FYCOMPA- perampanel tablet FYCOMPA- perampanel suspension
Fycompa by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Fycompa by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Eisai Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FYCOMPA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FYCOMPA®.
FYCOMPA® (perampanel) tablets, for oral use, CIII
FYCOMPA® (perampanel) oral suspension, CIII
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
WARNING: SERIOUS PSYCHIATRIC AND BEHAVIORAL REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
-
Serious or life-threatening psychiatric and behavioral adverse reactions including aggression, hostility, irritability, anger, and homicidal ideation and threats have been reported in patients taking FYCOMPA (5.1)
-
Monitor patients for these reactions as well as for changes in mood, behavior, or personality that are not typical for the patient, particularly during the titration period and at higher doses (5.1)
- FYCOMPA should be reduced if these symptoms occur and should be discontinued immediately if symptoms are severe or are worsening (5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FYCOMPA, a non-competitive AMPA glutamate receptor antagonist, is indicated for:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
-
Dosing in the absence of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers
- Starting dose: 2 mg once daily orally at bedtime (2.1, 2.2)
- May increase dose based on clinical response and tolerability by increments of 2 mg once daily no more frequently than at weekly intervals (2.1, 2.2)
- Recommended maintenance dose in monotherapy or adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures: 8 mg to 12 mg once daily at bedtime (2.1)
- Recommended maintenance dose in adjunctive therapy for primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures: 8 mg once daily at bedtime (2.2)
- Measure oral suspension using provided adaptor and dosing syringe (2.7)
Dosing in the presence of concomitant moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers: see section 2.3
Specific Populations
- Mild and Moderate Hepatic Impairment: Maximum recommended daily dose is 6 mg (mild) and 4 mg (moderate) once daily at bedtime (2.4)
- Severe Hepatic Impairment: Not recommended (2.4)
- Severe Renal Impairment or on Hemodialysis: Not recommended (2.5)
- Elderly: Increase dose no more frequently than every 2 weeks (2.6)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: Monitor for suicidal thoughts or behavior (5.2)
- Neurologic Effects: Monitor for dizziness, gait disturbance, somnolence, and fatigue (5.3)
- Patients should use caution when driving or operating machinery (5.3)
- Falls: Monitor for falls and injuries (5.4)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/ Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity: Discontinue if no alternate etiology (5.5)
- Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs: In patients with epilepsy, there may be an increase in seizure frequency (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and ≥1% higher than placebo) include dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, irritability, falls, nausea, weight gain, vertigo, ataxia, headache, vomiting, contusion, abdominal pain, and anxiety (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Eisai at 1-888-274-2378 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatchDRUG INTERACTIONS
- Contraceptives: 12 mg once daily may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives containing levonorgestrel (7.1)
- Moderate and Strong CYP3A4 Inducers (including carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and phenytoin): increase clearance of perampanel and decrease perampanel plasma concentrations. When moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers are introduced or withdrawn, monitor patients closely. Dose adjustment of FYCOMPA may be necessary (2.3, 7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2019
-
Serious or life-threatening psychiatric and behavioral adverse reactions including aggression, hostility, irritability, anger, and homicidal ideation and threats have been reported in patients taking FYCOMPA (5.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SERIOUS PSYCHIATRIC AND BEHAVIORAL REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Partial-Onset Seizures
1.2 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage for Partial-Onset Seizures
2.2 Dosage for Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
2.3 Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Enzyme Inducers
2.4 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.5 Dosage Information for Patients with Renal Impairment
2.6 Dosage Information for Elderly Patients
2.7 Administration of Oral Suspension
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Psychiatric and Behavioral Reactions
5.2 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
5.3 Neurologic Effects
5.4 Falls
5.5 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
5.6 Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Contraceptives
7.2 Moderate and Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
7.3 Alcohol and Other CNS Depressants
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Partial-Onset Seizures
14.2 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic (PGTC) Seizures
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: SERIOUS PSYCHIATRIC AND BEHAVIORAL REACTIONS
-
Serious or life-threatening psychiatric and behavioral adverse reactions including aggression, hostility, irritability, anger, and homicidal ideation and threats have been reported in patients taking FYCOMPA (5.1).
-
These reactions occurred in patients with and without prior psychiatric history, prior aggressive behavior, or concomitant use of medications associated with hostility and aggression (5.1).
-
Advise patients and caregivers to contact a healthcare provider immediately if any of these reactions or changes in mood, behavior, or personality that are not typical for the patient are observed while taking FYCOMPA or after discontinuing FYCOMPA (5.1).
-
Closely monitor patients particularly during the titration period and at higher doses (5.1).
- FYCOMPA should be reduced if these symptoms occur and should be discontinued immediately if symptoms are severe or are worsening (5.1).
-
Serious or life-threatening psychiatric and behavioral adverse reactions including aggression, hostility, irritability, anger, and homicidal ideation and threats have been reported in patients taking FYCOMPA (5.1).
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage for Partial-Onset Seizures
Monotherapy or Adjunctive Therapy
The recommended starting dosage of FYCOMPA in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older is 2 mg once daily taken orally at bedtime. Increase dosage no more frequently than at weekly intervals by increments of 2 mg once daily based on individual clinical response and tolerability.
The recommended maintenance dose range is 8 mg to 12 mg once daily, although some patients may respond to a dose of 4 mg daily. A dose of 12 mg once daily resulted in somewhat greater reductions in seizure rates than the dose of 8 mg once daily, but with a substantial increase in adverse reactions.
Dosage adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducing drugs, which include certain antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
2.2 Dosage for Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy
The recommended starting dosage of FYCOMPA in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is 2 mg once daily taken orally at bedtime. Increase dosage no more frequently than at weekly intervals by increments of 2 mg once daily based on individual clinical response and tolerability.
The recommended maintenance dose is 8 mg once daily taken at bedtime. Patients who are tolerating FYCOMPA at 8 mg once daily and require further reduction of seizures may benefit from a dose increase up to 12 mg once daily if tolerated.
Dosage adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducing drugs, which include certain AEDs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
2.3 Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of Moderate or Strong CYP3A4 Enzyme Inducers
Moderate and strong CYP3A4 inducers, including enzyme-inducing AEDs such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, and oxcarbazepine, cause a reduction in FYCOMPA plasma levels [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older receiving these concomitant enzyme-inducing drugs, the recommended starting dosage of FYCOMPA is 4 mg once daily taken orally at bedtime.
Increase dosage by increments of 2 mg once daily based on individual clinical response and tolerability, no more frequently than at weekly intervals. A maintenance dose has not been established in clinical trials. The highest dose studied in patients on concomitant enzyme-inducing AEDs was 12 mg once daily.
When moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers are introduced or withdrawn from a patient’s treatment regimen, the patient should be closely monitored for clinical response and tolerability. Dose adjustment of FYCOMPA may be necessary.
2.4 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, the starting dose of FYCOMPA is 2 mg once daily. Increase dosage by increments of 2 mg once daily no more frequently than every 2 weeks. The maximum recommended daily dose is 6 mg for patients with mild hepatic impairment and 4 mg for patients with moderate hepatic impairment. FYCOMPA is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Dosage Information for Patients with Renal Impairment
FYCOMPA can be used in patients with moderate renal impairment with close monitoring. A slower titration may be considered, based on clinical response and tolerability. FYCOMPA is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment or patients undergoing hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.6 Dosage Information for Elderly Patients
In elderly patients, increase dosage no more frequently than every 2 weeks during titration [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
2.7 Administration of Oral Suspension
FYCOMPA oral suspension, 0.5 mg/mL, should be shaken well before every administration. The provided adapter and graduated oral dosing syringe should be used to administer the oral suspension. A household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device. The adapter, which is supplied in the product carton, should be inserted firmly into the neck of the bottle before use and remain in place for the duration of the usage of the bottle. The dosing syringe should be inserted into the adapter and the dose withdrawn from the inverted bottle. The cap should be replaced after each use. The cap fits properly when the adapter is in place [see Instructions for Use].
Discard any unused FYCOMPA oral suspension remaining 90 days after first opening the bottle.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets
- 2 mg tablets: orange, round, debossed with “2” on one side and “Є 275” on the other.
- 4 mg tablets: red, round, debossed with “4” on one side and “Є 277” on the other.
- 6 mg tablets: pink, round, debossed with “6” on one side and “Є 294” on the other.
- 8 mg tablets: purple, round, debossed with “8” on one side and “Є 295” on the other.
- 10 mg tablets: green, round, debossed with “10” on one side and “Є 296” on the other.
- 12 mg tablets: blue, round, debossed with “12” on one side and “Є 297” on the other.
Oral Suspension
0.5 mg/mL white to off-white opaque liquid suspension for oral administration. - 2 mg tablets: orange, round, debossed with “2” on one side and “Є 275” on the other.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Psychiatric and Behavioral Reactions
In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, hostility- and aggression-related adverse reactions occurred in 12% and 20% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, compared to 6% of patients in the placebo group. These effects were dose-related and generally appeared within the first 6 weeks of treatment, although new events continued to be observed through more than 37 weeks. FYCOMPA-treated patients experienced more hostility- and aggression-related adverse reactions that were serious, severe, and led to dose reduction, interruption, and discontinuation more frequently than placebo-treated patients.
