REVUFORJ- revumenib tablet, film coated
Revuforj by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Revuforj by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use REVUFORJ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for REVUFORJ.
REVUFORJ (revumenib) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024WARNING: DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME, and QTc PROLONGATION and TORSADES DE POINTES
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Differentiation syndrome, which can be fatal, has occurred with REVUFORJ. If differentiation syndrome is suspected, immediately initiate corticosteroid therapy and hemodynamic monitoring until symptom resolution (2.3, 5.1)
QTc prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have occurred in patients receiving REVUFORJ. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment. Do not initiate REVUFORJ in patients with QTcF > 450 msec. If QTc interval prolongation occurs, interrupt, reduce, or permanently discontinue REVUFORJ. (2.3, 5.2).
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REVUFORJ is a menin inhibitor indicated for:
- the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a lysine methyltransferase 2A gene (KMT2A) translocation as determined by an FDA-authorized test in adult and pediatric patients 1 year and older. (1)
- the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a susceptible nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutation in adult and pediatric patients 1 year and older who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for treatment with REVUFORJ based on the presence of a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation. (2.1)
- Administer REVUFORJ orally twice daily fasted or with a low-fat meal at approximately the same time each day. (2.2)
- See Full Prescribing Information for recommended REVUFORJ dosage regimen, dosage modifications, and administration instructions. (2.2, 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 25 mg, 110 mg, 160 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) including laboratory abnormalities, are phosphate increased, hemorrhage, nausea, infection without identified pathogen, aspartate aminotransferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, creatinine increased, musculoskeletal pain, febrile neutropenia, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, potassium decreased, parathyroid hormone intact increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, diarrhea, bacterial infection, triglycerides increased, differentiation syndrome, fatigue, edema, viral infection, phosphate decreased, decreased appetite, and constipation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc., at 1-888-539-3REV or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Reduce the REVUFORJ dose. (2.2, 7.1)
- Strong or moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with REVUFORJ. (7.1)
- QTc Prolonging Drugs: Avoid concomitant use with REVUFORJ. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor patients more frequently for QTc interval prolongation. (5.2, 7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 2/2026
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME, QTc PROLONGATION and TORSADES DE POINTES
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Differentiation Syndrome
5.2 QTc Interval Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on REVUFORJ
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia with a KMT2A Translocation
14.2 Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an NPM1 Mutation
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME, QTc PROLONGATION and TORSADES DE POINTES
Differentiation syndrome, which can be fatal, has occurred with REVUFORJ. Signs and symptoms may include fever, dyspnea, hypoxia, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain or peripheral edema, hypotension, and renal dysfunction. If differentiation syndrome is suspected, immediately initiate corticosteroid therapy and hemodynamic monitoring until symptom resolution. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
QTc prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have occurred in patients receiving REVUFORJ. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment. Do not initiate REVUFORJ in patients with QTcF > 450 msec. If QTc interval prolongation occurs, interrupt, reduce, or permanently discontinue REVUFORJ. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia
- REVUFORJ is indicated for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a lysine methyltransferase 2A gene (KMT2A) translocation as determined by an FDA-authorized test in adult and pediatric patients 1 year and older.
- REVUFORJ is indicated for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia with a susceptible nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), and Clinical Studies (14.1)] in adult and pediatric patients 1 year and older who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia with a KMT2A Translocation
Select patients for treatment with REVUFORJ based on the presence of a KMT2A translocation [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Information on FDA authorized tests for the detection of a KMT2A translocation to determine eligibility for treatment is available at https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/denovo.cfm?id=DEN240067
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an NPM1 mutation
Select patients for treatment with REVUFORJ based on the presence of an NPM1 mutation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Clinical Studies (14.2)]. An FDA-approved companion diagnostic for the detection of an NPM1 mutation is not currently available.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of REVUFORJ varies by patient weight and concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. See Table 1 for the recommended dosage for patients 1 year and older. Do not start REVUFORJ until the WBC is reduced to less than 25 Gi/L. Continue REVUFORJ until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For patients without disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, treat for a minimum of 6 months to allow time for clinical response.
Table 1. REVUFORJ Recommended Dosage for Patients 1 Year and Older *See Table 2 for the total tablet dosage by BSA (body surface area) for patients weighing less than 40 kg. Patient Weight Without Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors With Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors 40 kg or more 270 mg orally twice daily 160 mg orally twice daily Less than 40 kg 160 mg/m2 orally twice daily* 95 mg/m2 orally twice daily* Table 2: Recommended Dosage using Tablets* for Patients Weighing Less than 40 kg * If needed, attain the desired dose by combining different strengths of REVUFORJ tablets. BSA (m2) REVUFORJ Dosage for 160 mg/m2 REVUFORJ Dosage for 95 mg/m2 1.4 220 mg twice daily 135 mg twice daily 1.3 220 mg twice daily 135 mg twice daily 1.2 185 mg twice daily 110 mg twice daily 1.1 185 mg twice daily 110 mg twice daily 1 160 mg twice daily 100 mg twice daily 0.9 135 mg twice daily 75 mg twice daily 0.8 135 mg twice daily 75 mg twice daily 0.7 110 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.6 100 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.5 75 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.4 50 mg twice daily 25 mg twice daily - If the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, increase the REVUFORJ dose after at least 5 half-lives of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor to the recommended dosage without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (Table 1).
- Concurrent use of standard intrathecal chemotherapy prophylaxis is recommended for patients with risk of central nervous system relapse.
Administration:
- Correct hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and other electrolyte abnormalities prior to treatment.
- Administer REVUFORJ twice daily fasted or with a low-fat meal (e.g., meals with approximately 400 calories, 25% or less fat).
- Administer REVUFORJ orally around the same time each day.
- Advise patients to swallow tablets whole and to not cut or chew tablets. If patients are unable to swallow tablets, they may be crushed and dispersed in water and taken within 2 hours of preparation [see Instructions for Use].
- If a dose of REVUFORJ is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible on the same day and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. Return to the normal schedule the following day. Do not administer 2 doses within 12 hours.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Assess blood counts, electrolytes, and liver enzymes prior to the initiation of REVUFORJ and monthly thereafter. Perform an electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to the initiation of REVUFORJ, at least once a week for the first 4 weeks, and at least monthly thereafter. Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and manage any abnormalities promptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Interrupt dosing or reduce dose for adverse reactions as per Table 3. Dose levels for dose reductions are listed in Table 4, Table 5, and Table 6.
Table 3. Recommended Management and Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions *Grade 1 is mild, Grade 2 is moderate, Grade 3 is severe, Grade 4 is life-threatening. Severity as defined by National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE version 5.0).
**See Tables 4, 5 and 6 for the reduced dose levels.Adverse reaction Recommended action Differentiation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] - If differentiation syndrome is suspected, administer systemic corticosteroids and initiate hemodynamic monitoring until symptom resolution and for a minimum of 3 days. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Interrupt REVUFORJ if severe signs and/or symptoms persist for more than 48 hours after initiation of systemic corticosteroids, or earlier for life-threatening symptoms such as pulmonary symptoms requiring ventilator support [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Resume REVUFORJ at the same dose when signs and symptoms improve to Grade 1* or lower.
Noninfectious leukocytosis - Initiate treatment with hydroxyurea in patients with an elevated or rapidly rising leukocyte count. Add leukapheresis if clinically indicated.
- Taper hydroxyurea only after leukocytosis improves or resolves.
QTc interval greater than 480 msec to 500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions(5.2)] - Interrupt REVUFORJ.
- Check electrolyte levels. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Restart REVUFORJ at the same dose level after the QTc interval returns to less than or equal to 480 msec.
QTc interval greater than 500 msec (Grade 3*) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] - Interrupt REVUFORJ.
- Check electrolyte levels. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Restart REVUFORJ at the reduced dose level** after the QTc interval returns to less than or equal to 480 msec.
