LUNSUMIO VELO- mosunetuzumab injection
Lunsumio Velo by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Lunsumio Velo by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Genentech, Inc., Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Roche Diagnostics, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Genentech, Inc. (Hillsboro), Genentech, Inc. (Oceanside). Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LUNSUMIO VELO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LUNSUMIO VELO.
LUNSUMIO VELO™ (mosunetuzumab-axgb) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LUNSUMIO VELO. Initiate treatment with the LUNSUMIO VELO step-up dosing schedule to reduce the risk of CRS. Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until CRS resolves or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.1, 2.4, 5.1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LUNSUMIO VELO is a bispecific CD20-directed CD3 T-cell engager indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- LUNSUMIO VELO and LUNSUMIO have different dosage and route of administration instructions. Administer LUNSUMIO VELO only as a subcutaneous injection. (2.1)
- Premedicate to reduce risk of CRS. (2.3, 5.1)
- Recommended dosage for LUNSUMIO VELO for subcutaneous injection (2.2):
Day of Treatment * Subcutaneous Dose of LUNSUMIO VELO - * Cycle length = 21 days
Cycle 1 Day 1 5 mg Day 8 45 mg Day 15 45 mg Cycles 2+ Day 1 45 mg See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome: Can cause serious and life-threatening neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicity during treatment; withhold or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.2)
- Infections: Can cause serious or fatal infections. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection, including opportunistic infections, and treat as needed. (5.3)
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Can cause serious or fatal reactions. For suspected cases, interrupt LUNSUMIO VELO and evaluate and treat promptly. (5.4)
- Cytopenias: Monitor complete blood cell counts during treatment. (5.5)
- Tumor Flare: Can cause serious tumor flare reactions. Monitor patients at risk for complications of tumor flare. (5.6)
- Risk of Medication Errors with Incorrect Product Use: Ensure that the correct formulation is being prescribed, dispensed, and administered. (5.7)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.8, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) are injection site reactions, fatigue, rash, CRS, COVID-19 infection, musculoskeletal pain, and diarrhea. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 15%) are decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, and increased uric acid. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Follicular Lymphoma
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Recommended Premedication
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome
5.3 Infections
5.4 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
5.5 Cytopenias
5.6 Tumor Flare
5.7 Risk of Medication Errors with Incorrect Product Use
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LUNSUMIO VELO. Initiate treatment with the LUNSUMIO VELO step-up dosing schedule to reduce the risk of CRS. Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until CRS resolves or permanently discontinue based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 and 2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Follicular Lymphoma
LUNSUMIO VELO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
-
LUNSUMIO VELO and LUNSUMIO have different dosage and administration instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- LUNSUMIO VELO is for subcutaneous use only.
- Check the product label to ensure that the correct formulation (LUNSUMIO VELO or LUNSUMIO) is being prescribed and administered.
- Do not substitute LUNSUMIO VELO for or with LUNSUMIO.
- Administer LUNSUMIO VELO to well-hydrated patients.
- Premedicate before each dose in Cycle 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- LUNSUMIO VELO should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional with appropriate medical support to manage severe reactions such as CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 and 5.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage for LUNSUMIO VELO subcutaneous injection is presented in Table 1.
Administer for 8 cycles unless patients experience unacceptable toxicity or disease progression.
For patients who achieve a complete response, no further treatment beyond 8 cycles is required. For patients who achieve a partial response or have stable disease in response to treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO after 8 cycles, an additional 9 cycles of treatment (17 cycles total) should be administered, unless a patient experiences unacceptable toxicity or disease progression.
Table 1. Recommended Dose and Schedule of LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection (21-Day Treatment Cycles) Day of Treatment Subcutaneous Dose of LUNSUMIO VELO Cycle 1 Day 1 5 mg Day 8 45 mg Day 15 45 mg Cycles 2+ Day 1 45 mg Table 2. Recommendations for Restarting Therapy with LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection After Dose Delay Last Subcutaneous Dose Administered Time Since Last Dose Administered Action for Next Subcutaneous Dose(s) - * Administer premedication as per Cycle 1.
5 mg
Cycle 1 Day 11 week to 2 weeks Administer 45 mg (Cycle 1 Day 8)*, then resume the planned treatment schedule. Greater than 2 weeks Repeat 5 mg (Cycle 1 Day 1)*, then administer 45 mg (Cycle 1 Day 8)* and resume the planned treatment schedule. 45 mg
Cycle 1 Day 81 week to less than 6 weeks Administer 45 mg (Cycle 1 Day 15)*, then resume the planned treatment schedule. Greater than or equal to 6 weeks Repeat 5 mg*, then administer 45 mg (Cycle 1 Day 15)* 7 days later and resume the planned treatment schedule. 45 mg
Cycle 1 Day 151 week to less than 6 weeks Administer 45 mg (Cycle 2 Day 1), then resume the planned treatment schedule. Greater than or equal to 6 weeks Repeat 5 mg (Cycle 2 Day 1)*, then administer 45 mg (Cycle 2 Day 8)* followed by 45 mg on Day 1 of subsequent cycles. 45 mg
Cycle 2 onwards3 weeks to less than 6 weeks Administer 45 mg, then resume the planned treatment schedule. Greater than or equal to 6 weeks Repeat 5 mg* on Day 1 during the next cycle, then administer 45 mg* on Day 8, followed by 45 mg on Day 1 of subsequent cycles. 2.3 Recommended Premedication
Premedications to reduce the risk of CRS are outlined in Table 3 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Table 3. Premedication to be Administered Prior to LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection Treatment Cycle Patients Requiring Premedication Premedication Dosage - * Antihistamine and antipyretic premedications are optional in all cycles.