In general, in placebo-controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, neuropsychiatric events were reported more frequently in patients being treated with FYCOMPA than in patients taking placebo. These events included irritability, aggression, anger, and anxiety, which occurred in 2% or greater of FYCOMPA-treated patients and twice as frequently as in placebo-treated patients. Other symptoms that occurred with FYCOMPA and were more common than with placebo included belligerence, affect lability, agitation, and physical assault. Some of these events were reported as serious and life-threatening. Homicidal ideation and/or threat were exhibited in 0.1% of 4,368 FYCOMPA-treated patients in controlled and open label trials, including non-epilepsy trials. Homicidal ideation and/or threat have also been reported postmarketing in patients treated with FYCOMPA.
In the partial-onset seizure clinical trials, these events occurred in patients with and without prior psychiatric history, prior aggressive behavior, or concomitant use of medications associated with hostility and aggression. Some patients experienced worsening of their pre-existing psychiatric conditions. Patients with active psychotic disorders and unstable recurrent affective disorders were excluded from the clinical trials. The combination of alcohol and FYCOMPA significantly worsened mood and increased anger. Patients taking FYCOMPA should avoid the use of alcohol [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Similar serious psychiatric and behavioral events were observed in the primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure clinical trial.
In healthy volunteers taking FYCOMPA, observed psychiatric events included paranoia, euphoric mood, agitation, anger, mental status changes, and disorientation/confusional state.
In the non-epilepsy trials, psychiatric events that occurred in perampanel-treated patients more often than placebo-treated patients included disorientation, delusion, and paranoia.
In the postmarketing setting, there have been reports of psychosis (acute psychosis, hallucinations, delusions, paranoia) and delirium (delirium, confusional state, disorientation, memory impairment) in patients treated with FYCOMPA [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that FYCOMPA may increase the risk of psychiatric events. Patients should be monitored during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose of FYCOMPA, and especially when taking higher doses and during the initial few weeks of drug therapy (titration period) or at other times of dose increases. Dose of FYCOMPA should be reduced if these symptoms occur. Permanently discontinue FYCOMPA for persistent severe or worsening psychiatric symptoms or behaviors and refer for psychiatric evaluation.
5.2 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including FYCOMPA, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI: 1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as 1 week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5-100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 1 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 1. Risk by indication for antiepileptic drugs in the pooled analysis Indication Placebo Patients with Events per 1000 Patients Drug Patients with Events per 1000 patients Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in drug Patients/ Incidence in Placebo Patients Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events per 1000 Patients Epilepsy 1.0 3.4 3.5 2.4 Psychiatric 5.7 8.5 1.5 2.9 Other 1.0 1.8 1.9 0.9 Total 2.4 4.3 1.8 1.9 The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing FYCOMPA or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
5.3 Neurologic Effects
Dizziness and Gait Disturbance
FYCOMPA caused dose-related increases in events related to dizziness and disturbance in gait or coordination [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, dizziness and vertigo were reported in 35% and 47% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, compared to 10% of placebo-treated patients. The gait disturbance related events (including ataxia, gait disturbance, balance disorder, and abnormal coordination) were reported in 12% and 16% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, compared to 2% of placebo-treated patients. Elderly patients had an increased risk of these adverse reactions compared to younger adults and pediatric patients.
These adverse reactions occurred mostly during the titration phase and led to discontinuation in 3% of FYCOMPA-treated patients compared to 1% of placebo-treated patients.
These adverse reactions were also observed in the primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure clinical trial.
Somnolence and Fatigue
FYCOMPA caused dose-dependent increases in somnolence and fatigue-related events (including fatigue, asthenia, and lethargy).
In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, 16% and 18% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, reported somnolence compared to 7% of placebo patients. In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, 12% and 15% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, reported fatigue-related events compared to 5% of placebo patients. Somnolence or fatigue-related events led to discontinuation in 2% of FYCOMPA-treated patients and 0.5% of placebo-treated patients. Elderly patients had an increased risk of these adverse reactions compared to younger adults and pediatric patients.
In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, these adverse reactions occurred mostly during the titration phase.
These adverse reactions were also observed in the primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure clinical trial.
Risk Amelioration
Prescribers should advise patients against engaging in hazardous activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating motor vehicles or dangerous machinery, until the effect of FYCOMPA is known. Patients should be carefully observed for signs of central nervous system (CNS) depression, such as somnolence and sedation, when FYCOMPA is used with other drugs with sedative properties because of potential additive effects.
5.4 Falls
An increased risk of falls, in some cases leading to serious injuries including head injuries and bone fracture, occurred in patients being treated with FYCOMPA (with and without concurrent seizures). In the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, falls were reported in 5% and 10% of patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg and 12 mg per day, respectively, compared to 3% of placebo-treated patients. Falls were reported as serious and led to discontinuation more frequently in FYCOMPA-treated patients than placebo-treated patients. Elderly patients had an increased risk of falls compared to younger adults and pediatric patients.
5.5 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as Multiorgan hypersensitivity, has been reported in patients taking antiepileptic drugs, including FYCOMPA. DRESS may be fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling, in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its expression, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. FYCOMPA should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established.
5.6 Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs
There is the potential of increased seizure frequency in patients with seizure disorders when antiepileptic drugs are withdrawn abruptly. FYCOMPA has a half-life of approximately 105 hours so that even after abrupt cessation, blood levels fall gradually. In epilepsy clinical trials FYCOMPA was withdrawn without down-titration. Although a small number of patients exhibited seizures following discontinuation, the data were not sufficient to allow any recommendations regarding appropriate withdrawal regimens. A gradual withdrawal is generally recommended with antiepileptic drugs, but if withdrawal is a response to adverse events, prompt withdrawal can be considered.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Psychiatric and Behavioral Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Neurologic Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Partial-Onset Seizures
Adult and Adolescent Patients (12 years of age and older)
A total of 1,038 patients receiving FYCOMPA (2, 4, 8, or 12 mg once daily) constituted the safety population in the pooled analysis of the placebo-controlled trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) in patients with partial-onset seizures. Approximately 51% of patients were female, and the mean age was 35 years.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In controlled clinical trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3), the rate of discontinuation as a result of an adverse reaction was 3%, 8%, and 19% in patients randomized to receive FYCOMPA at the recommended doses of 4 mg, 8 mg, and 12 mg per day, respectively, and 5% in patients randomized to receive placebo [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The adverse reactions most commonly leading to discontinuation (≥1% in the 8 mg or 12 mg FYCOMPA group and greater than placebo) were dizziness, somnolence, vertigo, aggression, anger, ataxia, blurred vision, irritability, and dysarthria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 2 gives the incidence in the controlled clinical trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) of the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients with partial-onset seizures in the FYCOMPA 12 mg dose group and more frequent than placebo (in order of decreasing frequency for the 12 mg dose group).
The most common dose-related adverse reactions in patients receiving FYCOMPA at doses of 8 mg or 12 mg (≥4% and occurring at least 1% higher than the placebo group) included dizziness (36%), somnolence (16%), fatigue (10%), irritability (9%), falls (7%), nausea (7%), ataxia (5%), balance disorder (4%), gait disturbance (4%), vertigo (4%), and weight gain (4%). For almost every adverse reaction, rates were higher on 12 mg and more often led to dose reduction or discontinuation.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions in Pooled Placebo-Controlled Trials in Adult and Adolescent Patients with Partial-Onset Seizures (Studies 1, 2, and 3) (Reactions ≥ 2% of Patients in Highest FYCOMPA Dose (12 mg) Group and More Frequent than Placebo)
Placebo n=442
%FYCOMPA 4 mg
n=172
%8 mg
n=431
%12 mg
n=255
%Dizziness 9 16 32 43 Somnolence 7 9 16 18 Headache 11 11 11 13 Irritability 3 4 7 12 Fatigue 5 8 8 12 Falls 3 2 5 10 Ataxia 0 1 3 8 Nausea 5 3 6 8 Vertigo 1 4 3 5 Back pain 2 2 2 5 Dysarthria 0 1 3 4 Anxiety 1 2 3 4 Blurred vision 1 1 3 4 Gait disturbance 1 1 4 4 Weight gain 1 4 4 4 Cough 3 1 1 4 Upper respiratory tract infection 3 3 3 4 Vomiting 3 2 3 4 Hypersomnia 0 1 2 3 Anger <1 0 1 3 Aggression 1 1 2 3 Balance disorder 1 0 5 3 Diplopia 1 1 1 3 Head injury 1 1 1 3 Hypoaesthesia 1 0 0 3 Pain in extremity 1 0 2 3 Constipation 2 2 2 3 Myalgia 2 1 1 3 Coordination abnormal 0 1 <1 2 Euphoric mood 0 0 <1 2 Confusional state <1 1 1 2 Hyponatremia <1 0 0 2 Limb injury <1 1 1 2 Mood altered <1 1 <1 2 Arthralgia 1 0 3 2 Asthenia 1 1 2 2 Contusion 1 0 2 2 Memory impairment 1 0 1 2 Musculoskeletal pain 1 1 1 2 Oropharyngeal pain 1 2 2 2 Paraesthesia 1 0 1 2 Peripheral edema 1 1 1 2 Skin laceration 1 0 2 2 Pediatric Patients (4 to <12 years of age)
In two studies in pediatric patients 4 to <12 years of age with epilepsy, a total of 225 patients received FYCOMPA, with 110 patients exposed for at least 6 months, and 21 patients for at least 1 year. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients 4 to <12 years of age were similar to those seen in patients 12 years of age and older.
