OLUX-E- clobetasol propionate aerosol, foam
OLUX-E by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
OLUX-E by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Prestium Pharma, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OLUX-E Foam safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OLUX-E Foam.
OLUX-E (clobetasol propionate) Foam, 0.05%
For topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1985INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- OLUX-E Foam is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses in patients aged 12 years or older. (1.1)
Limitations of Use
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Foam, 0.05%. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- OLUX-E Foam has been shown to suppress the HPA axis. Systemic absorption of OLUX-E Foam may produce reversible HPA axis suppression, Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and unmask latent diabetes. (5.1)
- Because of the potential for systemic absorption, use of topical corticosteroids may require that patients be periodically evaluated for HPA axis suppression. (5.1)
- Modify use should HPA axis suppression develop. (5.1)
- High potency corticosteroids, large treatment surface areas, prolonged use, use of occlusive dressings, altered skin barrier, and liver failure may predispose patients to HPA axis suppression. (5.1)
- Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity when treated with topical corticosteroids. (5.1, 8.4)
- The propellant in OLUX-E Foam is flammable. Avoid fire, flame, or smoking during and immediately following application. (5.4))
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥1%) are application site atrophy and application site reaction. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Prestium Pharma, Inc. at 1-866-897-5002 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2014
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Indication
1.2 Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
5.2 Local Adverse Reactions with Topical Corticosteroids
5.3 Concomitant Skin Infections
5.4 Flammable Contents
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Indication
OLUX-E® Foam is indicated for the treatment of inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses in patients 12 years and older.
1.2 Limitations of Use
- OLUX-E Foam should not be applied to the face, axillae, or groin.
- OLUX-E Foam should not be used if there is skin atrophy at the treatment site.
- Treatment should be limited to 2 consecutive weeks and patients should not use greater than 50 grams or more than 21 capfuls per week.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
OLUX-E Foam is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Apply a thin layer of OLUX-E Foam to the affected area(s) twice daily, morning and evening for up to 2 consecutive weeks; therapy should be discontinued when control has been achieved. The maximum weekly dose should not exceed 50 g or an amount greater than 21 capfuls per week. For proper dispensing of foam, shake the can, hold it upside down, and depress the actuator. Dispense a small amount of foam (about a capful) and gently massage the medication into the affected areas (excluding the face, groin, and axillae) until the foam is absorbed. Avoid contact with the eyes.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
OLUX-E Foam has been shown to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Systemic absorption of OLUX-E has caused reversible HPA axis suppression with the potential for clinical glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. This may occur during treatment or upon withdrawal of the topical corticosteroid. Use of OLUX-E Foam for longer than 2 weeks may suppress the immune system. [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
In a trial including 37 subjects aged 12 years and older with at least 30% body surface area (BSA), adrenal suppression was identified in 6 out of 37 subjects (16.2%) after 2 weeks of treatment with OLUX-E. [see Clinical Pharmacology(12.2)].
Because of the potential for systemic absorption, use of OLUX-E may require that patients be periodically evaluated for HPA axis suppression. Factors that predispose a patient using a topical corticosteroid to HPA axis suppression include the use of more potent steroids, use over large surface areas, use over prolonged periods, use under occlusion, use on an altered skin barrier, and use in patients with liver failure.
An adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA axis suppression. If HPA axis suppression is documented, an attempt should be made to gradually withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent steroid. Manifestations of adrenal insufficiency may require systemic corticosteroids. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids.
Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and unmasking of latent diabetes mellitus can also result from systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids.
Use of more than 1 corticosteroid-containing product at the same time may increase the total systemic corticosteroid exposure.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses because of their larger skin surface- to-body mass ratios. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.2 Local Adverse Reactions with Topical Corticosteroids
Local adverse reactions may be more likely to occur with occlusive use, prolonged use, or use of higher potency corticosteroids. Reactions may include atrophy, striae, telangiectasias, burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, and miliaria. Some local adverse reactions may be irreversible.
Allergic contact dermatitis to any component of topical corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by a failure to heal rather than a clinical exacerbation. Clinical diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis can be confirmed by patch testing.
