CEFOXITIN AND DEXTROSE- cefoxitin sodium injection, solution
Cefoxitin and Dextrose by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Cefoxitin and Dextrose by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by B. Braun Medical Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFOXITIN for injection and DEXTROSE injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFOXITIN for injection and DEXTROSE injection.
CEFOXITIN for injection and DEXTROSE injection,
for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1978
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is a cephalosporin antibacterial indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated bacteria (1):
- Lower respiratory tract infections (1.1);
- Urinary tract infections (1.2);
- Intra-abdominal infections (1.3);
- Gynecological infections (1.4);
- Septicemia (1.5);
- Bone and joint infections (1.6);
- Skin and skin structure infections (1.7);
- Prophylaxis (1.8).
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria (1.9).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For intravenous use only. (2)
- Use this formulation of cefoxitin only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof. (2.3)
- See full prescribing information for dose adjustment in patients with impaired renal function. (2.3)
- Recommended dosing schedule in patients with normal renal function. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions. If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue the drug. (5.1)
- Use in patients with renal impairment: Dosage adjustment required for patients with impaired renal function. (2.3)
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions: Local reactions. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact B. Braun Medical Inc. at 1-800-854-6851 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Aminoglycosides: Increased potential of nephrotoxicity. (7.1)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pediatric use: Safety and efficacy of this formulation not established. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
1.2 Urinary Tract Infections
1.3 Intra-abdominal Infections
1.4 Gynecological Infections
1.5 Septicemia
1.6 Bone and Joint Infections
1.7 Skin and Skin Structure Infections
1.8 Prophylaxis
1.9 Usage
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage in Adults for Treatment
2.2 Dosage in Adults for Prophylaxis
2.3 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
2.4 Preparation and Administration of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection in DUPLEX® Container
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Cefoxitin or other Beta-lactam Antibacterial Drugs
4.2 Hypersensitivity to Corn Products
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cefoxitin or other Beta-lactam Antibacterial Drugs
5.2 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
5.3 Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
5.4 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
5.5 Patients with a History of Gastrointestinal Disease
5.6 Patients with Overt or Known Subclinical Diabetes Mellitus or Carbohydrate Intolerance
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Cephalosporin-class Adverse Reactions
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aminoglycosides
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prophylaxis
14.2 Intra-abdominal infections
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia and lung abscess, caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, other streptococci (excluding enterococci, e.g., Enterococcus faecalis [formerly Streptococcus faecalis]), Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains), Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae, and Bacteroides species.
1.2 Urinary Tract Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Proteus mirabilis, Morganella morganii, Proteus vulgaris and Providencia species (including P. rettgeri).
1.3 Intra-abdominal Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscess, caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Bacteroides species including Bacteroides fragilis, and Clostridium species.
1.4 Gynecological Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of gynecological infections, including endometritis, pelvic cellulitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease caused by Escherichia coli, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase-producing strains), Bacteroides species including B. fragilis, Clostridium species, Peptococcus niger, Peptostreptococcus species, and Streptococcus agalactiae.
Cefoxitin has no activity against Chlamydia trachomatis. Therefore, when cefoxitin is used in the treatment of patients with pelvic inflammatory disease and C. trachomatis is one of the suspected pathogens, appropriate anti-chlamydial coverage should be added.
1.5 Septicemia
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of Septicemia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains), Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, and Bacteroides species including B. fragilis.
1.6 Bone and Joint Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of bone and joint infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains).
1.7 Skin and Skin Structure Infections
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes and other streptococci (excluding enterococci, e.g., Enterococcus faecalis [formerly Streptococcus faecalis]), Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Bacteroides species including B. fragilis, Clostridium species, Peptococcus niger, and Peptostreptococcus species.
1.8 Prophylaxis
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the prophylaxis of infection in patients undergoing uncontaminated gastrointestinal surgery, vaginal hysterectomy, abdominal hysterectomy, or cesarean section.
If there are signs of infection, specimens for culture should be obtained for identification of the causative organism so that appropriate treatment may be instituted.