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
A total of 81 patients receiving FYCOMPA 8 mg once daily constituted the safety population in the placebo-controlled trial in patients with primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (Study 4). Approximately 57% of patients were female, and the mean age was 27 years.
In the controlled primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure clinical trial (Study 4), the adverse reaction profile was similar to that noted for the controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3).
Table 3 gives the incidence of adverse reactions in patients receiving FYCOMPA 8 mg (≥4% and higher than in the placebo group) in Study 4. The most common adverse reactions in patients receiving FYCOMPA (≥10% and greater than placebo) were dizziness (32%), fatigue (15%), headache (12%), somnolence (11%), and irritability (11%).
The adverse reactions most commonly leading to discontinuation in patients receiving FYCOMPA 8 mg (≥2% and greater than placebo) were vomiting (2%) and dizziness (2%).
Table 3. Adverse Reactions in a Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures (Study 4) (Reactions ≥ 4% of Patients in FYCOMPA Group and More Frequent than Placebo) Placebo
n=82
%FYCOMPA 8 mg
n=81
%Dizziness 6 32 Fatigue 6 15 Headache 10 12 Somnolence 4 11 Irritability 2 11 Vertigo 2 9 Vomiting 2 9 Weight gain 4 7 Contusion 4 6 Nausea 5 6 Abdominal pain 1 5 Anxiety 4 5 Urinary tract infection 1 4 Ligament sprain 0 4 Balance disorder 1 4 Rash 1 4 Weight Gain
Weight gain has occurred with FYCOMPA.
In controlled partial-onset seizure clinical trials, FYCOMPA-treated adults gained an average of 1.1 kg (2.5 lbs) compared to an average of 0.3 kg (0.7 lbs) in placebo-treated adults with a median exposure of 19 weeks. The percentages of adults who gained at least 7% and 15% of their baseline body weight in FYCOMPA-treated patients were 9.1% and 0.9%, respectively, as compared to 4.5% and 0.2% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. Clinical monitoring of weight is recommended.
Similar increases in weight were also observed in adult and adolescent patients treated with FYCOMPA in the primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure clinical trial.
Elevated triglycerides
Increases in triglycerides have occurred with FYCOMPA use.
Comparison of Sex and Race
No significant sex differences were noted in the incidence of adverse reactions.
Although there were few non-Caucasian patients, no differences in the incidence of adverse reactions compared to Caucasian patients were observed.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of FYCOMPA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Psychiatric: Acute psychosis, hallucinations, delusions, paranoia, delirium, confusional state, disorientation, memory impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Serious Psychiatric and Behavioral Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Contraceptives
With concomitant use, FYCOMPA at a dose of 12 mg per day reduced levonorgestrel exposure by approximately 40% [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Use of FYCOMPA with contraceptives containing levonorgestrel may render them less effective. Additional non-hormonal forms of contraception are recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
7.2 Moderate and Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
The concomitant use of known moderate and strong CYP3A4 inducers including carbamazepine, phenytoin, or oxcarbazepine with FYCOMPA decreased the plasma levels of perampanel by approximately 50-67% [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The starting doses for FYCOMPA should be increased in the presence of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
When these moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers are introduced or withdrawn from a patient’s treatment regimen, the patient should be closely monitored for clinical response and tolerability. Dose adjustment of FYCOMPA may be necessary [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
7.3 Alcohol and Other CNS Depressants
The concomitant use of FYCOMPA and CNS depressants including alcohol may increase CNS depression. A pharmacodynamic interaction study in healthy subjects found that the effects of FYCOMPA on complex tasks such as driving ability were additive or supra-additive to the impairment effects of alcohol [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Multiple dosing of FYCOMPA 12 mg per day also enhanced the effects of alcohol to interfere with vigilance and alertness, and increased levels of anger, confusion, and depression. These effects may also be seen when FYCOMPA is used in combination with other CNS depressants. Care should be taken when administering FYCOMPA with these agents. Patients should limit activity until they have experience with concomitant use of CNS depressants (e.g., benzodiazepines, narcotics, barbiturates, sedating antihistamines). Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on FYCOMPA to gauge whether it adversely affects these activities.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), such as FYCOMPA, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking FYCOMPA during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry by calling 1-888-233-2334 or visiting http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org.
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with use in pregnant women. In animal studies, perampanel induced developmental toxicity in pregnant rat and rabbit at clinically relevant doses [see Data]. In the U.S. general population the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of perampanel (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis resulted in an increase in visceral abnormalities (diverticulum of the intestine) at all doses tested; maternal toxicity was observed at the mid and high doses. In a dose-ranging study at higher oral doses (10, 30, or 60 mg/kg/day), embryo lethality and reduced fetal body weight were observed at the mid and high doses tested. The lowest dose tested (1 mg/kg/day) is similar to a human dose of 8 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2).
Upon oral administration of perampanel (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits throughout organogenesis, embryo lethality and maternal toxicity were observed at the mid and high doses tested; the no-effect dose for embryo-fetal developmental toxicity in rabbit (1 mg/kg/day) is approximately 2 times a human dose of 8 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2).
Oral administration of perampanel (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day) to rats throughout gestation and lactation resulted in fetal and pup deaths at the mid and high doses (associated with maternal toxicity) and delayed sexual maturation in males and females at the highest dose tested. No effects were observed on measures of neurobehavioral or reproductive function in the offspring. The no-effect dose for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity in rat (1 mg/kg/day) is similar to a human dose of 8 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of perampanel in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Perampanel and/or its metabolites are present in rat milk, and are detected at concentrations higher than that in maternal plasma.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for FYCOMPA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from FYCOMPA or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Use of FYCOMPA may reduce the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives containing levonorgestrel. Advise women taking FYCOMPA who are using a levonorgestrel-containing contraceptive to use an additional non-hormonal form of contraception while using FYCOMPA and for a month after discontinuation [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of FYCOMPA for the treatment of partial-onset seizures have been established in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older.
The safety and effectiveness of FYCOMPA in patients 12 years of age and older was established by three randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies, which included 72 pediatric patients between 12 and 16 years of age exposed to FYCOMPA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Use of FYCOMPA for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients 4 years to less than 12 years of age is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of FYCOMPA in patients 12 years of age and older with partial onset seizures, pharmacokinetic data from adult and pediatric patients, and safety data in 225 pediatric patients 4 years to less than 12 years of age treated with FYCOMPA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The safety and efficacy of FYCOMPA for the adjunctive therapy of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older was established in a single randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (n=164), which included 11 pediatric patients 12 to 16 years of age exposed to FYCOMPA; an additional 6 patients were treated with FYCOMPA in the open-label extension of the study [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The safety and effectiveness of FYCOMPA for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age or for the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Data
Oral administration of perampanel (1, 3, 3/10/30 mg/kg/day; high dose increased on postnatal days [PND] 28 and 56) to young rats for 12 weeks starting on PND 7 resulted in reduced body weight, reduced growth, neurobehavioral impairment (water maze performance and auditory startle habituation) at the mid and high doses, and delayed sexual maturation at the high doses. CNS signs (reduced activity, incoordination, excessive grooming/scratching), pup death, decreased hindlimb splay, and decreased hindlimb grip strength were observed at all doses. Effects on pup body weight, pup growth, hindlimb splay, impairment in the water maze performance, and auditory startle persisted after dosing was stopped. A no-effect dose for postnatal developmental toxicity was not identified in this study.
Oral administration of perampanel (1, 5, 5/10 mg/kg/day; high dose increased on PND 56) to juvenile dogs for 33 weeks, starting on PND 42, resulted in CNS signs (incoordination, excessive grooming/licking/scratching, spatial disorientation, and/or ataxic gait) at all doses tested.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of FYCOMPA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine the safety and efficacy of FYCOMPA in the elderly population. Because of increased likelihood for adverse reactions in the elderly, dosing titration should proceed slowly in patients aged 65 years and older [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Use of FYCOMPA in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended, and dosage adjustments are recommended in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Dose adjustment is not required in patients with mild renal impairment. FYCOMPA should be used with caution in patients with moderate renal impairment, and slower titration may be considered. Use in patients with severe renal impairment or patients undergoing hemodialysis is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
FYCOMPA contains perampanel and is listed as a Schedule III controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects. Drug addiction, which develops after repeated drug abuse, is characterized by a strong desire to take a drug despite harmful consequences, difficulty in controlling its use, giving a higher priority to drug use than to obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes physical withdrawal. Drug abuse and drug addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence (for example, abuse may not be accompanied by physical dependence) [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
Studies of human abuse potential were performed to evaluate the abuse potential of FYCOMPA (8 mg, 24 mg, and 36 mg) as compared to alprazolam C-IV (1.5 mg and 3 mg), and oral ketamine C-III (100 mg) in recreational polydrug users. Supra-therapeutic doses of FYCOMPA 24 and 36 mg produced responses for “Euphoria” that were similar to ketamine 100 mg and alprazolam 3 mg. For “High,” FYCOMPA 24 mg and 36 mg produced responses comparable to ketamine 100 mg and significantly higher than both doses of alprazolam on a visual analog scale (VAS). “Drug Liking,” “Overall Drug Liking,” and “Take Drug Again” for FYCOMPA were each statistically lower than ketamine 100 mg. In addition, for “Bad Drug Effects,” FYCOMPA 24 mg and 36 mg produced responses significantly higher than ketamine 100 mg.