If irritation develops, treatment with OLUX-E Foam should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In controlled clinical trials involving 821 subjects exposed to OLUX-E Foam and vehicle foam, the pooled incidence of local adverse reactions in trials for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis with OLUX-E Foam was 1.9% for application site atrophy and 1.6% for application site reaction. Most local adverse events were rated as mild to moderate and they were not affected by age, race, or gender.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported with topical corticosteroids: folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, irritation, striae, and miliaria. They may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings and higher potency corticosteroids, such as clobetasol propionate.
Cushing’s syndrome has been reported in infants and adults as a result of prolonged use of topical clobetasol propionate formulations.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of clobetasol formulations: erythema, pruritus, burning, alopecia, and dryness.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category C.
There are no adequate and well-controlled trials of the teratogenic potential of clobetasol propionate in pregnant women. OLUX-E Foam should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. Some corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application to laboratory animals.
Clobetasol propionate has not been tested for teratogenicity when applied topically; however, it is absorbed percutaneously, and when administered subcutaneously, it was a significant teratogen in both the rabbit and the mouse. Clobetasol propionate has greater teratogenic potential than steroids that are less potent.
Teratogenicity studies in mice using the subcutaneous route resulted in fetotoxicity at the highest dose tested (1 mg/kg) and teratogenicity at all dose levels tested down to 0.03 mg/kg. These doses are approximately 1.4 and 0.04 times, respectively, the human topical dose of OLUX-E Foam based on body surface area comparisons. Abnormalities seen included cleft palate and skeletal abnormalities.
In rabbits, clobetasol propionate was teratogenic at doses of 0.003 and 0.01 mg/kg. These doses are approximately 0.02 and 0.05 times, respectively, the human topical dose of OLUX-E Foam based on body surface area comparisons. Abnormalities seen included cleft palate, cranioschisis, and other skeletal abnormalities.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when OLUX-E Foam is administered to a nursing woman.
If used during lactation, OLUX-E Foam should not be applied on the chest to avoid accidental ingestion by the infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use in pediatric patients younger than 12 years is not recommended because of the risk of HPA axis suppression.
After 2 weeks of twice-daily treatment with OLUX-E Foam, 7 of 15 subjects (47%) aged 6 to 11 years demonstrated HPA axis suppression. The laboratory suppression was transient; in all subjects serum cortisol levels returned to normal when tested 4 weeks post-treatment.
In 92 subjects aged 12 to 17 years, safety was similar to that observed in the adult population. Based on these data, no adjustment of dosage of OLUX-E Foam in adolescent patients aged 12 to 17 years is warranted. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA axis suppression and Cushing’s syndrome when they are treated with topical corticosteroids. They are therefore also at greater risk of adrenal insufficiency during and/or after withdrawal of treatment.
HPA axis suppression, Cushing’s syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and an absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles (in infants), headaches, and bilateral papilledema. Administration of topical corticosteroids to children should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children.
Adverse effects, including striae, have been reported with inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids in infants and children.
8.5 Geriatric Use
A limited number of subjects aged 65 years or older have been treated with OLUX-E Foam (n = 58) in US clinical trials. While the number of subjects is too small to permit separate analysis of efficacy and safety, the adverse reactions reported in this population were similar to those reported by younger subjects. Based on available data, no adjustment of dosage of OLUX-E Foam in geriatric patients is warranted.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
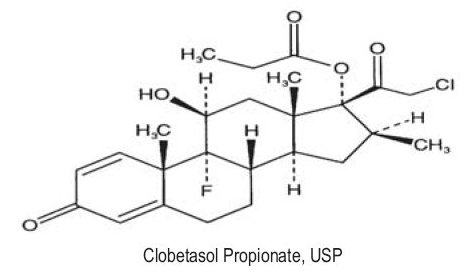
OLUX-E (clobetasol propionate) Foam, 0.05% is a white to off-white petrolatum-based emulsion aerosol foam containing the active ingredient clobetasol propionate USP, a synthetic corticosteroid for topical dermatologic use. Clobetasol, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of glucocorticoid activity and a slight degree of mineralocorticoid activity.
