gene mutation assay (CHO/HGPRT), cytogenetic assays using a Chinese hamster ovary cell line and a mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay following oral administration. Given the lack of genotoxic activity of nevirapine, the relevance to humans of hepatocellular neoplasms in nevirapine-treated mice and rats is not known.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Patients
The clinical efficacy of nevirapine extended-release tablets is based on 96-week data from an ongoing, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy Phase 3 trial (Trial 1100.1486, VERxVE) in treatment-naïve subjects and on 48-week data in an ongoing, randomized, open-label trial in subjects who switched from immediate-release nevirapine tablets administered twice daily to nevirapine extended-release tablets administered once daily (Trial 1100.1526, TRANxITION).
Treatment-naïve Subjects
Trial 1100.1486 (VERxVE) is a Phase 3 trial in which treatment-naïve subjects received immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg once daily for 14 days and then were randomized to receive either immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily or nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily. All subjects received tenofovir + emtricitabine as background therapy. Randomization was stratified by screening HIV-1 RNA level (less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL and greater than 100,000 copies per mL). Subject demographic and baseline disease characteristics were balanced between the two treatment groups. With respect to demographics: 85% of the subjects were male, 75% were white, 20% were black, and approximately 29% were from North America. With respect to baseline disease characteristics: mean viral load was 4.7 log10 copies per mL, mean CD4+ cell count was 228 cells/mm3 and 73% of subjects had clade B HIV-1 subtype. Approximately two-thirds of the subjects had a baseline HIV-RNA level of less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL.
Table 5 describes week 96 outcomes in the Trial 1100.1486 (VERxVE). These outcomes include all subjects who were randomized after the 14 day lead-in with immediate-release nevirapine and received at least one dose of blinded study medication.
Table 5: Outcomes at Week 96 in Trial 1100.1486 - * Includes subjects who changed optimized background therapy (OBT) to new class or changed OBT not permitted per protocol or due to lack of efficacy prior to Week 96, subjects who discontinued prior to Week 96 for lack or loss of efficacy and subjects with HIV RNA greater than or equal to 50 copies/mL in the Week 96 window.
- † Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse events or death at any time point from Day 1 through the Week 96 window if this resulted in no virologic data on treatment during the specified window.
- ‡ Other includes: withdrew consent, lost to follow-up, moved away, etc.
Week 96
Nevirapine
Immediate-Release
N = 506Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets
N = 505Virologic Success - HIV RNA < 50 copies/mL
67%
69%
Virologic Failure*
18%
17%
No Virologic Data at Week 96 Window
Reasons
Discontinued trial/study drug due to adverse event or death†
10%
8%
Discontinued trial/study drug for other reasons‡
5%
5%
Missing data during window but on trial
< 1%
1%
At 96 weeks, mean change from baseline in CD4+ cell count adjusting for baseline HIV-1 viral load stratum was 222 cells/mm3 and 244 cells/mm3 for the groups receiving immediate-release nevirapine and nevirapine extended-release tablets, respectively.
Subjects Switching from Immediate-Release Nevirapine to Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets
Trial 1100.1526 (TRANxITION) is a Phase 3 trial to evaluate safety and antiviral activity of switching from immediate-release nevirapine to nevirapine extended-release tablets. In this open-label trial, 443 subjects already on an antiviral regimen containing immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily or immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily. Approximately half of the subjects had tenofovir + emtricitabine as their background therapy, with the remaining subjects receiving abacavir sulfate + lamivudine or zidovudine + lamivudine. Approximately half of the subjects had at least 3 years of exposure to immediate-release nevirapine prior to entering the trial.
At 48 weeks after randomization in Trial 1100.1526, 91% of subjects receiving immediate-release nevirapine 200 mg twice daily and 93% of subjects receiving nevirapine extended-release tablets 400 mg once daily continued to have HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL.
