CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM tablet
CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Aurolife Pharma LLC, APL HEALTHCARE LIMITED. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS; ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION; and DEPENDENCE AND WITHDRAWAL REACTIONS
- Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
- The use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing clorazepate dipotassium and throughout out treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (See WARNINGS).
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of clorazepate dipotassium after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue clorazepate dipotassium or reduce the dosage (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and WARNINGS).
-
DESCRIPTION
Chemically, clorazepate dipotassium is a benzodiazepine. The empirical formula is C16H11ClK2N2O4; the molecular weight is 408.92; 1H-1, 4 Benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid, 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-, potassium salt compound with potassium hydroxide (1:1) and the structural formula may be represented as follows:
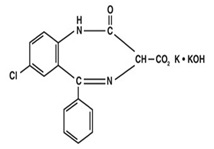
The compound occurs as a fine, white or light yellow crystalline powder. It is insoluble in the common organic solvents, but very soluble in water. Aqueous solutions are unstable, clear, light yellow, and alkaline.
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets, USP contain 3.75 mg, 7.5 mg or 15 mg of clorazepate dipotassium, USP for oral administration.
Inactive ingredients for clorazepate dipotassium tablets: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium oxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, potassium carbonate, sodium chloride and sodium lauryl sulfate. The 3.75 mg tablets also contain FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake and the 7.5 mg tablets also contain FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake. -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacologically, clorazepate dipotassium has the characteristics of the benzodiazepines. It has depressant effects on the central nervous system. The primary metabolite, nordiazepam, quickly appears in the blood stream. The serum half-life is about 2 days. The drug is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine.
Studies in healthy men have shown that clorazepate dipotassium has depressant effects on the central nervous system. Prolonged administration of single daily doses as high as 120 mg was without toxic effects. Abrupt cessation of high doses was followed in some patients by nervousness, insomnia, irritability, diarrhea, muscle aches, or memory impairment.
Since orally administered clorazepate dipotassium is rapidly decarboxylated to form nordiazepam, there is essentially no circulating parent drug. Nordiazepam, the primary metabolite, quickly appears in the blood and is eliminated from the plasma with an apparent half-life of about 40 to 50 hours. Plasma levels of nordiazepam increase proportionally with clorazepate dipotassium dose and show moderate accumulation with repeated administration. The protein binding of nordiazepam in plasma is high (97 to 98%).
Within 10 days after oral administration of a 15 mg (50 µCi) dose of 14C-clorazepate dipotassium to two volunteers, 62 to 67% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine and 15 to 19% was eliminated in the feces. Both subjects were still excreting measurable amounts of radioactivity in the urine (about 1% of the 14C-dose) on day ten.
Nordiazepam is further metabolized by hydroxylation. The major urinary metabolite is conjugated oxazepam (3-hydroxynordiazepam), and smaller amounts of conjugated p-hydroxynordiazepam and nordiazepam are also found in the urine.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the management of partial seizures.
The effectiveness of clorazepate dipotassium tablets in long-term management of anxiety, that is, more than 4 months, has not been assessed by systematic clinical studies. Long-term studies in epileptic patients, however, have shown continued therapeutic activity. The physician should reassess periodically the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are indicated for the symptomatic relief of acute alcohol withdrawal.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids: Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. If a decision is made to prescribe clorazepate dipotassium concomitantly with opioids, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use, and follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of clorazepate dipotassium than indicated in the absence of an opioid and titrate based on clinical response. If an opioid is initiated in a patient already taking clorazepate dipotassium, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid and titrate based upon clinical response.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when clorazepate dipotassium is used with opioids. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use with the opioid have been determined (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction: The use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium, exposes users to the risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines often (but not always) involve the use of doses greater than the maximum recommended dosage and commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes, including respiratory depression, overdose, or death (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Abuse).