For “Sedation,” FYCOMPA 24 and 36 mg produced responses similar to alprazolam 3 mg and higher than ketamine 100 mg.
Additionally, on VAS measures related to dissociative phenomena such as “Floating,” “Spaced Out,” and “Detached,” FYCOMPA at supra-therapeutic doses produced responses similar to ketamine 100 mg and greater than both doses of alprazolam tested. Of note, due to somnolence a number of subjects had missing data around Tmax of FYCOMPA. The above described data might represent an underestimate of FYCOMPA’s effects. The duration of effects of higher doses of FYCOMPA on the majority of measures was much greater than alprazolam 3 mg and ketamine 100 mg.
In this study, the incidence of euphoria following FYCOMPA administration 8 mg, 24 mg, and 36 mg was 37%, 46%, 46%, respectively, which was higher than alprazolam 3 mg (13%) but lower than ketamine 100 mg (89%).
9.3 Dependence
Physical dependence is characterized by withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
A nonclinical dependence study in rats demonstrated withdrawal symptoms, including hyperreactivity to handling, muscle rigidity, and decreases in food consumption and body weights.
FYCOMPA may cause dependence and withdrawal symptoms that may include anxiety, nervousness, irritability, fatigue, lethargy, asthenia, mood swings, and insomnia.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
The highest reported overdose of FYCOMPA was 300 mg. Events reported after FYCOMPA overdose include somnolence, stupor, coma, psychiatric or behavioral reactions, altered mental status, and dizziness or gait disturbances.
There is no available specific antidote to the overdose reactions of FYCOMPA. In the event of overdose, standard medical practice for the management of any overdose should be used. An adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation should be ensured; monitoring of cardiac rhythm and vital sign measurement is recommended. A certified poison control center should be contacted for updated information on the management of overdose with FYCOMPA. Due to its long half-life, the reactions caused by FYCOMPA could be prolonged.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
FYCOMPA tablets and oral suspension contain perampanel a non-competitive AMPA receptor antagonist as a 4:3 hydrate.
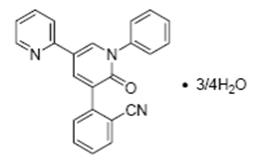
The chemical name of the active ingredient is 2-(1′,6′-dihydro-6′-oxo-1′-phenyl[2,3′-bipyridin]-5′-yl)-benzonitrile, hydrate (4:3).
The molecular formula is C23H15N3O ¾H2O and the molecular weight is 362.90 (349.39 for anhydrous perampanel). It is a white to yellowish white powder. It is freely soluble in 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone, sparingly soluble in acetonitrile and acetone, slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol and ethyl acetate, very slightly soluble in 1-octanol and diethyl ether, and practically insoluble in heptane and water. The chemical structure is:
Tablets
FYCOMPA tablets are round, bi-convex, film-coated tablets containing 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg, 8 mg, 10 mg, or 12 mg of perampanel. Tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Tablets of different strengths may contain yellow ferric oxide (10 mg and 2 mg), red ferric oxide (2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg, 8 mg), black ferric oxide (8 mg), and FD&C Blue No. 2 (indigo carmine) aluminum lake (10 mg and 12 mg).
Oral Suspension
FYCOMPA oral suspension is a white to off-white opaque liquid providing perampanel in a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. The oral suspension contains the following inactive ingredients: sorbitol, microcrystalline cellulose, carboxymethyl-cellulose sodium, poloxamer, simethicone, citric acid, sodium benzoate and purified water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Perampanel is a non-competitive antagonist of the ionotropic α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) glutamate receptor on post-synaptic neurons. Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and is implicated in a number of neurological disorders caused by neuronal over excitation.
The precise mechanism by which FYCOMPA exerts its antiepileptic effects in humans is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Psychomotor Performance
In a healthy volunteer study to assess the effects of FYCOMPA tablets on psychomotor performance using a standard battery of assessments including simulated driving, single and multiple daily doses of FYCOMPA 4 mg did not impair simple psychomotor tasks, driving performance, or sensorimotor coordination. Single and multiple doses of 8 mg and 12 mg impaired psychomotor performance in a dose-related manner. Car handling ability was impaired after dosing of FYCOMPA 12 mg, but postural stability was not significantly impaired. Performance testing returned to baseline within 2 weeks of cessation of FYCOMPA dosing.
Interactions with Alcohol
In the above study (see Psychomotor Performance), when administered to healthy subjects receiving alcohol to achieve a blood concentration of 80-100 mg/100 mL, FYCOMPA consistently impaired simple psychomotor performance after single doses of 4 to 12 mg, and after 21 days of multiple 12 mg/day doses. The effects of FYCOMPA on complex tasks such as driving ability were additive or supra-additive to the impairment effects of alcohol. FYCOMPA enhanced the effects of alcohol on vigilance and alertness, and increased levels of anger, confusion, and depression.
Potential to Prolong QT Interval
In a placebo-controlled thorough QT study of perampanel in healthy subjects, there was no evidence that perampanel caused QT interval prolongation of clinical significance at doses of 6 or 12 mg (i.e., the upper bound of the 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted baseline-corrected QTc was below 10 msec). The exposures observed with the 12 mg dose in this study will not cover the exposures expected in patients with hepatic impairment taking doses over 6 mg/day. At the highest recommended dose (12 mg), perampanel did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of perampanel are similar in healthy subjects, patients with partial-onset seizures, and patients with primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. The half-life of perampanel is about 105 hours, so that steady state is reached in about 2-3 weeks. AUC of perampanel increased in a dose-proportional manner after single-dose administration of 0.2-12 mg tablets and after multiple-dose administration of 1-12 mg tablets once daily.
FYCOMPA oral suspension has comparable bioavailability to FYCOMPA tablets under steady state. Both formulations may be used interchangeably.
The pharmacokinetics of perampanel are similar when used as monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures (in the absence of concomitant moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers).
Absorption
Perampanel is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration with negligible first-pass metabolism. Median time to reach peak concentration (tmax) ranged from 0.5 to 2.5 hours under fasted condition. Co-administration of FYCOMPA tablet with a high fat meal had no impact on the total exposure (AUC0-inf) of perampanel and reduced the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of perampanel by 11%-40%. The tmax was delayed by approximately 1-3 hours in fed state compared to that under fasted conditions.
Distribution
Data from in vitro studies indicate that, in the concentration range of 20 to 2000 ng/mL, perampanel is approximately 95-96% bound to plasma proteins, mainly bound to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. Blood to plasma ratio of perampanel is 0.55-0.59.
Metabolism
Perampanel is extensively metabolized via primary oxidation and sequential glucuronidation. Oxidative metabolism is primarily mediated by CYP3A4/5 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2 and CYP2B6, based on results of in vitro studies using recombinant human CYPs and human liver microsomes. Other CYP enzymes may also be involved.
Following administration of radiolabeled perampanel, unchanged perampanel accounted for 74-80% of total radioactivity in systemic circulation, whereas only trace amounts of individual perampanel metabolites were detected in plasma.
Elimination
Following administration of a radiolabeled perampanel tablet dose to 8 healthy elderly subjects, 22% of administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 48% in the feces. In urine and feces, recovered radioactivity was primarily composed of a mixture of oxidative and conjugated metabolites. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of pooled data from 19 Phase 1 studies reported that t1/2 of perampanel was 105 hours on average. Apparent clearance of perampanel in healthy subjects and patients was approximately 12 mL/min.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of perampanel following a single 1 mg tablet dose were evaluated in 12 subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A and B, respectively) compared with 12 demographically matched healthy subjects. The total (free and protein bound) exposure (AUC0-inf) of perampanel was 50% greater in subjects with mild hepatic impairment and more than doubled (2.55-fold) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment compared to their healthy controls. The AUC0-inf of free perampanel in subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment was 1.8-fold and 3.3-fold, respectively, of those in matched healthy controls. The t1/2 was prolonged in subjects with mild impairment (306 vs. 125 hours) and moderate impairment (295 vs. 139 hours). Perampanel has not been studied in subjects with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Renal Impairment
A dedicated study has not been conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of perampanel in patients with renal impairment. Population pharmacokinetic analysis was performed on pooled data from patients with partial-onset seizures and receiving FYCOMPA tablets up to 12 mg/day in placebo-controlled clinical trials. Results showed that perampanel apparent clearance was decreased by 27% in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50-80 mL/min) compared to patients with normal renal function (creatinine clearance >80 mL/min), with a corresponding 37% increase in AUC. Considering the substantial overlap in the exposure between normal and mildly impaired patients, no dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment. Perampanel has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment and patients undergoing hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Sex
In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures receiving FYCOMPA tablets in placebo-controlled clinical trials, perampanel apparent clearance in females (0.54 L/hr) was 18% lower than in males (0.66 L/hr). No dosage adjustment is necessary based on sex.
Pediatrics
In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of healthy subjects and pediatric and adult patients with partial onset seizures, including 123 children 4 years to less than 12 years of age, 226 adolescents 12 years to less than 18 years of age, and 1912 adults 18 years of age and older, no significant effect of age or body weight on perampanel clearance was found.