1.9 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage in Adults for Treatment
The usual adult dosage range is 1 gram to 2 grams every six to eight hours. Dosage should be determined by susceptibility of the causative organisms, severity of infection, and the condition of the patient (see Table 1 for dosage guidelines). Administer Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection intravenously over approximately 30 minutes.
If C. trachomatis is a suspected pathogen, appropriate anti-chlamydial coverage should be added, because cefoxitin sodium has no activity against this organism [see Indications and Usage (1.4)].
Antibacterial therapy for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections should be maintained for at least 10 days to guard against the risk of rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis.
In staphylococcal and other infections involving a collection of pus, surgical drainage should be carried out where indicated.
Use this formulation of cefoxitin only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof.
- * Including patients in whom bacteremia is absent or unlikely.
Table 1: Guidelines for Dosage of Cefoxitin for Injection Type of Infection Daily Dosage Frequency and Route Uncomplicated forms*
of infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract
infection, cutaneous infection3-4 grams 1 gram every 6-8 hours IV Moderately severe or severe infections 6-8 grams 1 gram every 4 hours or
2 grams every 6-8 hours IVInfections commonly needing antibacterial drugs
in higher dosage (e.g., gas gangrene)12 grams 2 grams every 4 hours or
3 grams every 6 hours IV
2.2 Dosage in Adults for Prophylaxis
Effective prophylactic use depends on the time of administration. Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection usually should be given one-half to one hour before the operation, which is sufficient time to achieve effective levels in the wound during the procedure. Prophylactic administration should usually be stopped within 24 hours since continuing administration of any antibacterial increases the possibility of adverse reactions but, in the majority of surgical procedures, does not reduce the incidence of subsequent infection.
For prophylactic use in uncontaminated gastrointestinal surgery, vaginal hysterectomy, or abdominal hysterectomy, the following doses are recommended:
2 grams administered intravenously just prior to surgery (approximately one-half to one hour
before the initial incision) followed by
2 grams every 6 hours after the first dose for no more than 24 hours.For patients undergoing cesarean section, either a single 2 gram dose administered intravenously as soon as the umbilical cord is clamped OR a 3-dose regimen consisting of 2 grams given intravenously as soon as the umbilical cord is clamped followed by 2 grams 4 and 8 hours after the initial dose is recommended [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
2.3 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
In adults with renal impairment, an initial loading dose of 1 gram to 2 grams may be given. After a loading dose, the recommendations for maintenance dosage (Table 2) may be used as a guide.
When only the serum creatinine level is available, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) may be used to convert this value into creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
Males: Weight (kg) x (140 - age)
72 x serum creatinine (mg/100 mL)
Females: 0.85 x above value
In patients undergoing hemodialysis, the loading dose of 1 to 2 grams should be given after each hemodialysis, and the maintenance dose should be given as indicated in Table 2.
Table 2: Maintenance Dosage of Cefoxitin for Injection in Adults with Renal Impairment Renal Function Creatinine Clearance
(mL/min)Dose
(grams)Frequency Mild impairment
Moderate impairment
Severe impairment
Essentially no function50-30
29-10
9-5
<51-2
1-2
0.5-1
0.5-1every 8-12 hours
every 12-24 hours
every 12-24 hours
every 24-48 hours
2.4 Preparation and Administration of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection in DUPLEX® Container
Important Administration Instructions
This reconstituted solution is for intravenous use only.
Administer Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection intravenously over approximately 30 minutes.
Do not use in series connections. Such use would result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete. If administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result.
Do not introduce additives into the DUPLEX® Container.
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection may be administered through the tubing system by which the patient may be receiving other intravenous solutions. However, during infusion of the solution containing Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, it is advisable to temporarily discontinue administration of any other solutions at the same site.
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, like most beta-lactam antibiotics, should not be added to aminoglycoside solutions (e.g., gentamicin sulfate, tobramycin sulfate, amikacin sulfate) because of potential interaction. However, Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection and aminoglycosides may be administered separately to the same patient.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration
prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.Use only if solution is clear and free from particulate matter and container and seals are intact. As with other cephalosporins, reconstituted Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection tends to darken depending on storage conditions, within the stated recommendations. However, product potency is not adversely affected.