Clobetasol propionate is 21-chloro-9-fluoro-11ß,17-dihydroxy-16ß-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17-propionate, with the empirical formula C25H32ClFO5, and a molecular weight of 466.97.
The following is the chemical structure:
Clobetasol propionate is a white to cream-colored crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water.
Each gram of OLUX-E Foam contains 0.5 mg clobetasol propionate, USP. The foam also contains anhydrous citric acid, cetyl alcohol, cyclomethicone, isopropyl myristate, light mineral oil, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, potassium citrate monohydrate, propylene glycol, purified water, sorbitan monolaurate, white petrolatum, and phenoxyethanol as a preservative.
OLUX-E Foam is dispensed from an aluminum can pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids play a role in cellular signaling, immune function, inflammation, and protein regulation; however, the precise mechanism of action in corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses is unknown.
The contribution to efficacy by individual components of the vehicle has not been established.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a trial evaluating the potential for HPA axis suppression using the cosyntropin stimulation test, OLUX-E Foam demonstrated reversible adrenal suppression after 2 weeks of twice-daily use in subjects with atopic dermatitis of at least 30% body surface area (BSA). The proportion of subjects aged 12 years and older demonstrating HPA axis suppression was 16.2% (6 out of 37). In this trial HPA axis suppression was defined as serum cortisol level ≤18 mcg/dL 30 minutes post cosyntropin stimulation. The laboratory suppression was transient; in all subjects serum cortisol levels returned to normal when tested 4 weeks post treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from intact healthy skin. The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including the product formulation and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusion, inflammation, and/or other disease processes in the skin may increase percutaneous absorption. The use of pharmacodynamic endpoints for assessing the systemic exposure of topical corticosteroids may be necessary due to the fact that circulating levels are often below the level of detection. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.
Following twice daily application of OLUX-E Foam for 1 week to 32 adult patients with mild to moderate plaque-type psoriasis, mean peak plasma concentrations (±SD) of 59 ± 36 pg/mL of clobetasol were observed at around 5 hours post dose on Day 8.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of OLUX-E Foam or clobetasol propionate.
In a 90-day repeat-dose toxicity study in rats, topical administration of OLUX-E Foam at dose concentrations from 0.001% to 0.1% or from 0.03 to 0.3 mg/kg/day of clobetasol propionate resulted in a toxicity profile consistent with long term exposure to corticosteroids including adrenal atrophy, histopathological changes in several organs systems indicative of severe immune suppression and opportunistic fungal and bacterial infections. A no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL) could not be determined in this study. Although the clinical relevance of the findings in animals to humans is not clear, sustained glucocorticoid-related immune suppression may increase the risk of infection and possibly the risk for carcinogenesis.
Topical doses of 0% (foam vehicle), 0.001%, 0.01%, and 0.05% clobetasol propionate foam were evaluated in a 52-week dermal photocarcinogenicity study (40 weeks of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation) conducted in hairless albino mice with concurrent exposure to low-level ultraviolet radiation. Topical treatment with increasing concentrations of clobetasol propionate foam did not have an adverse effect in this study. The results of this study suggest that topical treatment with OLUX-E Foam would not enhance photocarcinogenesis.
Clobetasol propionate was non-mutagenic in 4 different test systems: the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma test, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene conversion assay, and the E. coli B WP2 fluctuation test. In the in vivo mouse micronucleus test, a positive finding was observed at 24 hours, but not at 48 hours, following oral administration at a dose of 2,000 mg/kg.
Studies in the rat following subcutaneous administration of clobetasol propionate at dosage levels up to 0.05 mg/kg per day revealed that the females exhibited an increase in the number of resorbed embryos and a decrease in the number of living fetuses at the highest dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In a randomized trial of subjects 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, 251 subjects were treated with OLUX-E Foam and 126 subjects were treated with vehicle foam. Subjects were treated twice daily for 2 weeks. At the end of treatment, 131 of 251 subjects (52%) treated with OLUX-E Foam compared with 18 of 126 subjects (14%) treated with vehicle foam achieved treatment success. Treatment success was defined by an Investigator’s Static Global Assessment (ISGA) score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) with at least 2 grades improvement from baseline, and scores of absent or minimal (0 or 1) for erythema and induration/papulation.
