PENMENVY (meningococcal- groups a, b, c, w and y kit
PENMENVY by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PENMENVY by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PENMENVY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PENMENVY.
PENMENVY (Meningococcal Groups A, B, C, W, and Y Vaccine) for injectable suspension, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PENMENVY is a vaccine indicated for active immunization to prevent invasive disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, B, C, W, and Y in individuals 10 through 25 years of age. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injectable suspension. A single dose after reconstitution is approximately 0.5 mL. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of PENMENVY, to any component of this vaccine, or to any other diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Syncope (fainting) has occurred in association with administration of PENMENVY. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported (≥10%) solicited adverse reactions after Dose 1 and Dose 2, respectively:
- in individuals aged 10 through 25 years were pain at the injection site (92% and 88%), fatigue (51% and 42%), headache (42% and 36%), myalgia (15% and 12%), nausea (15% and 10%), erythema (13% and 12%), and swelling (13% and 12%). (6.1)
- in MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑experienced individuals aged 15 through 25 years were pain at the injection site (80% and 74%), headache (41% and 33%), fatigue (40% and 33%), myalgia (15% and 13%), and nausea (15% and 12%). (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1-888-825-5249 or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 or www.vaers.hhs.gov.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dose and Schedule
2.2 Preparation
2.3 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Management of Allergic Reactions
5.2 Syncope
5.3 Limitation of Vaccine Effectiveness
5.4 Altered Immunocompetence
5.5 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage Before Reconstitution
16.3 Storage After Reconstitution
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular use.
2.2 Preparation
PENMENVY is supplied as one vial of Lyophilized MenACWY Component (powder) and one prefilled syringe of MenB Component (liquid) which must be combined before administration.
Use only the supplied MenB Component to reconstitute the Lyophilized MenACWY Component.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not administer PENMENVY to individuals with a severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a previous dose of PENMENVY, to any component of this vaccine, or to any other diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine [see Description (11)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Management of Allergic Reactions
Appropriate medical treatment must be immediately available to manage potential anaphylactic reactions following administration of PENMENVY.
5.2 Syncope
Syncope (fainting) has occurred in association with administration of PENMENVY. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting.
5.3 Limitation of Vaccine Effectiveness
Vaccination with PENMENVY may not protect all vaccine recipients. PENMENVY may not provide protection against all meningococcal serogroup B strains [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
5.4 Altered Immunocompetence
Reduced Immune Response
Immunocompromised persons, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapy, may have reduced immune responses to PENMENVY.
Complement Deficiency
Persons with certain complement deficiencies and persons receiving treatment that inhibits terminal complement activation are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by N. meningitidis, including disease caused by serogroups A, B, C, W, and Y, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination with PENMENVY [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
5.5 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Guillain‑Barré syndrome (GBS) has been reported in temporal relationship following administration of a U.S.‑licensed meningococcal quadrivalent polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. The decision by the healthcare professional to administer PENMENVY to persons with a history of GBS should take into account the expected benefits and potential risks.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported (≥10%) solicited adverse reactions after Dose 1 and Dose 2, respectively, in Study 1 in participants aged 10 through 25 years (87% of whom were MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑naïve) were pain at the injection site (92% and 88%), fatigue (51% and 42%), headache (42% and 36%), myalgia (15% and 12%), nausea (15% and 10%), erythema (13% and 12%), and swelling (13% and 12%).
The most commonly reported (≥10%) solicited adverse reactions after Dose 1 and Dose 2, respectively, in Study 2 in MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑experienced participants aged 15 through 25 years were pain at the injection site (80% and 74%), headache (41% and 33%), fatigue (40% and 33%), myalgia (15% and 13%), and nausea (15% and 12%).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another vaccine and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of PENMENVY was evaluated in 12 clinical studies1 in which a total of 3,718 participants received at least one dose of PENMENVY. Participants in Study 1 (aged 10 through 25 years) and Study 2 (aged 15 through 25 years) were scheduled to receive PENMENVY according to the approved dosing schedule (2 doses administered 6 months apart). Participants in the other studies may have received PENMENVY according to unapproved dosing schedules. Across the 12 studies, 2,969 participants received at least 1 dose of BEXSERO (Meningococcal Group B Vaccine) and 361 participants received a single dose of MENVEO [Meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y, and W‑135) Oligosaccharide Diphtheria CRM197 Conjugate Vaccine]. Across the studies, the median age was 16 years, males comprised 46%, and 86% of participants were White, 6% were Black, 4% were Asian, and 4% were of other racial groups. In these studies, 13% of participants were Hispanic. Approximately 35% of participants were from the U.S.
Nine of the 12 studies (including Study 1 and Study 2) collected non‑serious unsolicited adverse events through 30 days after each vaccination, and the other 3 studies collected these events through 7 days after each vaccination. All studies collected serious adverse events through at least 1 month following the last vaccination. Study 1 and Study 2 collected serious adverse events through 12 months following the first vaccination and at least 5 months following the last vaccination.