QTc interval prolongation with signs/symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia, Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, signs/ symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia (Grade 4*) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Permanently discontinue REVUFORJ.
Potassium 3.6-3.9 mEq/L, and/or
Magnesium 1.7-1.9 mg/dL or 0.66-0.81 mmol/L- Supplement potassium and/or magnesium.
- Continue REVUFORJ.
Potassium ≤ 3.5 mEq/L, and/or
Magnesium ≤ 1.6 mg/dL or
≤ 0.65 mmol/L- Supplement potassium and/or magnesium, and recheck levels within 24 hours.
- On recheck of potassium and magnesium labs within 24 hours, if potassium is greater than 3.5 mEq/L and/or magnesium is greater than 1.6 mg/dL, continue REVUFORJ. If potassium is less than 3.5 mEq/L and/or magnesium is less than 1.6 mg/dL, hold REVUFORJ and continue supplementation; resume REVUFORJ at the same dose level when the correction is complete.
Other nonhematological adverse reactions Grade ≥ 3* [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] - Interrupt REVUFORJ until recovery to Grade 1* or baseline.
- If recovered in ≤ 7 days, restart REVUFORJ at the same dose level. If the same Grade ≥ 3* toxicity recurs, interrupt REVUFORJ until recovery to Grade 1* or baseline. Restart REVUFORJ at the reduced dose level.**
- If recovered in > 7 days, restart REVUFORJ at the reduced dose level.** If the same Grade ≥ 3* toxicity recurs, discontinue REVUFORJ.
Grade 4* neutropenia or thrombocytopenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] - Interrupt REVUFORJ until recovery to Grade ≤ 2* or baseline.
- Restart REVUFORJ at the same dose level.
- If Grade 4* neutropenia or thrombocytopenia recurs without attributable cause, interrupt REVUFORJ until recovery to Grade ≤ 3*. Restart REVUFORJ at the reduced dose level.**
Grade 3* or higher allergic reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] - Permanently discontinue REVUFORJ.
Table 4. REVUFORJ Dosage Reduction for Adverse Reactions in Patients NOT on Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors **See Table 6 for BSA-based dosage recommendations for the reduced dosage of 95 mg/m2 twice daily. Patients Weighing 40 kg or Greater
at Starting Dose 270 mg
orally twice dailyPatients Weighing Less Than 40 kg
at Starting Dose 160 mg/m2
orally twice dailyReduced Dose 160 mg orally twice daily 95 mg/m2 orally twice daily* Table 5. REVUFORJ Dosage Reduction for Adverse Reactions in Patients on Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors *See Table 6 for BSA-based dosage recommendations for the reduced dosage of 65 mg/m2 twice daily. Patients Weighing 40 kg or Greater
at Starting Dose 160 mg
orally twice dailyPatients Weighing Less Than 40 kg
at Starting Dose 95 mg/m2
orally twice dailyReduced Dose 110 mg orally twice daily 65 mg/m2 orally twice daily* Table 6: Recommended Reduced Dosage Using Tablets* for Patients Weighing Less than 40 kg * If needed, attain the desired dose by combining different strengths of REVUFORJ tablets. BSA (m2) REVUFORJ Dosage for 95 mg/m2 REVUFORJ Dosage for 65 mg/m2 1.4 135 mg twice daily 100 mg twice daily 1.3 135 mg twice daily 75 mg twice daily 1.2 110 mg twice daily 75 mg twice daily 1.1 110 mg twice daily 75 mg twice daily 1 100 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.9 75 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.8 75 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.7 50 mg twice daily 50 mg twice daily 0.6 50 mg twice daily 25 mg twice daily 0.5 50 mg twice daily 25 mg twice daily 0.4 25 mg twice daily 25 mg twice daily -
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 25 mg of revumenib: Pink modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “25” on the other side.
- 110 mg of revumenib: Beige modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “110” on the other side.
- 160 mg of revumenib: Purple modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “160” on the other side.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Differentiation Syndrome
REVUFORJ can cause fatal or life-threatening differentiation syndrome (DS). Symptoms of differentiation syndrome, including those seen in patients treated with REVUFORJ, include fever, dyspnea, hypoxia, peripheral edema, pleuropericardial effusion, acute renal failure, rash, and/or hypotension.
In clinical trials, DS occurred in 60 (25%) of 241 patients treated with REVUFORJ at the recommended dosage for relapsed or refractory acute leukemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Among those with a KMT2A translocation, DS occurred in 33% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), 33% of patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL), and 9% of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); DS occurred in 18% of patients with NPM1 mutated AML. DS was Grade 3 or 4 in 12% of patients and fatal in two patients. The median time to initial onset was 9 days (range 3-41 days). Some patients experienced more than 1 DS event. Treatment interruption was required for 7% of patients, and treatment was withdrawn for 1%.
Reduce the white blood cell count (WBC) to less than 25 Gi/L prior to starting REVUFORJ. If DS is suspected, immediately initiate treatment with systemic corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone 10 mg intravenously every 12 hours in adults or dexamethasone 0.25 mg/kg/dose intravenously every
12 hours in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg) for a minimum of 3 days and until resolution of signs and symptoms. Institute supportive measures and hemodynamic monitoring until improvement. Interrupt REVUFORJ if severe signs and/or symptoms persist for more than 48 hours after initiation of systemic corticosteroids, or earlier if life-threatening symptoms occur such as pulmonary symptoms requiring ventilator support. Restart steroids promptly if DS recurs after tapering corticosteroids [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 QTc Interval Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
REVUFORJ can cause QT (QTc) interval prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Of the 241 patients treated with REVUFORJ at the recommended dosage for relapsed or refractory acute leukemia in clinical trials, QTc interval prolongation was reported as an adverse reaction in 86 (36%) of patients. QTc interval prolongation was Grade 3 in 15% and Grade 4 in 2%. The heart-rate corrected QT interval (using Fridericia’s method) (QTcF) was greater than 500 msec in 10%, and the increase from baseline QTcF was greater than 60 msec in 24%. REVUFORJ dose reduction was required for 7% due to QTc interval prolongation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. QTc prolongation occurred in 21% of the 34 patients less than 17 years old, 35% of the 146 patients 17 years to less than 65 years old, and in 46% of the 61 patients 65 years or older. One patient had a fatal outcome of cardiac arrest, and one patient had nonsustained Torsades de Pointes.
Correct electrolyte abnormalities, including hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia, prior to and throughout treatment with REVUFORJ. Perform an ECG prior to initiation of treatment with
REVUFORJ, and do not initiate REVUFORJ in patients with QTcF > 450 msec. Perform an ECG at least once a week for the first 4 weeks on treatment, and at least monthly thereafter [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. In patients with congenital long QTc syndrome, congestive heart failure, electrolyte abnormalities, or those who are taking medications known to prolong the QTc interval, more frequent ECG monitoring may be necessary. Concomitant use of REVUFORJ with drugs known to prolong the QTc interval may increase the risk of QTc interval prolongation. [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Interrupt REVUFORJ if QTcF increases to greater than 480 msec and less than 500 msec, and restart REVUFORJ at the same dose twice daily after the QTcF interval returns to less than or equal to 480 msec. Interrupt REVUFORJ if QTcF increases to greater than 500 msec or by > 60 msec from baseline, and restart REVUFORJ twice daily at the lower dose level after the QTcF interval returns to less than or equal to 480 msec. Permanently discontinue REVUFORJ in patients with ventricular arrhythmias and in those who develop QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life- threatening arrhythmia [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, REVUFORJ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of revumenib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality, malformations, and altered fetal growth at maternal exposures approximately 0.5 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Differentiation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QTc Interval Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of REVUFORJ reflects exposure in 241 patients (207 adult and 34 pediatric patients) with relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation treated with REVUFORJ at a dose approximately equivalent to 160 mg in adults orally twice daily with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of exposure to REVUFORJ was 2.5 months (range < 1 to 40 months), and 10% of patients were exposed for more than 6 months.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 9 (4%) patients who received REVUFORJ, including 4 with sudden death, 2 with differentiation syndrome, 2 with hemorrhage, and 1 with cardiac arrest. Serious adverse reactions were reported in 184 (76%) patients. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were infection (29%), febrile neutropenia (20%), bacterial infection (15%), differentiation syndrome (13%), and hemorrhage (11%).