Before prescribing clorazepate dipotassium and throughout treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (e.g., using a standardized screening tool). Use of clorazepate dipotassium, particularly in patients at elevated risk, necessitates counseling about the risks and proper use of clorazepate dipotassium along with monitoring for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction. Prescribe the lowest effective dosage; avoid or minimize concomitant use of CNS depressants and other substances associated with abuse, misuse, and addiction (e.g., opioid analgesics, stimulants); and advise patients on the proper disposal of unused drug. If a substance use disorder is suspected, evaluate the patient and institute (or refer them for) early treatment, as appropriate.
Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions: To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue clorazepate dipotassium or reduce the dosage (a patient-specific plan should be used to taper the dose) (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation of Dosage Reduction of Clorazepate Dipotassium).
Patients at an increased risk of withdrawal adverse reactions after benzodiazepine discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction include those who take higher dosages, and those who have had longer durations of use.
Acute Withdrawal Reactions
The continued use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of clorazepate dipotassium after continued use, or administration of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening (e.g., seizures) (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Dependence).
Protracted Withdrawal Syndrome
In some cases, benzodiazepine users have developed a protracted withdrawal syndrome with withdrawal symptoms lasting weeks to more than 12 months (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Use in Depressive Neuroses or Psychotic Reactions: Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are not recommended for use in depressive neuroses or in psychotic reactions.
Use in Children: Because of the lack of sufficient clinical experience, clorazepate dipotassium tablets are not recommended for use in patients less than 9 years of age.
Interference with Psychomotor Performance: Patients taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring mental alertness, such as operating dangerous machinery including motor vehicles.
Concomitant Use with CNS Depressants: Since clorazepate dipotassium has a central nervous system depressant effect, patients should be advised against the simultaneous use of other CNS depressant drugs, and cautioned that the effects of alcohol may be increased.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including clorazepate dipotassium, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Table 1 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 1: Risk by indication for antiepileptic drugs in the pooled analysis Indication
Placebo Patients
with Events Per
1000 Patients
Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients
Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients
Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients
Epilepsy
1.0
3.4
3.5
2.4
Psychiatric
5.7
8.5
1.5
2.9
Other
1.0
1.8
1.9
0.9
Total
2.4
4.3
1.8
1.9
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing clorazepate dipotassium or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self- harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome: Use of clorazepate dipotassium late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy). Monitor neonates exposed to clorazepate dipotassium during pregnancy or labor for signs of sedation and monitor neonates exposed to clorazepate dipotassium during pregnancy for signs of withdrawal; manage these neonates accordingly.
-
PRECAUTIONS
In those patients in which a degree of depression accompanies the anxiety, suicidal tendencies may be present and protective measures may be required. The least amount of drug that is feasible should be available to the patient.
Patients taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets for prolonged periods should have blood counts and liver function tests periodically. The usual precautions in treating patients with impaired renal or hepatic function should also be observed.
In elderly or debilitated patients, the initial dose should be small, and increments should be made gradually, in accordance with the response of the patient, to preclude ataxia or excessive sedation.
Information for Patients
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of potentially fatal respiratory depression and sedation when clorazepate dipotassium is used with opioids and not to use such drugs concomitantly unless supervised by a health care provider. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use with the opioid have been determined (see WARNINGS, Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction: Inform patients that the use of clorazepate dipotassium, even at recommended dosages, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose and death, especially when used in combination with other medications (e.g., opioid analgesics), alcohol, and/or illicit substances. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of benzodiazepine abuse, misuse, and addiction; to seek medical help if they develop these signs and/or symptoms; and on the proper disposal of unused drug (see WARNINGS and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Withdrawal Reactions: Inform patients that the continued use of clorazepate dipotassium may lead to clinically significant physical dependence and that abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of clorazepate dipotassium may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. Inform patients that in some cases, patients taking benzodiazepines have developed a protracted withdrawal syndrome with withdrawal symptoms lasting weeks to more than 12 months. Instruct patients that discontinuation or dosage reduction of clorazepate dipotassium may require a slow taper (see WARNINGS and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Suicidal Thinking and Behavior: Patients, their caregivers, and families should be counseled that AEDs, including clorazepate dipotassium, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Pregnancy: Advise pregnant females that use of clorazepate dipotassium late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in newborns (see Warnings, Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome and Precautions, Pregnancy). Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant.