Study 1 (NCT04502693) was a randomized, controlled, observer‑blind study conducted in 7 countries (U.S., Australia, Canada, Czech Republic, Estonia, Finland, and Turkey). In this study, 1,657 participants aged 10 through 25 years received at least 1 dose of PENMENVY. Participants were scheduled to receive 2 doses of PENMENVY 6 months apart. Separate groups received BEXSERO either as a 0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule or 0‑, 6‑month schedule. A single dose of MENVEO was administered 1 month after the third dose in the 0‑, 2‑, 6‑month group and 2 months after the first dose of BEXSERO in the 0‑, 6‑month group (these participants received saline placebo at month 7). A separate group received a single dose of MENVEO at month 0, a saline placebo dose at month 2, and doses of BEXSERO at months 6 and 7 (an unapproved BEXSERO dosing regimen). All participants were MenB vaccine‑naïve. Both MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑naïve (87%) and MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑experienced (13%, vaccinated at least 4 years prior to study enrollment) participants were part of the study. The median age was 16 years, males comprised 47%, and 89% of participants were White, 5% were Asian, 4% were Black, and 2% were of other racial groups. Among study participants, 5% were Hispanic. Approximately 30% of participants were from the U.S.
Study 2 (NCT04707391) was a randomized, controlled, observer‑blind study conducted in 4 countries (U.S., Australia, Canada, and Argentina). In this study, 626 participants aged 15 through 25 years received at least 1 dose of PENMENVY. All participants were MenACWY conjugate vaccine‑experienced (vaccinated at least 4 years prior to study enrollment). A separate group received a single dose of MENVEO followed 6 months later by 2 doses of BEXSERO administered 1 month apart (an unapproved BEXSERO dosing regimen). In this study, the median age was 16 years, males comprised 47%, and 75% of participants were White, 14% were Black, 6% were of other racial groups, and 4% were Asian. Among study participants, 30% were Hispanic. Approximately 59% of participants were from the U.S.
Solicited Adverse Reactions
In Study 1, solicited local and systemic adverse reactions were collected for 7 days after study vaccination using electronic diaries. The rates of local and systemic adverse reactions reported in Study 1 among participants aged 10 through 25 years following each dose of PENMENVY administered 6 months apart, each dose of BEXSERO administered 6 months apart, or a single dose of MENVEO are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Percentage of Participants Aged 10 Through 25 Years Reporting Solicited Local and Systemic Adverse Reactions Within 7 Days of PENMENVY, BEXSERO, or MENVEO, by Dose in Study 1 Study 1: NCT04502693. N = Number of participants in Solicited Safety Set (participants who received at least 1 dose of study vaccine who reported solicited safety data). a Erythema, swelling, and induration: Any (≥25 mm); Severe (>100 mm). Pain, fatigue, nausea, myalgia, arthralgia, headache: Any includes Mild (transient with no limitation in normal daily activity), Moderate (some limitation in normal daily activity), and Severe (unable to perform normal daily activity). Fever: Any (≥38.0°C/100.4°F); Severe (≥40.0°C/104.0°F). PENMENVY
%
BEXSERO
%
MENVEO
%
Solicited Reactiona
Dose 1
Dose 2
Dose 1
Dose 2
Dose 1
N = 1,638
N = 1,428
N = 894
N = 759
N = 178
Local Adverse Reactions
Pain
Any
92
88
92
89
38
Severe
6
7
6
8
0
Erythema
Any
13
12
10
12
6
Severe
1
2
1
1
1
Swelling
Any
13
12
10
11
6
Severe
2
2
1
2
1
Induration
Any
9
8
7
8
4
Severe
1
1
2
1
0
Systemic Adverse Reactions
Fatigue
Any
51
42
46
45
44
Severe
3
3
1
3
2
Nausea
Any
15
10
12
11
15
Severe
0.3
0.3
1
0.4
1
Myalgia
Any
15
12
12
14
7
Severe
1
1
1
0.4
0
Arthralgia
Any
8
7
8
7
10
Severe
1
0.4
0.3
0
0
Headache
Any
42
36
37
37
39
Severe
2
1
1
1
2
Fever
Any
3
2
2
3
2
Severe
0.1
0.1
0.1
0
1
In Study 2, solicited local and systemic adverse reactions were collected for 7 days after study vaccination using electronic diaries. The rates of local and systemic adverse reactions reported in Study 2 among participants aged 15 through 25 years following each dose of PENMENVY administered 6 months apart or a single dose of MENVEO are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Percentage of Participants Aged 15 Through 25 Years Reporting Solicited Local and Systemic Adverse Reactions Within 7 Days of PENMENVY or MENVEO, by Dose in Study 2 Study 2: NCT04707391. N = Number of participants in Solicited Safety Set (participants who received at least 1 dose of study vaccine who reported solicited safety data). a Erythema, swelling, and induration: Any (≥25 mm); Severe (>100 mm). Pain, fatigue, nausea, myalgia, arthralgia, headache: Any includes Mild (transient with no limitation in normal daily activity), Moderate (some limitation in normal daily activity), and Severe (unable to perform normal daily activity). Fever: Any (≥38.0°C/100.4°F); Severe (≥40.0°C/104.0°F). PENMENVY
%
MENVEO
%
Solicited Reactiona
Dose 1
Dose 2
Dose 1
N = 608
N = 505-507
N = 600-601
Local Adverse Reactions
Pain
Any
80
74
32
Severe
3
3
0.3
Erythema
Any
5
6
2
Severe
0.5
0.6
0
Swelling
Any
4
6
2
Severe
0.3
0.6
0.3
Induration
Any
4
5
2
Severe
2
0.6
0.2
Systemic Adverse Reactions
Fatigue
Any
40
33
37
Severe
1
2
0.5
Nausea
Any
15
12
13
Severe
0.5
1
0.7
Myalgia
Any
15
13
11
Severe
0.2
0.4
0.3
Arthralgia
Any
7
6
8
Severe
0
0.2
0
Headache
Any
41
33
35
Severe
1
1
0.7
Fever
Any
2
2
1
Severe
0.2
0.4
0.2
Unsolicited Adverse Events
In an analysis across the 12 studies, unsolicited adverse events that were reported in participants who received PENMENVY (N = 3,718) and were determined to be causally related included syncope, dizziness, and pre‑syncope (0.9%); lymphadenopathy (0.2%); and hypersensitivity (0.1%). The onset of syncope, dizziness, pre‑syncope, and lymphadenopathy ranged from 1 to 30 days and the onset of hypersensitivity ranged from 9 to 27 days.