DUPLEX® Container Storage
To avoid inadvertent activation, DUPLEX® Container should remain in the folded position until activation is intended.
Patient Labeling and Drug Powder/Diluent Inspection
Apply patient-specific label on foil side of container. Use care to avoid activation. Do not cover any portion of foil strip with patient label.
Unlatch side tab and unfold DUPLEX® Container (see Diagram 1).
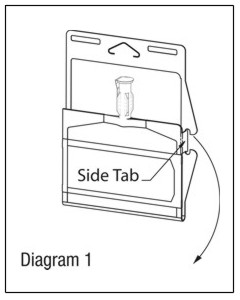
Visually inspect diluent chamber for particulate matter.
Use only if container and seals are intact.
To inspect the drug powder for foreign matter or discoloration, peel foil strip from drug chamber (see Diagram 2).
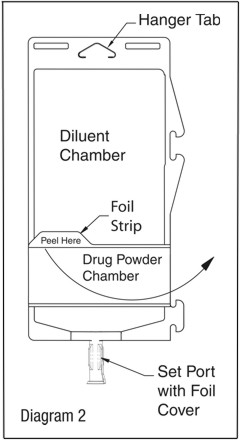
Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
Note: If foil strip is removed, the container should be re-folded and the side tab latched until ready to activate. The product must then be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date.
Reconstitution (Activation)
Do not use directly after storage by refrigeration, allow the product to equilibrate to room temperature before patient use.
Unfold the DUPLEX® Container and point the set port in a downward direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the diluent meniscus trapping all air above the fold. To activate, squeeze the folded diluent chamber until the seal between the diluent and powder opens, releasing diluent into the drug powder chamber (see Diagram 3).
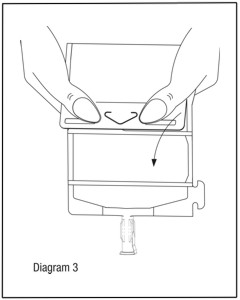
Agitate the liquid-powder mixture until the drug powder is completely dissolved.
Note: Following reconstitution (activation), product must be used within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within 7 days if stored under refrigeration.
Administration
Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter.
Point the set port in a downwards direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the solution meniscus trapping all air above the fold. Squeeze the folded DUPLEX® Container until the seal between reconstituted drug solution and set port opens, releasing liquid to set port (see Diagram 4).
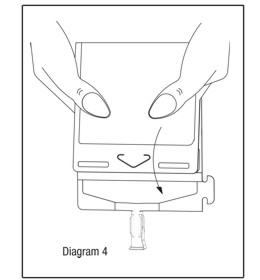
Prior to attaching the IV set, check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be compromised.
Using aseptic technique, peel foil cover from the set port and attach sterile administration set (see Diagram 5).
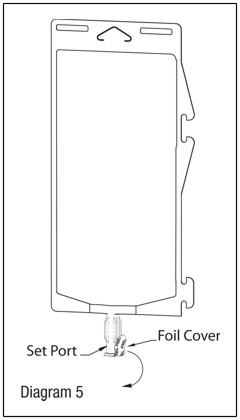
Refer to Directions for Use accompanying the administration set.
Discard unused portions.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cefoxitin or other Beta-lactam Antibacterial Drugs
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) have been reported in patients on β-lactam antibacterials, including cefoxitin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of β-lactam hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection or other β-lactam antibacterial drugs [see Contraindications (4)]. Before initiating therapy with Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, inquire about previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection and institute appropriate therapy.
5.2 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.3 Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
Prescribing Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Prolonged use of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient's condition is essential. Should superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
5.4 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
As with cephalothin, high concentrations of cefoxitin (>100 mcg/mL) may interfere with measurement of serum and urine creatinine levels by Jaffé reaction, and produce false increases of modest degree in the levels of creatinine reported. Serum samples from patients treated with cefoxitin should not be analyzed for creatinine if withdrawn within 2 hours of drug administration.
High concentrations of cefoxitin in the urine may interfere with measurement of urinary 17-hydroxy-corticosteroids by the Porter-Silber reaction, and produce false increases of modest degree in the levels reported.