14.2 Pediatric Patients
Trial 1100.1518 was an open-label, multiple-dose, non-randomized, crossover trial performed in 85 HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age who had received at least 18 weeks of immediate-release nevirapine and had plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL prior to trial enrollment. Subjects were stratified according to age (3 to less than 6 years, 6 to less than 12 years, and 12 to less than 18 years). Following a 10-day period with immediate-release nevirapine, subjects were treated with nevirapine extended-release tablets once daily in combination with other antiretrovirals for 10 days, after which steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters were determined. Forty of the 80 subjects who completed the initial part of the study were enrolled in an optional extension phase of the trial which evaluated the safety and antiviral activity of nevirapine extended-release tablets through a minimum of 24 weeks of treatment. Zidovudine or stavudine plus lamivudine were the most commonly used background therapies in subjects who entered the optional extension phase.
Baseline demographics included: 55% of the subjects were female, 93% were black, 7% were white, and approximately 84% were from Africa. Subjects had a median baseline CD4+ cell count of 925 cells/mm3 (range 207 to 2057 cells/mm3).
Of the 40 subjects who entered the treatment extension phase, 39 completed at least 24 weeks of treatment and one subject discontinued prematurely due to an adverse reaction. After 24 weeks or more of treatment with nevirapine extended-release tablets, all 39 subjects continued to have plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL. Median CD4+ cell counts for the 3 to less than 6 year, 6 to less than 12 year, and 12 to less than 18 year age groups were 1113 cells/mm3, 853 cells/mm3, and 682 cells/mm3, respectively. These CD4+ cell counts were similar to those observed at baseline.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets, USP are available containing 100 mg or 400 mg of nevirapine, USP.
The 100 mg tablets are white to off-white, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and N100 on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-6950-77
bottles of 90 tabletsThe 400 mg tablets are white to off-white, oval, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and N400 on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-4890-93
bottles of 30 tabletsStorage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Store in a safe place out of the reach of children.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Hepatotoxicity and Skin Reactions: Inform patients of the possibility of severe liver disease or skin reactions associated with nevirapine that may result in death. Instruct patients developing signs or symptoms of liver disease or severe skin reactions to discontinue nevirapine and seek medical attention immediately, including performance of laboratory monitoring. Symptoms of liver disease include fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, acholic stools, liver tenderness or hepatomegaly. Symptoms of severe skin or hypersensitivity reactions include rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, and/or hepatitis.
Intensive clinical and laboratory monitoring, including liver enzymes, is essential during the first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine to detect potentially life-threatening hepatotoxicity and skin reactions. However, liver disease can occur after this period; therefore, monitoring should continue at frequent intervals throughout nevirapine treatment. Extra vigilance is warranted during the first 6 weeks of therapy, which is the period of greatest risk of hepatic events. Advise patients with signs and symptoms of hepatitis to discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately. If nevirapine is discontinued due to hepatotoxicity, do not restart it. Patients, particularly women, with increased CD4+ cell count at initiation of nevirapine therapy (greater than 250 cells/mm3 in women and greater than 400 cells/mm3 in men) are at substantially higher risk for development of symptomatic hepatic events, often associated with rash. Advise patients that co-infection with hepatitis B or C and/or increased transaminases at the start of therapy with nevirapine are associated with a greater risk of later symptomatic events (6 weeks or more after starting nevirapine) and asymptomatic increases in AST or ALT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The majority of rashes associated with nevirapine occur within the first 6 weeks of initiation of therapy. Instruct patients that if any rash occurs during the two-week lead-in period with immediate-release nevirapine, do not initiate nevirapine extended-release tablets until the rash resolves. The total duration of the lead-in dosing period with immediate-release nevirapine should not exceed 28 days, at which point an alternative regimen may need to be started. Any patient experiencing a rash should have their liver enzymes (AST, ALT) evaluated immediately. Patients with severe rash or hypersensitivity reactions should discontinue nevirapine immediately and consult a physician. Nevirapine should not be restarted following severe skin rash or hypersensitivity reaction. Women tend to be at higher risk for development of nevirapine-associated rash. For patients who interrupt nevirapine extended-release tablet dosing for more than 7 days and for whom restarting nevirapine therapy is not contraindicated, restart the recommended lead-in dosing with immediate-release nevirapine using one 200 mg tablet daily (150 mg/m2/day in pediatric patients) for the first 14 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Administration and Missed Dosage: Inform patients to take nevirapine extended-release tablets every day as prescribed. Advise patients not to alter the dose without consulting their doctor. If a dose is missed, patients should take the next dose as soon as possible. However, if a dose is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose.