Geriatrics
In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures ranging in age from 12 to 74 years receiving FYCOMPA tablets in placebo-controlled trials, no significant effect of age on perampanel apparent clearance was found [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Race
In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, which included 614 Caucasians, 15 Blacks, 4 Japanese, 4 American Indians/Alaska Natives, 79 Chinese and 108 other Asians receiving FYCOMPA tablets in placebo-controlled trials, no significant effect of race on perampanel apparent clearance was found. No dosage adjustment is necessary.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Drug Metabolizing Enzymes
In human liver microsomes, perampanel at a concentration of 30 μmol/L, about 10 fold the steady state Cmax at a 12 mg dose, had a weak inhibitory effect on CYP2C8, CYP3A4, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7. Perampanel did not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, UGT1A1, UGT1A4, and UGT1A6 up to a concentration of 30 µmol/L.
Compared with positive controls (including phenobarbital and rifampin), perampanel was found to weakly induce CYP2B6 (30 µmol/L) and CYP3A4/5 (≥3 µmol/L) in cultured human hepatocytes. Perampanel also induced UGT1A1 (≥3 µmol/L) and UGT1A4 (30 µmol/L). Perampanel did not induce CYP1A2 at concentrations up to 30 µmol/L.
Transporters
In vitro studies showed that perampanel is not a substrate or significant inhibitor of the following: organic anion transporting polypeptides 1B1 and 1B3; organic anion transporters 1, 2, 3, and 4; organic cation transporters 1, 2, and 3; efflux transporters P-glycoprotein and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein.
In Vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
Drug Interactions with AEDs
Effect of Concomitant AEDs on FYCOMPA:
Carbamazepine. As an inducer of CYP enzymes, carbamazepine increases perampanel clearance. Steady state administration of carbamazepine at 300 mg BID in healthy subjects reduced the Cmax and AUC0-inf of a single 2 mg tablet dose of perampanel by 26% and 67%, respectively. The t1/2 of perampanel was shortened from 56.8 hours to 25 hours. In clinical studies examining partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, a population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that perampanel AUC was reduced by 64% in patients on carbamazepine compared to the AUC in patients not on enzyme-inducing AEDs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Oxcarbazepine. In clinical studies examining partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, a population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that perampanel AUC was reduced by 48% in patients on oxcarbazepine compared to patients not on enzyme-inducing AEDs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Eslicarbazepine. Eslicarbazepine is structurally similar to oxcarbazepine and thus may also reduce perampanel plasma concentrations when used concomitantly.
Phenytoin. In clinical studies examining partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, a population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that perampanel AUC was reduced by 43% in patients on phenytoin compared to patients not on enzyme-inducing AEDs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Phenobarbital and Primidone: In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in clinical trials (40 patients co-administered phenobarbital and 9 patients co-administered primidone), no significant effect on perampanel AUC was found. A modest effect of phenobarbital and primidone on perampanel concentrations cannot be excluded.
Topiramate: Population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in clinical trials showed that perampanel AUC was reduced by approximately 19% in patients on topiramate compared to patients not on enzyme-inducing AEDs.
Other AEDs: Population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in clinical trials showed that clobazam, clonazepam, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, valproate, and zonisamide did not have an effect on perampanel clearance.
Other strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John’s wort) may also greatly increase clearance of perampanel and reduce perampanel plasma concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Effect of FYCOMPA on Concomitant AEDs:
FYCOMPA tablets up to 12 mg/day did not significantly affect the clearance of clonazepam, levetiracetam, phenobarbital, phenytoin, topiramate, or zonisamide based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with partial-onset seizures in clinical trials. FYCOMPA had a statistically significant effect on the clearance of carbamazepine, clobazam, lamotrigine, and valproic acid, but the increases in clearance of these drugs were each less than 10% at the highest perampanel dose evaluated (12 mg/day). FYCOMPA co-administration resulted in a 26% decrease in oxcarbazepine clearance and increased its concentrations. The concentrations of 10-monohydroxy metabolite (MHD), the active metabolite of oxcarbazepine, were not measured.
Drug-drug Interaction Studies with Other Drugs
Effect of Other Drugs on FYCOMPA
Ketoconazole. Co-administration of single 1-mg dose of perampanel tablet with 400 mg once daily doses of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, for 8 days in healthy subjects prolonged perampanel t1/2 by 15% (67.8 vs. 58.4 hours) and increased AUC0-inf by 20%.
Contraceptives. Perampanel Cmax and AUC0-72h were not altered when a single 6-mg dose of perampanel tablet was administered to healthy female subjects following a 21-day course of oral contraceptives containing ethinylestradiol 30 µg and levonorgestrel 150 µg.
Effect of FYCOMPA on Other Drugs
Midazolam. Perampanel administered as 6 mg tablet once daily doses for 20 days decreased AUC0-inf and Cmax of midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate) by 13% and 15%, respectively, in healthy subjects.
Contraceptives. Co-administration of perampanel 4 mg tablet once daily with an oral contraceptive containing ethinylestradiol 30 µg and levonorgestrel 150 µg for 21 days did not alter Cmax or AUC0-24h of either ethinylestradiol or levonorgestrel in healthy female subjects. In another study, a single dose of the oral contraceptive was administered following 21-day once daily dosing of FYCOMPA 12 mg or 8 mg tablets in healthy females. FYCOMPA at 12 mg did not alter AUC0-24h of ethinylestradiol but decreased its Cmax by 18%, and also decreased Cmax and AUC0-24h of levonorgestrel by 42% and 40%, respectively. FYCOMPA at 8 mg did not have significant effect on Cmax or AUC0-24h of either ethinylestradiol or levonorgestrel, with a decrease in AUC0-24h of levonorgestrel (9% on average) [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Levodopa. Perampanel tablets administered as 4 mg once daily doses for 19 days had no effect on Cmax and AUC0-inf of levodopa in healthy subjects.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Perampanel was administered orally to mice (1, 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) and rats (10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day in males; 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day in females) for up to 104 weeks. There was no evidence of drug-related tumors in either species. Plasma perampanel exposures (AUC) at the highest doses tested were less than that in humans dosed at 8 mg/day.
Mutagenesis
Perampanel was negative in the in vitro Ames and mouse lymphoma tk assays, and in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In male and female rats administered perampanel (oral doses of 1, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) prior to and throughout mating and continuing in females to gestation day 6, there were no clear effects on fertility. Prolonged and/or irregular estrus cycles were observed at all doses but particularly at the highest dose tested. Plasma perampanel exposures (AUC) at all doses were lower than that in humans dosed at 8 mg/day.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Partial-Onset Seizures
The efficacy of FYCOMPA in partial-onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, was studied in patients who were not adequately controlled with 1 to 3 concomitant AEDs in 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) in adult and pediatric patients (12 years of age and older). All trials had an initial 6-week Baseline Period, during which patients were required to have more than five seizures in order to be randomized. The Baseline Period was followed by a 19-week Treatment Period consisting of a 6-week Titration Phase and a 13-week Maintenance Phase. Patients in these 3 trials had a mean duration of epilepsy of approximately 21 years and a median baseline seizure frequency ranging from 9 to 14 seizures per 28 days. During the trials, more than 85% of patients were taking 2 to 3 concomitant AEDs with or without concurrent vagal nerve stimulation, and approximately 50% were on at least one AED known to induce CYP3A4, an enzyme critical to the metabolism of FYCOMPA (i.e., carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, or phenytoin), resulting in a significant reduction in FYCOMPA’s serum concentration [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Each study evaluated placebo and multiple FYCOMPA dosages (see Figure 1). During the Titration period in all 3 trials, patients on FYCOMPA received an initial 2 mg once daily dose, which was subsequently increased in weekly increments of 2 mg per day to the final dose. Patients experiencing intolerable adverse reactions were permitted to have their dose reduced to the previously tolerated dose.
The primary endpoint in Studies 1, 2, and 3 was the percent change in seizure frequency per 28 days during the Treatment Period as compared to the Baseline Period. The criterion for statistical significance was p<0.05. A statistically significant decrease in seizure rate was observed at doses of 4 to 12 mg per day. Dose response was apparent at 4 to 8 mg with little additional reduction in frequency at 12 mg per day.
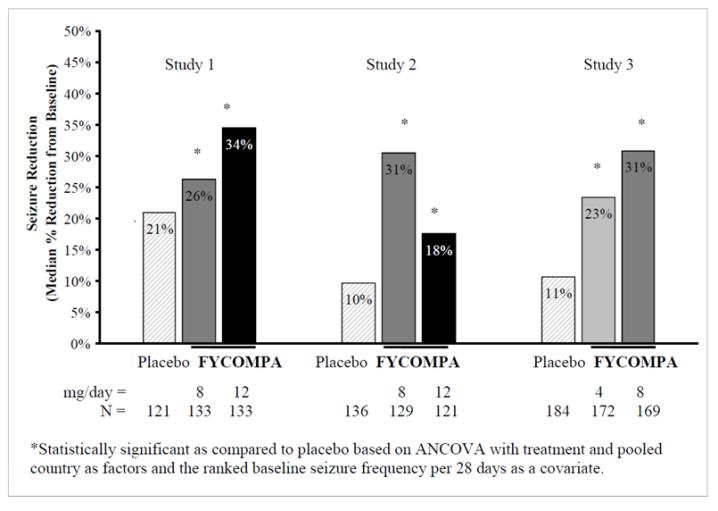
Figure 1. Median Percent Reduction in Seizure Frequency per 28 Days from Baseline to Treatment Period
Tables 4 and 5 present an analysis combining data from all 3 studies, grouping patients based upon whether or not concomitant enzyme-inducing AEDs (carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, or phenytoin) were used. The analysis revealed a substantially reduced effect in the presence of inducers.