Serious Adverse Events
In Study 1, serious adverse events that occurred through 12 months following the first vaccination and at least 5 months following the last vaccination were reported by 1.5% of participants in the PENMENVY group (N = 1,648), 2.4% of participants in the group who received BEXSERO as a 0‑, 6‑month schedule with a dose of MENVEO at month 2 (N = 900), and 2.8% of participants in the group who received MENVEO at month 0 and BEXSERO at months 6 and 7 (N = 178).
In Study 2, serious adverse events that occurred through 12 months following the first vaccination and at least 5 months following the last vaccination were reported by 2.9% of participants in the PENMENVY group (N = 626) and 1.1% of participants in the group who received MENVEO at month 0 and BEXSERO at months 6 and 7 (N = 621).
Across the 12 clinical studies, serious adverse events were reported within 30 days after any dose by 0.6% of participants who received PENMENVY (N = 3,718), 0.4% of participants who received BEXSERO (N = 2,969), and 0.3% of participants who received MENVEO (N = 361). Two serious adverse events reported following administration of PENMENVY were assessed as vaccine‑related and are described below.
In Study 3,1 connective tissue disorder was reported in an adolescent participant who developed 3 episodes of petechiae (7 days after PENMENVY Dose 1, 18 days after PENMENVY Dose 2 [given 1 month after Dose 1], and 17 days after HAVRIX [Hepatitis A Vaccine]) and was diagnosed with a connective tissue disorder 44 days after PENMENVY Dose 2.
In Study 3,1 seizures were reported in an adult participant with onset 9 hours after PENMENVY Dose 1.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during postapproval use of BEXSERO or MENVEO. The postmarketing safety experience with BEXSERO and MENVEO is relevant because PENMENVY contains the same group A, C, W, and Y CRM197‑conjugated oligosaccharide components and MenB recombinant protein components. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the vaccine exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Lymphadenopathy.a,b
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders
Hearing impaired,b ear pain,b vertigo,b vestibular disorder.b
Eye Disorders
Eyelid ptosis.b
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Injection site reactions (including injection site pruritus,b pain,b erythema,b inflammation,b swelling,b extensive swelling of the vaccinated limb,a,b blisters at or around the injection site,a and injection site nodule which may persist for more than 1 montha), fatigue,b malaise,b pyrexia.b
Immune System Disorders
Allergic reactions,a anaphylactic reactions,a eye swelling,a rash,a hypersensitivity reactions,b anaphylaxis.b
Infections and Infestations
Vaccination site cellulitis.b
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications
Fall,b head injury.b
Investigation
Alanine aminotransferase increased,b body temperature increased.b
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Arthralgia,b bone pain.b
Nervous System Disorders
Dizziness,b syncope,a,b tonic convulsion,b headache,b facial paresis,b balance disorder,b vasovagal responses to injection.a
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders
Oropharyngeal pain.b
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Skin exfoliation.b
a Observed with BEXSERO.
b Observed with MENVEO.
Postmarketing Observational Safety Study
In a postmarketing observational safety study conducted in a U.S. health maintenance organization, data from electronic health records of 48,899 persons aged 11 through 21 years were used to evaluate pre‑specified events of interest following vaccination with MENVEO. Using a self‑controlled case series method, Bell’s palsy showed a statistically significant increased risk in the period 1 to 84 days post vaccination compared with the control period, with an overall adjusted relative incidence of 2.9 (95% CI: 1.1‑7.5). Among the 8 reported cases of Bell’s palsy, 6 cases occurred in persons who received MENVEO concomitantly with one or more of the following vaccines: Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed (Tdap), a human papillomavirus vaccine, and Influenza Vaccine. All reported Bell’s palsy cases resolved.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of PENMENVY in pregnant women. Available human data on PENMENVY administered to pregnant women are insufficient to inform vaccine-associated risks in pregnancy.
A developmental toxicity study was performed in female rabbits administered a dose of PENMENVY (0.5 mL) on 5 occasions, three times prior to mating and twice during gestation. This study revealed no vaccine‑related effects on female fertility, fetal development or postnatal development (see Data).