Cycle 1 All patients Corticosteroid Dexamethasone 20 mg (preferred) oral or intravenous or methylprednisolone 80 mg oral or intravenous Antihistamine* Diphenhydramine hydrochloride 50 mg to 100 mg or equivalent oral or intravenous antihistamine Antipyretic* Oral acetaminophen (500 mg to 1,000 mg) Cycles 2+ Patients who experienced any grade CRS with the previous dose Corticosteroid Dexamethasone 20 mg (preferred) oral or intravenous or methylprednisolone 80 mg oral or intravenous Antihistamine* Diphenhydramine hydrochloride 50 mg to 100 mg or equivalent oral or intravenous antihistamine Antipyretic* Oral acetaminophen (500 mg to 1,000 mg) 2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
See Tables 4 and 5 for the recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity (ICANS). See Table 6 for the recommended dosage modifications for other adverse reactions following administration of LUNSUMIO VELO.
Dosage Modifications for Cytokine Release Syndrome
Identify CRS based on clinical presentation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Evaluate for and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia, and hypotension.
If CRS is suspected, withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until CRS resolves, manage according to the recommendations in Table 4 and per current practice guidelines. Administer supportive therapy for CRS, which may include intensive care for severe or life-threatening CRS.
Table 4. Recommendations for Management of Cytokine Release Syndrome with LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Administration Grade* Presenting Symptoms Actions† - * Based on American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) 2019 grading for CRS.
- † If CRS is refractory to management, consider other causes including hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
- ‡ Premedication may mask fever, therefore if clinical presentation is consistent with CRS, follow these management guidelines.
- § Refer to Table 2 for information on restarting LUNSUMIO VELO after dose delays [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- ¶ Refer to Table 3 for additional information on premedication.
- # Low-flow oxygen defined as oxygen delivered at < 6 L/minute; high-flow oxygen defined as oxygen delivered at ≥ 6 L/minute.
Grade 1 Fever ≥ 100.4°F (38°C)‡ Grade 2 Fever ≥ 100.4°F (38°C)‡ with: - Ensure CRS symptoms are resolved for at least 72 hours prior to the next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.§
Hypotension not requiring vasopressors - Administer premedication¶ prior to next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.
and/or - For the next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO, monitor more frequently and consider hospitalization.
hypoxia requiring low-flow oxygen# by nasal cannula or blow-by. Recurrent Grade 2 CRS - Manage per Grade 3 CRS.
Grade 3 Fever ≥ 100.4°F (38°C)‡ with: - Ensure CRS symptoms are resolved for at least 72 hours prior to the next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.§
Hypotension requiring a vasopressor (with or without vasopressin) - Administer premedication¶ prior to next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.
and/or - For the next dose of LUNSUMIO VELO, monitor more frequently and hospitalize for the next dose.
hypoxia requiring high flow oxygen# by nasal cannula, face mask, non-rebreather mask, or Venturi mask. - If CRS occurred after the 5 mg or 45 mg dose, administer 5 mg as the next dose. Resume treatment schedule after recovery. If the 5 mg dose is tolerated without grade 3 CRS, resume subsequent doses at 45 mg.
Recurrent Grade 3 CRS - Permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO.
- Manage CRS per current practice guidelines and provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care.
Grade 4 Fever ≥ 100.4°F (38°C)‡ with: - Permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO.
- Manage CRS per current practice guidelines and provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care.
Hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (excluding vasopressin) and/or hypoxia requiring oxygen by positive pressure (e.g., CPAP, BiPAP, intubation and mechanical ventilation). Dosage Modifications for Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS
Management recommendations for neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, are summarized in Table 5. At the first sign of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, consider neurology evaluation and withholding of LUNSUMIO VELO based on the type and severity of neurotoxicity. Rule out other causes of neurologic symptoms. Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care.
Table 5. Recommendations for Management of Neurologic Toxicity (including ICANS) Adverse Reaction Severity*,† Actions - * Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE), version 4.0.
- † Based on American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) 2019 grading for ICANS.
- ‡ See Table 2 for recommendations on restarting LUNSUMIO VELO after dose delays [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Neurologic Toxicity*
(including ICANS†)Grade 1 - Continue LUNSUMIO VELO and monitor neurologic toxicity symptoms.
- If ICANS, manage per current practice guidelines.
Grade 2 - Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until neurologic toxicity symptoms improve to Grade 1 or baseline for at least 72 hours.‡
- Provide supportive therapy, and consider neurologic evaluation.
- If ICANS, manage per current practice guidelines.
Grade 3 - Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until neurologic toxicity symptoms improve to Grade 1 or baseline for at least 72 hours.‡
- Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care, and consider neurology evaluation.
- If ICANS, manage per current practice guidelines.
- If recurrence of ICANS, permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO.
- Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care, and consider neurology evaluation.
- If ICANS, manage per current practice guidelines.
Other Adverse Reactions
Table 6. Recommended Dosage Modification for Other Adverse Reactions Adverse Reactions* Severity* Actions - * Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE), version 4.0.
- † See Table 2 for recommendations on restarting LUNSUMIO VELO after dose delays [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] Grades 1 – 4 - Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO in patients with active infection until the infection resolves.†
- For Grade 4, consider permanent discontinuation of LUNSUMIO VELO.
Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] Absolute neutrophil count less than 0.5 × 109/L - Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until absolute neutrophil count is 0.5 × 109/L or higher.†
Other Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 3 or higher - Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO until the toxicity resolves to Grade 1 or baseline.†
- Permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO if a Grade 4 injection site reaction occurs.