Inform patients that they may occasionally see soft remnants of nevirapine extended-release tablets in their stool, which sometimes resemble intact tablets. These occurrences have not been shown to affect drug levels or response.
Instruct patients to swallow nevirapine extended-release tablets whole. They must not be chewed, crushed, or divided.
To avoid overdose, inform patients that they should never take immediate-release nevirapine and extended-release nevirapine tablets concomitantly.
Drug Interactions: Nevirapine extended-release tablets may interact with some drugs; therefore, advise patients to report to their doctor the use of any other prescription, non-prescription medication or herbal products, particularly St. John’s wort [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome: Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately of any signs or symptoms of infection, as inflammation from previous infection may occur soon after combination antiretroviral therapy, including when nevirapine extended-release tablets are started [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Fat Redistribution: Inform patients that redistribution or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy and that the cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Pregnancy Registry: Advise patients that there is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to nevirapine extended-release tablets during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation: Instruct women with HIV-1 infection not to breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in the breast milk [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility: Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential for impaired fertility from nevirapine extended-release tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
-
Medication Guide
Nevirapine Extended-Release Tablets, USP
(ne vir′ a peen)What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine?
Nevirapine can cause severe liver and skin problems that may lead to death. These problems can happen at any time during treatment, but your risk is higher during the first 18 weeks of treatment.
Nevirapine can cause serious side effects, including:
-
Severe liver problems. Some people taking nevirapine may develop severe liver problems that can lead to liver failure and the need for a liver transplant, or death. If you have liver problems you may get a rash.
- o Women have a higher risk of developing liver problems during treatment with nevirapine than men.
- o People who have abnormal liver test results before starting nevirapine and people with hepatitis B or C also have a greater risk of getting liver problems.
-
People who have higher CD4+ cell counts when they begin nevirapine have a higher risk of liver problems, especially:
- o Women with CD4+ counts higher than 250 cells/mm3. This group has the highest risk.
- o Men with CD4+ counts higher than 400 cells/mm3.
- Stop taking nevirapine and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems with or without a skin rash:
- dark (tea colored) urine
- light-colored bowel movements (stools)
- feeling sick to your stomach (nausea)
- pain or tenderness on your right side below your ribs
- loss of appetite
- yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes
- fever
- feel unwell or like you have the flu
- tiredness
-
Severe skin reactions and rash. Some skin reactions and rashes may be severe, life-threatening, and in some people, may lead to death. Most severe skin reactions and rashes happen in the first 6 weeks of treatment with nevirapine.
- o Women have a higher risk of developing a rash during treatment with nevirapine than men.
- Stop taking nevirapine and call your doctor right away if you get a rash with any of the following symptoms:
- blisters
- red or inflamed eyes, like “pink eye” (conjunctivitis)
- swelling of your face
- feel unwell or like you have the flu
- muscle or joint aches
- mouth sores
- fever
- tiredness
- Your doctor should do blood tests often to check your liver function and check for severe skin reactions during the first 18 weeks of treatment with nevirapine. You should continue to see your doctor and have your liver checked regularly during your treatment with nevirapine. It is important for you to keep all of your doctor appointments.
- If your doctor tells you to stop treatment with nevirapine because you have had any of the severe liver or skin symptoms listed above, you should never take nevirapine again.