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 49% of patients. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) leading to dose interruption were electrocardiogram QT prolonged, infection, febrile neutropenia, differentiation syndrome, nausea, and hypokalemia. Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 12% of patients who received REVUFORJ. Adverse reactions leading to a dose reduction (≥ 5%) included electrocardiogram QT prolonged. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 20% of patients. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation (> 1%) included infection.
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions were phosphate increased, hemorrhage, nausea, infection without identified pathogen, aspartate aminotransferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, creatinine increased, musculoskeletal pain, febrile neutropenia, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, potassium decreased, parathyroid hormone intact increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, diarrhea, bacterial infection, triglycerides increased, differentiation syndrome, fatigue, edema, viral infection, phosphate decreased, decreased appetite, and constipation.
The common adverse reactions are summarised in Table 7.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 20% (Any Grade) or ≥ 5% (Grade 3 or 4) in Patients with R/R Acute Leukemia # Includes the following fatal adverse reactions: DS (n=2); hemorrhage (n=2)
a – Includes nausea and vomiting
b – includes diarrhea, colitis, and neutropenic colitis
c – includes epistaxis, contusion, petechiae, gingival bleeding, hematoma, hemoptysis, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, hematuria, ecchymosis, hemorrhage intracranial, subdural hematoma, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, post- procedural hemorrhage, rectal hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, vitreous hemorrhage, catheter site hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage, hematochezia, melaena, retinal hemorrhage, anal hemorrhage, brain stem hemorrhage, cystitis hemorrhagic, eye hematoma, genital contusion, injection site hematoma, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, mucosal hemorrhage, oral blood blister, oral contusion, oral purpura, pulmonary hemorrhage, shock hemorrhagic, spinal subdural hematoma
d – includes disseminated intravascular coagulation, pulmonary embolism, cerebrovascular accident, superficial vein thrombosis, deep vein thrombosis, acute myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, embolism, hemorrhoids thrombosed, medical device site thrombosis, myocardial infarction, renal infarction, splenic infarction, thrombosis, and transient ischaemic attack
e – includes pneumonia, sepsis, urinary tract infection, septic shock, sinusitis, skin infection, upper respiratory tract infection, osteomyelitis, device related infection, enterocolitis infectious, conjunctivitis, hordeolum, rhinitis, acute sinusitis, diverticulitis, endocarditis, perirectal abscess, rectal abscess, tooth abscess, abscess limb, appendicitis, bronchitis, epididymitis, eye infection, gastroenteritis, infection, mucosal infection, neutropenic sepsis, rash pustular, retinitis, shock, sialadenitis, soft tissue infection, tooth infection, vascular device infection
f – includes bacteraemia, clostridium difficile infection, cellulitis, escherichia bacteremia, paronychia, staphylococcal bacteremia, streptococcal bacteremia, alpha hemolytic streptococcal infection, clostridium difficile colitis, clostridium test positive, enterobacter infection, enterobacter sepsis, enterococcal bacteremia, escherichia urinary tract infection, pseudomonal bacteremia, pseudomonas infection, skin bacterial infection, bacteriuria, cellulitis staphylococcal, cornyebacterium bacteremia, enterobacter bacteremia, enterococcal infection, folliculitis, klebsiella infection, klebsiella sepsis, lactobacillus bacteremia, meningitis bacterial, stenotrophomonas infection
g – includes COVID-19, rhinovirus infection, herpes simplex reactivation, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, oral herpes, respiratory syncytial virus infection, enterovirus infection, adenovirus infection, coronavirus infection, cytomegalovirus infection, cytomegalovirus infection reactivation, cytomegalovirus viremia, COVID-19 pneumonia, cytomegalovirus test positive, enterovirus test positive, Epstein-Barr virus infection, herpes simplex pharyngitis, herpes virus infection, influenza, norovirus infection, parainfluenzae virus infection, pneumonia cytomegaloviral viremia
h – includes arthralgia, back pain, pain in extremity, neck pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, myositis, flank pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, and musculoskeletal pain
i – includes fatigue, asthenia, malaise
j – includes edema peripheral, generalised edema, edema, localized edema, peripheral swelling
REVUFORJ
N = 241TEAE All Grades
%Grade 3 or 4
%Gastrointestinal disorders Nauseaa 48 5 Diarrheab 29 5 Constipation 20 0 Vascular disorders Hemorrhage#,c 48 10 Thrombosisd 11 6 Infections and infestations Infection without identified pathogene 46 30 Bacterial infectionf 27 18 Viral Infectiong 23 6 Blood and lymphatic system disorders Febrile neutropenia 37 35 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Musculoskeletal painh 37 6 Investigations Electrocardiogram QT prolonged 36 17 Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) Differentiation syndrome# 25 12 General disorders and administration site conditions Fatiguei 24 5 Edemaj 24 0 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased appetite 20 5 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in less than 20% of patients who received REVUFORJ include:
Cardiac disorders: Premature ventricular complex, cardiac failure, pericardial effusion, ventricular tachycardia, cardiac arrest
Endocrine disorders: Hyperparathyroidism
Eye disorders: Cataract
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain
General disorders and administration site conditions: Sudden death
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
Nervous system disorders: Taste disorder, syncope, headache, paresthesia
Renal disorders: Renal impairment
Skin and subcutaneous disorders: Rash
Changes in selected post-baseline laboratory values that were observed in patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia are shown in Table 8.
Table 8. Selected New or Worsening Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with R/R Acute Leukemia *The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 139 to 240 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post baseline value.
REVUFORJ Laboratory Abnormality Grades 1-4*
%Grades 3-4
%Phosphate increased 51 - Aspartate aminotransferase increased 44 6 Alanine aminotransferase increased 40 8 Creatinine increased 38 2 Potassium decreased 34 12 Parathyroid hormone, intact increased 34 - Alkaline phosphatase increased 33 <1 Triglycerides increased 27 3 Phosphate decreased 25 - Cholesterol increased 17 0 Calcium corrected increased 15 0 -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on REVUFORJ
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
If concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is required, reduce the REVUFORJ dosage [see Recommended Dosage (2.2)].
Revumenib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor increases revumenib systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology(12.3)], which may increase the risk of REVUFORJ adverse reactions.
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant use with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
Revumenib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducer may decrease revumenib and increase M1 systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce REVUFORJ efficacy or increase the risk of QT prolongation associated with the M1 metabolite.
Drugs that Prolong QTc Interval
Avoid concomitant use of REVUFORJ with other drugs with a known potential to prolong QTc interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Withhold REVUFORJ if the QTc interval is greater than 480 msec. Restart REVUFORJ after the QTc interval returns to less than or equal to 480 msec [see Dosage andAdministration (2.3)].
REVUFORJ causes QTc interval prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Concomitant use of REVUFORJ with other drugs that prolong QTc interval may result in an increase in the QTc interval and adverse reactions associated with QTc interval prolongation [see Warnings andPrecautions(5.2)]. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], REVUFORJ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on REVUFORJ use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk.