A false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur. This has been observed with CLINITEST® reagent tablets.
5.5 Patients with a History of Gastrointestinal Disease
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis.
5.6 Patients with Overt or Known Subclinical Diabetes Mellitus or Carbohydrate Intolerance
As with other dextrose-containing solutions, Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection should be monitored if Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is prescribed in patients with overt or known subclinical diabetes mellitus or carbohydrate intolerance for any reason.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cefoxitin or other Beta-lactam Antibacterial Drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]
Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Patients with a History of Gastrointestinal Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Patients with Overt or Known Subclinical Diabetes Mellitus or Carbohydrate Intolerance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
The most common adverse reactions have been local reactions following intravenous injection.
Local Reactions
Thrombophlebitis has occurred with intravenous administration.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Rash (including exfoliative dermatitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis), urticaria, flushing, pruritus, eosinophilia, fever, dyspnea, and other allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, interstitial nephritis and angioedema have been noted.
Cardiovascular Disorders
Hypotension.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Diarrhea, including documented pseudomembranous colitis which can appear during or after antibiotic treatment. Nausea and vomiting have been reported.
Nervous System Disorders
Possible exacerbation of myasthenia gravis.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Eosinophilia, leukopenia including granulocytopenia, neutropenia, anemia including hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and bone marrow depression. A positive direct Coombs test may develop in some individuals, especially those with azotemia.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Reversible elevation in SGOT, SGPT, serum LDH, and serum alkaline phosphatase; and jaundice have been reported.Renal and Urinary Disorders
Elevations in serum creatinine and/or blood urea nitrogen levels have been observed. Acute renal failure has been reported.
6.1 Cephalosporin-class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefoxitin, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics: pruritus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, vomiting, abdominal pain, colitis, superinfection, vaginitis including vaginal candidiasis, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemorrhage, elevated bilirubin, pancytopenia, and neutropenia.
Several cephalosporins, including Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment, when the dosage was not reduced. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Overdosage (10)]. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from published prospective cohort studies, case series, and case reports over several decades with cephalosporin use, including cefoxitin, in pregnant women have not established drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed in pregnant rats and mice administered parenteral doses of cefoxitin at approximately 1 to 7.5 times the maximum recommended human dose (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. Cefoxitin is found in umbilical cord blood and amniotic fluid after maternal administration.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Maternal gonorrhea may be associated with preterm birth, low neonatal birth weight, chorioamnionitis, intrauterine growth restriction, small for gestational age and premature rupture of membranes. Perinatal transmission of gonorrhea to the offspring can result in infant blindness, joint infections and bloodstream infections.
Data
Human Data
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from prospective cohort studies, case series, and case reports over several decades have not identified an association with cephalosporin use, including cefoxitin, during pregnancy, and major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Available studies have methodologic limitations, including small sample size, retrospective data collection, and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies performed in pregnant rats and mice at parenteral doses of approximately one to seven and one-half times the maximum recommended human dose did not reveal teratogenic or fetal toxic effects, although a slight decrease in fetal weight was observed.
In the rabbit, cefoxitin was associated with a high incidence of abortion and maternal death. This was not considered to be a teratogenic effect but an expected consequence of the rabbit’s unusual sensitivity to antibiotic-induced changes in the population of the microflora of the intestine.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited data from published literature report the presence of cefoxitin in human milk. For an infant fed exclusively with human milk, the estimated infant daily dose through breastfeeding is less than 0.1% of maternal daily IV dose (see Data). Minimal data are available on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant; none of these reports suggest serious safety concerns. No data are available on the effects of the drug on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for cefoxitin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from cefoxitin or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In a published clinical lactation study, the concentration of cefoxitin ranged from 11.6 ± 0.8 to 0.49 ± 0.01 mcg/mL and 1.71 ± 0.08 to 0.57 ± 0.02 mcg/mL in human plasma and breast milk, respectively, at 1, 1.5, 2 or 2.5 hours following IV administration of 1 g cefoxitin twice daily.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of this formulation are not established. This formulation of cefoxitin is indicated for use only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1,775 subjects who received cefoxitin in clinical studies, 424 (24%) were 65 and over, while 124 (7%) were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
In patients with a reduced creatinine clearance the dose of Cefoxitin Injection and Dextrose Injection should be adjusted to compensate for the slower rate of renal elimination. Because high and prolonged cefoxitin concentrations can occur from usual dosages in patients with renal impairment or other conditions that may compromise renal function, the maintenance dosage should be reduced when Cefoxitin Injection and Dextrose Injection is administered to such patients. Continued dosage should be determined by the degree of renal impairment, severity of infection, and susceptibility of the causative organisms [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, single-dose packaged combination of cefoxitin sodium USP and Dextrose Injection (diluent) in the DUPLEX® sterile container. The DUPLEX® Container is a flexible dual chamber container.