See “What are the possible side effects of nevirapine?” for more information about side effects.
What is nevirapine?
Nevirapine tablets and nevirapine oral solution are prescription HIV-1 medicines used with other HIV-1 medicines to treat HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1) in adults and in children 15 days of age or older. HIV-1 is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
Nevirapine extended-release tablets are a prescription medicine used with other HIV-1 medicines to treat HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1) in adults and in children 6 years of age or older based on the child’s weight and height.
- If you are a woman with CD4+ counts higher than 250 cells/mm3 or a man with CD4+ counts higher than 400 cells/mm3, you and your doctor will decide if starting nevirapine is right for you.
- Nevirapine extended-release tablets are not recommended for use in children less than 6 years of age.
Do not take nevirapine:
- if you have liver problems.
- as part of occupational and non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimens. Nevirapine is only for people diagnosed with HIV-1. If you have not been diagnosed as HIV positive, then do not take nevirapine.
Before taking nevirapine, tell your doctor about all your or your child’s medical conditions, including if you or your child:
- have or have had hepatitis (inflammation of your liver) or problems with your liver. See “What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine?”
- receive dialysis
- have trouble swallowing pills
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if nevirapine will harm your unborn baby. Pregnancy Registry: There is a pregnancy registry for women who take nevirapine during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your doctor about how you can take part in this registry.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Nevirapine can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. You should not breastfeed if you have HIV-1 because of the risk of passing HIV-1 to your baby. Do not breastfeed during treatment with nevirapine. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Especially tell your doctor if you take St. John’s wort.
- Some medicines interact with nevirapine. Keep a list of your medicines to show your doctor or pharmacist.
- You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with nevirapine.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your doctor. Your doctor can tell you if it is safe to take nevirapine with other medicines.
How should I take nevirapine?
- Take nevirapine exactly as your doctor tells you to take it. Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to.
- Nevirapine is always taken in combination with other antiretroviral medicines.
-
Nevirapine comes in three different forms. Your doctor will prescribe the form of nevirapine that is right for you.
- o nevirapine tablets
- o nevirapine oral suspension
- o nevirapine extended-release tablets
- You should not take more than one form of nevirapine at the same time. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions.
- If your child is prescribed nevirapine, your child’s doctor will tell you exactly how nevirapine should be taken.
- Nevirapine can be taken with or without food.
- Swallow nevirapine extended-release tablets whole. Do not chew, crush, or divide nevirapine extended-release tablets.
- Do not miss a dose of nevirapine. If you miss a dose of nevirapine, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, do not take the missed dose. You should take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time.
- If you stop taking nevirapine for more than 7 days, ask your doctor how much to take before you start taking it again. You may need to begin taking the nevirapine starting dose again, which is taken 1 time each day for 14 days.
Starting nevirapine tablets:
- 1.
Your doctor should start you with 1 dose each day to lower your chance of getting a serious rash. It is important that you only take 1 dose of nevirapine each day for the first 14 days.
- Call your doctor right away if you get a skin rash during the first 14 days of nevirapine treatment.
- Do not increase your dose to 2 times a day if you have a rash.
- You should never take your starting dose for longer than 28 days. If after 28 days you are still receiving this starting dose because you have a rash, you and your doctor should talk about prescribing another HIV-1 medicine for you instead of nevirapine.
- 2. Day 15, you will take 1 nevirapine tablet 2 times a day.
Starting nevirapine extended-release tablets when this is the first time you are taking any form of nevirapine:
- 1.
Your doctor should start you with 1 dose of nevirapine tablets or oral suspension each day to lower your risk of getting a serious rash. It is important that you only take 1 dose of nevirapine each day for the first 14 days.
- Call your doctor right away if you get a skin rash during the first 14 days of nevirapine treatment.
- You should never take your starting dose for longer than 28 days. If after 28 days you are still receiving this starting dose because you have a rash, you and your doctor should talk about prescribing another HIV-1 medicine for you instead of nevirapine.