Animal Data: In a developmental toxicity study, female rabbits were administered a dose of PENMENVY (0.5 mL) by intramuscular injection on 5 occasions: 35, 21 and 7 days prior to mating, and on gestation days 7 and 20. No vaccine‑related adverse effects on female fertility, fetal development, or postnatal development were reported in the study.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether the vaccine components of PENMENVY are excreted in human milk. Available data are not sufficient to assess the effects of PENMENVY on the breastfed infant or on milk production/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for PENMENVY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from PENMENVY or from the underlying maternal condition. For preventive vaccines, the underlying maternal condition is susceptibility to disease prevented by the vaccine.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
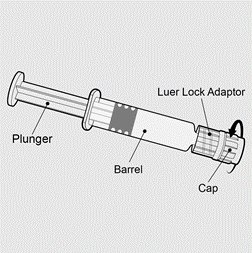
PENMENVY (Meningococcal Groups A, B, C, W, and Y Vaccine) is a sterile injectable suspension for intramuscular use. The vaccine is supplied as one vial of Lyophilized MenACWY Component which is reconstituted at the time of use with the accompanying prefilled syringe of MenB Component.
The Lyophilized MenACWY Component contains N. meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y oligosaccharides conjugated individually to Corynebacterium diphtheriae CRM197 protein. The polysaccharides are produced by bacterial fermentation of N. meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, or Y. N. meningitidis serogroup A, C, W, and Y strains are each cultured and grown on Franz Complete medium and treated with formaldehyde. MenA, MenW, and MenY polysaccharides are purified by several steps, including extraction, filtration, and precipitation. MenC polysaccharide is purified by a combination of extraction, chromatography, and precipitation steps.
The protein carrier (CRM197) is produced by bacterial fermentation and is purified by a series of chromatography and ultrafiltration steps. The C. diphtheriae is cultured and grown on CY medium containing yeast extracts and amino acids.
The oligosaccharides are prepared for conjugation from the purified polysaccharides which are processed by hydrolysis, sizing, and reductive amination. After activation, each oligosaccharide is covalently linked to the CRM197 protein. The resulting glycoconjugates are purified to yield the four drug substances, which are formulated with sucrose and phosphate and lyophilized to form the Lyophilized MenACWY Component. The Lyophilized MenACWY Component is a white to off‑white lyophilized cake.
The MenB Component contains recombinant N. meningitidis proteins Neisseria adhesin A (NadA), Neisserial Heparin Binding Antigen (NHBA), and factor H binding protein (fHbp), and Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMV). The NadA component is a fragment of the full‑length protein derived from N. meningitidis strain 2996 (peptide 8 variant 2/3).2 The NHBA component is a recombinant fusion protein comprised of NHBA (peptide 2)2 and accessory protein 953 derived from N. meningitidis strains NZ98/254 and 2996, respectively. The fHbp component is a recombinant fusion protein comprised of fHbp (variant 1.1)2 and the accessory protein 936 derived from N. meningitidis strains MC58 and 2996, respectively. These 3 recombinant proteins are individually produced in Escherichia coli and purified through a series of column chromatography steps. The OMV antigenic component is produced by fermentation of N. meningitidis strain NZ98/254 (expressing outer membrane protein Porin A [PorA] serosubtype P1.4),3 followed by inactivation of the bacteria by deoxycholate, which also mediates vesicle formation. The antigens are adsorbed onto aluminum hydroxide. The MenB Component is a white opalescent suspension.
After reconstitution, each approximately 0.5‑mL dose contains 10 mcg MenA oligosaccharide; 5 mcg of each of MenC, MenW, and MenY oligosaccharides; 25.9 to 64.1 mcg CRM197 protein; 50 mcg each of recombinant proteins NadA, NHBA, and fHbp; and 25 mcg of OMV. Each dose also contains 1.5 mg aluminum hydroxide (0.5 mg of Al3+), 3.125 mg sodium chloride, 0.776 mg histidine, 22.5 mg sucrose, and ≤0.7 mg potassium phosphate salts. Each dose contains less than 0.01 mcg kanamycin (by calculation). Residual formaldehyde per dose is estimated to be not more than 0.30 mcg. After reconstitution, PENMENVY is a white opalescent suspension.
The tip cap and rubber plunger of the prefilled syringe and the stopper of the vial are not made with natural rubber latex.
PENMENVY does not contain preservatives.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Protection against invasive meningococcal disease is conferred mainly by complement‑mediated antibody‑dependent killing of N. meningitidis strains.4 Immunization with PENMENVY is intended to stimulate the production of antibodies with bactericidal activity specific to the capsular polysaccharides of N. meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y and to the protein antigens NHBA, NadA, fHbp and OMV expressed by serogroup B meningococcal strains.
NHBA, NadA, and fHbp are proteins found on the surface of meningococci and contribute to the ability of the bacterium to cause disease. OMV derived from the bacterial outer membrane contains PorA and other surface proteins. The susceptibility of serogroup B meningococci to complement‑mediated antibody‑dependent killing following vaccination with PENMENVY is dependent on both the antigenic similarity of the bacterial and vaccine antigens, as well as the amount of antigen expressed on the surface of the invading meningococci.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of PENMENVY was assessed by measuring serum bactericidal activity (SBA) in an assay that used endogenous complement preserved in the serum samples collected from study participants (enc-hSBA) and an assay that used an exogenous source of human complement (hSBA).