2.5 Preparation and Administration
If the LUNSUMIO VELO dose is not administered immediately, refer to "Storage of Prepared Syringe" section below.
- To prevent medication errors, check the vial labels to ensure that the drug being prepared and administered is LUNSUMIO VELO for subcutaneous administration. A peel-off label is provided on the LUNSUMIO VELO Prescribing Information that should be attached to the final prepared syringe. Remove the peel-off label from the Prescribing Information in the LUNSUMIO VELO carton before discarding the carton. Affix the peel-off label to the prepared LUNSUMIO VELO syringe.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if the solution is discolored, or cloudy, or if foreign particles are present.
- Each LUNSUMIO VELO 5 mg/0.5 mL and 45 mg/mL vial are supplied as ready-to-use solution that do not need dilution prior to subcutaneous administration. LUNSUMIO VELO vials are for one-time use in one patient only.
- No incompatibilities between LUNSUMIO VELO and polypropylene or polycarbonate syringe material, stainless-steel transfer and injection needles, and polyethylene or polypropylene syringe closing caps have been observed.
Preparation of the Syringe
- Use aseptic technique to prepare LUNSUMIO VELO.
- Select the appropriate strength vial based on the prescribed dose.
- Withdraw the required volume of LUNSUMIO VELO solution from the vial with a syringe and an appropriately sized transfer needle (18G to 21G recommended). The smallest syringe that can accurately deliver the injection volume should be used. Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
- Remove the transfer needle and attach an appropriately sized injection needle (25G to 30G recommended).
- Apply peel-off label from the Prescribing Information to the prepared drug product.
- Once transferred from the vial to the syringe, LUNSUMIO VELO solution for injection should be injected immediately because LUNSUMIO VELO solution for injection does not contain any antimicrobial-preservative.
Administration
Inject the required volume of LUNSUMIO VELO into the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen or thigh, changing the site of injection with each dose. Do not inject into tattoos, moles, scars or areas where the skin is red, bruised, tender, hard, or not intact. The dose should be administered subcutaneously over approximately 30 seconds to 1 minute.
Storage of Prepared Syringe
- The prepared syringe should be used immediately. If not used immediately, replace the transfer needle with a syringe closing cap. Do not attach an injection needle.
- The capped syringe can be stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 32 hours protected from light and/or at 9°C to 25°C (37°F to 77°F) for up to 8 hours at ambient light.
- Once removed from refrigerated storage, the solution can be equilibrated to ambient temperature up to 25°C (77°F) prior to administration. Do not warm LUNSUMIO VELO in any other way.
-
LUNSUMIO VELO and LUNSUMIO have different dosage and administration instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause CRS, including serious or life-threatening reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
CRS occurred in 30% of patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO at the recommended dosage in the clinical trial (N = 94), with Grade 1 CRS occurring in 20%, Grade 2 in 7%, and Grade 3 in 2.1% of patients. Among 28 patients who experienced CRS, CRS recurred in 14%. CRS occurred most commonly after the first two doses: 19% of patients experienced CRS after the Cycle 1 Day 1 dose, 13% after the Cycle 1 Day 8 dose, and 2.1% after the Cycle 1 Day 15 dose.
The median time to CRS onset from the start of LUNSUMIO VELO administration was 17 hours (range: 7 to 33 hours) with the Cycle 1 Day 1 dose, and 62 hours (range: 30 to 113 hours) with the Cycle 1 Day 8 dose. CRS resolved in all patients, after a median duration of 2 days (range: 1 to 15 days).
Clinical signs and symptoms of CRS included fever, hypotension, hypoxia, chills, tachycardia, and headache. Concurrent neurologic adverse reactions occurred in 5% of patients and included but were not limited to headache, dizziness, lethargy, memory impairment, and peripheral neuropathy.
Initiate therapy according to LUNSUMIO VELO step-up dosing schedule to reduce the risk of CRS [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Administer pretreatment medications to reduce the risk of CRS, ensure adequate hydration, and monitor patients following administration of LUNSUMIO VELO accordingly.
At the first sign of CRS, immediately evaluate patients for hospitalization, manage per current practice guidelines, and administer supportive care; withhold or permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Patients who experience CRS (or other adverse reactions that impair consciousness) should be evaluated and advised not to drive and to refrain from operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery until resolution.
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious and life-threatening neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Neurologic toxicity occurred in 53% of patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO at the recommended dosage in the clinical trial (N = 94), with Grade 3 neurologic toxicity occurring in 1.1% of patients. The most frequent neurologic toxicities were headache (17%), insomnia (15%), dizziness (10%), and mental status changes (7%, including confusion and lethargy). ICANS or suspected ICANS was reported in 3.1% of patients (all Grade 1).
Across a broader clinical trial population, ICANS or suspected ICANS occurred in 2.2% (21/949) of patients who received LUNSUMIO or LUNSUMIO VELO. The most frequent manifestations included confusional state and lethargy. Twenty patients had Grade 1-2 reactions and 1 patient had a Grade 3 event. The majority of cases (75%) occurred during the first cycle of treatment. The median time to onset was 17 days (range: 1 to 48 days). In total, 88% of cases resolved after a median duration of 3 days (range: 1 to 20 days).
Coadministration of LUNSUMIO VELO with other products that cause dizziness or mental status changes may increase the risk of neurologic toxicity.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicity during treatment. At the first sign of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, immediately evaluate the patient, consider neurology evaluation as appropriate, and provide supportive therapy based on severity; withhold or permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO based on severity and follow management recommendations [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Patients who experience neurologic toxicity such as tremors, dizziness, insomnia, severe neurotoxicity, or any other adverse reactions that impair consciousness should be evaluated, including potential neurology evaluation, and patients at increased risk should be advised not to drive and to refrain from operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery until resolution.