Table 4. Median Percent Reduction for Combined Studies (Study 1, 2 and 3) Based on the Presence or Absence of Concomitant Enzyme-Inducing AEDs (carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin)a Without Enzyme-Inducing AEDs With Enzyme-Inducing AEDs Placebo
%FYCOMPA
%Placebo
%FYCOMPA
%2 mg/day 16 23 14 16 4 mg/day 16 22 14 33 8 mg/day 19 45 12 24 12 mg/day 19 54 9 22 aPatients from Latin American region are excluded because of a significant treatment-by-region interaction due to high placebo response
Table 5. Responder Rate for Combined Studies (Study 1, 2 and 3) Based on the Presence or Absence of Concomitant Enzyme-Inducing AEDs (carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin) a,b Without Enzyme-Inducing AEDs With Enzyme-Inducing AEDs Placebo
%FYCOMPA
%Placebo
%FYCOMPA
%2 mg/day 19 26 18 20 4 mg/day 19 35 18 26 8 mg/day 17 45 19 32 12 mg/day 15 54 21 33 aPatients from Latin American region are excluded because of a significant treatment-by-region interaction due to high placebo response
bThe proportion of patients with at least a 50% decrease in seizure frequency
Figure 2 shows the proportion of patients with different percent reductions during the maintenance phase over baseline across all three trials. Patients in whom the seizure frequency increased are shown at left as “worse.” Patients in whom the seizure frequency decreased are shown in the remaining four categories.
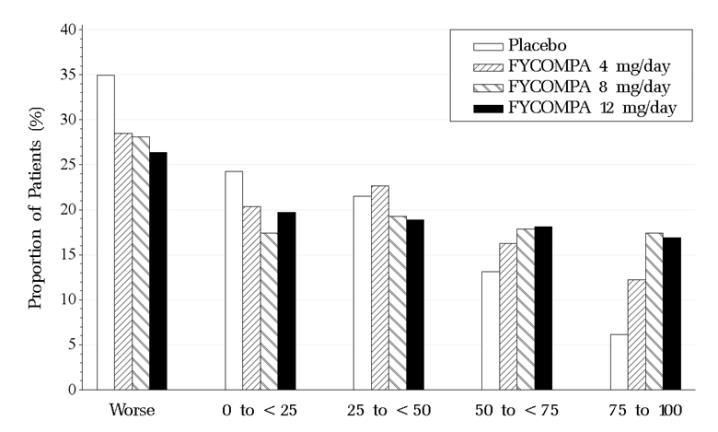
Figure 2. Proportion of Patients Exhibiting Different Percent Reductions During the Maintenance Phase Over Baseline Across All Three Trials.
The percentages of patients with a 50% or greater reduction in seizure frequency were 19%, 29%, 35%, 35% for placebo, 4, 8, and 12 mg, respectively.
14.2 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic (PGTC) Seizures
The efficacy of FYCOMPA as adjunctive therapy in patients 12 years of age and older with idiopathic generalized epilepsy experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (Study 4), conducted at 78 sites in 16 countries. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 to 3 AEDs experiencing at least 3 primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures during the 8-week baseline period were randomized to either FYCOMPA or placebo. Efficacy was analyzed in 162 patients (FYCOMPA N=81, placebo N=81) who received medication and at least one post-treatment seizure assessment. Patients were titrated over 4 weeks up to a dose of 8 mg per day or the highest tolerated dose and treated for an additional 13 weeks on the last dose level achieved at the end of the titration period. The total treatment period was 17 weeks. Study drug was given once per day.
The primary endpoint was the percent change from baseline in primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure frequency per 28 days during the treatment period as compared to the baseline period. The criterion for statistical significance was p<0.05. Table 6 shows the results of this study. A statistically significant decrease in seizure rate was observed with FYCOMPA compared to placebo.
Table 6. Median Percent Reduction from Baseline in Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure Frequency in Study 4 Placebo
(N=81)FYCOMPA
8 mg
(N=81)Percent Reduction During Treatment 38 76a a P-value compared to placebo: <0.0001. Statistically significant as compared to placebo based on ANCOVA with treatment and pooled country as factors and the ranked baseline seizure frequency per 28 days as a covariate. Figure 3 shows the proportion of patients with different percent reductions during the maintenance phase over baseline in primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure frequency. Patients in whom the seizure frequency increased are shown at left as “worse.” Patients in whom the seizure frequency decreased are shown in the remaining four categories.
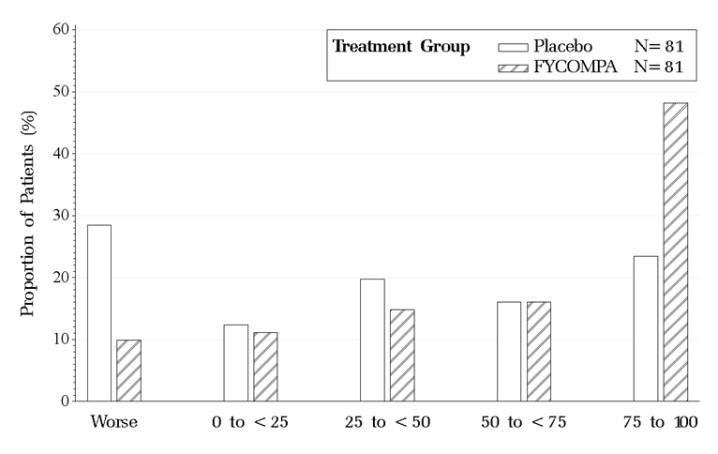
Figure 3. Proportion of Patients Exhibiting Different Percent Reductions During the Maintenance Phase Over Baseline in Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure Frequency.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
FYCOMPA Tablets
- 2 mg are orange, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “2” on one side and “Є 275” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-272-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-272-90
- 4 mg are red, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “4” on one side and “Є 277” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-274-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-274-90
- 6 mg are pink, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “6” on one side and “Є 294” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-276-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-276-90
- 8 mg are purple, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “8” on one side and “Є 295” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-278-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-278-90
- 10 mg are green, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “10” on one side and “Є 296” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-280-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-280-90
- 12 mg are blue, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “12” on one side and “Є 297” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 NDC: 62856-282-30
Bottles of 90 NDC: 62856-282-90
FYCOMPA Oral Suspension
- 0.5 mg/mL is a white to off-white opaque liquid. It is supplied in a round amber PET bottle with a child-resistant closure. It is packaged with a dispenser set that provides a 20-mL graduated oral dosing syringe and a push-in bottle adapter.
Bottle containing 340 mL NDC: 62856-290-38
- 2 mg are orange, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “2” on one side and “Є 275” on the other. They are supplied as follows:
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Administration of Oral Suspension
Advise patients who are prescribed the oral suspension to shake the bottle well before every administration and to use the adaptor and oral dosing syringe provided. Advise patients that a household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device. Instruct patients to discard any unused FYCOMPA oral suspension remaining 90 days after first opening the bottle [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
Serious Psychiatric and Behavioral Reactions
Counsel patients, families, and caregivers of patients of the need to monitor for the emergence of anger, aggression, hostility, hallucinations, delusions, confusion, unusual changes in mood, personality, or behavior, and other behavioral symptoms. Advise them to report any such symptoms immediately to their healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Suicidal Thinking and Behavior
Counsel patients, their caregivers, and families that AEDs, including FYCOMPA, may increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior and advise them of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Instruct patients, caregivers, and families to report behaviors of concern immediately to healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Neurologic Effects: Dizziness, Gait Disturbance, Somnolence, and Fatigue
Counsel patients that FYCOMPA may cause dizziness, gait disturbance, somnolence, and fatigue. Advise patients taking FYCOMPA not to drive, operate complex machinery, or engage in other hazardous activities until they have become accustomed to any such effects associated with FYCOMPA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Falls
Counsel patients that FYCOMPA may cause falls and injuries [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
DRESS/Multi-organ Hypersensitivity
Instruct patients that a fever associated with signs of other organ system involvement (e.g., rash, lymphadenopathy, hepatic dysfunction) may be drug-related and should be reported to their healthcare provider immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs
Counsel patients that abrupt discontinuation of FYCOMPA may increase seizure frequency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Contraceptives
Counsel females of reproductive potential that FYCOMPA may decrease efficacy of contraceptives containing levonorgestrel, and advise them to use an additional non-hormonal form of contraception while using FYCOMPA and for a month after discontinuation [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Alcohol and Other CNS Depressants
Counsel patients that FYCOMPA may enhance the impairment effects of alcohol. These effects may also be seen if FYCOMPA is taken with other CNS depressants [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Missed Doses
Counsel patients that if they miss a dose, they should resume dosing the following day at their prescribed daily dose. Instruct patients to contact their physician if more than one day of dosing is missed.