The enc-hSBA assay was used to assess effectiveness against diverse N. meningitidis serogroup B strains. Participants’ sera were tested for the presence or absence of bactericidal activity to measure breadth of immune response against a panel of 110 diverse U.S. disease-causing N. meningitidis serogroup B strains that were collected between 2000 and 2008. The panel includes most antigen types found among serogroup B isolates circulating in the U.S. between 2000 and 2017, and includes some strains with genetic profiles characterized as hypervirulent. Each participant’s serum was tested at a four-fold dilution against a maximum of 35 strains randomly selected from the panel.
The hSBA assay measured bactericidal activity in participants’ sera against the 5 N. meningitidis serogroups. For serogroup B, four meningococcal serogroup B indicator strains expressing different antigens (fHbp, NadA, NHBA and OMV) were utilized. For serogroups A, C, W, and Y, one strain was utilized per serogroup.
Breadth of Immune Response Elicited by PENMENVY Against Serogroup B (enc-hSBA Assay)
Study 1 evaluated enc-hSBA responses in participants aged 10 through 25 years at one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY, after Dose 2 of the BEXSERO 0-, 6-month schedule, after Dose 3 of the BEXSERO 0-, 2-, 6-month schedule, and after a single dose of MENVEO, using responder-based and test-based analyses.
Responder-based analyses (Table 3) evaluated the percentages of participants whose sera killed ≥70% of the tested strains.
Table 3. Percentage of Participants Whose Sera Killed ≥70% of Meningococcal Serogroup B Strains Testeda (Responder-Based) Following PENMENVY and BEXSERO, Study 1b Study 1: NCT04502693. N = Number of participants, CI = Confidence interval. a Each participant’s serum was tested using the enc‑hSBA assay for bactericidal activity (yes/no) against a maximum of 35 strains randomly selected from the 110‑strain panel. b Full Analysis Set includes all participants who received at least 1 dose of the study treatment and have post‑vaccination immunogenicity data. c enc‑hSBA response was measured one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY, one month after Dose 2 of BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule), or one month after Dose 3 of BEXSERO (0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule). d % Responders is defined as percentages of participants whose serum kills ≥70% of strains tested using the enc‑hSBA assay. e Predefined criterion (lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI >65%) met. CI calculated using Clopper‑Pearson method. Groupc
N
% Respondersd
(95% CI)
PENMENVY
817
84.1
(81.4e, 86.5)
BEXSERO (0, 6 Months)
813
89.8
(87.5, 91.8)
BEXSERO (0, 2, 6 Months)
790
93.4
(91.5, 95.0)
Of the approximately 35 serogroup B strains tested per participant in the enc‑hSBA assay at 1 month following vaccination, the median percentage killed by each participant’s serum was 85.3% (25th percentile, 74.3%; 75th percentile, 91.4%) after Dose 2 of PENMENVY; 88.2% (25th percentile, 80.0%; 75th percentile, 94.3%) after Dose 2 of the 0‑, 6‑month BEXSERO schedule; 88.6% (25th percentile, 80.0%; 75th percentile, 94.3%) after Dose 3 of the 0‑, 2‑, 6‑month BEXSERO schedule; and 17.1% (25th percentile, 11.1%; 75th percentile, 26.7%) after MENVEO.
Test‑based analyses evaluated the percentage of tests with bactericidal activity. The non‑inferiority criterion was met for the percentage of tests with bactericidal activity following PENMENVY compared with BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule) (Table 4).
Table 4. Percentages of Testsa With Bactericidal Activity Against Meningococcal Serogroup B Strains Following PENMENVY, BEXSERO, and MENVEO, Study 1b Study 1: NCT04502693. n = Number of tests with bactericidal activity, N = Total number of tests, CI = Confidence interval. a Each test qualitatively assessed (yes/no) the bactericidal activity of one participant’s serum using the enc‑hSBA assay against one of the 110 U.S. meningococcal serogroup B strains. Each participant’s serum was tested against a maximum of 35 strains randomly selected from the 110‑strain panel. b Per Protocol Set includes all participants in the Full Analysis Set minus participants with protocol deviations that lead to exclusion from the Per Protocol Set. c enc‑hSBA responses were measured one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY, one month after Dose 2 of BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule), one month after Dose 3 of BEXSERO (0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule), or one month after a single dose of MENVEO. d Predefined non‑inferiority criterion was defined as lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI for vaccine group differences [PENMENVY minus BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule)] above -5%. Criterion for non‑inferiority of PENMENVY to more than one comparator with respect to percent of tests with bactericidal activity was not pre‑specified. e Met predefined non‑inferiority criterion. CI calculated using Miettinen and Nurminen method. Groupc
Number of Participants
% of Tests with Bactericidal Activity
(n/N)
Percent Difference PENMENVY –
BEXSERO (0, 6 Months)
(95% CI)d
PENMENVY
754
82.5
(21,222 / 25,715)
-3.0
(-3.7e, -2.4)
BEXSERO
(0, 6 Months)
764
85.6
(22,365 / 26,142)
BEXSERO
(0, 2, 6 Months)
747
86.7
(22,184 / 25,596)
-
MENVEO
133
21.0
(918 / 4,374)
-
For each individual strain in the 110‑strain panel, the percentage of tests with bactericidal activity following PENMENVY ranged from 2% to 100%; the median was 97% (25th percentile, 70%; 75th percentile, 99%). For each individual strain, the percentage of tests with bactericidal activity following BEXSERO ranged from 4% to 100%; the median was 97% (25th percentile, 80%; 75th percentile, 99%) for the 0‑, 6‑month schedule and 98% (25th percentile, 85%; 75th percentile, 99%) for the 0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule. For each individual strain, the percentage of tests with bactericidal activity following MENVEO ranged from 0% to 100%; the median was 12% (25th percentile, 3%; 75th percentile, 28%).