5.3 Infections
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious or fatal infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Among patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO at the recommended dosage in the clinical trial, serious infections, including opportunistic infections, occurred in 17%, with Grade 3 or 4 infections in 16% and fatal infections in 3.2% of patients. The most common Grade 3 or greater infections were pneumonia, sepsis, and COVID-19.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection prior to and during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and treat appropriately. LUNSUMIO VELO should not be administered in the presence of active infection. Caution should be exercised when considering use in patients with a history of recurring or chronic infections (e.g., chronic, active Epstein-Barr Virus), with underlying conditions that may predispose to infections or who have had significant prior immunosuppressive treatment. Administer prophylactic antimicrobials according to guidelines.
Withhold LUNSUMIO VELO or consider permanent discontinuation based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause fatal or serious hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). HLH is a potentially life-threatening, hyperinflammatory syndrome that is independent of CRS. Common manifestations include fever, elevated ferritin, hemophagocytosis, cytopenias, coagulopathy, hepatitis, and splenomegaly.
Across a broader clinical trial population, HLH occurred in 0.5% (7/1536) of patients who received LUNSUMIO or LUNSUMIO VELO. Most cases (5/7) were identified within the first 28 days following initiation of treatment, with 3 cases preceded by diagnosed or suspected CRS. Of the 7 cases of HLH, 6 had fatal outcomes, with 2 deaths from HLH alone and 4 deaths with concurrent unresolved HLH. Of the 7 cases of HLH, 4 occurred in the context of concurrent EBV and/or CMV infection.
Monitor for clinical signs and symptoms of HLH. Consider HLH when the presentation of CRS is atypical or prolonged, or when there are features of macrophage activation. For suspected HLH, interrupt LUNSUMIO VELO and evaluate and treat promptly for HLH per current practice guidelines.
5.5 Cytopenias
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious or severe cytopenias, including lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Among patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO at the recommended dosage in the clinical trial (N = 94), Grade 3 or 4 decreased lymphocytes occurred in 69%, decreased neutrophils occurred in 26%, decreased hemoglobin in 10%, and decreased platelets in 6% of patients. Grade 4 decreased lymphocytes occurred in 22%, decreased neutrophils in 9% and decreased platelets in 3.2% of patients. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 2.1% of patients.
Monitor complete blood counts throughout treatment. Based on the severity of cytopenias, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue LUNSUMIO VELO. Consider prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration as applicable [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Tumor Flare
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious or severe tumor flare [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Among patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO at the recommended dosage in the clinical trial (N = 94), tumor flare occurred in 1.1% of patients. Manifestations may include new or worsening pleural effusions, localized pain and swelling at the sites of lymphoma lesions, and tumor inflammation.
Patients with bulky tumors or disease located in close proximity to airways or a vital organ should be monitored closely during initial therapy. Monitor for signs and symptoms of compression or obstruction due to mass effect secondary to tumor flare. If compression or obstruction develops, institute standard treatment of these complications.
5.7 Risk of Medication Errors with Incorrect Product Use
Mosunetuzumab-axgb is available in two formulations: as an injection for subcutaneous use (LUNSUMIO VELO) and an injection for intravenous use (LUNSUMIO). Check the product labels to ensure that the correct formulation is being prescribed, dispensed, and administered to the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 and 2.5)]. Do not substitute LUNSUMIO VELO for or with LUNSUMIO.
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, LUNSUMIO VELO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Tumor Flare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma
The safety of LUNSUMIO VELO was evaluated in an open-label, multicenter study which included a cohort of 94 patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) after at least two lines of systemic therapy [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients received step-up doses of 5 mg via subcutaneous injection on Cycle 1 Day 1 and 45 mg on Cycle 1 Day 8, followed by 45 mg on Cycle 1 Day 15, then 45 mg every 3 weeks in subsequent cycles. A treatment cycle was 21 days. The median number of cycles was 8 (range: 1 to 17), with 78% of patients exposed for at least 8 cycles and 6% exposed for 17 cycles.
The median age was 65 years (range: 35 to 84 years), 56% were male, 85% were White, 2.1% were Black or African American, 11% were Asian, and 2% were Hispanic or Latino.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 10% of patients included infection (17%, including pneumonia, other respiratory tract infections, and sepsis) and CRS (15%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.3% of patients from COVID-19 (3.2%) and HLH (1.1%).
Permanent discontinuation LUNSUMIO VELO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 7% of patients, including from COVID-19.
Dosage interruptions of LUNSUMIO VELO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 40% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients included COVID-19 and neutropenia.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%), excluding laboratory abnormalities, were injection site reactions, fatigue, rash, CRS, COVID-19 infection, musculoskeletal pain, and diarrhea. The most common Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 15%) were decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, and increased uric acid. Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in > 5% included lymphocyte count decreased (22%) and neutrophil count decreased (9%).
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory FL Who Received LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection in GO29781 Adverse Reaction LUNSUMIO VELO
(N = 94)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)Immune system disorders The table includes a combination of grouped and ungrouped terms. Adverse reactions were graded based on CTCAE Version 4.0, with the exception of CRS, which was graded per ASTCT 2019 criteria. - * Injection site reactions includes injection site reaction, injection site discharge, injection site erythema, injection site edema, injection site pain, injection site pruritus and injection site rash.
- † Fatigue includes fatigue, asthenia, and lethargy.
- ‡ Edema includes edema, edema peripheral, face edema, pulmonary edema, fluid overload, and related terms.