In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of revumenib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality, malformations, and altered fetal growth at maternal exposures approximately 0.5 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, revumenib was administered once daily via oral gavage at doses of 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6-17). Decreased maternal body weight gain and adverse embryo-fetal findings including decreases in the number of live fetuses, increases in resorptions and post-implantation loss, and decreases in fetal body weight were observed at all doses. At 300 mg/kg/day, total litter resorption and eye malformations were observed. At the dose of 30 mg/kg/day in rats, the maternal exposures (AUC) were approximately 0.5 times the human exposure at the recommended dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of revumenib or its metabolites in human milk or the effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, REVUFORJ can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential within 7 days prior to initiating REVUFORJ.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose.
Males
Advise males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose.
Infertility
Females and MalesBased on findings in animals, REVUFORJ may impair fertility. The effects on fertility were reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of REVUFORJ have been established in pediatric patients 1 year and older with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation. Use of REVUFORJ for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials in adults and pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14)] and additional pharmacokinetic and safety data in pediatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The patients included 25 infants (age < 2 years), 78 children (age 2 to < 12 years) and 29 adolescents (age 12 to < 17 years). The recommended dosage in patients weighing less than 40 kg is BSA-based.
The safety and efficacy of REVUFORJ in pediatric patients less than 1 year old have not been established.
Animal Data
In a repeat dose toxicity study in 6-7 week-old rats treated with revumenib at 75, 150, or 300 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks, an irreversible increase in femur growth plate closure was observed at revumenib exposures approximately 2 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose.
Based on the findings in animals, monitor bone growth and development in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 241 patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation in clinical studies of REVUFORJ, 61 (25%) patients were 65 years of age and older and 25 (10%) patients were 75 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14)].
No overall differences were observed in the effectiveness of REVUFORJ between patients who were 65 years and older and younger patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Compared to younger patients, the incidences of QTc prolongation and edema were higher in patients 65 years and older [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
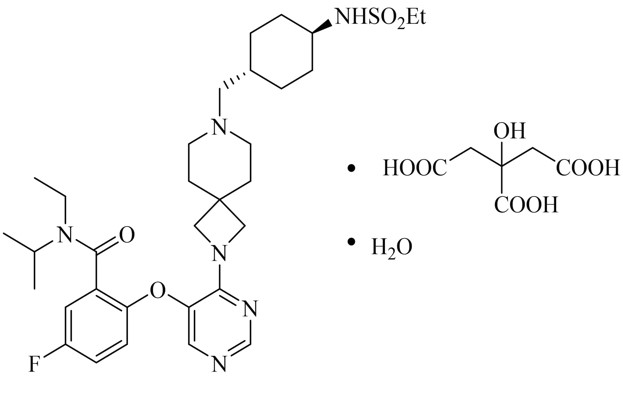
11 DESCRIPTION
REVUFORJ contains revumenib, a menin inhibitor. Revumenib is present as revumenib citrate hydrate with a chemical name of benzamide, N-ethyl-2-[[4-[7-[[trans-4- [(ethylsulfonyl)amino]cyclohexyl]methyl]-2,7-diazaspiro[3.5]non-2-yl]-5-pyrimidinyl]oxy]-5-fluoro-N-[1- methylethyl]-, 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid, hydrate (1:1:1). The molecular formula is C32H47FN6O4S●C6H8O7●H2O with a molecular weight 840.96 g/mol.
Revumenib citrate hydrate is a white to faint pink solid. Revumenib citrate hydrate is soluble at pH 1.2 and 6.8, and sparingly soluble at pH 4.5.
The chemical structure is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Chemical structure of Revumenib Citrate
REVUFORJ is available as tablets for oral use.
Each 25 mg strength tablet contains 25 mg revumenib, equivalent to 33.4 mg revumenib citrate, and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, dicalcium phosphate, crospovidone, hypromellose, sodium bicarbonate, hydrophobic colloidal silica, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, and red iron oxide.
Each 110 mg strength tablet contains 110 mg revumenib, equivalent to 146.5 mg revumenib citrate, and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, dicalcium phosphate, crospovidone, hypromellose, sodium bicarbonate, hydrophobic colloidal silica, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, and yellow iron oxide.
Each 160 mg strength tablet contains 160 mg revumenib equivalent to 213.2 mg revumenib citrate, and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, dicalcium phosphate, crospovidone, hypromellose, sodium bicarbonate, hydrophobic colloidal silica, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, and FD&C blue #2/indigo carmine aluminum lake.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Revumenib is a menin inhibitor that blocks the interaction of both wild-type lysine methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) and KMT2A fusion proteins with menin. The binding of wild-type KMT2A or KMT2A fusion proteins with menin is involved in NPM1 mutated acute myeloid leukemias and KMT2A- rearranged acute leukemias, respectively, through activation of a leukemogenic transcriptional pathway. Susceptible NPM1 mutations are defined as those that result in loss of the nucleolar localization signal and the insertion of a new nuclear export signal leading to the accumulation of mutant NPM1 in the cytoplasm of AML cells. The most common of such NPM1 mutations in patients with AML are Types A, B, and D.
In nonclinical studies using cells that express KMT2A fusions, inhibition of the menin-KMT2A interaction with revumenib altered the transcription of multiple genes including differentiation markers. In nonclinical in vitro and in vivo studies, revumenib demonstrated antiproliferative and antitumor activity in leukemia cells harboring KMT2A fusion proteins. Revumenib also showed antiproliferative activity in vitro in leukemia cells with an NPM1 mutation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Revumenib exposure-response relationships have not been fully characterized and the time course of pharmacodynamic response is unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of REVUFORJ on the QTc interval was evaluated across a dose range of 113 mg to 339 mg twice daily (1.2 times the highest adult approved recommended dosage) with and without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation.
The increase in QTc interval was concentration dependent with an increase in QTc predicted to be 23 msec (upper bound of 90% confidence interval: 25 msec) at the mean steady-state maximum concentration (Cmax) observed in patients at the highest approved recommended dosage without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. The increase in QTc interval was predicted to be 20 msec (upper bound of 90% confidence interval: 21 msec) at steady-state Cmax after administration of 160 mg twice daily with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of revumenib were characterized in patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation following single and multiple oral administration of revumenib with or without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters are presented as geometric mean [coefficient of variation (%CV)] unless otherwise specified.
Table 9. Revumenib Pharmacokinetics in Patients with R/R Acute Leukemia with a KMT2A translocation or an NPM1 mutation Abbreviations: Cmax = maximum plasma concentration; AUC = area under the time concentration curve;
Tmax = time to peak concentration
a - Steady-state
b - Dosage range of 113 mg to 339 mg (1.26 times the highest adult approved recommended dosage)
c - Approximately 400-500 calories, 25% of calories from fat
d - Independent of concentration
e - M1 contributes to revumenib’s clinically significant effects on QTc [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] but does not contribute to its efficacy at the approved recommended dosage
f - A single dose of radiolabeled revumenib 276 mg (1.02 times the highest adult approved recommended dosage) to adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute leukemiaParameter
Dosage
160 mg twice daily (with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors) 270 mg twice daily (without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors)
General Information Exposureba Cmax (ng/mL) 3028 (51%) 2344 (81%) AUC0-12h (ngh/mL) 20,050 (62%) 11,520 (70%) Dose Proportionalityb Dose proportional increases in Cmax and AUC0-12h Time to Steady-State 2 days Accumulationa 2-fold Absorption Tmax Median (range) hours 2 (0-12) 1 (0.5-4) Effect of Food Low fat mealc No clinically significant differences in revumenib pharmacokinetics observed (Cmax and AUC decreased by 27% and 12% respectively) Distribution Apparent Volume of
Distributiona (L)63 (84%) Protein Bindingd 90% Blood to plasma ratio 0.8 Elimination Half-Lifea (hours) 6.4 (52%) 3.0 (49%) Apparent Clearancea (L/h) 7 (64%) 20 (112%) Metabolism Primary Pathway CYP3A4 Active Metabolite M1f Excretionf Feces Approximately 52% (7% unchanged) Urine Approximately 25% (6% unchanged) Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of revumenib were observed based on age (1 to 84 years), race (67% White, 7% Asian, 8% Black), sex, mild to moderate (CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min) renal impairment, and mild (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and AST > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST) or moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr less than 30 mL/min), end- stage renal disease (CLcr less than 15 mL/min), or severe (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment is unknown.