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to clorazepate dipotassium during pregnancy (see Precautions, Pregnancy).
Nursing: Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with clorazepate dipotassium (see Precautions, Nursing Mothers).DRUG INTERACTIONS
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Limit dosage and duration of concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids, and monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
If clorazepate dipotassium is to be combined with other drugs acting on the central nervous system, careful consideration should be given to the pharmacology of the agents to be employed. Animal experience indicates that clorazepate dipotassium prolongs the sleeping time after hexobarbital or after ethyl alcohol, increases the inhibitory effects of chlorpromazine, but does not exhibit monoamine oxidase inhibition. Clinical studies have shown increased sedation with concurrent hypnotic medications. The actions of the benzodiazepines may be potentiated by barbiturates, narcotics, phenothiazines, monoamine oxidase inhibitors or other antidepressants.
If clorazepate dipotassium tablets are used to treat anxiety associated with somatic disease states, careful attention must be paid to possible drug interaction with concomitant medication.
In bioavailability studies with normal subjects, the concurrent administration of antacids at therapeutic levels did not significantly influence the bioavailability of clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to psychiatric medications, including clorazepate dipotassium, during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychiatric Medications at 1-866-961-2388 or visiting online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/pregnancyregistry/.
Risk Summary
Neonates born to mothers using benzodiazepines late in pregnancy have been reported to experience symptoms of sedation and/or neonatal withdrawal (see WARNINGS: Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome and Clinical Considerations). Available data from published observational studies of pregnant women exposed to benzodiazepines do not report a clear association with benzodiazepines and major birth defects (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Benzodiazepines cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression, hypotonia, and sedation in neonates. Monitor neonates exposed to clorazepate dipotassium during pregnancy or labor for signs of sedation, respiratory depression, hypotonia, and feeding problems. Monitor neonates exposed to clorazepate dipotassium during pregnancy for signs of withdrawal. Manage these neonates accordingly (see WARNINGS: Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome).
Data
Human Data
Published data from observational studies on the use of benzodiazepines during pregnancy do not report a clear association with benzodiazepines and major birth defects. Although early studies reported an increased risk of congenital malformations with diazepam and chlordiazepoxide, there was no consistent pattern noted. In addition, the majority of more recent case-control and cohort studies of benzodiazepine use during pregnancy, which were adjusted for confounding exposures to alcohol, tobacco and other medications, have not confirmed these findings.
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of clorazepate to pregnant rats and rabbits at doses up to 150 and 15 mg/kg, respectively, did not cause fetal toxicities or malformation. However, the sedative effects of high dose clorazepate interfered with the maternal care of the offspring.
Nursing Mothers:
Risk Summary
Clorazepate and its active metabolite, nordiazepam, are present in breast milk. There are reports of sedation, poor feeding and poor weight gain in infants exposed to benzodiazepines through breast milk. The effects of clorazepate on milk production are unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including sedation and withdrawal symptoms in infants, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with clorazepate dipotassium.
Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of clorazepate dipotassium were not adequate to determine whether subjects aged 65 and over respond differently than younger subjects. Elderly or debilitated patients may be especially sensitive to the effects of all benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium. In general, elderly or debilitated patients should be started on lower doses of clorazepate dipotassium and observed closely, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Dose adjustments should also be made slowly, and with more caution in this patient population (see PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The side effect most frequently reported was drowsiness. Less commonly reported (in descending order of occurrence) were: dizziness, various gastrointestinal complaints, nervousness, blurred vision, dry mouth, headache, and mental confusion. Other side effects included insomnia, transient skin rashes, fatigue, ataxia, genitourinary complaints, irritability, diplopia, depression, tremor, and slurred speech.
There have been reports of abnormal liver and kidney function tests and of decrease in hematocrit.
Decrease in systolic blood pressure has been observed.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets contains clorazepate, a Schedule IV controlled substance.
Abuse
Clorazepate dipotassium is a benzodiazepine and a CNS depressant with a potential for abuse and addiction. Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects. Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a health care provider or for whom it was not prescribed. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence. Even taking benzodiazepines as prescribed may put patients at risk for abuse and misuse of their medication. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines may lead to addiction.
Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines often (but not always) involve the use of doses greater than the maximum recommended dosage and commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes, including respiratory depression, overdose, or death. Benzodiazepines are often sought by individuals who abuse drugs and other substances, and by individuals with addictive disorders (see WARNINGS: Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction).
The following adverse reactions have occurred with benzodiazepine abuse and/or misuse: abdominal pain, amnesia, anorexia, anxiety, aggression, ataxia, blurred vision, confusion, depression, disinhibition, disorientation, dizziness, euphoria, impaired concentration and memory, indigestion, irritability, muscle pain, slurred speech, tremors, and vertigo.
The following severe adverse reactions have occurred with benzodiazepine abuse and/or misuse: delirium, paranoia, suicidal ideation and behavior, seizures, coma, breathing difficulty, and death. Death is more often associated with polysubstance use (especially benzodiazepines with other CNS depressants such as opioids and alcohol).
Dependence
Physical Dependence
Clorazepate dipotassium may produce physical dependence from continued therapy. Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of benzodiazepines or administration of flumazenil, a benzodiazepine antagonist, may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, including seizures, which can be life- threatening. Patients at an increased risk of withdrawal adverse reactions after benzodiazepine discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction include those who take higher dosages (i.e., higher and/or more frequent doses) and those who have had longer durations of use (see WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions).
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue clorazepate dipotassium or reduce the dosage (see DOSAGE and ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of Clorazepate Dipotassium and WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions).
Acute Withdrawal Signs and Symptoms
Acute withdrawal signs and symptoms associated with benzodiazepines have included abnormal involuntary movements, anxiety, blurred vision, depersonalization, depression, derealization, dizziness, fatigue, gastrointestinal adverse reactions (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, decreased appetite), headache, hyperacusis, hypertension, irritability, insomnia, memory impairment, muscle pain and stiffness, panic attacks, photophobia, restlessness, tachycardia, and tremor. More severe acute withdrawal signs and symptoms, including life-threatening reactions, have included catatonia, convulsions, delirium tremens, depression, hallucinations, mania, psychosis, seizures and suicidality.
Protracted Withdrawal Syndrome
Protracted withdrawal syndrome associated with benzodiazepines is characterized by anxiety, cognitive impairment, depression, insomnia, formication, motor symptoms (e.g., weakness, tremor, muscle twitches), paresthesia, and tinnitus that persists beyond 4 to 6 weeks after initial benzodiazepine withdrawal. Protracted withdrawal symptoms may last weeks to more than 12 months. As a result, there may be difficulty in differentiating withdrawal symptoms from potential re-emergence or continuation of symptoms for which the benzodiazepine was being used.
Tolerance
Tolerance to clorazepate dipotassium may develop from continued therapy. Tolerance is a physiological state characterized by a reduced response to a drug after repeated administration (i.e., a higher dose of a drug is required to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose). Tolerance to the therapeutic effect of clorazepate dipotassium may develop; however, little tolerance develops to the amnestic reactions and other cognitive impairments caused by benzodiazepines.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of benzodiazepines is characterized by central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild to moderate cases, symptoms can include drowsiness, confusion, dysarthria, lethargy, hypnotic state, diminished reflexes, ataxia, and hypotonia. Rarely, paradoxical or disinhibitory reactions (including agitation, irritability, impulsivity, violent behavior, confusion, restlessness, excitement, and talkativeness) may occur. In severe overdosage cases, patients may develop respiratory depression and coma. Overdosage of benzodiazepines in combination with other CNS depressants (including alcohol and opioids) may be fatal (see WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions). Markedly abnormal (lowered or elevated) blood pressure, heart rate, or respiratory rate raise the concern that additional drugs and/or alcohol are involved in the overdosage.