- Do not start nevirapine extended-release tablets if you have a rash.
- 2. Day 15, take nevirapine extended-release tablets 1 time a day as prescribed by your doctor.
Switching from nevirapine tablets or oral suspension to nevirapine extended-release tablets:
- Take nevirapine extended-release tablets 1 time a day as prescribed by your doctor.
- You may sometimes pass a soft mass in your stools (bowel movement) that looks like your nevirapine extended-release tablets. This will not affect the way your medicine works.
What are the possible side effects of nevirapine?
Nevirapine may cause serious side effects, including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine?”
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV-1 medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your doctor right away if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV-1 medicine.
- Changes in body fat can happen in people who take HIV-1 medicines. These changes may include increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck (“buffalo hump”), breast, and around the middle of your body (trunk). Loss of fat from your legs, arms, and face may also happen. The exact cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known.
The most common side effect of nevirapine is rash.
Nevirapine may cause decreased fertility in females. Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about fertility. These are not all the possible side effects of nevirapine. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store nevirapine extended-release tablets?
- Store nevirapine extended-release tablets at room temperature between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
Keep nevirapine extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of nevirapine extended-release tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use nevirapine extended-release tablets for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give nevirapine extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. They may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about nevirapine extended-release tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in nevirapine extended-release tablets?
Active ingredient: nevirapine
Inactive ingredients:
Nevirapine extended-release tablets: hypromellose, lactose monohydrate and sodium stearyl fumarate
Manufactured for: Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc., Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Manufactured by: Mylan Laboratories Limited, Hyderabad — 500 096, India
For more information, call Mylan at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX).
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.Manufactured by:
Mylan Laboratories Limited
Hyderabad — 500 096, India
75069725
Revised: 10/2019
MXA:NEV1:R6 -
Severe liver problems. Some people taking nevirapine may develop severe liver problems that can lead to liver failure and the need for a liver transplant, or death. If you have liver problems you may get a rash.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 mg
NDC: 0378-6950-77
Nevirapine
Extended-Release
Tablets, USP
100 mgPHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.Rx only 90 Tablets
Each tablet contains:
Nevirapine, USP 100 mgUsual Dosage: See accompanying
prescribing information.Tablets must be swallowed whole and
must not be chewed, crushed, or divided.Keep this and all medication out of
the reach of children.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See
USP Controlled Room Temperature.]Manufactured for:
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.Made in India
Mylan.com
RMXA6950MM2
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant
container as defined in the USP
using a child-resistant closure.Keep container tightly closed.
Code No.: MH/DRUGS/AD/089
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 400 mg
NDC: 0378-4890-93
Nevirapine
Extended-Release
Tablets, USP
400 mgPHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.Rx only 30 Tablets
Each tablet contains:
Nevirapine, USP 400 mgUsual Dosage: See accompanying
prescribing information.Tablets must be swallowed whole and
must not be chewed, crushed, or divided.Keep this and all medication out of
the reach of children.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See
USP Controlled Room Temperature.]Manufactured for:
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.Made in India
Mylan.com
RMXA4890H2
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant
container as defined in the USP
using a child-resistant closure.Keep container tightly closed.
Code No.: MH/DRUGS/AD/089
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NEVIRAPINE
nevirapine tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0378-6950 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NEVIRAPINE (UNII: 99DK7FVK1H) (NEVIRAPINE - UNII:99DK7FVK1H) NEVIRAPINE 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM STEARYL FUMARATE (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code M;N100 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0378-6950-77 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/09/2015 10/31/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206271 11/09/2015 10/31/2019 NEVIRAPINE
nevirapine tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0378-4890 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NEVIRAPINE (UNII: 99DK7FVK1H) (NEVIRAPINE - UNII:99DK7FVK1H) NEVIRAPINE 400 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM STEARYL FUMARATE (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code M;N400 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0378-4890-93 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/29/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA205651 10/29/2014 Labeler - Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. (059295980)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.