Body weight (6-151 kg) has a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of revumenib, with higher revumenib exposures in patients with lower body weight (less than 40 kg). This supports the use of BSA-based dosage in patients weighing less than 40 kg.
Pediatric Patients
Revumenib geometric mean (CV%) steady-state Cmax was 3137 (39%) ng/mL and AUC0-tau was 14,630 (55%) ng·hr/mL following 95 mg/m2 twice daily with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Revumenib predicted geometric mean (%CV) steady-state Cmax was 1597 (70%) ng/mL and AUC0- tau was 12,570 (56%) ng·hr/mL following 160 mg/m2 twice daily without strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors:Revumenib AUC and Cmax is increased by 2-fold following concomitant use of multiple doses of revumenib with certain azole antifungals that are strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (i.e., posaconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole). Similarly, revumenib AUC and Cmax is increased by 2.5-fold following concomitant use of multiple doses of revumenib with cobicistat (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor).
Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers:Revumenib exposure is expected to decrease and M1 exposure is expected to increase with strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
Other Drugs:No clinically significant differences in revumenib pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with fluconazole (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor), isavuconazole (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor).
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes:Revumenib inhibits CYP3A4, but does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP2E1.
Revumenib does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4.
Transporter Systems:Revumenib is a substrate of OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, and MATE1, but is not a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MATE2-K, or BSEP. M1 is a substrate of OATP1B1, but is not a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B3, MATE1, or MATE2-K.
Revumenib inhibits MATE1, but does not inhibit P-gp, BCRP, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BSEP, and MATE2-K. M1 inhibits MATE1, but does not inhibit OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and MATE2-K.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with revumenib. In a repeat dose toxicity study in rats treated with revumenib for 13 weeks, lymphoma was observed in multiple organs in one animal.
Revumenib was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, an in vitro micronucleus assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, or an in vivo rat peripheral blood reticulocyte micronucleus assay.
Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with revumenib.
In a repeat dose toxicity study in dogs treated with revumenib at 12.5, 25 or 40 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks, microscopic findings in the testes and epididymis consisted of depletion of germ cells and decreased sperm at ≥12.5 mg/kg/day. In females, microscopic changes of atrophy in the mammary glands, uterus, and vagina and decreased number of corpora lutea in the ovaries were observed at ≥12.5 mg/kg/day. At the end of the 13-week recovery period, the findings in the female reproductive organs were reversed at all doses, and the testicular and epididymal effects were reversed at 12.5 mg/kg/day. At the dose of 12.5 mg/kg/day in dogs, exposures (AUC) were approximately 1.3 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a repeat dose toxicity study in dogs treated with revumenib at 12.5, 25, or 40 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks, microscopic findings of nerve fiber degeneration in the brain, sciatic nerves, and spinal cord segments were observed at ≥ 12.5 mg/kg/day and were not reversed at the end of a 13-week recovery period.
In a repeat dose toxicity study in rats treated with revumenib at 75, 150, 300 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks, dose dependent ocular findings of lens opacities were observed at ≥ 75 mg/kg/day; the findings progressed during the dosing and recovery periods and were not reversed.
Hyperplasia was observed in multiple organs including the testes, mammary gland, uterus, pancreas, and kidney in rats treated at ≥ 75 mg/kg/day for up to 13 weeks. The findings were irreversible in the testes, mammary gland, and pancreas. Revumenib exposures at 75 mg/kg/day in rats are approximately 2 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia with a KMT2A Translocation
SNDX-5613-0700
The efficacy of REVUFORJ was evaluated in a single-arm cohort of an open-label, multicenter trial (SNDX-5613-0700, NCT04065399; AUGMENT-101) in adult and pediatric patients at least 30 days old with relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute leukemia with a KMT2A translocation by local testing, including karyotyping. Patients with an 11q23 partial tandem duplication were excluded. Eligibility required a QTcF < 450 msec, estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, total bilirubin < 1.5 x the upper limit of normal (ULN), aminotransferases < 3 x ULN, and ejection fraction > 50% at study baseline. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score was to be 0–2 if ≥ 18 years old, Karnofsky Performance Scale score ≥ 50 (if 16 to < 18 years old, and Lansky Performance score ≥ 50 if < 16 years old). Treatment consisted of REVUFORJ at a dose approximately equivalent to 160 mg in adults orally twice daily with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, failure to achieve morphological leukemia-free state by 4 cycles of treatment, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics of the 104 treated patients are shown in Table 10. Twenty-four (23%) patients underwent HSCT following treatment with REVUFORJ.
Table 10. Baseline Demographic and Disease Characteristics in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia with KMT2A translocation (Study SNDX-5613-0700) 1. One patient did not have a translocation type reported. Demographic and Disease Characteristics REVUFORJ
N = 104
Demographics Median Age (years) (Range) 37 (1, 79) Age, n (%) < 17 years old 25 (24) ≥ 17 years old 79 (76) Sex, n (%) Male 37 (36) Female 67 (64) Race, n (%) Black or African American 8 (8) Asian 10 (10) White 75 (72) Multiple 1 (1) Unknown 10 (10) Ethnicity, n (%) Hispanic or Latino 23 (22) Not Hispanic or Latino 76 (73) Unknown 5 (5) Disease Characteristics Leukemia morphological type, n (%) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) 86 (83) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) 16 (15) Mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) 2 (2) Translocations1, n (%) t(9;11) 23 (22) t(11;19)
20 (19) t(6;11) 10 (10) t(10;11) 10 (10) t(4;11) 7 (7) t(1;11) 3 (3) t(11;17)
2 (2) t(11;22) 2 (2) t(11;16) 1 (1) KMT2A fusion partner unknown 26 (25) Disease status, n (%) Primary refractory 22 (21) Untreated relapse 21 (20) Refractory relapse 61 (59) Prior treatment Number of prior regimens, median (range) 2 (1, 11) Prior stem cell transplantation, n (%) 46 (44) Number of prior relapses, n (%) 0 22 (21) 1 55 (53) 2 20 (19) ≥3 7 (7) Efficacy was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR) plus CR with partial hematological recovery (CRh), the duration of CR+CRh, and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence. The median follow-up was 5.7 months (range, 0.3 to 28.9 months). The efficacy results are shown in Table 11. On subgroup analysis, CR+CRh was achieved by 18/86 (21%) of patients with AML, 3/16 (19%) of patients with ALL, and 1/2 (50%) of patients with MPAL.
Table 11. Efficacy Results in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia with KMT2A translocation (Study SNDX-5613-0700) CI: confidence interval; NE = not estimable; DOCR = duration of CR; DOCRh = duration of CRh.
1. CR is defined as bone marrow blasts <5%; absence of circulating blasts and blasts with Auer rods; absence of extramedullary disease; ANC ≥1.0 × 109/L and platelet count ≥100 × 109/L.
2. CRh is defined as bone marrow blasts <5%; absence of circulating blasts and blasts with Auer rods; absence of extramedullary disease; residual neutropenia (>0.5 × 109/L) and thrombocytopenia (>50 × 109/L), but the count recovery criteria for CR are not met.
3. Duration of CR+CRh is defined as the time from first CR or CRh to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
4. Duration of CR is defined as the time from first CR to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
5. Duration of CRh is defined as the time from first CRh to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
6. The 95% CI of the response rate is derived using the exact method based on binomial distribution. The median of the response duration is derived using Kaplan-Meier method.
