CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE capsule
Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Contract Pharmacy Services-PA, Coupler Enterprises Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION:
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is the prototype for the benzodiazepine compounds.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is 7-chloro-2-(methylamino)-5-phenyl-3 H-1, 4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide hydrochloride. A white to practically white crystalline substance, it is soluble in water. It is unstable in solution and the powder must be protected from light. The structural formula of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is as follows:
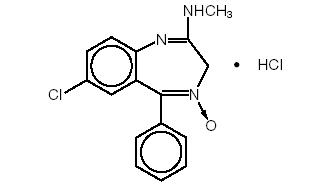
Available as capsules for oral administration containing either 5 mg, 10 mg or 25 mg of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride.
-
ACTIONS:
Chlordiazepoxide HCI has antianxiety, sedative, appetite-stimulating and weak analgesic actions. The precise mechanism of action is not known. The drug blocks EEG arousal from stimulation of the brain stem reticular formation. It takes several hours for peak blood levels to be reached and the half-life of the drug is between 24 and 48 hours. After the drug is discontinued plasma levels decline slowly over a period of several days. Chlordiazepoxide is excreted in the urine, with 1 to 2% unchanged and 3 to 6% as a conjugate.
Animal Pharmacology:
The drug has been studied extensively in many species of animals and these studies are suggestive of action on the limbic system of the brain, which recent evidence indicates is involved in emotional responses.
Hostile monkeys were made tame by oral drug doses which did not cause sedation. Chlordiazepoxide revealed a “taming” action with the elimination of fear and aggression. The taming effect of chlordiazepoxide was further demonstrated in rats made vicious by lesions in the septal area of the brain. The drug dosage which effectively blocked the vicious reaction was well below the dose which caused sedation in these animals.
The LD 50 of parenterally administered chlordiazepoxide HCI was determined in mice (72 hours) and rats (5 days), and calculated according to the method of Miller and Tainter, with the following results: mice, I.V., 123 ± 12 mg/kg; mice, I.M., 336 ± 7 mg/kg; rats, I.V., 120 ± 7 mg/kg; rats, I.M., >160 mg/kg.
Effects on Reproduction:
Reproduction studies in rats fed 10, 20, and 80 mg/kg daily and bred through one or two mating showed no congenital anomalies, nor were there adverse effects on lactation of the dams or growth of the newborn. However, in another study at 100 mg/kg daily there was noted a significant decrease in the fertilization rate and a marked decrease in the viability and body weight of offspring which may be attributable to sedative activity, thus resulting in lack of interest in mating and lessened maternal nursing and care of the young. One neonate in each of the first and second matings in the rat reproduction study at the 100 mg/kg dose exhibited major skeletal defects. Further studies are in progress to determine the significance of these findings.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Chlordiazepoxide HCI Capsules are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety, withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism, and preoperative apprehension and anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
The effectiveness of chlordiazepoxide in long-term use, that is, more than 4 months, has not been assessed by systematic clinical studies. The physician should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS:
Chlordiazepoxide may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery. Similarly, it may impair mental alertness in children. The concomitant use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may have an additive effect. PATIENTS SHOULD BE WARNED ACCORDINGLY.
Usage in Pregnancy: An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of minor tranquilizers (chlordiazepoxide, diazepam and meprobamate)during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies. Because use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, their use during this period should almost always be avoided. The possibility that a woman of childbearing potential may be pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant during therapy or intend to become pregnant they should communicate with their physicians about the desirability of discontinuing the drug.
Withdrawal symptoms of the barbiturate type have occurred after the discontinuation of benzodiazepines. (See DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE section.)
-
PRECAUTIONS:
In elderly and debilitated patients, it is recommended that the dosage be limited to the smallest effective amount to preclude the development of ataxia or oversedation (10 mg or less per day initially, to be increased gradually as needed and tolerated). In general, the concomitant administration of chlordiazepoxide HCI and other psychotropic agents is not recommended. If such combination therapy seems indicated, careful consideration should be given to the pharmacology of the agents to be employed — particularly when the known potentiating compounds such as the MAO inhibitors and phenothiazines are to be used. The usual precautions in treating patients with impaired renal or hepatic function should be observed.
Paradoxical reactions, e.g., excitement, stimulation and acute rage, have been reported in psychiatric patients and in hyperactive aggressive children, and should be watched for during chlordiazepoxide therapy. The usual precautions are indicated when chlordiazepoxide HCI capsules are used in the treatment of anxiety states where there is any evidence of impending depression; it should be borne in mind that suicidal tendencies may be present and protective measures may be necessary. Although clinical studies have not established a cause and effect relationship, physicians should be aware that variable effects on blood coagulation have been reported very rarely in patients receiving oral anticoagulants and chlordiazepoxide. In view of isolated reports associating chlordiazepoxide with exacerbation of porphyria, caution should be exercised in prescribing chlordiazepoxide to patients suffering from this disease.