In an additional randomized trial of subjects 12 years and older with mild to moderate plaque-type psoriasis, 253 subjects were treated with OLUX-E Foam and 123 subjects were treated with vehicle foam. Subjects were treated twice daily for 2 weeks. At the end of treatment, 41 of 253 subjects (16%) treated with OLUX-E Foam compared with 5 of 123 subjects (4%) treated with vehicle foam achieved treatment success. Treatment success was defined by an ISGA score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) with at least 2 grades improvement from baseline, scores of none or faint/minimal (0 or 1) for erythema and scaling, and a score of none (0) for plaque thickness.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
OLUX-E (clobetasol propionate) Foam, 0.05% is a white to off-white aerosol foam supplied as follows:
- 50-g aluminum can NDC: 40076-101-50
- 100-g aluminum can NDC: 40076-101-00
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at controlled room temperature 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) with excursions permitted between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
FLAMMABLE. AVOID FIRE, FLAME OR SMOKING DURING AND IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWING APPLICATION.
Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not expose to heat or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
Keep out of reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Unless directed by the prescriber, it should not be used on the face or in skin-fold areas, such as the underarms or groin. Avoid contact with the eyes or other mucous membranes. Wash hands after use.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- The treated skin area should not be bandaged, wrapped, or otherwise covered so as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician.
- Patients should report any signs of local or systemic adverse reactions to the physician.
- Patients should inform their physicians that they are using OLUX-E Foam if surgery is contemplated.
- As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, contact the physician.
- Patients should not use more than 50 grams per week of OLUX-E Foam, or an amount greater than 21 capfuls per week [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- This medication is flammable; avoid heat, flame, or smoking when applying this product.
Manufactured for:
Prestium Pharma, Inc.
Newtown, PA 18940
By DPT Laboratories, Ltd.
San Antonio, TX 78215
OLUX-E is a registered trademark of Stiefel Laboratories, Inc.
2013 Delcor Asset Corporation, an affiliate of Prestium Pharma, Inc.
June 2013 -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
OLUX-E (O-lux-E)
(clobetasol propionate)
Foam
IMPORTANT: For skin use only. Do not get OLUX-E Foam in your eyes, mouth, or vagina.
Read the Patient Information that comes with OLUX-E Foam before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition or treatment.
What is OLUX-E Foam?
OLUX-E Foam is a prescription corticosteroid medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat adults and children 12 years and older with certain skin conditions that cause red, flaky, and itchy skin.
OLUX-E Foam should not be used:
- on your face, underarms, or groin area
- if you have skin thinning (atrophy) at the treatment area
You should not use OLUX-E Foam for longer than 2 weeks in a row.
You should not use more than 50 grams or 21 capfuls of OLUX-E Foam in 1 week.
What should I tell my doctor before using OLUX-E Foam?
Before you use OLUX-E Foam, tell your doctor if you:
- have had irritation or other skin reaction to a steroid medicine in the past.
- have a skin infection. You may need medicine to treat the skin infection before using OLUX-E Foam.
- have diabetes.
- have adrenal gland problems.
- have liver problems.
- plan to have surgery.
- have any other medical condition.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if OLUX-E Foam will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if OLUX-E Foam passes into your breast milk.
Do not apply OLUX-E Foam to your chest area if you are breastfeeding a baby. This will help to prevent the baby from accidentally getting OLUX-E Foam into the baby's mouth.
Tell your doctor about all the medicine you take including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially tell your doctor if you take other corticosteroid medicines by mouth or use other products on your skin that contain corticosteroids. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use OLUX-E Foam?
- See “What is OLUX-E Foam?”
- Use OLUX-E Foam exactly as your doctor tells you to use it. See the “Instructions for applying OLUX-E Foam”.
- This medicine is for use on the skin only. Do not get OLUX-E Foam in your eyes, mouth, or vagina.
- Apply OLUX-E Foam 2 times each day, 1 time in the morning and 1 time at night, or as directed by your doctor.