- § Rash includes rash, injection site rash, erythema, dermatitis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, erythema multiforme, urticaria, and related terms.
- ¶ Peripheral neuropathy includes peripheral neuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy, paresthesia, dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, burning sensation, and neuralgia.
- # Dizziness includes dizziness and vertigo.
- Þ Musculoskeletal pain includes musculoskeletal pain, back pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, and neck pain.
- ß Adverse reaction with fatal outcome.
- à Grade 5 COVID-19 occurred in 3.2% of patients.
- è Upper respiratory tract infection includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, rhinovirus infection, and related terms.
- ð Pneumonia includes lung consolidation and specific types of pneumonia including COVID-19 pneumonia.
Cytokine release syndrome 30 2.1 General disorders and administration site conditions Injection site reactions* 69 0 Fatigue† 39 0 Edema‡ 13 0 Pyrexia 11 1.1 Chills 11 0 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash§ 35 3.2 Dry skin 11 0 Nervous system Headache 17 0 Peripheral neuropathy¶ 11 0 Dizziness# 10 0 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Musculoskeletal painÞ 20 0 Arthralgia 13 0 Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders Cough 13 0 Dyspnea 11 0 Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea 20 0 Nausea 14 0 Constipation 14 0 Abdominal pain 13 0 Infections COVID-19ß,à 27 4.3 Upper respiratory tract infectionè 15 2.1 Pneumoniað 13 4.3 Psychiatric disorder Insomnia 15 0 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received LUNSUMIO VELO included pruritus, skin exfoliation, herpes zoster infection, tremor, sepsis, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, ICANS, febrile neutropenia, capillary leak syndrome, tumor flare, and HLH .
Table 8 summarizes select laboratory abnormalities.
Table 8. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 20%) That Worsened from Baseline in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory FL Who Received LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection in GO29781 Laboratory Abnormality LUNSUMIO VELO* All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)Hematology - * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 85 to 94 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Lymphocyte count decreased 84 69 Hemoglobin decreased 60 10 Neutrophils decreased 50 26 Platelets decreased 33 6.4 Chemistry Phosphate decreased 48 11 Alanine aminotransferase increased 34 1.1 Gamma-glutamyl transferase increased 31 1.1 Uric acid increased 28 28 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 28 2.1 Potassium decreased 27 0 Magnesium decreased 25 2.1 Clinically relevant laboratory abnormalities in < 20% of patients included glucose increased.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effect of LUNSUMIO VELO on CYP450 Substrates
LUNSUMIO VELO causes release of cytokines [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] that may suppress activity of CYP450 enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP450 substrates. Increased exposure of CYP450 substrates is more likely to occur after the first dose of LUNSUMIO VELO on Cycle 1 Day 1 and up to 14 days after the 45 mg dose on Cycle 1 Day 8 and during and after CRS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Monitor for toxicity or concentrations of drugs that are CYP450 substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. Consult the concomitant CYP450 substrate drug prescribing information for recommended dosage modification.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action, LUNSUMIO VELO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on the use of LUNSUMIO VELO in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. No animal reproductive or developmental toxicity studies have been conducted with mosunetuzumab-axgb.
Mosunetuzumab-axgb causes T-cell activation and cytokine release; immune activation may compromise pregnancy maintenance. In addition, based on expression of CD20 on B-cells and the finding of B-cell depletion in non-pregnant animals, mosunetuzumab-axgb can cause B-cell lymphocytopenia in infants exposed to mosunetuzumab-axgb in-utero. Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) is known to cross the placenta; therefore, LUNSUMIO VELO has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to the fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% – 4% and 15% – 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of mosunetuzumab-axgb in human milk, the effect on the breastfed child, or milk production. Because human IgG is present in human milk, and there is potential for mosunetuzumab-axgb absorption leading to B-cell depletion, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and for 3 months after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
LUNSUMIO VELO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating LUNSUMIO VELO.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and for 3 months after the last dose.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Mosunetuzumab-axgb is a bispecific CD20-directed CD3 T-cell engager. It is a humanized monoclonal anti-CD20xCD3 T-cell-dependent bispecific antibody of the immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) isotype. Mosunetuzumab-axgb is produced in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells by recombinant DNA technology. The approximate molecular weight is 146 kDa.
LUNSUMIO VELO (mosunetuzumab-axgb) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow solution for subcutaneous use.
Each single-dose vial contains a 0.5 mL solution of mosunetuzumab-axgb (5 mg), acetic acid (0.2 mg), histidine (0.8 mg), methionine (0.7 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.3 mg), sucrose (41 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. The pH is 5.8.
Each single-dose vial contains a 1 mL solution of mosunetuzumab-axgb (45 mg), acetic acid (0.4 mg), histidine (1.6 mg), methionine (1.5 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.6 mg), sucrose (82.1 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. The pH is 5.8.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mosunetuzumab-axgb is a T-cell engaging bispecific antibody that binds to the CD3 receptor expressed on the surface of T-cells and CD20 expressed on the surface of lymphoma cells and some healthy B-lineage cells.
In vitro, mosunetuzumab-axgb activated T-cells, caused the release of proinflammatory cytokines, and induced lysis of B-cells.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
After subcutaneous administration of the recommended dosage of LUNSUMIO VELO, peripheral B-cell counts decreased to undetectable levels (< 5 cells/microliter) in most patients (94%) by Cycle 2 Day 1 and the depletion was sustained at later cycles including at Cycle 4 and Cycle 8.