Information for Patients:
To assure the safe and effective use of benzodiazepines, patients should be informed that, since benzodiazepines may produce psychological and physical dependence, it is advisable that they consult with their physician before either increasing the dose or abruptly discontinuing the drug.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The necessity of discontinuing therapy because of undesirable effects has been rare. Drowsiness, ataxia and confusion have been reported in some patients —particularly the elderly and debilitated. While these effects can be avoided in almost all instances by proper dosage adjustment, they have occasionally been observed at the lower dosage ranges. In few instances syncope has been reported.
Other adverse reactions reported during therapy include isolated instances of skin eruptions, edema, minor menstrual irregularities, nausea and constipation, extrapyramidal symptoms, as well as increased and decreased libido. Such side effects have been infrequent and are generally controlled with reduction of dosage. Changes in EEG patterns (low-voltage fast activity) have been observed in patients during and after chlordiazepoxide treatment.
Blood dyscrasias (including agranulocytosis), jaundice and hepatic dysfunction have occasionally been reported during therapy. When chlordiazepoxide treatment is protracted, periodic blood counts and liver function tests are advisable.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE:
Chlordiazepoxide HCI Capsules are classified by the Drug Enforcement Administration as a schedule IV controlled substance.
Withdrawal symptoms, similar in character to those noted with barbiturates and alcohol (convulsions, tremor, abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting and sweating), have occurred following abrupt discontinuance of chlordiazepoxide. The more severe withdrawal symptoms have usually been limited to those patients who had received excessive doses over an extended period of time. Generally milder withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria and insomnia) have been reported following abrupt discontinuance of benzodiazepines taken continuously at therapeutic levels for several months. Consequently, after extended therapy, abrupt discontinuation should generally be avoided and a gradual dosage tapering schedule followed. Addiction-prone individuals (such as drug addicts or alcoholics) should be under careful surveillance when receiving chlordiazepoxide or other psychotropic agents because of the predisposition of such patients to habituation and dependence.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Because of the wide range of clinical indications for chlordiazepoxide, the optimum dosage varies with the diagnosis and response of the individual patient. The dosage, therefore, should be individualized for maximum beneficial effects.
ADULTS Usual Daily Dose Relief of mild and moderate anxiety disorders and symptoms of anxiety
5 mg or 10 mg, 3 or 4 times daily Relief of severe anxiety disorders and
symptoms of anxiety20 mg or 25 mg, 3 or 4 times daily Geriatric patients, or in the presence of
debilitating disease5 mg, 2 to 4 times daily Preoperative apprehension and anxiety: On days preceding surgery, 5 to 10 mg orally, 3 or 4 times daily. If used as preoperative medication, 50 to 100 mg IM* one hour prior to surgery.
CHILDREN Usual Daily Dose Because of the varied response of children to CNS-acting drugs, therapy should be initiated with the lowest dose and increased as required. Since clinical experience in children under 6 years of age is limited, the use of the
drug in this age group is not recommended.5 mg, 2 to 4 times daily (may be increased in some children to 10 mg, 2 or 3 times daily) For the relief of withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism, the parenteral form* is usually used initially. If the drug is administered orally, the suggested initial dose is 50 to 100 mg, to be followed by repeated doses as needed until agitation is controlled — up to 300 mg per day. Dosage should then be reduced to maintenance levels.
*See package insert for Sterile Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride.
Management of Overdosage:
Manifestations of chlordiazepoxide overdosage includes somnolence, confusion, coma and diminished reflexes. Respiration, pulse and blood pressure should be monitored, as in all cases of drug overdosage, although, in general, these effects have been minimal following chlordiazepoxide overdosage. General supportive measures should be employed, along with immediate gastric lavage. Intravenous fluids should be administered and an adequate airway maintained. Hypotension may be combated by the use of norepinephrine or metaraminol. Dialysis is of limited value. There have been occasional reports of excitation in patients following chlordiazepoxide overdosage; if this occurs barbiturates should not be used. As with the management of intentional overdosage with any drug, it should be borne in mind that multiple agents may have been ingested.
Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine receptor antagonist, is indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines and may be used in situations when an overdose with a benzodiazepine is known or suspected. Prior to the administration of flumazenil, necessary measures should be instituted to secure airway, ventilation, and intravenous access. Flumazenil is intended as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, proper management of benzodiazepine overdose. Patients treated with flumazenil should be monitored for resedation, respiratory depression, and other residual benzodiazepine effects for an appropriate period after treatment. The prescriber should be aware of a risk of seizure in association with flumazenil treatment, particularly in long-term benzodiazepine users and in cyclic antidepressant overdose. The complete flumazenil package insert including CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS should be consulted prior to use.