Endpoint REVUFORJ N=104 CR1+CRh2 n (%) 22 (21.2) 95% CI (13.8, 30.3)6 Median DOCR+CRh3 (months) 6.46 95% CI (2.7, NE) CR n (%) 13 (12.5) 95% CI (6.8, 20.4)6 Median DOCR4 (months) 4.36 95% CI (1.0, NE) CRh n (%) 9 (8.7) 95% CI (4.0, 15.8)6 Median DOCRh5 (months) 6.46 95% CI (1.9, NE) For the 22 patients who achieved a CR or CRh, the median time to CR or CRh was 1.9 months (range: 0.9, 5.6 months).
Of the 83 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 12 (14%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post- baseline period. Of the 21 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 10 (48%) remained transfusion independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
14.2 Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an NPM1 Mutation
SNDX-5613-0700
The efficacy of REVUFORJ was evaluated in a single-arm cohort of an open-label, multicenter trial (SNDX-5613-0700, NCT04065399; AUGMENT-101) described above [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. A susceptible mutation was confirmed in enrolled patients using next generation sequencing or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of the last exon of NPM1. The baseline demographic and disease characteristics of the 65 patients in the pivotal cohort are shown in Table 12. Seven patients (11%) underwent HSCT following treatment with REVUFORJ.
Table 12. Baseline Demographic and Disease Characteristics in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an NPM1 Mutation (Study SNDX-5613-0700) Demographic and Disease Characteristics N = 65 Demographics Median Age (years) (Range) 65 (11, 84) Age, n (%) < 17 years old 1 (1.5) 17 to < 65 years old 31 (47.7) 65 years old 33 (50.8) Sex, n (%) Male 26 (40.0) Female 39 (60.0) Race, n (%) Black or African American 6 (9.2) Asian 4 (6.2) White 38 (58.5) Multiple 1 (1.5) Other 3 (4.6) Unknown 13 (20.0) Ethnicity Hispanic or Latino 5 (7.7) Not Hispanic or Latino 50 (76.9) Not Reported 9 (13.8) Missing 1 (1.5) Disease Characteristics NPM1 mutation type Type A 43 (66.2) Type B 4 (6.2) Type D 4 (6.2) Non-A, B, or D 5 (7.7) Not Available 9 (13.8) Prior treatment Median number of prior regimens (min, max) 2 (1, 7) Prior stem cell transplantation, n (%) 15 (23.1) Efficacy was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR) plus CR with partial hematological recovery (CRh), the duration of CR+CRh, and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence. The median follow-up was 3.8 months (range, 0.1 to 29.9) months. The efficacy results are shown in Table 13.
Table 13. Efficacy Results in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an NPM1 mutation (Study SNDX-5613-0700) CI: confidence interval; NE = not estimable; DOCR = duration of CR; DOCRh = duration of CRh.
1. CR is defined as bone marrow blasts <5%; absence of circulating blasts and blasts with Auer rods; absence of extramedullary
disease; ANC ≥1.0 × 109/L and platelet count ≥100 × 109/L.
2. CRh is defined as bone marrow blasts <5%; absence of circulating blasts and blasts with Auer rods; absence of extramedullary
disease; residual neutropenia (>0.5 × 109/L) and thrombocytopenia (>50 × 109/L), but the count recovery criteria for CR are not met.
3. Duration of CR+CRh is defined as the time from first CR or CRh to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
4. Duration of CR is defined as the time from first CR to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
5. Duration of CRh is defined as the time from first CRh to the first documented relapse or death, whichever occurs first.
6. The 95% CI of the response rate is derived using the exact method based on binomial distribution. The median of the response duration is derived using Kaplan-Meier method.
Endpoint REVUFORJ N = 65 CR1+CRh2 n (%) 15 (23.1) 95% CI (13.5, 35.2)6 Median DOCR+CRh3 (months) 4.56 95% CI (1.2, 8.1) CR n (%) 12 (18.5) 95% CI (9.9, 30)6 Median DOCR4 (months) 3.76 95% CI (1.0, 8.1) CRh n (%) 3 (4.6) 95% CI (1.0, 12.9)6 Observed DOCRh5 (months) 1.8, 2.0, 4.5 For the 15 patients who achieved a CR or CRh, the median time to response was 2.8 months (range: 1.8, 9.6 months).
Of the 46 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 8 (17%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post- baseline period. Of the 19 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 13 (68%) remained transfusion independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
25 mg: Pink modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “25” on the other side.
- 30-count bottles with a desiccant and child resistant closure (NDC: 73555-500-00)
110 mg: Beige modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “110” on the other side.
- 30-count bottles with a desiccant and child resistant closure (NDC: 73555-501-00)
160 mg: Purple modified oval film-coated tablet debossed with “S” on one side and “160” on the other side.
- 30-count bottles with a desiccant and child resistant closure (NDC: 73555-502-00)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) and Instructions for Use.
Differentiation Syndrome
Advise patients of the risks of developing differentiation syndrome as early as 3 days after the start of therapy and during treatment. Ask patients to immediately report any symptoms suggestive of differentiation syndrome, such as fever, cough or difficulty breathing, rash, low blood pressure, rapid weight gain, swelling of their arms or legs, or decreased urinary output, to their healthcare provider for further evaluation [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prolonged QT Interval and Torsades de Pointes
Advise patients to consult their healthcare provider immediately if they feel faint, lose consciousness, or have signs or symptoms suggestive of arrhythmia. Advise patients with a history of hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia of the importance of monitoring their electrolytes [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to notify their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential of the potential for impaired fertility from REVUFORJ [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant products, including over-the counter products and supplements [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Dosing Instructions
Advise patients to swallow tablets whole with a cup of water and not to cut or chew tablets. If patients are unable to swallow the tablets, they may be crushed and dispersed in water [see Instructions for Use]. Instruct patients that, if they miss a dose of REVUFORJ, to take it as soon as possible on the same day, and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose, and return to the normal schedule the following day [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 10/2025 Medication Guide
REVUFORJ (REV-you-forge)
(revumenib)
tablets, for oral useWhat is the most important information I should know about REVUFORJ?
REVUFORJ may cause serious side effects including:- differentiation syndrome. Differentiation syndrome is a serious, but common condition that affects your blood cells which may be life threatening or lead to death if not treated. Differentiation syndrome has happened as early as 3 days and up to 41 days after starting REVUFORJ. Tell any healthcare provider caring for you that you are taking a medicine that can cause differentiation syndrome. Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you develop any of the following symptoms of differentiation syndrome during treatment with REVUFORJ:
- fever
- cough
- shortness of breath
- severe headache
- confusion
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- fast weight gain
- swelling of arms, legs, neck, groin, or underarm area
- decreased urination
- rash
If you develop any of these symptoms of differentiation syndrome, your healthcare provider may start you on a medicine given through a vein (intravenous) called corticosteroids and may monitor you in the hospital.
- changes in electrical activity of your heart called QT prolongation. QT prolongation is a serious, but common side effect that can cause irregular heartbeats that can be life-threatening, such as a heart attack, and can lead to death. Your healthcare provider will check the electrical activity of your heart with a test called an electrocardiogram (ECG) and will also do blood tests to check your potassium and magnesium levels before and during treatment with REVUFORJ. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you feel faint, lightheaded, dizzy, or if you feel your heart beating irregularly or fast during treatment with REVUFORJ.
See "What are the possible side effects of REVUFORJ?" for more information about side effects. What is REVUFORJ?
REVUFORJ is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 1 year and older with:
- acute leukemia with a lysine methyltransferase 2A gene (KMT2A) translocation whose disease has come back or has not improved after previous treatment(s).
- acute myeloid leukemia with a nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutation whose disease has come back or has not improved after previous treatment(s) and who have no other satisfactory treatment options
It is not known if REVUFORJ is safe and effective in children less than 1 year of age.Before taking REVUFORJ, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have any heart problems, including a condition called long QT syndrome.