- Do not bandage or cover your treated area unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not use OLUX-E Foam for longer than 2 weeks in a row.
- Talk to your doctor if your skin does not improve after 2 weeks of treatment with OLUX-E Foam.
- See your doctor regularly to check your symptoms and side effects while taking OLUX-E Foam.
- OLUX-E Foam is flammable. Avoid heat, flame, or smoking during and right after using OLUX-E Foam.
Instructions for applying OLUX-E Foam
1. Before applying OLUX-E Foam for the first time, break the tiny plastic piece at the base of the can's rim by gently pushing back (away from the piece) on the nozzle. See Figure A.
Figure A: Break tiny plastic piece on the nozzle of the can of OLUX-E Foam.
2. Shake the can of OLUX-E Foam before use.
Figure B: Shake the can of OLUX-E Foam.
3. Turn the can of OLUX-E Foam upside down and press the nozzle. See Figure C.
Figure C: Turn the can of OLUX-E Foam upside down and press nozzle.
4. Dispense a small amount of OLUX-E Foam into the palm of your hand. See Figure D.
Figure D: Dispense OLUX-E Foam into hand.
5. Use enough OLUX-E Foam to cover the affected area with a thin layer. Gently rub the foam into affected area until it disappears into the skin.
Figure E: Cover affected area with thin layer of OLUX-E Foam. Rub foam gently into affected skin.
6. Avoid getting OLUX-E Foam in or near your mouth, eyes, or vagina; if contact happens, rinse well with water. Wash your hands well after applying OLUX-E Foam (excluding affected areas of hands).
What should I avoid while using OLUX-E Foam?
OLUX-E Foam is flammable. Avoid heat, flame, or smoking during and right after you apply it to your skin.
If you are taking other corticosteroid medicines, either by mouth or injection, your doctor may advise you to stop taking them once you begin using OLUX-E Foam.
What are the possible side effects of OLUX-E Foam?
OLUX-E Foam may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Symptoms of a disorder where the adrenal gland does not make enough of certain hormones (adrenal insufficiency) during treatment or after stopping treatment. Your doctor may do blood tests to check you for adrenal insufficiency while you are using OLUX-E Foam. Tell your doctor if you have any of these persistent symptoms of adrenal insufficiency:
- ∘tiredness that worsens and does not go away
- ∘muscle weakness
- ∘loss of appetite
- ∘nausea or vomiting
- ∘dizziness or fainting
- ∘irritability and depression
- ∘weight loss
-
Cushing’s syndrome, when the body is exposed to too much of the hormone cortisol. Your doctor may do tests to check for this. Symptoms can include:
- ∘weight gain, especially around your upper back and midsection
- ∘tiredness and muscle weakness
- ∘roundness of your face (moon face)
- ∘slow healing of cuts, insect bites and infections
- ∘depression, anxiety and irritability
- ∘new or worsening high blood pressure
- high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) or diabetes mellitus that has not been diagnosed can happen with treatment. Your doctor may do tests to check you for this.
- skin problems, including reactions where the medicine is applied, skin infections, and allergic reactions (allergic contact dermatitis). Tell your doctor if you get any new skin problems.
- effects on growth and weight in children.
The most common side effects of OLUX-E Foam include:
- thinning of skin
- burning
- redness
- itching
- dryness
Tell your doctor if you have any reaction on your treated skin such as pain, tenderness, swelling, or healing problems.
These are not all the side effects of OLUX-E Foam. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch, or to Prestium Pharma, Inc. at 1-866-897-5002.
How should I store OLUX-E Foam?
- Store OLUX-E Foam at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). OLUX-E Foam is flammable. Keep the can away from fire and heat.
- Do not pierce or burn the can of OLUX-E Foam. Never throw the can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
Keep OLUX-E Foam and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about OLUX-E Foam
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use OLUX-E Foam for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give OLUX-E Foam to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about OLUX-E Foam. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about OLUX-E Foam that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in OLUX-E Foam?