LUNSUMIO VELO caused hypogammaglobulinemia (defined as IgG levels < 500 mg/dL). Among 49 patients with baseline IgG levels ≥ 500 mg/dL, 39% experienced a decrease in their IgG levels to < 500 mg/dL after receiving LUNSUMIO VELO.
Plasma concentrations of cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α and IFN-γ) were measured with subcutaneous administration of LUNSUMIO VELO, and transient elevation of cytokines were observed at doses of 1.6 mg and above. After administration of the recommended dosage of LUNSUMIO VELO, the highest elevation of cytokines was generally observed within 48 hours after the first dose on Cycle 1 Day 8 and generally returned to baseline prior to the third 45 mg full dose on Cycle 2 Day 1. The observed pattern of cytokine release appeared slower and reduced relative to intravenous administration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mosunetuzumab-axgb subcutaneously administered PK exposure increased proportionally over a dose range from 1.6 mg to 45 mg (0.04 to 1 times the recommended treatment dosage).
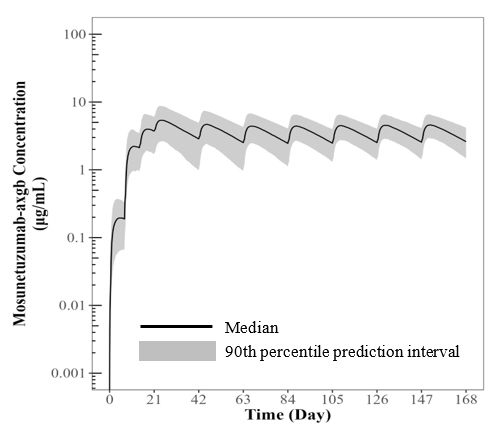
When comparing mosunetuzumab exposures following the recommended LUNSUMIO VELO subcutaneous dosing regimen to the recommended LUNSUMIO intravenous dosing regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma in Study GO29781 [see Clinical Studies (14)], the geometric mean ratios (GMRs) (90% CI) for observed Cycle 3 Ctrough was 1.39 (1.20 to 1.61) and AUC over 0-84 days was 1.06 (0.92 to 1.21). PK exposures for the recommended dosage of LUNSUMIO VELO via subcutaneous injection are summarized in Table 9 and Figure 1.
Table 9. Exposure Parameters of Mosunetuzumab-axgb Subcutaneous Injection AUC (day∙µg/mL)* Cmax (µg/mL)* Ctrough (µg/mL)* All values reported are model-predicted exposure metrics. - * Values are geometric mean with geometric CV%.
- † Steady state values are approximated at Cycle 4 (63 – 84 days).
Cycle 1 (0 – 21 days) 36.7 (57.0) 3.8 (53.9) 3.5 (54.1) Cycle 2 (21 – 42 days) 82.3 (50.9) 5.2 (50.3) 2.5 (55.7) Cycle 3 (42 – 63 days) 72.9 (42.8) 4.5 (44.0) 2.4 (52.3) Steady state† 72.8 (34.5) 4.4 (36.7) 2.4 (34.2) Figure 1. Model-Predicted Mosunetuzumab-axgb Subcutaneous Injection Concentration Time Profile
Pharmacokinetic parameters (Table 10) were evaluated at the recommended dosage and are presented as geometric mean (CV%) unless otherwise specified.
Table 10. Mosunetuzumab-axgb Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma Parameter LUNSUMIO VELO via Subcutaneous Infusion Tmax = time to peak concentration - * Steady-state
Bioavailability 89.8% Tmax median (range), days* 4.2 (2.5 – 7.1) Volume of distributiona (L) 5.5 (31%) Half-lifea (days) 17.0 (15%) Systemic clearance (L/day) 1.1 (63%) at baseline
0.58 (18%) at steady stateSpecific Populations
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of mosunetuzumab-axgb based on age (18 to 96 years), sex, race (Asian and Non-Asian), ethnicity (Hispanic/Latino and not Hispanic/Latino), mild or moderate renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance [CrCL] by Cockcroft-Gault formula: 30 to 89 mL/min), or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin less than or equal to upper limit of normal [ULN] with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST).
The effects of severe renal impairment (CrCL 15 to 29 mL/min) or moderate to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 times ULN with any AST) on the pharmacokinetics of mosunetuzumab-axgb are unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
No clinical studies evaluating the drug interaction potential of mosunetuzumab-axgb have been conducted.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the study described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of mosunetuzumab-axgb.
During treatment in Study GO29781 (up to 12 months) [see Clinical Studies (14)], using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), no patients (N = 216) treated with LUNSUMIO VELO monotherapy developed anti-mosunetuzumab-axgb antibodies. Based on these data, the clinical relevance of anti-mosunetuzumab-axgb antibodies could not be assessed.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or genotoxicity studies have been conducted with mosunetuzumab-axgb.
No dedicated studies have been conducted to evaluate the effects of mosunetuzumab-axgb on fertility. No adverse effects on either male or female reproductive organs were identified in a 26-week repeat dose chronic toxicity study in sexually mature cynomolgus monkeys.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of LUNSUMIO VELO was evaluated in an open-label, multicenter, multi-cohort study (GO29781, NCT02500407) in patients with relapsed or refractory FL after at least two lines of systemic therapy, including an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and an alkylating agent. The study excluded patients with active infections, history of autoimmune disease, prior allogeneic transplant, or any history of central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma or CNS disorders.