Controlled Substance
Counsel patients that FYCOMPA is a controlled substance that can be misused and abused [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.1)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise women who are exposed to FYCOMPA during pregnancy that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes. Encourage these patients to enroll in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
FYCOMPA® is a registered trademark owned by Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd.
Marketed by Eisai Inc., Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677
©2019 Eisai Inc.
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE FYCOMPA® (fī-COM-puh) (perampanel) tablets, for oral use, CIII FYCOMPA® (fī-COM-puh)
(perampanel)
oral suspension, CIIIWhat is the most important information I should know about FYCOMPA?
1. FYCOMPA may cause mental (psychiatric) problems, including:
- new or worse aggressive behavior (including homicidal behavior), hostility, anger, anxiety, or irritability
- being suspicious or distrustful (believing things that are not true)
- seeing objects or hearing things that are not there
- confusion
- difficulty with memory
- other unusual or extreme changes in behavior or mood
2. Like other antiepileptic drugs, FYCOMPA may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- new or worse depression
- feeling agitated or restless
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- attempt to commit suicide
- new or worse anxiety
- panic attacks
- new or worse irritability
- acting on dangerous impulses
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Do not stop FYCOMPA without first talking with a healthcare provider. Stopping FYCOMPA suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping FYCOMPA suddenly can cause you to have seizures more often.What is FYCOMPA?
FYCOMPA is a prescription medicine used:
- to treat partial-onset seizures with or without secondarily generalized seizures in people with epilepsy who are 4 years of age and older
- with other medicines to treat primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in people with epilepsy who are 12 years of age and older
It is not known if FYCOMPA is safe and effective for partial onset seizures in children under 4 years of age or for primary generalized tonic clonic seizures in patients under 12 years of age.Before taking FYCOMPA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had depression, mood problems, aggressive or hostile behavior (for example, homicidal behavior), suicidal thoughts or behavior, or other psychiatric problems.
- have liver or kidney problems
- drink alcohol
- have abused prescription medicines, street drugs, or alcohol in the past
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if FYCOMPA will harm your unborn baby.
○ If you become pregnant while taking FYCOMPA, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334 or go to http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of FYCOMPA and other antiepileptic medicine during pregnancy.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if FYCOMPA passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take FYCOMPA. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take FYCOMPA or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Taking FYCOMPA with certain other medicines can cause side effects or reduce the benefit of either drug. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:- contraceptives (birth control). FYCOMPA may lower your contraceptive’s ability to prevent pregnancy if your contraceptive contains levonorgestrel. Use an additional non-hormonal form of contraception (like condoms or a diaphragm and spermicide) while using FYCOMPA and for 1 month after you have stopped taking FYCOMPA.
- carbamazepine (CARBATROL®, TEGRETOL®, TEGRETOL-XR®, EQUETRO®, EPITOL®)
- phenytoin (DILANTIN®, PHENYTEK®)
- oxcarbazepine (TRILEPTAL®)
- rifampin (RIFADIN®, RIMACTANE®)
- St. John’s Wort
How should I take FYCOMPA? - See the Instructions for Use below for complete information on how to use the dosing syringe and how to measure your dose of FYCOMPA Oral Suspension.
- Take FYCOMPA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much FYCOMPA to take and when to take it. FYCOMPA is usually taken 1 time a day at bedtime.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose without talking to your healthcare provider.
- If you take FYCOMPA Oral Suspension, shake the bottle well before you take each dose.
- Measure your dose of FYCOMPA Oral Suspension using the bottle adapter and dosing syringe provided. Do not use a household teaspoon.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about what to do if you miss 1 or more doses of FYCOMPA.
- If you take too much FYCOMPA, call your local Poison Control Center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking FYCOMPA? - Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how FYCOMPA affects you. FYCOMPA may make you dizzy, sleepy, or tired.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking FYCOMPA until you talk to your healthcare provider. FYCOMPA taken with alcohol or medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse. FYCOMPA when taken with alcohol may also make your mood worse, increase anger, confusion, and depression.
What are the possible side effects of FYCOMPA?
See “What is the most important information I should know about FYCOMPA?”
FYCOMPA may cause other serious side effects, including:
-
Dizziness, vertigo (sense of spinning), and problems walking normally. You may have problems walking normally if you are unsteady because you feel dizzy. These symptoms can increase when your dose of FYCOMPA is increased. Your risk of feeling dizzy and having problems walking normally may be higher if you are elderly.
-
Sleepiness and tiredness. See “What should I avoid while taking FYCOMPA?”
-
Increased risk of falls. Taking FYCOMPA can increase your chance of falling. These falls can cause serious injuries. Your risk of falling may be higher if you are elderly.
-
A serious allergic reaction that may affect your skin or other parts of your body such as your liver, kidneys, heart, or blood cells. This allergic reaction can be life-threatening and can cause death. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
○ a skin rash, hives
○ fever or swollen glands that do not go away
○ swelling of your face
○ shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, or dark urine.
- dizziness
- sleepiness
- tiredness
- irritability
- falls
- nausea and vomiting
- weight gain
- vertigo (sense of spinning)
- problems walking normally
- problems with muscle coordination
- headache
- bruising
- abdominal pain
- anxiety
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store FYCOMPA?
- Store FYCOMPA tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store FYCOMPA oral suspension below 86°F (30°C). Do not freeze.
- Replace the cap tightly after opening.
- Use FYCOMPA oral suspension within 90 days after the bottle is first opened.
General information about the safe and effective use of FYCOMPA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use FYCOMPA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FYCOMPA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about FYCOMPA that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in FYCOMPA?
Active ingredient: perampanel
Inactive ingredients (tablets): lactose monohydrate, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Tablets of different strengths also may contain yellow ferric oxide (10 mg and 2 mg), red ferric oxide (2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg, 8 mg), black ferric oxide (8 mg), and FD&C blue # 2 (indigo carmine) aluminum lake (10 mg and 12 mg).
Inactive ingredients (oral suspension): sorbitol, microcrystalline cellulose, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, poloxamer, simethicone, citric acid, sodium benzoate, and purified water.Marketed by Eisai Inc., Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677
FYCOMPA® is a trademark owned by Eisai R&D Management Co. Ltd. For more information, go to www.FYCOMPA.com or 1-888-274-2378.This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised 5/2019
- new or worse aggressive behavior (including homicidal behavior), hostility, anger, anxiety, or irritability
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for Use
FYCOMPA® (fī-COM-puh)
(perampanel)
Oral SuspensionRead this Instructions for Use before you start using FYCOMPA Oral Suspension and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Prepare the FYCOMPA Oral Suspension dose
You will need the following supplies: See Figure A- FYCOMPA Oral Suspension bottle
- Bottle adapter
- Dosing syringe (1 dosing syringe is included in the FYCOMPA Oral Suspension box)
Figure A
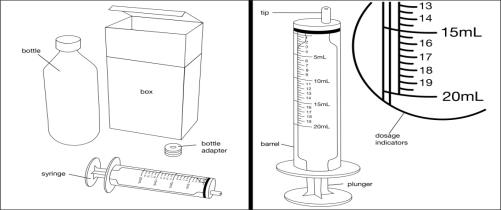
Step 1. Remove the FYCOMPA Oral Suspension bottle, bottle adapter, and syringe from the box. See Figure A
Step 2. Shake the bottle well before each use. See Figure B
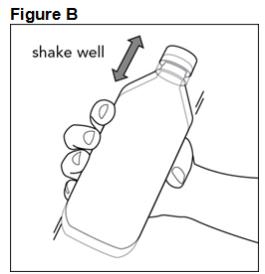
Step 3. Uncap the bottle and insert the bottle adapter into the bottle by pressing downward. See Figure C and Figure D
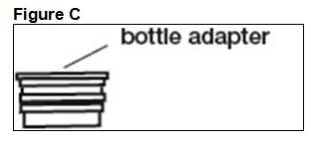
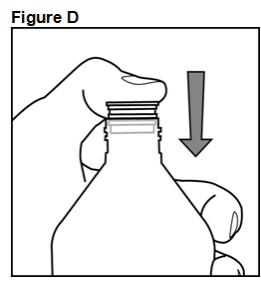
After the bottle adapter is in place, it cannot be removed.
Step 4. Check the dose in milliliters (mL) as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Find this number on the syringe. See Figure E
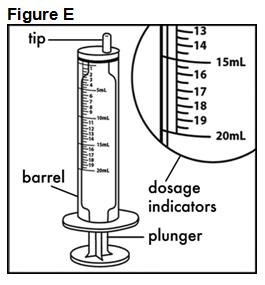
Step 5. Push the plunger of the syringe all the way down then insert the syringe into the upright bottle through the opening in the bottle adapter. See Figure F
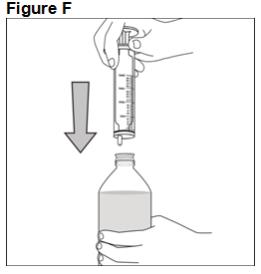
Step 6. With the syringe in place, turn the bottle upside down. Pull the plunger to withdraw the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider (the amount of liquid medicine in Step 4). If you see air bubbles in the oral syringe, fully push in the plunger so that the oral solution flows back into the bottle. Then, withdraw your prescribed dose of oral suspension. See Figure G
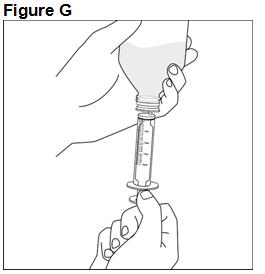
Measure the mLs of medicine from the white layer at the end of the plunger, not the black layer.