In managing benzodiazepine overdosage, employ general supportive measures, including intravenous fluids and airway management. Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine receptor antagonist indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in the management of benzodiazepine overdosage, can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions, including seizures, particularly in the context of mixed overdosage with drugs that increase seizure risk (e.g., tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants) and in patients with long-term benzodiazepine use and physical dependency. The risk of withdrawal seizures with flumazenil use may be increased in patients with epilepsy. Flumazenil is contraindicated in patients who have received a benzodiazepine for control of a potentially life-threatening condition (e.g., status epilepticus). If the decision is made to use flumazenil, it should be used as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, supportive management of benzodiazepine overdosage. See the flumazenil injection Prescribing Information.
Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For the Symptomatic Relief of Anxiety: Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are administered orally in divided doses. The usual daily dose is 30 mg. The dose should be adjusted gradually within the range of 15 to 60 mg daily in accordance with the response of the patient. In elderly or debilitated patients it is advisable to initiate treatment at a daily dose of 7.5 to 15 mg.
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets may also be administered in a single dose daily at bedtime; the recommended initial dose is 15 mg. After the initial dose, the response of the patient may require adjustment of subsequent dosage. Lower doses may be indicated in the elderly patient. Drowsiness may occur at the initiation of treatment and with dosage increment.
For the Symptomatic Relief of Acute Alcohol Withdrawal:
The following dosage schedule is recommended:
1st 24 hours
(Day 1)
30 mg initially; followed by 30 to 60 mg in divided doses
2nd 24 hours
(Day 2)
45 to 90 mg in divided doses
3rd 24 hours
(Day 3)
22.5 to 45 mg in divided doses
Day 4
15 to 30 mg in divided doses
Thereafter, gradually reduce the daily dose to 7.5 to 15 mg. Discontinue drug therapy as soon as patient’s condition is stable.
The maximum recommended total daily dose is 90 mg. Avoid excessive reductions in the total amount of drug administered on successive days.
As an Adjunct to Antiepileptic Drugs: In order to minimize drowsiness, the recommended initial dosages and dosage increments should not be exceeded.
Adults: The maximum recommended initial dose in patients over 12 years old is 7.5 mg three times a day. Dosage should be increased by no more than 7.5 mg every week and should not exceed 90 mg/day.
Children (9 to 12 years): The maximum recommended initial dose is 7.5 mg two times a day. Dosage should be increased by no more than 7.5 mg every week and should not exceed 60 mg/day.
Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of Clorazepate Dipotassium Tablets: To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue clorazepate dipotassium tablets or reduce the dosage. If a patient develops withdrawal reactions, consider pausing the taper or increasing the dosage to the previous tapered dosage level. Subsequently decrease the dosage more slowly (see WARNINGS and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
-
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY AND TOXICOLOGY
Studies in rats and monkeys have shown a substantial difference between doses producing tranquilizing, sedative and toxic effects. In rats, conditioned avoidance response was inhibited at an oral dose of 10 mg/kg; sedation was induced at 32 mg/kg; the LD50 was 1320 mg/kg. In monkeys aggressive behavior was reduced at an oral dose of 0.25 mg/kg; sedation (ataxia) was induced at 7.5 mg/kg; the LD50 could not be determined because of the emetic effect of large doses, but the LD50 exceeds 1600 mg/kg.
Twenty-four dogs were given clorazepate dipotassium orally in a 22-month toxicity study; doses up to 75 mg/kg were given. Drug-related changes occurred in the liver; weight was increased and cholestasis with minimal hepatocellular damage was found, but lobular architecture remained well preserved.
Eighteen rhesus monkeys were given oral doses of clorazepate dipotassium from 3 to 36 mg/kg daily for 52 weeks. All treated animals remained similar to control animals.
Although total leucocyte count remained within normal limits it tended to fall in the female animals on the highest doses.
Examination of all organs revealed no alterations attributable to clorazepate dipotassium. There was no damage to liver function or structure.
Reproduction Studies: In fertility studies, clorazepate did not alter the fertility indices or reproductive capacity of adult animals (see Pregnancy). -
HOW SUPPLIED
Clorazepate Dipotassium Tablets, USP are available containing 3.75 mg, 7.5 mg or 15 mg of clorazepate dipotassium, USP.