- have been told you have low blood levels of potassium or magnesium.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. REVUFORJ can harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:
o Your healthcare provider will perform a pregnancy test within 7 days before you start treatment with REVUFORJ.
o Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with REVUFORJ.
o Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose of REVUFORJ.Males who have female partners who are able to become pregnant:
o Use effective birth control during treatment with REVUFORJ and for 4 months after the last dose of REVUFORJ.
o Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods you can use during this time.- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if REVUFORJ passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during your treatment with REVUFORJ or for 1 week after your last dose of REVUFORJ.
Tell your healthcare provider about any other medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
REVUFORJ and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take REVUFORJ?
- Take REVUFORJ exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Do not change your dose or stop taking REVUFORJ unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- REVUFORJ tablets come in different strengths. Each strength is a different color. Your healthcare provider may prescribe more than 1 strength of REVUFORJ tablets for you, so it is important that you understand how to take your medicine the right way. Be sure that you understand exactly how many tablets you need to take, and what strengths to take.
- Take REVUFORJ 2 times a day at about the same time each day about 12 hours apart.
- Take REVUFORJ fasted (on an empty stomach) or with a low-fat meal (400 calories, 25% or less fat). Talk to your healthcare provider about examples of low-fat meals that you can eat.
- Swallow REVUFORJ tablets whole with a cup of water. Do not cut or chew tablets. If you are unable to swallow tablets, crush the tablets and break them apart in water. See the Instructions for Use for detailed instructions on how to prepare and give REVUFORJ tablets.
- If you miss a dose of REVUFORJ or did not take it at the usual time, take your dose as soon as possible and at least 12 hours before your next dose. Do not take 2 doses within 12 hours. Return to your normal scheduled dose the following day.
What are the possible side effects of REVUFORJ?
REVUFORJ may cause serious side effects including:
- see “What is the most important information I should know about REVUFORJ?”
- infections, including bacterial and viral infections
- changes in liver function tests
- bleeding (hemorrhage)
- nausea and vomiting
- muscle pain
- low white blood cell counts with fever
- diarrhea
- tiredness
- swelling in the arms and legs
- decreased appetite
- constipation
Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with REVUFORJ if you develop certain side effects.
REVUFORJ may cause fertility problems in females and males, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all possible side effects of REVUFORJ.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store REVUFORJ?
- Store REVUFORJ at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store the tablets in the bottle that it comes in until you are ready to take it.
- The REVUFORJ bottle has a drying agent (desiccant) and child resistant closure.
Keep REVUFORJ and all medicines out of reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of REVUFORJ.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use REVUFORJ for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give REVUFORJ to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or health professionals for information about REVUFORJ that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in REVUFORJ?
Active ingredient: revumenib
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, dicalcium phosphate, crospovidone, hypromellose, sodium bicarbonate, hydrophobic colloidal silica, magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, and red iron oxide.
The 110 mg tablet also includes yellow iron oxide.
The 160 mg tablet also includes FD&C blue #2/indigo carmine aluminum lake.
Manufactured for: Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc., New York, NY 10017
REVUFORJ ® is a registered trademark of Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Copyright © 2025 Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
For more information, go to www.revuforj.com or call Syndax at 1-888-539-3REV.
218944-SYND-MG-003
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
REVUFORJ (REV-you-forge)
revumenib tablets, for oral use
Read these Instructions for Use to prepare and take or give a dose of REVUFORJ tablets broken apart (dispersed) in water and each time you or your child get a prescription refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about you or your child’s medical condition or your treatment. Important information you need to know before preparing to break apart the REVUFORJ tablets in water:
- For more information about REVUFORJ tablets, see the Medication Guide.
- REVUFORJ tablets broken apart in water should be prepared for people who are unable to swallow whole REVUFORJ tablets. People who can swallow the tablets whole should not cut, chew, or break the tablets apart in water.
- Take or give REVUFORJ tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Do not change your dose or stop taking REVUFORJ unless your provider tells you to.
- REVUFORJ tablets come in different strengths. Each strength is a different color. Your healthcare provider may prescribe more than 1 strength of REVUFORJ tablets for you or your child, so it is important that you understand how to take or give the medicine the right way. Be sure that you understand exactly how many tablets you need to take, and what strengths to take.
- Check the expiration date on the REVUFORJ tablet bottles. Do not use REVUFORJ if the expiration date on the bottles have passed. Contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- The REVUFORJ tablets should be crushed in a clean and dry pill crusher.
- Use room temperature water to dissolve the REVUFORJ tablets.
- Use a teaspoon to measure the room temperature water. Use a 20 mL oral syringe to administer the medicine.
o Oral syringes can look different. Talk to your pharmacist if you are not sure if you have the correct oral syringe size.
o Replace the oral syringe if there are signs of damage. See Step 15.
Supplies needed to prepare and break apart the REVUFORJ tablets in water. You will need to get the 20 mL oral syringe and pill crusher, which are available from your pharmacy. Figure A
Preparing to dissolve the REVUFORJ tablets Step 1: Gather and place the REVUFORJ bottles and supplies on a clean, flat surface.
Check your prescribed dose. Count out the strengths and number of REVUFORJ tablets needed for the prescribed dose.
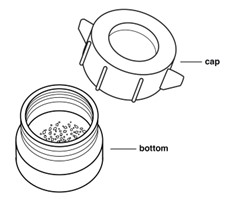
Add all the REVUFORJ tablets to a clean and dry pill crusher. Screw the top of the pill crusher down until it touches the REVUFORJ tablets.
Turn the pill crusher cap back and forth to crush the REVUFORJ tablets. Continue turning the pill crusher cap back and forth, increasing the crushing pressure on the REVUFORJ tablets each time.
Repeat until all large REVUFORJ tablet pieces are broken up. The crushed REVUFORJ tablets should be like the consistency of flour.
Step 2: Use two teaspoons to measure 10 mL of room temperature water. Add the 10 mL of water to the small cup.
Add water to the cup first and then add the crushed REVUFORJ tablets.
Do not add the crushed REVUFORJ tablets first followed by the room temperature water.
Step 3: Tip the crushed REVUFORJ tablets from the pill crusher into the small cup that contains 10 mL of water. Carefully add all of the crushed REVUFORJ tablets to the small cup.
Hold the pill crusher upside down over the small cup. Tap the pill crusher to make sure no more crushed REVUFORJ tablet pieces are left in the pill crusher.
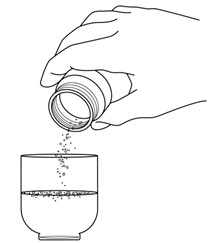
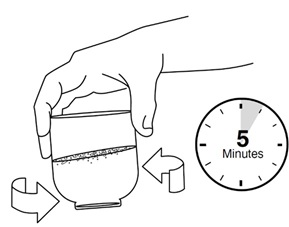
Step 4: Carefully swirl the cup right after adding the crushed REVUFORJ tablets to the small cup with water. Swirl the small cup every 30 seconds to 1 minute for a total of 5 minutes.
The crushed REVUFORJ tablets in water will look cloudy.
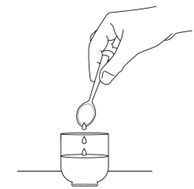
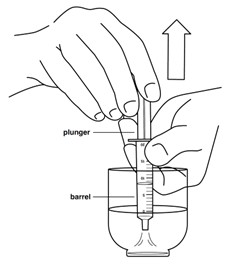
Step 5: Draw up the medicine into the 20 mL oral syringe right away.
Push the plunger of the oral syringe all the way up towards the tip. Place the tip of the oral syringe in the small cup. Pull the oral syringe plunger to draw up all of the medicine in the small cup.
The medicine must be taken within 2 hours of preparation. Turn the oral syringe upside down and back several times before taking or giving the medicine.