Patients received 5 mg on Cycle 1 Day 1 and 45 mg on Cycle 1 Day 8, followed by 45 mg on Cycle 1 Day 15, then 45 mg via subcutaneous injection every 3 weeks in subsequent cycles. A treatment cycle was 21 days. LUNSUMIO VELO was administered for 8 cycles unless patients experienced progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity. After 8 cycles, patients with a complete response discontinued therapy; patients with a partial response or stable disease continued treatment up to 17 cycles, unless patients experienced progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
Among the 94 patients, the median age was 65 years (range: 35 to 84) with 49% being age > 65; 56% were male; 85% were White, 11% Asian, 2% Black, and 2% Hispanic or Latino. All had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1. The median number of prior lines of systemic therapy was 3 (range: 2 to 9), with 47% receiving 2 prior lines, 19% receiving 3 prior lines, and 34% receiving 4 or more prior lines.
Sixty-seven percent of patients had refractory disease to prior anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy, 46% had refractory disease to both an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and alkylator, 20% had prior autologous stem cell transplant, 16% had prior rituximab plus lenalidomide, and 4% had prior CAR-T therapy. Twenty-five percent had bulky disease, and 44% had progression of disease within 24 months of first systemic therapy.
Efficacy was established on the basis of objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) as assessed by an independent review facility using 2007 International Working Group criteria. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 11. The median follow-up for DOR was 16.0 months.
Table 11. Efficacy Results in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory FL Who Received LUNSUMIO VELO Subcutaneous Injection Response LUNSUMIO VELO
N=94DOR = duration of response; CI = confidence interval - * DOR is defined as time from first documented PR or CR to documented disease progression or death due to any cause.
- † Kaplan-Meier estimate.
Objective response rate, n (%) 70 (75) (95% CI) (64, 83) Complete response, n (%) 55 (59) (95% CI) (48, 69) Partial response, n (%) 15 (16) (95% CI) (9, 25) Duration of response*,† N = 70 Median DOR†, months (95% CI) 22.4 (16.8, 22.8) Rate of continued response† At 12 months,% 70 (95% CI) (59, 81) At 18 months, % 60 (95% CI) (46, 73) The median time to first response was 2.8 months (range: 1.2 to 16.0).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LUNSUMIO VELO (mosunetuzumab-axgb) injection is a sterile, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, preservative-free solution for subcutaneous injection supplied as follows:
- One 5 mg/0.5 mL single-dose vial in a carton (NDC: 50242-177-01)
- One 45 mg/mL single-dose vial in a carton (NDC: 50242-201-01).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) – Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with CRS, including fever, chills, hypotension, tachycardia, hypoxia, and headache. Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur at any time. Advise patients who experience symptoms that impair consciousness not to drive and refrain from operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery until events resolve [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS – Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, headache, peripheral neuropathy, dizziness, or mental status changes. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicity. Advise patients who experience neurologic toxicity that impairs consciousness to refrain from driving or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery until neurologic toxicity resolves [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Infections – Discuss the signs or symptoms associated with infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) – Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with HLH, including fever, coagulopathy, cytopenias, and splenomegaly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Cytopenias – Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with cytopenias, including neutropenia and febrile neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Tumor Flare – Inform patients of the potential risk of tumor flare reaction and to report any signs and symptoms associated with this event to their healthcare provider for evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Injection-Site Reactions – Inform patients that injection site reactions may occur and to report any severe reactions [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity – Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation – Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
LUNSUMIO VELO™ (lun-SUM-mee-oh VEH-low)
(mosunetuzumab-axgb)
injection, for subcutaneous useThis Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: Dec 2025 What is the most important information I should know about LUNSUMIO VELO?
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), a serious side effect that is common during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO, and can also be severe or life-threatening.
Get medical help right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of CRS at any time, including:- fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- chills
- low blood pressure
- fast or irregular heartbeat
- tiredness or weakness
- difficulty breathing
- headache
- confusion
- feeling anxious
- dizziness or light-headedness
- nausea
- vomiting
Due to the risk of CRS, you will receive LUNSUMIO VELO on a "step-up dosing schedule". - The step-up dosing schedule is when you receive smaller "step-up" doses before receiving higher doses of LUNSUMIO VELO during your first cycle of treatment.
- If your dose of LUNSUMIO VELO is delayed for any reason, you may need to repeat the "step-up dosing schedule."
- You may receive medicines to help reduce your risk of CRS before your dose.
- See "How will I receive LUNSUMIO VELO?" for more information about how you will receive LUNSUMIO VELO.
See "What are the possible side effects of LUNSUMIO VELO?" for more information about side effects.What is LUNSUMIO VELO?
LUNSUMIO VELO is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with follicular lymphoma whose cancer has come back or did not respond to previous treatment, and who have already received two or more treatments.
It is not known if LUNSUMIO VELO is safe and effective in children.Before receiving LUNSUMIO VELO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have an infection or have had an infection in the past which lasted a long time or keeps coming back.
- have or had Epstein-Barr Virus.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. LUNSUMIO VELO may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO.
- use an effective method of birth control (contraception) during your treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if LUNSUMIO VELO passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of LUNSUMIO VELO.
How will I receive LUNSUMIO VELO? - LUNSUMIO VELO will be given to you by your healthcare provider as an injection under your skin (subcutaneous) in your stomach area (abdomen) or thigh.
- After you complete the weekly "step-up dosing schedule" in Cycle 1, LUNSUMIO VELO is given every 21 days.
- After Cycle 1, your healthcare provider will decide if you need to continue to take other medicines to help reduce side effects from LUNSUMIO VELO during future cycles.
- Your healthcare provider will decide how many treatment cycles you will receive of LUNSUMIO VELO.
What should I avoid while receiving LUNSUMIO VELO?
Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities if you develop dizziness, confusion, tremors, sleepiness, or any other symptoms that impair consciousness until your signs and symptoms go away. These may be signs and symptoms of CRS or neurologic problems.