Active ingredient: clobetasol propionate, USP, 0.05%
Inactive Ingredients: anhydrous citric acid, cetyl alcohol, cyclomethicone, isopropyl myristate, light mineral oil, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, potassium citrate monohydrate, propylene glycol, purified water, sorbitan monolaurate, white petrolatum, and phenoxyethanol as a preservative, pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
Manufactured for:
Prestium Pharma, Inc.
Newtown, PA 18940
By DPT Laboratories, Ltd.
San Antonio, TX 78215
OLUX-E is a registered trademark of Stiefel Laboratories, Inc.
2013 Delcor Asset Corporation, an affiliate of Prestium Pharma, Inc.
June 2013
-
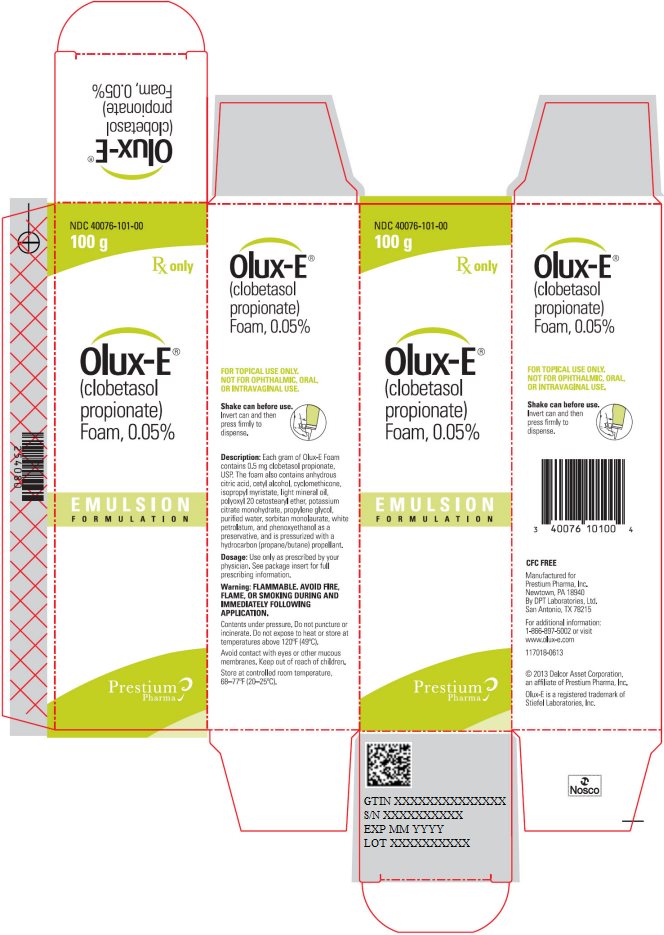
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 40076-101-00
100 g Rx only
Olux-E®
(clobetasol propionate) Foam, 0.05%
Emulsion Formulation
Prestium Pharma -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
OLUX-E
clobetasol propionate aerosol, foamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 40076-101 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE (UNII: 779619577M) (CLOBETASOL - UNII:ADN79D536H) CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE 0.5 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) CETYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 936JST6JCN) CYCLOMETHICONE (UNII: NMQ347994Z) ISOPROPYL MYRISTATE (UNII: 0RE8K4LNJS) LIGHT MINERAL OIL (UNII: N6K5787QVP) POLYOXYL 20 CETOSTEARYL ETHER (UNII: YRC528SWUY) POTASSIUM CITRATE (UNII: EE90ONI6FF) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SORBITAN MONOLAURATE (UNII: 6W9PS8B71J) PETROLATUM (UNII: 4T6H12BN9U) PHENOXYETHANOL (UNII: HIE492ZZ3T) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 40076-101-00 100 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/12/2007 09/30/2019 2 NDC: 40076-101-50 50 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/12/2007 07/31/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022013 02/12/2007 07/31/2020 Labeler - Prestium Pharma, Inc. (078304674)
Trademark Results [OLUX-E]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 OLUX-E 77077055 3437044 Live/Registered |
STIEFEL LABORATORIES, INC. 2007-01-05 |
 OLUX-E 77077028 3437043 Live/Registered |
STIEFEL LABORATORIES, INC. 2007-01-05 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.