Immune Response to PENMENVY Against Serogroup B (hSBA Assay)
In Study 1, immune responses in participants aged 10 through 25 years were measured at one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY, after Dose 2 of the BEXSERO 0‑, 6‑month schedule, and after Dose 3 of the BEXSERO 0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule with hSBA assays using indicator strains representative of each of the 4 antigenic components of PENMENVY (fHbp, NadA, NHBA, and OMV). The percentages of participants who achieved a 4‑fold or greater increase in hSBA titer for each of the 4 strains (seroresponse) and the percentages of participants with a titer greater than or equal to the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) of the assay for all 4 strains (composite response) are shown in Table 5.
Non‑inferiority of PENMENVY compared with BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule) for the proportion of participants with a seroresponse was demonstrated for meningococcal serogroup B indicator strains for fHbp and NadA, but not for indicator strains for NHBA or OMV (Table 5).
Table 5. Percentages of Participants With hSBA Seroresponse and Composite Response Against Meningococcal Serogroup B Indicator Strains Following PENMENVY and BEXSERO, Study 1a Study 1: NCT04502693. hSBA = Serum bactericidal activity measured using an exogenous source of human complement, CI = Confidence interval, fHbp = Factor H binding protein, N = Number of participants, NadA = Neisseria adhesin A, NHBA = Neisserial Heparin Binding Antigen, OMV = Outer Membrane Vesicles, LOD = Limit of detection, LLOQ = Lower limit of quantitation. a hSBA responses were measured one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY or one month after Dose 2 of BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule). b Per Protocol Set includes all participants in the Full Analysis Set minus participants with protocol deviations that lead to exclusion from the Per Protocol Set. c Seroresponse is defined as: a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LOD or ≥LLOQ, whichever is greater, for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer <LOD, a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LLOQ for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LOD and <LLOQ, and a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the pre‑vaccination hSBA titer for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LLOQ. d LOD = 4 for fHbp; 6 for NadA; 4 for NHBA; 4 for OMV. LLOQ = 5 for fHbp; 14 for NadA; 6 for NHBA; 6 for OMV. e CI calculated using Clopper‑Pearson method. f Met predefined non‑inferiority criterion (lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI above -10% for vaccine group differences [PENMENVY minus BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule)]). CI calculated using Miettinen and Nurminen method. g Did not meet predefined non‑inferiority criterion (lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI below -10% for vaccine group differences [PENMENVY minus BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule)]). CI calculated using Miettinen and Nurminen method. h Full Analysis Set includes all participants who received at least 1 dose of the study treatment and have post‑vaccination immunogenicity data. i Composite Response is defined as hSBA ≥LLOQ for all 4 meningococcal B indicator strains. j Criterion for non‑inferiority of PENMENVY to BEXSERO (0‑, 6‑month schedule) with respect to the composite response was not pre‑specified. % Seroresponse
(95% CI)b,c,d,e
Antigen
(Indicator Strain)
PENMENVY
BEXSERO
(0, 6 Months)
Percent Difference
PENMENVY –
BEXSERO
fHbp
(M14459)
N = 675
73.2
(69.7, 76.5)
N = 654
78.1
(74.8, 81.2)
-5.0
(-9.6f, -0.3)
NadA
(96217)
N = 671
92.7
(90.5, 94.5)
N = 655
95.9
(94.1, 97.3)
-3.2
(-5.8f, -0.7)
NHBA
(M13520)
N = 678
61.8
(58.0, 65.5)
N = 659
69.7
(66.0, 73.1)
-7.9
(-12.9g, -2.8)
OMV
(NZ98/254)
N = 642
42.2
(38.4, 46.1)
N = 624
58.3
(54.4, 62.2)
-16.1
(-21.5g, -10.6)
% Composite Response
(95% CI)d,e,h,i,j
Timepoint
PENMENVY
BEXSERO
(0, 6 Months)
-
Baseline
(pre‑vaccination)
N = 747
1.1
(0.5, 2.1)
N = 708
0.6
(0.2, 1.4)
-
1 Month
post‑dose 2
N = 707
70.0
(66.5, 73.4)
N = 683
80.1
(76.9, 83.0)
-
The percentages of participants with seroresponses after Dose 3 of BEXSERO (0‑, 2‑, 6‑month schedule) were 81.1% (95% CI: 77.8, 84.1) for fHbp; 98.8% (95% CI: 97.6, 99.5) for NadA; 66.4% (95% CI: 62.6, 70.0) for NHBA; 56.4% (95% CI: 52.3, 60.4) for OMV (Per Protocol Set). The composite response at baseline and 1 month after dose 3 was 1.1% (95% CI: 0.5, 2.2.) and 81.5% (95% CI: 78.3, 84.4), respectively (Full Analysis Set).