The drug chamber is filled with cefoxitin sodium USP, a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibacterial sealed under nitrogen for intravenous administration. Cefoxitin sodium USP is derived from cephamycin C, which is produced by Streptomyces lactamdurans. Its chemical name is sodium (6R,7S)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-7-methoxy-8-oxo-7-[2-(2-thienyl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate carbamate (ester).
The empirical formula is C16H16N3NaO7S2, and the molecular weight is 449.44. The structural formula is:
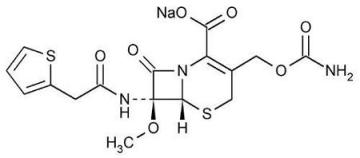
Cefoxitin sodium contains approximately 53.8 mg (2.3 mEq) of sodium per gram of cefoxitin activity.
The diluent chamber contains Dextrose Injection. The concentration of Dextrose Hydrous USP in Water for Injection USP has been adjusted to render the reconstituted drug product iso-osmotic. Dextrose Hydrous USP has been added to adjust the osmolality to approximately 290 mOsmol/kg (approximately 2 g (4% w/v) and 1.1 g (2.2% w/v) to the 1 g and 2 g doses, respectively). Dextrose Injection is sterile, nonpyrogenic, and contains no bacteriostatic and antimicrobial agents.
Dextrose Hydrous USP has the following structural (molecular) formula:
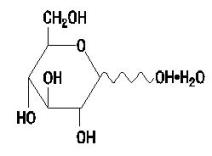
The molecular weight of Dextrose Hydrous USP is 198.17.
After removing the peelable foil strip, activating the seals, and thoroughly mixing, the reconstituted drug product is intended for single intravenous use. When reconstituted according to instructions in the product labeling, the approximate osmolality of the reconstituted solution of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is approximately 290 mOsmol/kg. After reconstitution, each 50 mL contains 1 gram of cefoxitin (equivalent to 1.05 gram of cefoxitin sodium) or 2 grams of cefoxitin (equivalent to 2.10 grams of cefoxitin sodium), with a pH of approximately 6.5. Solutions of Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection range from colorless to light amber.
The DUPLEX® dual chamber container is made from a specially formulated material. The product (diluent and drug) contact layer is a mixture of thermoplastic rubber and a polypropylene ethylene copolymer that contains no plasticizers. The safety of the container system is supported by USP biological evaluation procedures.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following an intravenous dose of 1 gram, serum concentrations were 110 mcg/mL at 5 minutes, declining to less than 1 mcg/mL at 4 hours.
Distribution
Cefoxitin passes into pleural and joint fluids and is detectable in antibacterial concentrations in bile.
Elimination
Metabolism
The half-life after an intravenous dose is 41 to 59 minutes.
Excretion
Approximately 85 percent of cefoxitin is excreted unchanged by the kidneys over a 6-hour period, resulting in high urinary concentrations. Probenecid slows tubular excretion and produces higher serum levels and increases the duration of measurable serum concentrations.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
In a published study of geriatric patients ranging in age from 64 to 88 years with normal renal function for their age (creatinine clearance ranging from 31.5 to 174.0 mL/min), the half-life for cefoxitin ranged from 51 to 90 minutes, resulting in higher plasma concentrations than in younger adults. These changes were attributed to decreased renal function associated with the aging process.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Cefoxitin is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cefoxitin has activity in the presence of some beta-lactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Resistance
Resistance to Cefoxitin is primarily through hydrolysis by beta-lactamase, alteration of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), and decreased permeability.