The 3.75 mg tablets are mottled blue colored, round, flat face tablets, debossed with "CL" and "11" separated by score-line on one side and plain on other side. They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC: 13107-282-01
Bottles of 500 NDC: 13107-282-05
The 7.5 mg tablets are mottled peach colored, round, flat face tablets, debossed with "CL" and "14" separated by score-line on one side and plain on other side.They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC: 13107-283-01
Bottles of 500 NDC: 13107-283-05
The 15 mg tablets are mottled white to off white colored, round, flat face tablets, debossed with "CL" and "17" separated by score-line on one side and plain on other side. They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC: 13107-284-01
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light and moisture.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
PHARMACIST: Dispense a Medication Guide with each prescription.
Dispense with Medication Guide available at:www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, India
Revised: 09/2023
Dispense with Medication Guide available at:www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
Clorazepate Dipotassium Tablets, USP CIV
(klor azʹ e pate dyeʺ poe tasʹ ee um)
What is the most important information I should know about clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
-
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are a benzodiazepine medicine. Taking benzodiazepines with opioid medicines, alcohol, or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, breathing problems (respiratory depression), coma and death. Get emergency help right away if any of the following happens:
- shallow or slowed breathing
- breathing stops (which may lead to the heart stopping)
- excessive sleepiness (sedation)
-
Risk of abuse, misuse, and addiction. There is a risk of abuse, misuse, and addiction with benzodiazepines including clorazepate dipotassium tablets which can lead to overdose and serious side effects including coma and death.
- Serious side effects including coma and death have happened in people who have abused or misused benzodiazepines, including clorazepate dipotassium tablets. These serious side effects may also include delirium, paranoia, suicidal thoughts or actions, seizures, and difficulty breathing. Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you get any of these serious side effects.
- You can develop an addiction even if you take clorazepate dipotassium tablets as prescribed by your healthcare provider
- Take clorazepate dipotassium tablets exactly as your healthcare provider prescribed.
- Do not share your clorazepate dipotassium tablets with other people.
- Keep clorazepate dipotassium tablets in a safe place and away from children.
-
Physical dependence and withdrawal reactions. Clorazepate dipotassium tablets can cause physical dependence and withdrawal reactions,.
- Do not suddenly stop taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets. Stopping clorazepate dipotassium tablets suddenly can cause serious and life-threatening side effects, including, unusual movements, responses, or expressions, seizures, sudden and severe mental or nervous system changes, depression, seeing or hearing things that others do not see or hear, an extreme increase in activity or talking, losing touch with reality, and suicidal thoughts or actions. Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you get any of these symptoms.
- Some people who suddenly stop benzodiazepines have symptoms that can last for several weeks to more than 12 months, including, anxiety, trouble remembering, learning, or concentrating, depression, problems sleeping, feeling like insects are crawling under your skin, weakness, shaking, muscle twitching, burning or prickling feeling in your hands, arms, legs or feet, and ringing in your ears.
- Physical dependence is not the same as drug addiction. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the differences between physical dependence and drug addiction.
- Do not take more clorazepate dipotassium tablets than prescribed or take clorazepate dipotassium tablets for longer than prescribed.
- Like other antiepileptic medicines, clorazepate dipotassium tablets may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- feeling agitated or restless
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- attempts to commit suicide
- panic attacks
- acting on dangerous impulses
- new or worse depression
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- new or worse anxiety
- new or worse irritability
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
What are clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are a prescription medicine used:
- to treat anxiety disorders
- with other medicines to treat partial seizures
- to treat the symptoms of sudden alcohol withdrawal
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are a federally controlled substance (C-IV) because it contains clorazepate dipotassium that can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep clorazepate dipotassium tablets in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away clorazepate dipotassium tablets may harm others, and is against the law. Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or street drugs.
It is not known if clorazepate dipotassium tablets are safe and effective in children less than 9 years of age.
Do not take clorazepate dipotassium tablets if you:
- are allergic to clorazepate dipotassium or any of the ingredients in clorazepate dipotassium tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
Before you take clorazepate dipotassium tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems
- have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- have a history of abnormal thinking and behavior (psychotic reactions)
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- Taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets late in pregnancy may cause your baby to have symptoms of sedation (breathing problems, sluggishness, low muscle tone), and/or withdrawal symptoms (jitteriness, irritability, restlessness, shaking, excessive crying, feeding problems).