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Chlordiazepoxide HCI Capsules is available as:
25 mg: Green/white capsule. Identified with stylized barr/159. Available in blisters of: 30
NDC: 67046-910-30 Dispense with a child-resistant closure in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF.
Store at controlled room temperature 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) in a dry place.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
Chlordiazepoxide (KLOR-dye-AZ-e-POX-ide) Hydrochloride Capsules, C-IV
What is the most important information I should know about chlordiazepoxide?
Chlordiazepoxide is a benzodiazepine medicine. Taking benzodiazepines with opioid medicines, alcohol, or other central nervous system depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, breathing problems (respiratory depression), coma and death.
Chlordiazepoxide can make you sleepy or dizzy, and can slow your thinking and motor skills.Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how chlordiazepoxide affects you.
Do not drink alcohol or take other drugs that may make you sleepy or dizzy while taking chlordiazepoxide without first talking to your healthcare provider. When taken with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness, chlordiazepoxide may make your sleepiness or dizziness much worse.Do not take more chlordiazepoxide than prescribed.
What is chlordiazepoxide?
Chlordiazepoxide is a prescription medicine used:
to treat anxiety disorders
for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety
to treat withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism
preoperatively to treat apprehension and anxietyChlordiazepoxide is a federal controlled substance (C-IV) because it can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep chlordiazepoxide in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away chlordiazepoxide may harm others, and is against the law. Tell your healthcare provider if you have abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or street drugs.
It is not known if chlordiazepoxide is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.
It is not known if chlordiazepoxide is safe and effective for use for longer than 4 months.Do not take chlordiazepoxide if you are allergic to chlordiazepoxide or to any of the ingredients in chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride capsules.
See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride capsules.
Before you take chlordiazepoxide, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
have a history of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction
have liver or kidney problems
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Chlordiazepoxide may harm your unborn baby. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you should take chlordiazepoxide while you are pregnant
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Chlordiazepoxide may pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take chlordiazepoxide.Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking chlordiazepoxide with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well chlordiazepoxide or the other medicines work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
How should I take chlordiazepoxide?
Take chlordiazepoxide exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much chlordiazepoxide to take and when to take it.
If you take too much chlordiazepoxide, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.What should I avoid while taking chlordiazepoxide?
Chlordiazepoxide can cause you to be drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate heavy machinery until you know how chlordiazepoxide affects you.
You should not drink alcohol while taking chlordiazepoxide. Drinking alcohol can increase your chances of having serious side effects.What are the possible side effects of chlordiazepoxide?
Chlordiazepoxide may cause serious side effects, including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about chlordiazepoxide?”
Abuse and dependence. Taking chlordiazepoxide can cause physical and psychological dependence. Physical and psychological dependence is not the same as drug addiction. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the differences between physical and psychological dependence and drug addiction.
Withdrawal symptoms. You may have withdrawal symptoms if you stop taking chlordiazepoxide suddenly. Withdrawal symptoms can be serious and include seizures. Mild withdrawal symptoms include a depressed mood and trouble sleeping. Talk to your healthcare provider about slowly stopping chlordiazepoxide to avoid withdrawal symptoms.The most common side effects of chlordiazepoxide include:
drowsiness
loss of control of body movements (ataxia)
confusion
These are not all the possible side effects of chlordiazepoxide. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store chlordiazepoxide?
Store chlordiazepoxide at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride capsules in a tightly closed container and out of the light.
Keep chlordiazepoxide and all medicines out of the reach of children.General information about the safe and effective use of chlordiazepoxide.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use chlordiazepoxide for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give chlordiazepoxide to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about chlordiazepoxide that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride capsules?
Active ingredient: chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, D&C yellow no. 10, FD&C blue no. 1, FD&C blue no. 1 aluminum lake, gelatin, hydrogenated vegetable oil, microcrystalline cellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, and titanium dioxide. The 5 mg and 25 mg also contain D&C yellow no. 10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue no. 2 aluminum lake, FD&C red no. 40 aluminum lake, propylene glycol, and synthetic black iron oxide. In addition, the 5 mg contains D&C red no. 33 and the 10 mg also contains butyl paraben, edetate calcium disodium, dimethyl polysiloxane, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, FD&C red no. 40, methyl paraben, propyl paraben, sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium propionate, and soya lecithin.
Manufactured by:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454
For more information, go to www.tevagenerics.com or call 1-888-838-2872.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 8/2016
- Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67046-910(NDC:0555-0159) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIV Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: MFM6K1XWDK) (CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE - UNII:6RZ6XEZ3CR) CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE 25 mg Product Characteristics Color green (GREEN) , white (WHITE) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (CAPSULE) Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code barr;159 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67046-910-30 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/07/2010 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA084769 04/07/2010 Labeler - Contract Pharmacy Services-PA (945429777) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Coupler Enterprises Inc. 945429777 repack(67046-910)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