Antimicrobial Activity
Cefoxitin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenesGram-negative bacteria
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella spp.
Morganella morganii
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Providencia spp.Anaerobic bacteria
Clostridium spp.
Peptococcus niger
Peptostreptococcus spp.
Bacteroides distasonis
Bacteroides fragilis
Bacteroides ovatus
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
Bacteroides spp.The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for cefoxitin against isolates of similar genus or organism group. However, the efficacy of cefoxitin in treating clinical infections caused by these bacteria has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-negative bacteria
Eikenella corrodens [non- β-lactamase producers]
Anaerobic bacteria
Clostridium perfringens
Prevotella biviaSusceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria, and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: http://www.fda.gov/STIC.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long term studies in animals have not been performed with cefoxitin to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Mutagenesis
Long term studies in animals have not been performed with cefoxitin to evaluate mutagenic potential.
Impairment of Fertility
Studies in rats treated intravenously with 400 mg/kg of cefoxitin (approximately three times the maximum recommended human dose) revealed no effects on fertility or mating ability.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prophylaxis
A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted to determine the efficacy of short-term prophylaxis with cefoxitin in patients undergoing cesarean section who were at high risk for subsequent endometritis because of ruptured membranes. Patients were randomized to receive either three doses of placebo (n=58), a single dose of cefoxitin (2 g) followed by two doses of placebo (n=64), or a three-dose regimen of cefoxitin (each dose consisting of 2 g) (n=60), given intravenously, usually beginning at the time of clamping of the umbilical cord, with the second and third doses given 4 and 8 hours post-operatively. Endometritis occurred in 16/58 (27.6%) patients given placebo, 5/63 (7.9%) patients given a single dose of cefoxitin, and 3/58 (5.2%) patients given three doses of cefoxitin. The differences between the two groups treated with cefoxitin and placebo with respect to endometritis were statistically significant (p<0.01) in favor of cefoxitin. The differences between the one-dose and three-dose regimens of cefoxitin were not statistically significant.
Two double-blind, randomized studies compared the efficacy of a single 2 gram intravenous dose of cefoxitin to a single 2 gram intravenous dose of cefotetan in the prevention of surgical site-related infection (major morbidity) and non-site-related infections (minor morbidity) in patients following cesarean section. In the first study, 82/98 (83.7%) patients treated with cefoxitin and 71/95 (74.7%) patients treated with cefotetan experienced no major or minor morbidity. The difference in the outcomes in this study (95% CI: -0.03, +0.21) was not statistically significant. In the second study, 65/75 (86.7%) patients treated with cefoxitin and 62/76 (81.6%) patients treated with cefotetan experienced no major or minor morbidity. The difference in the outcomes in this study (95% CI: -0.08, +0.18) was not statistically significant.
14.2 Intra-abdominal infections
In clinical trials of patients with intra-abdominal infections due to Bacteroides fragilis group microorganisms, eradication rates at 1 to 2 weeks post-treatment for isolates were in the range of 70% to 80%. Eradication rates for individual species are listed below:
Bacteroides distasonis 7/10 (70%)
Bacteroides fragilis 26/33 (79%)
Bacteroides ovatus 10/13 (77%)
B. thetaiotaomicron 13/18 (72%)
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection in the DUPLEX® Container is a flexible dual chamber single-dose container supplied in two concentrations. After reconstitution, the delivered doses are equivalent to 1 g and 2 g cefoxitin. The diluent chamber contains approximately 50 mL of Dextrose Injection. Dextrose Injection has been adjusted to 4% w/v and 2.2% w/v for the 1 g and 2 g doses, respectively, such that the reconstituted solution is iso-osmotic.
Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in the DUPLEX® Container packaged 24 units per case.
NDC REF Dose Volume 0264-3123-11 3123-11 1 g 50 mL 0264-3125-11 3125-11 2 g 50 mL
Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP).
Storage
Store the unactivated unit at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Do not freeze.