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
- There is a pregnancy registry for women who take clorazepate dipotassium tablets during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. If you become pregnant during treatment with clorazepate dipotassium tablets, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychiatric Medications. You can register by calling 1-866-961-2388-or visiting https://womensmentalhealth.org/pregnancyregistry/.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Clorazepate dipotassium passes into breast milk.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
- Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
Taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well clorazepate dipotassium tablets or the other medicines work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
How should I take clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
- Take clorazepate dipotassium tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much clorazepate dipotassium tablets to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed. Do not change your dose of clorazepate dipotassium tablets without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not stop taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping clorazepate dipotassium tablets suddenly can cause serious problems.
- If you take too much clorazepate dipotassium tablets, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets may cause serious side effects, including: See “What is the most important information I should know about clorazepate dipotassium tablets?”
- Clorazepate dipotassium tablets can make you sleepy or dizzy and can slow your thinking and motor skills. Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how clorazepate dipotassium tablets affects you.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other drugs that may make you sleepy or dizzy while taking clorazepate dipotassium tablets without first talking to your healthcare provider. When taken with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness, clorazepate dipotassium tablets may make your sleepiness or dizziness much worse.
The most common side effects of clorazepate dipotassium tablets include:
- drowsiness
- upset stomach
- dry mouth
- dizziness
- blurred vision
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
- Store clorazepate dipotassium tablets at room temperature between 68ºF to 77ºF (20ºC to 25ºC).
- Keep clorazepate dipotassium tablets in a tightly closed container, dry, and out of the light.
- Keep clorazepate dipotassium tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of clorazepate dipotassium tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use-clorazepate dipotassium tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give clorazepate dipotassium tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about clorazepate dipotassium tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in clorazepate dipotassium tablets?
Active ingredient: clorazepate dipotassium
Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium oxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, potassium carbonate, sodium chloride and sodium lauryl sulfate. The 3.75 mg tablets also contain FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake and the 7.5 mg tablets also contain FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, India
Revised: 09/2023 -
Clorazepate dipotassium tablets are a benzodiazepine medicine. Taking benzodiazepines with opioid medicines, alcohol, or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, breathing problems (respiratory depression), coma and death. Get emergency help right away if any of the following happens:
-
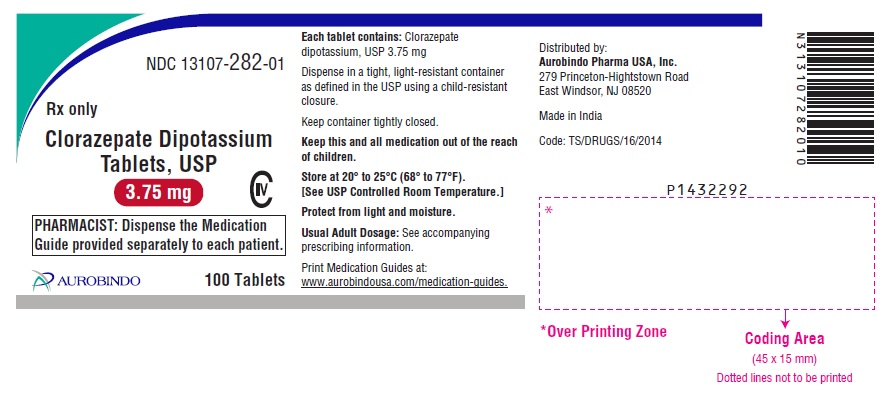
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 3.75 mg (100 Tablets Bottle)
NDC: 13107-282-01
Rx only
Clorazepate Dipotassium
Tablets, USP
3.75 mg CIVPHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication
Guide provided separately to each patient.AUROBINDO 100 Tablets
-
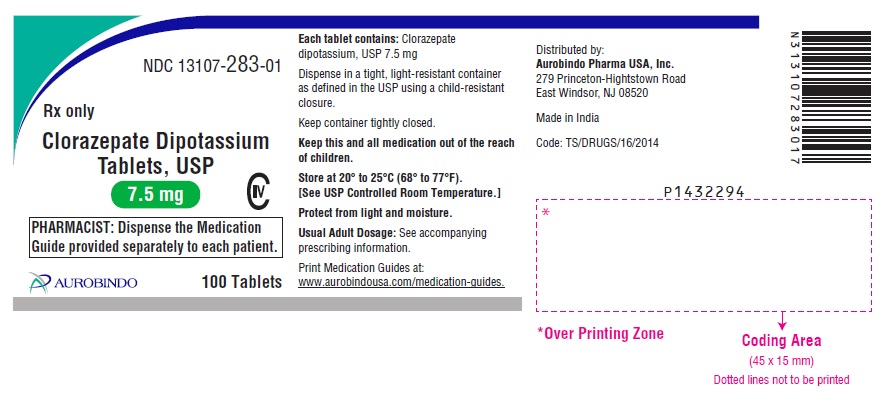
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7.5mg (100 Tablets Bottle)
NDC: 13107-283-01
Rx only
Clorazepate Dipotassium
Tablets, USP
7.5 mg CIV
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication
Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO 100 Tablets
-
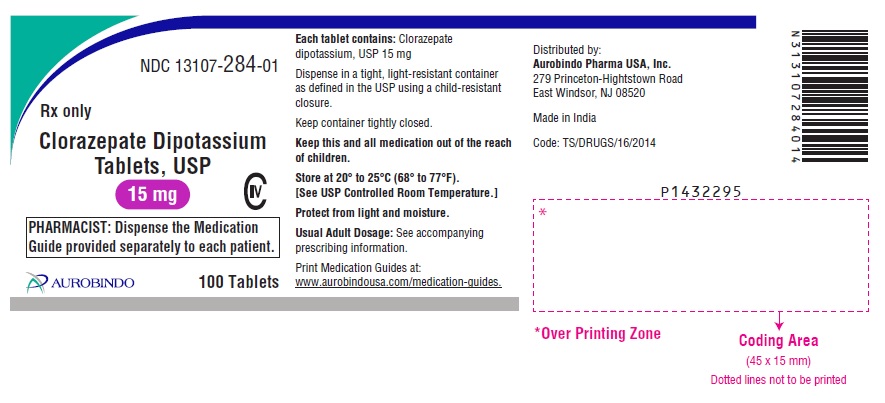
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7.5 mg (100 Tablets Bottle)
NDC: 13107-284-01
Rx only
Clorazepate Dipotassium
Tablets, USP
15 mg CIV
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication
Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO 100 Tablets
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM
clorazepate dipotassium tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 13107-282 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIV Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM (UNII: 63FN7G03XY) (CLORAZEPIC ACID - UNII:D51WO0G0L4) CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM 3.75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POTASSIUM CARBONATE (UNII: BQN1B9B9HA) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code CL;11 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 13107-282-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/23/2023 2 NDC: 13107-282-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/23/2023 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA071858 09/23/2023 CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM
clorazepate dipotassium tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 13107-283 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIV Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM (UNII: 63FN7G03XY) (CLORAZEPIC ACID - UNII:D51WO0G0L4) CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM 7.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POTASSIUM CARBONATE (UNII: BQN1B9B9HA) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (peach) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code CL;14 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 13107-283-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/23/2023 2 NDC: 13107-283-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/23/2023 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA071858 09/23/2023 CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM
clorazepate dipotassium tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 13107-284 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIV Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM (UNII: 63FN7G03XY) (CLORAZEPIC ACID - UNII:D51WO0G0L4) CLORAZEPATE DIPOTASSIUM 15 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POTASSIUM CARBONATE (UNII: BQN1B9B9HA) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off white) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code CL;17 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 13107-284-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/23/2023 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA071858 09/23/2023 Labeler - Aurolife Pharma LLC (829084461) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations APL HEALTHCARE LIMITED 650844777 ANALYSIS(13107-282, 13107-283, 13107-284) , MANUFACTURE(13107-282, 13107-283, 13107-284)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.