See "What is the most important information I should know about LUNSUMIO VELO?" and "What are the possible side effects of LUNSUMIO VELO?" for more information about signs and symptoms of CRS and neurologic problems.What are the possible side effects of LUNSUMIO VELO?
LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious side effects, including:
See "What is the most important information I should know about LUNSUMIO VELO?"- Neurologic problems. LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious and life-threatening neurologic problems. Your healthcare provider will check you for neurologic problems during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO. Your healthcare provider may also refer you to a healthcare provider who specializes in neurologic problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of neurologic problems during or after treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO, including:
- headache
- numbness and tingling of the arms, legs, hands, or feet
- dizziness
- confusion and disorientation
- difficulty paying attention or understanding things
- forgetting things or forgetting who or where you are
- trouble speaking, reading, or writing
- sleepiness or trouble sleeping
- tremors
- loss of consciousness
- seizures
- muscle problems or muscle weakness
- loss of balance or trouble walking
- tiredness
- Serious infections. LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious infections that may lead to death. Your healthcare provider will check you for signs and symptoms of infection before and during treatment. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of infection during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO, including:
- fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- cough
- chest pain
- tiredness
- shortness of breath
- painful rash
- sore throat
- pain during urination
- feeling weak or generally unwell
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). LUNSUMIO VELO can cause overactivity of the immune system, a condition called hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). HLH can be life-threatening and has led to death in people treated with LUNSUMIO VELO. Your healthcare provider will check you for HLH especially if your CRS lasts longer than expected. Signs and symptoms of HLH include:
- fever
- enlarged spleen
- easy bruising
- low blood cell counts
- liver problems
- Low blood cell counts. Low blood cell counts are common during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO and can also be serious or severe. Your healthcare provider will check your blood cell counts during treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO. LUNSUMIO VELO can cause the following low blood cell counts:
- low white blood cell counts (lymphopenia and neutropenia). Low white blood cells can increase your risk for infection.
- low red blood cell counts (anemia). Low red blood cells can cause tiredness and shortness of breath.
- low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia). Low platelet counts can cause bruising or bleeding problems.
- Growth in your tumor or worsening of tumor related problems (tumor flare). LUNSUMIO VELO can cause serious or severe worsening of your tumor. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any of these signs or symptoms of tumor flare during your treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO:
- chest pain
- cough
- trouble breathing
- tender or swollen lymph nodes
- pain or swelling at the site of the tumor
Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop or permanently stop treatment with LUNSUMIO VELO if you develop severe side effects.
The most common side effects of LUNSUMIO VELO include:- injection site reactions
- tiredness
- rash
- CRS
- COVID-19
- muscle and joint pain
- diarrhea
The most common severe abnormal blood test results with LUNSUMIO VELO include: decreased white blood cell counts and increased uric acid levels.
These are not all of the possible side effects of LUNSUMIO VELO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of LUNSUMIO VELO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about LUNSUMIO VELO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in LUNSUMIO VELO?
Active ingredient: mosunetuzumab-axgb
Inactive ingredients: acetic acid, histidine, methionine, polysorbate 20, sucrose, and Water for Injection.
Manufactured by: Genentech, Inc., A Member of the Roche Group, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
U.S. License No.: 1048
LUNSUMIO VELO is a trademark of Genentech, Inc.
For more information, call 1-844-832-3687 or go to www.LUNSUMIO.com. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg/0.5 mL Vial Carton
NDC: 50242-177-01
Lunsumio Velo™
(mosunetuzumab-axgb)
Injection5 mg/0.5 mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only.
Single-Dose Vial.
Discard Unused Portion.ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.1 vial
Rx only
Genentech
11027680
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 45 mg/mL Vial Carton
NDC: 50242-201-01
Lunsumio Velo™
(mosunetuzumab-axgb)
Injection45 mg/mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only.
Single-Dose Vial.
Discard Unused Portion.ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.1 vial
Rx only
Genentech
11027612
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LUNSUMIO VELO
mosunetuzumab injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50242-177 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MOSUNETUZUMAB (UNII: LDJ89SS0YG) (MOSUNETUZUMAB - UNII:LDJ89SS0YG) MOSUNETUZUMAB 5 mg in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 0.8 mg in 0.5 mL ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) 0.2 mg in 0.5 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 41 mg in 0.5 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 0.3 mg in 0.5 mL METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) 0.7 mg in 0.5 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50242-177-01 1 in 1 CARTON 12/19/2025 1 0.5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761263 12/19/2025 LUNSUMIO VELO
mosunetuzumab injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50242-201 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MOSUNETUZUMAB (UNII: LDJ89SS0YG) (MOSUNETUZUMAB - UNII:LDJ89SS0YG) MOSUNETUZUMAB 45 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) 1.6 mg in 1 mL ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) 0.4 mg in 1 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 82.1 mg in 1 mL POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) 0.6 mg in 1 mL METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) 1.5 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50242-201-01 1 in 1 CARTON 12/19/2025 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761263 12/19/2025 Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Registrant - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genentech, Inc. 080129000 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) , API MANUFACTURE(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Roche Diagnostics GmbH 315028860 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Roche Diagnostics 323105205 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG 485244961 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) , PACK(50242-177, 50242-201) , LABEL(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG 482242971 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) , API MANUFACTURE(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genentech, Inc. (Hillsboro) 833220176 MANUFACTURE(50242-177, 50242-201) , PACK(50242-177, 50242-201) , LABEL(50242-177, 50242-201) , ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genentech, Inc. (Oceanside) 146373191 ANALYSIS(50242-177, 50242-201)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.