As with other cephalosporins, reconstituted Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection tends to darken depending on storage conditions, within the stated recommendations. However, product potency is not adversely affected.
Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate matter.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Allergic Reactions
Inform patients that Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is a cephalosporin that can cause allergic reactions in some individuals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Inform patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterials, including Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection, and it usually ends when the antibacterial is discontinued.
Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterials, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken their last dose of the antibacterial. If this occurs, advise patients to contact their physician as soon as possible.
Drug Resistance
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Cefoxitin for Injection and Dextrose Injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mL Container Label
Cefoxitin for Injection
and Dextrose Injection1g*
REF 3123-11
NDC: 0264-3123-11DUPLEX® CONTAINER
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Iso-osmotic Single-Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic* Contains cefoxitin sodium equivalent to 1 g cefoxitin.
Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold
the diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze
folded diluent chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens,
releasing diluent into drug chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the
drug powder is completely dissolved. Fold the container a second time and
squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set port opens.After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Cefoxitin Sodium USP
(equivalent to 1 g cefoxitin) with approx. 2 g (4% w/v) Hydrous Dextrose USP in
Water for Injection USP. Sodium content is 53.8 mg (2.3 mEq) per gram of cefoxitin.
Approximate osmolality: 290 mOsmol/kg
Prior to Reconstitution: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to
15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Use only if container
and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip
removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled
expiration date. Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from
particulate matter. Use within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within
7 days if stored under refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not
introduce additives into this container. Prior to administration check for minute
leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and
solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
Rx only
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524Prepared in USA. API from USA and Italy.
Y37-002-561
LD-204-3EXP
LOT

PEEL HERE
Drug Chamber
Discard unit if foil strip is damaged. Peel foil strip only when ready for use. Visually inspect drug prior to reconstitution.
See package insert for complete directions for reconstitution and administration.
LD-336-1 X27-001-485

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mL Container Label-
Cefoxitin for Injection
and Dextrose Injection2g*
REF 3125-11
NDC: 0264-3125-11DUPLEX® CONTAINER
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Iso-osmotic Single-Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic
* Contains cefoxitin sodium equivalent to 2 g cefoxitin.Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold
the diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze
folded diluent chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens,
releasing diluent into drug chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the
drug powder is completely dissolved. Fold the container a second time and
squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set port opens.After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Cefoxitin Sodium USP
(equivalent to 2 g cefoxitin) with approx. 1.1 g (2.2% w/v) Hydrous Dextrose USP in
Water for Injection USP. Sodium content is 53.8 mg (2.3 mEq) per gram of cefoxitin.
Approximate osmolality: 290 mOsmol/kg
Prior to Reconstitution: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to
15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Use only if container
and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip
removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled
expiration date. Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from
particulate matter. Use within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within
7 days if stored under refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not
introduce additives into this container. Prior to administration check for minute
leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and
solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
Rx onlyB. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524Prepared in USA. API from USA and Italy.
Y37-002-562
LD-205-3EXP
LOT

PEEL HERE
Drug Chamber
Discard unit if foil strip is damaged. Peel foil strip only when ready for use. Visually inspect drug prior to reconstitution.
See package insert for complete directions for reconstitution and administration.
LD-336-1 X27-001-485

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CEFOXITIN AND DEXTROSE
cefoxitin sodium injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-3123 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFOXITIN SODIUM (UNII: Q68050H03T) (CEFOXITIN - UNII:6OEV9DX57Y) CEFOXITIN 1 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE (UNII: IY9XDZ35W2) 2 g in 50 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-3123-11 24 in 1 CASE 03/10/2006 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA065214 03/10/2006 CEFOXITIN AND DEXTROSE
cefoxitin sodium injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-3125 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFOXITIN SODIUM (UNII: Q68050H03T) (CEFOXITIN - UNII:6OEV9DX57Y) CEFOXITIN 2 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE (UNII: IY9XDZ35W2) 1.1 g in 50 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-3125-11 24 in 1 CASE 03/10/2006 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA065214 03/10/2006 Labeler - B. Braun Medical Inc. (002397347)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.