Immune Response to PENMENVY Against Serogroups A, C, W, and Y (hSBA Assay)
The serum bactericidal antibody responses were measured using hSBA assay against serogroups A, C, W, and Y in MenACWY vaccine‑naïve participants in Study 1 and in MenACWY vaccine‑experienced participants in Study 2.
The non‑inferiority criteria for the percentages of participants achieving a seroresponse against each of the four serogroups A, C, W, and Y were met at one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY compared to a single dose of MENVEO in MenACWY vaccine‑naïve participants (Table 6) and in MenACWY vaccine‑experienced participants (Table 7).
Table 6. Percentages of Participants With hSBA Seroresponses Against Meningococcal Serogroups A, C, W, and Y Strains Following PENMENVY and MENVEO, MenACWY-Naïve, Study 1a,b Study 1: NCT04502693. hSBA = Serum bactericidal activity measured using an exogenous source of human complement, CI = Confidence interval, N = Number of participants, LOD = Limit of detection, LLOQ = Lower limit of quantitation. a Per Protocol Set includes all participants in the Full Analysis Set minus participants with protocol deviations that lead to exclusion from the Per Protocol Set. b Immune responses were measured one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY or a single dose of MENVEO relative to baseline. c Seroresponse is defined as: a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LOD for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer <LOD, a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LLOQ for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LOD and <LLOQ, and a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the pre‑vaccination hSBA titer for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LLOQ. d LOD = 5 for MenA; 4 for MenC, MenW, and MenY. LLOQ = 12 for MenA; 8 for MenC; 8 for MenW; 10 for MenY. e CI calculated using Clopper‑Pearson method. f Met predefined non‑inferiority criterion (lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI above -10% for vaccine group differences [PENMENVY minus MENVEO]). CI calculated using Miettinen and Nurminen method. Serogroup
% Seroresponsec,d
(95% CI)e
Percent Difference PENMENVY –
MENVEO
(95% CI)
PENMENVY
MENVEO
A
N = 1,170
96.8
(95.7, 97.8)
N = 111
85.6
(77.6, 91.5)
11.3
(5.8f, 19.0)
C
N = 1,189
97.2
(96.1, 98.1)
N = 114
50.0
(40.5, 59.5)
47.2
(38.1f, 56.3)
W
N = 1,185
97.0
(95.9, 97.9)
N = 115
61.7
(52.2, 70.6)
35.3
(26.9f, 44.5)
Y
N = 1,196
96.7
(95.6, 97.7)
N = 119
69.7
(60.7, 77.8)
27.0
(19.4f, 35.8)
Table 7. Percentages of Participants With hSBA Seroresponses Against Meningococcal Serogroups A, C, W, and Y Strains Following PENMENVY and MENVEO, MenACWY-Experienced, Study 2a,b Study 2: NCT04707391. hSBA = Serum bactericidal activity measured using an exogenous source of human complement, CI = Confidence interval, N = Number of participants, LOD = Limit of detection, LLOQ = Lower limit of quantitation. a Per Protocol Set includes all participants in the Full Analysis Set minus participants with protocol deviations that lead to exclusion from the Per Protocol Set. b Immune responses were measured one month after Dose 2 of PENMENVY or a single dose of MENVEO relative to baseline. c Seroresponse is defined as: a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LOD for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer <LOD, a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the LLOQ for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LOD and <LLOQ, and a post‑vaccination hSBA titer at least 4‑fold the pre‑vaccination hSBA titer for participants with pre‑vaccination hSBA titer ≥LLOQ. d LOD = 5 for MenA; 4 for MenC, MenW, and MenY. LLOQ = 12 for MenA; 8 for MenC; 8 for MenW; 10 for MenY. e CI calculated using Clopper‑Pearson method. f Met predefined non‑inferiority criterion (lower limit of the 2‑sided 95% CI above -10% for vaccine group differences [PENMENVY minus MENVEO]). CI calculated using Miettinen and Nurminen method. Serogroup
% Seroresponsec,d
(95% CI)e
Percent Difference
PENMENVY –
MENVEO
(95% CI)
PENMENVY
MENVEO
A
N = 168
95.8
(91.6, 98.3)
N = 501
95.2
(93.0, 96.9)
0.6
(-3.8f, 3.8)
C
N = 181
94.5
(90.1, 97.3)
N = 546
94.0
(91.6, 95.8)
0.5
(-4.1f, 4.0)
W
N = 181
95.6
(91.5, 98.1)
N = 544
93.9
(91.6, 95.8)
1.6
(-2.7f, 4.9)
Y
N = 180
95.0
(90.7, 97.7)
N = 537
94.4
(92.1, 96.2)
0.6
(-3.9f, 3.9)
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1. Study 1 (NCT04502693), Study 2 (NCT04707391), Study 3 (NCT02212457), Study 4 (NCT02451514), Study 5 (NCT01272180), Study 6 (NCT01992536), Study 7 (NCT02946385), Study 8 (NCT02140762), Study 9 (NCT02285777), Study 10 (NCT01210885), Study 11 (NCT01367158), Study 12 (GSK Study V102P1)
- 2. Wang X, et al. Prevalence and genetic diversity of candidate vaccine antigens among invasive Neisseria meningitidis isolates in the United States. Vaccine. 2011; 29:4739‑4744.