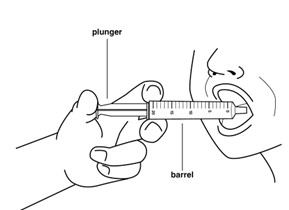
Step 6: The adult or child should sit up straight or stand before taking the medicine.
Place the tip of the oral syringe into the mouth against the inside of the cheek. Slowly and gently press down on the plunger to gently squirt the medicine into the mouth. Allow the adult or child to swallow the medicine. Make sure that no medicine is left in the mouth.
The adult or child should remain sitting up straight or standing for 2 to 3 minutes right after receiving a dose of the medicine.
If the medicine is vomited or all of the medicine is not swallowed, do not give another dose. Wait until the next scheduled dose.
Step 7: The small cup must be rinsed to make sure the adult or child receives the full dose of REVUFORJ tablets.
Place two teaspoons (10 mL) of room temperature water in the cup rinsing down the sides (Figure H)
Swirl the water around the sides of the small cup to make sure any remaining crushed REVUFORJ tablets is mixed with the water (Figure I).
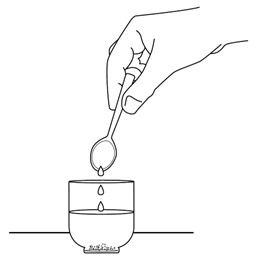
Figure I
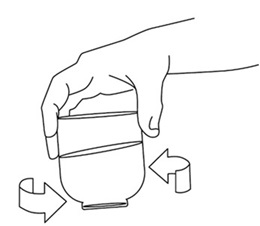
Step 8: Repeat Step 5 and Step 6 until no more medicine is left in the cup. Cleaning the oral syringe after use
Follow the instructions below for cleaning and storing the oral syringe (Step 9 through Step 15). Throw away the oral syringe in your household trash if it is damaged (See Step 15), and use a new 20 mL oral syringe.
Step 9: Remove the plunger from the barrel of the oral syringe. 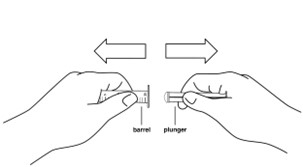
Step 10: Rinse the barrel and plunger in warm running water to help make sure all of the medicine has been removed from the oral syringe.
Do not boil the oral syringe.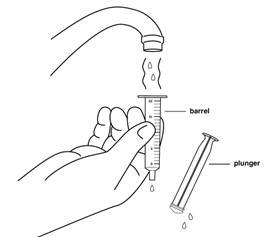
Step 11: Put the plunger into the barrel of the oral syringe. 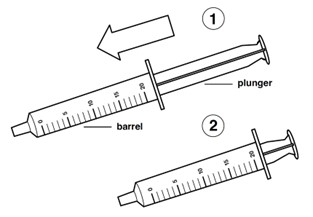
Step 12: Hold the oral syringe tip under water and draw warm water several times into the oral syringe and squirt out again until all of the medicine has been removed from the oral syringe. Repeat this Step until the oral syringe is clean. 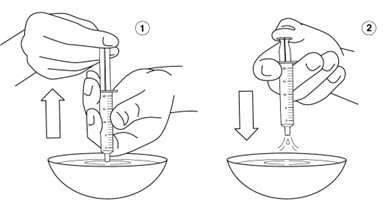
Step 13: Remove the plunger from the barrel of the oral syringe. Rinse the barrel and plunger again with warm water. 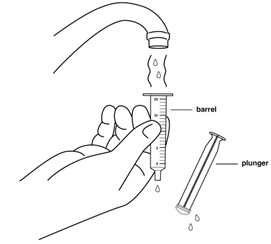
Step 14: Shake off excess water or wipe off the outside of the plunger and barrel. Place the barrel and plunger on a clean, dry paper towel to dry. 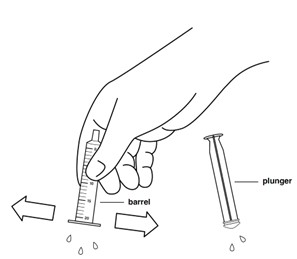
Step 15: Make sure the oral syringe parts are fully dry before putting the plunger back into the barrel of the oral syringe. Store the oral syringe in a clean place until the next use.
Replace the oral syringe if:
- there is any damage to the barrel, plunger, or tip.
- you cannot see the dosage markings or it becomes difficult to move the plunger.
Cleaning the pill crusher after use Step 16: Rinse both parts of the pill crusher with water after use. Shake off excess water or wipe both parts of the pill crusher. Place both parts of the pill crusher on a clean, dry paper towel to dry. Storing REVUFORJ
- Store REVUFORJ at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store the tablets in the bottle that it comes in until you are ready to take it.
- The REVUFORJ bottle has a drying agent (desiccant) and child resistant closure.
Keep REVUFORJ and all medicines out of reach of children.
Manufactured for: Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc., New York, NY 10017
REVUFORJ ® is a registered trademark of Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Copyright © 2025 Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
For more information, go to www.revuforj.com or call Syndax at 1-888-539-3REV.
218944-SYND-IFU-003This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Revuforj 25 mg carton/container labels

Principle Display Panel
30 tablets
Revuforj®
(revumenib) tablets25 mg
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Swallow tablets whole or crush and disperse in water.
Do not cut or chew tablets.Syndax Rx Only

This bottle contains 30 tablets (25 mg each) of Revuforj®
revumenib. Swallow tablets whole or crush and (revumenib) tablets Keep out of
disperse in water. Do not cut or chew tablets. 25 mg the reach of
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions children.
permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Recommended dosage: See Prescribing information.
Manufactured for: Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Syndax Rx Only 30 tablets -
Revuforj 110 mg carton/container labels

Principle Display Panel
30 tablets
Revuforj®
(revumenib) tablets110 mg
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Swallow tablets whole or crush and
disperse in water. Do not cut or
chew tablets.Syndax Rx Only
This bottle contains 30 tablets
(110 mg each) of revumenib. 30 tablets
Swallow tablets whole or crush
and disperse in water. Do not cut or
chew tablets. Revuforj®Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); (revumenib) tablets
excursions permitted between 15°C
to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). 110 mgRecommended dosage:
See Prescribing information.Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufactured for: Syndax Rx Only
Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc. -
Revuforj 160 mg carton/container labels

Principle Display Panel
30 tablets
Revuforj®
(revumenib) tablets160 mg
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Swallow tablets whole or crush and
disperse in water. Do not cut or
chew tablets.Syndax Rx Only
This bottle contains 30 tablets
(160 mg each) of revumenib. 30 tablets
Swallow tablets whole or crush
and disperse in water. Do not cut or
chew tablets. Revuforj®Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); (revumenib) tablets
excursions permitted between 15°C
to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). 160 mgRecommended dosage:
See Prescribing information.Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufactured for: Syndax Rx Only
Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc. -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
REVUFORJ
revumenib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73555-500 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength revumenib citrate (UNII: YL4RYN734D) (revumenib - UNII:LZ0M43NNF2) revumenib 25 mg Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape OVAL Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code S;25 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73555-500-00 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/15/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218944 11/15/2024 REVUFORJ
revumenib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73555-501 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength revumenib citrate (UNII: YL4RYN734D) (revumenib - UNII:LZ0M43NNF2) revumenib 110 mg Product Characteristics Color white (Beige) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 15mm Flavor Imprint Code S;110 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73555-501-00 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/15/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218944 11/15/2024 REVUFORJ
revumenib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73555-502 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength revumenib citrate (UNII: YL4RYN734D) (revumenib - UNII:LZ0M43NNF2) revumenib 160 mg Product Characteristics Color PURPLE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 17mm Flavor Imprint Code S;160 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73555-502-00 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/15/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218944 11/15/2024 Labeler - Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (944546089)
Trademark Results [Revuforj]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 REVUFORJ 97760175 not registered Live/Pending |
Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2023-01-19 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.