Step 7. If the dose is more than 20 mL, you can use:
- 1 syringe, taking 2 steps to draw up the medicine in that same syringe
For example:
If your dose is 24 mL, draw up 20 mL in the syringe and squirt the medicine into your mouth, then draw up the remaining 4 mL in that same syringe.
If your dose is more than 20 mL, repeat Steps 4 through 6 when drawing up the remaining dose of medicine.
Step 8. Turn the bottle right-side up and remove the syringe from the bottle adapter. See Figure H
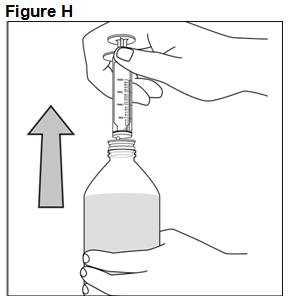
Step 9. Slowly squirt the FYCOMPA oral suspension directly into the corner of your mouth until all of the liquid medicine is given. If your dose is more than 20 mL, draw up 20 mL in the syringe and squirt the medicine into your mouth, then draw up the remaining amount in that same syringe. See Figure I
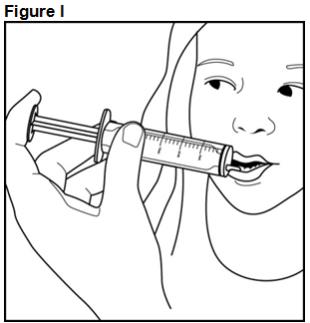
Step 10. Rinse the syringe with tap water after each use. See Figure J
- Fill a cup with water
- Pull back on the plunger and draw the water from the cup into the syringe
- Push down on the plunger to release the water into the sink
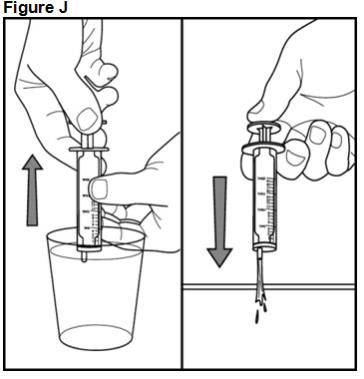
Step 11. Cap the bottle tightly. The cap will fit over the bottle adapter. See Figure K
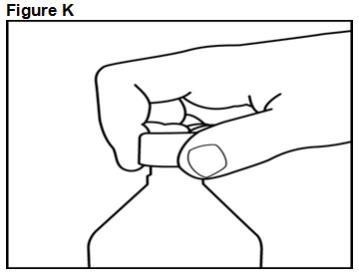
How should I store FYCOMPA Oral Suspension?
- Store FYCOMPA oral suspension below 86°F (30°C). Do not freeze.
- Replace the cap tightly after opening.
- Use FYCOMPA oral suspension within 90 days after the bottle is first opened.
- After 90 days safely throw away any FYCOMPA Oral Suspension that has not been used.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
FYCOMPA is a registered trademark owned by Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd.
Marketed by Eisai Inc., Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677
©2019 Eisai Inc.
Revised: May 2019
- FYCOMPA Oral Suspension bottle
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-272-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
2 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-272-14
14 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa
(perampanel) tabletsCIII
2 mg
2 week sample Kit
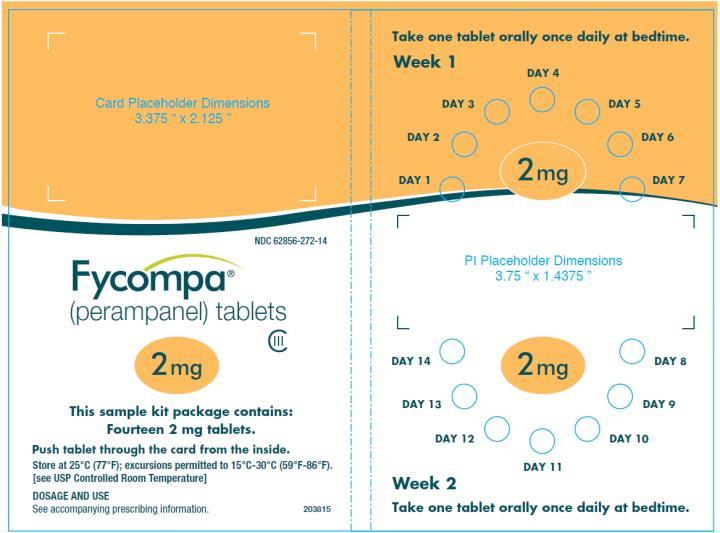
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 4 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-274-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
4 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 4 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-274-14
14 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa
(perampanel) tabletsCIII
4 mg
2 week sample Kit
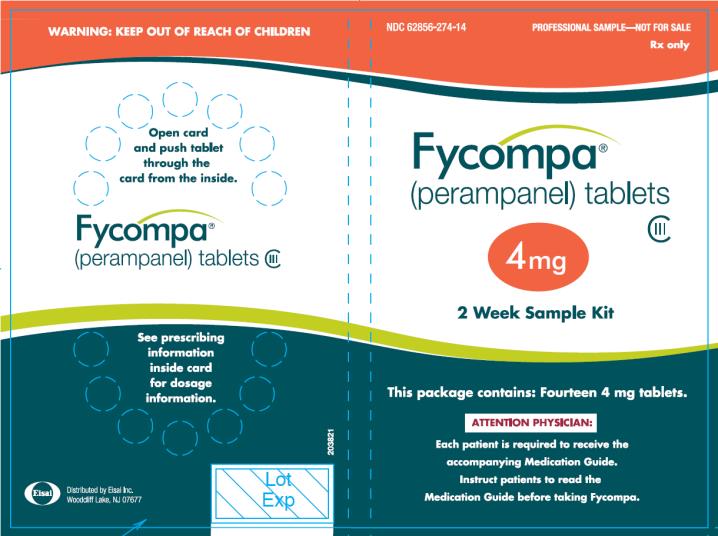

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 6 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-276-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
6 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.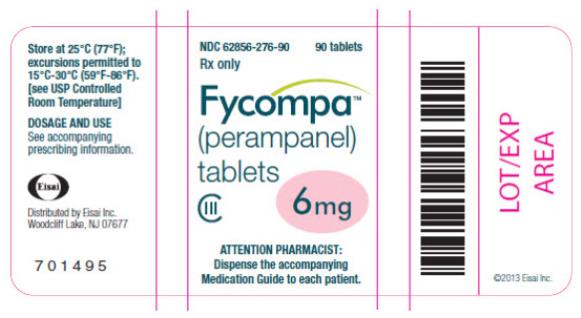
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-278-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
8 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-280-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
10 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.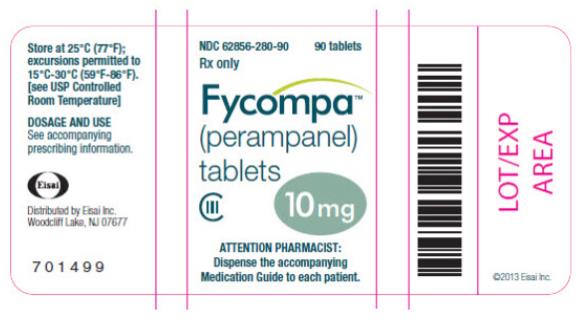
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 12 mg Tablet
NDC: 62856-282-90
90 tablets
Rx only
Fycompa™
(perampanel)
tabletsCIII
12 mg
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg/mL Oral Suspension
NDC: 62856-290-38
0.5 mg/mL
Rx only
Fycompa®
(perampanel)
ORAL SUSPENSIONCIII
340 mL

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-272 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 2 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE (orange) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code 2;275 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-272-14 14 in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/08/2018 2 NDC: 62856-272-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 3 NDC: 62856-272-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-274 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color RED (red) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code 4;277 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-274-14 14 in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/08/2018 2 NDC: 62856-274-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 3 NDC: 62856-274-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-276 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 6 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color PINK (pink) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code 6;294 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-276-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 2 NDC: 62856-276-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-278 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 8 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color PURPLE (purple) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code 8;295 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-278-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 2 NDC: 62856-278-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-280 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color GREEN (green) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code 10;296 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-280-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 2 NDC: 62856-280-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-282 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 12 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (11% HYDROXYPROPYL; 120000 MW) (UNII: NZ94SDL6WR) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color BLUE (blue) Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code 12;297 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-282-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 2 NDC: 62856-282-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/22/2012 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202834 10/22/2012 FYCOMPA
perampanel suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 62856-290 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PERAMPANEL (UNII: H821664NPK) (PERAMPANEL - UNII:H821664NPK) PERAMPANEL 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM (UNII: K679OBS311) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) DIMETHICONE (UNII: 92RU3N3Y1O) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 62856-290-38 340 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/30/2016 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208277 04/30/2016 Labeler - Eisai Inc. (831600833)
Trademark Results [Fycompa]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FYCOMPA 86018781 4530970 Live/Registered |
Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. 2013-07-24 |
 FYCOMPA 86018771 4530969 Live/Registered |
Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. 2013-07-24 |
 FYCOMPA 85227848 4526076 Live/Registered |
Eisai R&D Management Co., Ltd. 2011-01-27 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.