- 3. Hosking J, et al. Immunogenicity, reactogenicity, and safety of a P1.7b,4 strain‑specific serogroup B meningococcal vaccine given to preteens. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007;14:1393‑1399.
- 4. Goldschneider I, Gotschlich EC, Artenstein MS. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969;129:1307‑1326.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
PENMENVY is supplied in cartons containing:
- 10 vials of Lyophilized MenACWY Component (powder) and
- 10 prefilled TIP‑LOK syringes (Luer Lock syringes) of MenB Component (liquid) packaged without needles.
TIP‑LOK syringes are to be used with Luer Lock compatible needles.
The tip cap and rubber plunger of the prefilled syringe and the stopper of the vial are not made with natural rubber latex.
Table 8. Product Presentation for PENMENVY Presentation
Carton NDC Number
Components
Lyophilized MenACWY Component (powder)
MenB Component
(liquid)
Carton of 10 doses
NDC 58160‑757‑15
10 Vials
NDC 58160‑730‑03
10 Prefilled syringes
NDC 58160‑750‑03
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Give the patient, parent, or guardian the Vaccine Information Statements, which are required by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986 to be given prior to immunization. These materials are available free of charge at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (www.cdc.gov/vaccines).
Provide the following information to the vaccine recipient, parent, or guardian:
- Potential benefits and risks of immunization with PENMENVY.
- The importance of completing the immunization series.
- Potential for adverse reactions that have been temporally associated with administration of PENMENVY or other vaccines containing similar components.
- Advise them to report any adverse reactions to their healthcare provider, to GlaxoSmithKline at 1-888-825-5249, or through the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) at 1-800-822-7967 (or online at www.vaers.hhs.gov).
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.Manufactured by:
GSK Vaccines, Srl
Bellaria-Rosia 53018, Sovicille (SI), Italy
U.S. License No. 1617
Distributed by:
GlaxoSmithKline
Durham, NC 27701
©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
PMV:2PI -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 58160-757-15
PENMENVY
Meningoccal Groups A, B, C, W, and Y Vaccine
MenABCWY
Rx only
Notice: Lyophilized MenACWY Component and MenB Component must be combined before use.
10 Years through 25 Years of Age
Contents (10 doses of PENMENVY):
10 vials of Lyophilized MenaCWY Component
10 prefilled syringes of MenB Component
After reconstitution, a single dose of PENMENVY is approximately 0.5 mL
For intramuscular use
TIP-LOK syringes to be used with Luer Lock compatible needles
NEEDLES NOT INCLUDED
PENMENVY
©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
Rev. 2/25
520997
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PENMENVY
meningococcal (groups a, b, c, w and y) kitProduct Information Product Type VACCINE Item Code (Source) NDC: 58160-757 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58160-757-15 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 10 VIAL 5 mL Part 2 10 SYRINGE 5 mL Part 1 of 2 MENACWY
meningococcal (groups a, c, w and y) injection, powder, lyophilized, for suspensionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 58160-730 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP A CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN (UNII: 3O44U6XYQK) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP A CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN - UNII:3O44U6XYQK) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP A CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN 10 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP C CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN (UNII: H2W22AGF1P) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP C CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN - UNII:H2W22AGF1P) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP C CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN 5 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP W-135 CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN (UNII: 5JT3N61JSP) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP W-135 CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN - UNII:5JT3N61JSP) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP W-135 CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN 5 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP Y CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN (UNII: 2W566Z2PEJ) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP Y CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN - UNII:2W566Z2PEJ) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP Y CAPSULAR OLIGOSACCHARIDE DIPHTHERIA CRM197 PROTEIN CONJUGATE ANTIGEN 5 ug in 0.5 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58160-730-03 0.5 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125819 02/14/2025 Part 2 of 2 MENB
meningococcal (groups b) solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 58160-750 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NHBA FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN (UNII: 28E911Y7AE) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NHBA FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN - UNII:28E911Y7AE) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NHBA FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN 50 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B FHBP FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN (UNII: 25DB599G64) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B FHBP FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN - UNII:25DB599G64) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B FHBP FUSION PROTEIN ANTIGEN 50 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NADA PROTEIN ANTIGEN (UNII: 1S25R442RS) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NADA PROTEIN ANTIGEN - UNII:1S25R442RS) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B NADA PROTEIN ANTIGEN 50 ug in 0.5 mL NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B STRAIN NZ98/254 OUTER MEMBRANE VESICLE ANTIGEN (UNII: 91523M4S24) (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B STRAIN NZ98/254 OUTER MEMBRANE VESICLE ANTIGEN - UNII:91523M4S24) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS GROUP B STRAIN NZ98/254 OUTER MEMBRANE VESICLE ANTIGEN 25 ug in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ALUMINUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 5QB0T2IUN0) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) DIBASIC POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: CI71S98N1Z) MONOBASIC POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: 4J9FJ0HL51) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58160-750-03 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125819 02/14/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125819 02/14/2025 Labeler - GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA (372748392)
Trademark Results [PENMENVY]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PENMENVY 97251141 not registered Live/Pending |
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA 2022-02-02 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.